The Construction of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event Knowledge Graph Considering Evolutionary Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Methodology
3.1. Analysis of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Events
3.2. Knowledge Representation Model for Urban Rainstorm Events
- Event Layer
- 2.
- Object–State Layer
- 3.
- Feature Layer
- 4.
- Relationship Layer
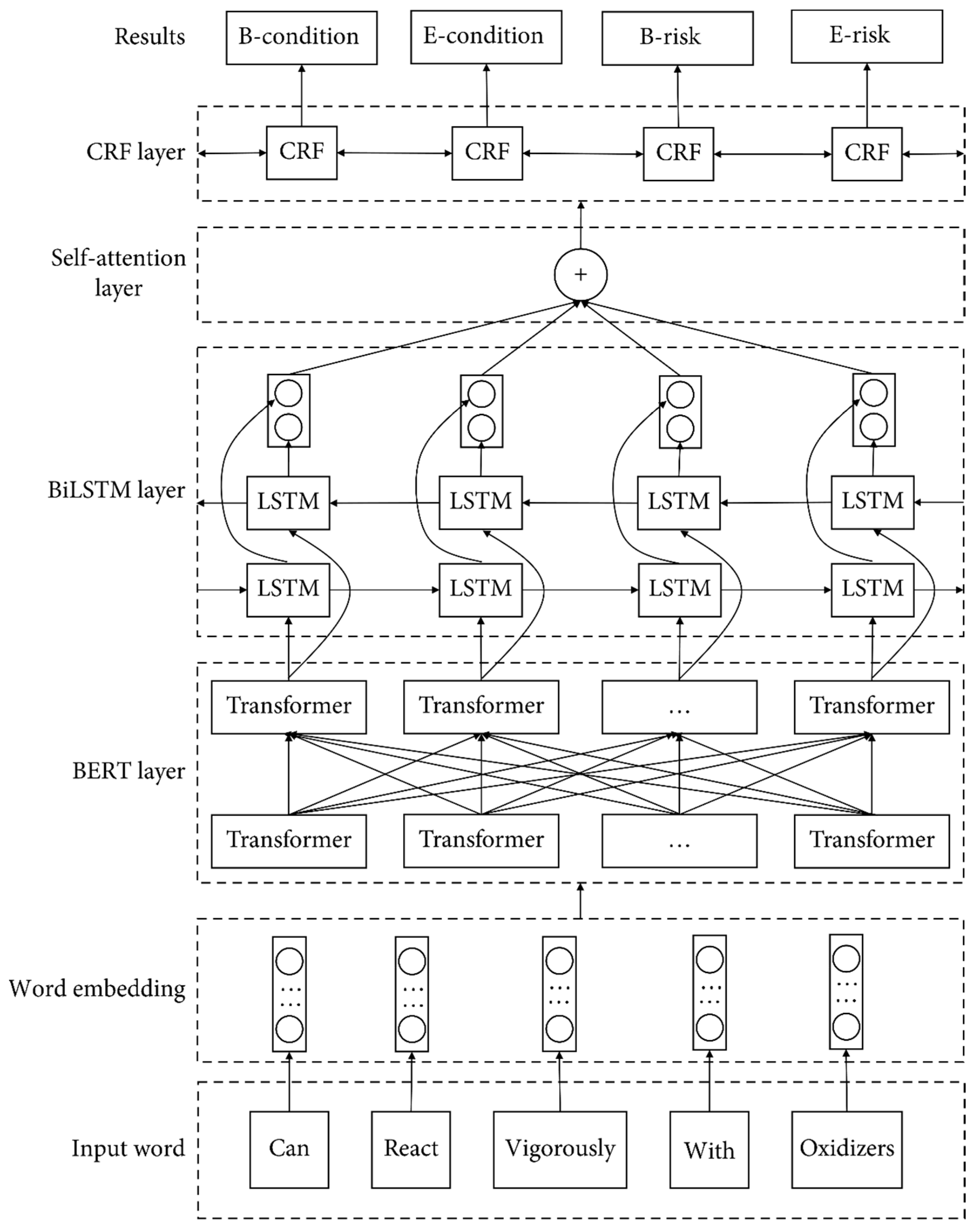
3.3. Knowledge Extraction Model
4. Results
4.1. Knowledge Extraction and Fusion for Urban Rainstorm Disasters
4.2. Experimental Evaluation and Analysis
- (1)
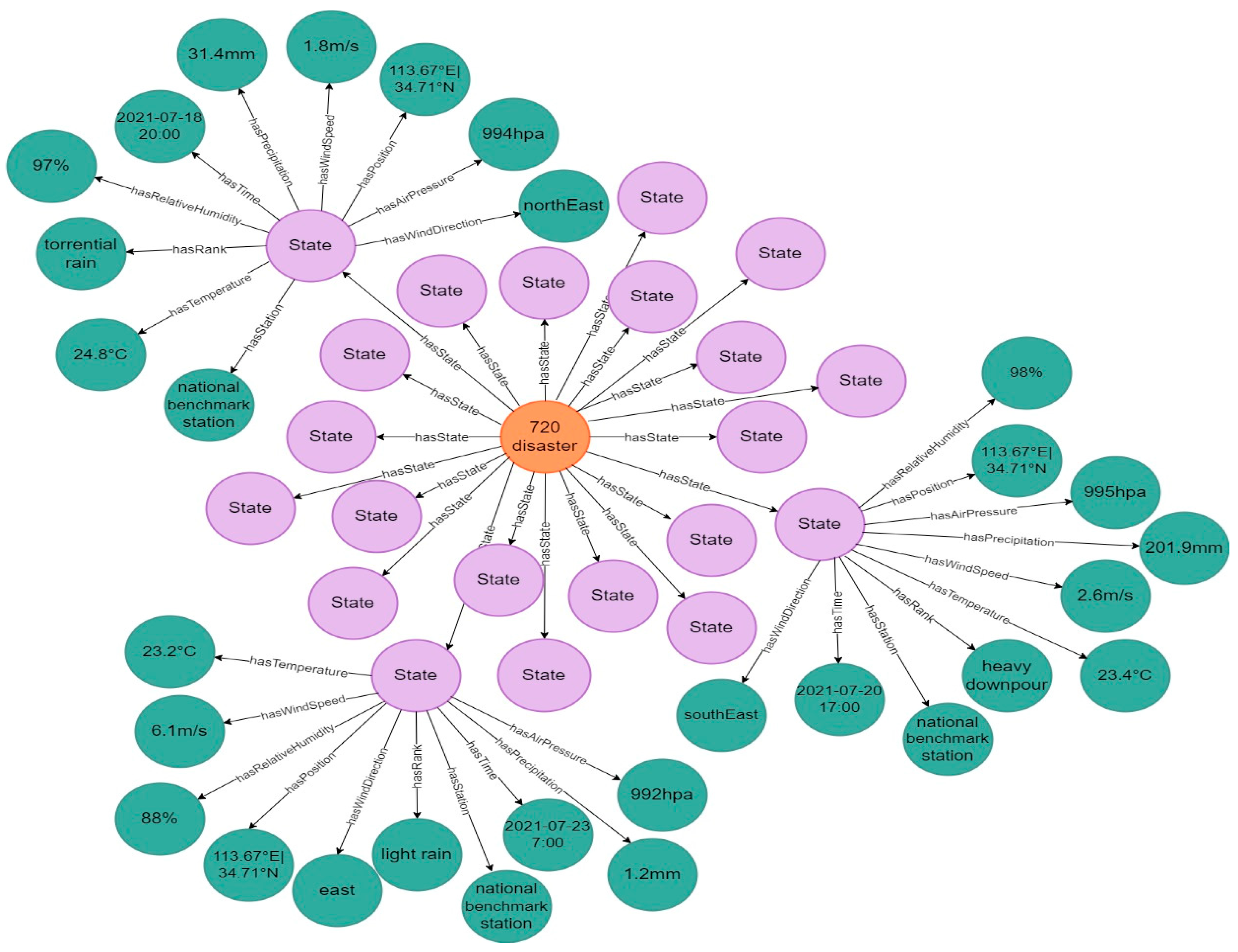
- Representation of the Evolution Process of an Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event
- (2)
- Retrieval of Disaster Condition
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ziegler, A.D. Water management: Reduce urban flood vulnerability. Nature 2012, 481, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, M.J. Urban flood impact assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Vasiliades, L.; Dalezios, N.R. Flood producing mechanisms identification in southern British Columbia. J. Hydrol. 2000, 227, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Tuoliewubieke, D.; Yang, L. Analysis of the water vapour transport and accumulation mechanism during the “7.31” extreme rainstorm event in the southeastern Hami area, China. Meteorl. Appl. 2020, 27, e1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Dynamic assessment of the impact of flood disaster on economy and population under extreme rainstorm events. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3924. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, W.L.; Balogun, A.L.; Olayide, O.E.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Ayal, D.Y.; Munoz, P.D.C.; Nagy, G.J.; Bynoe, P.; Oguge, O.; Toamukum, N.Y.; et al. Assessing the impacts of climate change in cities and their adaptive capacity: Towards transformative approaches to climate change adaptation and poverty reduction in urban areas in a set of developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 1175–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cheng, T.; Hong, S.; Wang, L. Review on applications of remote sensing in urban flood modeling. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, Z.J.; Rong, L.L. A scenario modelling method for regional cascading disaster risk to support emergency decision making. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 77, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, Y.C.; Bai, R.Z.; Chen, A. Regional disaster risk evaluation of China based on the universal risk model. Nat. Hazards 2017, 89, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.J. Theory and practice on disaster system research in a fourth time. J. Nat. Disasters 2005, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Willner, S.N.; Otto, C.; Levermann, A. Global economic response to river floods. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Z.F.; Wu, Y.Y. A review of urban flood risk assessment based on the framework of hazard-exposure-vulnerability. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.; Ashmore, P.; Darby, S.E. Beyond just floodwater. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.A.; Cheng, J.; Yin, C.L.; Li, Q.; Chen, R.S.; Fang, J.Y. The extraordinary Zhengzhou flood of 7/20, 2021: How extreme weather and human response compounding to the disaster. Cities 2023, 134, 104168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, R.; Krywkow, J.; van der Veen, A. Flood risk perceptions and spatial multi-criteria analysis: An exploratory research for hazard mitigation. Nat. Hazards 2008, 46, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Z.; Duan, C.F.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, Z.X. Disaster loss calculation method of urban flood bimodal data fusion based on remote sensing and text. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, F.; Li, N. Urban rainstorm waterlogging disaster simulation of Guiyang based on 3S technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics, Shanghai, China, 24–26 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Cui, L. Research on knowledge graph model about rainstorm disaster based on simple event model. J. Catastrophol. 2021, 36, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich, H.; Loon, A.F.; Kai, S.; Ward, P.J.; Mazzoleni, M.; Sairam, N.; Abeshu, G.W.; Agafonova, S.; Aghakouchak, A.; Aksoy, H. The challenge of unprecedented floods and droughts in risk management. Nature 2022, 608, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songchon, C.; Wright, G.; Beevers, L. Quality assessment of crowdsourced social media data for urban flood management. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 90, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Liang, Q.; James, P.; Lin, W. Assessing the utility of social media as a data source for flood risk management using a real-time modelling framework. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2015, 10, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tang, C.Q.; Liang, Q.H.; Wang, Z.N.; Wu, X.L.; Zhao, S. Rapid urban flood risk mapping for data-scarce environments using social sensing and region-stable deep neural network. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Wu, H.; Liang, G.; Cardenas-Tristan, A.; Li, D. A big data-driven dynamic estimation model of relief supplies demand in urban flood disaster. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, G.; Sun, X. A Big-Data-Based Urban Flood Defense Decision Support System. Int. J. Smart Home 2015, 9, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimiano, P.; Bielefeld, U. Knowledge graph refinement: A survey of approaches and evaluation methods. Semant. Web 2017, 8, 489–508. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, C.; Sequeda, J.F. Knowledge Graphs. Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ye, P. Geoscience Knowledge Graph (GeoKG): Development, construction and challenges. Trans. GIS 2022, 26, 2480–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Du, M.; Lu, Y.; Xue, H. Geographic Knowledge Graph (GeoKG): A Formalized Geographic Knowledge Representation. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2019, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.S.; Hou, Z.Q.; Zheng, Z.M.; Shen, S.Z.; Cheng, Q.M.; Feng, Z.Q.; Wang, X.B.; Lv, H.R.; et al. Geoscience knowledge graph in the big data era. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Wu, M.G.; Lv, G.N. Spatio-temporal features based geographical knowledge graph construction (in Chinese). Sci. Sin. Inform. 2020, 50, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffart, J.; Suchanek, F.M.; Berberich, K.; Weikum, G. YAGO2: A spatially and temporally enhanced knowledge base from Wikipedia. Artif. Intell. 2013, 194, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, S.; Bizer, C.; Kobilarov, G.; Lehmann, J.; Cyganiak, R.; Ives, Z. DBpedia: A nucleus for a web of open data. In Proceedings of the The Semantic Web ISWC 2007, ASWC 2007, Busan, Republic of Korea, 11–15 November 2007; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Aberer, K., Choi, K.-S., Noy, N., Allemang, D., Lee, K.-I., Nixon, L., Golbeck, J., Mika, P., Maynard, D., Mizoguchi, R., et al., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4825, pp. 722–735. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, G.A.; Saha, A.; Kumar, V.; Bhambhani, M.; Sankaranarayanan, K.; Chakrabarti, S. Neural program induction for KBQA without gold programs or query annotations. In Proceedings of the 28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 10–16 August 2019; AAAI Press: Macao, China, 2019; pp. 4890–4896. [Google Scholar]
- Nakashole, N.; Theobald, M.; Weikum, G. Scalable knowledge harvesting with high precision and high recall. In Proceedings of the Fourth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, Hong Kong, China, 9–12 February 2011; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, A.; Betteridge, J.; Kisiel, B.; Settles, B.; Hruschka, E.R., Jr.; Mitchell, T.M. Toward an architecture for never-ending language learning. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, AAAI 2010, Atlanta, GA, USA, 11–15 July 2010; pp. 1306–1313. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.D.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Liang, D. Scientific big data and Digital Earth. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 5066–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.G.; Ma, C.; Wang, C.B. A new structure for representing and tracking version information in a deep time knowledge graph. Comput. Geosci. 2020, 145, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Sheng, Y.H.; Min, X.Q.; Cao, Y.W. Using Geographic Ontologies and Geo-characterization to Represent Geographic Scenarios. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2019, 8, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Xie, M.H.; Zhang, J.B.; Xie, J.; Xia, S.H. A knowledge representation model based on the geographic spatiotemporal process. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.C.; You, X.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Wen, H. Interactive Visual Analysis of COVID-19 Epidemic Situation Using Geographic Knowledge Graph. Geomat. Inform. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 836–845. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Qiu, Q.J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, K.; Tao, L. Understanding geological reports based on knowledge graphs using a deep learning approach. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 168, 105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.; Seker, R.; Bayrak, C.; Ramaswamy, S.; Connelly, J.B. Ontology for disaster mitigation and planning. In Proceedings of the 2007 Summer Computer Simulation Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–19 July 2007; Volume 26, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Wu, X.L. A novel knowledge representation method based on ontology for natural disaster decision-making. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Computer Science and Automation Engineering (CSAE), Zhangjiajie, China, 25–27 May 2012; pp. 241–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, P.; Zhang, X.Y.; Shi, G.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, Z.W.; Tang, W. TKRM: A Formal Knowledge Representation Method for Typhoon Events. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.S.; Zhong, S.B.; Yao, S.M.; Wang, C.L.; Huang, Q.Y. Ontology-based representation of meteorological disaster system and its application in emergency management Illustration with a simulation case study of comprehensive risk assessment. Kybern. Int. J. Syst. Cyber 2016, 45, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D. Research on Decision Support System based on Agricultural Risk Management Ontology. Int. J. Digit. Content Tech. App. 2011, 5, 290–297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.B.; Wang, C.L.; Yao, G.N.; Huang, Q.Y. Emergency Decision of Meteorological Disasters: A Geo-Ontology Based Perspective. In Proceedings of the CMSAM 2016: 2016 International Conference on Computational Modeling, Simulation and Applied Mathematics, Bangkok, Thailand, 24–25 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Nyerges, T.L.; Nie, G. Modeling and representation for earthquake emergency response knowledge: Perspective for working with geo-ontology. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Tan, J. The construction of personalized virtual landslide disaster environments based on knowledge graphs and deep neural networks. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2020, 13, 1637–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, B.; Tiainen, E.; Von Brasch, T.E.; Janssen, P.; Kotzinos, D.; Čeh, M.; Rijsdijk, M.; Folmer, E.; Van Damme, M.D.; Zhral, M. Conciliating perspectives from mapping agencies and web of data on successful European SDIs: Toward a European geographic knowledge graph. ISPRS Int. J. Geoinf. 2020, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, D.; Ma, K.; Tao, L.F.; Tan, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Jiang, B.D. Knowledge graph for identifying geological disasters by integrating computer vision with ontology. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 34, 1418–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, G.; Su, L.; Cao, Y.; Mi, L. Construction of power projects knowledge graph based on graph database Neo4j. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS), Hangzhou, China, 5–7 October 2020; pp. 3612–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; Weng, W.; Yang, W. Named Entity Recognition of Hazardous Chemical Risk Information Based on Multihead Self-Attention Mechanism and BERT. Rev. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 8300672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.C.; Botzen, W.J.; Clarke, K.C.; Cutter, S.L.; Hall, J.W.; Merz, B.; Michel-Kerjan, E.; Mysiak, J.; Surminski, S.; Kunreuther, H. Integrating human behaviour dynamics into flood disaster risk assessment. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. Environmental Hazards: Assessing Risk and Reducing Disaster; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alamdar, F.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A. An evaluation of integrating multisourced sensors for disaster management. Int. J. Digit. Earth. 2015, 8, 727–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Feng, R.; et al. A survey of machine learning and deep learning in remote sensing of geological environment: Challenges, advances, and opportunities. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 202, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


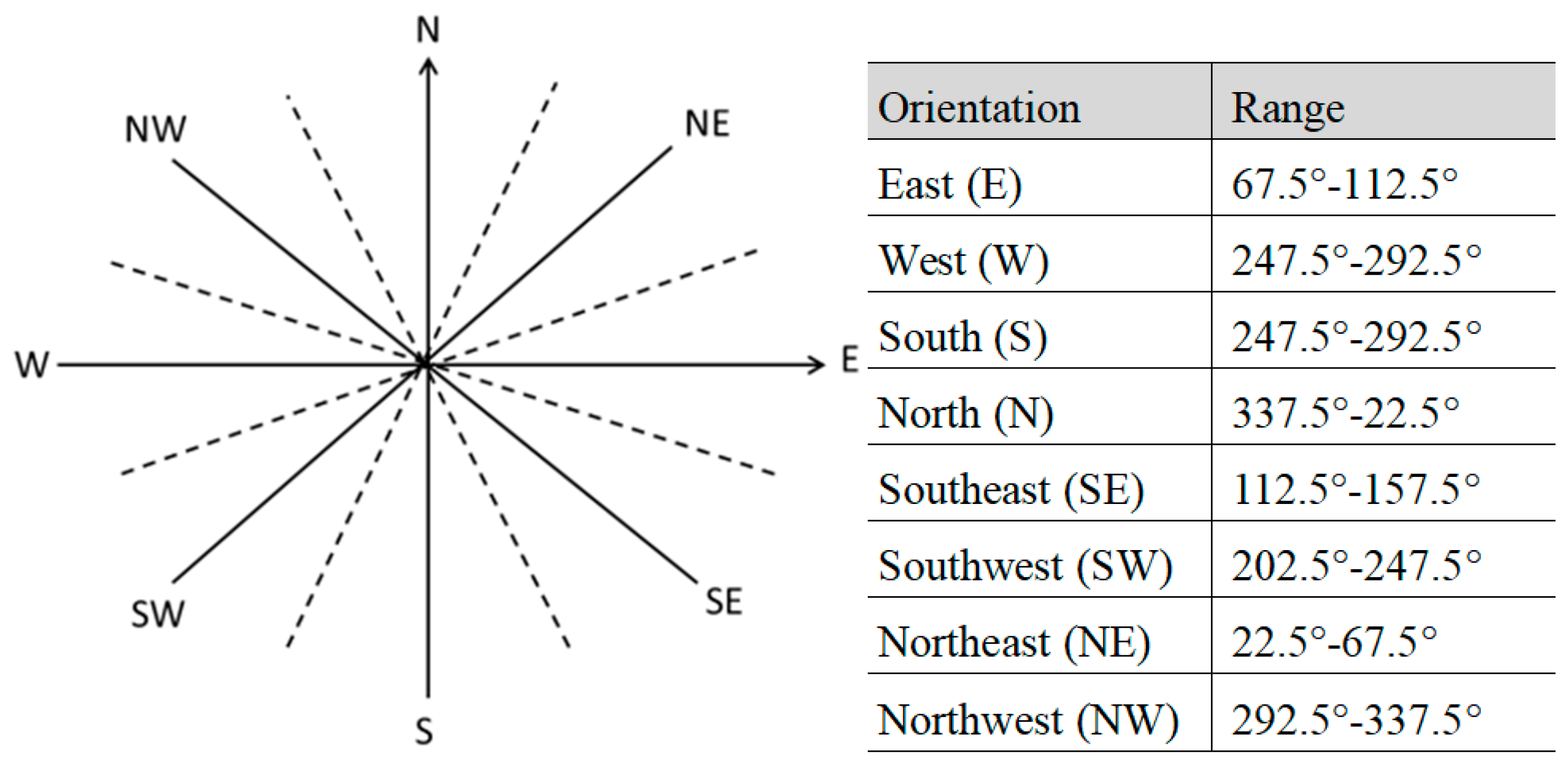

| Type | Sub-Type | Third Level |
|---|---|---|
| Disaster-pregnant environment | Landform | Mountain |
| Flatland | ||
| Hill | ||
| … | ||
| Atmosphere | Troposphere | |
| Hydrosphere | River | |
| Reservoir | ||
| Lake | ||
| … | ||
| Disaster-inducing factor | Primary factor | Rainstorm |
| Secondary factor | Gale | |
| Landslide | ||
| Debris flow | ||
| Flooding | ||
| Collapse | ||
| … | ||
| Disaster-bearing body | Human being | Individual |
| Crowd | ||
| Property | Building | |
| Infrastructure (electricity, communication, transportation, etc.) | ||
| Public service facility | ||
| Industrial facility | ||
| … | ||
| Resources and environment | Land resource | |
| Mineral resource | ||
| Water resource | ||
| Living resource | ||
| … |
| Model | Entity | Attribute | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (%) | R (%) | F1 (%) | P (%) | R (%) | F1 (%) | |
| CRF | 80.12 | 71.56 | 76.88 | 79.01 | 72.22 | 74.23 |
| BiLSTM | 81.17 | 75.81 | 78.03 | 80.52 | 75.08 | 77.11 |
| BiLSTM–CRF | 83.04 | 78.02 | 79.31 | 82.66 | 77.83 | 79.19 |
| BiLSTM–Attention–CRF | 85.24 | 80.37 | 83.17 | 84.28 | 80.01 | 82.33 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | F1 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BiLSTM | 76.65 | 70.38 | 73.53 |
| Attention–BiLSTM | 81.47 | 75.62 | 79.62 |
| BERT–BiLSTM–Attention–CRF | 85.73 | 80.29 | 83.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Xia, Y.; Shen, Z. The Construction of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event Knowledge Graph Considering Evolutionary Processes. Water 2024, 16, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070942
Zou Y, Huang Y, Wang Y, Zhou F, Xia Y, Shen Z. The Construction of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event Knowledge Graph Considering Evolutionary Processes. Water. 2024; 16(7):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070942
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Yalin, Yi Huang, Yifan Wang, Fangrong Zhou, Yongqi Xia, and Zhenhong Shen. 2024. "The Construction of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event Knowledge Graph Considering Evolutionary Processes" Water 16, no. 7: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070942
APA StyleZou, Y., Huang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, F., Xia, Y., & Shen, Z. (2024). The Construction of Urban Rainstorm Disaster Event Knowledge Graph Considering Evolutionary Processes. Water, 16(7), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16070942






