Irrigation Distribution Network Design Parameters and Their Influence on Sustainability Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
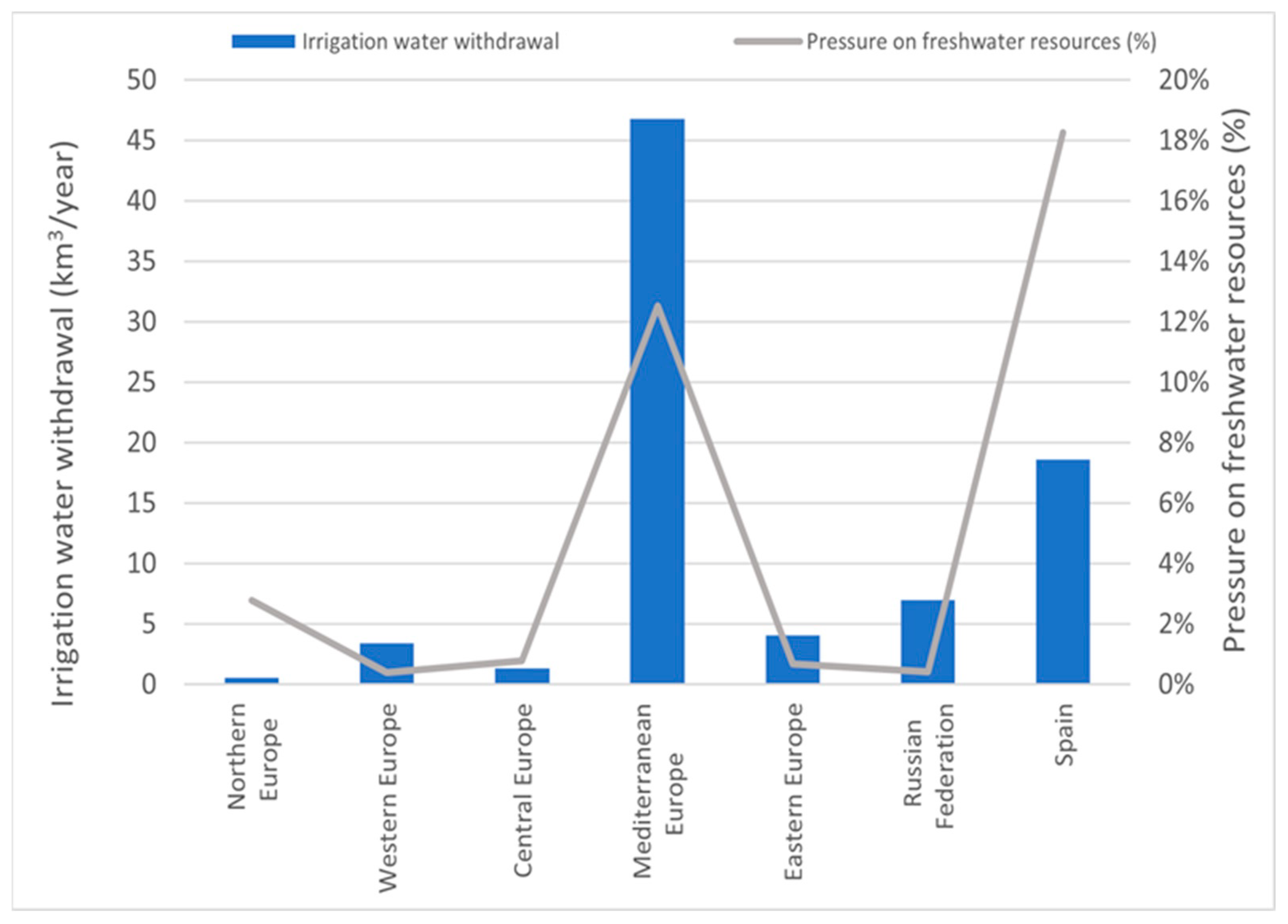
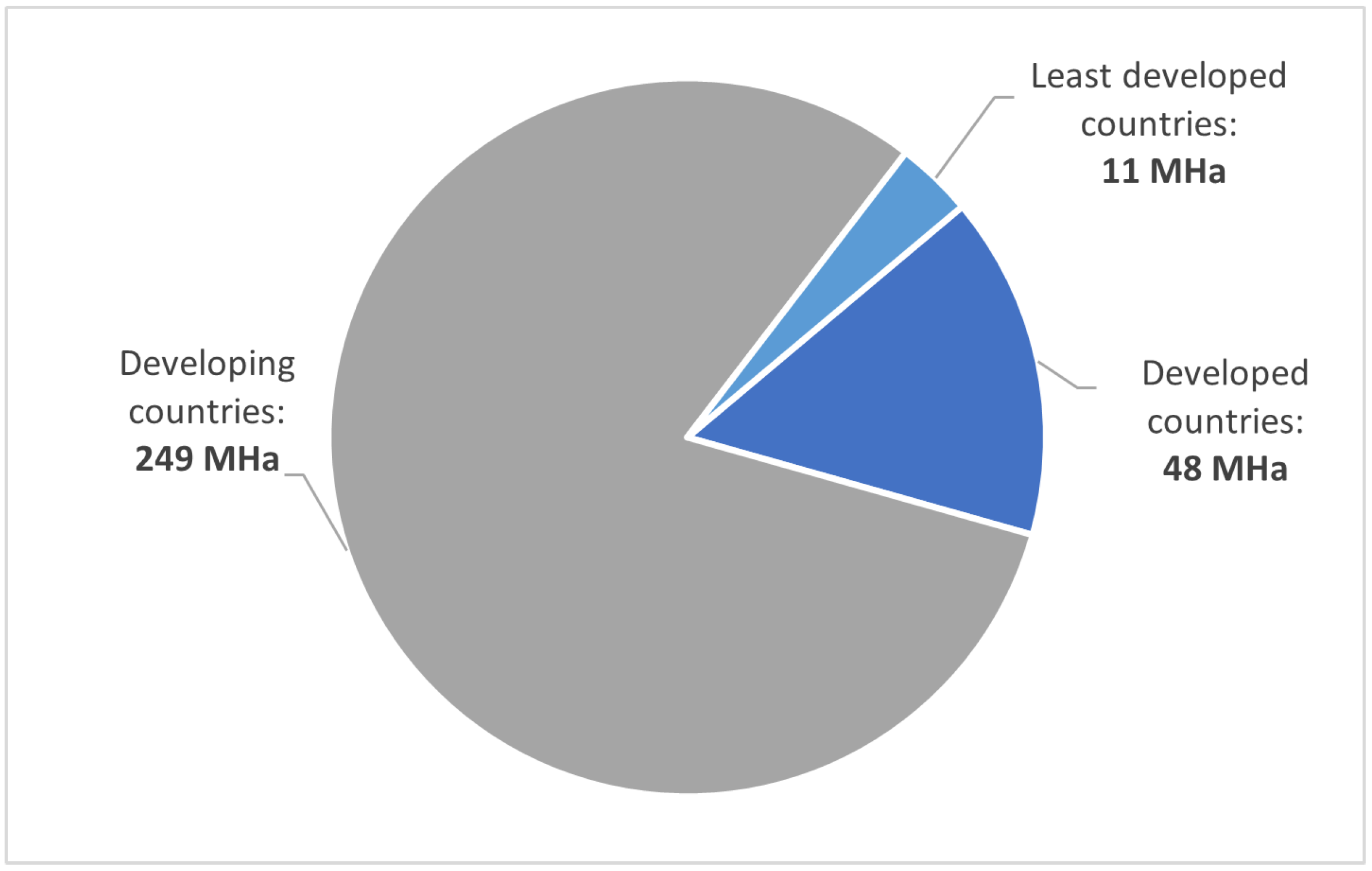
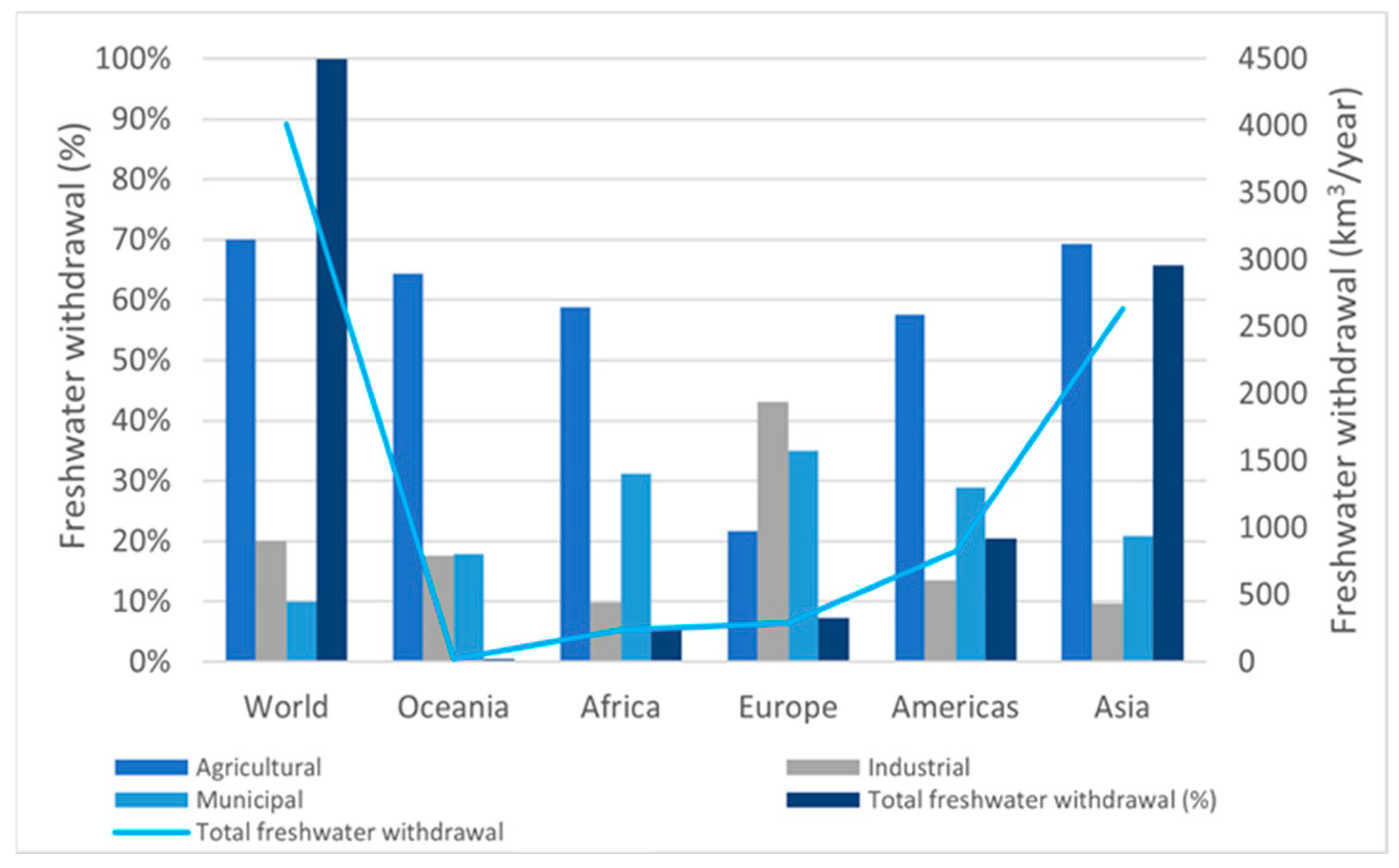
1.1. Irrigation Water Use
1.2. Environmental Implications
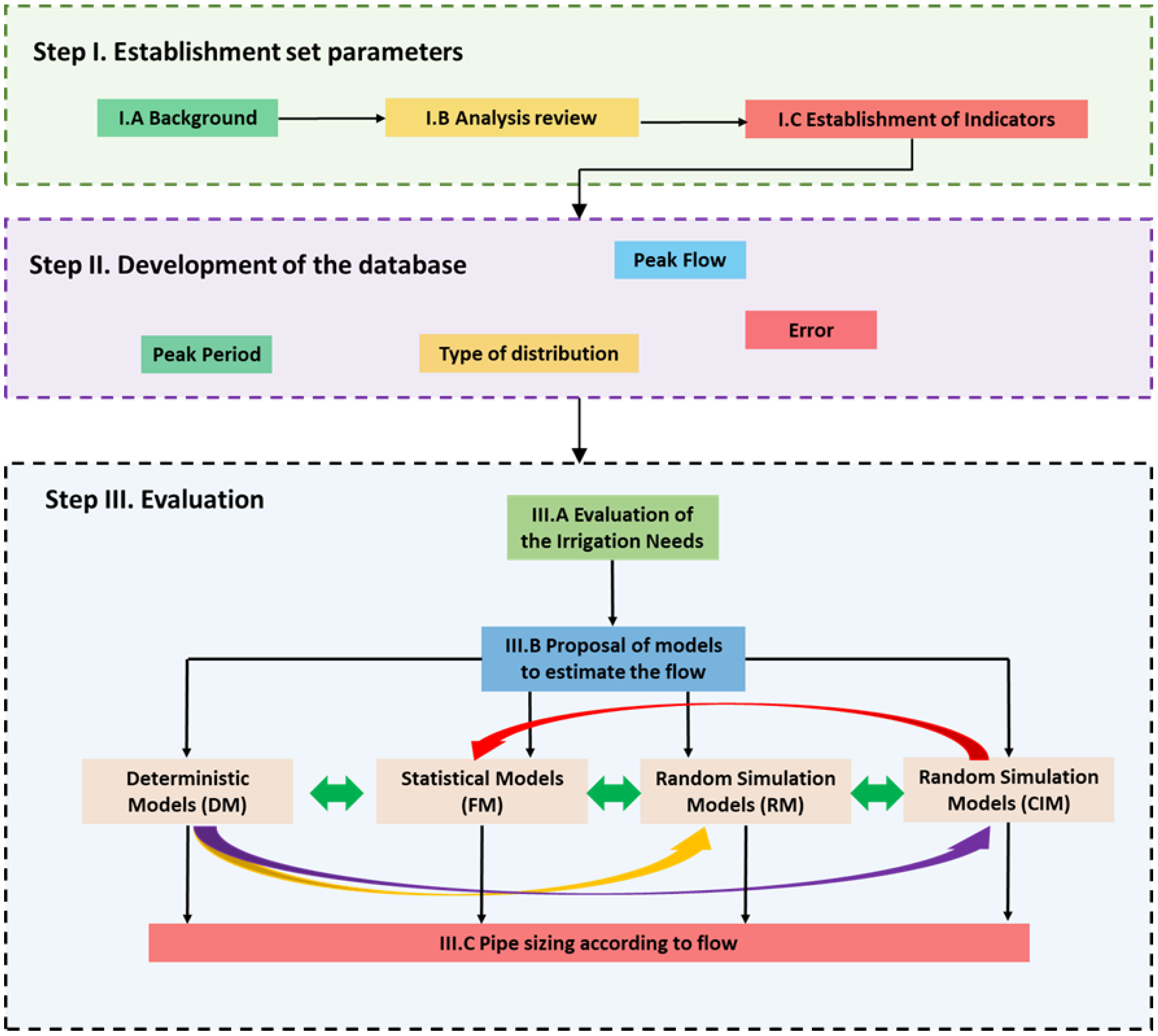
2. Evaluation Methodology and Materials
3. Determination of Flows to Design Irrigation Water Networks
3.1. Parameters of Study
3.2. Proposed Methods: Forecasting Irrigation Demand Flow
3.2.1. Deterministic Models (D)
| ID | Reference | Main Results |
|---|---|---|
| D.1 | [124] |
|
| D.2 | [126] |
|
| D.3 | [120] |
Human behaviour affects uniform probability prediction. |
| D.4 | [125] |
|
3.2.2. Statistical Models (F)
| ID | Reference | Type | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| S.1 | [119] | Statistical |
|
| S.2 | [121] | Frequentist |
Moreover, the model with Clément’s first formula seems robust enough in the conditions studied, so using more complicated models is unnecessary |
| S.3 | [120] | Deterministic |
|
| S.4 | [134] | Statistical |
|
| S.5 | [135] | Random Simulation |
The underestimation caused by the Clément methodology is due to using the average opening hydrant probability concept. |
| S.6 | [137] | Statistical |
|
3.2.3. Random Simulation Models (R)
| ID | Reference | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|
| R.1 | [141] |
|
| R.2 | [142] |
|
| R.3 | [143] |
|
| R.4 | [135] |
|
| R.5 | [144] |
|
| R.6 | [136] |
|
| R.7 | [145] |
|
3.2.4. Computational Intelligence Models (CI)
| ID | Reference | Model Type | Conclusions |
|---|---|---|---|
| CI.1 | [152] | Computational Neural Networks (CNNs) |
|
| CI.2 | [157] | Linear Regressions and Computational Neural Networks (CNNs) |
|
| CI.3 | [151] | Hybrid Computational Neural Networks + Fuzzy Logic + Genetic Algorithm (CNNs + FL + GA) |
|
| CI.4 | [159] | Artificial Neuro-Genetic Networks (ANGNs) |
|
| CI.5 | [158] | Principal Component Analysis (PCA) + Regression Analysis Methods |
|
| CI.6 | [160] | Hybrid Computational Neural Networks + Fuzzy Logic + Genetic Algorithm (CNNs + FL + GA) |
|
| CI.7 | [161] | Decision Trees + Genetic Algorithm (DTs + GA) |
|
3.3. Flow Pipe Sizing: Indicators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| CFF | Clément’s first formula |
| CNNs | Computer Neuronal Networks |
| DESA | Department of Economic and Social Affairs |
| DESA | Department of Economic and Social Affairs |
| FAO | Food and Agriculture of the United Nations |
| EEA | European Environmental Agency |
| ICID | International Commission on Irrigation and Drainage |
| IPCC | International Panel on Climate Change |
| IWMI | International Water Management Institute |
| RGM | Random Generated Model |
| SFRs | Several Flow Regimes |
| UN | United Nations |
| UN | United Nations |
| WEF | World Economic Forum |
| WWAP | United Nations World Water Assessment Programme |
| WWDR | World Water Development Report |
| Shape parameter of the Weibull distribution | |
| Annual average water saving coefficient | |
| Soil moisture change | |
| Slope vapour pressure | |
| Psychrometric constant | |
| Outlet flow assignment of group i | |
| Water loss out of the root due to deep percolation | |
| Fixed flow assignment of outlet group i | |
| Crop evapotranspiration | |
| Reference evapotranspiration | |
| Relative humidity by saturation vapour pressure deficit | |
| Irrigation area | |
| Cumulative distribution function (cdf) | |
| Probability density function | |
| Soil heat flux | |
| Irrigation | |
| Net irrigation water needs | |
| Crop coefficient | |
| Vector representing the jth event | |
| Total number of vectors analysed | |
| Number of outlets with the same assigned flow at group i | |
| Precipitation; rainfall | |
| Effective rainfall | |
| Probability of Q being Qi | |
| Probability of the operation of hydrant group i | |
| Discrete random variable flow vector | |
| Estimated water demand in day t | |
| Flow to forecast (Clément’s first formula) | |
| Observed water demand in day t − 1 | |
| Observed water demand in day t − 2 | |
| Nominal flow rate of vector i | |
| Surface runoff | |
| Extraterrestrial radiation | |
| Radiation at crop surface | |
| Rainfall | |
| Air temperature | |
| Temperature range | |
| Average daily temperature | |
| Forecasting year | |
| Data series corresponding to the first year | |
| Time between two demands in group i | |
| Guaranteed service level of group i | |
| Wind speed | |
| Predicted amount of water demanded | |
| Capillary rise |
References
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2019—Highlights; Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- WWDR; UN. Water and Energy, The United Nations World Water Development Report 2014 (2 Volumes). UN World Water Assessment Programme; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2014; Available online: http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0022/002257 (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- World Economic Forum. The Global Risks Report 2018 13th Edition; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Water for Sustainable Food and Agriculture a Report Produced for the G20 Presidency of Germany; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.D.; Lee, H.F.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Pei, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, Y. The Causality Analysis of Climate Change and Large-Scale Human Crisis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17296–17301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO World Water Assessment Program. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2019: Leaving No One Behind; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, C.; Snowden, M. Environment and Society: Human Perspectives on Environmental Issues; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapagain, A.K.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The Blue, Green and Grey Water Footprint of Rice from Production and Consumption Perspectives. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammini, A.; Puri, M.; Pluschke, L.; Dubois, O. Walking the Nexus Talk: Assessing the Water-Energy-Food Nexus in the Context of the Sustainable Energy for All Initiative; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 9251084874. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, D.; Philbrick, M.; Vallario, B.; Battey, H.; Clement, Z.; Fields, F. The Water-Energy Nexus: Challenges and Opportunities; US Department of Energy: Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. The European Environment: State and Outlook 2020: Knowledge for Transition to a Sustainable Europe; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2019; ISBN 978-92-9480-090-9. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. Use of Freshwater Resources in Europe—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/ims/use-of-freshwater-resources-in-europe-1?utm_source=EEASubscriptions&utm_medium=RSSFeeds&utm_campaign=Generic (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Del Borghi, A.; Moreschi, L.; Gallo, M. Circular Economy Approach to Reduce Water–Energy–Food Nexus. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2020, 13, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, A.; Frenken, K. Cooling Water for Energy Generation and Its Impact on National-Level Water Statistics; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Averyt, K.B.; Fisher, J.B.; Huber-Lee, A.T.; Lewis, A.; Macknick, J.; Madden, N.T.; Rogers, J.; Tellinghuisen, S. Freshwater Use by US Power Plants Electricity’s Thirst for a Precious Resource: A Report of the Energy and Water in a Warming World Initiative; NREL/TP-6A20-53273; Union of Concerned Scientists: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; 62p. [Google Scholar]
- Kanakoudis, V.; Tsitsifli, S.; Zouboulis, A.I. WATERLOSS Project: Developing from Theory to Practice an Integrated Approach towards NRW Reduction in Urban Water Systems. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Energy-Smart Food for People and Climate; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Climate-Smart Agriculture Sourcebook; Palombi, L., Sessa, R., Eds.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; ISBN 978-92-5-107720-7. [Google Scholar]
- Daccache, A.; Ciurana, J.S.; Rodriguez Diaz, J.A.; Knox, J.W. Water and Energy Footprint of Irrigated Agriculture in the Mediterranean Region. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 124014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M. Food, Agriculture & the Environment: Can We Feed the World & Save the Earth? Daedalus 2015, 144, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science (1979) 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development United Nations United Nations Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. Adoption of the Paris Agreement. In Proceedings of the Conference of the Parties on Its Twenty-First Session, Paris, France, 30 November–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, R.K.; Singh, V.P.; Upadhyay, A. Planning and Evaluation of Irrigation Projects: Methods and Implementation; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Franz, K.J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, J.; Jia, G.; Yang, Y. Irrigation Plays Significantly Different Roles in Influencing Hydrological Processes in Two Breadbasket Regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Alon, L.; Loftness, V.; Harries, K.A.; Cochran Hameen, E. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Natural vs Conventional Building Assemblies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Bertaki, M. Sustainable Water Management in Agriculture under Climate Change. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 4, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture (SOLAW). Available online: https://www.fao.org/nr/solaw/solaw-home/en/ (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- de Vrese, P.; Hagemann, S.; Claussen, M. Asian Irrigation, African Rain: Remote Impacts of Irrigation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3737–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayide, O.E.; Tetteh, I.K.; Popoola, L. Differential Impacts of Rainfall and Irrigation on Agricultural Production in Nigeria: Any Lessons for Climate-Smart Agriculture? Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Knox, J.W.; Camacho, E. Climate Change Impacts on Irrigation Water Requirements in the Guadalquivir River Basin in Spain. Reg. Environ. Change 2007, 7, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moragues-Faus, A. How Is Agriculture Reproduced? Unfolding Farmers’ Interdependencies in Small-Scale Mediterranean Olive Oil Production. J. Rural Stud. 2014, 34, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICID. World Irrigated Area—2021. Available online: https://icid-ciid.org/Knowledge/world_irrigated_area/ (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- García-Tejero, I.F.; Durán-Zuazo, V.H.; Muriel-Fernández, J.L.; Rodríguez-Pleguezuelo, C.R. Water and Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 1–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cirelli, A.; Arumí, J.L.; Rivera, D.; Boochs, P.W. Environmental Effects of Irrigation in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 69, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, K.; Gillet, V. Irrigation Water Requirement and Water Withdrawal by Country; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson, Å.; Faurès, J.-M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J. AQUASTAT—Getting to Grips with Water Information for Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003; Available online: https://www.fao.org/statistics/methods-and-standards/general/en (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- IPCC. Climate Change and Land; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. AQUASTAT—FAO’s Global Information System on Water and Agriculture. Available online: https://www.fao.org/aquastat/en/ (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Kehrein, P.; Van Loosdrecht, M.; Osseweijer, P.; Garfí, M.; Dewulf, J.; Posada, J. A Critical Review of Resource Recovery from Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants—Market Supply Potentials, Technologies and Bottlenecks. Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 877–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate Change Impacts on Soil Salinity in Agricultural Areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roga, S.; Bardhan, S.; Kumar, Y.; Dubey, S.K. Recent Technology and Challenges of Wind Energy Generation: A Review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.J. Measuring and Decomposing Agricultural Productivity and Profitability Change. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2010, 54, 527–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, S.; Manzo, M.; Beck, T. Corporate Reputation and Culture: The Link between Knowledge Management and Sustainability. J. Knowl. Manag. 2023. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. A Systematic Literature Review on Machine Learning Applications for Sustainable Agriculture Supply Chain Performance. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 119, 104926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Obaideen, K.; Elsaid, K.; Wilberforce, T.; Sayed, E.T.; Maghrabie, H.M.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Assessment of the Pre-Combustion Carbon Capture Contribution into Sustainable Development Goals SDGs Using Novel Indicators. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 153, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Morales, Y. Evaluación de Indicadores de Sustentabilidad Agroecológica En Sistemas de Producción Agrícola de Baja California Sur, México; CIBNOR: La Paz, Mexico, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Seager, J. Sex-Disaggregated Indicators for Water Assessment, Monitoring and Reporting; UNESCO Publishing: Paris, France, 2015; ISBN 9231001191. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.N.; Ritu, N.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, M.N.I. Impact of COVID-19 on Urban Environment in Developing Countries: Case Study and Environmental Sustainability Strategy in Bangladesh. Green Technol. Sustain. 2024, 2, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira Vilanova, M.R.; Filho, P.M.; Perrella Balestieri, J.A. Performance Measurement and Indicators for Water Supply Management: Review and International Cases. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNDP Human Development Index | Human Development Reports. Available online: https://hdr.undp.org/data-center/human-development-index#/indicies/HDI (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Delang, C.O.; Yu, Y.H. MEASURING WELFARE BEYOND ECONOMICS: The Genuine Progress of Hong Kong and Singapore; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780367332853. [Google Scholar]
- Schepelmann, P.; Goossens, Y.; Makipaa, A. Towards Sustainable Development: Alternatives to GDP for Measuring Progress; Wuppertal Spezial: Wuppertal, Germany, 2009; ISBN 3929944812. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.C.; Jiang, P.; Yang, L.; Van Fan, Y.; Klemeš, J.J.; Wang, Y. Extended Water-Energy Nexus Contribution to Environmentally-Related Sustainable Development Goals. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 150, 111485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.; Stone, W.; Botes, M.; Feil, E.J.; Wolfaardt, G.M. Wastewater Treatment Works: A Last Line of Defense for Preventing Antibiotic Resistance Entry Into the Environment. Front. Water 2022, 4, 883282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Cobo, M.T.; Camacho-Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A. Assessing the Potential of Solar Energy in Pressurized Irrigation Networks. The Case of Bembézar MI Irrigation District (Spain). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, J.M.; Rodriguez-Diaz, J.A.; Abadía, R.; Camacho, E.; Rocamora, C.; Moreno, M.A. Efficient Water and Energy Use in Irrigation Modernization: Lessons from Spanish Case Studies. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 162, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Assessing Water Urban Systems to the Compliance of SDGs through Sustainability Indicators. Implementation in the Valencian Community. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Díaz, J.A.; Camacho-Poyato, E.; López-Luque, R.; Pérez-Urrestarazu, L. Benchmarking and Multivariate Data Analysis Techniques for Improving the Efficiency of Irrigation Districts: An Application in Spain. Agric. Syst. 2008, 96, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández García, I.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P. Optimal operation of pressurized irrigation networks with several supply sources. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2855–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Calejo, M.J.; Lamaddalena, N.; Douieb, A.; Bounoua, R. Design and Performance Analysis of Low Pressure Irrigation Distribution Systems. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2003, 17, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calejo, M.J.; Lamaddalena, N.; Teixeira, J.L.; Pereira, L.S. Performance analysis of pressurized irrigation systems operating on-demand using flow-driven simulation models. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Blanco Pérez, M. Evaluation of Water and Energy Use in Pressurized Irrigation Networks in Southern Spain. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2011, 137, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzini, G.; de Wrachien, D. Performance Assessment of Sprinkler Irrigation Systems: A New Indicator for Spray Evaporation Losses. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoliadis, O.G. Environmental Indices In Irrigation Management. Environ. Manag. 2001, 28, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Improved Indicators of Water Use Performance and Productivity for Sustainable Water Conservation and Saving. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L.; Pérez-Sánchez, M.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Romero, L.; Pérez-Sánchez, M.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Improvement of Sustainability Indicators When Traditional Water Management Changes: A Case Study in Alicante (Spain). AIMS Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 502–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darouich, H.; Gonçalves, J.M.; Muga, A.; Pereira, L.S. Water Saving vs. Farm Economics in Cotton Surface Irrigation: An Application of Multicriteria Analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 115, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, D.; Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E. Chapter 1: FAO Crop-Water Productivity Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water; AquaCrop; Version 6.0-6.1: Reference Manual; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; 19p. [Google Scholar]
- Zoidou, M.; Tsakmakis, I.D.; Gikas, G.D.; Sylaios, G. Water Footprint for Cotton Irrigation Scenarios Utilizing CROPWAT and AquaCrop Models. Eur. Water 2017, 59, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- van Halsema, G.E.; Vincent, L. Efficiency and Productivity Terms for Water Management: A Matter of Contextual Relativism versus General Absolutism. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D. Water for Food Water for Life: A Comprehensive Assessment of Water Management in Agriculture; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Hao, X.; Du, T.; Tong, L.; Su, X.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Huo, Z.; Li, S.; Ding, R. Improving Agricultural Water Productivity to Ensure Food Security in China under Changing Environment: From Research to Practice. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, M.; Rijsberman, F.R.; Saleth, R.M. More Crop Per Drop—Revisiting a Research Paradigm: Results and Synthesis of IWMI’s Research 1996–2005. Water Intell. Online 2015, 6, 9781780402284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigas, H.; Morris, T.; Sandford, B.; Adeel, Z. The Global Water Crisis: Addressing an Urgent Security Issue; UNU-INWEH: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Green, S.R.; Kirkham, M.B.; Clothier, B.E. Root Uptake and Transpiration: From Measurements and Models to Sustainable Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Urrestarazu, L.; Smout, I.K.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Carrillo Cobo, M.T. Irrigation Distribution Networks’ Vulnerability to Climate Change. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 136, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Fu, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F. A Modeling Framework for the Dynamic Correlation between Agricultural Sustainability and the Water-Land Nexus under Uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.; Mieno, T.; Brozović, N. Satellite-Based Monitoring of Irrigation Water Use: Assessing Measurement Errors and Their Implications for Agricultural Water Management Policy. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR028378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uralovich, K.S.; Toshmamatovich, T.U.; Kubayevich, K.F.; Sapaev, I.B.; Saylaubaevna, S.S.; Beknazarova, Z.F.; Khurramov, A. A Primary Factor in Sustainable Development and Environmental Sustainability Is Environmental Education. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 21, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N. Prabhat Deep Learning and Process Understanding for Data-Driven Earth System Science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavasso-Rita, Y.L.; Papalexiou, S.M.; Li, Y.; Elshorbagy, A.; Li, Z.; Schuster-Wallace, C. Crop Models and Their Use in Assessing Crop Production and Food Security: A Review. Food Energy Secur. 2024, 13, e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauberger, B.; Jägermeyr, J.; Gornott, C. A Systematic Review of Local to Regional Yield Forecasting Approaches and Frequently Used Data Resources. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 120, 126153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Paola, A.; Valentini, R.; Santini, M. An Overview of Available Crop Growth and Yield Models for Studies and Assessments in Agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.W.; Antle, J.M.; Basso, B.; Boote, K.J.; Conant, R.T.; Foster, I.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Herrero, M.; Howitt, R.E.; Janssen, S.; et al. Brief History of Agricultural Systems Modeling. Agric. Syst. 2017, 155, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siad, S.M.; Iacobellis, V.; Zdruli, P.; Gioia, A.; Stavi, I.; Hoogenboom, G. A Review of Coupled Hydrologic and Crop Growth Models. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 224, 105746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Jimenez, J.; Vande Wouwer, A.; Quijano, N. Dynamic Modeling of Crop–Soil Systems to Design Monitoring and Automatic Irrigation Processes: A Review with Worked Examples. Water 2022, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narmilan, A.; Sugirtharan, M. Application of FAO-CROPWAT Modelling on Estimation of Irrigation Scheduling for Paddy Cultivation in Batticaloa District, Sri Lanka. Agric. Rev. 2020, 42, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.K.; Delgoda, D.K.; Ooi, S.K.; Dassanayake, K.B.; Liu, L.; Halgamuge, M.N.; Malano, H. Model Predictive Control for Real-Time Irrigation Scheduling. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements (No. 56); FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Xu, C.Y.; Chen, D.; Halldin, S.; Chen, Y.D. Sensitivity of the Penman–Monteith Reference Evapotranspiration to Key Climatic Variables in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Basin. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G.; Smith, M.; Raes, D. Crop Evapotranspiration Estimation with FAO56: Past and Future. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisekka, I.; DeJonge, K.C.; Ma, L.; Paz, J.; Douglas-Mankin, K. Crop Modeling Applications in Agricultural Water Management. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Walter, I.A.; Elliott, R.; Howell, T.A.; Itenfisu, D.; Jensen, M.E. The ASCE Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration Equation; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berti, A.; Tardivo, G.; Chiaudani, A.; Rech, F.; Borin, M. Assessing Reference Evapotranspiration by the Hargreaves Method in North-Eastern Italy. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 140, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Asce, F.; Allen, R.G. History and Evaluation of Hargreaves Evapotranspiration Equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farg, E.; Arafat, S.M.; Abd El-Wahed, M.S.; El-Gindy, A.M. Estimation of Evapotranspiration ETc and Crop Coefficient Kc of Wheat, in South Nile Delta of Egypt Using Integrated FAO-56 Approach and Remote Sensing Data. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S. Estimating Crop Coefficients from Fraction of Ground Cover and Height. Irrig. Sci. 2009, 28, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cob, A. Necesidades Hídricas En Cultivos Hortícolas. Rev. Hortic. 2004, 177, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Mateos, L.; González-Dugo, M.P.; Testi, L.; Villalobos, F.J. Monitoring Evapotranspiration of Irrigated Crops Using Crop Coefficients Derived from Time Series of Satellite Images. I. Method Validation. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brower, C.; Heibloem, M. Irrigation Water Management Training Manual No. 3: Irrigation Water Management: Irrigation Water Needs. FAO, Inter-national Support Program for Irrigation Water Management. In Land and Water Development Division; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Dastane, N.G. Effective Rainfall in Irrigated Agriculture. In Bulletins FAO d’Irrigation et de Drainage (FAO)-Estudios FAO; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- DeJonge, K.C.; Thorp, K.R. Implementing Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration and Dual Crop Coefficient Approach in the DSSAT Cropping System Model. Trans. ASABE 2017, 60, 1965–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, D.; Makowski, D.; Jones, J.W.; Brun, F. Working with Dynamic Crop Models: Methods, Tools and Examples for Agriculture and Environment, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzotsi, K.A.; Basso, B.; Jones, J.W. Development, Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis of the Simple SALUS Crop Model in DSSAT. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 260, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO CropWat | Land & Water | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations | Land & Water | Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/land-water/databases-and-software/cropwat/en/ (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Jones, J.W.; Hoogenboom, G.; Porter, C.H.; Boote, K.J.; Batchelor, W.D.; Hunt, L.A.; Wilkens, P.W.; Singh, U.; Gijsman, A.J.; Ritchie, J.T. The DSSAT Cropping System Model. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 18, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöckle, C.O.; Kemanian, A.R.; Nelson, R.L.; Adam, J.C.; Sommer, R.; Carlson, B. CropSyst Model Evolution: From Field to Regional to Global Scales and from Research to Decision Support Systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, L.; Martin, G.; Ballot, R.; Benoit, M.; Bergez, J.E.; Bockstaller, C.; Cerf, M.; Deytieux, V.; Hossard, L.; Jeuffroy, M.H.; et al. Key Research Challenges to Supporting Farm Transitions to Agroecology in Advanced Economies. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Turner, L.; Harrison, M.T.; Monjardino, M.; deVoil, P.; Rodriguez, D. Application, Adoption and Opportunities for Improving Decision Support Systems in Irrigated Agriculture: A Review. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 257, 107161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratiadou, I.; Wezel, A.; Kamilia, K.; Marchetti, A.; Paracchini, M.L.; Bàrberi, P. The Socio-Economic Performance of Agroecology. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 44, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antle, J.M.; Basso, B.; Conant, R.T.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Jones, J.W.; Herrero, M.; Howitt, R.E.; Keating, B.A.; Munoz-Carpena, R.; Rosenzweig, C.; et al. Towards a New Generation of Agricultural System Data, Models and Knowledge Products: Design and Improvement. Agric. Syst. 2017, 155, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.B.; Karagiannis, E.; Manzoor, M.; Ziogas, V. From Stress to Success: Harnessing Technological Advancements to Overcome Climate Change Impacts in Citriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2023, 42, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, Z.; Fathian, F.; Eslamian, S. Climate Change Impact on Agriculture and Irrigation Network. In Climate Change Management; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Martínez, J.F.; Beltran, V.; Martínez, N.L. Decision Support Systems for Agriculture 4.0: Survey and Challenges. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 170, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari Variani, H.; Afshar, A.; Vahabzadeh, M.; Molajou, A. A Review on Food Subsystem Simulation Models for The Water-Food-Energy: Development Perspective. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 95197–95214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clément, R. Calcul Des Débits Dans Les Réseaux d’irrigation Fonctionnant à La Demande. La Houille Blanche 1966, 52, 553–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Calvo, I.; Roldán, J.; López-Luque, R.; Gutiérrez-Estrada, J.C. Water Delivery System Planning Considering Irrigation Simultaneity. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Camacho Poyato, E.; López Luque, R. Model to Forecast Maximum Flows in On-Demand Irrigation Distribution Networks. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat, J.; Poch, R.; Colomer, M.A.; Mora, F. Analysis of Clément’s First Formula for Irrigation Distribution Networks. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2004, 130, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikrishnan, V.; Lafferty, D.C.; Wong, T.E.; Lamontagne, J.R.; Quinn, J.D.; Sharma, S.; Molla, N.J.; Herman, J.D.; Sriver, R.L.; Morris, J.F.; et al. Uncertainty Analysis in Multi-Sector Systems: Considerations for Risk Analysis, Projection, and Planning for Complex Systems. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2021EF002644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangirala, A.K. Principles of System Identification: Theory and Practice; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 1315222507. [Google Scholar]
- D’Urso, G. Simulation and Management of On-Demand Irrigation Systems: A Combined Agrohydrological and Remote Sensing Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Minacapilli, M.; Iovino, M.; D’Urso, G. A Distributed Agro-Hydrological Model for Irrigation Water Demand Assessment. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minacapilli, M.; Iovino, M.; D’Urso, G. Crop And Irrigation Water Management Using High Resolution Remote Sensing And Agrohydrological Models. AIP Conf. Proc. 2006, 852, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, M.; Cao, X. Fuzzy Composite Risk Assessment of Water-Energy-Food-Carbon Nexus in the Dispark Pumped Irrigation System. J. Hydrol. 2023, 624, 129879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, N.; Rezaei-Moghaddam, K.; Hayati, D. Analyzing Iranian Farmers’ Behavioral Intention towards Acceptance of Drip Irrigation Using Extended Technology Acceptance Model. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, M.M.; Mirchi, A.; Bavani, A.R.M.; Goharian, E.; Madani, K. System Dynamics Simulation of Regional Water Supply and Demand Using a Food-Energy-Water Nexus Approach: Application to Qazvin Plain, Iran. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados García, A. Criterios Para el Dimensionamiento de Redes de Riego Robustas Frente a Cambios en la Alternativa de Cultivos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid (UPM), Madrid, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Clément, R. Le Calcul Des Débits Dans Les Canalisations d’irrigation [The Calculation of Flows in Irrigation Pipes]. Association Amicale des Ingenieurs du Genie Rural, journees d’ etudes sur l’irrigation, 1955. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- de Boissezon, J.; Haït, J.-R. Calcul Des Débits Dans Les Réseaux d’irrigation. La Houille Blanche 1965, 51, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavropoulos, T.I. Development of a New Demand Formula for Determination of the Peak Discharges in Irrigation Networks Operating On-Demand. Irrig. Dren. 1997, 44, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mavropoulos, T.I.; Lotidi, P.A. Validity of the Theory of Probability in On-Demand Irrigation Networks. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.A.; Planells, P.; Ortega, J.F.; Tarjuelo, J. New Methodology to Evaluate Flow Rates in On-Demand Irrigation Networks. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, J.; Latorre, J.; Gamazo, P. Alternative Method to the Clément’s First Demand Formula for Estimating the Design Flow Rate in On-Demand Pressurized Irrigation Systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Carrero, L.M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; Amparo López-Jiménez, P. Comparison between Clément’s First Formula and Other Statistical Distributions in A Real Irrigation Network. Irrig. Drain. 2018, 67, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; Ramos, H.M.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Modeling Irrigation Networks for the Quantification of Potential Energy Recovering: A Case Study. Water 2016, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadra, R.; Lamaddalena, N.; Inoubli, N. Optimization of on Demand Pressurized Irrigation Networks and On-Farm Constraints. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2013, 19, 942–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labye, Y. Design and Optimization of Irrigation Distribution Networks, 44th ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1988; ISBN 9251026661. [Google Scholar]
- Lamaddalena, N.; Sagardoy, J.A. Performance Analysis of On-Demand Pressurized Irrigation Systems; FAO: Rome, Italy; CIHEAM-IAMB: Rome, Italy, 2000; ISBN 92-5-104437-6. [Google Scholar]
- Calejo, M.J.; Teixeira, J.L.; Pereira, L.S.; Lamaddalena, N. Modelling the Irrigation Demand Hydrograph in a Pressurized System. In Proceedings of the EFITA/WCCA 2005, Vila Real, Portugal, 25–28 July 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Khadra, R.; Lamaddalena, N. A Simulation Model to Generate the Demand Hydrographs in Large-Scale Irrigation Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 93, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, D.; Lamaddalena, N.; Neale, C.M.U.; Merkley, G.P.; Palmisano, N.; Passarella, G. Simulation of Peak-Demand Hydrographs in Pressurized Irrigation Delivery Systems Using a Deterministic-Stochastic Combined Model. Part I: Model Development. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouial, A.; Lamaddalena, N.; Díaz, J.A.R. Generating Hydrants’ Configurations for Efficient Analysis and Management of Pressurized Irrigation Distribution Systems. Water 2020, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, A.P. Computational Intelligence: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-03561-0. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, D.; Mackworth, A.; Goebel, R. Computational Intelligence; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Palit, A.K.; Popović, D. Computational Intelligence in Time Series Forecasting: Theory and Engineering Applications; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Krupakar, H.; Jayakumar, A. A Review of Intelligent Practices for Irrigation Prediction. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.02893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce Cruz, P. Inteligencia Artificial Con Aplicaciones a La Ingeniería; Marcombo: Barcelona, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pulido-Calvo, I.; Gutiérrez-Estrada, J.C. Improved Irrigation Water Demand Forecasting Using a Soft-Computing Hybrid Model. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 102, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Calvo, I.; Roldán, J.; López-Luque, R.; Gutiérrez-Estrada, J.C. Demand Forecasting for Irrigation Water Distribution Systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J. Fuzzy Logic and Fuzzy Set Theory: Overview of Mathematical Preliminaries; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.H.; Tilt, K. Application of Fuzzy Logic in an Irrigation Control System. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT’96), Shanghai, China, 2–6 December 1996; pp. 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalewicz, Z. Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, C.; Oger, B.; Taylor, J.A.; Scholasch, T.; Metay, A.; Tisseyre, B. A Review of the Issues, Methods and Perspectives for Yield Estimation, Prediction and Forecasting in Viticulture. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 130, 126339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido-Calvo, I.; Montesinos, P.; Roldán, J.; Ruiz-Navarro, F. Linear Regressions and Neural Approaches to Water Demand Forecasting in Irrigation Districts with Telemetry Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 97, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lei, X.; Guo, X.; You, J.; Wang, H. Forecast of Irrigation Water Demand Considering Multiple Factors. IAHS-AISH Proc. Rep. 2015, 368, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- González Perea, R.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A. Irrigation Demand Forecasting Using Artificial Neuro-Genetic Networks. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 5551–5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Perea, R.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A. Prediction of Applied Irrigation Depths at Farm Level Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Perea, R.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Montesinos, P.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A. Prediction of Irrigation Event Occurrence at Farm Level Using Optimal Decision Trees. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 157, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.S.; Ramos, H.M. Sustainable Application of Renewable Sources in Water Pumping Systems: Optimized Energy System Configuration. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Sanchez, M.; Lopez-Jimenez, P.A.; Sanchez-Romero, F.J. ¿Cuál es la mejor consigna para operar con bombas trabajando como turbinas? In Proceedings of the EN VI Jornadas de Ingeniería del Agua (JIA 2019), Toledo, Spain, 22–25 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Urrestarazu, L.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A.; Camacho Poyato, E.; Lopez Luque, R. Quality of Service in Irrigation Distribution Networks: Case of Palos de La Frontera Irrigation District (Spain). J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Lamaddalena, N.; Fratino, U. Assessing Pressure Changes in an On-Demand Water Distribution System on Drip Irrigation Performance—Case Study in Italy. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 136, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, M.A.; Riquelme, A.J.; Jodar-Abellan, A.; Melgarejo, J. Water and Energy Demand Management in Pressurized Irrigation Networks. Water 2020, 12, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.J.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Ramos, H.M. PATs Selection towards Sustainability in Irrigation Networks: Simulated Annealing as a Water Management Tool. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, J.R.; Luque, R.L.; Cobo, M.C.; Montesinos, P.; Poyato, E.C. Exploring energy saving scenarios for on-demand pressurised irrigation networks. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 104, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; del Teso, R.; Gómez, E.; Estruch-Juan, E.; Soriano, J. Quick Energy Assessment of Irrigation Water Transport Systems. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 188, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; Cabrera, E.; Cobacho, R.; Soriano, J. Towards an Energy Labelling of Pressurized Water Networks. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamouli, P.; Dercas, N.; Baltas, E. Performance Analysis of On-Demand Pressurized Irrigation Networks—Case Study in Greece. Water Util. J. 2017, 16, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Karimov, A.; Molden, D.; Khamzina, T.; Platonov, A.; Ivanov, Y. A Water Accounting Procedure to Determine the Water Savings Potential of the Fergana Valley. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 108, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Morillo, J.; McNabola, A.; Camacho, E.; Montesinos, P.; Rodríguez Díaz, J.A. Hydro-Power Energy Recovery in Pressurized Irrigation Networks: A Case Study of an Irrigation District in the South of Spain. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 204, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhau, S.P.; Moharil, R.M.; Adhau, P.G. Mini-Hydro Power Generation on Existing Irrigation Projects: Case Study of Indian Sites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4785–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.A.; Carrión, P.A.; Planells, P.; Ortega, J.F.; Tarjuelo, J.M. Measurement and Improvement of the Energy Efficiency at Pumping Stations. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 98, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Smairan, M. Application of Photovoltaic Array for Pumping Water as an Alternative to Diesel Engines in Jordan Badia, Tall Hassan Station: Case Study. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4500–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, E.; Gómez, E.; Cabrera, E.; Soriano, J.; Espert, V. Energy Assessment of Pressurized Water Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 04014095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

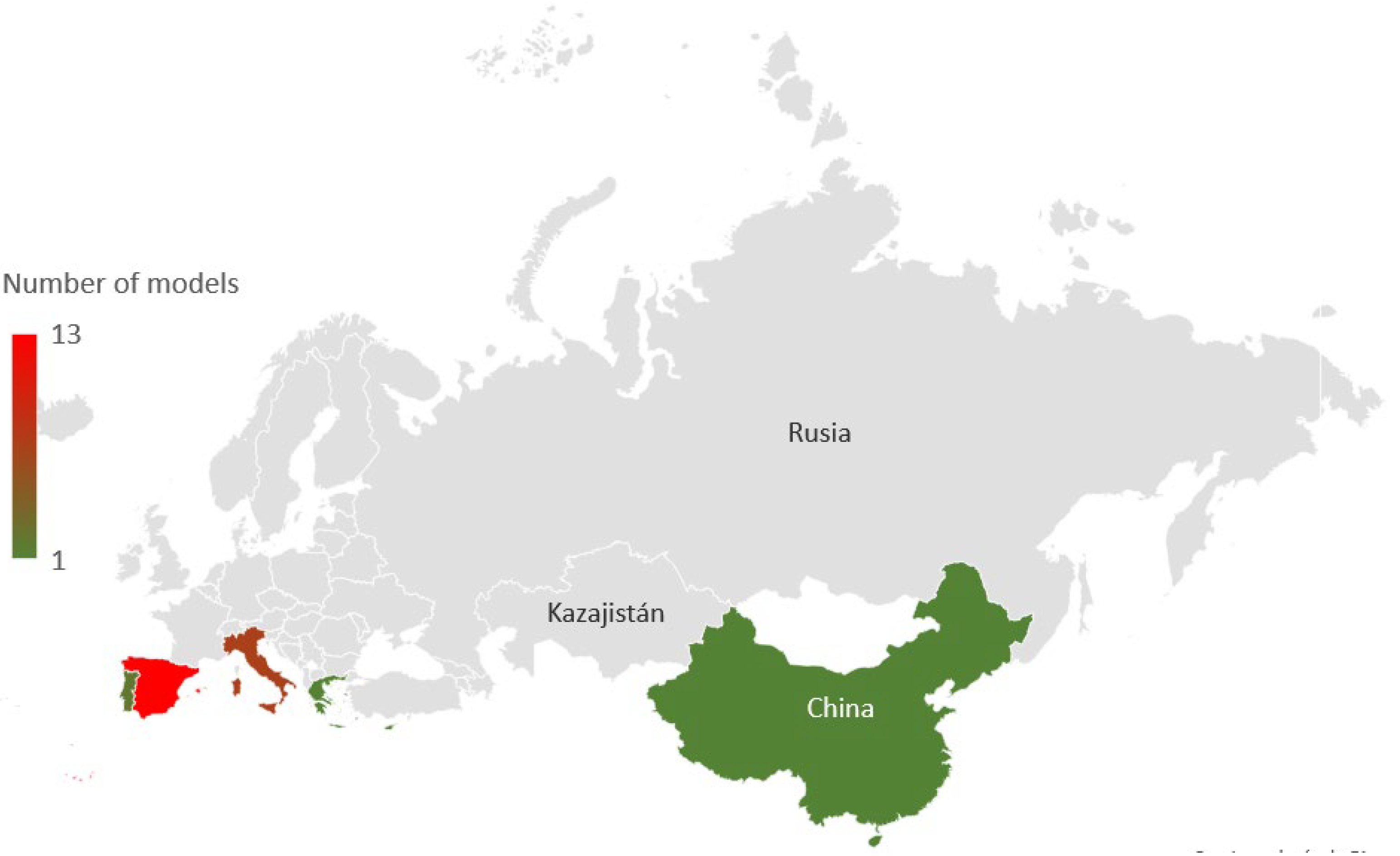


| No. | Reference | Country | Average Flow (L/s) | Average Leakage (L/s) | Annual Energy Consumed (MWh) | Annual Carbon Emission (TnCO2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [162] | Portugal | 17.36 | 3.47 | 139.09 | 257 |
| 2 | [163] | Spain | 31.17 | 6.23 | 2949.01 | 2.98 |
| 3 | [138] | Spain | 29.34 | 5.87 | 2776.28 | 2.81 |
| 4 | [164] | Spain | 4012 | 802.40 | 379,567.30 | 383.97 |
| 5 | [165] | Italy | 1200 | 240.00 | 113,529.60 | 114.85 |
| 6 | [166] | Spain | 17.81 | 3.56 | 1685.21 | 13 |
| 7 | [167] | Spain | 10 | 2.00 | 946.08 | 0.96 |
| 8 | [168] | Spain | 479.8 | 95.96 | 45,392.92 | 1140.2 |
| 9 | [168] | Spain | 1428 | 285.60 | 135,100.22 | 136.67 |
| 10 | [169] | Spain | 221.80 | 6.76 | 20,984.58 | 21.23 |
| 11 | [169] | Spain | 0.036 | 0.01 | 1245.95 | 1.26 |
| 12 | [169] | Peru | 250 | 50.00 | 23,652.00 | 23.93 |
| 13 | [170] | Spain | 76.27 | 2.32 | 7215.78 | 7.3 |
| 14 | [171] | Greece | 774 | 154.80 | 73,226.59 | 74.08 |
| 15 | [172] | Uzbekistan | 619.61 | 123.92 | 58,620.00 | 59.29 |
| 16 | [173] | Spain | 4800 | 960.00 | 454,118.40 | 459.39 |
| 17 | [174] | India | 6.3 | 1.26 | 596.03 | 0.6 |
| 18 | [175] | Spain | 120 | 24.00 | 11,352.96 | 11.48 |
| 19 | [176] | Jordan | 520.8 | 104.16 | 49,271.85 | 49.84 |
| 20 | [177] | Italy | 215.04 | 43.01 | 20,345.10 | 20.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Espinal, M.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M.; Sánchez-Romero, F.-J.; López-Jiménez, P.A. Irrigation Distribution Network Design Parameters and Their Influence on Sustainability Management. Water 2024, 16, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081131
Garcia-Espinal MA, Pérez-Sánchez M, Sánchez-Romero F-J, López-Jiménez PA. Irrigation Distribution Network Design Parameters and Their Influence on Sustainability Management. Water. 2024; 16(8):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081131
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Espinal, Melvin Alfonso, Modesto Pérez-Sánchez, Francisco-Javier Sánchez-Romero, and P. Amparo López-Jiménez. 2024. "Irrigation Distribution Network Design Parameters and Their Influence on Sustainability Management" Water 16, no. 8: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081131
APA StyleGarcia-Espinal, M. A., Pérez-Sánchez, M., Sánchez-Romero, F.-J., & López-Jiménez, P. A. (2024). Irrigation Distribution Network Design Parameters and Their Influence on Sustainability Management. Water, 16(8), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081131