Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns and Retention Mechanisms in Column Core Sediments in the Caohai Region of Dianchi Lake
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
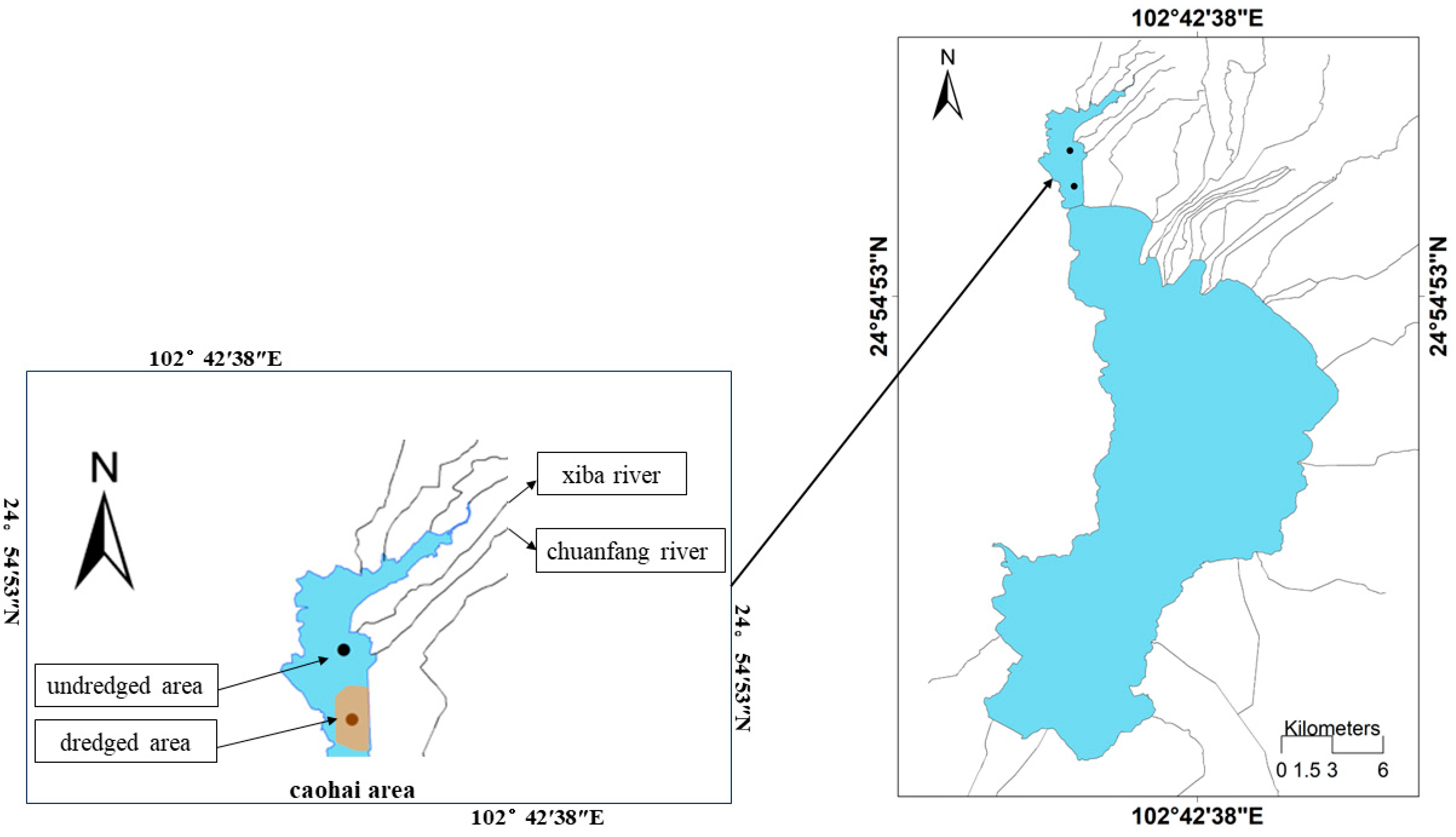
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Dredging Project
2.3. Experimental Method
2.4. Release Contribution of N and P
3. Results
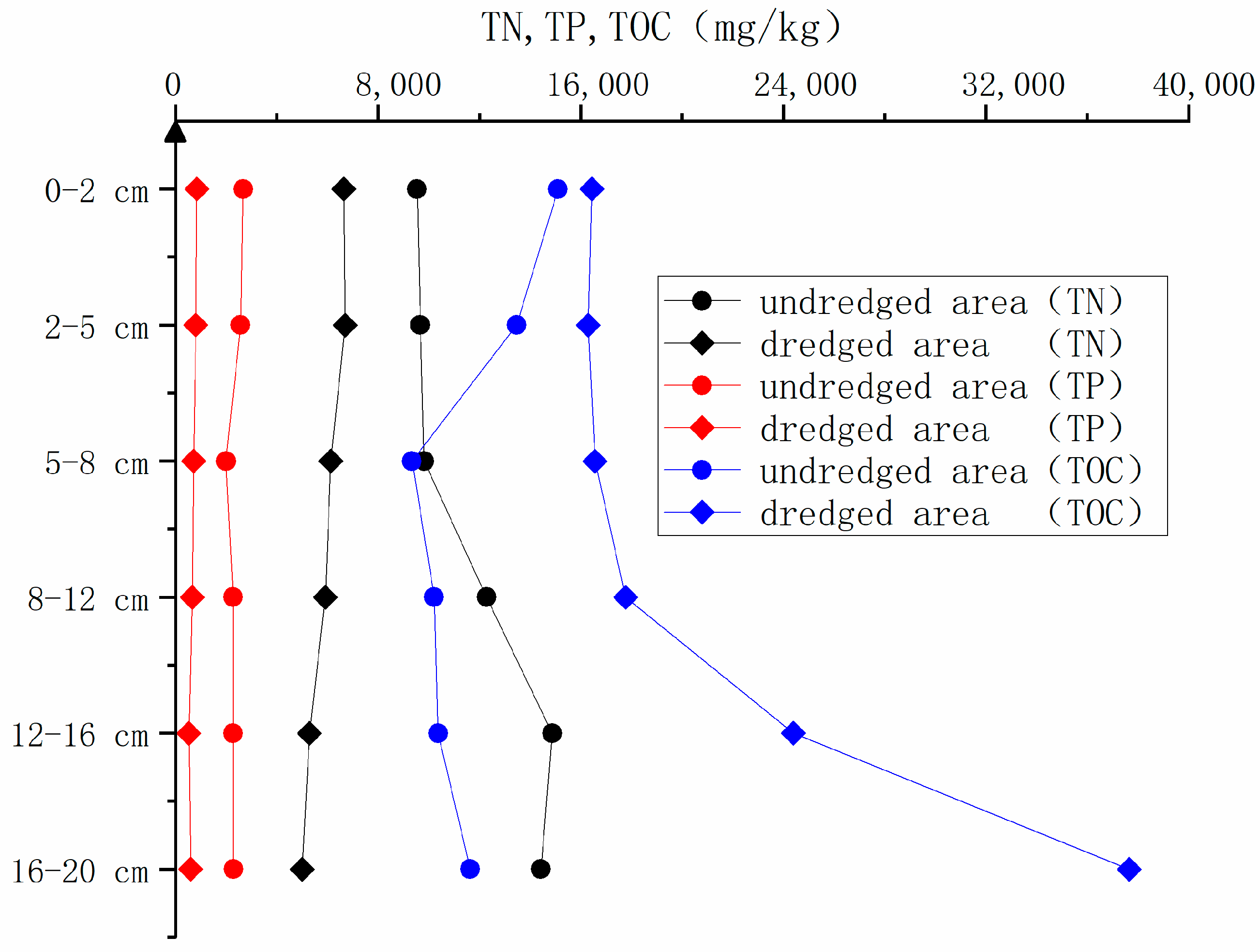
3.1. Basic Properties of Sediment Column Cores in Dredged and Undredged Areas
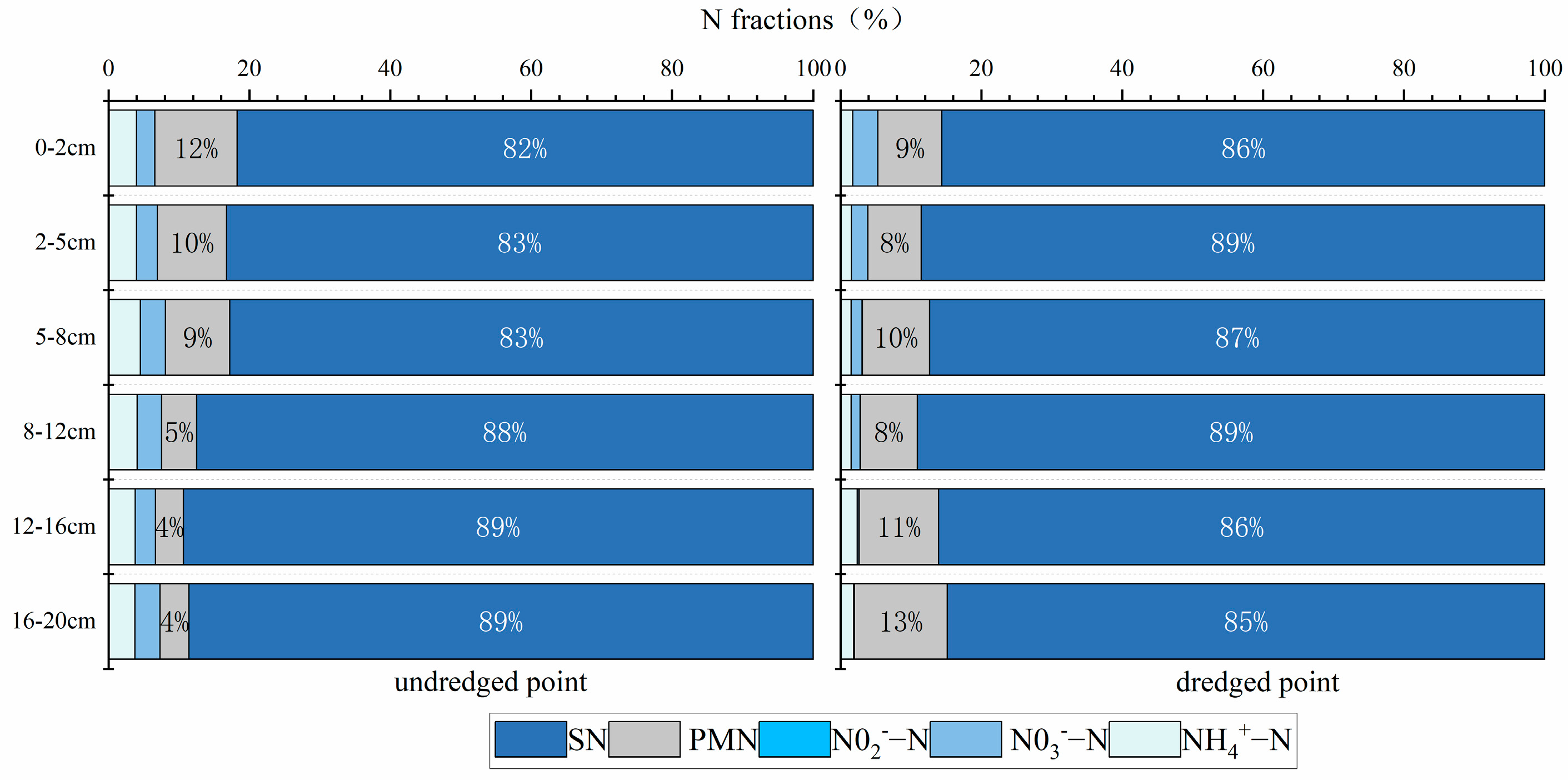
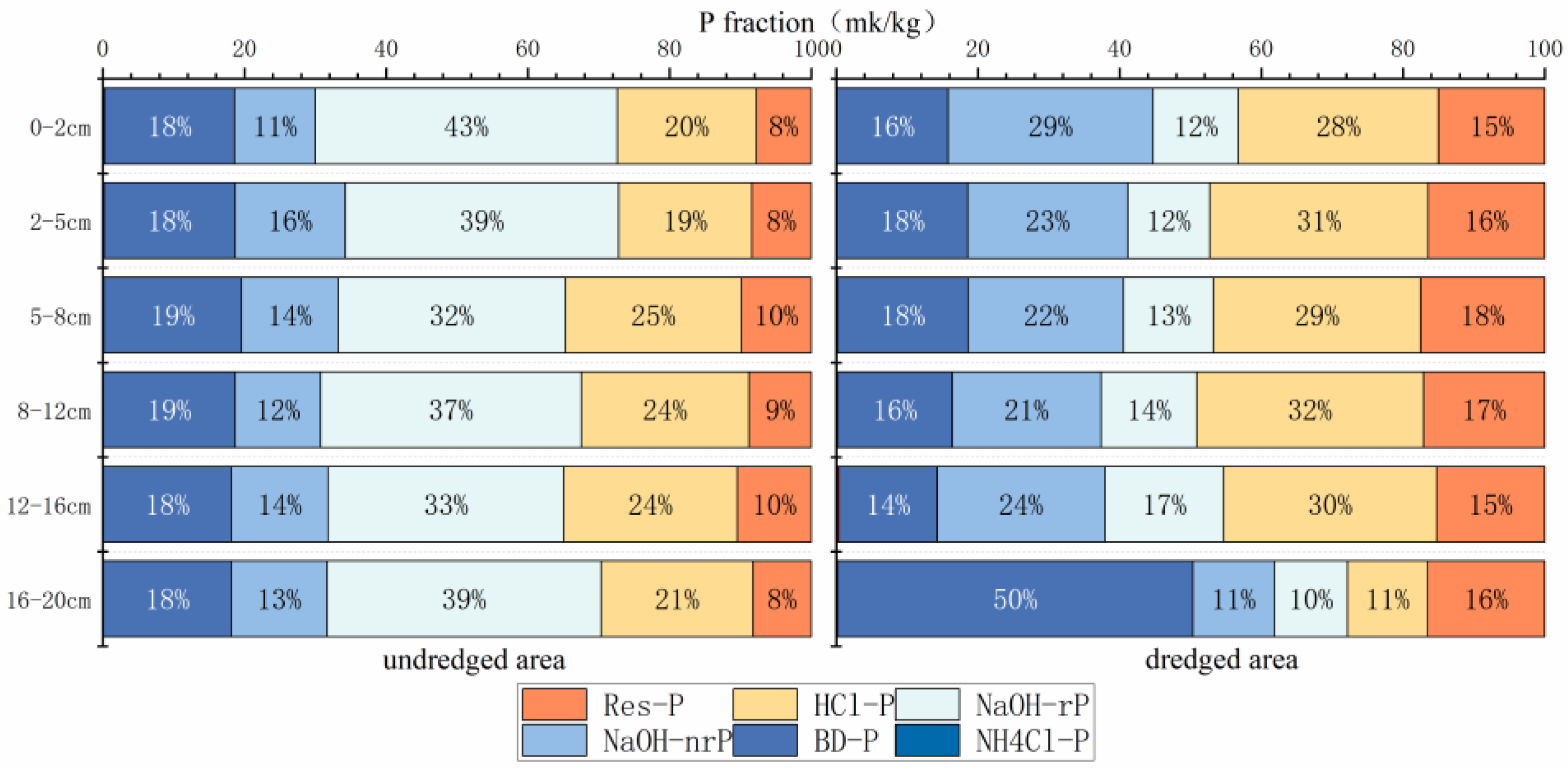
3.2. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fate of Column Core Sediments in Dredged and Undredged Areas
3.3. Sediment Nutrient Balance Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Pollution Components of Dredging and Reversion Phenomenon
4.2. Mechanisms by Which Dredging Affects Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns in Lake Sediments
4.2.1. Mechanism by Which Dredging Affects the Nitrogen Storage Pattern in Lake Sediments
4.2.2. Mechanisms by Which Dredging Affects Phosphorus Storage Patterns in Lake Sediments
4.3. Impact of Dredging on Lake Ecosystems
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| N | Nitrogen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| EN | Exchangable nitrogen |
| SN | Stabilized nitrogen |
| PMN | Potentially mobile nitrogen |
| PMON | Potential mineralizable organic nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| MP | Mobile phosphorus |
| SP | Stabilized phosphorus |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
References
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Tang, T.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Strokal, M.; Sorger-Domenigg, F.; Wada, Y. Recent advancement in water quality indicators for eutrophication in global freshwater lakes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 063004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Maren, D.; van Kessel, T.; Cronin, K.; Sittoni, L. The impact of channel deepening and dredging on estuarine sediment concentration. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 95, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcil, A.; Erust, C.; Ozdemiroglu, S.; Fonti, V.; Beolchini, F. A review of approaches and techniques used in aquatic contaminated sediments: Metal removal and stabilization by chemical and biotechnological processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 86, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patmont, C.; LaRosa, P.; Narayanan, R.; Forrest, C. Environmental dredging residual generation and management. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2018, 14, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erftemeijer, P.L.; Riegl, B.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Todd, P.A. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1737–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Song, C.; Wang, L.; Du, G.; Qiao, S.; Sun, J.; Nuamah, L.A. Dredging effects on nutrient release of the sediment in the long-term operational free water surface constructed wetland. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Wen, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C. Nitrogen budget at sediment-water interface altered by sediment dredging and settling particles: Benefits and drawbacks in managing eutrophication. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kong, M.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Shen, Q.-S.; Zhong, J.-C.; Fan, C.-X. Dredging method effects on sediment resuspension and nutrient release across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 25861–25869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, J. Attribution of lake eutrophication risk to anthropogenic forcing adjacent to the agriculture areas: A case study of Chagan Lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 112159–112172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Z.-P.; Chu, Y.-X.; Tian, G.; He, R. Eutrophication levels increase sulfur biotransformation and emissions from sediments of Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Determann, M.; Andersen, T.K.; Barbosa, C.C.; Dadi, T.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Paule-Mercado, M.C.; Pujoni, D.G.F.; Schultze, M.; Rinke, K. Synergistic Effects of Warming and Internal Nutrient Loading Interfere with the Long-Term Stability of Lake Restoration and Induce Sudden Re-eutrophication. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4003–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawiska, I.; Jasiewicz, J.; Rzodkiewicz, M.; Woszczyk, M. Relative impact of environmental variables on the lake trophic state highlights the complexity of eutrophication controls. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Yu, J.; Xu, W.; Wu, Y.; Lei, X.; Ye, J.; Geng, J.; Ding, Z. Long-time series ecological environment quality monitoring and cause analysis in the Dianchi Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wei, D.; Zhang, R.; Yu, Y.; Wu, D.; et al. Strategy for cost-effective BMPs of non-point source pollution in the small agricultural watershed of Poyang Lake: A case study of the Zhuxi River. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Li, Z.; Xie, P.; Hao, Q.; Tang, X.; Wu, Y.; Du, P. Temporal Variation and Reduction Strategy of Nutrient Loads from an Urban River Catchment into a Eutrophic Lake, China. Water 2019, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, S.; Zhong, J.; Fan, C.; Chen, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: Focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ye, C. Effects of Sediment Dredging on Nutrient Release and Eutrophication in the Gate-Controlled Estuary of Northern Taihu Lake. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 7451832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.-C.; Yu, J.-H.; Zheng, X.-L.; Wen, S.-L.; Liu, D.-H.; Fan, C.-X. Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment-Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Water 2018, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.D.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, H.G.; Ao, H.Y. The effects of dredging on nitrogen balance in sediment-water microcosms and implications to dredging projects. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Liu, X.; Bai, S.; Wu, C.; Ao, H.; Liu, J. Effects of sediment dredging on internal phosphorus: A comparative field study focused on iron and phosphorus forms in sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.; Huang, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, A.-X.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Carbon and nitrogen burial in a plateau lake during eutrophication and phytoplankton blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Jiao, L.; Cheng, Q.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, S. The evolution of a typical plateau lake from macrophyte to algae leads to the imbalance of nutrient retention. Water Res. 2023, 236, 119937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.S.; Qi, W.Q.; Sun, Z.G.; Huang, Y.R.; Shen, Y.W. Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Method; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Dan, S.F.; Liu, Y.; He, J.; Zhu, D.; Jiao, L. Importance of ammonia nitrogen potentially released from sediments to the development of eutrophication in a plateau lake. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Liu, Y.; Dan, S.F.; Jiao, L. Historical changes of sedimentary P-binding forms and their ecological driving mechanism in a typical “grass-algae” eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruban, V.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Pardo, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.; Li, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, L. Spatiotemporal correlations between water quality and microbial community of typical inflow river into Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 63722–63734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Kong, Y. Government Governance, Legal Environment and Sustainable Economic Development. Sustainability 2014, 6, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jian, Y.; Zhou, F. Decline in nitrogen concentrations of eutrophic Lake Dianchi associated with policy interventions during 2002–2018. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S.; Guo, H. Internal cycling, not external loading, decides the nutrient limitation in eutrophic lake: A dynamic model with temporal Bayesian hierarchical inference. Water Res. 2017, 116, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J. Forms, migration and transportation of nitrogen in sediments and suspended solids of endogenous nutrient-controlled lakes. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 126, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, W. Effect of algal blooms outbreak and decline on phosphorus migration in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 296, 118761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Gao, G.; Wang, S. Processes and mechanism of effects of sludge dredging on internal source release in lakes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Fisher, M.M.; Wang, Y.; White, J.R.; James, R.T. Potential effects of sediment dredging on internal phosphorus loading in a shallow, subtropical lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.C.; Liu, G.F.; Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.M.; Ren, X.L. Environmental effect of sediment dredging in lake (I): The role of sediment dredging in reducing internal phosphorous release. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 84–93. [Google Scholar]
- Gautreau, E.; Volatier, L.; Nogaro, G.; Gouze, E.; Mermillod-Blondin, F. The influence of bioturbation and water column oxygenation on nutrient recycling in reservoir sediments. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C. Fifteen-year study of environmental dredging effect on variation of nitrogen and phosphorus exchange across the sediment-water interface of an urban lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Sediment-Water Interface Process of Lakes: Nitrogen and Phosphorus Biogeochemistry; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-H.; Yin, P.; Zhang, L.; Yin, H.-B. Effects of Sediment Dredging on the Reduction in Sediment Internal Loading of Lake Taihu and the Self-recovery Ability of Benthic Organism. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2023, 44, 828–838. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D. Environmental impact and optimization of lake dredged-sludge treatment and disposal technologies based on life cycle assessment (LCA) analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.-C.; You, B.-S.; Fan, C.-X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.-M. Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

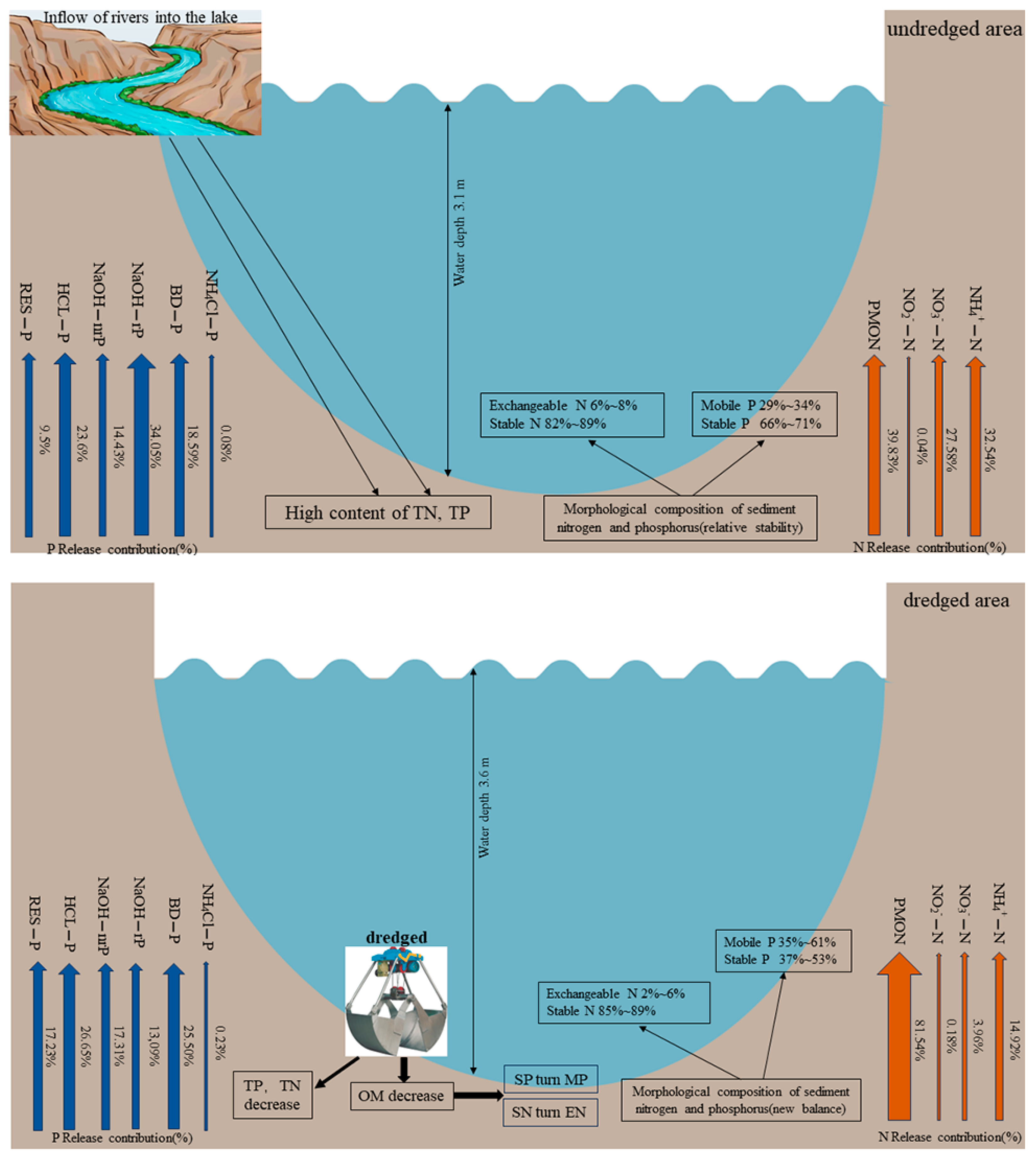
| Nitrogen and Phosphorus Form | Release Contribution (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Undredged Point | Dredged Point | ||
| N | NH4+-N | 32.54 | 14.32 |
| NO3−-N | 27.58 | 3.96 | |
| NO2−-N | 0.04 | 0.18 | |
| PMON | 39.83 | 81.54 | |
| P | NH4Cl-P | 0.08 | 0.23 |
| BD-P | 18.59 | 25.50 | |
| NaOH-rP | 34.05 | 13.09 | |
| NaOH-nrP | 14.43 | 17.31 | |
| HCl-P | 23.36 | 26.65 | |
| Res-P | 9.50 | 17.23 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, M.; Jiao, L.; Song, D.; Li, J.; et al. Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns and Retention Mechanisms in Column Core Sediments in the Caohai Region of Dianchi Lake. Water 2024, 16, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030449
Liu M, Yang Y, Shao Z, Liu Y, Wang Z, Chen Z, Chen M, Jiao L, Song D, Li J, et al. Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns and Retention Mechanisms in Column Core Sediments in the Caohai Region of Dianchi Lake. Water. 2024; 16(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Mingyan, Yan Yang, Zhi Shao, Yaping Liu, Ziqi Wang, Zhengqing Chen, Mingang Chen, Lixin Jiao, Di Song, Jingyu Li, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns and Retention Mechanisms in Column Core Sediments in the Caohai Region of Dianchi Lake" Water 16, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030449
APA StyleLiu, M., Yang, Y., Shao, Z., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Chen, Z., Chen, M., Jiao, L., Song, D., Li, J., & Wang, J. (2024). Effects of Dredging on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Storage Patterns and Retention Mechanisms in Column Core Sediments in the Caohai Region of Dianchi Lake. Water, 16(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16030449






