Study on Properties of Micro-Nano Magnetic Composite Prepared by Mechanochemical Method of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Removal of As (V) from Mine Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Material
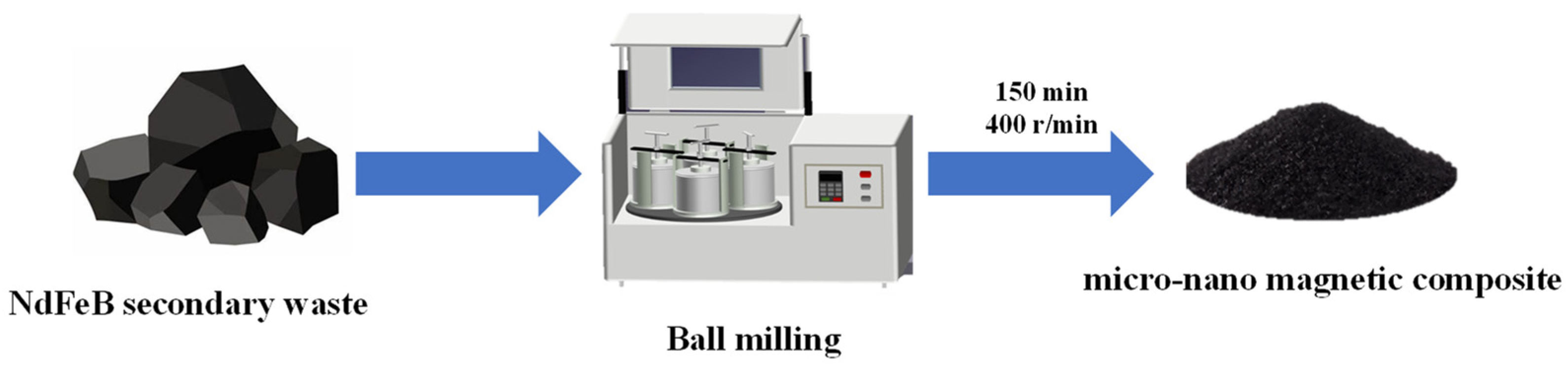
2.2. Magnetic Micro-Nano Composite Materials Preparation
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Batch Sorption
3. Results
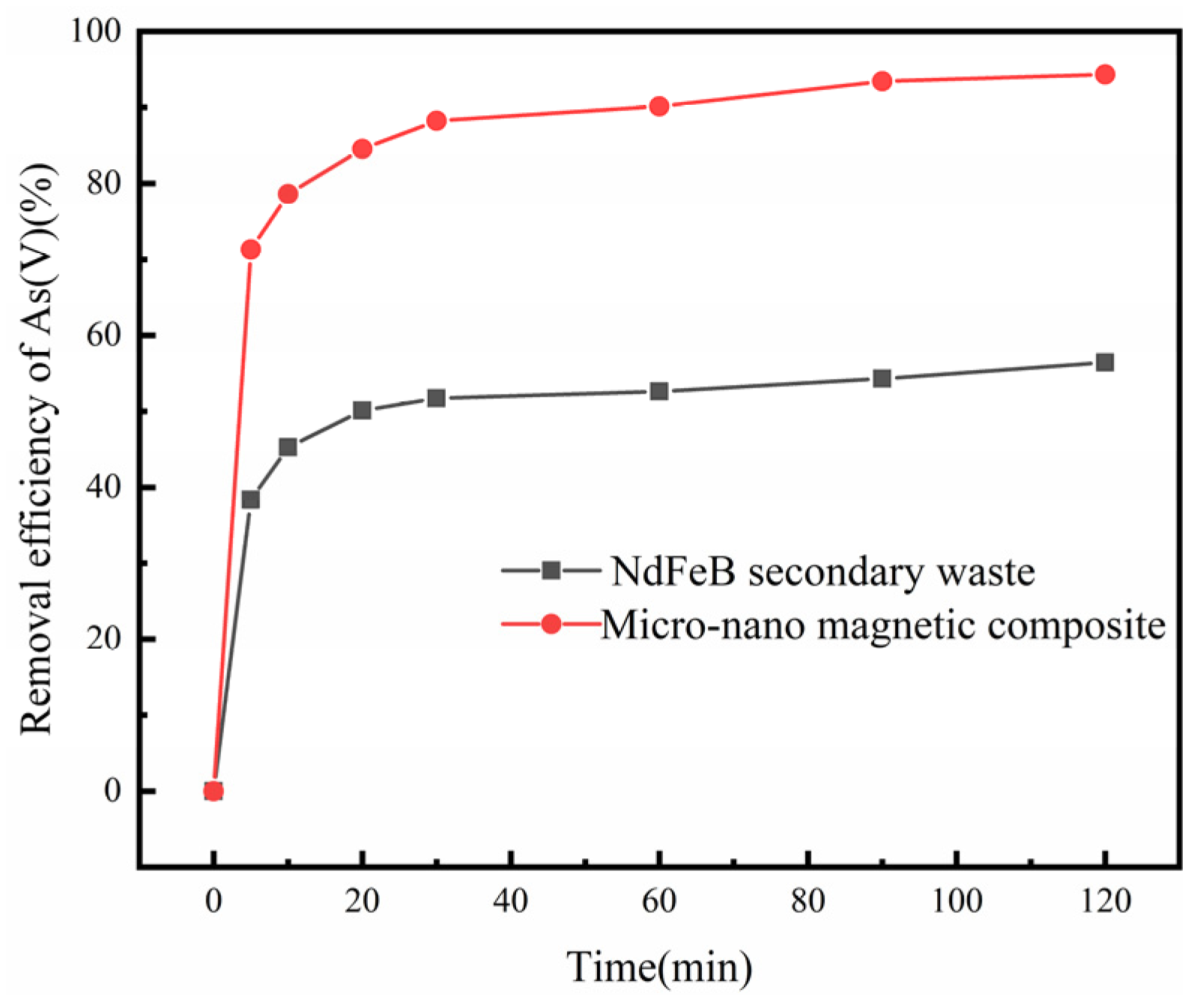
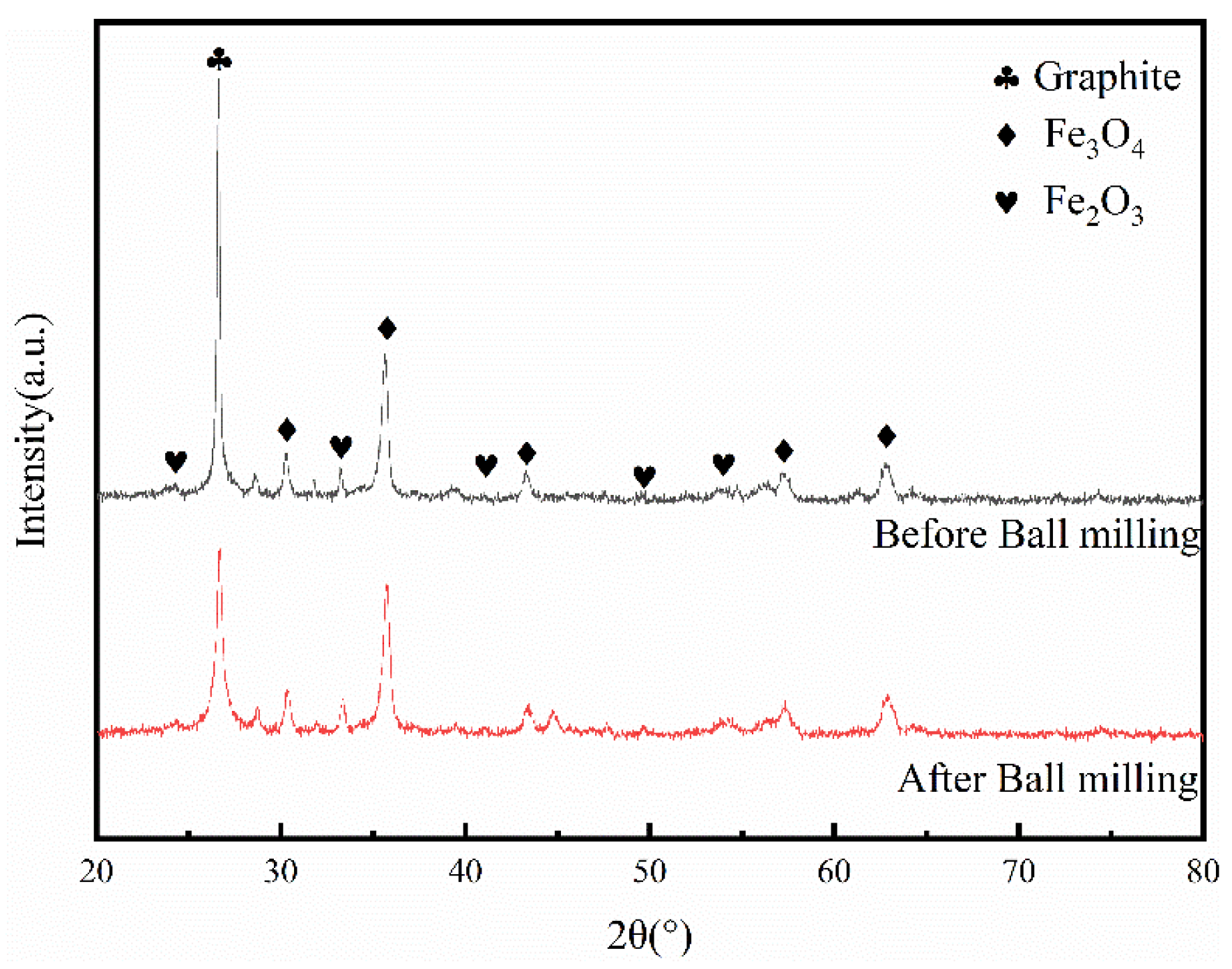
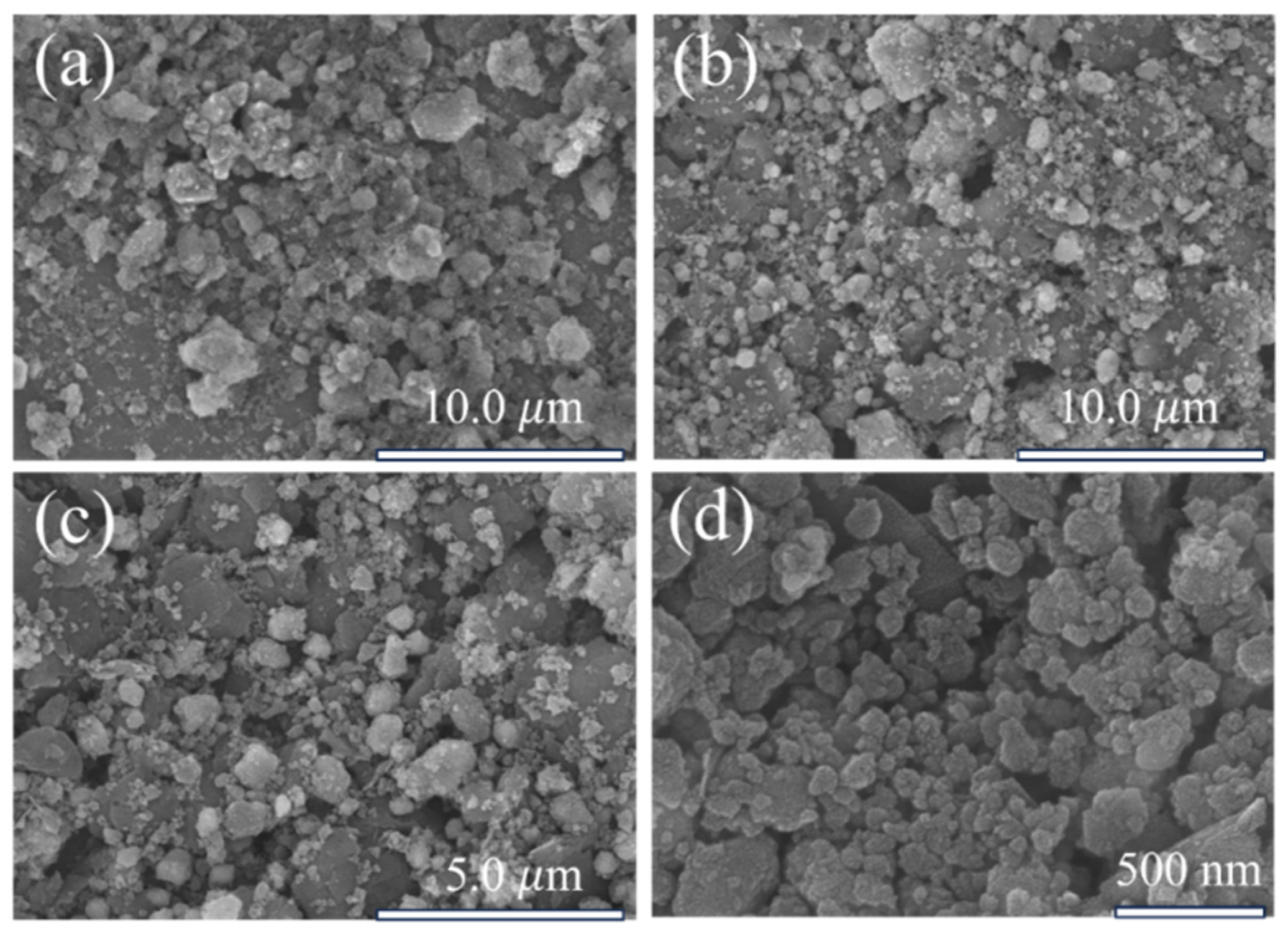
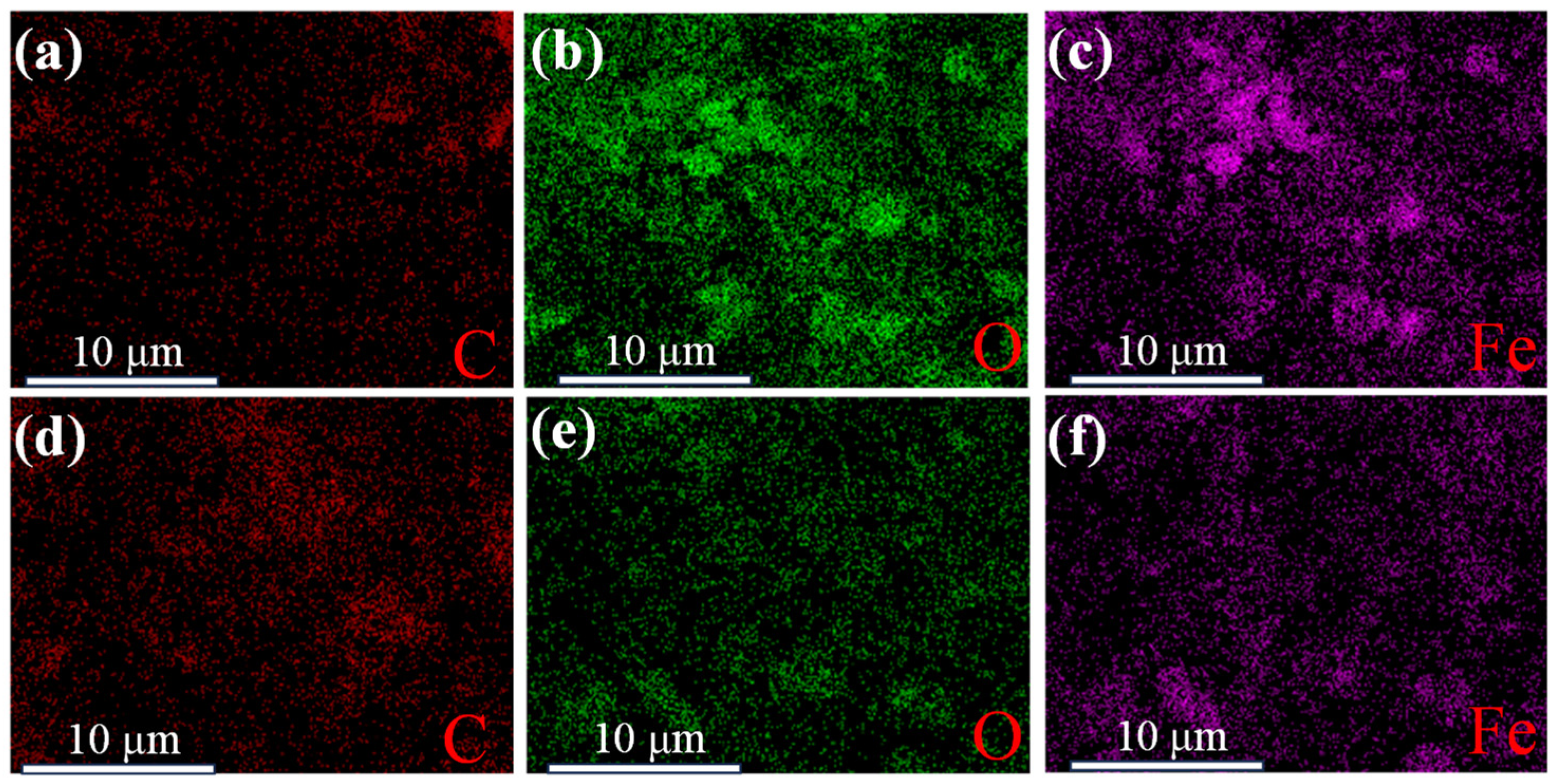
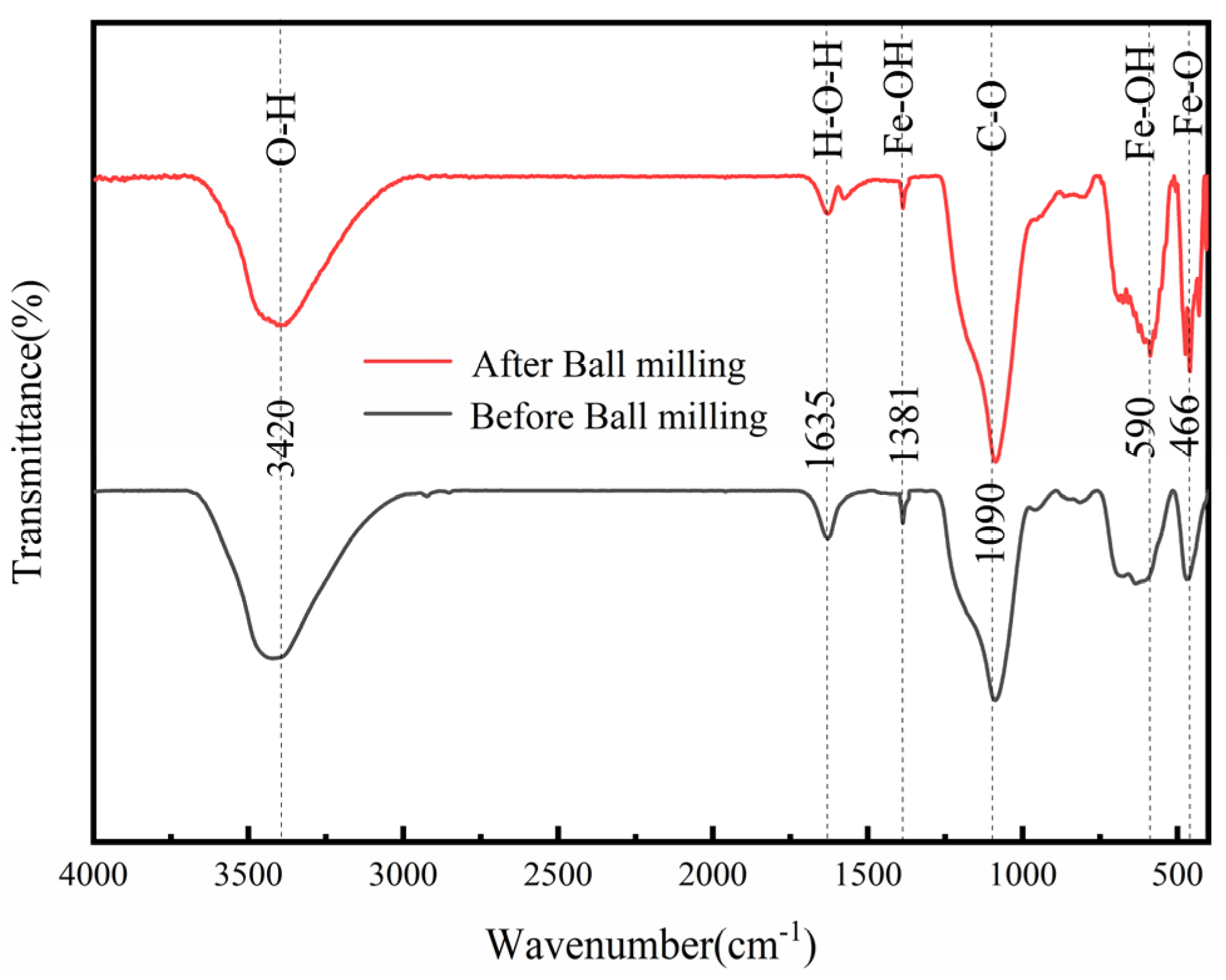
3.1. Comparison of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Magnetic Micro-Nano Composite Materials
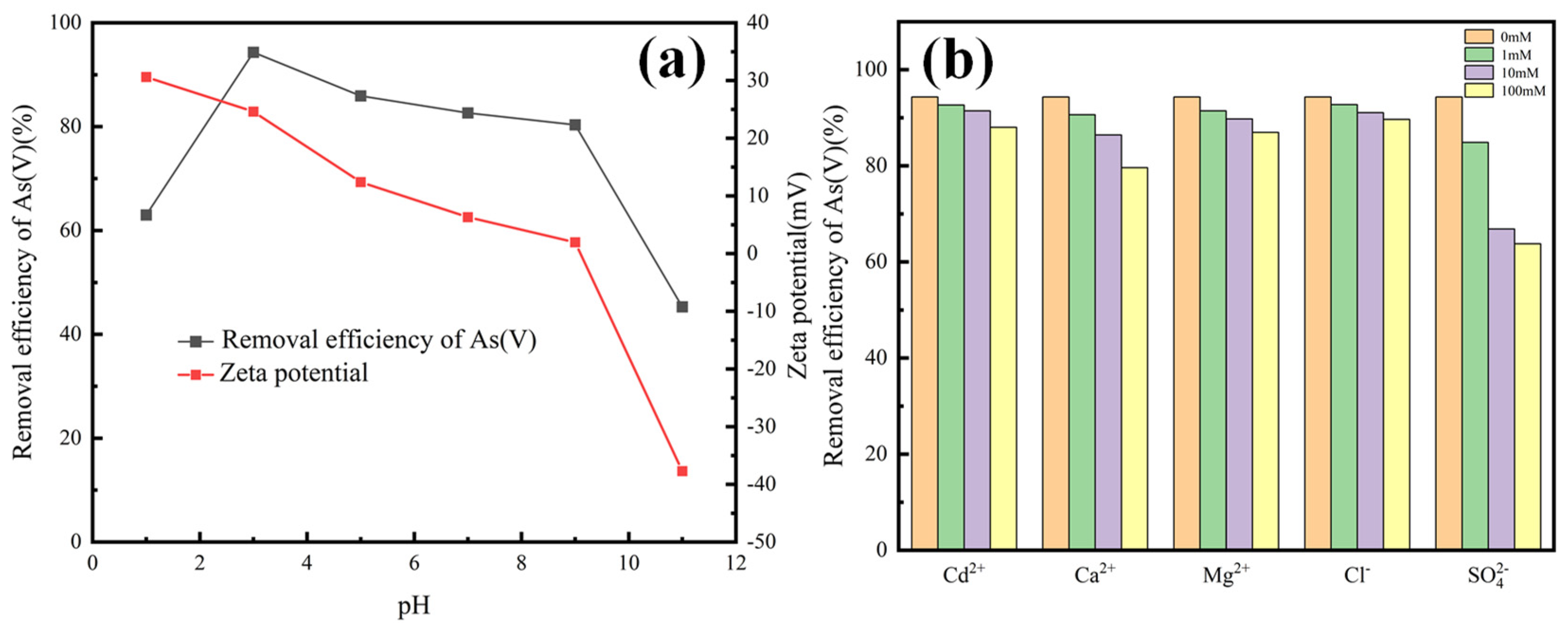
3.2. As (V) Removal by Magnetic Micro-Nano Composite Materials
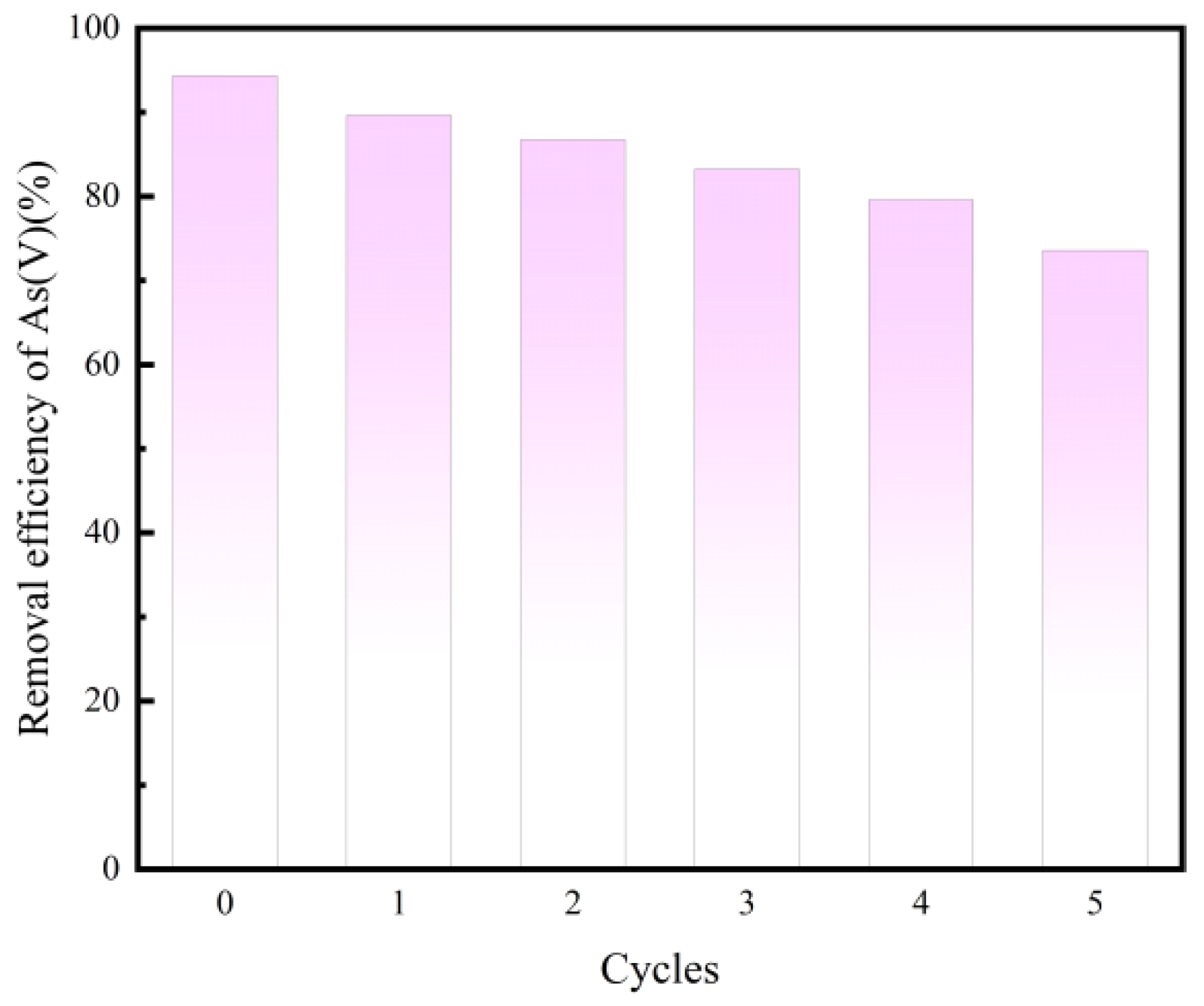
3.3. Regeneration of Magnetic Micro-Nano Composite Materials
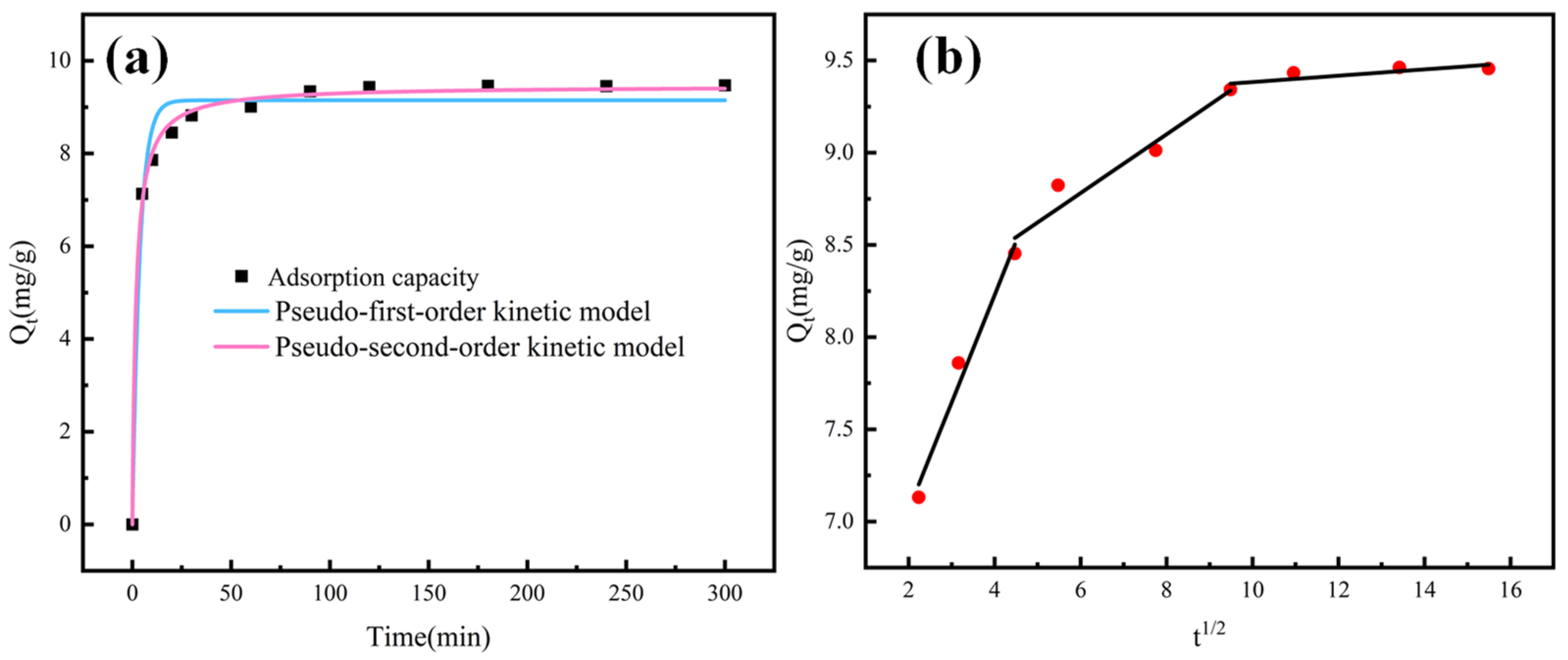
3.4. Kinetics for As (V) Uptake
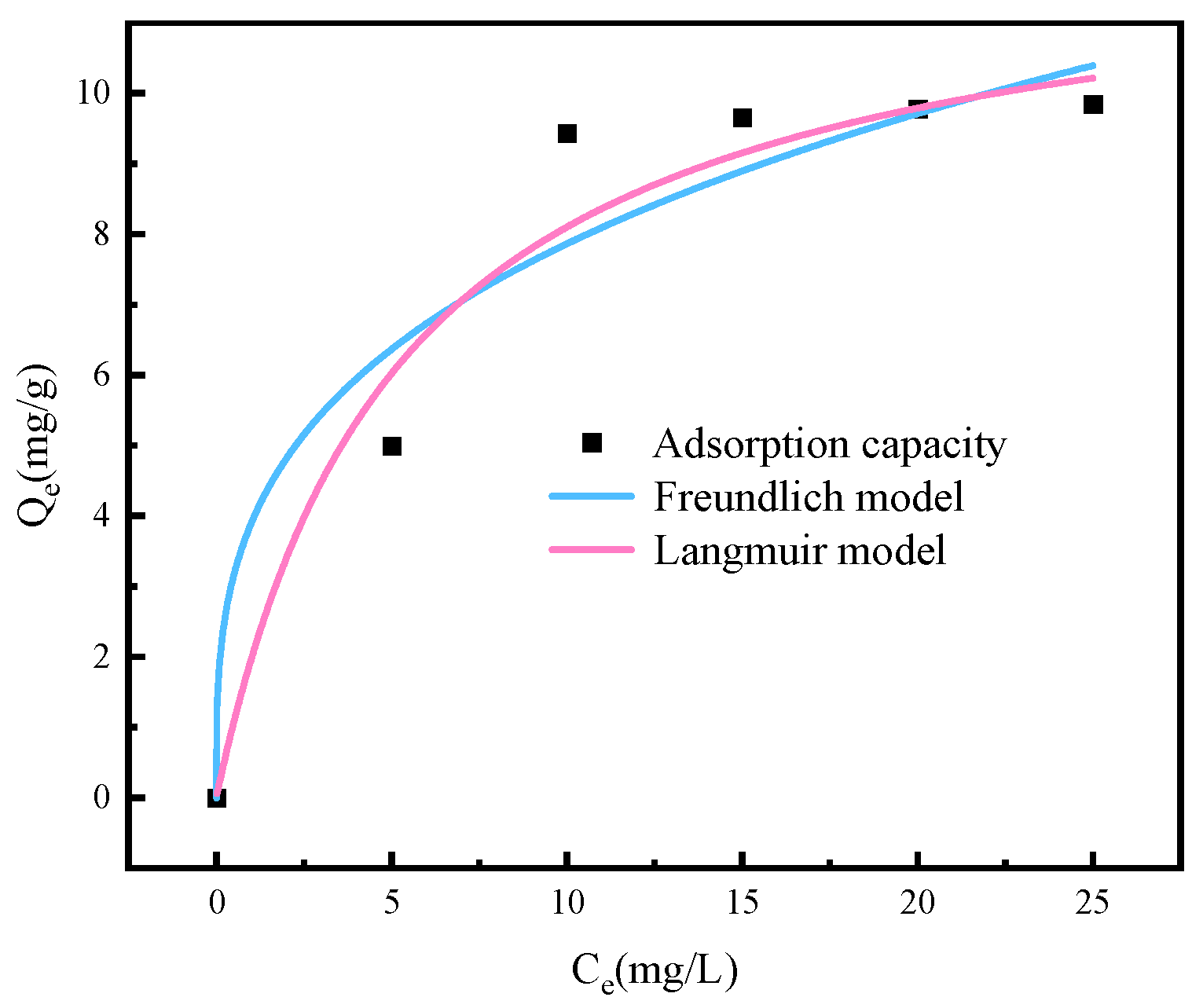
3.5. As (V) Uptake Isotherms
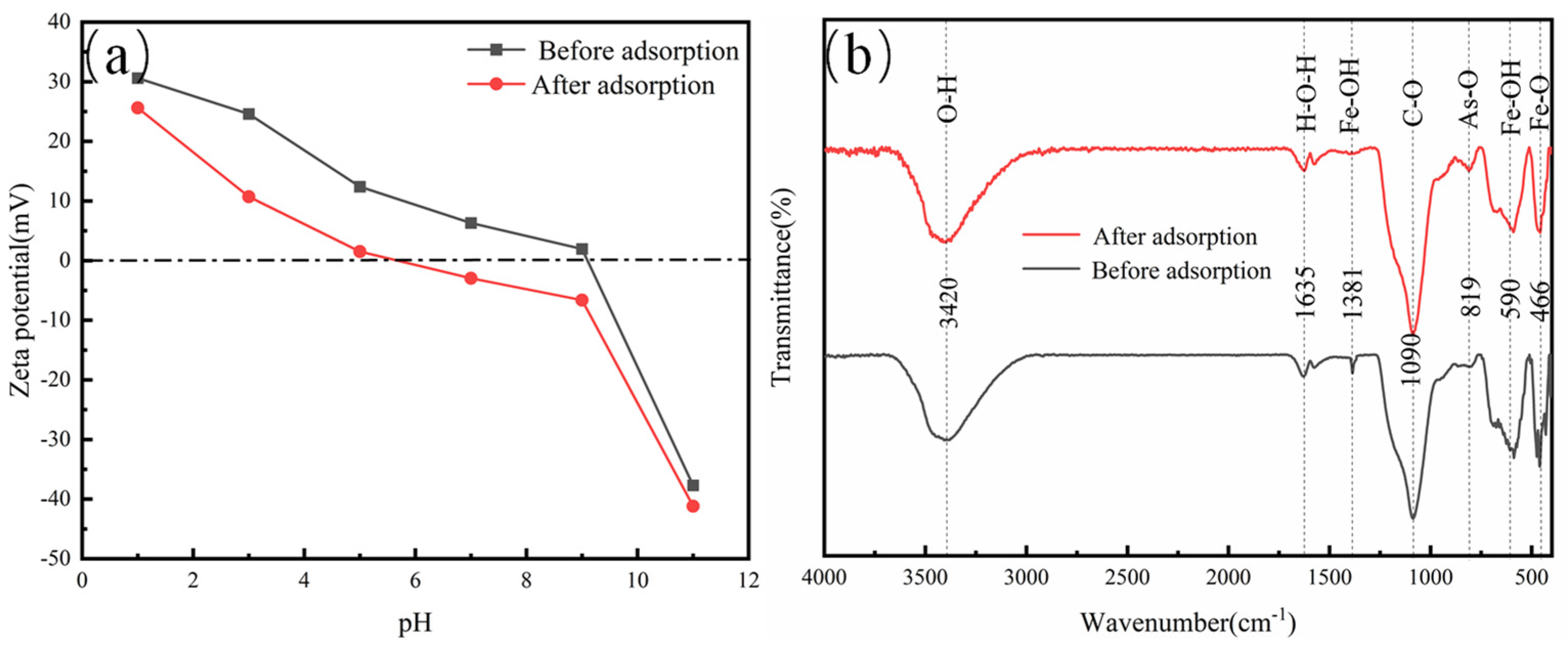
3.6. Surface Analysis of As (V)-Adsorbed Magnetic Micro-Nano Composite Materials
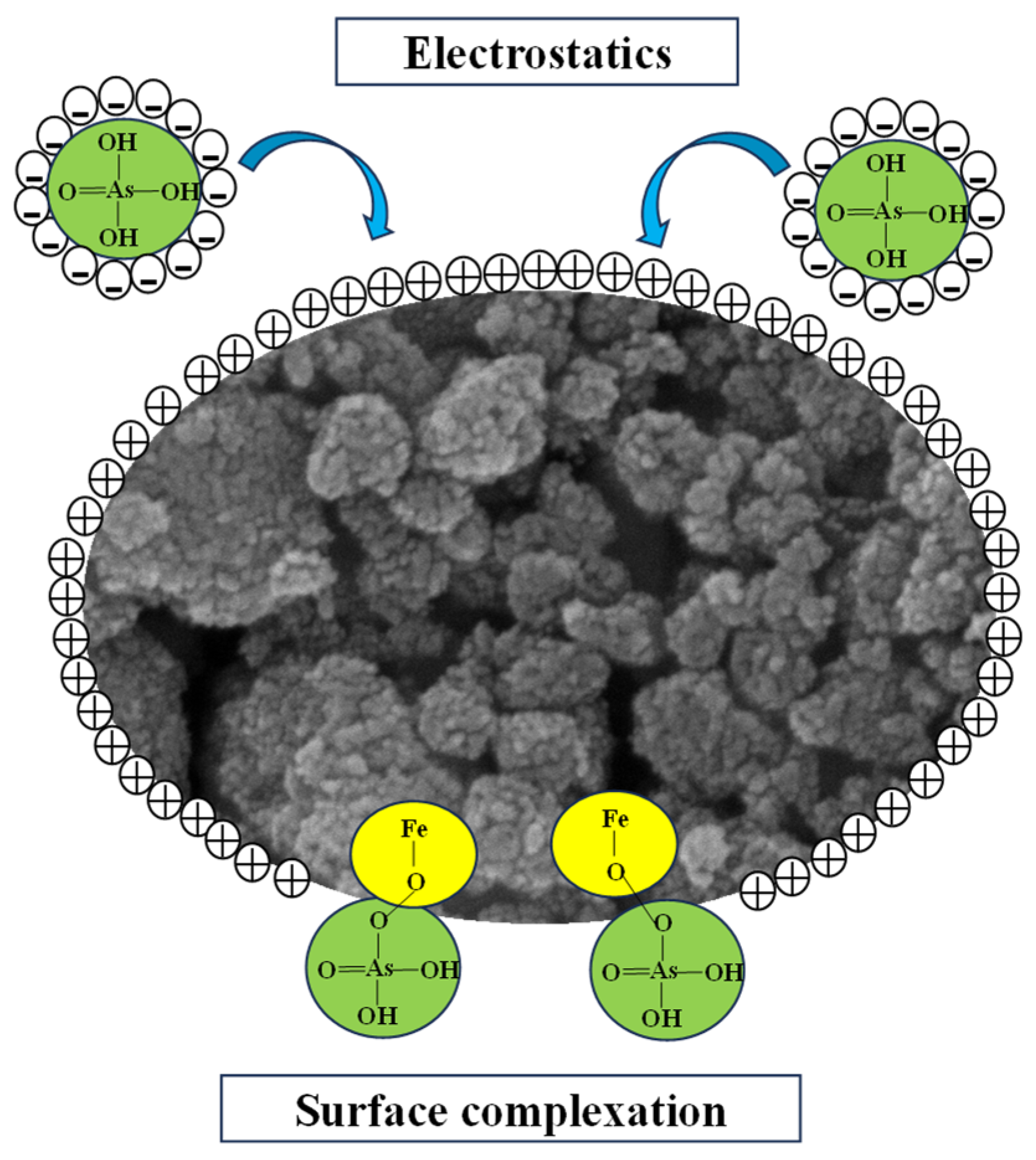
3.7. As (V) Removal Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peiró, L.T.; Méndez, G.V.; Ayres, R.U. Material flow analysis of scarce metals: Sources, functions, end-uses and aspects for future supply. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2939–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, M.; Fujimura, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuura, Y.; Hiraga, K. Permanent magnet materials based on the rare earth-iron-boron tetragonal compounds. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1984, 20, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Buchert, M. Estimates of global REE recycling potentials from NdFeB magnet material. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirayama, S.; Okabe, T.H. Selective Extraction and Recovery of Nd and Dy from Nd-Fe-B Magnet Scrap by Utilizing Molten MgCl2. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P.; Hoogerstraete, T.V.; Hennebel, T.; Binnemans, K.; Sietsma, J.; Yang, Y. Selective electrochemical extraction of REEs from NdFeB magnet waste at room temperature. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Sinha, M.K.; Pramanik, S.; Sahu, S.K. Recovery of rare earths from spent NdFeB magnets of wind turbine: Leaching and kinetic aspects. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.; Dang, Z.; Ke, Y. Efficient recovery of rare earth elements from discarded NdFeB magnets. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 124, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkaraaslan, H.; Çetintaş, S.; Bingöl, D. A novel composite derived from carbonized hawthorn waste pulp/marble waste powder by ball milling: Preparation, characterization, and usability as bifunctional adsorbent. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 3765–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, J.-L.; Friščić, T. Mechanochemistry: A Force of Synthesis. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 3, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Mao, Q.; Buekens, A.; Chang, W.; Wang, X.; Yan, J. Suppressing Heavy Metal Leaching through Ball Milling of Fly Ash. Energies 2016, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.-M.; Zhang, C.-C.; Zhang, F.-S. An environmental benign process for cobalt and lithium recovery from spent lithium-ion batteries by mechanochemical approach. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhao, J.; He, F.; Zhong, Z.; Huang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, F.; Bashir, M.A.; et al. Ball milling biochar iron oxide composites for the removal of chromium (Cr(VI)) from water: Performance and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Novel ball-milled biochar-vermiculite nanocomposites effectively adsorb aqueous As(V). Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiyang, X.; Ziling, S.; Xiaoliang, Z.; Jiyang, L. Review of the recent advances in the prevention, treatment, and resource recovery of acid mine wastewater discharged in coal mines. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 52, 103555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Guo, Z.; Yi, L.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Pollution characteristics and source identification of soil metal(loid)s at an abandoned arsenic-containing mine, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenna, T.; Craig, S.; Peter, E.H. Arsenic contamination and rare earth element composition of acid mine drainage impacted soils from South Africa. Miner. Eng. 2023, 203, 108288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, K.; Li, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, Q. Arsenopyrite weathering in acidic water: Humic acid affection and arsenic transformation. Water Res. 2021, 194, 116917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrom, D.K.; Alpers, C.N. Negative pH, efflorescent mineralogy, and consequences for environmental restoration at the Iron Mountain Superfund site, California. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3455–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, E.D.; Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G.; Schoepfer, V.A.; Choppala, G.; Lamb, D. Arsenic-Imposed Effects on Schwertmannite and Jarosite Formation in Acid Mine Drainage and Coupled Impacts on Arsenic Mobility. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2021, 5, 1418–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Routh, J.; Dario, M.; Sarkar, S.; Wei, L.; Luo, D.; Liu, Y. Distribution and mobilization of heavy metals at an acid mine drainage affected region in South China, a post-remediation study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, S.; Tong, M. Arsenic oxidation and immobilization in acid mine drainage in karst areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, T.A.; Sebastián, S.; Julio, S.; Bernabé, L.R. Arsenic oxidation and its subsequent removal from water: An overview. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 309, 123055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.V.; Bringas, E.; Yadav, G.D.; Rathod, V.K.; Ortiz, I.; Marathe, K.V. Arsenic and fluoride contaminated groundwaters: A review of current technologies for contaminants removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 162, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Kuila, A. Bioremediation of heavy metals by microbial process. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.; Lee, M.-K.; Ojeda, A.S.; Rogers, S.R. GIS interpolation is key in assessing spatial and temporal bioremediation of groundwater arsenic contamination. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 280, 111683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidli, A.; Huang, Y.; Ben Rejeb, Z.; Zaoui, A.; Park, C.B. Sustainable and efficient technologies for removal and recovery of toxic and valuable metals from wastewater: Recent progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Chemosphere 2021, 292, 133102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J.; Frost, R.L. The As behavior of natural arsenical-containing colloidal ferric oxyhydroxide reacted with sulfate reducing bacteria. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 332, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Cagnetta, G.; Li, X.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J. Enhanced adsorption of potassium nitrate with potassium cation on H3PO4 modified kaolinite and nitrate anion into Mg-Al layered double hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 154, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T. Enhanced elimination of V5+ in wastewater using zero-valent iron activated by ball milling: The overlooked crucial roles of energy input and sodium chloride. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Gu, Q.; Chen, S.; Huang, H. Photocatalytic reforming of C3-polyols for H2 production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2011, 106, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.; Kong, F. Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution using microflower-like δ-Bi2O3 as adsorbent: Adsorption characteristics and mechanisms. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, B.R.C.; Pintor, A.M.A.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Botelho, C.M.S.; Santos, S.C.R. Arsenic removal from water using iron-coated seaweeds. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Zheng, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Ren, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Efficient oxidation and sorption of arsenite using a novel titanium(IV)-manganese(IV) binary oxide sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 353, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrullah, A.; Khan, A.S.; Bhat, A.H.; Din, I.U.; Inayat, A.; Muhammad, N.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Effect of short time ball milling on physicochemical and adsorption performance of activated carbon prepared from mangosteen peel waste. Renew. Energy 2020, 168, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenglong, Z.; Zhiwei, X.; Fahui, N.; Kun, G.; Jiacheng, L. Application of hydroxyapatite-modified carbonized rice husk for the adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 371, 121137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S.; Johnston, C.T. Mechanisms of Arsenic Adsorption on Amorphous Oxides Evaluated Using Macroscopic Measurements, Vibrational Spectroscopy, and Surface Complexation Modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 234, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, M.L.; Moore, C.B. Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate on amorphous iron hydroxide. Water Res. 1982, 16, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Na, P. Synthesis of magnetic orderly mesoporous α-Fe2O3 nanocluster derived from MIL-100(Fe) for rapid and efficient arsenic(III,V) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 343, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Q.; Wang, D. Facile fabrication of nanostructured cerium-manganese binary oxide for enhanced arsenite removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 334, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, Y.O.; Fuchida, S.; Tokoro, C. Insight into the Mechanism of Arsenic(III/V) Uptake on Mesoporous Zerovalent Iron–Magnetite Nanocomposites: Adsorption and Microscopic Studies. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 49755–49767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Elements | Wt/% | At/% |
|---|---|---|
| O | 51.9 | 0.5 |
| C | 24.7 | 0.6 |
| Fe | 23.4 | 0.3 |
| PFO Kinetic Model | PSO Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg.g−1) | K1 (min−1) | R2 | (mg/g) | K2 (g.mg−1.min−1) | R2 |
| 9.148 | 0.266 | 0.9772 | 9.459 | 0.0579 | 0.9977 |
| Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qm (mg.g−1) | KL (L.mg−1) | R2 | KF | n | R2 |
| 10.477 | 0.189 | 0.853 | 25.62 | 0.25 | 0.793 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Rao, Y. Study on Properties of Micro-Nano Magnetic Composite Prepared by Mechanochemical Method of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Removal of As (V) from Mine Water. Water 2024, 16, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091234
Feng X, Rao Y. Study on Properties of Micro-Nano Magnetic Composite Prepared by Mechanochemical Method of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Removal of As (V) from Mine Water. Water. 2024; 16(9):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091234
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xiujuan, and Yicheng Rao. 2024. "Study on Properties of Micro-Nano Magnetic Composite Prepared by Mechanochemical Method of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Removal of As (V) from Mine Water" Water 16, no. 9: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091234
APA StyleFeng, X., & Rao, Y. (2024). Study on Properties of Micro-Nano Magnetic Composite Prepared by Mechanochemical Method of NdFeB Secondary Waste and Removal of As (V) from Mine Water. Water, 16(9), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091234






