Unraveling the Coupled Dynamics between DOM Transformation and Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer Systems during Microbial Sulfate Reduction: Evidence from Sediment Incubation Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Microcosm Setup
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Analysis of the arsM, arrA, and dsrB Genes
2.5. Characterization of DOM Fluorescence and Molecular Compositions
3. Results
3.1. Geochemical Compositions of Sediments and Major Constituents of Groundwater
3.2. Variations in the Astotal, Fe(II)total, and Sulfate Concentrations
3.3. Variations in the Aqueous As Species
3.4. Variations in the dsrB, arrA, and arsM Gene Abundance
3.5. Variations in the DOM Fluorescence Components
3.6. Variations in the Molecular Characteristics of DOM
4. Discussion
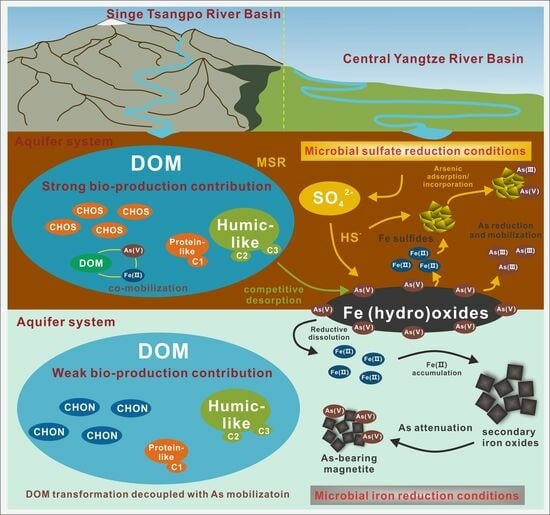
4.1. Microbial Sulfate Reduction Facilitates As Mobilization
4.2. Co-Evolution between DOM Transformation and As Mobilization under Microbial Sulfate Reduction
4.3. Environmental Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; van Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, B.; Zheng, Y. Enrichment of Arsenic in Surface Water, Stream Sediments and Soils in Tibet. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Yan, Y.-N.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-D.; Guo, J.-Y.; Ding, H.; Cui, L.-F.; Meng, J.-L.; Liu, C.-Q. Spatial and seasonal variations of dissolved arsenic in the Yarlung Tsangpo River, southern Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 760, 143416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Deng, Y.; Lin, H.; Xie, Y.; Pei, X. Hydrogeochemical controls on As and B enrichment in the aqueous environment from the Western Tibetan Plateau: A case study from the Singe Tsangpo River Basin. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 817, 152978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, B.D.; Herbel, M.J.; Tufano, K.J.; Fendorf, S. Contrasting effects of dissimilatory iron(III) and arsenic(V) reduction on arsenic retention and transport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6715–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coker, V.S.; Gault, A.G.; Pearce, C.I.; van der Laan, G.; Telling, N.D.; Charnock, J.M.; Polya, D.A.; Lloyd, J.R. XAS and XMCD evidence for species-dependent partitioning of arsenic during microbial reduction of ferrihydrite to magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7745–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muehe, E.M.; Morin, G.; Scheer, L.; Le Pape, P.; Esteve, I.; Daus, B.; Kappler, A. Arsenic(V) incorporation in vivianite during microbial reduction of arsenic(V)-bearing biogenic Fe(III) (Oxyhydr)oxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, X.-C.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Mu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Sulfate enhances the dissimilatory arsenate-respiring prokaryotes-mediated mobilization, reduction and release of insoluble arsenic and iron from the arsenic-rich sediments into groundwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 339, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, M.F.; Holm, T.R.; Park, J.; Jin, Q.; Sanford, R.A.; Fouke, B.W.; Bethke, C.M. Bacterial sulfate reduction limits natural arsenic contamination in groundwater. Geology 2004, 32, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Ma, T.; Liu, Y.; Su, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z. Remediation of arsenic-contaminated groundwater by in-situ stimulating biogenic precipitation of iron sulfides. Water Res. 2017, 109, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wei, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Diversity and abundance of arsenic methylating microorganisms in high arsenic groundwater from Hetao Plain of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Liu, W.; Luan, F. Microbial mobilization of arsenic from iron-bearing clay mineral through iron, arsenate, and simultaneous iron-arsenate reduction pathways. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 763, 144613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pi, K.; Fendorf, S.; Deng, Y.; Xie, X. Sedimentogenesis and hydrobiogeochemistry of high arsenic Late Pleistocene-Holocene aquifer systems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 189, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, L.K.; Andersen, M.S.; Behnke, M.I.; Rutlidge, H.; Oudone, P.; Meredith, K.; O’carroll, D.M.; Santos, I.R.; Marjo, C.E.; Spencer, R.G.M.; et al. A new conceptual framework for the transformation of groundwater dissolved organic matter. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xue, J.; Tian, S.; Du, Y.; Xie, X.; Gan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y. Organic matter degradation and arsenic enrichment in different floodplain aquifer systems along the middle reaches of Yangtze River: A thermodynamic analysis. Water Res. 2023, 239, 120072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikutta, C.; Kretzschmar, R. Spectroscopic evidence for ternary complex formation between arsenate and ferric iron complexes of humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9550–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Sudo, T.; Watanabe, M.; Tsuboi, S.; Soda, S.; Ike, M.; Amachi, S. Effect of extracellular electron shuttles on arsenic-mobilizing activities in soil microbial communities. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Blodau, C. Mobilization of arsenic by dissolved organic matter from iron oxides, soils and sediments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2006, 354, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.M.; Sanford, R.A.; Ryu, H.; Bethke, C.M.; Levine, A.D.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Domingo, J.W.S. Functional microbial diversity explains groundwater chemistry in a pristine aquifer. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Deng, Y.; Xie, X.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y. Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter in high arsenic shallow groundwater systems. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Su, C.; Wang, M.; Ren, F.; Huq, M.E. Unraveling the impact of dissolved organic matter on arsenic mobilization in alluvial aquifer of the lower Yellow River basin, Northern China. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 158, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Gao, Z.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Han, S.; Guo, H. Molecule-based quantification of dissolved organic matter sources in high-arsenic groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Cui, J.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Ye, T.; Gan, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Liang, W.; Guo, P.; et al. Key drivers regulating arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Pearl River Delta: Comprehensive analyses of iron, competitive anions, and dissolved organic matter. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 151, 105602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Lin, H.; Deng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, J.; Du, X.; Pei, X. Hydrogeochemical processes regulating the enrichment and migration of As and B from the river sediments in the Singe Tsangpo River Bain, Western Tibetan plateau. Appl. Geochem. 2023, 148, 105549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, X.; Dong, C. Temporal variation of groundwater level and arsenic concentration at Jianghan Plain, central China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 149, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Guo, X.; Ding, X. Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Jianghan Plain, central China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 138, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Butler, K.D.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Stedmon, C.A.; Boehme, J.R.; Aiken, G.R. Measurement of dissolved organic matter fluorescence in aquatic environments: An interlaboratory comparison. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9405–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Bro, R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2008, 6, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, T.; Du, Y.; Jiang, H.; Pi, K.; Xie, X.; Gan, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, Y. New evidence for linking the formation of high arsenic aquifers in the central Yangtze River Basin to climate change since Last Glacial Maximum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, P.L.; Kinniburgh, D.G. A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl. Geochem. 2002, 17, 517–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.A.; Kominoski, J.S.; Gaiser, E.E.; Price, R.M.; Troxler, T.G. Stormwater runoff and tidal flooding transform dissolved organic matter composition and increase bioavailability in urban coastal ecosystems. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG006146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Ma, R.; Yang, S.; Cai, H.; Xue, Z.; Wang, T. Roles of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in shaping the distribution pattern of heavy metal in the Yangtze River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Liu, G.; Zhao, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Complexion between mercury and humic substances from different landfill stabilization processes and its implication for the environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 209–210, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-M.; Seo, Y.-S.; Hur, J. Investigation of adsorptive fractionation of humic acid on graphene oxide using fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC. Water Res. 2015, 73, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.-D.; Guo, T.; Lv, P.-L.; Niu, Z.-F.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Tang, X.-J.; Zheng, P.; Zhu, L.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Kappler, A.; et al. Coupled anaerobic methane oxidation and reductive arsenic mobilization in wetland soils. Nat. Geosci. 2020, 13, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zheng, T.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H. Microbially mediated mobilization of arsenic from aquifer sediments under bacterial sulfate reduction. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 768, 144709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Quicksall, A.N.; Chillrud, S.N.; Mailloux, B.J.; Bostick, B.C. Arsenic mobilization from sediments in microcosms under sulfate reduction. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocar, B.D.; Borch, T.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic repartitioning during biogenic sulfidization and transformation of ferrihydrite. Geochim. et Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 980–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.A.; Goldberg, S. Modeling competitive adsorption of arsenate with phosphate and molybdate on oxide minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; Ma, T. Effect of microbially mediated iron mineral transformation on temporal variation of arsenic in the Pleistocene aquifers of the central Yangtze River basin. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, T.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xie, X.; Gan, Y. Microbial sulfate reduction facilitates seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in groundwater of Jianghan Plain, Central China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 735, 139327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quéméneur, M.; Garrido, F.; Billard, P.; Breeze, D.; Leyval, C.; Jauzein, M.; Joulian, C. Bacterial community structure and functional arra gene diversity associated with arsenic reduction and release in an industrially contaminated soil. Geomicrobiol. J. 2016, 33, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Xiu, W.; He, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, A. Controls of organic matter bioreactivity on arsenic mobility in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, P.R. China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 571, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, D.; Yu, C.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Qiao, W.; Kersten, M. Transformation of dissolved organic matter and related arsenic mobility at a surface water-groundwater interface in the Hetao Basin, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethke, C.M.; Sanford, R.A.; Kirk, M.F.; Jin, Q.; Flynn, T.M. The thermodynamic ladder in geomicrobiology. Am. J. Sci. 2011, 311, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, H.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Xing, S.; Gao, Z. Identification of processes mobilizing organic molecules and arsenic in geothermal confined groundwater from Pliocene aquifers. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Burton, E.D.; Si, D.; Fan, T.; Cheng, H.; Yu, Z.; Shao, X.; Cui, P.; Wang, Y. Coupling of Dissolved Organic Matter Molecular Fractionation with Iron and Sulfur Transformations during Sulfidation–Reoxidation Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16327–16339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Guo, H.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Zhao, B. Unraveling roles of dissolved organic matter in high arsenic groundwater based on molecular and optical signatures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, S.; Xue, L.; Liao, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Q. Effects of dam construction on arsenic mobility and transport in two large rivers in Tibet, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 741, 140406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Qin, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, H. Review of arsenic geochemical characteristics and its significance on arsenic pollution studies in karst groundwater, Southwest China. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 77, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurischat, P.; Seidel, M.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G. Complex dissolved organic matter (DOM) on the roof of the world–Tibetan DOM molecular characteristics indicate sources, land use effects, and processing along the fluvial–limnic continuum. Biogeosciences 2023, 20, 3011–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, R.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, L. Groundwater plays an important role in controlling riverine dissolved organic matter in a cold alpine catchment, the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2022WR032426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sediment | STR (Depth = 72 m) | JHP (Depth = 20 m) | Groundwater_Mean | STR (n = 13) | JHP (n = 186) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na2O (%) | 2.2 | 1.8 | T (°C) | 7.7 | 20 |
| MgO (%) | 1.3 | 3 | pH | 8.4 | 7 |
| Al2O3 (%) | 15.9 | 16.2 | Eh (mV) | 215.5 | −136 |
| SiO2 (%) | 61 | 67.7 | EC (μs/cm) | 322.2 | 818.1 |
| P2O5 (%) | 0.2 | 0.3 | K (mg/L) | 3.3 | 4 |
| K2O (%) | 4.5 | 2.4 | Na (mg/L) | 24.5 | 17 |
| CaO (%) | 10.7 | 1.4 | Ca (mg/L) | 40.7 | 92 |
| Fe2O3 (%) | 3.4 | 5.1 | Mg (mg/L) | 9 | 29 |
| S (%) | 0.019 | 0.0096 | Fe (mg/L) | 0.03 | 1 |
| Ti (mg/kg) | 2761.9 | 4885 | As (μg/L) | 32.2 | 532 |
| V (mg/kg) | 59.2 | 97 | DOC (mg/L) | – | 6 |
| Cr (mg/kg) | 39.2 | 61 | HCO3− (mg/L) | 157.8 | 550 |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 486.3 | 616 | Cl− (mg/L) | 11.2 | 9 |
| As (mg/kg) | 59.3 | 108 | NO3− (mg/L) | 9.3 | 2 |
| Rb (mg/kg) | 164.8 | 97 | SO42− (mg/L) | 38 | 4 |
| Sr (mg/kg) | 342.3 | 190 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zheng, T. Unraveling the Coupled Dynamics between DOM Transformation and Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer Systems during Microbial Sulfate Reduction: Evidence from Sediment Incubation Experiment. Water 2024, 16, 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091266
Du X, Li H, Jiang Y, Yuan J, Zheng T. Unraveling the Coupled Dynamics between DOM Transformation and Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer Systems during Microbial Sulfate Reduction: Evidence from Sediment Incubation Experiment. Water. 2024; 16(9):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091266
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xingguo, Hui Li, Yue Jiang, Jianfei Yuan, and Tianliang Zheng. 2024. "Unraveling the Coupled Dynamics between DOM Transformation and Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer Systems during Microbial Sulfate Reduction: Evidence from Sediment Incubation Experiment" Water 16, no. 9: 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091266
APA StyleDu, X., Li, H., Jiang, Y., Yuan, J., & Zheng, T. (2024). Unraveling the Coupled Dynamics between DOM Transformation and Arsenic Mobilization in Aquifer Systems during Microbial Sulfate Reduction: Evidence from Sediment Incubation Experiment. Water, 16(9), 1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091266