Non-Point Source Pollution Risk Assessment in Karst Basins: Integrating Source–Sink Landscape Theory and Soil Erosion Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
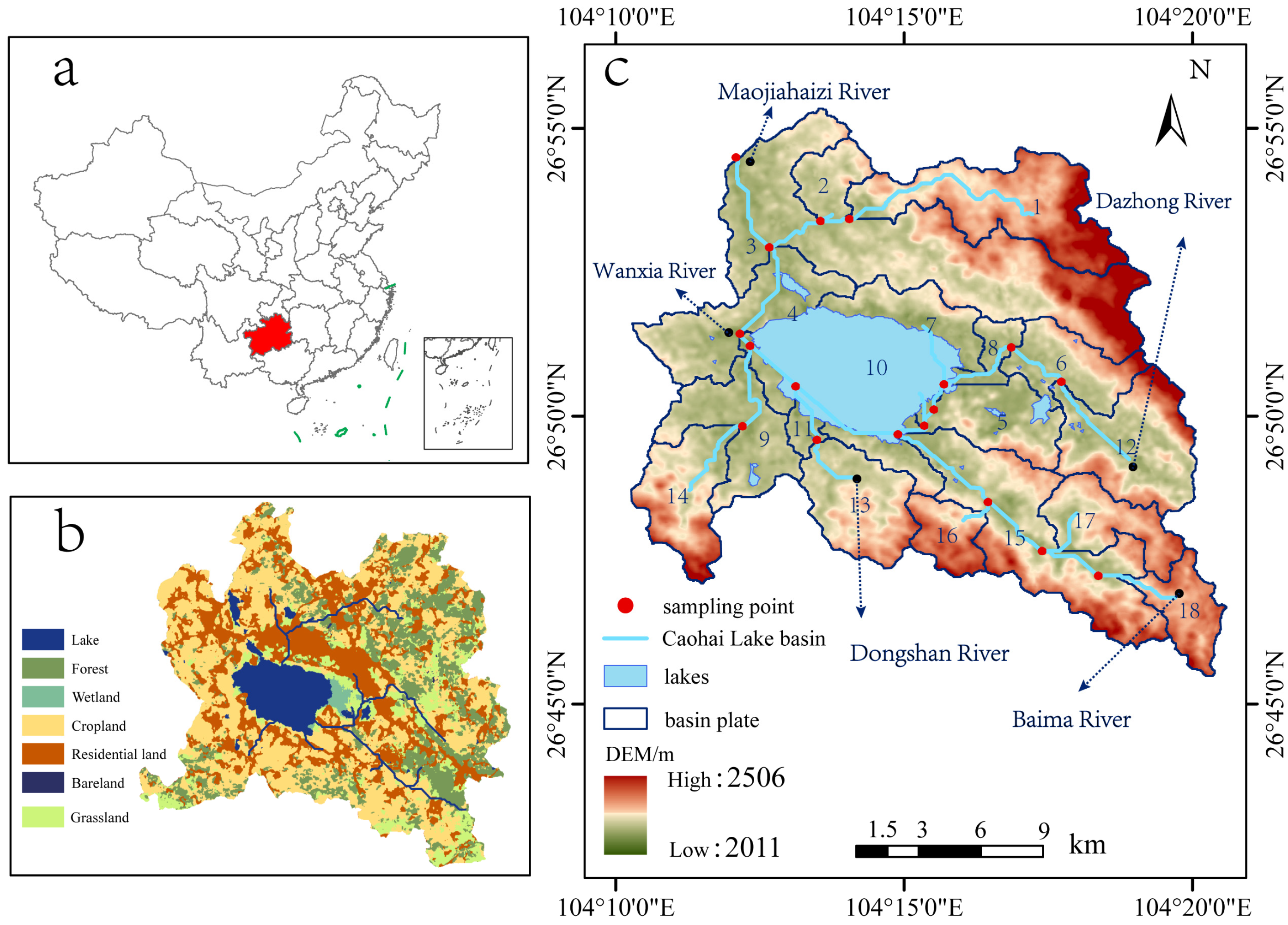
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. NPS Pollution Risk Assessment Based on the Source–Sink Theory
2.4. Identification Method of CSA for NPS Pollution
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Landscape Characteristics of the Karst Basin
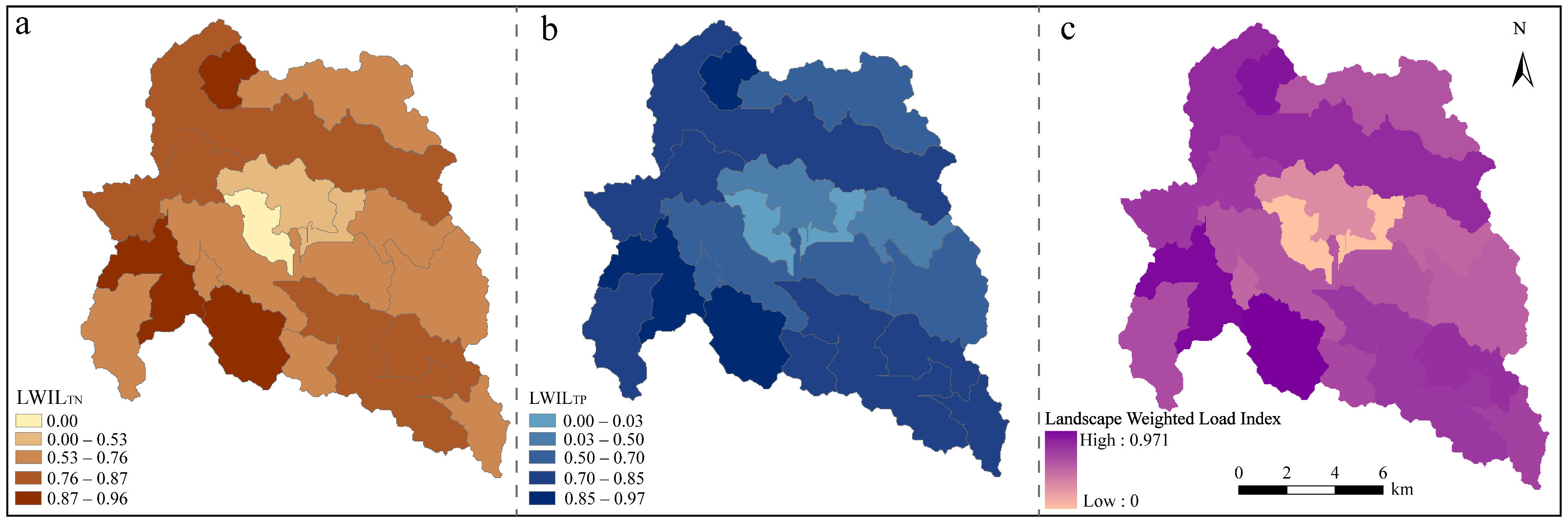
3.2. Spatial Risk Assessment of “Source–Sink” Landscapes in the Karst Basin
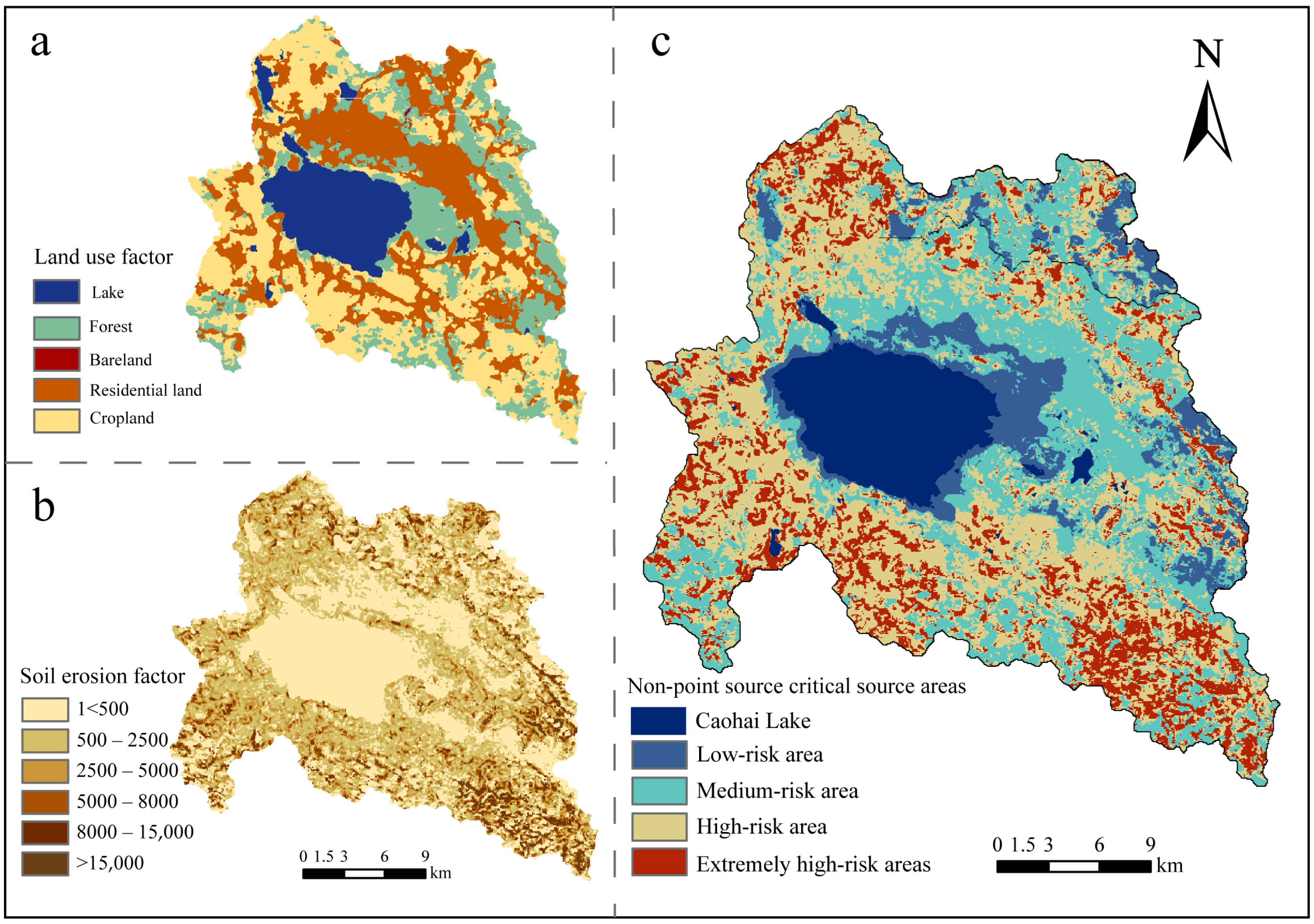
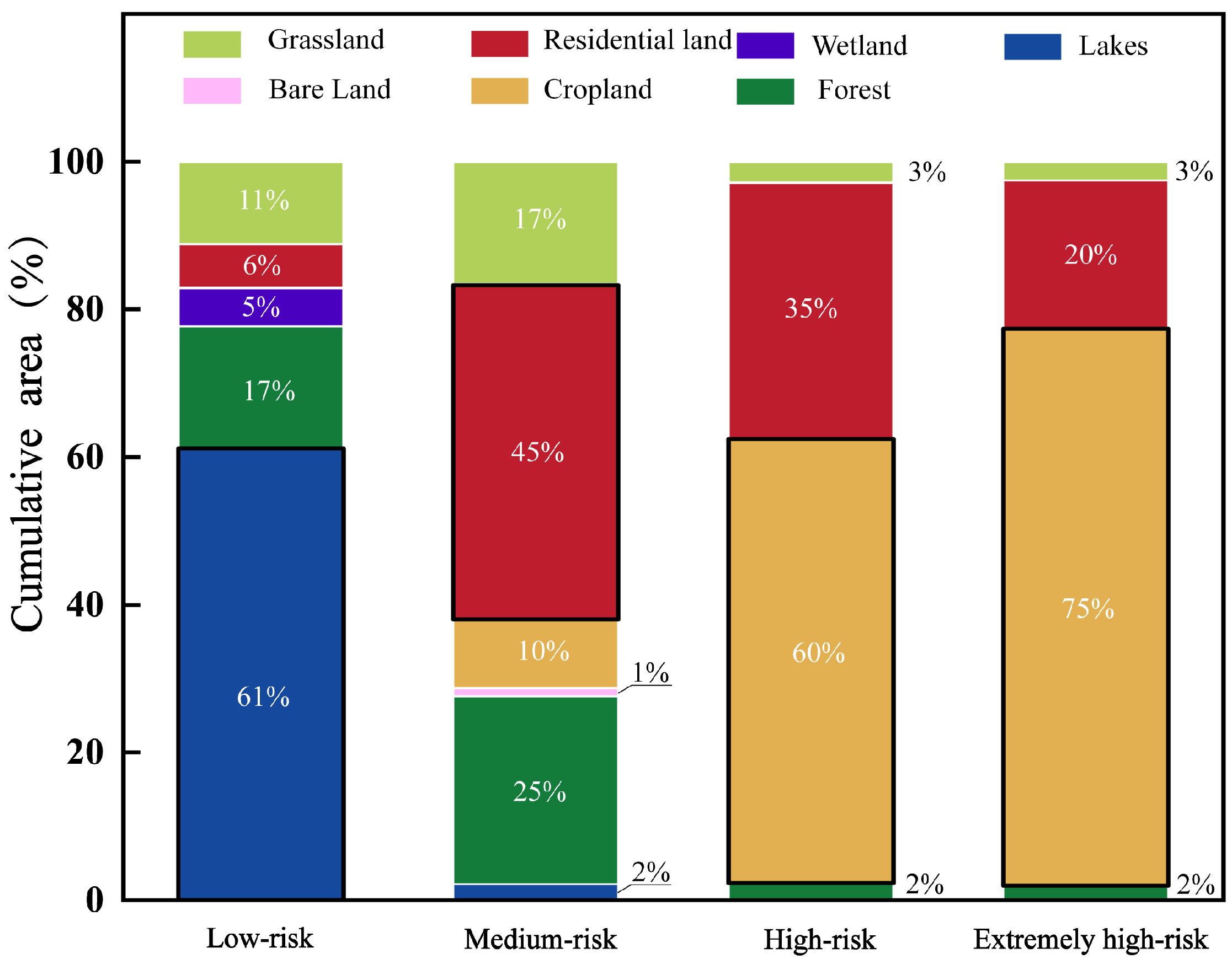
3.3. Identification and Composition of Critical Source Areas (CSAs) in the Karst Basin
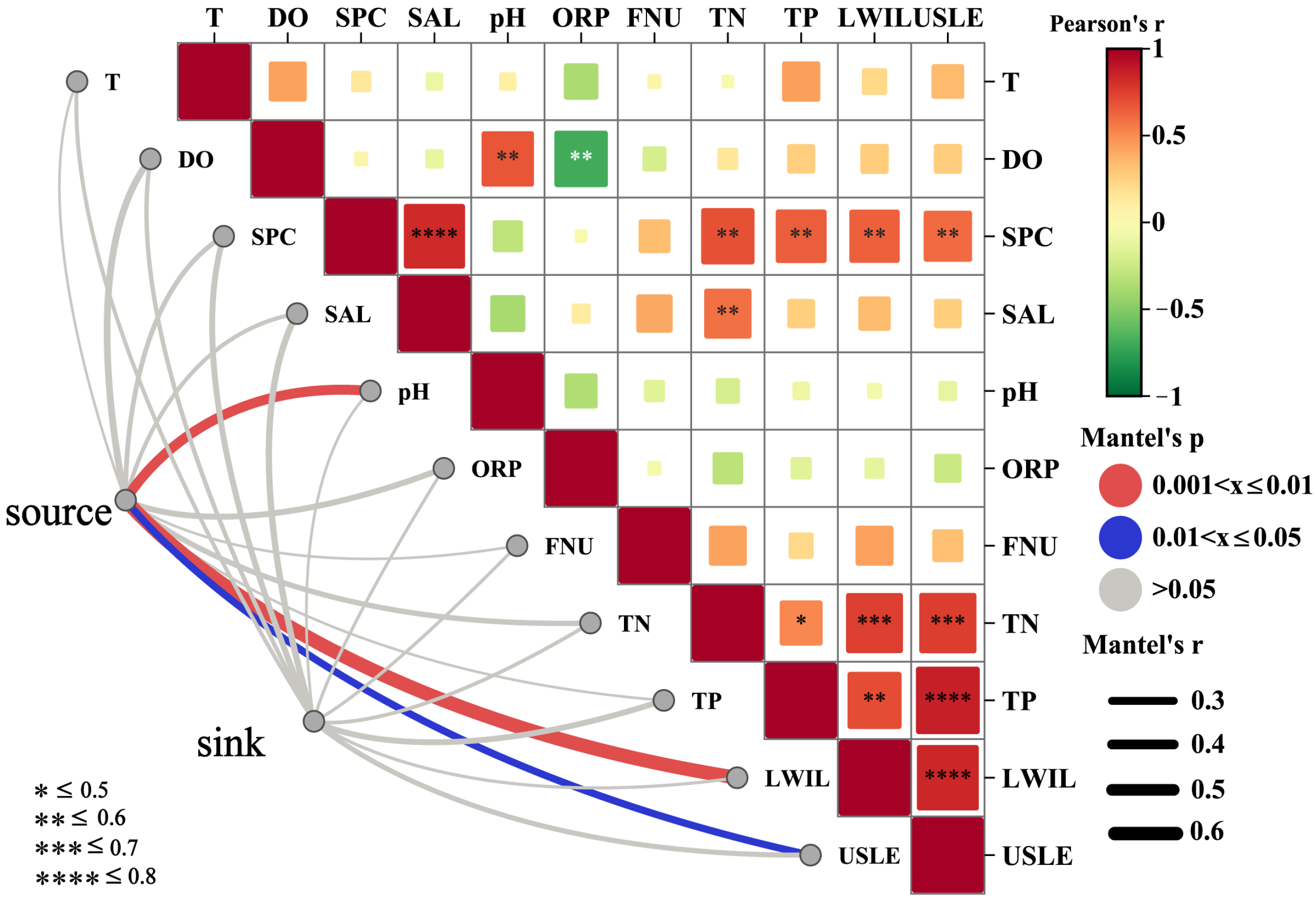
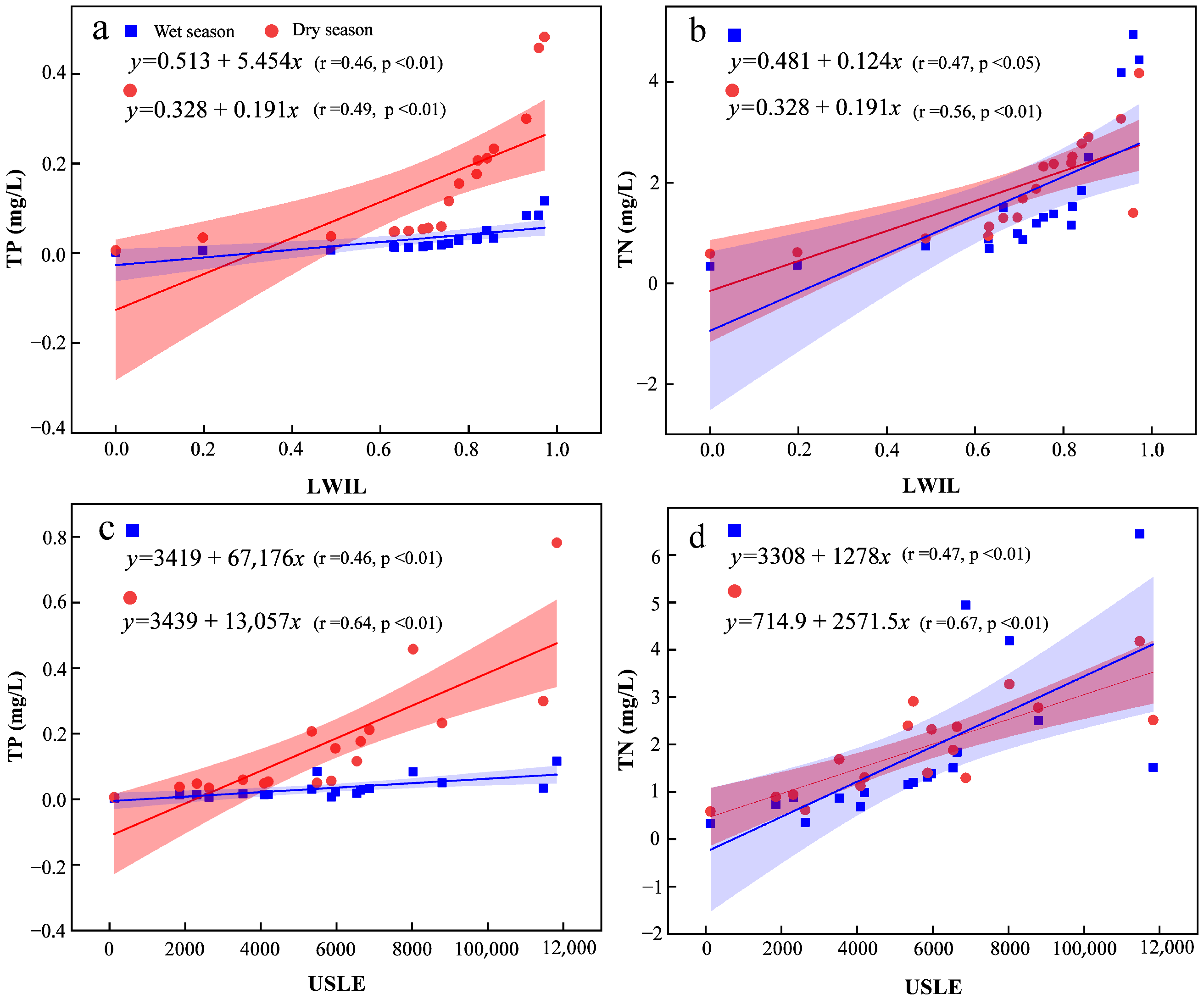
3.4. Coupling Relationships Between CSA Key Factors and Basin Water Quality
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of NPS Pollution Risks and Major Sources in the Karst Basin
4.2. Influence of CSA Key Factors on TP and TN in the Basin
4.3. Management Recommendations for Non-Point Source Pollution in the Karst Caohai Lake Basin
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varekar, V.; Yadav, V.; Karmakar, S. Rationalization of water quality monitoring locations under spatiotemporal heterogeneity of diffuse pollution using seasonal export coefficient. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978–2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Ren, G.; Feng, Y. Analysis of the environmental behavior of farmers for non-point source pollution control and management: An integration of the theory of planned behavior and the protection motivation theory. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamizar, M.L.; Brown, C.D. Modelling triazines in the valley of the River Cauca, Colombia, using the annualized agricultural non-point source pollution model. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Qiu, J.; Hong, Q.; Chen, L. Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, R. Mitigating Emerging Contaminants from Urban Non-Point Source Pollution: The Key to Achieving the SDGs. ACS ES T Water 2024, 4, 3115–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.C.; Froemke, P. Nationwide Assessment of Nonpoint Source Threats to Water Quality. Bioscience 2012, 62, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Liersch, S.; Schmidt, G. Towards the implementation of the European Water Framework Directive?: Lessons learned from water quality simulations in an agricultural watershed. Land Use Policy 2009, 26, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tan, X.; Liang, J.; Cui, Y.; Gao, Q. Impact of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution on River Water Quality: Evidence From China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 858822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Asci, S.; Vorotnikova, E. Valuing the Potential Benefits of Water Quality Improvements in Watersheds Affected by Non-Point Source Pollution. Water 2016, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosendorf, P.; Vyskoc, P.; Prchalova, H.; Fiala, D. Estimated Contribution of Selected Non-point Pollution Sources to the Phosphorus and Nitrogen Loads in Water Bodies of the Vltava River Basin. Soil Water Res. 2016, 11, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Cai, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L. “Period-area-source” hierarchical management for agricultural non-point source pollution in typical watershed with integrated planting and breeding. J. Hydrol. 2024, 635, 131198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Gao, L.; Liu, M. Uncertainty in simulation of land-use change impacts on catchment runoff with multi-timescales based on the comparison of the HSPF and SWAT models. J. Hydrol. 2019, 573, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, M.; Bosch, D.; Nangia, V.; Narasimhan, B. SWAT: Agricultural water and Nonpoint source pollution management at a watershed scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 175, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Lai, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal distribution of nitrogen biogeochemical processes in the coastal regions of northern Beibu Gulf, south China sea. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Cai, C.; Zhang, J. Discussing on “source-sink” landscape theory and phytoremediation for non-point source pollution control in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44797–44806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Pan, X.; Fang, H. Improving the accuracy of nonpoint-source pollution estimates in inland waters with coupled satellite-UAV data. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Fu, T.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, Y. Identification of the potential risk areas for soil heavy metal pollution based on the source-sink theory. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, R.; Parise, M. Karst environments: Problems, management, human impacts, and sustainability an introduction to the special issue. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, S. Karst ecosystem and environment: Characteristics, evolution processes, and sustainable development. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, S.; Wang, T.; Yue, F.; Peng, T.; Zhong, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; et al. Effects of agricultural activities coupled with karst structures on riverine biogeochemical cycles and environmental quality in the karst region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Qiao, G. Effect of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling Characteristic on Eutrophication of Water Body. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 8, 82–85, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken ME, S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lv, L.; He, C. Study on the causes and countermeasures of water pollution and water environment problems in the Caohai sub-watershed of Weining, Guizhou Province. Groundwater 2022, 44, 83–85. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Tong, D.; Zhang, H. Analysis of the ecological status and control measures of Caohai. Soil Water Conserv. China 2018, 3, 59–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Zhao, W. Source-sink landscape theory and its ecological significance. Front. Biol. China 2008, 3, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Xue, B.; Yinglan, A.; Liu, T. Non-point source pollution risks in a drinking water protection zone based on remote sensing data embedded within a nutrient budget model. Water Res. 2019, 157, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Guo, Q.; Wei, R.; Wei, Y. Anthropogenic nitrogen and phosphorus inputs in a new perspective: Environmental loads from the mega economic zone and city clusters. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, H.; Qi, L. Critical Source Area Identification and Risk Assessment of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution of the Source Areas of Liaohe River Watershed. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2014, 36, 670–677. [Google Scholar]
- Karra, K.; Kontgis, C.; Weil, Z.S.; Mazzariello, M.M.; Steven, P.M.; Brumby, S.P. Global land use/land cover with Sentinel-2 and deep learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 11–16 July 2021; pp. 4704–4707. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Study on the prediction of soil erosion in small watersheds using the USLE model and GIS IDRISI. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- King, R.S.; Richardson, C.J. Integrating Bioassessment and Ecological Risk Assessment: An Approach to Developing Numerical Water-Quality Criteria. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.S.; King, R.S.; Richardson, C.J. Two statistical methods for the detection of environmental thresholds. Ecol. Model. 2003, 166, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Qin, S.; Yao, S.; Chen, J.; Lei, S.; Tan, S.; Zhou, B. Effects of “source-sink” landscape on spatiotemporal differentiation of phosphorus output in multiple watersheds in mountainous areas based on the modified location-weighted landscape index. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narany, T.S.; Aris, A.Z.; Sefie, A.; Keesstra, S. Detecting and predicting the impact of land use changes on groundwater quality, a case study in Northern Kelantan, Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahearn, D.S.; Sheibley, R.W.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Anderson, M.; Johnson, J.; Tate, K.W. Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the western Sierra Nevada, California. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Lu, Y. A conceptual model for a process-oriented landscape pattern analysis. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Luo, Q.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Tang, J.; Liang, X.; Ma, E.; Cheng, R.; Fensholt, R.; Brandt, M.; et al. Mapping global lake dynamics reveals the emerging roles of small lakes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Rousseau, A.N.; Yan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, Y.; Cui, H. Identifying the critical lakeshore zone to optimize landscape factors for improved lake water quality in a semi-arid region of Northeastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Tang, Q.; Sheng, Y. Effect of salinity on the determination of dissolved non-reactive phosphorus and total dissolved phosphorus in coastal waters. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.W.; Baillie, B.R.; Bishop, K.; Ferraz, S.; Hogbom, L.; Nettles, J. The effects of forest management on water quality. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 522, 120397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trogisch, S.; Liu, X.; Rutten, G.; Xue, K.; Bauhus, J.; Brose, U.; Bu, W.; Cesarz, S.; Chesters, D.; Connolly, J.; et al. The significance of tree-tree interactions for forest ecosystem functioning. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2021, 55, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; O’Donoghue, C.; Ryan, M.; Kilcline, K.; Upton, V.; Spillane, C. The impact of forestry as a land use on water quality outcomes: An integrated analysis. For. Policy Econ. 2020, 116, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, C.A.; Bubenzer, G.D.; Lee, G.B.; Madison, F.W.; McHenry, J.R. Nutrient trapping by sediment deposition in a seasonally flooded lakeside wetland. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dalabay, N.; Lu, P.; Wu, F. Effects of tillage practices and slope on runoff and erosion of soil from the Loess Plateau, China, subjected to simulated rainfall. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro Correa, T.L.; de Queiroz, M.V.; de Araujo, E.F. Cloning, recombinant expression and characterization of a new phytase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 170, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Tang, X.; Chen, J. Combined use of stable nitrogen and oxygen isotopes to constrain the nitrate sources in a karst lake. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrebos, D.; Beauchard, O.; Meire, P. The impact of land use and spatial mediated processes on the water quality in a river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficetola, G.F.; Denoel, M. Ecological thresholds: An assessment of methods to identify abrupt changes in species-habitat relationships. Ecography 2009, 32, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. A source-sink landscape approach to mitigation of agricultural non-point source pollution: Validation and application. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Lai, X.; Li, K. Water quality assessment of rivers in Lake Chaohu Basin (China) using water quality index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, G.-B.; Zhang, Z.; Tuo, D.-F.; Bai, R.-R.; Qiao, F.-F. Relative contribution of root physical enlacing and biochemistrical exudates to soil erosion resistance in the Loess soil. Catena 2017, 153, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salhi, A.; Benabdelouahab, S.; Bouayad, E.O.; Benabdelouahab, T.; Larifi, I.; El Mousaoui, M.; Acharrat, N.; Himi, M.; Ponsati, A.C. Impacts and social implications of landuse-environment conflicts in a typical Mediterranean watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pereira, P.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W. Global karst vegetation regime and its response to climate change and human activities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, F.R.; Gerhard, P.; de Barros Ferraz, S.F.; Wenger, S.J. Multi-scale assessment of forest cover in an agricultural landscape of Southeastern Brazil: Implications for management and conservation of stream habitat and water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ni, J.P.; Chen, C.L.; Xie, D.T.; Shao, J.A.; Chen, F.X.; Lei, P. Source-sink landscape spatial characteristics and effect on non-point source pollution in a small catchment of the Three Gorge Reservoir Region. J. Mt. Sci. 2018, 15, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, J. Landscape patterns regulate non-point source nutrient pollution in an agricultural watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xu, G.; Li, Z.; Dang, Y.; Li, Q.; Min, Z.; Gu, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Effects of comprehensive landscape patterns on water quality and identification of key metrics thresholds causing its abrupt changes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Turner, M.G. Importance of landscape heterogeneity in sustaining hydrologic ecosystem services in an agricultural watershed. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Q. Biogeochemical Processes and Matter Cycle of the Earth’s Surface—The Basin Weathering of South-West Karst Area and Nutrients Elements Cycle; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 169–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.-M.; Wen, Z.-G. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juncal MJ, L.; Masino, P.; Bertone, E.; Stewart, R.A. Towards nutrient neutrality: A review of agricultural runoff mitigation strategies and the development of a decision-making framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Jin, Z.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous removal of phosphate and ammonium nitrogen from agricultural runoff by amending soil in lakeside zone of Karst area, Southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 289, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Luo, G.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Tian, S.; Li, C.; Deng, Y. Changes in ecosystem service values in karst areas of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 301, 107026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.; Ciais, P.; Rudbeck Jepsen, M.; Penuelas, J.; Wigneron, J.P.; Xiao, X.; Song, X.P.; Horion, S.; et al. Forest management in southern China generates short term extensive carbon sequestration. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Wang, J. Effects of source-sink landscape proximity on the spatial-temporal water quality from the perspective of cost distance in an agricultural basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhong, Q.; Ni, J. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics and storage of C, N, and P in secondary forests of the karst region on the Guizhou Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 8606–8614. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, F.; Du, S. Assessment and analysis of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus loads in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area of Hubei Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 412, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, S.; Chen, F.; Hu, X. Availability of soil nitrogen and phosphorus at typical stages of forest succession in the hilly red soil region of the central subtropics. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 4673–4680. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Skinner, M. Wetland phosphorus dynamics and phosphorus removal potential. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.R.; Zak, D.; Audet, J.; Petersen, R.J.; Lange, J.; Oehmke, C.; Wichtmann, W.; Kreyling, J.; Grygoruk, M.; Jablonska, E.; et al. Wetland buffer zones for nitrogen and phosphorus retention: Impacts of soil type, hydrology and vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Land Use Type | Area (hm2) | User Accuracy | Producer Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sink landscapes | Wetland | 269 | 81.81% | 84.37% |
| Forest | 6544 | 92.72% | 96.22% | |
| Grassland | 3352 | 86.50% | 82.35% | |
| Lake | 2497 | 86.36% | 79.16% | |
| Source landscapes | Cropland | 14,211 | 95.10% | 91.80% |
| Residential land | 9539 | 90.78% | 94.52% | |
| Bare land | 25 | 75.00% | 75.00% | |
| Kappa coefficient: 0.88 | Overall accuracy: 91% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, W.; Huang, X.; Lu, J.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Non-Point Source Pollution Risk Assessment in Karst Basins: Integrating Source–Sink Landscape Theory and Soil Erosion Modeling. Water 2025, 17, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010132
Hu S, Yang Y, Chen J, Yu W, Huang X, Lu J, He Y, Zhang Y, Yang H, Xu X. Non-Point Source Pollution Risk Assessment in Karst Basins: Integrating Source–Sink Landscape Theory and Soil Erosion Modeling. Water. 2025; 17(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010132
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Senhua, Yongqiong Yang, Jingan Chen, Wei Yu, Xia Huang, Jia Lu, Yun He, Yeyu Zhang, Haiquan Yang, and Xiaorong Xu. 2025. "Non-Point Source Pollution Risk Assessment in Karst Basins: Integrating Source–Sink Landscape Theory and Soil Erosion Modeling" Water 17, no. 1: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010132
APA StyleHu, S., Yang, Y., Chen, J., Yu, W., Huang, X., Lu, J., He, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, H., & Xu, X. (2025). Non-Point Source Pollution Risk Assessment in Karst Basins: Integrating Source–Sink Landscape Theory and Soil Erosion Modeling. Water, 17(1), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010132








