Allelopathic Suppression of Cyanobacterial Blooms by the Aquatic Plant Vallisneria natans Enhanced by Red and Blue LED Light Supplementation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquisition of V. natans Culture Media for LED Light Supplementation
2.2. Stock Culture of M. aeruginosa and Experimental Treatments
2.3. Algal Conditions and Biochemical Parameters
2.3.1. Cell Density and Fluorescence Parameters
2.3.2. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Phycocyanin Content
2.4. Data Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
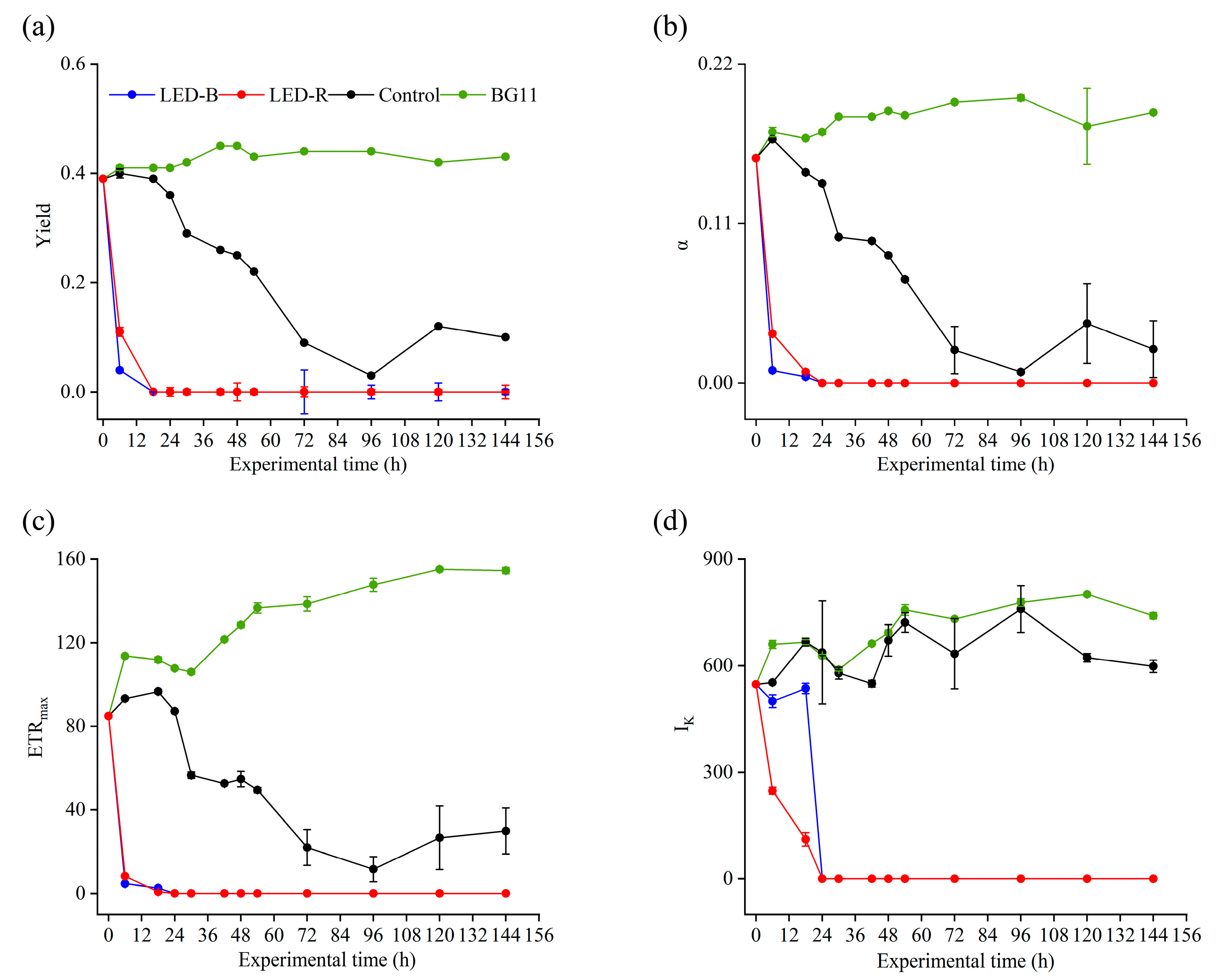
3.1. Cell Conditions and Fluorescence Parameters
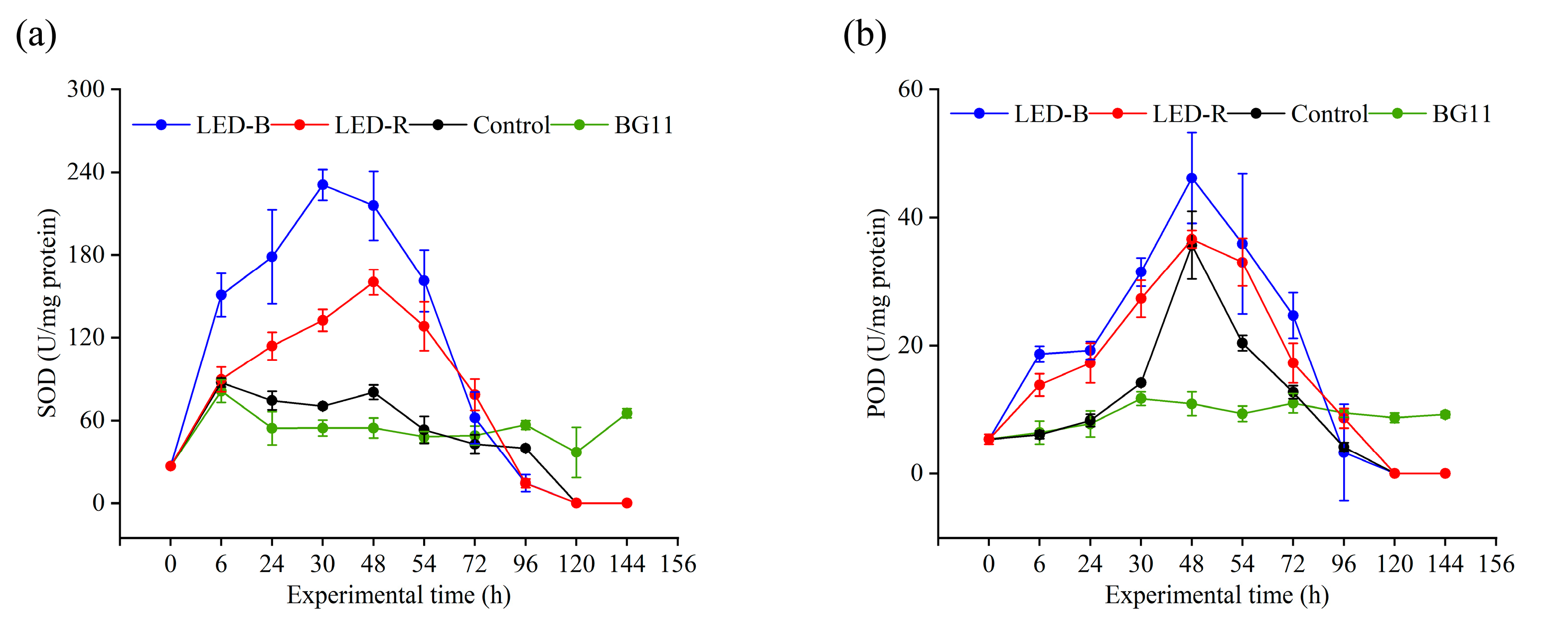
3.2. SOD and POD Activity
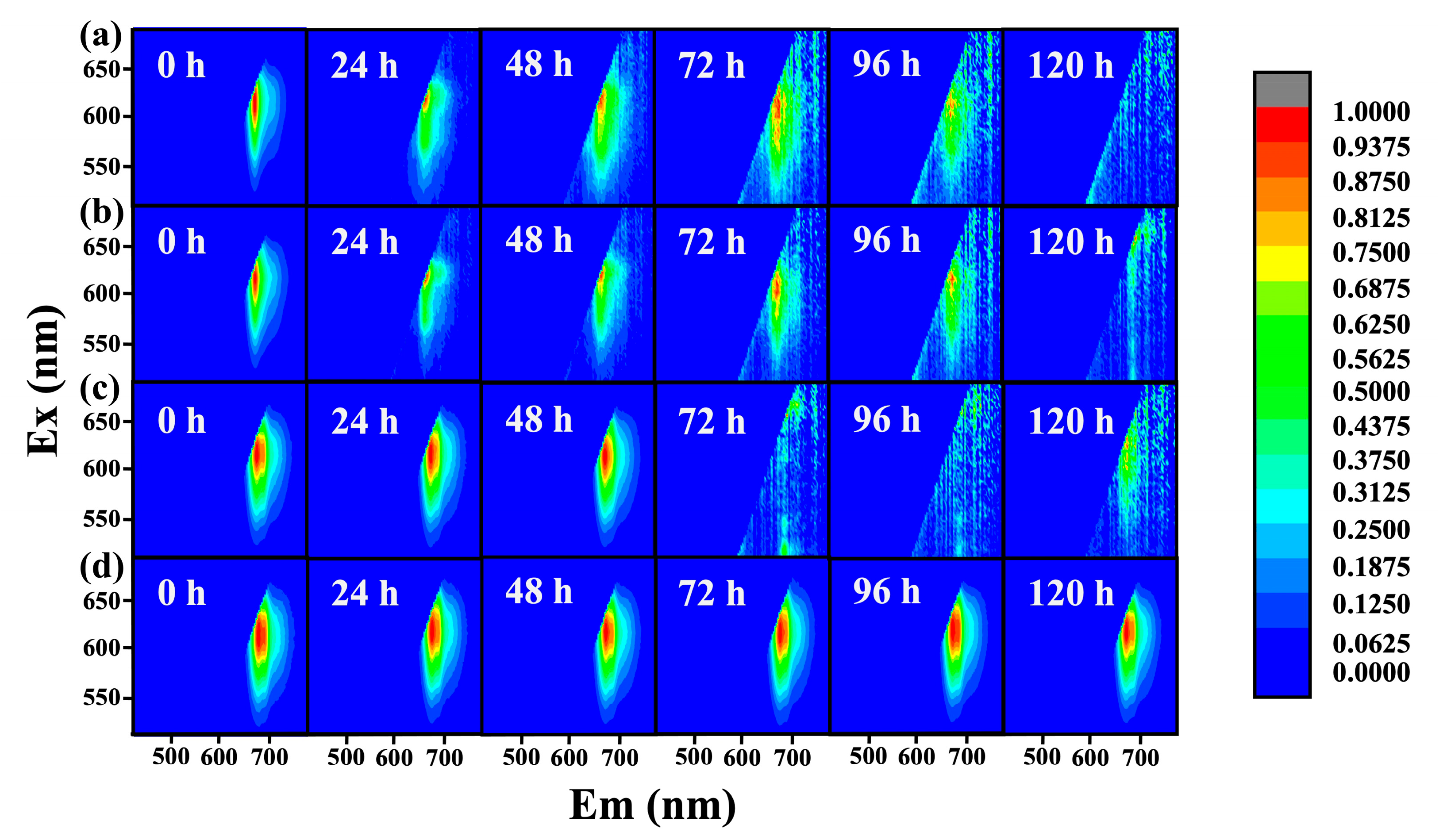
3.3. Fluorescence Intensity of Phycocyanin
4. Discussion
4.1. Inhibition of Cell Activities and Photosynthesis
4.2. Inhibition of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4.3. Phycocyanin Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Y.; Hu, X. Research status and prospect of lake eutrophication prevention and control. Beijing Water 2005, 6, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Yang, G.; Ma, J.; Deng, J.; Li, M.; Wu, T.; Liu, L.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y. Dynamics of variability and mechanism of harmful cyanobacteria bloom in Lake Taihu, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 759–770. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, A.; Yu, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Xia, D.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Effects of light-emitting diode illumination on sediment surface biological activities and releases of nutrients and metals to overlying water in eutrophic Lake Microcosms. Water 2022, 14, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, M. Factors in Chaohu Lake study on the seasonal succession of phytoplankton community and its driving. Environ. Monit. China 2024, 40, 129–142. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Chong, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhu, W. Allelopathic effects of three submerged macrophytes on five eutrophic algae. J. S. China Agric. Univ. 2007, 28, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, S.S.; Jain, S.K. Hans Molisch (1856–1937): The father of allelopathy. Allelopath. J. 1994, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, K.; Ma, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Zhu, S.; Rong, M.; Qin, W. Progress in the study of allelopathy in plants: A case study of inhibiting Microcystis aerugingosa growth. Biotechnol. Bull. 2021, 37, 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Yu, L.; Peng, Z.; Fan, P.; Li, Y.; Ren, K. Research progresses on algae inhibition by allelopathy of aquatic plants. J. Biol. 2021, 38, 104–108. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, E.M. Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2003, 22, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Hu, H.; Xie, X.; Sakoda, A.; Sagehashi, M.; Li, F. Gramine-induced growth inhibition, oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in freshwater cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2009, 91, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Zhao, W.; Da, L. Thea research and application of the allelopathic effects of submerged plants inhibit the growth of algae. Environ. Dev. 2012, 24, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Sun, D.; Lin, X.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Xu, J. Research progress on allelopathic algae-inhibiting effects and action modes of submerged macrophytes. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2022, 51, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Men, Y.; Hu, H. Effects of allelochemical EMA from reed on the production and release of cyanotoxins in Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. 2007, 28, 2058–2062. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Xian, Q.; Zou, H. Allelopathic effects of Ceratophyllum demersum and Microcystis aeruginosa in co-cultivation. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2008, 28, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Chong, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Q. Analysis on antialgal allelochemicals in culture solutions of three submerged macrophytes. J. S. China Agric. Univ. 2010, 31, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Xie, D.; Zhou, H.; An, S. Influences of chemical components of water extracts from submerged macrophyte leaves on the growth of three common epiphytic algae. Chin. J. Ecol. 2015, 34, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J.; Zhao, W.J.; Chen, J.Q.; Wang, F. Dosage impact of submerged plants extracts on Microcystis aeruginosa growth: From hormesis to inhibition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Huang, H.; Mi, Q.; Iseri, Y. Effects of substrate and water depth of a eutrophic pond on the physiological status of a submerged plant, Vallisneria natans. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Yan, N.; Xia, D.; Zhao, M.; Iseri, Y. Improvement of water quality using a circulation device equipped with oxidation carriers and light emitting diodes in eutrophic pond mesocosms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. Impact of artificial lights on submerged plants’ decolorization and enzyme activity. Environ. Eng. 2015, 33, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, I.K.; Takano, T. Effects of supplemental blue- and red-lights in the morning twilight on the growth and physiological responses of cucumber seedlings. Environ. Control Biol. 1997, 35, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zha, L. Effect of LED red and blue continuous lighting before harvest on growth and nutrient absorption of hydroponic lettuce cultivated under different nitrogen forms and light qualities. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 2215–2221. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ni, L.; Jiang, Z.; Du, C.; Fang, Y. Effects of salinity on growth and chlorophyll fluorescence of Microcystis aeruginosa under artemisinin stress. Environ. Eng. 2023, 41, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhong, C.; Yang, H. Effect of disturbance intensity on the growth and chlorophyll fluorescence of Microcystis flos-aquae colony in Lake Taihu. Res. Environ. Sci. 2018, 31, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Song, F.; Jia, F. Growth inhibitory mechanism of quercetin on the Anabena flos-aquae. Adv. Environ. Prot. 2018, 8, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.E.; Johnson, G.N. In vivo temperature dependence of cyclic and pseudocyclic electron transport in barley. Planta 2001, 212, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Li, Y. A preliminary study on toxicity mechanism of monocrotophos on marine microalgae III. changes of activity of superoxide dismutase and peroxidase. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 1998, 18, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Beutler, M.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Meyer, B.; Moldaenke, C.; Luering, C.; Meyerhoefer, M.; Hansen, U.P.; Dau, H. A fluorometric method for the differentiation of algal populations in vivo and in situ. Photosynth. Res. 2002, 72, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, G.; Zhao, N.; Qin, Z.; Liu, W. Research on fluorescence spectral characteristics of phycocyanin under different habitat conditions. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2017, 37, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar]
- IBM. IBM SPSS Statistics (Predictive Analytics Software and Solutions), version 27.0.0.0. 64-bit ed. IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2020.
- Jia, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Du, L.; Han, L.; Liu, J. Allelopathic effect of five aquatic plants on Microcystis aeruginosa. Res. Agric. Mod. 2019, 40, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y. Physiological mechanism of Eichhornia crassipes in inhibiting the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 66, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, Y.; Sun, L.; Du, F. Abundant allelochemicals and the inhibitory mechanism of the phenolic acids in water dropwort for the control of Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Plants 2021, 10, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zeng, G.; Cai, X.; Liu, S.; Yin, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, X.; Tan, X. Growth inhibition and oxidative damage of Microcystis aeruginosa induced by crude extract of Sagittaria trifolia tubers. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 43, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, F. Physiological and biochemical effects of allelochemical ethyl 2-methyl acetoacetate (EMA) on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Ge, F.; Liu, B.; Wu, Z. Combined effects of allelopathic polyphenols on Microcystis aeruginosa and response of different chlorophyll fluorescence parameters. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 614570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; He, F.; Liang, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Z. Allelopathic effects of phenolic compounds released by Vallisneria spiralis on Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 761–766. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, F.; Bell, P.R.F. Growth N2 fixation and photosynthesis in a cyanobacterium Trichodesmium sp. under Fe stress. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhang, X.; Kang, R.; Hu, H.; Cong, W.; Tan, T. Effects of Fe3+ on growth and photosynthesis of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Beijing Univ. Chem. Technol. 2006, 33, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, Q.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, M. Effects of different concentrations of Vallisneria spiralis Linn. on growth and antioxidant system of Microcystis aeruginosa. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, G. Effect of Underwater Light Quality on Growth of Potamageton crispus and Vallisneria natans. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China, 2008; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y. The studied on culture spirulina platensis in the photobioreactor with LED illuminant panel. Mar. Sci. 2001, 25, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, B. The Study on Inhibition Mechanism of Cyanobacteria Growth by Irradiation Treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012; pp. 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Study on the Allelopathic Effects of Four Aquatic Plants Extracts on Microcystis flosaquae. Master’s Thesis, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, China, 2013; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H. Investigation on the Inhibition Mechanism of Ceratophyllum demersum and Spirogyra on Microcystis aeruginosa. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan Agricultural University, Changsha, China, 2014; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Ye, J.; Zhong, B. Study on the release routes of allelochemicals from Pistia stratiotes Linn., and its anti-cyanobacteria mechanisms on Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18994–19001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, A.; Sun, Z.; Shi, X.; Xia, D.; Liu, X.; Iseri, Y. Allelopathic Suppression of Cyanobacterial Blooms by the Aquatic Plant Vallisneria natans Enhanced by Red and Blue LED Light Supplementation. Water 2025, 17, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010131
Hao A, Sun Z, Shi X, Xia D, Liu X, Iseri Y. Allelopathic Suppression of Cyanobacterial Blooms by the Aquatic Plant Vallisneria natans Enhanced by Red and Blue LED Light Supplementation. Water. 2025; 17(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Aimin, Zhouzhou Sun, Xiaoyu Shi, Dong Xia, Xin Liu, and Yasushi Iseri. 2025. "Allelopathic Suppression of Cyanobacterial Blooms by the Aquatic Plant Vallisneria natans Enhanced by Red and Blue LED Light Supplementation" Water 17, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010131
APA StyleHao, A., Sun, Z., Shi, X., Xia, D., Liu, X., & Iseri, Y. (2025). Allelopathic Suppression of Cyanobacterial Blooms by the Aquatic Plant Vallisneria natans Enhanced by Red and Blue LED Light Supplementation. Water, 17(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17010131





