A Systematic Review on the Influence of Drainage Systems on the Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Analysis of the increasing popularity of drainage systems’ influence on water quality over the years;
- Examination of the growing interest in studying climate change and its effects on drainage-related water quality;
- Identification of key computer tools used for modelling drainage systems;
- Recognition of the main biogenic substances tested within drainage systems influencing water quality;
- Detailed justification of the advantages of controlled drainage over free drainage from the water quality perspective;
- Identification of the main topics analyzed in the papers on drainage systems and water quality.
2. Review Materials and Methods
2.1. Planning SLR
2.1.1. Define Research Questions
2.1.2. Identify Data Sources
2.1.3. Formulate Search Sting
- Web of Science: Water Resources; Environmental Sciences; Agronomy, Agricultural Engineering, Engineering Civil, Ecology, Engineering Environmental, Soil Science, Agriculture Multidisciplinary, Engineering Multidisciplinary, Environmental Studies, Geosciences Multidisciplinary;
- Scopus: Environmental Sciences; Agricultural and Biological Sciences, Engineering, Earth and Planetary Sciences, Multidisciplinary.
2.1.4. Define Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.1.5. Formulate Paper Selection Strategy
- PSS-1. Run the search strings at the selected sources;
- PSS-2. Apply research field (i.e., search scope) and language restrictions (i.e., in Table 1, IC5, EC5);
- PSS-3. Merge two sets of papers (i.e., from WoS and Scopus);
- PSS-4. Exclude duplicating papers (i.e., in Table 1, IC6 and EC6);
- PSS-5. Extract the title, abstract, and keywords for the primary set of papers (i.e., in Table 1, IC8 and EC8);
- PSS-6. Evaluate a primary set of papers (the title, abstract, and keywords) according to IC1 and EC1;
- PSS-7. Read whole text of the secondary set of papers and extract necessary information based on data extraction strategy (see Section 2.1.6).
2.1.6. Formulate Data Extraction Strategy
2.1.7. Formulating Data Synthesis and Analysis Strategy
2.2. Conducting the Review
2.2.1. Selecting Primary Studies
2.2.2. Performing Data Extraction and Data Synthesis
2.3. Validity Evaluation
3. Results
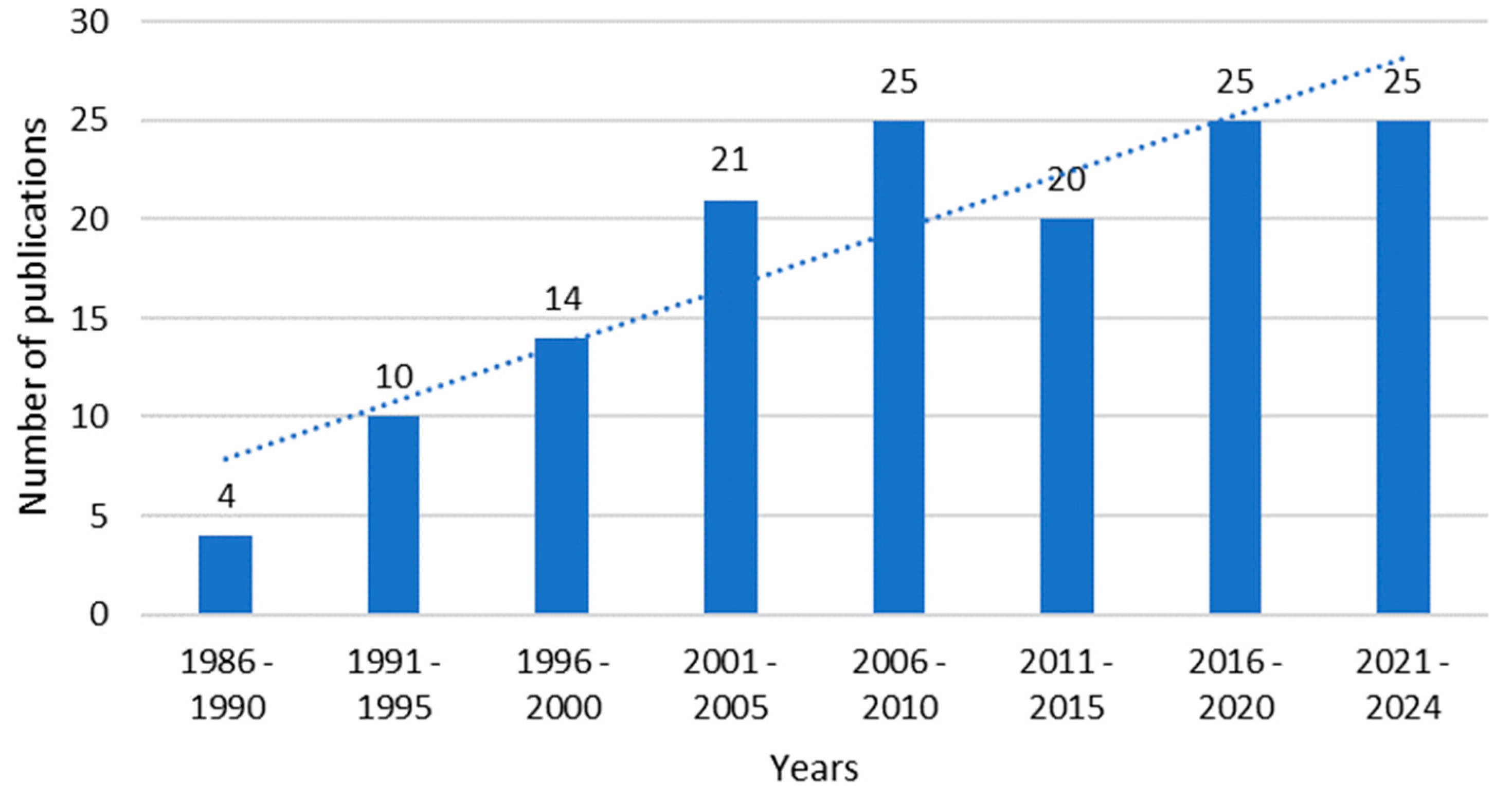
3.1. When Are Studies on the Drainage Topic Published? (RQ1)
3.2. Is Climate Change Considered in Drainage Water Quality Studies? (RQ2)
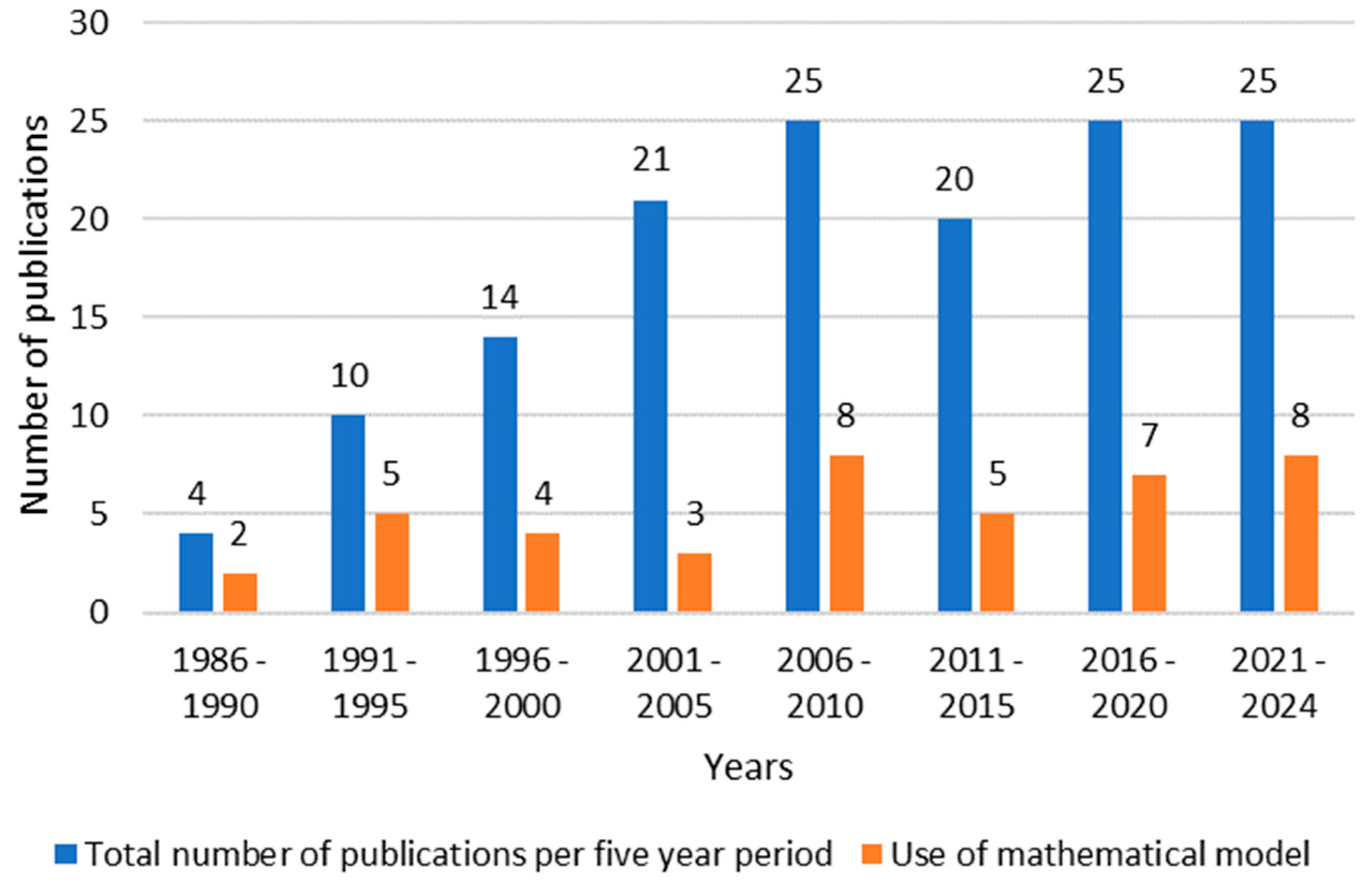
3.3. What Computer Tools Are Used to Model and Analyze Drainage Systems? Is Artificial Intelligence Used? (RQ3)
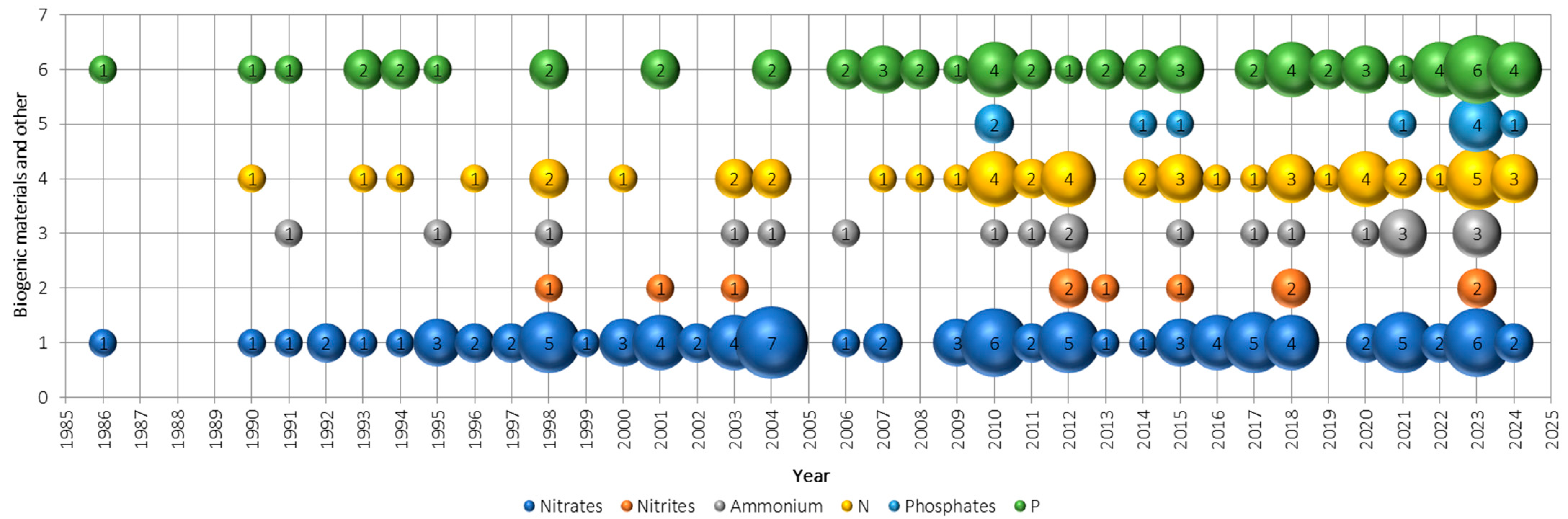
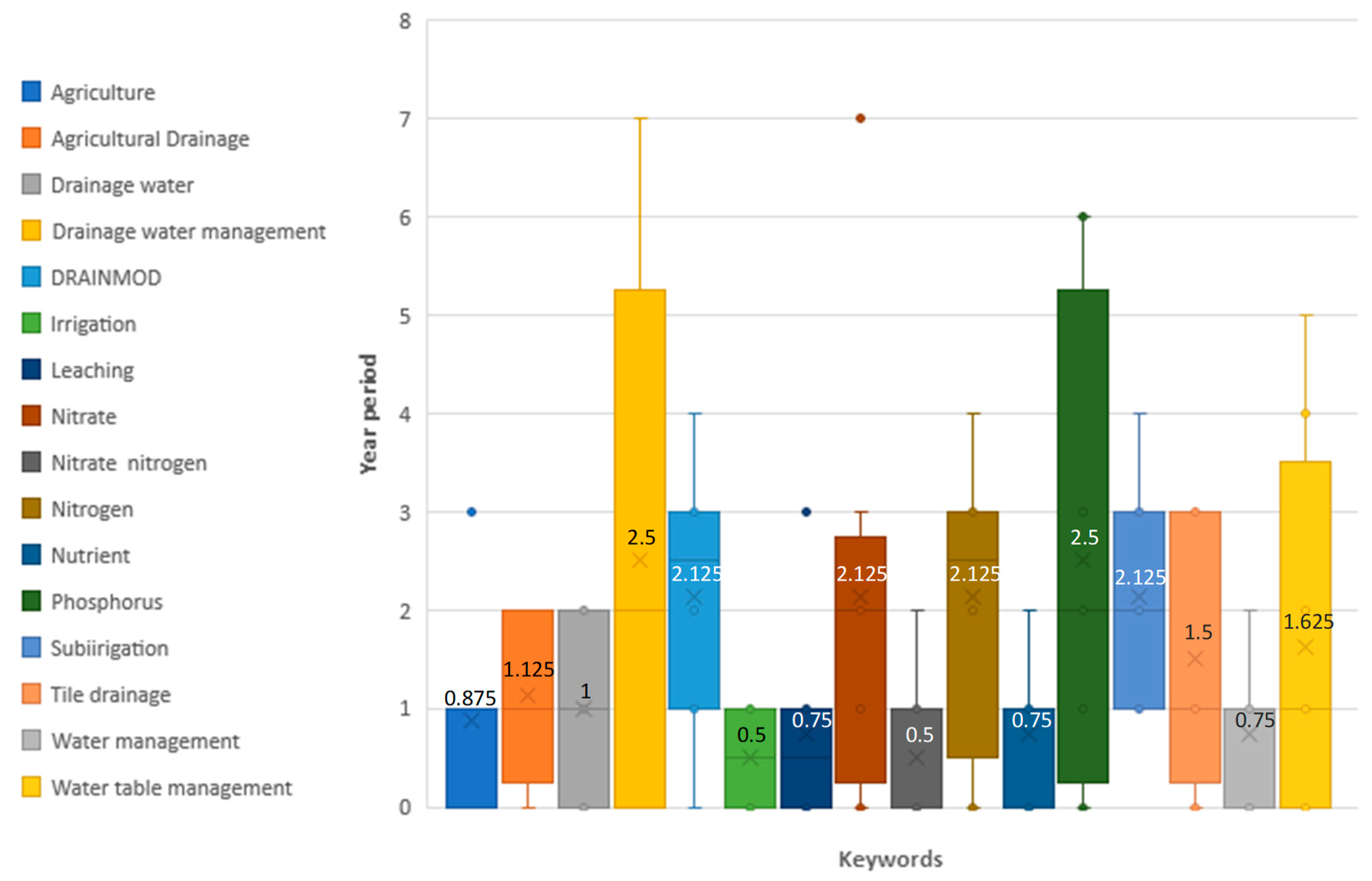
3.4. What Biogenic Substances Are Considered in Drainage Water Quality Analyses? (RQ4)
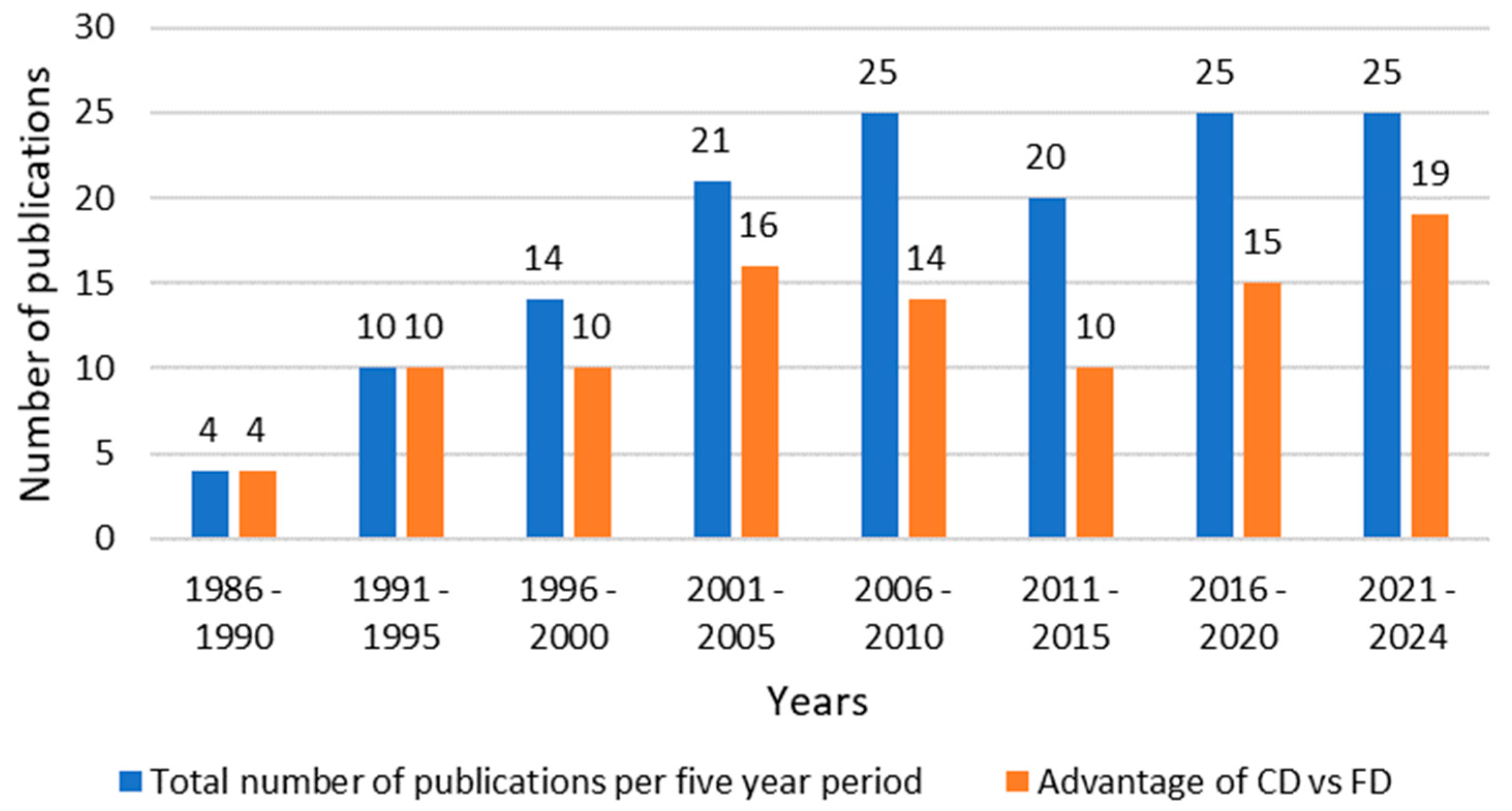
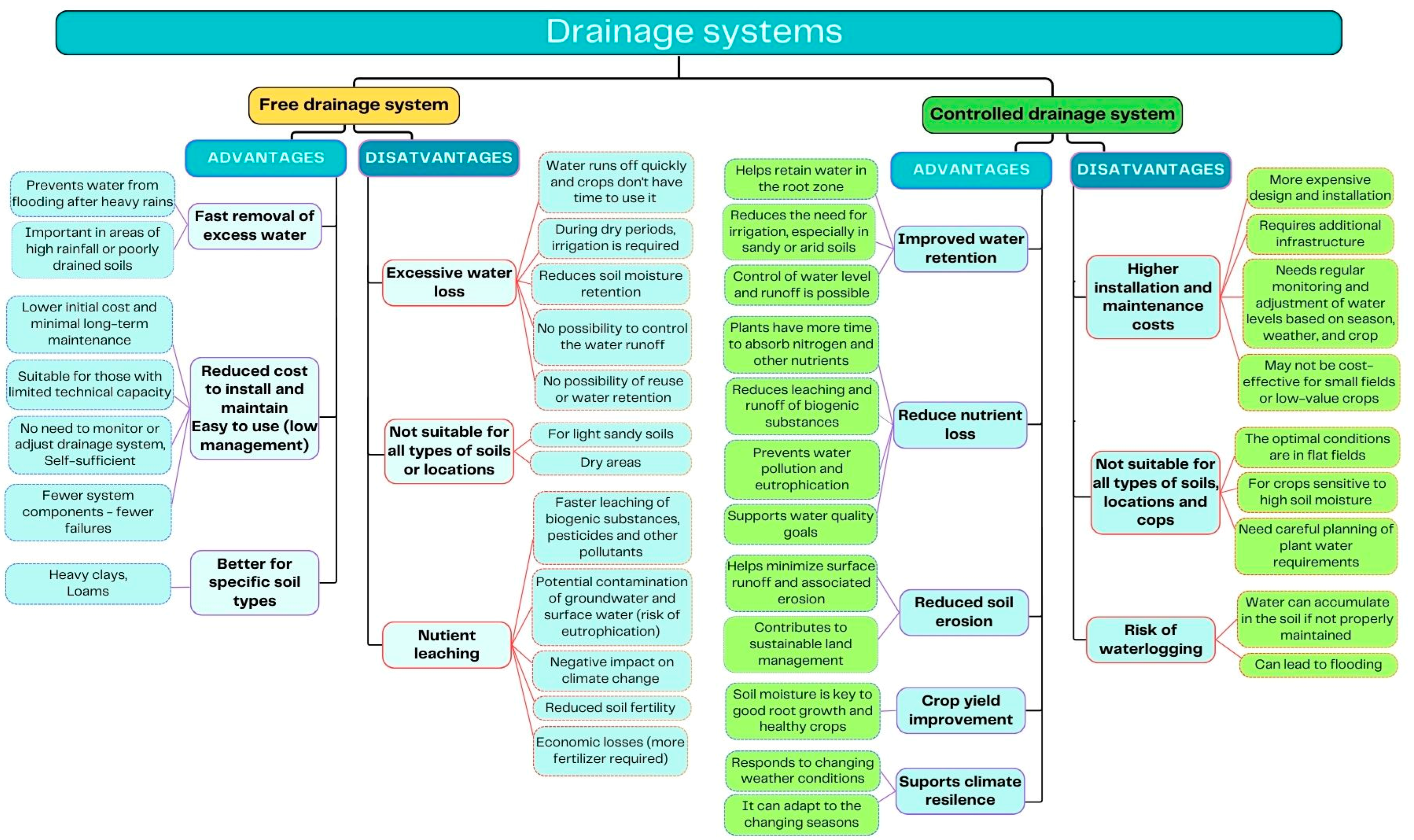
3.5. Is Controlled Drainage Always Better than Free Drainage? (RQ5)
3.6. What Are the Main Topics Found in the Analyzed Papers on Drainage Systems? (RQ6)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AnnAGNPS | The Annualized Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution Model |
| CD | Controlled Drainage |
| DBR | Denitrifying Bioreactors |
| DIs | Data Items |
| DNDC | DeNitrification-DeComposition |
| FD | Free Drainage |
| FWS | Free Water Surface |
| GFDL-ESM4 | Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Earth System Model |
| IBZs | Integrated Buffer Zones |
| MPI-ESM1-2-HR | Max Planck Institute Earth System Model |
| N | Nitrogen |
| NN | Neural network |
| P | Phosphorus |
| PA | Precision Agriculture |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PSS | Paper Selection Strategy |
| RQ | Research Question |
| RZWQM | Root Zone Water Quality Mode |
| SBZs | Saturated Buffer Zones |
| SRL | Systematic Literature Review |
| UKESM1-0-LL | United Kingdom Earth System Model |
References
- Almen, K.; Jia, X.; Desutter, T.; Scherer, T.; Lin, M. Impact of Controlled Drainage and Subirrigation on Water Quality in the Red River Valley. Water 2021, 13, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, W.F. Agricultural Drainage in the Northeastern U.S.: Past History and Future Challenges. In Proceedings of the World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2017, Sacramento, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2017; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Rudzianskaitė, A.; Misevičienė, S. Effects of Controlled Drainage on Soil Water Regime and Quality in Lithuania. Agrofor 2019, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povilaitis, A.; Rudzianskaite, A.; Miseviciene, S.; Gasiunas, V.; Miseckaite, O.; Živatkauskiene, I. Efficiency of Drainage Practices for Improving Water Quality in Lithuania. Trans. ASABE Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 61, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Bowling, L.; Frankenberger, J.; Kladivko, E. Nitrate and Phosphorus Transport through Subsurface Drains under Free and Controlled Drainage. Water Res. 2018, 142, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, P.K.; Cooke, R.A.C.; Anderson, S.M.; Hirschi, M.C.; Mitchell, J.K. Subsurface Drainage and Water Quality: The Illinois Experience. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevičienė, R. Comparative Analysis of Nitrogen Compounds Pollution in Controlled and Free Drainage Water. Environ. Eng. 2022, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokochynskyi, A.; Volk, P.; Turcheniuk, V.; Tokar, L.; Volk, L.; Mazhayskiy, Y.; Chernikova, O. Drainage Module as Important Factor in Design of Drainage System Reconstruction and Construction Projects in the Polesia Region. In Proceedings of the 19th International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development Proceedings, Jelgava, Latvia, 20–22 May 2020; Faculty of Engineering, Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies: Jelgava, Latvia, 2020; Volume 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ballantine, D.J.; Tanner, C.C. Controlled Drainage Systems to Reduce Contaminant Losses and Optimize Productivity from New Zealand Pastoral Systems. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2013, 56, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Zhang, T.Q.; Drury, C.F.; Welacky, T.W.; Reynolds, W.D. Impacts of Liquid and Solid Manures under Controlled Drainage with Sub-Irrigation Recycling Systems on Water Quality and Crop Production; The 2009 Reno, Nevada, 21–24 June 2009; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wahba, M.A.S.; El-Ganainy, M.; Abdel-Dayem, M.S.; Gobran, A.; Kandil, H. Controlled Drainage Effects on Water Quality under Semi-Arid Conditions in the Western Delta of Egypt. Irrig. Drain. 2001, 50, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Evans, R.O.; Smith, J.T. Effect of Controlled Drainage and Vegetative Buffers on Drainage Water Quality from Wastewater Irrigated Fields. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, I.; Mushtaq, A. Water Pollution from Agricultural Activities: A Critical Global Review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Mishra, A.; Goyal, M.K. Water Neutrality: Concept, Challenges, Policies, and Recommendations. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 26, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, M.; Qin, R.; Mao, X. A Review on Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence, and Smart Technology in Water Treatment and Monitoring. Water 2022, 14, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayioğlu, M.A.; Türker, U. Digital Transformation for Sustainable Future-Agriculture 4.0: A Review. Tarim. Bilim. Derg. 2021, 27, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Halder, S.; Koley, B.; Adak, E.; Sengupta, S. The Role of Precision Farming in Sustainable Agriculture: An Overview. Int. J. Agric. Ext. Soc. Dev. 2024, 7, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kęsicka, B.; Stasik, R.; Kozłowski, M.; Choryński, A. Is Controlled Drainage of Agricultural Land a Common Used Practice?—A Bibliographic Analysis. Land 2023, 12, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannazarova, Z.; Juliev, M.; Abuduwaili, J.; Muratov, A.; Bekchanov, F. Drainage in Irrigated Agriculture: Bibliometric Analysis for the Period of 2017–2021. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 305, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstensen, M.V.; Hashemi, F.; Hoffmann, C.C.; Zak, D.; Audet, J.; Kronvang, B. Efficiency of Mitigation Measures Targeting Nutrient Losses from Agricultural Drainage Systems: A Review. Ambio 2020, 49, 1820–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kęsicka, B.; Stasik, R.; Kozłowski, M. Effects of Modelling Studies on Controlled Drainage in Agricultural Land on Reduction of Outflow and Nitrate Losses–a Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, G.; Lu, J.; Kun, Z.; Yang, G.; Ding, J. Effects of Controlled Drainage on Crop Yield, Drainage Water Quantity and Quality: A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchenham, B.; Charters, S.M. Guidelines for Performing Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering; Keele University: Staffs, UK; Durham University: Durham, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchenham, B.; Pearl Brereton, O.; Budgen, D.; Turner, M.; Bailey, J.; Linkman, S. Systematic Literature Reviews in Software Engineering—A Systematic Literature Review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2009, 51, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration: Updated Guidance and Exemplars for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusenbauer, M.; Haddaway, N.R. Which Academic Search Systems Are Suitable for Systematic Reviews or Meta-Analyses? Evaluating Retrieval Qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 Other Resources. Res. Synth. Methods 2020, 11, 181–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garousi, V.; Felderer, M.; Mäntylä, M.V. Guidelines for Including Grey Literature and Conducting Multivocal Literature Reviews in Software Engineering. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2019, 106, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybå, T.; Dingsøyr, T. Empirical Studies of Agile Software Development: A Systematic Review. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2008, 50, 833–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Youssef, M.A.; Chescheir, G.M. DRAINMOD: Model Use, Calibration, and Validation. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Chescheir, G.M.; Skaggs, R.W.; Negm, L.M. DRAINMOD Modeling Framework for Simulating Controlled Drainage Effect on Lateral Seepage from Artificially Drained Fields. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 254, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, L.M.; Youssef, M.A.; Jaynes, D.B. Evaluation of DRAINMOD-DSSAT Simulated Effects of Controlled Drainage on Crop Yield, Water Balance, and Water Quality for a Corn-Soybean Cropping System in Central Iowa. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, G.; Rudra, R.P.; Parkin, G.W.; Kulasekera, P.B.; Macrae, M.; Goel, P.K. Assessment of Impacts of Climate Change on Tile Discharge and Nitrogen Yield Using the Drainmod Model. Hydrology 2021, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, O.; Wesström, I.; Youssef, M.A.; Skaggs, R.W.; Joel, A. Evaluation of the DRAINMOD–N II Model for Predicting Nitrogen Losses in a Loamy Sand under Cultivation in South-East Sweden. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevé, M.A.; Skaggs, R.W.; Parsons, J.E.; Gilliam, J.W. Using the DRAINMOD-N Model to Study Effects of Drainage System Design and Management on Crop Productivity, Profitability and NO3–N Losses in Drainage Water. Agric. Water Manag. 1998, 35, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development Team, R.; Hanson, J.D.; Ahuja, L.R.; Shaffer, M.D.; Rojas, K.W.; DeCoursey, D.G.; Farahani, H.; Johnson, K. RZWQM: Simulating the Effects of Management on Water Quality and Crop Production. Agric. Syst. 1998, 57, 161–195. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, H.S.; Qi, Z.; Shedekar, V.; King, K. Using RZWQM2-P to Capture Tile Drainage Phosphorus Dynamics in Ohio. J. Environ. Qual. 2024, 54, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Malone, R.W.; Heilman, P.; Jaynes, D.B.; Ahuja, L.R.; Saseendran, S.A.; Kanwar, R.S.; Ascough, J.C. RZWQM Simulated Effects of Crop Rotation, Tillage, and Controlled Drainage on Crop Yield and Nitrate-N Loss in Drain Flow. Geoderma 2007, 140, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilhespy, S.L.; Anthony, S.; Cardenas, L.; Chadwick, D.; del Prado, A.; Li, C.; Misselbrook, T.; Rees, R.M.; Salas, W.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; et al. First 20 Years of DNDC (DeNitrification DeComposition): Model Evolution. Ecol. Model. 2014, 292, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Grant, B.; Qi, Z.; He, W.; VanderZaag, A.; Drury, C.F.; Helmers, M. Development of the DNDC Model to Improve Soil Hydrology and Incorporate Mechanistic Tile Drainage: A Comparative Analysis with RZWQM2. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 123, 104577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin Salehi, A.; Navabian, M.; Varaki, M.E.; Pirmoradian, N. Evaluation of HYDRUS-2D Model to Simulate the Loss of Nitrate in Subsurface Controlled Drainage in a Physical Model Scale of Paddy Fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, H.; Raeisi, E.; Hoehn, E.; Zare, M. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Irrigation Return Flow in Semi-Arid Regions of Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, Z.; Seidou, O.; Droste, R.L.; Wilkes, G.; Sunohara, M.; Topp, E.; Lapen, D.R. Using AnnAGNPS to Predict the Effects of Tile Drainage Control on Nutrient and Sediment Loads for a River Basin. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kęsicka, B.; Kozłowski, M.; Stasik, R.; Pińskwar, I. Controlled Drainage Effectiveness in Reducing Nutrient Outflow in Light of Climate Changes. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenon, G.; Hamrani, A.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Singh, B.; von Sperber, C. Neural Network Model Predictions for Phosphorus Management Strategies on Tile-Drained Organic Soils. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Brevé, M.A.; Mohammad, A.T.; Parsons, J.E.; Gilliam, J.W. Simulation of Drainage Water Quality with DRAINMOD. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 1995, 9, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Qi, Z.; Lu, C.; Tan, C.S.; Zhang, T.; Prasher, S.O. Evaluating RZ-SHAW Model for Simulating Surface Runoff and Subsurface Tile Drainage under Regular and Controlled Drainage with Subirrigation in Southern Ontario. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 237, 106179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Fei, L. Simulation and Evaluation of Water Quality Purification Performance in Irrigation District Drainage Ditch Wetlands under the Influence of Regional External Water Inputs. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 212, 107538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagage, M.; Abdulaziz, A.M.; Elbeih, S.F.; Hewaidy, A.G.A. Monitoring Soil Salinization and Waterlogging in the Northeastern Nile Delta Linked to Shallow Saline Groundwater and Irrigation Water Quality. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagage, M.; Hewaidy, A.G.A.; Abdulaziz, A.M. Groundwater Quality Assessment for Drinking, Irrigation, Aquaculture, and Industrial Uses in the Waterlogged Northeastern Nile Delta, Egypt: A Multivariate Statistical Approach and Water Quality Indices. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleff, T. Exploratory Data Analysis in Business and Economics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; ISBN 978-3-319-01516-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, T.; Yli-Halla, M.; Marttila, H.; Lötjönen, T.; Liimatainen, M.; Kekkonen, J.; Läpikivi, M.; Klöve, B.; Joki-Tokola, E. Leaching of Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Other Solutes from a Controlled Drainage Cultivated Peatland in Ruukki, Finland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.C.; Zak, D.; Kronvang, B.; Kjaergaard, C.; Carstensen, M.V.; Audet, J. An Overview of Nutrient Transport Mitigation Measures for Improvement of Water Quality in Denmark. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 155, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madramootoo, C.A.; Abbasi, N.A. One Hundred Years of Drainage Development in the Holland Marsh, Canada, and Implications for Long-term Sustainability. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 73, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.R.; Miranda, L.E.; Moore, M.T.; Krutz, L.J.; Czarnecki, J.M.P.; Kröger, R.; Baker, B.H.; Hogue, J.; Allen, P.J. Reduction of Solids and Nutrient Loss from Agricultural Land by Tailwater Recovery Systems. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2018, 73, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, R.; Moore, M.T.; Farris, J.L.; Gopalan, M. Evidence for the Use of Low-Grade Weirs in Drainage Ditches to Improve Nutrient Reductions from Agriculture. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2011, 221, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, D.M.; Gilliam, J.W.; Skaggs, R.W.; Lebo, M.E.; Campbell, R.G. Effects of Controlled Drainage on Forest Water Quality. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.R.; King, K.W.; Fausey, N.R. Drainage Water Management Effects on Tile Discharge and Water Quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.L.; Melvin, S.W.; Lemke, D.W.; Lawlor, P.A.; Crumpton, W.G.; Helmers, M.J. Subsurface Drainage in Iowa and the Water Quality Benefits and Problem. In Proceedings of the Drainage VIII, Sacramento, CA, USA, 21–24 March 2004; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2004; pp. 39–050. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoska, E.; Bastiene, N.; Saulys, V. Evaluation of Controlled Drainage Efficiency in Lithuania. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 60, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchithanantham, S.; Sri Ranjan, R.; Bullock, P. Protecting Water Quality Using Controlled Drainage as an Agricultural Bmp for Potato Production. Trans. ASABE 2014, 57, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morari, F.; Lugato, E.; Polese, R.; Berti, A.; Giardini, L. Nitrate Concentrations in Groundwater under Contrasting Agricultural Management Practices in the Low Plains of Italy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 147, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, S.; Shao, G.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Alternate Drought and Flooding Stress on Water Use, and Nitrogen and Phosphorus Losses in a Paddy Field. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejia, M.N.; Madramootoo, C.A. Improved Water Quality through Water Table Management in Eastern Canada. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1998, 124, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.Y.F.; Drury, C.F.; Serem, V.K.; Tan, C.S.; Gaynor, J.D. Modeling and Testing of the Effect of Tillage, Cropping and Water Management Practices on Nitrate Leaching in Clay Loam Soil. Agric. Water Manag. 2000, 43, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Drury, C.F.; Soultani, M.; Van Wesenbeeck, I.J.; Ng, H.Y.F.; Gaynor, J.D.; Welacky, T.W. Effect of Controlled Drainage and Tillage on Soil Structure and Tile Drainage Nitrate Loss at the Field Scale. Water Sci. Technol. 1998, 38, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Singh, G. Subsurface Drainage and Subirrigation for Increased Corn Production in Riverbottom Soils. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 4865–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Drury, C.F.; Soultani, M.; Gaynor, J.D.; Welacky, T.W.; van Wesenbeeck, I.J.; Ng, H.Y.F. Effect of Controlled Drainage/Subirrigation on Tomato Yield and Water Quality. Acta Hortic. 1997, 449, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenon, G.; Madramootoo, C.A.; von Sperber, C.; Ebtehaj, I.; Bonakdari, H.; Singh, B. Nutrient Release in Drainage Discharge from Organic Soils under Two Different Agricultural Water Management Systems. Hydrol. Process 2023, 37, e14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesström, I.; Messing, I.; Linnér, H.; Lindström, J. Controlled Drainage—Effects on Drain Outflow and Water Quality. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 47, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Shi, H.; Li, R.; Miao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B. Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, W.F. Drainage on the Delmarva Peninsula: Past History and Future Challenges. In Proceedings of the 9th International Drainage Symposium Held Jointly with CIGR and CSBE/SCGAB Proceedings, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–16 June 2010; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fausey, N.R. Comparison of Free Drainage, Controlled Drainage, and Subirrigation Water Management Practices in an Ohio Lakebed Soil. In Proceedings of the 2004 ASAE Annual Meeting, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1–4 August 2004; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Nelson, K.A.; Singh, G.; Udawatta, R.P. Long-Term Drainage Water Recycling Affects Soil Health and Soil Properties. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2023, 78, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, R.; Verma, S. Performance of Drainage Water Management Systems in Illinois, United States. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2012, 67, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.Q.; Tan, C.S.; Zheng, Z.M.; Welacky, T.; Wang, Y.T. Drainage Water Management Combined with Cover Crop Enhances Reduction of Soil Phosphorus Loss. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Valero, C.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Stämpfli, N. Water Table Management Impacts on Phosphorus Loads in Tile Drainage. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 89, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Youssef, M.A.; Chescheir, G.M. Methods to Estimate Effects of Drainage Water Management on Annual Nitrogen Losses to Surface Waters. In Proceedings of the 9th International Drainage Symposium Held Jointly with CIGR and CSBE/SCGAB Proceedings, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–16 June 2010; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]


| Reference | Review Type, Years | Research Questions /Aim/Focus | Search Keywords | Database |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | Bibliometric analysis 2000–2022 | To identify research progress and trends related to CD. | ((‘control* drainage’ OR ‘control* tile drainage’ OR ‘drainage water management’ OR ‘groundwater management’) AND (‘agricultural drainage’ OR ‘subsurface drainage’ OR ‘water quality’)) | Web of Science |
| [19] | Bibliometric analysis 2017–2021 | To analyze hot topics and important regions of irrigation and drainage research as well as to use historical bibliometric data to gain new insights into trends and the emphasis of international irrigation and drainage research. | “Irrigation and Drainage”. | Scopus |
| [20] | Meta-analysis 1900–2019 | This review compiles the available evidence on nitrate and TP removal efficiencies from both pilot and full-scale field studies on drainage mitigation measures to provide a synthesis of the existing body of peer-reviewed literature. | NA | Web of Science |
| [21] | Meta-analysis until 31 December 2020 | In this study, the authors focused on comparing the results obtained for DRAINMOD model studies under CD vs. FD conditions and its effect on the reduction in outflow and nitrate losses of drained agricultural land. They used meta-analyses to synthetically and also statistically indicate the effectiveness of CD use in quantitative and qualitative aspects of drainage outflow. | “controlled drainage” AND “drainmod” | Web of Science, Scopus |
| [22] | Meta-analysis 1960–2019 | The specific objectives of this study were the following: a) estimate the effects of CD on crop yield and drainage water quantity and quality; and b) identify a cropping system, drainage method, and climate type that benefit crop yield and drainage water quantity and quality under CD systems. | controlled drainage, drainage water management, water table management, yield, nitrogen, phosphorus, and drainage water quality | Web of Science |
| This review | SLR 1986–2024 | When are studies on the drainage topic published? Is controlled drainage always better than free drainage? Is climate change considered in drainage water quality studies? What computer tools are used to model drainage systems? Is artificial intelligence used? What biogenic substances are considered in drainage water quality analyses? | (“fre* drainag*” OR “control* drainag*”) AND (“water* qual*”) | Web of Science, Scopus |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| IC1: Universally accepted works related to water quality of drainage systems. | EC1: Exclude articles not primarily about water quality in drainage systems, even if they contain relevant keywords. EC1.2: Reject articles containing an economic analysis as the primary idea. EC1.3: Reject articles that refer to pollutants other than biogenic substances. EC1.4: Reject articles analyzing specific soils (e.g., saline soils) or urbanized areas. EC1.5: Reject the articles in which the primary idea is to analyze drainage’s influence on crop production. |
| IC2. Include original not repeating papers on water quality of drainage systems. | EC2: Exclude relevant sources that repeat ideas described in earlier works. If there are several papers of the same authors with a similar abstract, i.e., one paper is an extension of another, the less extended (i.e., containing less pages) paper is excluded. |
| IC3. The full-text paper must be available to download. | EC3. The full-text paper is not available. |
| IC4. Include fully described scientific papers. | EC4: Exclude papers whose length is less than 6 pages, since such short papers can present only a general idea but not describe overall approach. |
| IC5. The paper must be written in English. | EC5. The paper is written in other languages, i.e., not English |
| IC6. Include original not duplicating papers on water quality of drainage systems. | EC6. Exclude duplicating papers. |
| IC7. Include peer-reviewed journal publications (research papers), proceeding papers, and reviews. | EC7. Exclude shoer papers, grey literature, posters, Master’s theses, Doctoral theses, and books. |
| IC8. The bibliometric data (i.e., title, keywords, and abstract) of the paper is provided. | EC8. The bibliometric data are missing. |
| DI No. | Extracted Item | Description or Possible Values | RQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reference | Reference to the study | -- |
| 2. | Year | Year of publication | RQ1, RQ6 |
| 3. | Advantage of CD drainage over FD | Advantage of controlled drainage (CD) over free drainage (FD) | RQ5, RQ6 |
| 4. | Climate changes | Does the article discuss the impact of climate change on the research results? | RQ2, RQ6 |
| 5. | Type of model | Use of artificial intelligence (AI) | RQ3, RQ6 |
| 6. | Used approach (computer model) | DRAINMOD; RZWQM; RZ-SHAW; DNDC; HYDRUS-2D; PHREEQC; AnnAGNPS; GFDL-ESM4; UKESM1–0-LL; MPI-ESM1-2-HR | RQ3, RQ6 |
| 7. | Field studied/application domain (biogenic materials and other) | Nitrates; nitrites; ammonium; nitrogen; phosphates; phosphorus | RQ4, RQ6 |
| Years | PSS-1 | PSS-2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | PPs | Rs | All | As | PPs | Rs | All | |
| Web of Science (WoS) | ||||||||
| 1985–2024 | 158 | 37 | 8 | 192 * | 147 | 36 | 8 | 180 |
| Scopus | ||||||||
| 1985–2024 | 163 | 74 | 8 | 245 | 149 | 73 | 7 | 229 |
| The merged set of papers (PSS-3) | Exclude duplicating papers (PSS-4) | |||||||
| 1985–2024 | 296 | 109 | 15 | 409 | 231 | 87 | 0 ** | 318 |
| Filtered set of papers (PSS-6) | A final set of papers (PSS-7) | |||||||
| 1986–2024 | 128 | 42 | 0 | 170 | 106 | 38 | 0 | 144 |
| Year | Number | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) | (11) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1986 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1987 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1989 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1990 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1991 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1992 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1993 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 1994 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 1995 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1996 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1997 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1998 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 1999 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2000 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2001 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2002 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2003 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 2004 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 2006 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2007 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| 2008 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2009 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 2010 | 9 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 4 |
| 2011 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 2012 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
| 2013 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 2014 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 2015 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
| 2016 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2017 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2018 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 2019 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2020 | 6 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 3 |
| 2021 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 2022 | 5 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| 2023 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 2 (AI) | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| 2024 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 4 |
| Computer Tools | Description | References |
|---|---|---|
| DRAINMOD | DRAINMOD is a hydrological model used to analyze drainage and soil moisture conditions. It is a process-based, distributed, field-scale model developed to describe the hydrology of soils with poor drainage and those that have been artificially drained. The model is based on water balances in the soil profile, on the field surface, and, in some cases, in the drainage system [29]. | [30,31,32,33,34] |
| RZWQM | Root Zone Water Quality Mode (RZWQM) is a root zone water and nutrient model with a focus on water quality and plant interactions. It simulates major physical, chemical, and biological processes in an agricultural crop production system. RZWQM is a process-based model that simulates the growth of the plant and the movement of water, nutrients, and pesticides over, within, and below the crop root zone of a unit area [35]. It is one-dimensional, meaning it is vertical in the soil profile. | [35,36,37] |
| DNDC | DeNitrification-DeComposition (DNDC) is a model of the land and nitrogen cycles used to simulate greenhouse gas emissions [38]. | [39] |
| HYDRUS-2D | HYDRUS-2D is a model of soil moisture and solute movement that is based on physical equations. | [40] |
| PHREEQC | PHREEQC is a chemical reaction model that focuses on geochemical processes in solutions. | [41] |
| AnnAGNPS | The Annualized Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollution Model (AnnAGNPS) is a model used to predict erosion and pollution in the agricultural sector. | [42] |
| GFDL-ESM4, UKESM1-0-LL, MPI-ESM1-2-HR |
The Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Earth System Model (GFDL-ESM4) is a comprehensive earth system model designed for climate change simulations. The United Kingdom Earth System Model (UKESM1-0-LL) is a sophisticated tool used to make precise climate predictions. The Max Planck Institute Earth System Model (MPI-ESM1-2-HR) employs physical equations to model climate systems. As with GFDL and UKESM, AI components can be used in specific areas. | [43] |
| NN | In the field of machine learning, a neural network (NN) is a model that draws inspiration from the structure and function of biological neural networks present in the brains of animals. In the analyzed article, seven NN models were found. The seven models consist of the following: NN (FNN), deep feedforward NN (DFNN), long short-term memory (LSTM), bidirectional LSTM (Bi-LSTM), closed recurrent block (GRU), general regression NN (GRNN), and radial basis function NN (RBFNN). | [44] |
| Nitrates | Nitrites | Ammonium | N | Phosphates | P | Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrates | 1 | 0.456 | 0.648 | 0.579 | 0.415 | 0.306 | 0.377 |
| Nitrites | 0.456 | 1 | 0.507 | 0.526 | 0.352 | 0.384 | 0.301 |
| Ammonium | 0.648 | 0.507 | 1 | 0.627 | 0.567 | 0.364 | 0.411 |
| N | 0.579 | 0.526 | 0.627 | 1 | 0.641 | 0.660 | 0.628 |
| Phosphates | 0.415 | 0.352 | 0.567 | 0.641 | 1 | 0.619 | 0.418 |
| P | 0.306 | 0.384 | 0.364 | 0.659 | 0.619 | 1 | 0.634 |
| Years | 0.377 | 0.301 | 0.411 | 0.628 | 0.418 | 0.634 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalibatienė, D.; Stankevičienė, R.; Survilė, O. A Systematic Review on the Influence of Drainage Systems on the Environment. Water 2025, 17, 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101408
Kalibatienė D, Stankevičienė R, Survilė O. A Systematic Review on the Influence of Drainage Systems on the Environment. Water. 2025; 17(10):1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101408
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalibatienė, Diana, Rasa Stankevičienė, and Oksana Survilė. 2025. "A Systematic Review on the Influence of Drainage Systems on the Environment" Water 17, no. 10: 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101408
APA StyleKalibatienė, D., Stankevičienė, R., & Survilė, O. (2025). A Systematic Review on the Influence of Drainage Systems on the Environment. Water, 17(10), 1408. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17101408









