Abstract
The transition from the linear economy paradigm to the circular economy in industrial wastewater treatment is on the global agenda. The search for new simple, eco-innovative and low-cost processes for treating industrial wastewater, which can also be used by small- and medium-sized industries, has been a constant challenge to ensure environmental sustainability in all types of industries. The present work aimed to evaluate the suitability of the treated slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW) obtained by the integrated process composed of immediate one-step lime precipitation (IOSLM) and atmospheric carbonation (AC) for the production of aromatic plants by hydroponics. Results showed a significant increase in plant height of 177 and 147% and root length of 64 and 37% for Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants, respectively, after 26 days. No signs of toxicity or symptoms of micronutrient deficiency were detected in aromatic plants.
1. Introduction
The reuse of wastewater has been strongly driven by the United Nations according to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) defined in the 2030 Agenda, as a need to address global water scarcity [1]. Many industries have promoted the circular economy through the reuse of treated wastewater. However, other industries, such as most slaughterhouses, have still followed the linear production model discharging their wastewaters into the water lines or municipal collectors [2]. The low potential of treated slaughterhouse wastewater (SWW) for reuse in slaughterhouse facilities is associated with the need for high-quality water, such as drinking water, for food security reasons [3]. However, slaughterhouses can have an important role in the circular economy through wastewater recovery in the agricultural sector due to the nutrients still present after in situ treatment. The recovery and recycling of nutrients from SWW in the framework of a circular economy model has been developed [4]. Matheyarasu et al. [5] obtained a significant increase in biomass yield and plant growth by applying treated SWW in soil. Menegassi et al. [6] observed that the treated SWW favors the production of grass in soil without the need for nitrogen supplementation. Although treated SWW has a high potential for reuse in agriculture, the sludge resulting from the treatment still needs to be stabilized and contain metallic residues that can limit plant growth due to lower nutrient availability [7,8], so its disposal is landfill. Therefore, it is necessary to rethink how SWW should be treated and then recovered. Recently, a low-cost and easy-to-apply pretreatment process composed of immediate one-step lime precipitation (IOSLM) and atmospheric carbonation (AC) has been developed to treat SWW [9]. High removals of organic matter, suspended solids, oils and fats, and nutrients were obtained, and the sludge obtained has potential recovery as a coagulant aid [10,11]. However, to the best of our knowledge, no reuse solutions were developed for the treated SWW.
Hydroponic systems have been considered a promising economical and environmental biotechnology for plant production (e.g., lettuce, tomatoes, and others) [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Compared to soil, hydroponic systems require less water (which is important in water-scarce regions), can have faster growth rates, and make better use of space (in vertical) [20,21]. Lately, there has been interest in producing aromatic herbs, for example, the plants Mentha, since they have high economic importance due to their essential oil content to produce pharmaceutical products and biopesticides [22,23]. Surendran et al. [24] observed that the productivity of M. spicata was higher with hydroponics-grown plants than with soil-grown plants for crop biometric properties, yield, and its influence on the biochemical properties, using Hoagland’s nutrient solution. On the other hand, Zeljković et al. [25] observed that all mint species studied (Mentha arvensis L., Mentha × piperita L., and Mentha spicata L.) increased their height growth by more than 50% from the 17th to 24th day irrespective of the NO3- concentration (1.25, 10 and 20 mM), using half-strength Hoagland’s solution in hydroponics, although the Mentha × piperita was the best mint species performing under low nitrate content (1.25 mM). However, it is not mentioned in the literature which form of nitrogen (i.e., nitrate or ammonium nitrogen) is preferably assimilable for these species. Mumivand et al. [26] observed that the reuse of treated urban wastewater can improve the vegetative growth of peppermint, essential oil content, and the yield of plants. Since the concentration of nitrates is generally negligible in urban wastewater, these results may highlight that ammonium nitrogen can also contribute to plant growth. Insignificant concentrations of nitrate (<2 mg N L−1) and low concentrations of ammonium nitrogen (c.a. 12 to 22 mg N L−1) have also been reported in SWW treated by the IOSLM/AC process [10,11], but to the best of our knowledge, the potential of these waters for plant production has never been studied. Thus, to fill the gaps mentioned, this work aims to evaluate the growth of two species of mint plant using treated SWW from the IOSLM/AC process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Slaughterhouse Wastewater Sampling
SWW results from the slaughter of animals and washing and disinfection of facilities and equipment. The pretreatment processes at the slaughterhouse under study consist of a sieving, aeration, and homogenization operation, followed by coagulation–flocculation/dissolved air flotation with the addition of ferric sulfate and a polyelectrolyte, before being discharged into the municipal collectors (Figure 1). Since SWW may vary due to changes in the number and type of animals slaughtered, the amount of water consumed in the washing, and in the processes of the slaughterhouse facilities [27,28,29], a representative SWW sample was collected from the aeration and homogenization tank (hereinafter referred to as raw SWW) (Figure 1) from the slaughterhouse located in the Alentejo region, southern Portugal, during opening hours. All collected samples were stored in containers and kept at 4 °C until their respective analysis or the IOSLM/AC tests started.
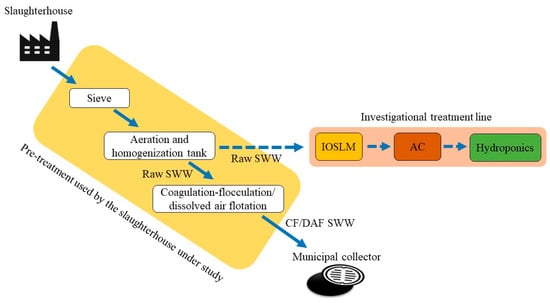
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the slaughterhouse wastewater pretreatment line in the slaughterhouse and the treatment line under investigation.
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.2.1. IOSLM/AC Test
Raw SWW was treated by the IOSLM/AC sequence (Figure 2) according to the optimal conditions found by Madeira et al. [9]. Briefly, raw SWW was treated by IOSLM which consisted of adding a hydrated lime solution (200 g L−1), under vigorous stirring, until reaching pH 12. Then, sedimentation occurred for 1 h and the sludge was separated from the supernatant. Additionally, the supernatant obtained (IOSLM SWW) was neutralized with atmospheric CO2 using the AC process, under a reactor ratio area/volume of 9.5 m2/m3, without stirring and outside, until reaching a pH of around 8. Then, the final supernatant (IOSLM/AC SWW) was characterized according to Section 2.3 for subsequent reuse in hydroponics.
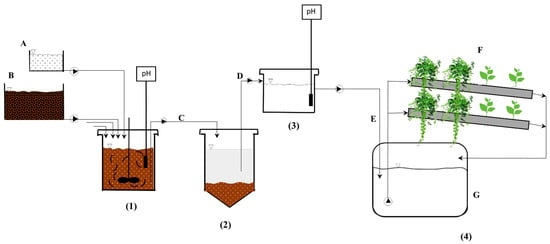
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram containing operations and processes of treatment used in this work, namely: (1) IOSLM process, (2) sedimentation process, (3) AC process, and (4) hydroponic system. A—hydrated lime tank, B—SWW tank, C—IOSLM SWW, D—supernatant, E—hydroponic nutrient solution, F—aromatic plant grow bed, G—hydroponic nutrient solution tank.
2.2.2. Hydroponics Test
The hydroponics essay was performed outdoors at the beginning of summer for 26 days. During this period, the average maximum and minimum daily temperatures were 33 °C and 18 °C, respectively. A hydroponic system nutrient film technique (NFT) was used for the growth of Pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium L.) and Chocolate Peppermint (Mentha · piperita f. citrata ‘Chocolate’). The NFT contained a tank with hydroponic nutrient solution (50 L); 2 cultivation channels (circular PVC tubes with 3 m length and 90 mm diameter) without substrate, inclined at 3%, with a flooding level of 4 cm and capacity of up to 13 plants per channel; a pumping system which works in continuous mode with a flow rate of 12 L h−1; and a system of returning the solution to the tank by gravity. A bypass tap was connected to the pumping system to create oxygen in the system. After washing the roots of the plants (to remove the soil), 13 plants (9 Pennyroyal plants and 4 Chocolate Peppermint plants) were planted in each cultivation channel. The plants of the same species were followed one after the other, and the Pennyroyal plants were placed to be the first to receive the nutrient solution. The hydroponic nutrient solution used in the hydroponic essay was the IOSLM/AC SWW (obtained in Section 2.2.1). On the 15th day, the hydroponic system’s solution was changed and, until the 26th day, it was analyzed (Section 2.3). Plant root length, plant height, and the flowering of both species were analyzed at the beginning and the end of the tests. The physical aspects of the plants were observed throughout the experiment, to identify possible signs of toxicity.
2.3. Analytical Methods
The SWW physicochemical parameters were determined according to the standard analytical methods defined by Baird et al. [30]. pH was measured by the potentiometric method using the WTW InoLab pH Level 1 apparatus (WTW, Weilheim, Germany) and a SenTix® 4 pH electrode. Electrical conductivity was measured by the electrometric method using a Jenway 4510 conductivity meter (Jenway, Corroios, Portugal) and a conductivity sensor VWR phenomenal CO 11. Total suspended solids (TSS) were quantified by the gravimetric method using Whatman® glass microfiber filters (Grade 934-AH®). Chemical oxygen demand (COD) was determined by the closed reflux colorimetric method, using a COD digester WPA Hydrocheck HC 6016 (ILC, Lisbon, Portugal) and a UV/Vis spectrophotometer Pharmacia Biotech Ultrospec (2000) (Pharmacia Biotech, Cambridge, UK). Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) was determined on the 5th day by the respirometric method using the WTW OxiTop® IS 12 system (VWR International, Amadora, Portugal). Total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN) was quantified by the Kjeldahl method using a Bloc Digest 6 P-Selecta digester (JP Selecta, Barcelona, Spain) and a distillation unit BUCHI B-316 (BUCHI, Barcelona, Spain). Ammonium nitrogen (NH4+) was quantified by the distillation method using a distillation unit BUCHI B-316. Nitrate and nitrites were determined by the colorimetric method, using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer Pharmacia Biotech Ultrospec (2000) (Pharmacia Biotech, Cambridge, UK). Oils and fats were quantified by the gravimetric method using a Soxhlet extractor with petroleum ether and a Soxhlet heating mantles electrothermal EM O250/CE. Total phosphorus (TP) was measured by the colorimetric method using a muffle P SELECTA-HORN 186331 and a UV/Vis spectrophotometer Pharmacia Biotech Ultrospec (2000) (Pharmacia Biotech, Cambridge, UK). Turbidity was measured by the nephelometric method using a HACH 2100 N turbidimeter (Hach, London, UK). E. coli was quantified by the most probable number method. Absorbances at 254 nm and at 410 nm were measured by the spectroscopic method using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer Pharmacia Biotech Ultrospec (2000) (Pharmacia Biotech, Cambridge, UK). Total alkalinity was determined by neutralization titration. Dissolved oxygen (DO) was quantified by a modification of the Winkler method. Total hardness was determined by volumetric complexation with EDTA.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The physicochemical parameters and IOSLM/AC assays were carried out in triplicate, and the respective averages were subsequently calculated. Then, the means were compared by a one-way ANOVA at a 95% confidence level, through the IBM SPSS Statistics (version 20.0 for Windows, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The graphs were drawn by GraphPad Prism (version 5.0 for Windows).
Removal efficiencies were calculated according to Expression (1).
where Removal (%) is the removal efficiency, Ci is the initial concentration, and Cf is the final concentration.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Raw SWW
The raw SWW was quite heterogeneous. Table 1 shows the physicochemical characteristics of the raw SWW from the slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. According to Table 1, the effluent had a pH close to neutral (6.7 ± 0.2) and a high conductivity (1.6 ± 0.0 mS cm−1). The range of raw SWW pH values obtained were in the typical pH range (4.9 to 8.1 according to Bustillo-Lecompte and Mehrvar [28]) for slaughterhouse wastewaters. High pH values in SWW are generally associated with the use of detergents and other cleaning products. This effluent also had a high BOD5/COD ratio (i.e., 0.5) indicating that the biodegradable fraction was high. High COD (3982 ± 330 mg O2 L−1), BOD5 (2000 ± 190 mg O2 L−1), TSS (1841 ± 171 mg L−1), TP (491.6 ± 90.0 mg L−1), total Kjeldahl nitrogen (242 ± 22 mg N L−1), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+) (115 ± 5 mg N-NH4+ L−1), and E. coli (10,000 MPN/100 mL) concentrations, and high turbidity (1596 ± 40 NTU) were observed. The average concentrations of TSS, COD, BOD, and TKN in raw SWW were close to the average value mentioned by Bustillo-Lecompte and Mehrvar [28] in typical slaughterhouse wastewater. The organic matter present in slaughterhouse wastewater is mainly due to the content of rumen, feces, skin fat, undigested food, blood, suspended material, urine, and loose meat [31]. TSS include insoluble and slowly biodegradable compounds such as pieces of hair, fat, flesh, grease, undigested feed and manure, as well as colloidal solids [32]. Phosphorus present in SWW is due to blood, manure, and cleaning products [33]. As expected, low concentrations of nitrites (<0.05 mg N L−1) and nitrates (<2 mg N L−1) were observed (Table 1). Generally, most of the SWW nitrogen is in organic form or ammonium nitrogen, with concentrations of nitrates or nitrites being quite residual. The nitrogen in SWW is mainly due to blood, urine, and feces [33].

Table 1.
Physicochemical characterization of raw SWW.
3.2. IOSLM/AC
The performance of the IOSLM/AC sequence was evaluated using raw SWW whose characteristics are shown in Table 1. Figure 3 shows the removal efficiencies obtained for the various parameters analyzed. After the IOSLM/AC sequence, the effluent had a pH of 7.7 ± 0.1. High removal efficiencies of COD (89.7 ± 9.0%), BOD (95.0 ± 9.0%), TKN (88.4 ± 8.4%), NH4+ (78.3 ± 4.2%), TP (99.4 ± 16.6%), TSS (96.2 ± 19.0%), oils and fats (92.6 ± 12.4%), turbidity (95.7 ± 2.5%), and E. coli (100%) were achieved. These removals corresponded to COD concentrations of 411 ± 24 mg L−1, BOD of 100 ± 0 mg L−1, TKN of 28 ± 1 mg N L−1, NH4+ of 25 ± 1 mg N L−1, TP of 3.0 ± 0.5 mg L−1, TSS of 70 ± 12 mg L−1, oils and fats of 44 ± 3 mg L−1, turbidity of 69 ± 1 NTU, and the absence of E. coli. As expected, nitrite and nitrate concentrations remained below detectable limits. So, all parameters meet the limits for discharge to municipal collectors.
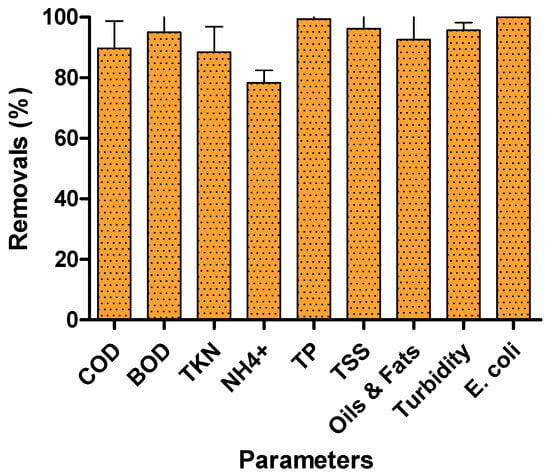
Figure 3.
Removal efficiencies obtained in the treatment of raw SWW by IOSLM/AC process. Bars represent standard deviation of the mean.
The IOSLM process’ removals of COD, BOD, organic nitrogen, TSS, oils and fats, and turbidity are explained by the extensive formation of calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide precipitates formed at a high reaction pH with the addition of hydrated lime, which can act as a coagulant and drag impurities present in the effluent during sedimentation [9]. Furthermore, phosphorus can be removed in the form of calcium phosphate and octacalcium phosphate [34,35]. On the other hand, E. coli is removed under high pH (ca. pH 12) and a certain contact time, as well as by its adsorption to the formed precipitates [36]. Subsequently, the effluent is subjected to the AC process to reduce the pH. The decrease in the pH of the effluent to around neutrality occurs through the reaction with atmospheric CO2 [9,37]. While the effluent is neutralized, the ammonia present in the effluent is removed by volatilization until equilibrium is reached [38].
3.3. Hydroponics
Figure 4 shows the effect of the IOSLM/AC SWW on the development of the morphological characteristics (that is, plant height, root length, and flowering) of Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants grown in the NFT hydroponic system. According to Figure 4A, a significant increase (p < 0.05) of plant height, about 177 and 147%, was observed for Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants, respectively, after 26 days. The final height of the Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants were 39.3 ± 10 cm and 41.8 ± 16.8 cm, respectively (Figure 4A). The heights obtained from both plant species are within the range defined by some authors, for example, plant heights between 23 and 47 cm for Pennyroyal [39], and between 30 and 90 cm for Chocolate Peppermint [40]. A significant increase (p < 0.05) in root length, about 64 and 37%, was also observed for Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants, respectively (Figure 4B). These results show that the growth of the aromatic plants studied is not dependent on the presence of nitrates, but that the plants can assimilate ammonium nitrogen as observed by Mumivand et al. [26] when the authors reused treated urban wastewater for peppermint growth.
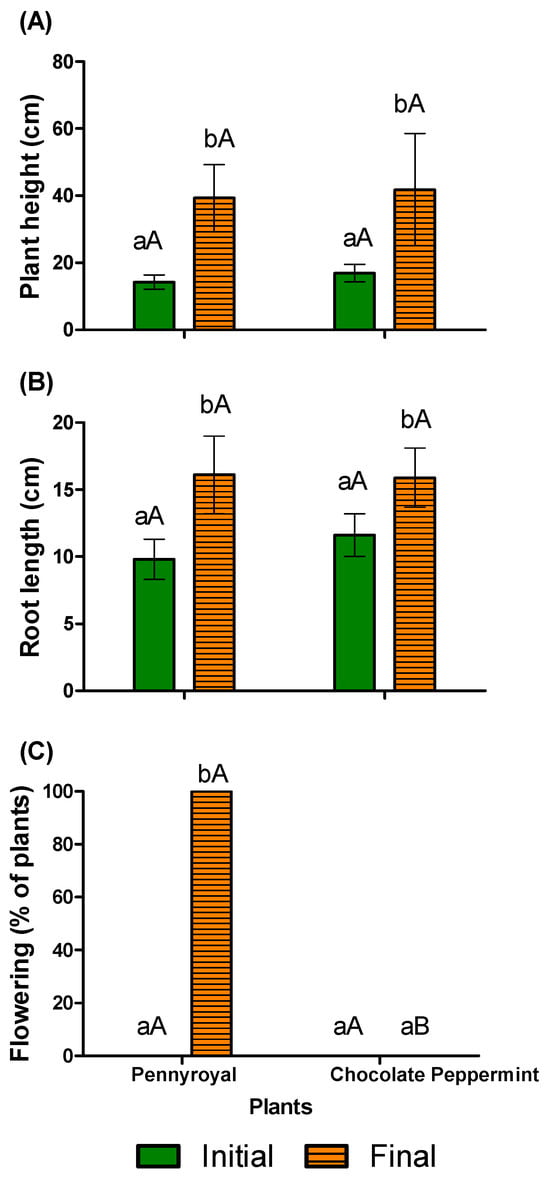
Figure 4.
Initial and final morphological characteristics of Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint plants used in hydroponic system in terms of: (A) plant height, (B) root length, and (C) flowering. Bars represent one standard deviation of the mean. Note: different lowercase letters in the same type of plant represent a significant difference (p < 0.05); different capital letters for the same temporal condition indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
There were no significant differences (p < 0.05) in plant height and root length between plants (Figure 4A,B). After 26 days, 100% of the Pennyroyal plants had flowered, while for the Chocolate Peppermint plant, no flowering was observed (Figure 4C). The flowering of both species of plants is expected in the summer. Although Chocolate Peppermint plants were expected to have greater growth than Pennyroyal plants, this did not happen because Chocolate Peppermint plants were the last plants of the cultivation channel to receive the hydroponic nutrient solution, which possibly delayed their flowering. Even so, no signs of toxicity and no symptoms of micronutrient deficiency (e.g., yellowing of the leaves) were detected in both plants by visual inspection. Interestingly, no damage to plant growth (e.g., Vetiveria zizanioides) was reported lately when they were fed by effluents treated by IOSLM/AC [41,42].
Table 2 shows the initial and final physicochemical composition of the IOSLM/AC SWW used in the hydroponic system. On average, a slight decrease in pH (ca. 7.5), conductivity (ca. 1.13 mS cm−1), absorbance at 254 nm, absorbance at 410 nm, and total alkalinity were observed. Despite the decrease in conductivity, these values are still close to 1.4 mS cm−1, a value considered excellent for the growth of Chocolate Peppermint according to Tabatabaie et al. [43]. About 90% of ammonium nitrogen was removed (Table 2). It is not expected that the decrease in ammonium nitrogen in the effluent during the hydroponic test was due to ammonia volatilization since the pH of the IOSLM/AC SWW was around neutrality, nor due to the increase or conversion of ammonium nitrogen to nitrates or nitrites, as the latter remained below the detectable limit (Table 2). So, the plants may have absorbed the ammonium nitrogen since they have grown (Figure 4A,B). Turkdogan et al. [44] also showed that Lemna minor pools can be a polishing step for ammonium nitrogen removal from pretreated poultry SWW by dissolved air flotation. As expected, an increase in dissolved oxygen was observed since a bypass tap was connected to the pumping system to create oxygen to the system. The evaporation phenomenon occurred during hydroponics tests, and consequently, the total hardness increased (Table 2).

Table 2.
Characteristics of the initial and final IOSLM/AC SWW in hydroponics.
From an economic point of view, it is expected that the proposed treatment system (IOSLM + AC + hydroponics) is inevitably associated with operating costs that include energy expenditure (e.g., resulting from the use of SWW agitation in the rapid mixing tank and the use of the pump of water in hydroponics), as well as the consumption of reagents (e.g., hydrated lime in the IOSLM process). During the AC process, no reagent or energy consumption is expected. Therefore, considering these assumptions and that the average price of hydrated lime is €220/ton [45], it is expected that the proposed treatment system (IOSLM + AC + hydroponics) will have an average operating cost of €6.73/m3. Around 95.5% of this operating cost corresponds to energy costs.
4. Conclusions
In this work, the treated SWW from the IOSLM/AC sequence was reused in the growth of aromatic plants (Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint) by the NFT hydroponic system. The IOSLM process is recognized in SWW treatment to highly remove organic matter, TSS, oils and fats, and nutrients (such as organic nitrogen and phosphorus). The AC process helps to reduce the effluent pH and the ammonia nitrogen concentration. It was demonstrated that the effluent resulting from the IOSLM/AC sequence can contribute to the growth of some aromatic plants such as Pennyroyal and Chocolate Peppermint, and these plants can remove most of the nitrogen present in the effluent.
IOSLM/AC sequence is recognized for its low-cost and easy-to-apply treatment, low energy demand, and capability of operating in remote locations, contributing to the atmospheric mitigation of CO2 emissions. Furthermore, it is a promising circular sequence alternative to combat the global scarcity of drinking water. All these benefits are aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) defined in the 2030 Agenda.
Future work should quantify and characterize the essential oil content present in aromatic plants grown with SWW treated by the IOSLM/AC sequence since essential oil has high economic importance in producing pharmaceutical products and biopesticides.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. and A.A.; Funding acquisition, F.C. and A.A.; Investigation, L.M. and S.N.; Methodology, M.R.T. and A.A.; Supervision, M.R.T., F.C. and A.A.; Writing—original draft, L.M.; Writing—review and editing, L.M., M.R.T., F.C. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and the APC were funded by NETA project: New Strategies in Wastewater Treatment (POCI-01-0247-FEDER-046959), through PORTUGAL2020.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the slaughterhouse for providing the effluent and help during effluent sample collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norsyahariati, N.; Daud, N.; Anijiofor, S.C. Chicken Slaughterhouse Wastewater Disposal: The Challenges Ahead. Asian J. Agri. Biol. 2018, 18, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Karlis, P.; Presicce, F.; Giner-Santonja, G.; Brinkmann, T.; Roudier, S. Best Available Techniques (BAT) Reference Document for the Slaughterhouses, Animal By-Products and Edible Co-Products Industries; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berden-Zrimec, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Cerar, A.; Resman, L.; Mihelic, R.; Lazar, B.; Slapnik, M. Turning Wastewater into added-value products for circular economy in agriculture. Project Water2Return—Recovery and Recycling of Nutrients. In Proceedings of the TBMCE 2019, Portorož, Slovenia, 24–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheyarasu, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Naidu, R. Abattoir Wastewater Irrigation Increases the Availability of Nutrients and Influences on Plant Growth and Development. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegassi, L.C.; Rossi, F.; Dominical, L.D.; Tommaso, G.; Montes, C.R.; Gomide, C.A.; Gomes, T.M. Reuse in the agro-industrial: Irrigation with treated slaughterhouse effluent in grass. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahedi, M.; Cetin, B.; Dayioglu, A.Y. Leaching behavior of aluminum, copper, iron and zinc from cement activated fly ash and slag stabilized soils. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 334–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, A.P.; Marchetti, M.E.; Dupas, E.; Carducci, C.E.; Silva, E.F.; da Pinheiro, E.R. Phosphorus in Forage Production. In New Perspectives in Forage Crops; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madeira, L.; Carvalho, F.; Almeida, A.; Ribau Teixeira, M. Integrated Process of Immediate One-Step Lime Precipitation, Atmospheric Carbonation, Constructed Wetlands, or Adsorption for Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Water 2023, 15, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Carvalho, F.; Almeida, A.; Ribau Teixeira, M. Optimization of atmospheric carbonation in the integrated treatment immediate one-step lime precipitation and atmospheric carbonation. The case study of slaughterhouse effluents. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Ribau Teixeira, M.; Almeida, A.; Santos, T.; Carvalho, F. Reuse of lime sludge from immediate one-step lime precipitation process as a coagulant (aid) in slaughterhouse wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Regato, M.; Patanita, M.; Luz, S.; Carvalho, M.J.; Fernandes, A.; Lopes, A.; Almeida, A.; Costa, I.; Carvalho, F. Reuse of Pretreated Agro-Industrial Wastewaters for Hydroponic Production of Lettuce. Water 2023, 15, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Carvalho, M.J.; Correia, T.; Correia, P.; Regato, M.; Costa, I.; Fernandes, A.; Almeida, A.; Lopes, A.; et al. Pretreated Agro-Industrial Effluents as a Source of Nutrients for Tomatoes Grown in a Dual Function Hydroponic System: Tomato Quality Assessment. Sustainability 2023, 16, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.d.S.C.; Bastos, R.G.; Souza, C.F. Influence of the use of wastewater on nutrient absorption and production of lettuce grown in a hydroponic system. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbuikwem, P.N.; Mierzwa, J.C.; Saroj, D.P. Assessment of suspended growth biological process for treatment and reuse of mixed wastewater for irrigation of edible crops under hydroponic conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebeyehu, A.; Shebeshe, N.; Kloos, H.; Belay, S. Suitability of nutrients removal from brewery wastewater using a hydroponic technology with Typha latifolia. BMC Biotechnol. 2018, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magwaza, S.T.; Magwaza, L.S.; Odindo, A.O.; Mditshwa, A. Hydroponic technology as decentralised system for domestic wastewater treatment and vegetable production in urban agriculture: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magwaza, S.T.; Magwaza, L.S.; Odindo, A.O.; Mditshwa, A.; Buckley, C. Partially treated domestic wastewater as a nutrient source for tomatoes (Lycopersicum solanum) grown in a hydroponic system: Effect on nutrient absorption and yield. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Albuquerque, A.; Luz, S.; Jerónimo, E.; Carvalho, F. Hydroponic System: A Promising Biotechnology for Food Production and Wastewater Treatment. In Food Biosynthesis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 317–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomoni, D.I.; Koukou, M.K.; Vrachopoulos, M.G.; Vasiliadis, L. A Review of Hydroponics and Conventional Agriculture Based on Energy and Water Consumption, Environmental Impact, and Land Use. Energies 2023, 16, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoliva, S.G.; Gwyn-Jones, D.; Detheridge, A.; Robson, P. Controlled comparisons between soil and hydroponic systems reveal increased water use efficiency and higher lycopene and β-carotene contents in hydroponically grown tomatoes. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 279, 109896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqeel, U.; Aftab, T.; Khan, M.M.A.; Naeem, M. Regulation of essential oil in aromatic plants under changing environment. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2023, 32, 100441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, P.M.; Santos, L. Essential oil of pennyroyal (Mentha pulegium): Composition and applications as alternatives to pesticides—New tendencies. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 139, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, U.; Chandran, C.; Joseph, E.J. Hydroponic cultivation of Mentha spicata and comparison of biochemical and antioxidant activities with soil-grown plants. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017, 39, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljkovic, S.C.; Aucique-Perez, C.E.; Stefelova, N.; De Diego, N. Optimizing growing conditions for hydroponic farming of selected medicinal and aromatic plants. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mumivand, H.; Izadi, Z.; Amirizadeh, F.; Maggi, F.; Morshedloo, M.R. Biochar amendment improves growth and the essential oil quality and quantity of peppermint (Mentha × piperita L.) grown under waste water and reduces environmental contamination from waste water disposal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Smadi, B.M.; Al-Hayek, W.; Abu Hajar, H.A. Treatment of Amman Slaughterhouse Wastewater by Anaerobic Baffled Reactor. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo-Lecompte, C.; Mehrvar, M. Slaughterhouse Wastewater: Treatment, Management and Resource Recovery. In Physico-Chemical Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoya, M.; Basitere, M.; Ntwampe, S.K.O. Analysis of the characteristics of poultry slaughterhouse wastewater (PSW) and its treatability. Water Pract. Technol. 2019, 14, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.; Eaton, A.D.; Rice, E.W.; Bridgewater, L.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mutairi, N.Z.; Hamoda, M.F.; Al-Ghusain, I. Coagulant selection and sludge conditioning in a slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husam, A.-N.; Nassar, A. Slaughterhouses Wastewater Characteristics in the Gaza Strip. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 11, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nery, V.; De Nardi, I.R.; Damianovic, M.H.R.Z.; Pozzi, E.; Amorim, A.K.B.; Zaiat, M. Long-term operating performance of a poultry slaughterhouse wastewater treatment plant. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nan, X.; Li, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Li, Q. Advances in the treatment of phosphorus-containing wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 647, 012163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Luz, S.; Fernandes, F.; Jeronimo, E. Cheese wastewater treatment by acid and basic precipitation: Application of H2SO4, HNO3, HCl, Ca(OH)2 and NaOH. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerjian, L.; Ayoub, G.M. High-pH–magnesium coagulation–flocculation in wastewater treatment. Adv. Environ. Res. 2003, 7, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Teixeira, M.R.; Carvalho, F. Modeling and optimization of atmospheric CO2 capture for neutralization of high alkaline wastewaters using response surface methodology. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 81, 102705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Almeida, A.; Ribau Teixeira, M.; Prazeres, A.; Chaves, H.; Carvalho, F. Immediate one-step lime precipitation and atmospheric carbonation as pre-treatment for low biodegradable and high nitrogen wastewaters: A case study of explosives industry. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, N. Melliferous charactheristics of spontaneous Lamiaceae species, identified in the danube valley. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 40, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Malekmohammad, K.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Sardari, S.; Sewell, R.D.E. Toxicological effects of Mentha × piperita (peppermint): A review. Toxin Rev. 2021, 40, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Almeida, A.; da Costa, A.M.R.; Mestre, A.S.; Carvalho, F.; Teixeira, M.R. Tunning processes for organic matter removal from slaughterhouse wastewater treated by immediate one-step lime precipitation and atmospheric carbonation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, L.; Carvalho, F.; Teixeira, M.R.; Ribeiro, C.; Almeida, A. Vertical flow constructed wetland as a green solution for low biodegradable and high nitrogen wastewater: A case study of explosives industry. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaie, S.J.; Nazari, J.; Nazemiyeh, H.; Zehtab, S.; Azarmi, F. Influence of various electrical conductivity levels on the growth and essential oil content of Peppermint (Menta piperita L.) grown in hydroponic. Acta Hortic. 2007, 747, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkdogan, F.I.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Goncaloglu, B.I.; Keskintimur, N.; Gungordu, M.; Akyol, C. Removal of Ammonium Nitrogen from the DAF-Pretreated Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater by Lemna minor. Eur. J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2019, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Spasiano, D.; Petrella, A.; Lacedra, V. Chemical Destabilization of Fresh and Spent Cutting Oil Emulsions: Differences between an Ecofriendly and Two Commercial Synthetic Lubricants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).