Abstract
The Dong Taijinar (DT) and Xi Taijinar (XT) Salt Lakes have been extensively researched for their mineral richness. However, the composition and distribution of their microbial communities are still poorly known. In this study, we employed metagenomic sequencing to explore the diversity and potential functions of the microbial populations in DT and XT. Our findings indicate that the salinity levels in DT (332.18–358.30 g/L) were tenfold higher than in XT (20.09–36.83 g/L). Notably, archaea dominated the DT domain at 96.16%, while bacteria prevailed in XT at 93.09%. In DT, the bacterial community comprised 33 phyla and 1717 genera, with Marinobacter emerging as the dominant genus, showing a positive correlation with the total phosphorus content. The archaeal community in DT included four main phyla and 153 genera. The most abundant genera were Natronomonas (24.61%) and Halorubrum (23.69%), which had a strong positive correlation with the concentrations of Na+, Ca2+, and Cl−. Conversely, XT hosted 33 phyla and 1906 bacterial genera, with Loktanella as the dominant genus. The archaeal taxonomy in XT encompassed four phyla and 149 genera. In both salt lakes, Proteobacteria and Euryarchaeota were the most abundant bacterial and archaeal phyla, respectively. Our analysis of the halophilic mechanisms of these microorganisms suggests that the bacteria in XT tend to synthesize compatible solutes, whereas the archaea in DT adopt a ‘salt-in’ strategy, integrating salt into their cellular machinery to cope with the high-salinity environment.
1. Introduction
Hypersaline salt lakes and marshes arise in arid or semi-arid regions when evaporation surpasses precipitation, leading to a continuous concentration of salts [1,2]. The Qaidam Basin, on the northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau, is China’s largest continuous salt marsh [3]. Within this basin, the Dong Taijinar (DT) and Xi Taijinar (XT) Salt Lakes are two prominent salt lakes that share similar geographical and climatic conditions (Figure 1). Both lakes sit at approximately 2628 m above sea level and span an area of around 100 km2 [4,5]. DT is known for being a significant lithium salt production area, and along with XT and Qarhan Salt Lake, it provides a substantial portion of the lithium resources for China and the global market [6,7]. The abundance of boron, potassium, and lithium in DT and XT is largely attributed to the consistent inflow from the Nalenggler catchment [3,8].
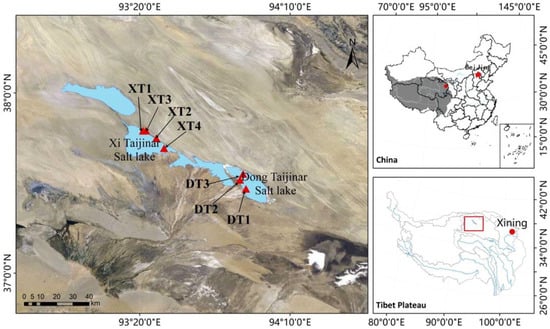
Figure 1.
Location of the DT and XT samples. The samples from DT were obtained from the west side of the lake, and the samples from XT were obtained from the east side of the lake.
Measurements by Zheng et al. in 2010 recorded the salinities of DT and XT at 332.0 g/L and 338.0 g/L, respectively, placing them between the deeper brines of the Qaidam Basin’s western and northern parts [4,9,10]. Both lakes predominantly contain magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) in their brine. However, the salinity gap between DT and XT has been widening recently, with XT experiencing a notable decrease [4,11]. This reduction in XT’s salinity is thought to result from various climatic and natural factors [7].
Salinity has a profound impact on microbial diversity, community structure, and metabolic processes [12]. Even lakes in proximity, sharing the same water source, can exhibit different salinity levels. Bishav et al. observed that such variations in the Great Salt Lake’s northern and southern regions resulted in distinct species diversity [13]. The diverse microbial communities in the Plitvice lakes were linked to unique network ecosystems formed by varying salinity across different landforms [14]. This suggests that salinity differences within the same region may create a unique barrier affecting microbial diversity. Consequently, the extreme conditions in DT and XT could harbor distinct microbial life. However, to our knowledge, there is a scarcity of research on the functional distribution and presence of microorganisms in DT and XT’s hypersaline lakes, with most studies concentrating on human impact and salt extraction. The extremely saline environment of these lakes presents an excellent opportunity for investigating the mechanisms of salt tolerance and the function of salt-tolerant microorganisms.
Metagenomic analysis has proven effective for structural and functional community assessments. It goes beyond 16S rRNA gene analysis by identifying and characterizing many prokaryotes that are currently unculturable in labs, and it provides a more comprehensive environmental gene pool and potential functions of microbial communities [15]. This study is the first to report on the diversity of microbial communities in DT and XT using metagenomics sequencing. Our primary objectives were to (1) identify key microbial entities in both lakes and (2) conduct a preliminary investigation into ecological functions, such as the salt tolerance mechanisms of microorganisms in these extreme environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Physicochemical Analysis
A mixture of sediment and water was collected from DT and XT during the summer of 2020 (July 20) (Figure 1). Two-liter turbid water samples were obtained 2 m from the lakeshore at a 15 cm depth from the water surface at each site. The temperature, pH, altitude, latitude, and longitude of the water were recorded during sampling. After removing impurities such as sand and stone, the pretreated solution was treated using a 0.45 μm polyether sulfone acetate membrane (Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA) to obtain filtrate. The residue was immediately transferred to a −80 °C freezer for further DNA extraction. The filtrate was stored at 4 °C and sent to Micor-Analysis Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China, for physicochemical analysis.
2.2. Metagenomic DNA Extraction and Sequencing
Total genomic DNA was extracted from all the collected samples using the E.Z.N.A.® Soil DNA kit (Omega Bio-tek, Norcross, GA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The concentration and purity of the extracted DNA were determined with a TBS-380 and NanoDrop 2000, respectively. The extracted DNA quality was analyzed using a 1% agarose gel and then was fragmented using a Covaris M220 (Gene Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) with an average size of approximately 400 bp. Paired-end sequencing libraries were prepared using NEXTFLEX™ Rapid DNA-Seq (Bioo Scientific, Austin, TX, USA). Paired-end sequencing was performed on an Illumina Novaseq 6000 system (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) using NovaSeq reagent kits according to the manufacturer’s instructions (www.illumina.com, accessed on 18 June 2022).
The raw data sequences were trimmed to obtain high-quality short reads using Fastp (https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp (accessed on 20 November 2022), version 0.20.0) by removing low-quality and ambiguous reads. The high-quality short reads with contigs ≥ 300 bp were assembled using Megahit software (https://github.com/voutcn/megahit (accessed on 22 November 2022), version 1.1.2). Subsequently, MetaGene (http://metagene.cb.k.u-tokyo.ac.jp/, accessed on 22 November 2022) was used to predict the open reading frames (ORFs) of the assembled contigs for functional annotation. Non-redundant gene catalogs were clustered and constructed using CD-HIT (http://www.bioinformatics.org/cd-hit/ (accessed on 27 November 2022), version 4.6.1) with 90% sequence identity and 90% coverage [16]. High-quality reads from each sample were aligned to the non-redundant gene catalogs separately using SOAPaligner software (http://soap.genomics.org.cn/ (accessed on 1 December 2022), version 2.21) to calculate the gene abundance with 95% identity [17].
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
For the bioinformatic analysis, an E-value ≤ 1 × 10−5 was employed during the sequence blasting operation. Taxonomic and functional annotations were derived by aligning the representative sequences from the non-redundant gene catalogs with NR databases, the EggNOG database (http://eggnog.embl.de/, accessed on 13 March 2023) [18], and the KEGG database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/, accessed on 13 March 2023) [19], using DIAMOND tool (http://www.diamondsearch.org/index.php (accessed on 13 March 2023), version 0.8.35) [20]. This process uses the relative number of reads as a method of abundance calculation by visualizing the composition of dominant genes or functions. In addition, an alpha diversity test was performed on the reads in the gene set according to the ACE index and Shannon index algorithms to assess the significant differences in diversity indices among different subgroups.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Species annotations were determined using the best-hit, with Bray–Curtis dissimilarity serving as the distance algorithm. Group differences were calculated using Welch’s test, with an inverted confidence level of 0.95. Differential enzyme activity and pathway visualization based on KEGG annotation and Alpha diversity tests were performed using a two-sided Wilcoxon test (p < 0.05 for significance). To explore the relationship between environmental factors and the microbial sample, canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was employed, yielding regression R2 values and p-values.
3. Results
3.1. Environmental Factors in XT and DT
The environmental factors of DT and XT are influenced by their respective inflow stream [3], with DT showing significantly higher total salinity (TS) and ionic composition than XT. The TS in DT was measured between 332.18–358.30 g/L, while XT had a lower range of 20.09–36.83 g/L (Table 1). The total organic carbon (TOC) content also varied, with DT ranging from 8.3 mg/L to 146 mg/L and XT from 4.6 mg/L to 52 mg/L. The total nitrogen (TN) differed as well, though specific values were not provided. Major cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) and anions (Cl−, SO42−) were more enriched in DT compared to XT. Differences in physicochemical characteristics may influence the microbial communities within each lake.

Table 1.
Sampling record and Environmental conditions ac.
3.2. DNA Sequencing
The DNA sequencing analysis of samples from the DT and XT Salt Lakes involved rigorous quality control measures, resulting in high-quality genetic data (Table S1). The DT samples yielded between 85,776,056 and 88,722,652 raw reads, with clean reads after quality control ranging from 83,483,230 to 87,440,932. XT samples had a broader range of raw reads, from 84,456,600 to 105,040,790, and clean reads, from 82,990,342 to 103,270,840, indicating a higher overall read count compared to DT. The quality control process ensured that over 97% of the raw reads were of high quality. Subsequent bioinformatic processing of the DT samples resulted in the identification of 1,677,194 open-reading frames (ORFs), while the XT samples yielded a significantly higher number of ORFs, totaling 5,353,555. Therefore, ORFs greatly represent a vast repository of microbial genetic information from the two lakes, providing valuable insights into the microbial diversity and potential functional capabilities within these unique environments.
3.3. Statistical Analysis in Diversity
The alpha diversity analysis of the bacterial and archaeal species in the two salt lakes, DT and XT, revealed distinct differences in their composition (Figure S3). Alpha diversity is a measure of the variety of species within a particular community or ecosystem. The ACE (Abundance-based Coverage Estimator) and Shannon diversity indices are commonly used metrics for assessing biodiversity. In the case of XT, both the ACE and Shannon indices were higher compared to DT, indicating a greater diversity of species within XT. This suggests that XT may have a more complex microbial ecosystem with a wider variety of bacterial and archaeal species. This study also found that the abundance and evenness of the bacterial species were higher than those of archaeal species in both lakes (Table 2). The ACE index for bacteria ranged from 1572 to 1878, while for archaea, it was much lower, ranging from 136–151. The Shannon index, which accounts for both the abundance and evenness of the species present, was also higher for bacteria (4.06–6.17) than for archaea (2.57–3.69). Although bacteria had higher diversity, the Shannon index and Shannoneven indicated a wider diversity gap among archaea between the two salt lakes. This suggests that the environmental differences between the two lakes may have a greater impact on the distribution of archaeal species.

Table 2.
Alpha diversity indices for genus level species in DT and XT.
3.4. Overview of Microbial Communities
The taxonomic classification of metagenomic data from the DT and XT Salt Lakes reveals a stark contrast in the microbial composition of the two environments. In DT, a vast majority of the sequence, 96.16%, were identified as archaea, which indicates a highly specialized community dominated by this domain. The other domains, including bacteria, viruses, and eukaryotes, collectively make up less than 5% of the sequence, with bacteria at 2.71%, viruses at 1.06%, and eukaryotes at a mere 0.02% (Figure S1). In sharp contrast, the XT Salt Lake’s sequences are predominantly bacteria, with 93.09% of sequences falling under this domain. Furthermore, viruses also have a notable presence in XT at 4.38%, which is higher than in DT. The other domains in XT are present in abundance of less than 1%, except for viruses (4.38%). This significant difference in the distribution of microbial life between the two lakes underscores the influence of environmental factors on microbial community structure. The high percentage of archaea in DT could be indicative of extreme conditions that favor the survival of these organisms, which are often known to thrive in more extreme environments. Conversely, the dominance of bacteria in XT suggests conditions that support a more typical microbial ecosystem. The note regarding sequences with relative abundances of less than 0.01% being classified as “other” in subsequent analyses is a standard practice in metagenomic studies to focus on the most prevalent and potentially ecologically significant members of the community.
3.5. Taxonomic Composition of Bacterial Communities
The bacterial distribution in the two salt lakes, DT and XT, was extensively analyzed, revealing the presence of 33 bacterial phyla in both environments (Table S2). The dominant phyla and genera within these lakes highlight the unique microbial landscapes of each. In DT, the most prevalent phyla were Proteobacteria (61.84%), Firmicutes (8.81%), Bacteroidetes (8.48%), Actinobacteria (7.89%), and Cyanobacteria (2.29%) (Figure 2A). For XT, the leading phyla were Proteobacteria (65.59%), Actinobacteria (7.81%), Bacteroidetes (7.57%), Verrucomicrobia (4.14%), and Planctomycetes (4.05%).
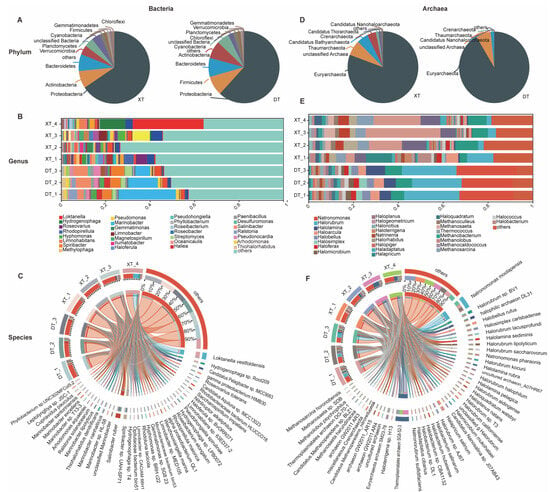
Figure 2.
Taxonomic analysis of the DT and XT samples at the phylum, genus, and species levels of bacteria and archaea. (A) Pie chart of the distribution of bacteria at the phylum level in the DT and XT samples. (B) Histogram of the distribution of bacteria at the genus level in DT and XT samples. (C) Circus plot of the distribution of bacteria at the species level in the DT and XT samples. (D) Pie chart of the distribution of archaea in DT and XT samples at the genus level. (E) Histogram of the distribution of archaea in DT and XT samples at the genus level. (F) Circus plot of the distribution of archaea in DT and XT samples at the genus level.
The genera distribution also showed diversity, which was 1717 and 1906 different genera in DT and XT, respectively (Figure S1). In DT, the most abundant genus was Marinobacter at 18.01%, followed by Salinibacter (5.09%), Spiribacter (4.43%), Ralstonia (2.35%), Thioalkalivibrio (2.18%), and Streptomyces (2.06%) (Figure 2B). These genera are primarily from the Proteobacteria phylum. In XT, the genera with higher abundances included Loktanella (8.64%), Hydrogenophaga (3.17%), Candidatus Pelagibacter (2.03%), Roseovarius (1.71%), and Rhodopirellila (1.44%). In addition, dominant genera varied across the individual samples. For instance, in XT, samples XT1 to XT4 each had a dominant genus: Roseovarius (4.00%), Gemmatimonas (2.01%), Candidatus Pelagibacter (5.95%), and Loktanella (26.58%), respectively. However, in DT, aside from Marinobacter, the abundance of other genera in individual samples was generally below 5%. The dominant strains identified in the lakes were Salinibacter ruber (5.09%) in DT and Loktanella vestfoldensis (8.25%) in XT (Figure 2C; Table S5).
3.6. Taxonomic Composition of Archaeal Communities
The analysis of archaea in the salt lakes DT and XT revealed a smaller diversity compared to bacteria, with four phyla identified in both environments (Figure S1). In DT, Euryarchaeota (91.48%) was the most abundant phylum. Other phyla, including Candidatus Nanohaloarchaeota and Thaumarchaeota, were present in less than 5% (Figure 2D; Table S6). In XT, the distribution was slightly different, with Euryarchaeota still being the most abundant at 80.63% but with a more significant presence of Thaumarchaeota (5.18%) and Candidatus Bathyarchaeota (3.40%).
At the genus level, DT and XT differed notably, with 153 archaeal genera identified in DT and 149 in XT. The major genera in DT were Halorubrum (23.69%) and Natronomonas (24.61%), with Natronomonas moolapensis being the dominant strain at 22.33% (Figure 2E,F; Table S9). DT also contained unique genera not found in XT, such as Halomicroarcula, Haloarchaeobius, Halomarina, Haloparvum Halohasta, Salinigranum, Halosiccatus, and Natronoarchaeum. The top four genera in XT were Thermoplasmatales (17.01%), Euryarchaeota (7.62%), Halorubrum (5.74%), and Methanosarcina (4.81%), with distinct genera like Nanoarchaeum, Acidianus, Candidatus Thalassoarchaea, and Methanosarcinales. The dominant strain in XT was the Thermoplasmatales archaeon at 14.05% (Figure 2F). Methanosarcina barkeri, primarily found in XT, has been the subject of studies regarding the metabolic regulation of ammonium inhibition [21]. These findings highlight the distinct archaeal communities in DT and XT, with each lake hosting a unique set of genera and strains. The presence of specific archaeal members, such as Natronomonas moolapensis in DT and Methanosarcina barkeri in XT, points to the specialized adaptations of these microorganisms to their respective saline environments.
3.7. Functional Annotation of Clusters of Orthologous Groups
The visual analysis of Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COGs) at the category level provided insights into the prevalent genes associated with the basic metabolic functions of the microbial communities in the DT and XT Salt Lakes (Table S10). A total of 17 different COG categories were identified, gene abundance below 0.01% being classified as “other” (Figure 3A). A few categories associated with key metabolic processes in microbial communities were significantly enriched (accounting for >5%), including amino acid transport and metabolism (E), replication, recombination, and repair (L), energy production and conversion (C), and inorganic ion transport and metabolism (P) (Table S11). It is noteworthy that the cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis (M) function abundance in XT was significantly higher than that in DT. In addition, categories with this trend include carbohydrate transport and metabolism (G), transcription (K), lipid transport and metabolism (I), energy production and conversion (C), and other categories that are not listed. In contrast, several categories in DT are all higher in abundance than XT, such as replication, recombination, and repair (L), signal transduction mechanisms (T), and coenzyme transport and metabolism (H). The highest abundance was functional unknown (S), suggesting that the potential functional resources of these two salt lakes deserve further exploration.
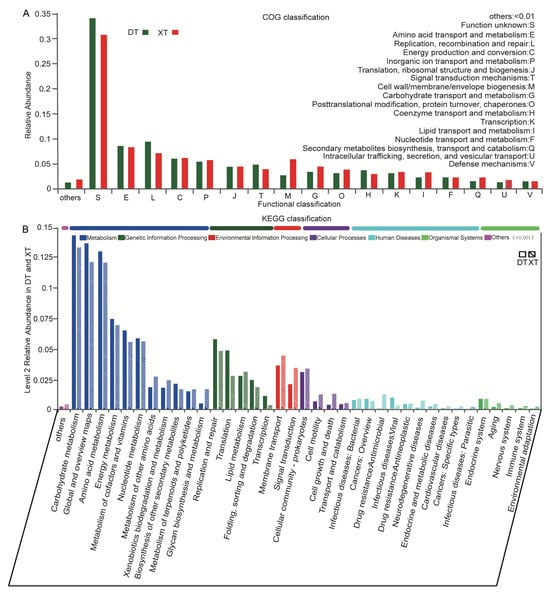
Figure 3.
COG and KEGG function annotation of the DT and XT communities. (A) The x-axis represents the functions in the COG classification, the y-axis represents the proportion of each function in the sample, and different colors represent the two lakes. (B) The x-axis indicates the KEGG metabolic pathways at classification level 2; the y-axis indicates the corresponding percentages of the samples, and different colors show the clustering results.
3.8. Functional Annotation of the KEGG Metabolic Network
The metagenomic analysis of the DT and XT Salt Lakes, as interpreted through the KEGG metabolic network, reveals distinct microbial metabolic strategies adapted to their respective extreme environments. The pathway category with the highest percentage in both lakes was metabolism, followed by Genetic Information Processes. The categories with the highest abundance in metabolism were carbohydrate metabolism, global and overview maps, and amino acid metabolism (Figure 3B). These dominant pathways demonstrated higher abundance in DT, suggesting that the microbial community prioritizes carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, which is essential for energy production in its saline habitat. In addition, replication and repair, translation and folding sorting, and degradation of the Genetic Information Process were more abundant in DT. In contrast, the lipid metabolism pathway was relatively enriched in XT. The full range of pathways in Environmental Information Processing and Cellular Processes, including membrane transportation, signal transduction, and cellular motility, were more abundant in XT than in DT. Enhanced membrane transport capabilities suggest a refined system for nutrient uptake and waste expulsion, indicative of sophisticated osmoregulatory adaptations.
3.9. Major Metabolic Pathways and Halophilic Mechanisms
In this research, we explored the adaptive mechanisms of microbial halophiles, which are primarily characterized by the regulation of genes associated with sodium efflux and potassium uptake components of the ‘salt-in’ strategy and the biosynthesis and transport of organic compatible solutes, either through uptake or de novo synthesis [22,23]. Building upon this foundation, our study utilized KEGG gene annotations to delve into the transport and the biosynthesis pathways of microorganisms in DT, a hypersaline salt lake, and XT, a moderately saline counterpart.
Our analysis identified the ko00260 pathway, which governs amino acid metabolic, as the most prominent in DT and XT, with alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism (ko00250), and cysteine and methionine metabolism (ko00270) also being notable (Figure S2). A comparative assessment revealed eight metabolic pathways with significant differences between the two lakes (Figure 4A). In DT, biosynthetic pathways for phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthesis (ko00400), arginine (ko00220), lysine (ko00300), and valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis (ko00290) were markedly upregulated. Conversely, XT exhibited upregulation in pathways associated with the metabolism and degradation of tryptophan metabolism (ko00380), phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360), histidine metabolism (ko00340), and lysine degradation (ko00310).
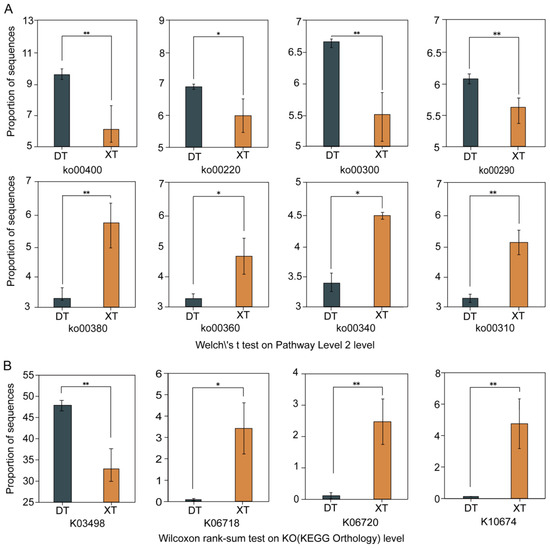
Figure 4.
(A) Eight pathways with the most significant differences at level 2 of KEGG; (B) KEGG orthology with significant differences in the ko00260 pathway; 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05 * and 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01 **. Phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan biosynthesis (ko00400). Arginine biosynthesis (ko00220). Lysine biosynthesis (ko00300). Valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis (ko00290). Tryptophan metabolism (ko00380). Phenylalanine metabolism (ko00360). Histidine metabolism (ko00340). Lysine Degradation (ko00310). trk/ktr type potassium uptake protein (K03498). L-2,4-diaminobutyric acid acetyltransferase (K06718). L-ectoine synthetase (K06720). Ectoine hydroxylase (K10674).
In DT, a significant upregulation of genes related to potassium ion uptake, such as K03498-related trkH, trkG, ktrB, and ktrD, was observed [24], indicating an enhanced response to salt stress through the upregulation of trk/ktr potassium uptake proteins (Figure 4B). In contrast, XT displayed an upregulation of ectoine hydroxylase (K10674) and L-ectoine synthetase (K06720), facilitating the synthesis of ectoine and hydroxyectoine, which are crucial for countering environmental stresses. These distinct mechanisms underscore the resilience and metabolic adaptability of microorganisms in DT and XT, reflecting their tailored survival strategies in response to their respective saline conditions.
3.10. Association Analysis of Dominant Genera and Environmental Factors
The unique brines of hypersalinity environments present an ideal setting for investigating the diversity and adaptation strategies of polyextremophilic microorganisms. To elucidate the relationships between microbial community composition and environmental parameters, we employed detrended correspondence analysis (DCA) to establish the significance of axis lengths greater than 4. Subsequently, Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) was utilized to discern the pivotal environmental factors influencing the interactions of the dominant genera (Table S14), with the correlation coefficients (R2) and p-values detailed in Supplementary Materials (Table S15).
Marinobacter, Salinibacter, and Spiribacter were identified as the most prevalent bacterial genera (exceeding >5%) in all samples. Additionally, Natronomonas emerged as the predominant archaeal genus, with Halorubrum and Methanosarcina also detected in specific samples. The CCA results indicated a strong positive correlation between the total phosphorus (TP) content and the abundance of Marinobacter, as well as with other genera such as Spiribacter, Roseovarius, Hyphomonas, llumatobacter, and Gemmatimonas in bacteria (Figure 5). Notably, Salinibacter exhibited a correlation with TOC content. Other dominant genera from DT1-3 samples demonstrated a robust association with environmental factors such as pH, total nitrogen (TN), sodium (Na+), chloride (Cl−), bicarbonate (HCO3−), and calcium (Ca2+). These genera also showed a high positive correlation with total salt (TS), potassium (K+), and magnesium (Mg2+) levels.
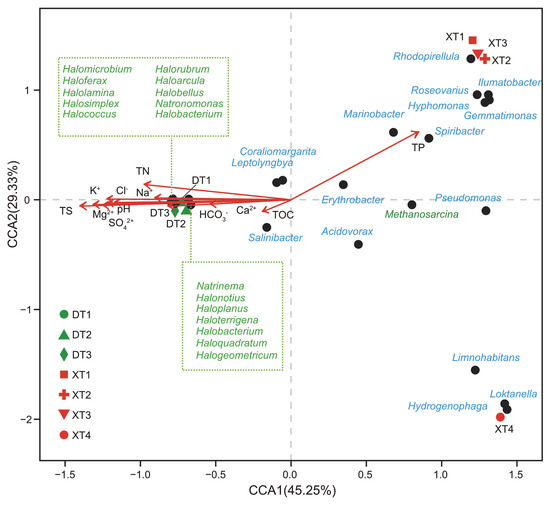
Figure 5.
CCA of the relationship among dominant genera and physicochemical variables in the two salt lakes. The sample coordinate table shows the relative positions of samples in each dimension after dimension reduction. Environmental factors are represented by arrows in red, and the length of the arrow line represents the magnitude of the correlation. The longer the line, the greater the correlation, and vice versa. The black dots in the figure represent the genus of bacteria and archaea with names in different colors. Green represents archaea and blue represents bacteria. Different colors and shapes represent different subgroups.
The interplay between the dominant microbial genera and their environment displayed marked differences between the two salt lakes. In DT, the dominant genus exhibited a positive correlation with TS, predominantly composed of sodium, chlorine, magnesium, and sulfate ions. Conversely, in XT, despite XT4 being geographically distant from the other samples, the microbial communities were primarily associated with a bacterial presence, with TP emerging as the key environmental determinant. This divergence underscores the distinct ecological dynamics governing microbial life in each lake, reflecting the specialized adaptation mechanisms that these extremophiles have evolved in response to their respective extreme conditions.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Salinity Vary in XT and DT Lakes
The salinity of lakes is influenced by various factors, including evaporation, seepage, river water, groundwater, and brine, which contribute to the stability of water levels and salinity [7]. Seasonal changes can affect the variation in these factors, which can lead to fluctuations in ion concentrations, such as those observed in the Taijinar Salt Lake, which experienced a reduction in size due to evaporation [25,26]. The Nalenggler River’s influx of fresh water into XT has contributed to the observed decrease in salinity [27]. According to Fang’s important findings, the Qinghai–Tibetan lakes are experiencing a water increase and salinity decrease due to climate warming [28].
Salinity plays a pivotal role in defining the nature of a lake and distinguishing the dominant microbial taxa together with the certain brine chemical composition. In 2010, both salt lakes XT and DT were categorized as hypersaline due to their high-salinity levels (TDSDT ≈ 332.0 g/L and TDSXT ≈ 338.0 g/L) [4,29]. Ten years later, DT continues to be a hypersaline lake with a salinity of 337–354 g/L. However, the salinity of XT shows a decrease, with a slight increase in Na+, K+, and SO42− content and slight decreased in Mg2+ and Cl− content [27,29]. Strangely, only 20–36 g/L of salinity in XT was detected in our study (Table 1). The big salinity gap between the salinity of the XT measured in this study and measured by Qin et al. was most probably related to the sampling position [27]. This is because we collected the samples XT1~4 from the shore of XT, which was very near the road, while Qin’s research was collected from the inter-brine area in the core mining area of XT Salt Lake. The samples DT1~3 were collected the same as in Qin’s study; therefore, the salinity of DT did not obviously change (332–358 g/L in our research).
4.2. The Microbial Community and Dominant Groups in XT and DT
Microbial community analysis revealed a high abundance of bacteria (93.09%) in XT, while archaea (96.16%) was high in DT (Figure S1). Similarly, Loubna et al. isolated and identified more archaea in the Great Salt Lake, which has significant salinity differences between the northern and southern regions [30]. Xie et al. also demonstrated that the diversity and composition of archaea in the brines of the Mahai potash mine on the Tibetan Plateau are mainly influenced by the chemical properties of the hypersaline water [31]. While unique microbial community distributions do exist, our study suggests that salinity is the primary driver of species composition differences in lake ecosystems, whereas other factors such as pH, nutrition, and temperature usually occupy the second place in microbial community construction [13,29,32]. Compared to bacteria, archaea are better adapted to high-salinity environment (DT); on the contrary, bacteria are highly distributed in XT with lower salinity (20–36 g/L in this study). Furthermore, CCA analysis showed that most bacteria in XT had a strong correlation with TP. The geochemical conditions in salt lakes exert significant selective pressure on the microbial community and their activity [33]. In MgSO4 subtype lakes with high salinity, bacterial growth, and diversity may be constrained [34,35]. This is because fewer bacterial sequences were found in the DT samples compared to those from XT in this study (Table S1). These results agreed with the hypothesis that microbial diversity tends to be lower in high-salinity conditions.
Although bacterial sequences occupied merely 2.71% in DT, several dominant bacterial genera still existed. For example, Marinobacter (18.01%) was the genus with the highest proportion of bacteria, which was positively correlated with the total phosphorus (TP) content (Figure 5). This genus possesses the capability to synthesize diverse compounds and degrade hydrocarbons in saline environments, as well as influence biofilm formations in relation to calcium levels [36,37]. Other genera with relatively high abundance in DT were Salinibacter (5.09%) and Spiribacter (4.43%). In addition, a lower abundance but unique genus Salicola was found in this lake. What is more interesting is that Salicola marasensis, a member of Salicola, performs functions in tolerating UV-B irradiation and accumulating glycine betaine across a broad salinity spectrum [38,39].
Bacterial community analysis around the lakeside of XT revealed that Proteobacteria (65.59%) was the predominant phylum, followed by Actinobacteria (7.81%) and Bacteroidetes (7.57%) (Figure 2A). Loktanella was an active complex carbon and nitrogen source and is potentially beneficial in biogeochemical cycling within the lake [40]. In this study, it was the most abundant genus in XT with 8.64%. Beyond the dominant genera, the predicted functions of the protein families shared by different strains of the low-abundance genus Candidatus Poribacteria cover most features in central metabolism [41]. The presence of Poribacteria, together with previous findings, concluded that halophilic bacteria are often found in the Proteobacteria and Firmicutes phyla [42]. In addition, genome sequencing has unveiled unique functional traits of Proteobacteria, particularly its metabolism of the osmolyte-like ectoine and glycine betaine and its potential for cellulose-anchoring enzyme complexes. Hydrogenophaga plays an important role in biodegradation processes and potential industrial applications, especially in the syngas conversion and degradation of 4-aminobenzenesulfonate [43,44]. It was predominantly present in the XT4 sample, although not in the highest abundance. Additionally, Haloplasma, a member of Haloplasmatales, was relatively abundant in the XT4 sample. These abundant genera in XT suggest that the microbial community in salt lakes may have a robust ability to maintain a stable ecosystem in XT. However, the dynamics of these microbial interactions and their evolutionary transformations warrant further investigation.
The microbial communities in Tibetan plateau lakes are mainly influenced by the physicochemical parameters of the lake [45]. Among all the factors, salinity was the major driving force in the assembly of microbial community structures. In both DT and XT samples, the dominant archaeal phylum was Euryarchaeota, which thrived in higher salinity conditions, albeit with reduced diversity [46,47]. Furthermore, Candidatus Nanohaloarchaeota, and Thaumarchaeota were among the top five dominant archaeal groups. Thaumarchaeota was also identified during the microbial diversity analysis of Gahai Lake and Xiaochaidan Lake [46]. It seems that this phylum is widespread in low-, medium-, and high-salt lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. However, members of Nanohaloarchaeota are especially prevalent in high-salinity conditions, with a notable abundance of Halorubrum and Natronomonas in DT. The symbiotic relationship between Halorubrum lacusprofundi and Candidatus Nanohaloarchaeum antarctic strengthened the intricate survival strategies of microorganisms in extreme environments like DT [46], which may explain the mechanism of life’s resilience and adaptability under hypersaline conditions.
4.3. Microbial Adaptation Strategy and Metabolism in XT and DT
The halophilic archaea predominantly employ a ‘salt-in’ strategy to cope with osmotic stress, either by accumulating K+ in the cell and effluxing Na+ or by using inorganic ions to maintain a stable internal K+ concentration [45,48]. This strategy, along with the metabolism of sulfur, carbon, and nitrogen, is crucial for sustaining stable ecosystem functions in hypersaline environments [49,50,51]. The regulation mechanism involved in community function may be different for microorganisms of various salinitie. COG and KEGG enrichment results indicated that amino acid transport and metabolism play a crucial role in osmotic adaptation to both a moderate- and high-salinity level (Figure 4). Interestingly, microorganisms in DT, the hypersaline lake, show more activity in amino acid and carbon metabolism than those in XT, the moderate saline lake. However, membrane transport and lipid metabolism critical for microbial survival appear to be relatively inhibited in DT. The regulation of membrane proteins is crucial for prokaryote survival under hyperosmotic stress and contributes to the unique structure of Haloarchaea [52,53].
In this study, glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism (ko00260) accounted for a similar proportion of the total amino acid metabolic pathway in microorganisms from both salt lakes, 13.98% in DT and 13.22% in XT (Figure S2). Han et al. emphasized the significance of the glycine, serine, and threonine metabolic pathways (ko00260) in the mechanisms of resistance to salt stress [54]. Both DT and XT microbial communities have distinct dominant metabolic pathways suited to their respective environments. For example, metabolism-related pathways such as ko00400, ko00220, ko00300, and ko00290 were prominent in DT, while ko00380, ko00360, ko00340, and ko00310 were significantly annotated in XT. This variation was consistent with their microbial composition and function.
Different adaptation strategies are employed in DT and XT to cope with the extreme conditions. In XT, gene clusters involved in the synthesis of compatible solutes like ectoine (K06720) and hydroxyectoine (K10674) were significantly annotated (Figure 4B), providing a mechanism for various life forms to thrive [55]. In contrast, microorganisms in DT appear to focus on enhancing basic metabolism and upregulating the expression of trk/ktr-type potassium uptake proteins, adopting a ‘salt-in’ adaptation strategy to counteract salt stress [24]. This strategy may also explain the low pathogenicity and limited secondary metabolite synthesis in DT’s microorganisms. The synthesis of ectoine and hydroxyectoine, which is typically found in bacteria from extreme environments, was also well-studied; it seems that salinity variations were posited to influence the expression of solute synthase [56].
Some low or moderate halophilic bacteria primarily use the synthesis or uptake of compatible solutes to manage osmotic stress [45,48]. In contrast, most halophilic archaea (even nonhalophilic archaea) typically respond to high osmotic pressure by accumulating K+ and expelling Na+ [24,57]. This ‘salt-in’ strategy enables halophilic archaea to thrive and dominate in extreme hypersaline environments [45,47]. The intracellular enzyme of halophilic archaea, such as Halobacterium and Haloferax, requires a certain concentration of salt for normal function and activity [58]. Consequently, halophilic archaea may outcompete bacteria in high-salinity lakes due to their energetic efficiency in carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism, energy metabolism, and metabolism of cofactors and vitamins [45]. Our findings suggest that higher salinity in DT may bolster amino acid biosynthesis, carbon metabolism, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, DNA replication, and the TCA cycle as a response to extreme osmotic stress (Figure 4B). Physical and chemical properties changes in the environment also play a role in shaping microbial community composition and functions. The distinct ecosystems of the two salt lakes, which were comprised of the microbial community and diversity, were mainly due to adapting to specific conditions and forming complex interaction networks with various environmental factors.
The study attempts to utilize metagenomic sequencing to begin uncovering the complexities of salt lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. However, the variation in environmental factors such as seasonal variations, temperature, and precipitation still have complex effects on microbial abundance and species composition, and the complicated mechanism remains to be fully understood. This preliminary analysis provides a foundational reference for future studies exploring the intricate relationships between microbial diversity and environmental conditions in salt lakes on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau.
5. Conclusions
Although the microbial ecosystems of saline lakes were complex and changeable, particularly in hypersaline, this research area is blooming. Currently, the diversity and ecological roles of archaea in extreme environments have been explored more in-depth. This study is the first discussion on the microbial structural composition of DT and XT through metagenomic analysis, highlighting the distinct microbial communities present in these two geographically proximate salt lakes with different salinity and other environmental factors. The findings emphasize the significant influence of salinity on species distribution and microbial function within these lakes. The microbial communities in DT and XT were found to be vastly different, with each sampling site being dominated by a few specific genera. This suggests that, while the lakes are close in location, the salinity levels are a critical determinant in shaping the microbial landscape. Furthermore, the study suggests that the interaction networks between environmental characteristics and microbial community composition are likely fine-tuned to cope with high-salinity conditions, contributing to the stability of the saline ecosystems. The adaptive functions of these microbial communities in such harsh environments have been explored, providing valuable insights into the biodiversity of saline lakes on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. The main results disclosed in this study not only contribute to the understanding of microbial life in extreme conditions but also have broader implications for studying the resilience and adaptability of life forms in changing environments. The unique adaptations and interactions observed in the microbial communities of DT and XT offer a window into the complex dynamics that support life in some of the most challenging habitats on Earth.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16030451/s1, Figure S1: A Venn diagram of Classification of two salt lakes at the domain level; B Venn diagram of bacteria and archaea at the Genus classification level; Figure S2: Map of significant differences in KEGG metabolic Level2 and Level3 of Pathways and KO (KEGG Orthology); 0.01 < p ≤ 0.05 * and 0.001 < p ≤ 0.01 **; Figure S3: Results of Alpha diversity for differences of bacteria and archaea in two salt lakes. Table S1: Statistics of control sequences prediction gene in each sample; Table S2: Profiles of bacteria with abundance greater than 0.001 at phylum level; Table S3: The main bacteria present at the Class taxonomic level; Table S4: Overview of the main dominant bacteria at genus level; Table S5: Overview of the main dominant bacteria at species level; Table S6: Statistical overview at archaea at phylum level; Table S7: A statistical survey of the all archaea of class level; Table S8: The main archaea at the level of genus classification; Table S9: Overview of the main dominant archaea at species level; Table S10: Summary of COG classifications at category; Table S11: An overview of COG classifications at the functional level; Table S12: Summary of KEGG categories at Level 1 and Level 2; Table S13: KEGG difference test statistics at Level 2 and KO (KEGG Orthology); Table S14: Analysis of CCA initial assessment results; Table S15: env fit Environment factor table.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparations were performed by Q.L. and G.S. Data collections were performed by D.Z., J.X. and Y.L. Data analysis were performed by Y.L. and M.Z. The first draft of the manuscript was written by M.Z. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by [the National Natural Science Foundation Project of China] grant number [21967018].
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during the current study are available in the NCBI repository, (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/PRJNA984434, accessed on 20 June 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to three anonymous reviewers and the Associate Editor whose constructive comments greatly improved the quality and clarity of an earlier version of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Charles, H.; Dukes, J.S. Effects of warming and altered precipitation on plant and nutrient dynamics of a New England salt marsh. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1758–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.K.; Qi, H.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Jin, L. Lithium isotopic compositions of brine, sediments and source water in Qaidam Lake, Qinghai, China. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1994, 4, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.Z.; Jiang, S.Y.; Tan, H.B.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, B.K.; Yang, T.L. Boron isotope geochemistry of salt sediments from the Dongtai salt lake in Qaidam Basin: Boron budget and sources. Chem. Geol. 2014, 10, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.P.; Liu, X.F. Hydrochemistry and minerals assemblages of salt lakes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 2010, 84, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.S.; Han, F.Q. Geological Characteristics and Lithium Distribution of East Taijinar Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2013, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yu, D.; Fu, Y.; Yan, M. Tectonic evolution and differential deformation controls on oilfield water distribution in western Qaidam Basin. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2020, 7, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Xu, J.; Yi, L.; Chang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, H. Seasonal Interaction of River Water-Groundwater-Salt Lake Brine and Its Influence on Water-Salt Balance in the Nalenggele River Catchment in Qaidam Basin, NW China. J. Earth Sci. 2022, 33, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, J. The hydrological features of Caidam Basin. Arid Zone Res. 1996, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Miao, W.; Li, W.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y. Hydrochemical Charateristics of Oilfield Waters in Lenghu No. 3 Structure Area of North Edge of Qaidam Basin. J. Salt Lake Res. 2016, 2, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Z. Preliminary studies on deposition characters and ages of the salt sediments of Dong Taijineier Salt Lake in Qinghai province. Geol. Chem. Miner. 2001, 83, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kushner, D.J. Life in high salt and solute concentrations: Halophilic bacteria. Microb. Life Extrem. Environ. 1978, 317–368. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H.; Han, J. Microbial Responses to Simulated Salinization and Desalinization in the Sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan Lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, B.; Bhattacharjee, A.S.; Coutinho, F.H.; Goel, R.K. Viruses and Their Interactions with Bacteria and Archaea of Hypersaline Great Salt Lake. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 701414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čačković, A.; Kajan, K.; Selak, L.; Marković, T.; Brozičević, A.; Pjevac, P.; Orlić, S. Hydrochemical and Seasonally Conditioned Changes of Microbial Communities in the Tufa-Forming Freshwater Network Ecosystem. mSphere 2023, 8, e0060222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Metagenomics for studying unculturable microorganisms: Cutting the Gordian knot. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Fang, L.; Xu, X. Using SOAPaligner for Short Reads Alignment. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 44, 11.11.1–11.11.17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.J.; Julien, P.; Kuhn, M.; von Mering, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. eggNOG: Automated construction and annotation of orthologous groups of genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D250–D254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; He, P.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; Lü, F. Metabolic Regulation of Mesophilic Methanosarcina barkeri to Ammonium Inhibition. Env. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8897–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piubeli, F.; Salvador, M.; Argandoña, M.; Nieto, J.J.; Bernal, V.; Pastor, J.M.; Cánovas, M.; Vargas, C. Insights into metabolic osmoadaptation of the ectoines-producer bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens through a high-quality genome scale metabolic model. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitaš, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Yang, N.; Liu, J. The Osmoprotectant Switch of Potassium to Compatible Solutes in an Extremely Halophilic Archaea Halorubrum kocurii 2020YC7. Genes 2022, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Lu, B.; Ling, Z. Remote Sensing Analysis on the Landscape Pattern Variation Influenced by Resources Exploitation in Taijinar Salt Lake Area from 1990 to 2015. J. Salt Lake Res. 2020, 1, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Han, J.B.; Liu, J.B. Variation characteristics of LiCl deposit under condition of mining in East Taijnar Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Inorg. Chem. Ind. 2020, 12, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.J.; Li, Q.K.; Li, W.X.; Fan, Q.S.; Chen, T.Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.P.; Shan, F.S. Elemental Variations and Mechanisms of Brines in the Context of Large-Scale Exploitation: A Case Study of Xitaijnar Salt Lake, Qaidam Basin. Aquat. Geochem. 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Wu, G.; Hua, Z.; Dong, H.; Hedlund, B.P.; Baker, B.J.; Jiang, H. Compositional and Metabolic Responses of Autotrophic Microbial Community to Salinity in Lacustrine Environments. mSystems 2022, 7, e0033522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Xie, A.; Zhang, S.; Li, C. Research on development status and countermeasure of brine resources in East-West Ginair and Yiliping Salt Lake. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 2, 48–51+56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazi, L.; Breakwell, D.P.; Harker, A.R.; Crandall, K.A. Life in extreme environments: Microbial diversity in Great Salt Lake, Utah. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yu, S.; Lu, X.; Liu, S.; Tang, Y.; Lu, H. Different Responses of Bacteria and Archaea to Environmental Variables in Brines of the Mahai Potash Mine, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Dong, H.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive census of lake microbial diversity on a global scale. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo-Medina, M.; Bowles, M.W.; Samarkin, V.A.; Hunter, K.S.; Joye, S.B. Microbial diversity and activity in seafloor brine lake sediments (Alaminos Canyon block 601, Gulf of Mexico). Geobiology 2016, 14, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Long, Q.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Zhu, D. Microbial community structure and diversity within hypersaline Keke Salt Lake environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Murcia, A.; Acinas, S.G.; Rodríguez-Valera, F. Evaluation of prokaryotic diversity by restrictase digestion of 16S rDNA directly amplified from hypersaline environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1995, 17, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.J.; Mickol, R.L.; Eddie, B.J.; Thakur, M.; Yates, M.D.; Glaven, S.M. Marinobacter: A case study in bioelectrochemical chassis evaluation. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 16, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, L.J.; Wang, Z.; Malanoski, A.P.; Onderko, E.L.; Johnson, B.J.; Moore, M.H.; Phillips, D.A.; Chu, B.J.; Doyle, J.F.; Eddie, B.J.; et al. Development of a Genetic System for Marinobacter atlanticus CP1 (sp. nov.), a Wax Ester Producing Strain Isolated from an Autotrophic Biocathode. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigui, H.; Masmoudi, S.; Brochier-Armanet, C.; Maalej, S.; Dukan, S. Survival of extremely and moderately halophilic isolates of Tunisian solar salterns after UV-B or oxidative stress. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno Mde, L.; García, M.T.; Ventosa, A.; Iglesias-Guerra, F.; Mellado, E. The extremely halophilic bacterium Salicola marasensis IC10 accumulates the compatible solute betaine. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 33, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.M.; Cho, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.H.; Bhatia, S.K.; Gurav, R.; Jeon, J.M.; Yoon, J.J.; Kim, W.; et al. Finding of novel polyhydroxybutyrate producer Loktanella sp. SM43 capable of balanced utilization of glucose and xylose from lignocellulosic biomass. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, S.; Blanton, J.M.; Neu, A.; Agarwal, V.; Biggs, J.S.; Moore, B.S.; Allen, E.E. Pangenomic comparison of globally distributed Poribacteria associated with sponge hosts and marine particles. ISME J. 2019, 13, 468–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, J.T.; Tague, E.D.; Zinke, L.; Schmidt, J.M.; Steen, A.D.; Reese, B.; Marshall, I.P.G.; Webster, G.; Weightman, A.; Castro, H.F.; et al. Uncultured Microbial Phyla Suggest Mechanisms for Multi-Thousand-Year Subsistence in Baltic Sea Sediments. mBio 2019, 10, e02376-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, H.M.; Chew, T.H.; Tay, Y.L.; Lye, S.F.; Yahya, A. Genome sequence of Hydrogenophaga sp. strain PBC, a 4-aminobenzenesulfonate-degrading bacterium. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 4759–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenz, S.; Baumann, P.T.; Rückert, C.; Nebel, B.A.; Siebert, D.; Schwentner, A.; Eikmanns, B.J.; Hauer, B.; Kalinowski, J.; Takors, R.; et al. Exploiting Hydrogenophaga pseudoflava for aerobic syngas-based production of chemicals. Metab. Eng. 2019, 55, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, J.F.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Pei, L.; Du, Z.; Hao, C.; Dong, H. Both pH and salinity shape the microbial communities of the lakes in Badain Jaran Desert, NW China. Sci. Total Env. 2021, 791, 148108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Biswas, R.; Misra, A.; Sar, A.; Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Dam, B. Poorly known microbial taxa dominate the microbiome of hypersaline Sambhar Lake salterns in India. Extremophiles 2020, 24, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banciu, H.L.; Muntyan, M.S. Adaptive strategies in the double-extremophilic prokaryotes inhabiting soda lakes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Ventosa, A. International Committee on Systematics of Prokaryotes subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halobacteria and subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halomonadaceae. Minutes of the joint open meeting, 26 June 2019, Cluj-Napoca, Romania. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3657–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Messina, E.; La Cono, V.; Ferrer, M.; Ciordia, S.; Mena, M.C.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Golyshin, P.N.; Yakimov, M.M. Sulfur Respiration in a Group of Facultatively Anaerobic Natronoarchaea Ubiquitous in Hypersaline Soda Lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Shao, N.; Akinyemi, T.; Whitman, W.B. Methanogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R727–R732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Chen, Y.L.; Sun, Y.H.; Pan, J.; Cai, M.W.; Li, M. Diversity, metabolism and cultivation of archaea in mangrove ecosystems. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Su, N.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Luo, J.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Membrane Protein-Mediated Hypersaline Sensitivity and Adaptation in Halophilic Nocardiopsis xinjiangensis. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhao, D.; Hou, J.; Wu, J.; Cai, S.; Dassarma, P.; Xiang, H. Cellular and organellar membrane-associated proteins in haloarchaea: Perspectives on the physiological significance and biotechnological applications. Sci. China Life Sci. 2012, 55, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Gao, Q.X.; Zhang, Y.G.; Li, L.; Mohamad, O.A.A.; Rao, M.P.N.; Xiao, M.; Hozzein, W.N.; Alkhalifah, D.H.M.; Tao, Y.; et al. Transcriptomic and Ectoine Analysis of Halotolerant Nocardiopsis gilva YIM 90087(T) Under Salt Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czech, L.; Hermann, L.; Stöveken, N.; Richter, A.A.; Höppner, A.; Smits, S.H.J.; Heider, J.; Bremer, E. Role of the Extremolytes Ectoine and Hydroxyectoine as Stress Protectants and Nutrients: Genetics, Phylogenomics, Biochemistry, and Structural Analysis. Genes 2018, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremer, E.; Krämer, R. Responses of Microorganisms to Osmotic Stress. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.F. Osmoadaptation and osmoregulation in archaea. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D796–D812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shporer, M.; Civan, M.M. Pulsed nuclear magnetic resonance study of 39K within halobacteria. J. Membr. Biol. 1977, 33, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).