Survival and Development Strategies of Cyanobacteria through Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Factors Affecting Akinete Germination and the Ranges of Tolerances
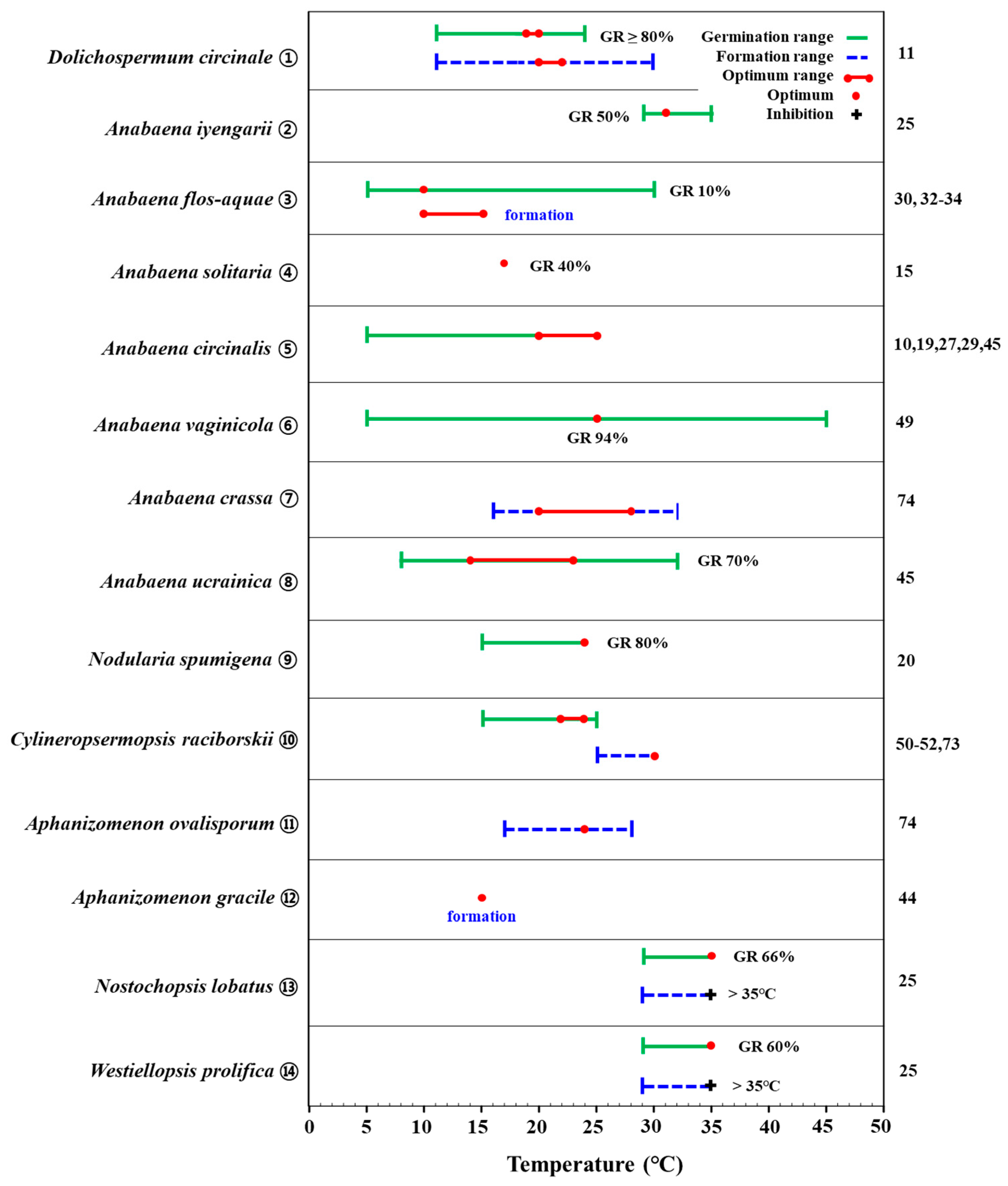
2.1. Temperature
2.2. Light
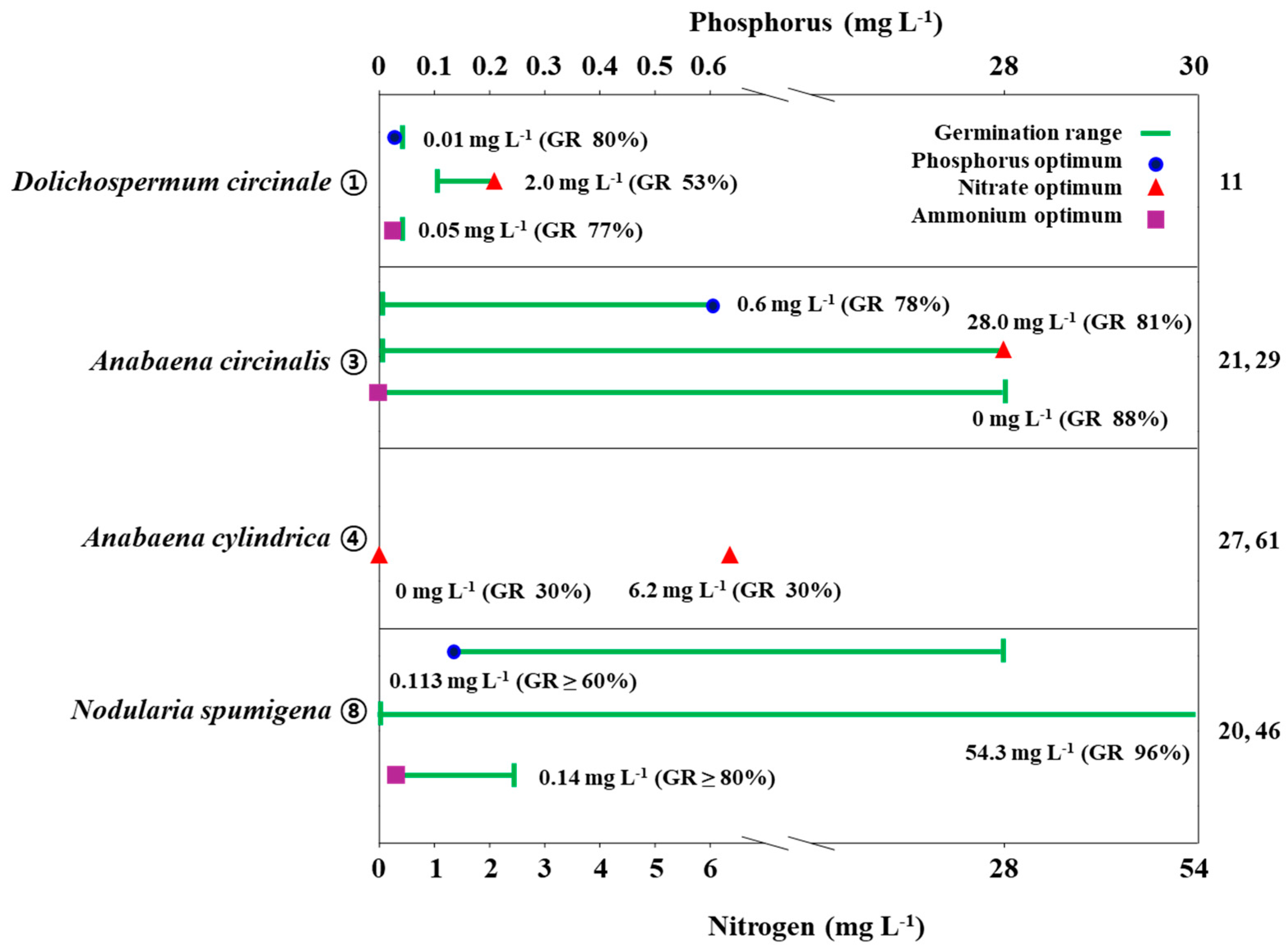
2.3. Nutrients
| No | Cyanobacteria Species | Effects of N and P on AKINETE | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| ① | Dolichospermum circinale | With nitrate: Germination rate (GR) > 80% in (-N or +N)+P condition (Little effect of nitrate) With ammonium: GR 91% in +N-P condition (Little effect of P) The highest akinete formation (420 akinetes/g) in +N+P (N=NH4-N) condition | [11] |
| ② | Anabaena iyengarii | GR 50% in +N+P (N=NO3-N); GR 20% in -N-P (N=NO3-N) Formation rate (FR) 6% in +N+P condition | [37] |
| ③ | Anabaena circinalis | GR 55% in +N+P; GR 50% in +N-P; GR 25% in -N+P; GR 10% in -N-P Akinete formation in P (0.06mg/L) addition; no formation without N | [21,29] |
| ④ | Anabaena cylindrica | No akinete formation in the absence of N | [61] |
| ⑤ | Anabaena vaginicola | GR 96% in NO3-N addition; GR 43% in P deprivation | [49] |
| ⑥ | Anabaena lemmermannii | Akinete formation in the absence of P | [43] |
| ⑦ | Anabaena crassa | No formation when depriving both N and P | [34] |
| ⑧ | Nodularia spumigena | High germination (>80%) under broad range of NO3-N (0–54.3 mg/L) | [20] |
| ⑨ | Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii | FR increased with increasing P conc. Maximum akinete formation (2310 akinetes/mL) in 70 μgP/L | [62] |
| ⑩ | Nostoc palusodum | Akinete formation in the absence of P | [63] |
| ⑪ | Nostochopsis lobatus | GR 54% in +N+P; GR 38% in -N+P; GR 35% in +N-P; GR 24% in -N-P FR 55% in +N+P | [37] |
| ⑫ | Westiellopsis prolifica | GR 58% in +N+P; GR 35% in -N+P; GR 26% in +N-P; GR 20% in -N-P FR 70% in +N+P | [37] |
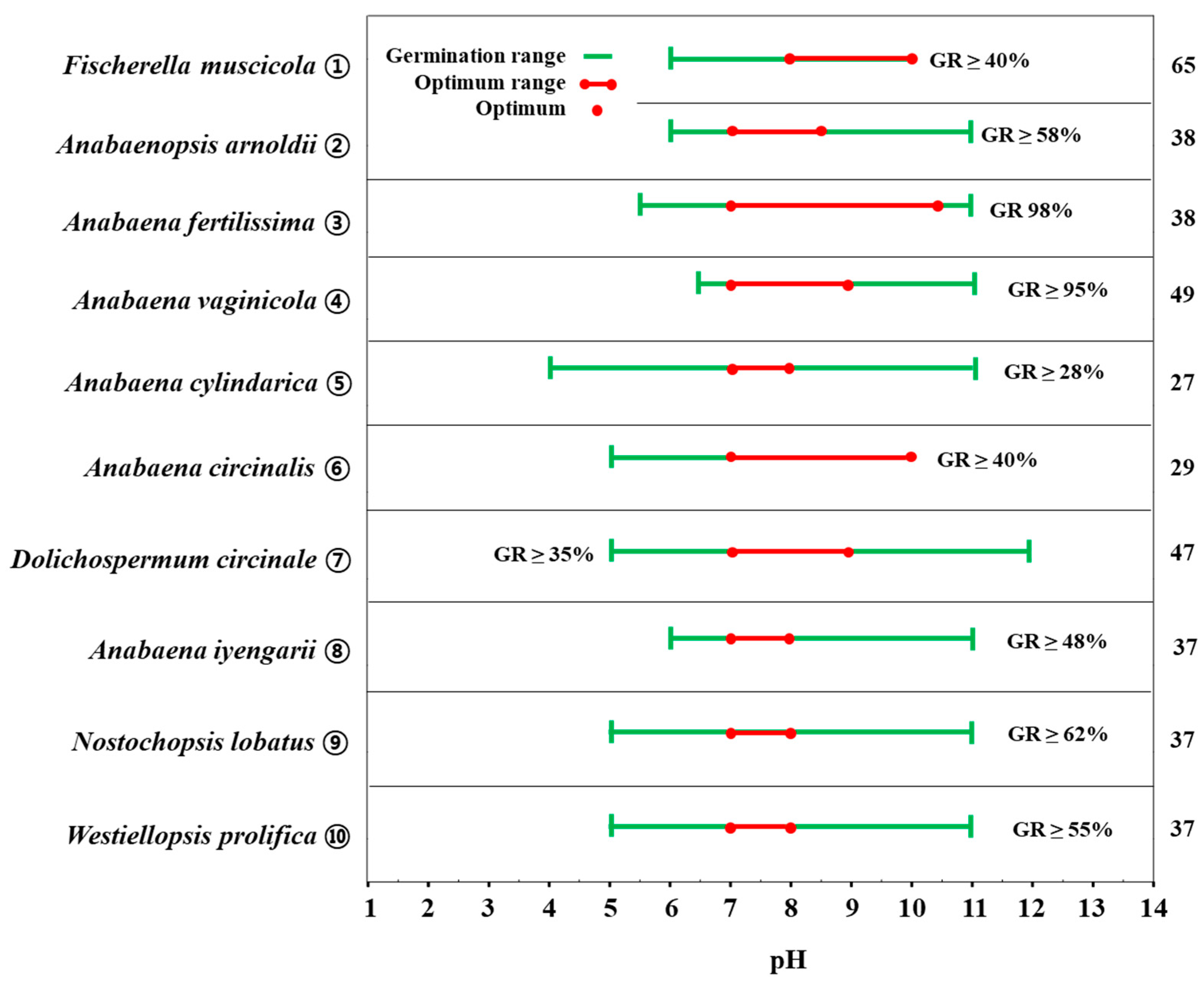
2.4. Hydrogen Ion (H+) Concentration
2.5. Dissolved Oxygen (DO), Salinity, and Sediment Disturbance (Mixing and Turnover)
3. Factors Affecting Akinete Formation and the Range of Tolerances
3.1. Temperature
3.2. Light
3.3. Nutrients
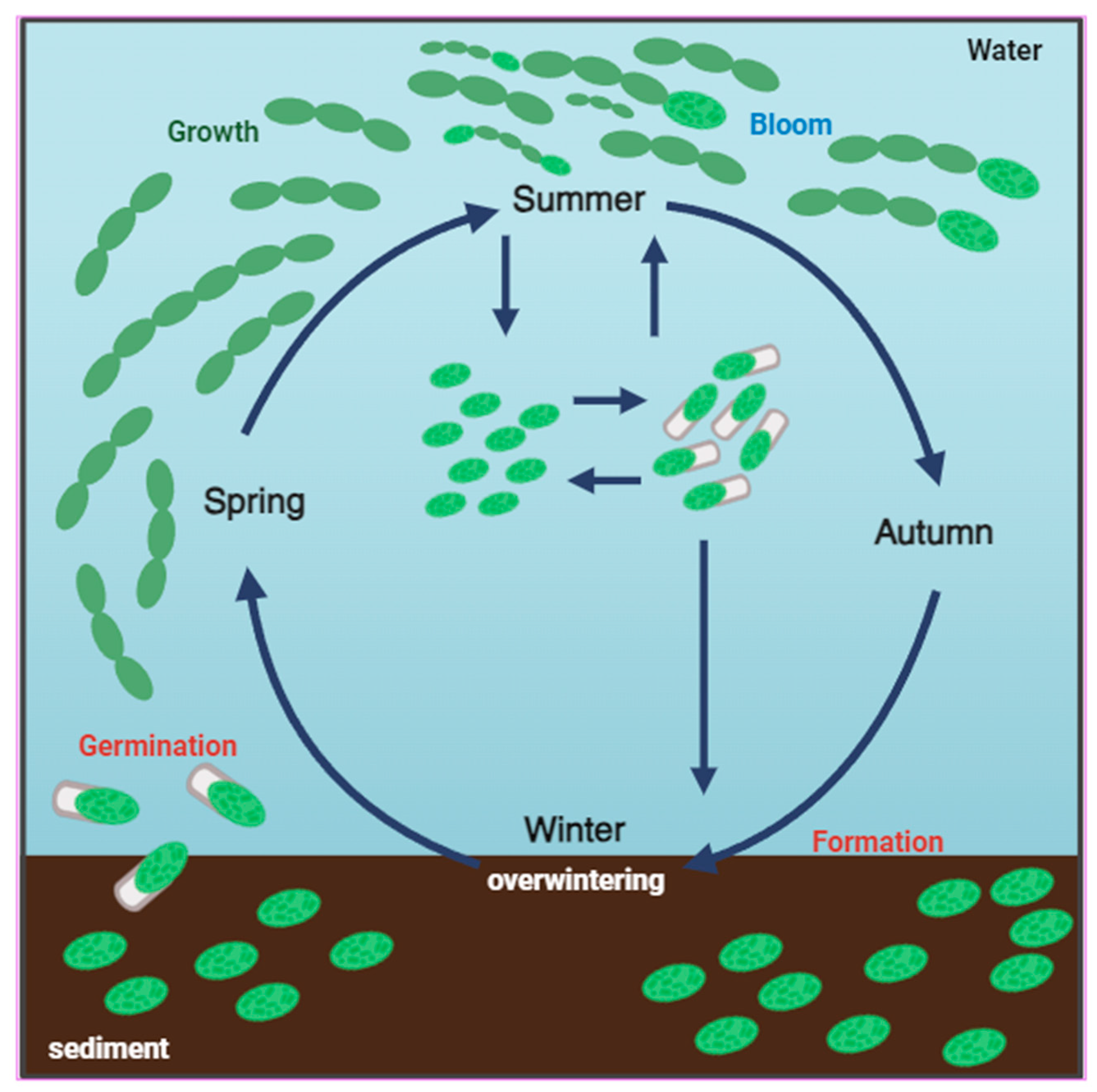
4. The Link between Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle of Cyanobacteria
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dokulil, M.T.; Teubner, K. Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, P.E. Muddy odour: A problem associated with extreme eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 1982, 86, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management; Taylor & Francis: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Höckelmann, C.; Jüttner, F. Off-flavours in water: Hydroxyketones and β-ionone derivatives as new odour compounds of freshwater cyanobacteria. Flavour Fragr. J. 2005, 20, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbiero, R.P.; Welch, E. Contribution of benthic blue-green algal recruitment to lake populations and phosphorus translocation. Freshw. Biol. 1992, 27, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.D. Role of akinetes in the development of cyanobacterial populations in the lower Murray River, Australia. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1999, 50, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvořák, P.; Casamatta, D.A.; Hašler, P.; Jahodářová, E.; Norwich, A.R.; Poulíčková, A. Diversity of the cyanobacteria. In Modern Topics in the Phototrophic Prokaryotes; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–46. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D.G.; Duggan, P.S. Tansley Review No. 107. Heterocyst and akinete differentiation in cyanobacteria. New Phytol. 1999, 144, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, P. Viability of akinetes of the planktonic cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1988, 234, 283–301. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H. Study on the Akinete Life Cycle and Vegetative Cell Dynamics in a Harmful Cyanobacterium. Dolichospermum circinale (Nostocales). Ph.D Thesis, University of Konkuk, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sukenik, A.; Rücker, J.; Maldener, I. Dormant cells (akinetes) of filamentous cyanobacteria demonstrate a great variability in morphology, physiology, and ecological function. In Cyanobacteria: From Basic Science to Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, G.; Maldener, I. The formation of spore-like Akinetes; A survival strategy of filamentous cyanobacteria. Microb. Physiol. 2021, 31, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suikkanen, S.; Kaartokallio, H.; Hällfors, S.; Huttunen, M.; Laamanen, M. Life cycle strategies of bloom-forming, filamentous cyanobacteria in the Baltic Sea. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengefors, K.; Gustafsson, S.; Ståhl-Delbanco, A. Factors regulating the recruitment of cyanobacterial and eukaryotic phytoplankton from littoral and profundal sediments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.M.; Adams, D.G. Akinetes. In The Biology of Cyanobacteria; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA; Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1982; pp. 387–412. [Google Scholar]
- Herdman, M. Akinetes: Structure and function. In The Cyanobacteria; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 227–250. [Google Scholar]
- Yema, L.; O’farrell, I.; de Tezanos Pinto, P. The sediment akinete bank links past and future blooms of Nostocales in a shallow lake. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.D.; Bellifemine, D. Environmental influences on akinete germination of Anabaena circinalis and implications for management of cyanobacterial blooms. Hydrobiologia 2000, 427, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, A.L. Factors affecting the germination of akinetes of Nodularia spumigena (Cyanobacteriaceae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dok, W.; Hart, B.T. Akinete germination in Anabaena circinalis (cyanophta). J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faithfull, C.L.; Burns, C.W. Effects of salinity and source of inocula on germination of Anabaena akinetes from a tidally influenced lake. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl-Delbanco, A.; Hansson, L.A. Effects of bioturbation on recruitment of algal cells from the “seed bank” of lake sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, M. Cellular differentiation: Akinetes. Methods Enzymol. 1988, 167, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.C.; Singh, V. Vegetative survival, akinete formation and germination in three blue-green algae and one green alga in relation to light intensity, temperature, heat shock and UV exposure. Folia Microbiol. 2000, 45, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, J.A.; Fay, P. Blue-green algal growth and sporulation in response to simulated surface bloom conditions. Br. Phycol. J. 1979, 14, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y. Effect of some physical and chemical factors on the germination of akinetes of Anabaena cylindrica. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1976, 22, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J.H. Relationships between the development of cyanobacterial bloom and the changes of environmental factors in Lake Daechung. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 36, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.H.; Lim, B.J.; You, K.A.; Park, M.H.; Hwang, S.-J. Effects of environmental factors on akinete germination of Anabaena circinalis (Cyanobacteriaceae) isolated from the North Han River, Korea. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 47, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, Y.O.; Lee, H.O.; Han, M.S. Relationship between akinete germination and vegetative population of Anabaena flos-aquae (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) in Seokchon reservoir (Seoul, Korea). Arch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 163, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, T.T.; Oglesby, R.T. Ecological observations on the planktonic cyanophyte Gleotrichia echinulata. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1970, 15, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchuk, E.S.; Ivanova, E.A.; Gladyshev, M.I. Seasonal dynamics of akinetes of Anabaena flos-aquae in bottom sediments and water column of small Siberian reservoir. Aquat. Ecol. 2006, 40, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Nakahara, H. Life cycle of cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Taiwania 2009, 54, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Watanabe, M.; Watanabe, M.M. Akinete formation in planktonic Anabaena spp. (Cyanobactefua) by treatment with low temperature. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.; O’Donohue, M.A.R.K.; Garnett, C.; Critchley, C.; Shaw, G. Factors affecting akinete differentiation in Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.C. Factors controlling induction of reproduction in algae—Review: The text. Folia Microbiol. 2012, 57, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Misra, U. Vegetative survival, akinete and zoosporangium formation and germination in some selected algae as affected by nutrients, pH, metals, and pesticides. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.M. Influence of pH on Sporulation, Spore Germination and Germling Survival in Blue-green Algae. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 1984, 12, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvat, F.; Corre, B.; Herdman, M.; Joset-Espardellier, F. Energetic and metabolic requirements for the germination of akinetes of the cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7524. Arch. Microbiol. 1982, 133, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunberg, A.K.; Blomqvist, P. Recruitment of Microcystis (Cyanophyceae) from lake sediments: The importance of littoral inocula. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.B.; Meyer, K.A.; Šulčius, S.; Brown, N.M.; Dick, G.J.; Cao, H.; Timinskas, A.; Yin, Y.; Landry, Z.C.; Otten, T.G.; et al. A closely-related clade of globally distributed bloom-forming cyanobacteria within the Nostocales. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeks, J.C.; Campbell, E.L.; Summers, M.L.; Wong, F.C. Cellular differentiation in the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme. Arch. Microbiol. 2002, 178, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olli, K.; Kangro, K.; Kabel, M. Akinete production of Anabaena lemmermannii and A. cylindrica (cyanophyceae) in natural populations of N-and P-limited coastal mesocosms. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, G.; Rücker, J.; Wiedner, C. Population dynamics and akinete formation of an invasive and a native cyanobacterium in temperate lakes. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, S.; Okubo, T. Development of Anabaena blooms in a small reservoir with dense sediment akinete population, with special reference to temperature and irradiance. J. Plankton Res. 2003, 25, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.H.; Beardall, J.; Allinson, G.; Salzman, S.; Gunthorpe, L. Environmental influences on akinete germination and development in Nodularia spumigena (Cyanobacteriaceae), isolated from the Gippsland Lakes, Victoria, Australia. Hydrobiologia 2010, 649, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Kim, K.; Jo, H.; Lee, S.D.; Yun, S.M.; Park, C. Environmental factors affecting akinete germination and resting cell awakening of two cyanobacteria. Appl. Microsc. 2023, 53, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, U.; Adrian, R.; De Senerpont Domis, L.; Elser, J.J.; Gaedke, U.; Ibelings, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Lurling, M.; Molinero, J.C.; Mooij, W.M.; et al. Beyond the Plankton Ecology Group (PEG) model: Mechanisms driving plankton succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.K.; Pandey, G.P. Influence of environmental stress on the germination of Anabaena vaginicola akinetes. Ann. Bot. 1981, 48, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzó, G. Fizikai és kémiai faktorok hatása a Balatonban elöforduló heterocisztás cianobaktériumok spóráinak csírázására (The influence of physical and chemical factors on the germination of spores of heterocystic cyanobacteria in lake Balaton). Hidrológiai Közlön 1987, 67, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Padisák, J. Estimation of minimum sedimentary inoculum (akinete) pool of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii: A morphology and life-cycle based method. In Phytoplankton and Equilibrium Concept: The Ecology of Steady-State Assemblages; Springer Science: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 389–394. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Steinman, A.; Biddanda, B.; Rediske, R.; Fahnenstiel, G. Occurrence of the toxin-producing cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Mona and Muskegon Lakes, Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2006, 32, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, B.; Wiencke, C. Temperature ecotypes and biogeography of Acrosiphoniales (Chlorophyta) with Arctic-Antarctic disjunct and Arctic/cold-temperature distributions. Eur. J. Phycol. 1995, 30, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, G. Occurrence of Raphidiopsis raciborskii blooms in cool waters: Synergistic effects of nitrogen availability and ecotypes with adaptation to low temperature. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 270, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccini, C.; Aubriot, L.; Fabre, A.; Amaral, V.; González-Piana, M.; Giani, A.; Figueredo, C.C.; Vidal, L.; Kruk, C.; Bonilla, S. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calomeni, A.J.; McQueen, A.D.; Kinley-Baird, C.M.; Clyde, G.A. Identification and Preventative Treatment of Overwintering Cyanobacteria in Sediments: A Literature Review; ERDC/EL TR-22-10; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson-Elfgren, I.; Brunberg, A.K. The Importance of Shallow Sediments in the Recruitment of Anabaena and Aphanizomenon (Cyanophyceae). J. Phycol. 2004, 40, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.D. Inclusion bodies in the cyanobacteria: Cyanophycin, polyphosphate, polyhedral bodies. In The Cyanobacteria; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 199–225. [Google Scholar]
- Sukenik, A.; Hadas, O.; Kaplan, A.; Quesada, A. Invasion of Nostocales (cyanobacteria) to subtropical and temperate freshwater lakes–physiological, regional, and global driving forces. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.C.; Sharma, U.K. Sporulation and spore germination in Westiellopsis prolifica JANET in various culture conditions. Phykos 1994, 33, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hori, K.; Ishii, S.I.; Ikeda, G.; Okamoto, J.I.; Tanji, Y.; Weeraphasphong, C.; Unno, H. Behavior of filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena spp. in water column and its cellular characteristics. Biochem. Eng. J. 2002, 10, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.; O’donohue, M.; Shaw, G.; Critchley, C. Potential triggers for akinete differentiation in an Australian strain of the cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (AWT 205/1). Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dextro, R.B.; Moutinho, F.H.M.; Nordi, C.S.F. Growth and special structures production of Nostoc paludosum (Nostocaceae, Cyanobacteria) under nutrient starvation and different light intensities. Rev. Ambiente Água 2018, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Archilla, A.I.; Moreira, D.; López-García, P.; Guerrero, C. Phytoplankton diversity and cyanobacterial dominance in a hypereutrophic shallow lake with biologically produced alkaline pH. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.N.; Kaushik, M.S.; Abraham, G.; Singh, P.K. Physico-chemical factors influencing spore germination in cyanobacterium Fischerella muscicola. J. Basic Microbiol. 2018, 58, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm-Hansen, O. Ecology, physiology, and biochemistry of blue-green algae. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1968, 22, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K. Algicidal effect of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid on blue-green alga Cylindrospermum sp. Arch. Microbiol. 1974, 97, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.C. Factors affecting spore germination in algae. Folia Microbiol. 2009, 54, 273–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Talpasayi, E.R.S. Factors affecting germination of spores in a blue-green alga Nodularia spumigena. Acta Bot. Indica 1981, 9, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, S.B.; Odebrecht, C. Effects of salinity and temperature on the growth, toxin production, and akinete germination of the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadas, O.; Pinkas, R.; Delphine, E.; Vardi, A.; Kaplan, A.; Sukenik, A. Limnological and ecophysiological aspects of Aphanizomenon ovalisporum bloom in Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Plankton Res. 1999, 21, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, J.A.; Fay, P. Sporulation and the development of planktonic blue-green algae in two Salopian meres. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B. Biol. Sci. 1977, 196, 317–332. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Shiah, F.K. Growth, trichome size and akinete production of C ylindrospermopsis raciborskii (cyanobacteria) under different temperatures: Comparison of two strains isolated from the same pond. Phycol. Res. 2014, 62, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Viner-Mozzini, Y.; Quesada, A.; Hadas, O. Potassium deficiency triggers the development of dormant cells (akinetes) in Aphanizomenon ovalisporum (Nostocales, Cyanoprokaryota). J. Phycol. 2013, 49, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, P. Cell differentiation and pigment composition in Anabaena cylindrica. Arch. Mikrobiol. 1969, 67, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, P.; Lynn, J.A.; Majer, S.C. Akinete development in the planktonic blue-green alga Anabaena circinalis. Br. Phycol. J. 1984, 19, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, M.; Fay, P. Interaction between light quality and nitrogen availability in the differentiation of akinetes in the planktonic cyanobacterium Gloeotrichia echinulata. Br. Phycol. J. 1986, 21, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Jameson, I.; Blackburn, S.I. The influence of light quality on akinete formation and germination in the toxic cyanobacterium Anabaena circinalis. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolk, C.P. Control of sporulation in a blue-green alga. Dev. Biol. 1965, 12, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.N.; Srivastava, B.S. Studies on morphogenesis in a blue-green alga. I. Effect of inorganic nitrogen sources on developmental morphology of Anabaena doliolum. Can. J. Microbiol. 1968, 14, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dok, W.; Hart, B.T. Akinete Differentiation in Anabaena Circinalis (Cyanophyta). J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, J.H.; Beardall, J.; Allinson, G.; Salzman, S.; Robertson, S.; Gunthorpe, L. Potential triggers of akinete differentiation in Nodularia spumigena (Cyanobacteriaceae) isolated from Australia. Hydrobiologia 2011, 671, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, G.; Khattar, J.S.; Sarma, T.A. Interaction between carbon and nitrogen metabolism during akinete development in the cyanobacterium Anabaena torulosa. J. Basic Microbiol. 2008, 48, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, J.M.; Herdman, M.; Stewart, W.D. Akinetes of the cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7524: Macromolecular composition, structure and control of differentiation. Microbiology 1979, 115, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignum, M.; Matthijs, H.; Pel, R.; Laanbroek, H.; Mur, L. Nutrient limitation of freshwater cyanobacteria. In Harmful Cyanobacteria; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 65–86. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.M. Symposium introductory remarks: A brief history of aquatic microbial ecology. J. Protozool. 1991, 38, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.H.; Fitzwater, S.E.; Gordon, R.M. Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton growth in Antarctic waters. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1990, 4, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, L.A.; Rudstam, L.G.; Johnson, T.B.; Soranno, P.; Allen, Y. Patterns in algal recruitment from sediment to water in a dimictic, eutrophic lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 51, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.S.; Kong, F.X.; Tan, J.K.; Zhang, X.F.; Tao, Y.; Yang, Z. Recruitment of total phytoplankton, chlorophytes and cyanobacteria from lake sediments recorded by photosynthetic pigments in a large, shallow lake (Lake Taihu, China). Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2005, 90, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan-Levy, R.N.; Hadas, O.; Summers, M.L.; Rücker, J.; Sukenik, A. Akinetes: Dormant cells of cyanobacteria. In Dormancy and Resistance in Harsh Environments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 5–27. [Google Scholar]
- Verspagen, J.M.; Snelder, E.O.; Visser, P.M.; Joehnk, K.D.; Ibelings, B.W.; Mur, L.R.; Huisman, J.E.F. Benthic–pelagic coupling in the population dynamics of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, H.-I.; Park, C.-H.; Yoo, K.-E.; Kim, N.-Y.; Hwang, S.-J. Survival and Development Strategies of Cyanobacteria through Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle. Water 2024, 16, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050770
Ho H-I, Park C-H, Yoo K-E, Kim N-Y, Hwang S-J. Survival and Development Strategies of Cyanobacteria through Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle. Water. 2024; 16(5):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050770
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Hye-In, Chae-Hong Park, Kyeong-Eun Yoo, Nan-Young Kim, and Soon-Jin Hwang. 2024. "Survival and Development Strategies of Cyanobacteria through Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle" Water 16, no. 5: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050770
APA StyleHo, H.-I., Park, C.-H., Yoo, K.-E., Kim, N.-Y., & Hwang, S.-J. (2024). Survival and Development Strategies of Cyanobacteria through Akinete Formation and Germination in the Life Cycle. Water, 16(5), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16050770







