Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope
Abstract
1. Introduction
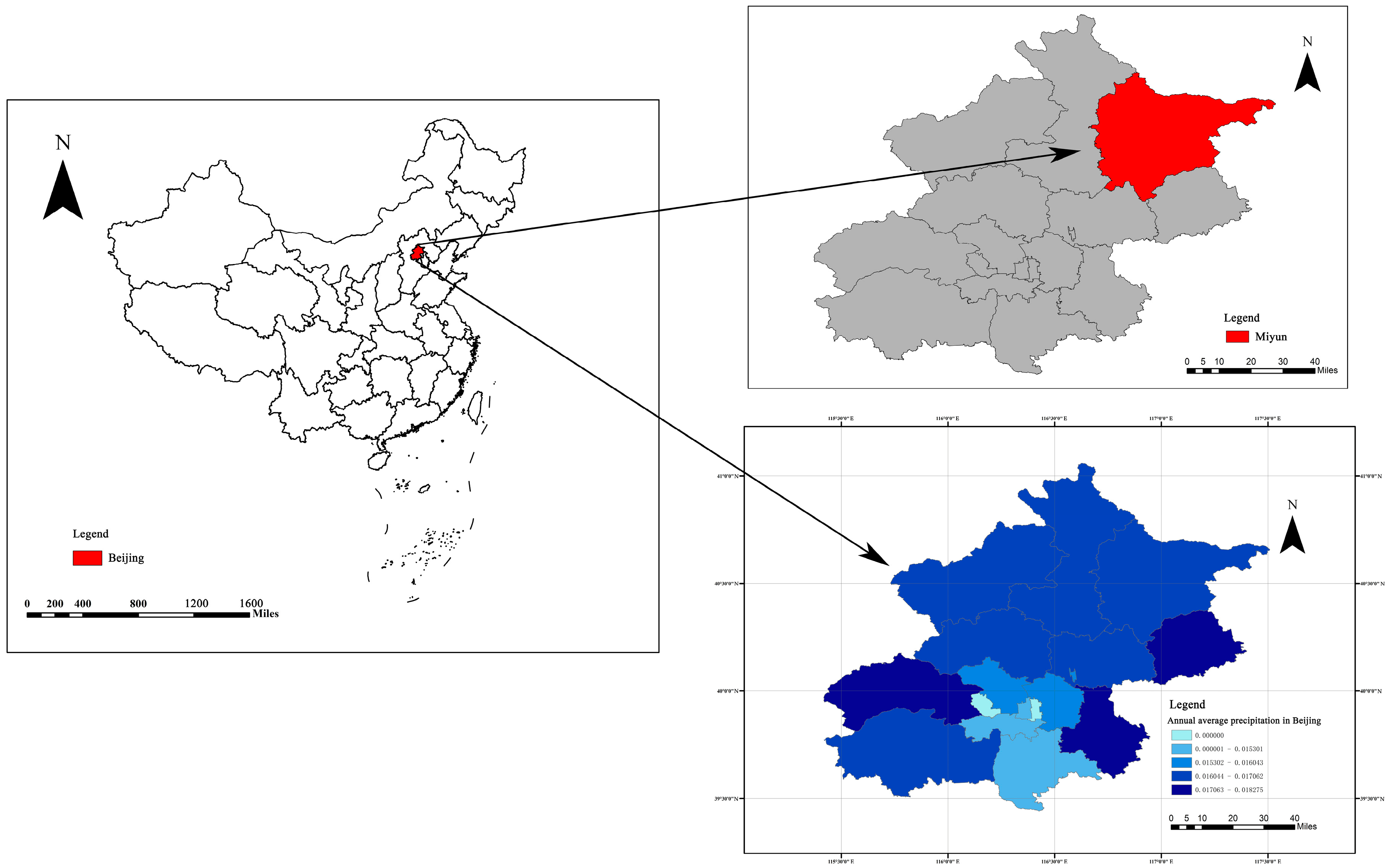
2. Materials and Methods
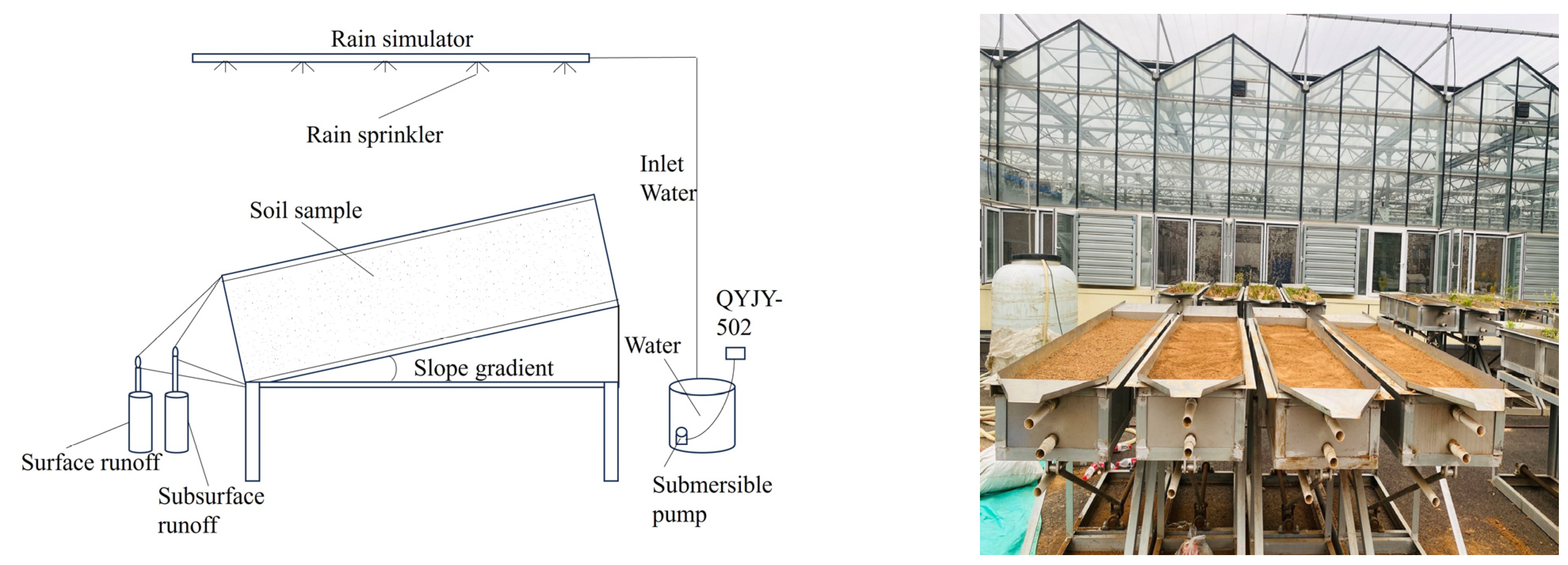
2.1. Test Equipment and Materials
2.2. Test Soil
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Data Acquisition and Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Influence of Rainfall Intensity and Slope on Surface Runoff
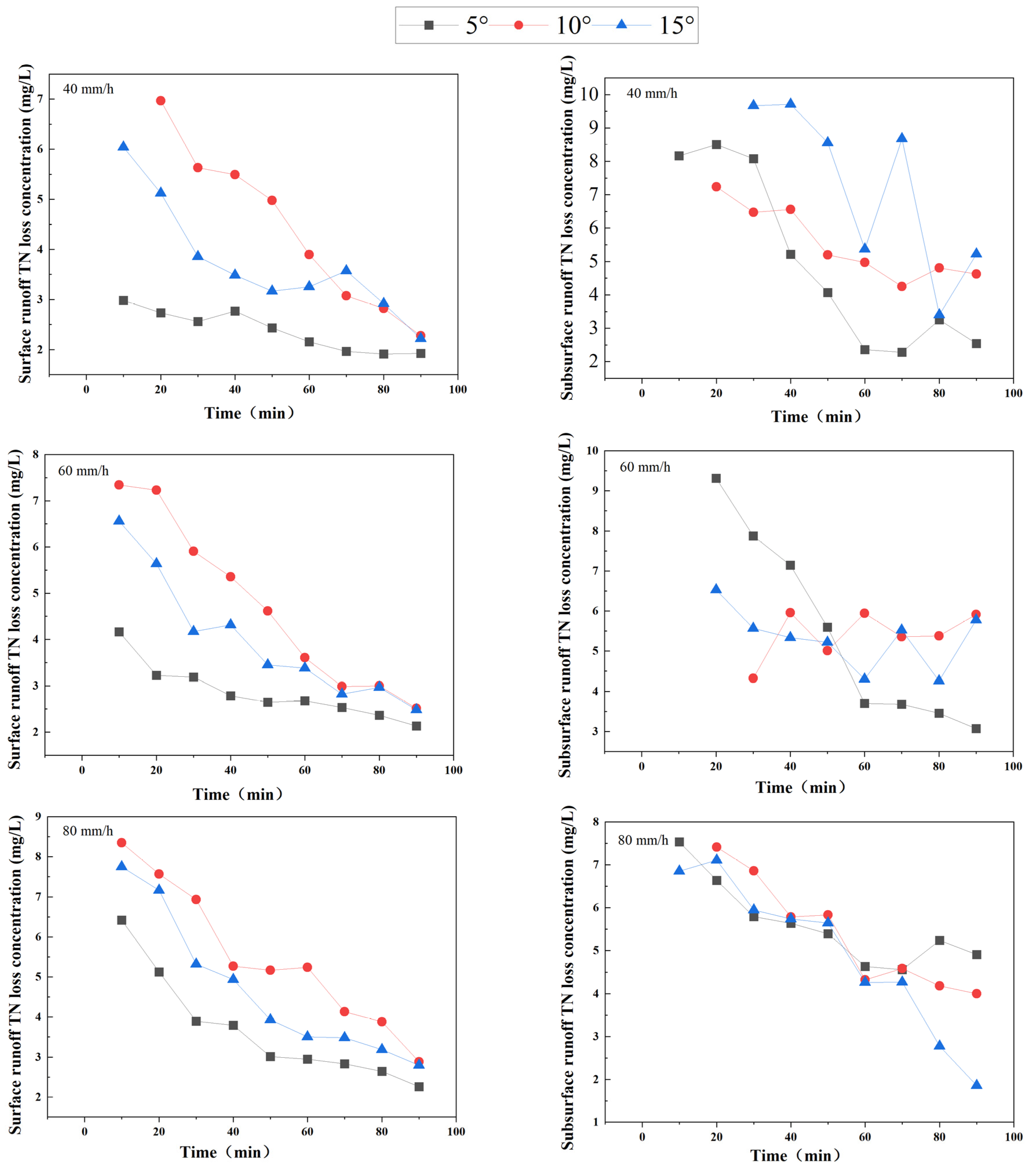
3.2. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on Nitrogen Loss on Slopes
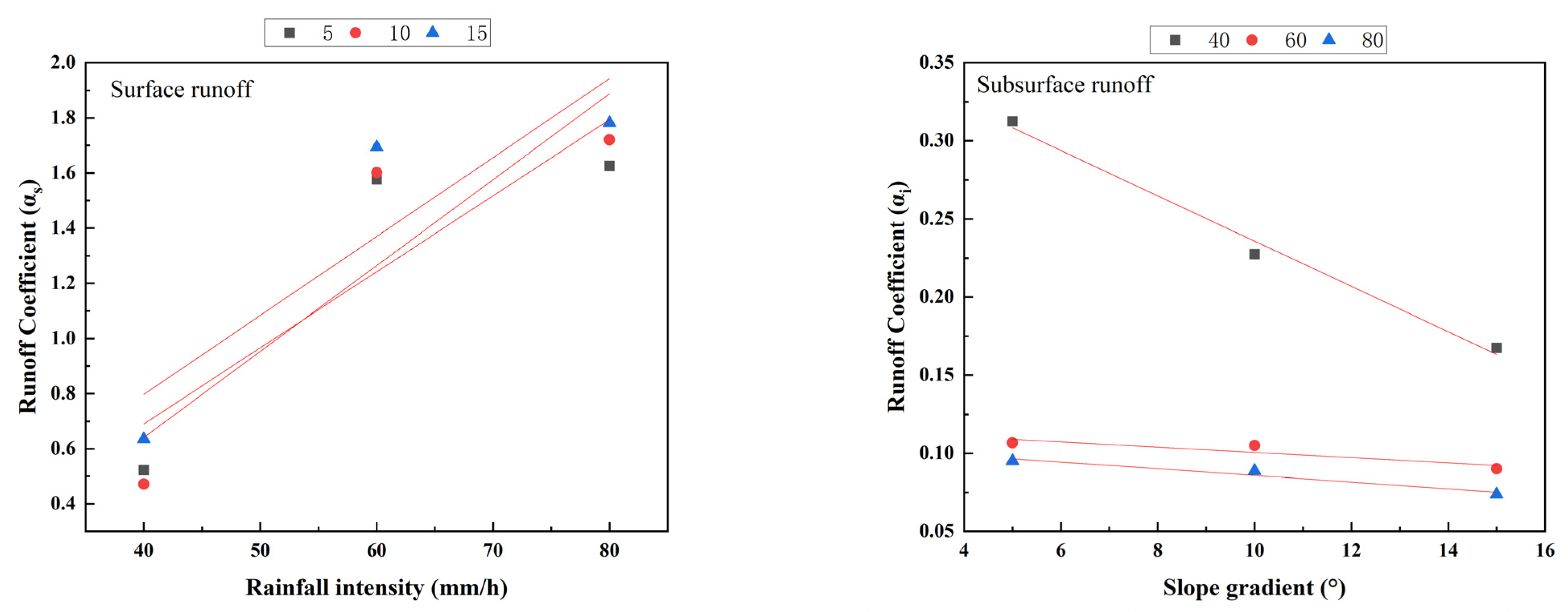
3.3. Runoff Coefficients of Surface Runoff and Subsurface Runoff
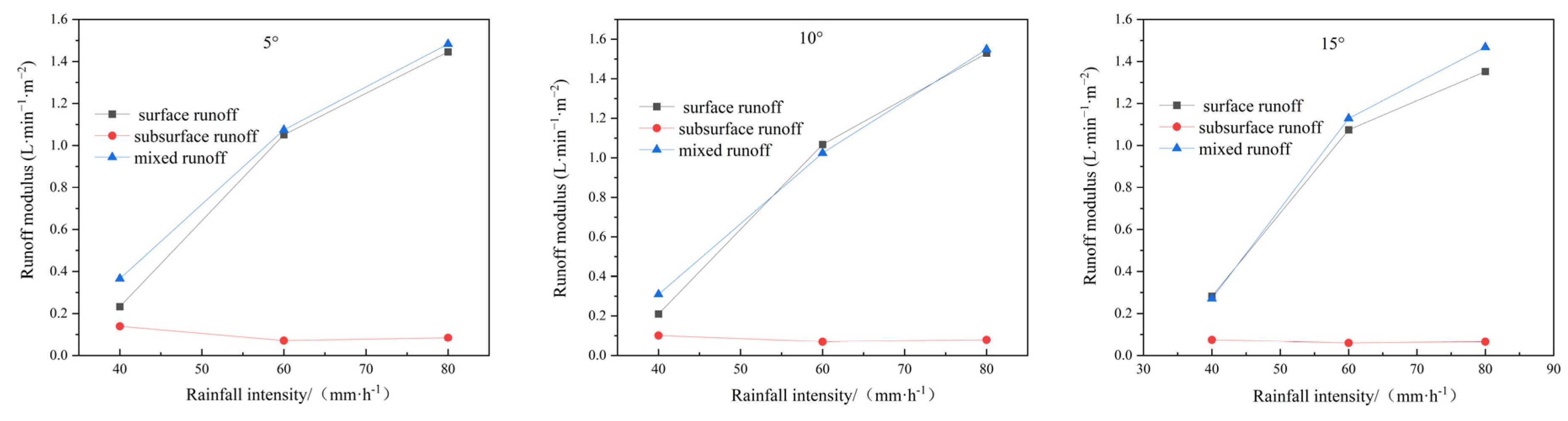
3.4. Slope Surface Runoff, Nitrogen Loss Distribution and Runoff Modulus
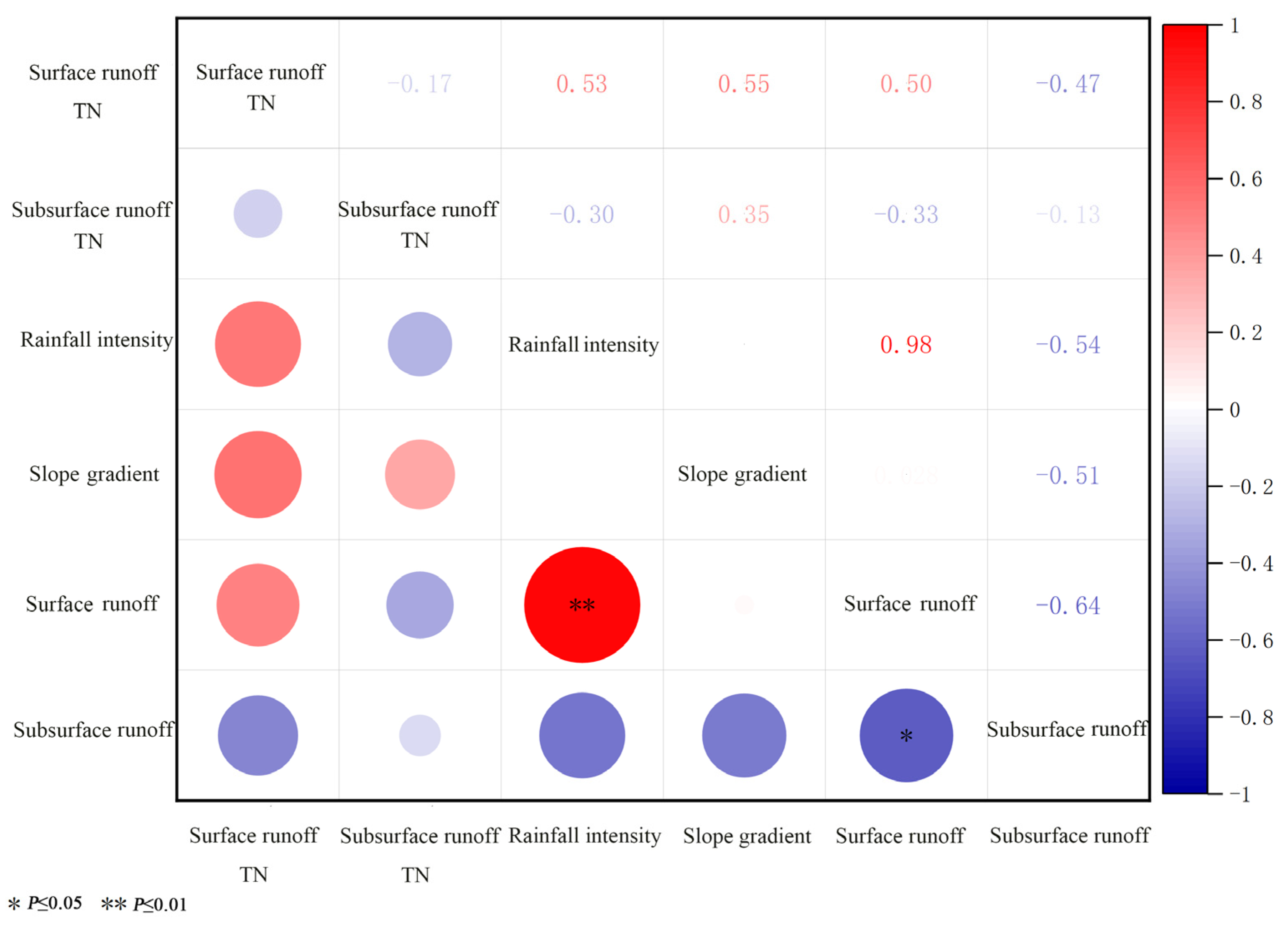
3.5. Factors Influencing Slope Surface Runoff and Nitrogen Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, Y.; Tang, D.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Meng, C.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, J. Influences of riparian landscape pattern on river phosphorus output in typical subtropical agroforestry mixed watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.F.; Gong, A.M.; Ning, D.W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, B. Characteristics of soil erosion and nutrient loss in Yunnan Province based on RUSLE model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.L.; Li, H.B. Influence of landscape pattern change on soil erosion in Han River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2248–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.H.; Sun, L.; Su, X.K.; Chen, L. Study on the coupling of landscape pattern and ecological process: Inheritance and innovation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 415–421. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; An, Z.; Suo, L.; Ding, J.; Li, S.; Wei, D.; Jin, L. Effects of the Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on Soil Erosion and Nitrogen Loss on the Sloping Fields of Miyun Reservoir. Plants 2023, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Lan, R.; Zhangzhong, L.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Yu, J. A Hybrid Approach for Soil Total Nitrogen Anomaly Detection Integrating Machine Learning and Spatial Statistics. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.X.; Gao, B.; Yan, X.Y.; Jiang, X.; Dun, C. Contribution of agricultural sources to water nitrogen pollution in the Taihu Lake Lake area: A case study of Yili River basin. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2015, 34, 2318–2326. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Wu, Y.; Sun, T.; Fei, K. Characteristics of runoff and sediment yield under different rainfall intensities and slope gradients in erosive weathered granite area. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.; Yang, J.; Zhan, M.; Dai, S.; Sheng, J. Experimental Study on the Influence of Slope and Rainfall Intensity on Slope Erosion and Sediment Production Process. Water Resour. Power 2015, 33, 101–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Gu, L.B.; Zhang, K.L. Effects of slope on abortion and sediment production on slope in northwest Guizhou. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 29, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. The erosion process of fine gullies on loess slopes. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.W. Improved interrill erosion prediction by considering the impact of the near-surface hydraulic gradient. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 203, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Shi, P.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, J. The synergistic effect of terraced fields and siltation dam slope and gully control measures on runoff and sediment production in the Loess Plateau. J. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Schulin, R. Erosion-induced losses of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus and heavy metals from agricultural soils of contrasting organic matter management. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.Z.; Fei, K.; Sun, T.Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Fan, X.J.; Ni, L. Characteristics of runoff processes and nitrogen loss via surface flow and interflow from weathered granite slopes of Southeast China. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1048–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ouyang, X.Q.; Shen, J.L.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.R.; Jiang, W.Q.; Wu, J.S. Nitrogen and phosphorus runoff losses were influenced by chemical fertilization but not by pesticide application in a double rice-cropping system in the Subtropical Hilly Region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Elliott, J.A.; Lobb, D.A.; Flaten, D.N.; Braul, L.; Wilson, H.F. Changes in runoff chemistry and soil fertility after multiple years of cattle winter bale feeding on annual cropland on the Canadian prairies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhang, L.P.; Deng, L.Z.; Fan, X.J. Simulation of slope and rainfall intensity effects of slope nitrogen loss. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Jin, Z.; Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Y. Simultaneous removal of phosphate and ammonium nitrogen from agricultural runoff by amending soil in lakeside zone of Karst area, Southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 289, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Xie, J.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; Jin, L. Effects of Different Hedgerow Patterns on the Soil Physicochemical Properties, Erodibility, and Fractal Characteristics of Slope Farmland in the Miyun Reservoir Area. Plants 2022, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S. Soil agrochemical analysis. China Agricultural Publishing. 2000.
- Villatoro, S.M.; Bissonnais, Y.L.; Moussa, R.; Rapidel, B. Temporal dynamics of runoff and soil loss on a plotscale under a coffee plantation on steep soil (Ultisol), Costa Rica. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Wu, J.; Shi, C.; Li, S.; Xie, J.; An, Z.; Suo, L.; Ding, J.; Wei, D.; et al. Laws Governing Nitrogen Loss and Its Numerical Simulation in the Sloping Farmland of the Miyun Reservoir. Plants 2023, 12, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Dai, Q.; Ding, G.; Li, C. Role of underground leakage in soil, water and nutrient loss from a rock-mantled slope in the Karst rocky desertification area. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.R.; Polebitski, A.S.; Penn, M.R.; Busch, D.L. Long-term Variation in Agricultural Edge-of-Field Phosphorus Transport during Snowmelt, Rain, and Mixed Runoff Events. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Yao, M.; Zhou, J.; Wu, K.; Hu, M.; Shen, H.; Chen, D. Estimation of nitrogen runoff loss from croplands in the Yangtze River Basin: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Ma, L.; Wainwright, J. Particle selectivity of sediment deposited over grass barriers and the effect of rainfall. Water Resour Res. 2016, 52, 7963–7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Chu, Y.; Shen, Y. Simulation of surface runoff and sediment yield under different land-use in a Taihang Mountains watershed, North China. J. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 153, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Peng, M.; Qiao, S.; Ma, X.Y. Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on runoff and sediment yield characteristics of bare loess soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; He, R.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, M.; Deng, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Identifying conservation priority zones and their driving factors regarding regional ecosystem services. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Gao, Y.; Green, S.M.; Dungait, J.A.J.; Peng, T.; Quine, T.A.; Xiong, B.; Wen, X.; He, N. Nitrogen loss from Karst area in China in recent 50 years: An in-situ simulated rainfall experiment’s assessment. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 10131–10142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Dai, Q.; Gan, Y.; Peng, X.; Yan, Y. The production processes and characteristics of nitrogen pollution in bare sloping farmland in a Karst region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 26900–26911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F. Research on Particles Detachment and Transport Processes of the Slope in Beijing Mountainous Area. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Cai, Q.G.; Sun, L.Y. Analysis of interaction effects of rainfall intensity, slope degree and slope length on rill erosion. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 9, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Lu, X.; Gu, S.; Guo, X. Improving nutrient and water use efficiencies using water-drip irrigation and fertilization technology in Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengren, O.; Kaixian, W.; Bozhi, W. Characteristics of Flow Hydraulics and Soil Erosion in Maize and Potato Intercropping Systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5097–5108. [Google Scholar]

| pH | Soil Organic Matter (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | Available Phosphorous (mg/kg) | Available Potassium (mg/kg) | Sand Content (%) | Silt Content (%) | Clay Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.33 | 9.97 | 0.448 | 4.55 | 45.9 | 75.12 | 16.5 | 8.38 |
| Types of Runoff | Rainfall Intensity (mm/h) | Slope Gradient (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 10 | 15 | ||
| 40 | 6.23 | 4.76 | 3 | |
| Surface Runoff | 60 | 3.83 | 1.75 | 0.97 |
| 80 | 1.96 | 1.12 | 0.24 | |
| 40 | 18.85 | 14.42 | 10.79 | |
| Subsurface Runoff | 60 | 13.33 | 9.14 | 7.55 |
| 80 | 10.92 | 8.65 | 4.21 | |
| 40 | 12.62 | 9.66 | 7.79 | |
| Surface Runoff - Subsurface Runoff | 60 | 9.5 | 7.39 | 6.58 |
| 80 | 8.96 | 7.53 | 3.97 | |
| Slope Gradient S/(°) | Surface Runoff (L) | Subsurface Runoff (L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mm/h | 60 mm/h | 80 mm/h | 40 mm/h | 60 mm/h | 80 mm/h | |
| 5 | 22.43 ± 0.32 Cc | 52.3 ± 0.82 Bc | 87.2 ± 0.82 Ac | 7.17 ± 0.7 Bb | 8.27 ± 0.61 Ab | 11.37 ± 0.7 Ac |
| 10 | 25.93 ± 0.61 Cb | 58.4 ± 0.85 Bb | 93.37 ± 0.85 Ab | 6.3 ± 0.66 Bab | 7.3 ± 0.8 Bab | 9.63 ± 0.61 Ab |
| 15 | 27.77 ± 0.35 Ca | 65.1 ± 0.7 Ba | 98.3 ± 0.79 Aa | 5.77 ± 0.55 Ba | 6.67 ± 0.75 Aa | 7.4 ± 0.75 Aa |
| Slope Gradient S/(°) | Surface Runoff TN Concentration (mg/L) | Subsurface Runoff TN Concentration (mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mm/h | 60 mm/h | 80 mm/h | 40 mm/h | 60 mm/h | 80 mm/h | |
| 5 | 22.41 ± 0.93 Cc | 25.14 ± 0.72 Bc | 32.76 ± 0.57 Ac | 22.23 ± 0.86 Cc | 43.44 ± 1.06 Ba | 50.29 ± 1.01 Aa |
| 10 | 35.16 ± 1.07 Ca | 43.35 ± 0.86 Ba | 50.05 ± 0.57 Aa | 36.31 ± 1.08 Ba | 37.46 ± 1.07 Bb | 42.81 ± 0.88 Ab |
| 15 | 33.06 ± 0.53 Cb | 36.01 ± 0.24 Bb | 42.63 ± 0.60 Ab | 32.45 ± 1.06 Bb | 42.33 ± 1.03 Aa | 43.41 ± 0.97 Ab |
| Types of Runoff | Simulate Conditions | Fitted Equation | Fitting Degree R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Runoff | Slope Gradient S/(°) | 5 | α5 = 0.02759I − 0.41382 | 0.7836 |
| 10 | α10 = 0.03119I − 0.60653 | 0.8204 | ||
| 15 | α15 = 0.02866I − 0.34951 | 0.8072 | ||
| Subsurface Runoff | Raionfall Intensity I/(mm/h) | 40 | α5 = −0.0145S + 0.38083 | 0.9902 |
| 60 | α10 = −0.00167S + 0.11722 | 0.8242 | ||
| 80 | α15 = −0.00213S + 0.10708 | 0.9465 | ||
| Rainfall Intensity/(mm/h) | 5° | 10° | 15° |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 62.57 | 67.5 | 79.13 |
| 60 | 93.66 | 93.85 | 94.95 |
| 80 | 94.16 | 95.09 | 95.53 |
| Rainfall Intensity/(mm/h) | 5° | 10° | 15° |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 67.49 | 55.67 | 60.09 |
| 60 | 63.01 | 51.83 | 54.30 |
| 80 | 60.46 | 51.14 | 51.38 |
| Factor | Surface Runoff | Subsurface Runoff | TN of Surface Runoff | TN of Subsurface Runoff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall Density | 99.6 | 52.8 | 30.2 | 21.4 |
| Slope Gradient | 0.1 | 26.9 | 66.8 | 37.5 |
| Rainfall Density × Slope Gradient | 0.3 | 20.3 | 3.0 | 41.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, N.; Wang, L.; Jin, L.; Wu, J.; Pang, M.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z.; et al. Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope. Water 2024, 16, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050786
Wang N, Wang L, Jin L, Wu J, Pang M, Wei D, Li Y, Wang J, Xu T, Yang Z, et al. Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope. Water. 2024; 16(5):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050786
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Na, Lei Wang, Liang Jin, Jiajun Wu, Min Pang, Dan Wei, Yan Li, Junqiang Wang, Ting Xu, Zhixin Yang, and et al. 2024. "Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope" Water 16, no. 5: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050786
APA StyleWang, N., Wang, L., Jin, L., Wu, J., Pang, M., Wei, D., Li, Y., Wang, J., Xu, T., Yang, Z., & Xie, J. (2024). Rainfall Runoff and Nitrogen Loss Characteristics on the Miyun Reservoir Slope. Water, 16(5), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050786







