Abstract
This study analyzed the horizontal and vertical distribution characteristics of temperature and salinity in the central and eastern regions of the Beibu Gulf, based on conductivity measurements in summer 2022, temperature, and depth (CTD) measurement data from the Sino–Vietnamese cooperative project “Demonstration Study on Ecological Protection and Management in Typical Bays: Seasonal Survey of the Beibu Gulf”. Furthermore, the study utilized the computational results from the numerical Finite-Volume Coastal Ocean Model (FVCOM) to elucidate the intrinsic patterns that formed the temperature and salinity distribution characteristics in August 2022 from both thermodynamic and dynamic perspectives. The circulation in the Beibu Gulf drives external seawater to move northward from the bay mouth. During this movement, numerous upwelling areas are created by lateral Ekman transport. The formation of different scales of cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices and current convergence zones is influenced by topography, runoff, and the water flux from the Qiongzhou Strait, which are key factors in the formation of upwelling and downwelling. The surface circulation in August 2022 significantly differed from the 20-year average surface circulation, with an influx of 1.15 × 104 m3/s more water entering the Beibu Gulf compared to the multi-year average. The water flux from the Qiongzhou Strait is a critical factor affecting the circulation patterns in the Beibu Gulf. The northeastern waters of the Beibu Gulf are characterized by current convergence zones, where extensive upwelling occurs. The rich nutrient salts in these areas promote the reproduction and growth of phytoplankton and zooplankton, making this the most favorable ecological environment in the Beibu Gulf and serving as a natural reserve for fisheries, coral reefs, dugongs, and Bryde’s whales.
1. Introduction
The Beibu Gulf, situated in the northwestern region of the South China Sea (SCS), is bordered by southern China and northern Vietnam, covering an area of approximately 140,000 km2 with an average depth of 46 m [1]. This partially enclosed gulf is linked to the SCS through the Qiongzhou Strait and the southern mouth of the gulf. The Beibu Gulf experiences a tropical to subtropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons influenced by the East Asian monsoon system. Wind patterns in the region are primarily driven by monsoonal winds, which blow from the south during the summer and from the northeast in autumn and winter. These winds have a significant impact on evaporation rates and surface currents within the gulf [2]. The average annual precipitation ranges from 1200 to 2000 mm, with the majority falling during the summer months [3]. River discharges significantly contribute to the gulf’s hydrology, transporting fresh water and nutrients that affect local marine ecosystems [4]. Understanding these hydrological and climatic dynamics is crucial for comprehending the environmental conditions of the Beibu Gulf and their implications for regional fisheries and marine management.
Bays in China are generally surrounded by land on three sides and are open to the sea on one side, which results in a relatively simple water and heat balance. In contrast, the Beibu Gulf has two channels for water exchange with the open sea. During winter, under the influence of the northerly winds, seawater flows towards the bay mouth, allowing a large volume of water from the Qiongzhou Strait to enter the Beibu Gulf [2] to compensate for the water that flows out, forming a single cyclonic circulation. In summer, the Beibu Gulf is dominated by southerly winds, with seawater entering the Gulf at the bay mouth and accumulating in the northern part of the Gulf, hindering the inflow of water from the Qiongzhou Strait. Additionally, increased runoff during the summer leads to a complex multi-vortex structure in the Beibu Gulf’s circulation [5]. Thus, it is evident that the monsoon, water flux from the Qiongzhou Strait, and runoff are the main factors influencing the variations in the circulation of the Beibu Gulf. Under the influence of these factors, as well as sunlight, the spatial distribution and vertical structure of temperature and salinity in the Beibu Gulf exhibit complex changes [6,7].
In 1960, based on observational data from joint Chinese–Vietnamese surveys, circulation patterns in the Beibu Gulf during winter and summer were identified: in winter, the Beibu Gulf is influenced by an open large cyclonic circulation; conversely, in summer, it is influenced by an open anticyclonic circulation. Research on circulation in the Beibu Gulf has advanced significantly over the years, driven by improvements in observational methods and modeling techniques. Early studies, such as those conducted by Tan [8] and Yu and Liu [9], established circulation models by analyzing historical salinity distribution maps and more than 60 years of current data. Their results showed a general agreement between the calculated circulation patterns and data from collaborative Sino–Vietnamese surveys, although minor discrepancies were noted in seasonal current directions, particularly for the northward current along the Vietnamese coast in summer and the westward current in the Qiongzhou Strait in winter. As research methodologies advanced, subsequent studies have focused on revealing seasonal changes in the circulation structure of the Beibu Gulf. Xu et al. [10] used dynamic height data from more than 6000 stations spanning 50 years (1921–1970) to show that the Beibu Gulf exhibits a cyclonic circulation pattern year-round and observed that during the summer months, characterized by a strong southwest monsoon, anticyclonic circulation patterns can appear at the surface. Moreover, Zhuang et al. [11] analyzed historical data and proposed a dominant cyclonic circulation during the winter months, with smaller counterclockwise eddies forming at 19° N. Several studies, including those that presented modeling results [12,13,14,15], support this cyclonic structure, particularly in winter, while acknowledging a more intricate circulation pattern in summer. Various interpretations of the summer circulation in the Beibu Gulf exist, with some studies proposing a dual-eddy structure. This structure comprises a closed cyclonic circulation in the northern gulf and an open anticyclonic circulation at the gulf mouth [16,17]. Due to limitations in the temporal and spatial resolutions of observational data, researchers are increasingly employing numerical modeling to investigate circulation patterns in the Beibu Gulf. Wu et al. [14] employed the Estuarine and Coastal Ocean Model with a Semi-implicit Scheme (ECOMSI) and found that the inflow through the Qiongzhou Strait is responsible for maintaining the cyclonic circulation during the summer. Gao et al. [4], utilizing the Princeton Ocean Model (POM), identified the summer circulation structure in the Beibu Gulf as follows: the southern region is dominated by an anticyclonic vortex, while the northern circulation exhibits a cyclonic curvature. Chen et al. [6] utilized FVCOM and arrived at similar conclusions, emphasizing the interannual and monthly variations in the strength and extent of these opposing vortices.
Overall, this study aims to analyze the distribution of temperature and salinity in the central and eastern regions of the Beibu Gulf, as well as to elucidate the dynamic mechanisms underlying these patterns. By comparing the circulation anomalies observed in August 2022 with the multi-year average, this study highlights the significant influence of the Qiongzhou Strait transport on the ecological environment of the Beibu Gulf. This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 analyzes the distribution of the temperature and salinity based on observations; Section 3 provides the model setup and the model results; Section 4 discusses the impacts of the circulation in the Beibu Gulf on ecosystems; and Section 5 offers the conclusions.
2. Analysis of Temperature and Salinity Distribution Characteristics in Summer 2022
2.1. Data
In 1962, the Sino–Vietnamese Joint Marine Comprehensive Survey in the Beibu Gulf filled a historical gap in marine scientific research in the region for the first time, laying the foundation for the gradual development of marine scientific studies in the Beibu Gulf. It was not until 45 years later, during the comprehensive offshore environmental survey conducted in China from 2005 to 2011 (the Chinese National “908” Special Project (908-01-ST09), that a second set of systematic data on temperature and salinity specific to the Chinese waters of the Beibu Gulf became available.
The data for this study come from the summer survey results (8–15 August 2022) of the Sino–Vietnamese cooperative project “Demonstration Study on Ecological Protection and Management in Typical Bays: Seasonal Survey of the Beibu Gulf”, conducted in 2021–2022. The survey area covered an area from approximately 107° E to 111° E and 18.5° N to 21.5° N with a total of seven cross-sections established, all oriented east–west. Based on the length of each cross-section, 6–10 measurement stations were evenly distributed along each, resulting in a total of 51 stations (Figure 1). The measuring equipment utilized is the SBE911plus CTD, manufactured by Seabird (Bellevue, WA, USA). This instrument is equipped with dual temperature and conductivity sensors, featuring a temperature accuracy of 0.001 °C and a conductivity accuracy of 0.0003 S/m. All measurement stations utilized conductivity, temperature, and depth (CTD) instruments, and quality control and interpolation calculations were conducted throughout the process, yielding profile data at 1 m intervals.
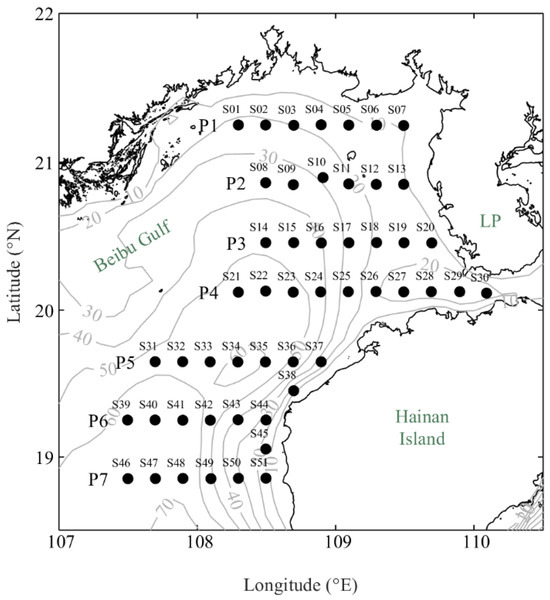
Figure 1.
Locations of the Sino–Vietnam joint temperature and salinity survey stations in 2022 and bathymetry map.
2.2. Spatial Distribution of Temperature and Salinity
Figure 2 shows the distribution characteristics of temperature and salinity in the surface and bottom layers of the Beibu Gulf. From the figure, the following can be observed:
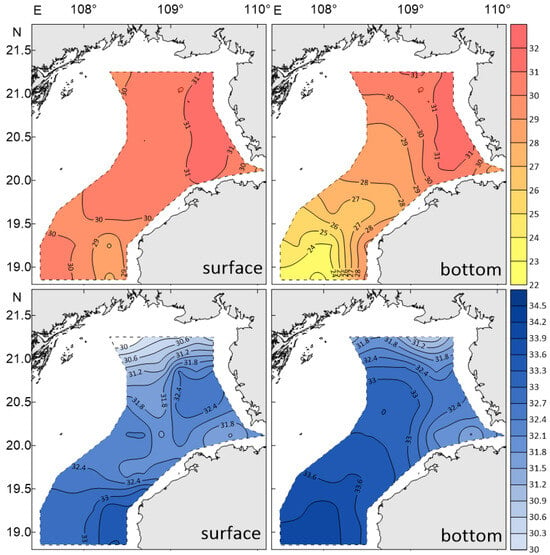
Figure 2.
Measured spatial distribution of temperature ((top), °C) and salinity (bottom) in the surface and bottom layers of Beibu Gulf. The dashed lines denote the data boundaries.
(1) Surface Temperature and Salinity Distribution Characteristics
At the bay mouth of the Beibu Gulf, there is a low-temperature, high-salinity tongue of water that advances northward towards the southwestern coast of Hainan Island, with a minimum temperature of 28 °C and a maximum salinity of 33.5. This tongue meets the high-temperature (31 °C) and low-salinity (32) water from the western Qiongzhou Strait at around 19.5° N to 20° N in the central Beibu Gulf, forming a weak front that runs east–west.
(2) Bottom Temperature and Salinity Distribution Characteristics
The low-temperature, high-salinity tongue at the bay mouth advances northward from the central deep trough of the Beibu Gulf, with a minimum temperature of only 23 °C, which is 5 °C lower than that of the surface layer, and a maximum salinity of 34.1, which is 0.6 higher than that of the surface layer. Near 20° N, it first encounters low-temperature (29 °C) and low-salinity (31.7) water from the Qiongzhou Strait, forming a north–south-oriented front. The low-temperature, high-salinity tongue continues to advance northward and encounters nearshore high-temperature (31 °C) and low-salinity (32.3) water near 20°45′ N, forming a second east–west-oriented front.
It is evident that the low-temperature, high-salinity water from the bay mouth can penetrate deeply into the northwestern coastal area of the Beibu Gulf, as it is much stronger than the surface layer. Its strong advance towards the coastal waters of Guangxi causes the surface water to flow southeastward, creating a compensatory situation.
2.3. Section Distribution of Temperature and Salinity
The section distribution characteristics of temperature and salinity are depicted in Figure 3. The following features can be observed from the figure:
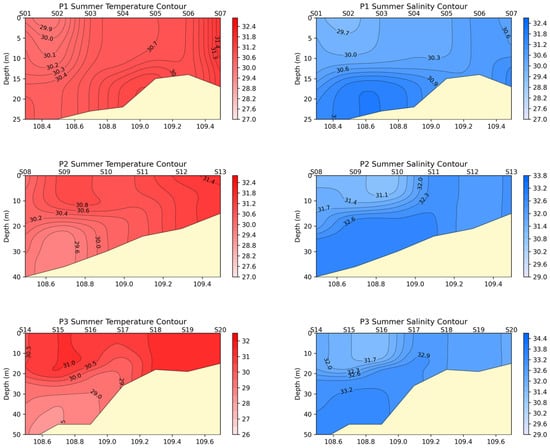
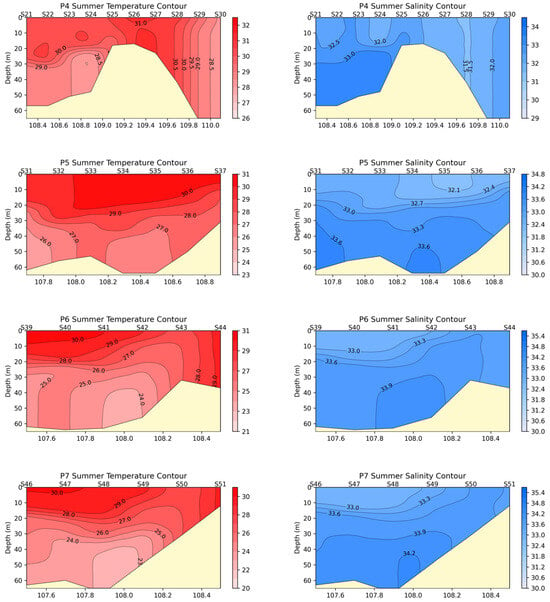
Figure 3.
The temperature and salinity distribution across sections.
(1) In summer, due to increased solar radiation, the surface temperature is higher than the temperature of the lower layers. There are thermoclines of varying intensities, mostly in the depth range of 15–20 m.
(2) In summer, with abundant rainfall, the surface salinity is lower than the salinity of the lower layers, and there are haloclines of varying intensities, mostly in the depth range of 15–20 m.
(3) The appearance of upwelling. The bottom water flows northward, and Ekman transport is directed to the right. Influenced by the shallowing coastal topography, varying-intensity upwelling occurs, causing the isotherms and isohalines to have different degrees of uplift near the coast. This is most evident at stations P3, P4, P6, and P7.
(4) The existence of downwelling. In sections P1, P3, and P4, near 108°30′ E, the isotherms and isohalines clearly descend downward, indicating the presence of downwelling in this area.
(5) The P4 section connected to the Qiongzhou Strait is relatively unique: on the left side of the submarine hill (about 15 m from the surface), there is a clear upwelling area with obvious stratification; on the right side of the submarine hill, although the water depth reaches 60 m, the water column is vertically mixed and uniform, without any stratification. This is caused by the obstruction and accumulation of water from the SCS from the eastern end of the Qiongzhou Strait.
To gain an intrinsic mechanistic understanding of the above temperature and salinity distribution characteristics, we performed numerical calculations on the temperature and circulation in the Beibu Gulf.
3. Numerical Calculation of Temperature and Circulation in the Beibu Gulf
3.1. Model Description and Configuration
To better suit the intricate coastline of the SCS, this study employed an unstructured grid model (FVCOM) [18,19]. Its use of a triangular grid in the horizontal direction facilitates the flexible representation of complex coastlines and allows for localized refinement in critical areas. FVCOM has been frequently and successfully used in previous multi-scale studies of ocean processes in various marine regions worldwide, such as the East China Sea and the Gulf of Mexico [20,21]. The model domain spans from 13.2° N to 20.6° N and from 105.6° E to 120.7° E, with 50 vertical sigma levels. The horizontal resolution is approximately 4.5 km to 30 km (Figure 4). This model has been effectively applied to investigate the Qiongzhou Strait throughflow [22]. The model depth truncation is set to 3 m. The external and internal time steps are set to 10 and 100 s, respectively. Vertical mixing is based on the MY-2.5 turbulence closure scheme [23]. Horizontal mixing utilizes the Smagorinsky turbulence closure scheme [24], with horizontal viscosity and diffusion coefficients set at 0.2. Bottom stress is determined by matching a logarithmic bottom layer to the model at a height above the bottom, with a minimum bottom roughness value of 0.0025 m. The hourly meteorological forcing data (surface wind stress, net heat flux at the surface, surface air pressure gradient, precipitation, and evaporation) are derived from the climatological average results of Climate Forecast System Reanalysis/Climate Forecast System version 2 (CFSR/CFSv2, http://cfs.ncep.noaa.gov/cfsv2.info, accessed on 15 August 2024) and European Reanalysis 5th Generation (ERA5, https://www.ecmwf.int/en/forecasts/dataset/ecmwf-reanalysis-v5, accessed on 15 August 2024) for the years 1991–2010, 2021, and 2022. The lateral boundaries utilize a nesting approach, incorporating low-frequency forcings such as sea surface height (SSH) and velocity components (u/v), as well as temperature and salinity data obtained from the Simple Ocean Data Assimilation (SODA, https://dsrs.atmos.umd.edu/DATA/soda3.4.2/REGRIDED/ocean, accessed on 15 August 2024). This dataset features a horizontal resolution of 0.5° × 0.5°, a vertical resolution comprising 50 levels, and a temporal resolution of 5 days covering the years 1991 to 2010, 2021, and 2022. The assimilated data in SODA include the World Ocean Historical Hydrographic Profile Database, the International Comprehensive Ocean-Atmosphere Data Set (ICOADS), and in situ and remote sensing sea surface temperature (SST) data obtained from the Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR). Additionally, tidal levels and tidal currents were sourced from the Tidal Prediction Experiment (TPXO) version 7.2 (TPXO7.2, https://www.tpxo.net/, accessed on 15 August 2024) for the years 2021 and 2022. Discharge data for the Red River were obtained from Luu et al. [25], while data for the other six rivers were extracted from Gao et al. [26]. The initial fields for temperature and salinity were derived from the SODA climatological average for January 1991–2010.
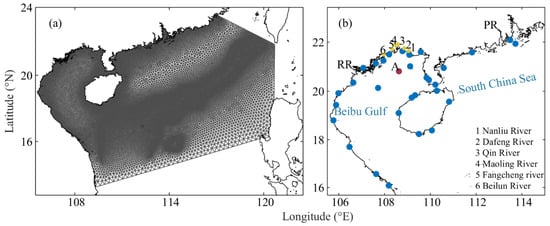
Figure 4.
(a) Unstructured mesh of the nested model in the Beibu Gulf and SCS and (b) observation stations for runoff (yellow dots), tides (blue dots), and currents (red dot, A). RR denotes Red River. PR denotes Pearl River.
The initialization procedure of the model includes two phases. Initially, the FVCOM is run from a static ocean state (“cold start”) using the initial fields and climatological forcing fields. After a 30-year spin-up period, the model reaches a quasi-equilibrium state. Subsequently, the model is run for an additional two years, from 2021 to 2022, with the second year’s results used for analysis. The validation of the climate model has been conducted by Chen et al. [22].
3.2. Numerical Calculation of the Surface Temperature Field in the Beibu Gulf in 2022
Figure 5 presents the simulated distribution of the average SST in the Beibu Gulf survey area for August 2022. Compared to the surface temperature in Figure 2, the distribution of SST is generally consistent: there is a low-temperature tongue extending northward at the bay mouth, with a minimum temperature of 28 °C, which meets the high-temperature water (31 °C) from the western Qiongzhou Strait in the central Beibu Gulf at around 19.5° N to 20° N, forming a weak front that runs east–west.
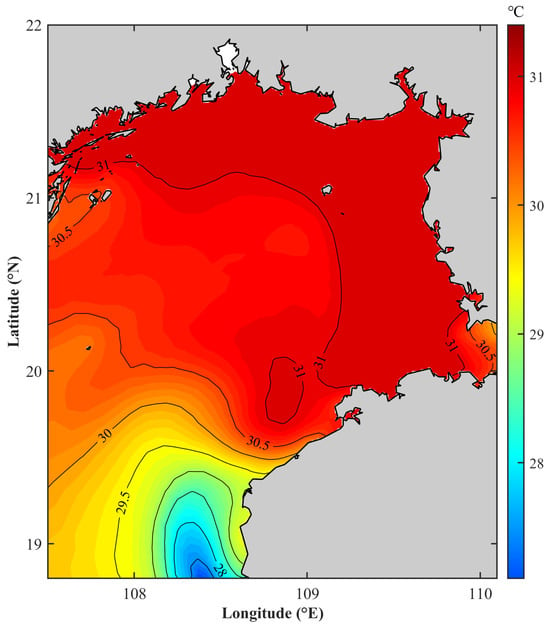
Figure 5.
Simulated sea surface temperature (SST) distribution in the Beibu Gulf for August 2022.
3.3. Results of the Circulation in the Beibu Gulf in August 2022
Figure 6 shows the surface, middle, bottom, and full-layer average circulation in the Beibu Gulf in August 2022. Compared to Figure 2, the following characteristics can be observed:
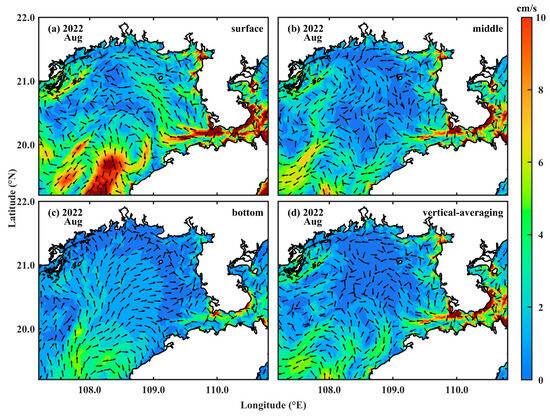
Figure 6.
Average circulation in the Beibu Gulf in the (a) surface, (b) middle, (c) bottom, and (d) full layers in August 2022.
(1) The bottom-layer circulation is very consistent with the bottom-layer temperature and salinity distribution in Figure 2.
Offshore water enters the Beibu Gulf from the middle of the bay mouth at 108° E and then moves northeastward along the gulf’s deep trough. During this movement, an anticyclonic return flow is constantly generated on the right side. The leading edge of the main flow mixes with the nearshore water on the west coast of the Leizhou Peninsula and the water from the Qiongzhou Strait, forming a front.
(2) The relationship between the surface circulation and the surface temperature and salinity distribution in Figure 2 is relatively complex.
Offshore water enters the Beibu Gulf from 108°30′ E at the bay mouth, about 30′ east of the bottom layer, and then moves northeastward along the eastern edge of the gulf’s deep trough. Near 20° N, an anticyclonic eddy forms on the eastern side of the main flow, and a relatively strong cyclonic eddy forms on the western side. This cyclonic eddy pulls the high-temperature and low-salinity water in the north towards the bay mouth so that on the western side of the advancing offshore water, the relatively high-temperature and low-salinity water in the north occupies the area. This is more obvious from the surface temperature distribution. The downwelling caused by the anticyclonic eddy on the eastern side of the main flow is the main reason for the downward concavity of the isotherms and isohalines near 108°30′ E in section P4.
(3) From the average circulation and middle-layer circulation maps, it can be seen that near 108°30′ E on sections P1 at 21°20′ N and P3 at 20°30′ N, there are current convergence zones where water converges and sinks; this is the main dynamic factor causing the downwelling in sections P1 and P3.
Figure 7 shows the multi-year average (1993–2012) of the average circulation in the Beibu Gulf in August in the surface, middle, bottom, and full layers. Compared to Figure 6, the following features can be observed:
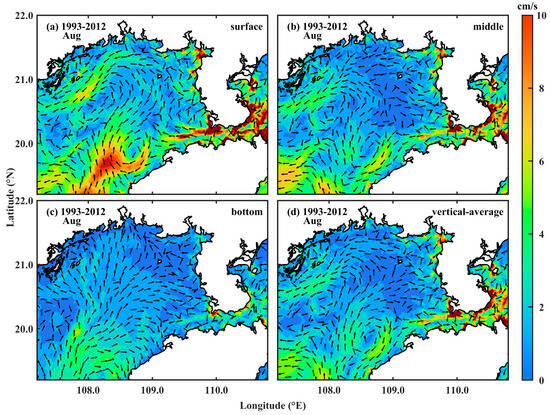
Figure 7.
Multi-year average (1993–2012) circulation in the Beibu Gulf in August at the (a) surface, (b) middle, and (c) bottom, with (d) vertical averaging.
- (1)
- The surface circulation in August 2022 was significantly different from the 20-year average surface circulation: in August 2022, the SCS water coming from the bay mouth only reached as far north as 20°20′ N before returning to the bay mouth from both sides of the main flow, whereas in the multi-year average circulation, the SCS water reached as far north as 21°20′ N before turning left and moving in a cyclonic manner.
- (2)
- The middle-layer circulation in August 2022 showed significant differences from the 20-year average middle circulation: the multi-year average circulation pattern was similar to that of the surface layer, but the SCS water only reached as far north as 21° N before turning left and moving in a cyclonic manner; in August 2022, two southward currents north of 20° N forced the SCS water coming from the bay mouth to stop near 20° N.
- (3)
- The bottom-layer circulation was basically similar between the two, indicating that the bottom-layer circulation in August, a typical summer month for the Beibu Gulf, is very stable.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of the Qiongzhou Strait Flux
What causes the aforementioned differences? We believe that the water flux in the Qiongzhou Strait is a key factor influencing the circulation patterns in the Beibu Gulf.
Table 1 presents the water flux in the Qiongzhou Strait from January to August 2022 compared to the average water flux for the same months over a 20-year period (1993–2012). Here, “positive values” indicate water entering the Beibu Gulf, while “negative values” indicate water exiting the gulf. A comparison reveals that from January to August (except for June and July, which show eastward flow), westward flow is exhibited, indicating that water from the Qiongzhou Strait enters the Beibu Gulf. In July, the difference is minimal, while in August, the difference is 1.15 × 104 m3/s, indicating that in August 2022, there was 1.15 × 104 m3/s more water entering the Beibu Gulf compared to the multi-year average.

Table 1.
Water flux in the Qiongzhou Strait from January to August 2022 and the multi-year average (Unit: 104 m3/s).
According to Xu et al.’s research results [27], the runoff during normal years for the Yangtze River is 26,460 to 29,010 m3/s; during flood years, it is 29,010 to 33,260 m3/s; and during extreme flood years, it exceeds 33,260 m3/s. It can be seen that the excess water entering the Beibu Gulf in August is nearly half of the runoff during normal years for the Yangtze River. Such a large water flux will inevitably have a significant impact on the Beibu Gulf, especially in the northern part of the Gulf; the water from the Qiongzhou Strait comes from the SCS at the eastern entrance of the strait, and August is the period when upwelling is strongest at the eastern entrance, where the temperature is lower than that at the western entrance. Both salinity and density are higher than those observed near the coastal waters of Guangxi. After entering the Beibu Gulf, the water from the Qiongzhou Strait mainly contributes to the circulation from the middle layer. Due to a high ridge underwater at the western entrance of the Qiongzhou Strait, with its top only about 15 m from the water’s surface, some of the water from the Qiongzhou Strait enters the Beibu Gulf by passing through the northerly and southerly directions of the high ridge. The water passing from the south mainly flows southward along the coast of Hainan Island; the water passing from the north of the high ridge generally moves westward along the Guangxi coast but is then deflected southward due to the obstruction of the western Vietnamese coast. In August 2022, the increased water volume compared to the multi-year average disrupted the normal water balance, causing a shift from the central coast of Guangxi to the south. As a result, two parallel southward currents emerged, altering the cyclonic movement observed in the multi-year average.
4.2. Impact of the Circulation in the Beibu Gulf on the Ecosystem
Based on the observational data and numerical calculation results for August, the northeastern part of the Beibu Gulf is a current convergence zone—the SCS water entering from the bay mouth converges with the inflow water from the Qiongzhou Strait. Large amounts of bottom water move northward, forming numerous upwelling areas along the coast. In summer, when vertical convective mixing is weakest, the upwelling can bring abundant nutrients, stimulating the reproduction and growth of phytoplankton and zooplankton and making this region an area with an excellent ecological environment in the Beibu Gulf.
This is not only the case in summer—it is also similar in winter. Figure 8 shows the multi-year average middle- and bottom-layer circulation in February. It can be seen from the figure that the northwestern part of the Beibu Gulf is where the SCS water entering from the bay mouth meets and mixes with the coastal water from the eastern mouth of the Qiongzhou Strait. The nutrient content here is richer than that in other sea areas.
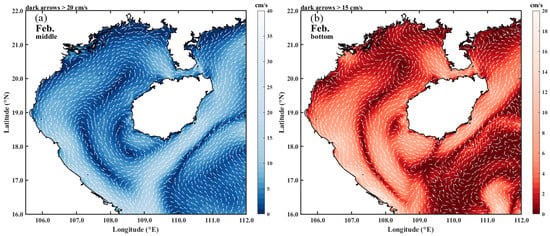
Figure 8.
Multi-year average (1993–2012) of the (a) middle- and (b) bottom-layer circulation in the Beibu Gulf in February.
There are a total of 3 phyla, 20 genera, and 59 species of large seaweeds in the Beibu Gulf. Red algae have the richest species diversity, while green algae have the fewest species, which is consistent with the number of species in each phylum of seaweeds in China [28]; the discovery sites of seaweeds are mainly concentrated in Xuwen, Guangdong, Weizhou Island, Guangxi, Lingshui, and Chengmai, Hainan.
Recognized by experts from multiple authoritative domestic institutions after marine scientific expeditions, the sea area of Weizhou Island, Guangxi, has revealed the first case of a large whale group near the coast of mainland China—the migration area of Bryde’s whales. Bryde’s whale is a national first-class key protected wild animal, with a body length of up to 12–14 m.
Dugongs are distributed in the northern part of Weizhou Island in the Beibu Gulf, feeding on seaweeds, aquatic grasses, and other succulent aquatic plants. The dugong is listed in the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. In February 2021, the dugong was listed in the National Key Protected Wild Animal List of China as a first-class species; China has established a dugong nature reserve in Hepu, Guangxi, and has strengthened the comprehensive treatment of the coastal environment, prohibiting illegal fishing.
The coastal waters in the northeastern part of the Beibu Gulf are among the gulf’s fishing grounds and are areas where pomfrets, large-scaled tongue soles, and two-spined porgies spawn all year round.
It should be particularly pointed out that typical Holocene (60 million years ago) coral fringing reefs developed in the southwestern coastal areas of Xuwen, Guangdong, the northwestern part of Lingshui, Hainan, and the waters near Weizhou Island, Guangxi (Figure 9). Based on the distribution of coral reefs in the SCS, the fringing reefs in the Beibu Gulf are the highest-latitude coral reefs along the mainland coast [29]. Their existence is related to the convergence of various waters here, forming a convergence zone front.
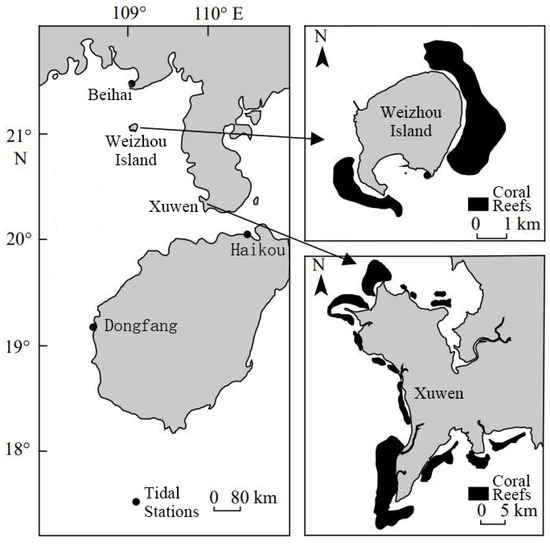
Figure 9.
Distribution of coral reefs in the northeastern Beibu Gulf [30].
5. Conclusions
Based on the summer CTD observational data from the China–Vietnam cooperative project, “Demonstration Study on Typical Bay Ecosystem Protection and Management—Four Seasons Survey of the Beibu Gulf”, this paper analyzes the horizontal and vertical distribution characteristics of temperature and salinity in the central and eastern waters of the Beibu Gulf. Using numerical results from FVCOM, the intrinsic mechanisms behind distribution characteristics in August 2022 were explored from thermodynamic and dynamic perspectives.
The surface circulation drives offshore water into the Beibu Gulf from 108°30′ E at the bay mouth, moving northeastward. An anticyclonic eddy forms near 20° N on the eastern side of the main flow, while a cyclonic eddy forms on the western side, pushing high-temperature, low-salinity water from the north towards the bay mouth. The downwelling caused by the anticyclonic eddy is the primary factor for the downwelling at 108°30′ E in section P4. The bottom-layer circulation pushes low-temperature, high-salinity water from the bay mouth northwestward along the central trough of the Beibu Gulf, forming a north–south-oriented front near 20° N upon encountering SCS water from the Qiongzhou Strait. This continues northward, forming an east–west-oriented front near 20°45′ N when it meets high-temperature, low-salinity nearshore water.
As South China Sea water flows northward, Ekman transport causes upwelling due to coastal topography, leading to the upward concavity of isotherms and isohalines near the coast, especially at stations P3, P4, P6, and P7, while convergence zones near 108°30′ E in sections P1 and P3 drive downwelling.
In August 2022, surface circulation deviated from the 20-year average due to a 1.15 × 104 m3/s increase in west flux from the Qiongzhou Strait, nearly half the Yangtze River’s annual runoff. This disrupted the typically observed cyclonic movement, causing a shift from the central coast of Guangxi to the south and resulting in two parallel southward currents.
The northeastern Beibu Gulf’s current convergence and upwelling enrich nutrients, boosting plankton growth and supporting natural marine reserves. This research is constrained by incomplete data coverage of the Beibu Gulf and the model smoothing of the complex topography of the Qiongzhou Strait, which introduces uncertainties and biases in the accuracy of the model results. This highlights the need for further refinement in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Z. and Y.C.; Data curation, Y.C., B.C., M.S. and W.H.; Formal analysis, Z.Z.; Funding acquisition, J.L. and B.C.; Investigation, Z.Z., J.L., X.Z. and M.S.; Methodology, Z.Z. and Y.C.; Project administration, B.C.; Resources, X.Z., Z.C., B.C. and M.S.; Software, Z.C.; Supervision, X.Z. and Y.C.; Validation, X.Z., Y.C., and W.H.; Visualization, Z.Z., Z.C., Y.C. and W.H.; Writing—original draft, Z.Z.; Writing—review and editing, Z.C., Y.C. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42066002, and the Science R&D Foundation of Guangxi Academy of Sciences, grant number 022107438.
Data Availability Statement
All datasets used in this study are publicly available. The model results will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
We are also grateful to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their comments and suggestions that have helped us improve the final manuscript. The survey work of the voyage received support and cooperation from all survey members of the “Asian Cooperation Special Fund Project—Exemplary Research on Gulf Ecological Protection and Management” project team and all members of maritime surveillance ship 203. The model simulation was carried out using the high-performance computer of the Marine Big Data Center, Institute for Advanced Ocean Study, Ocean University of China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, H.; Fu, D.; Liu, D.; Xiao, X.; He, X.; Liu, B. Analysis and Prediction of Significant Wave Height in the Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC017144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Ya, H.; Chen, X.; Xu, M. Impact of the water input from the eastern Qiongzhou Strait to the Beibu Gulf on Guangxi coastal circulation. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2019, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Xing-hu, W. Spatiotemporal Variation in Precipitation During Rainy Season in Beibu Gulf, South China, From 1961 to 2016. Water 2020, 12, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, B.; Shi, M. Summer circulation structure and formation mechanism in the Beibu Gulf. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 58, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Bao, M.; Guan, W.; Chen, Q. Water-mass evolution and the seasonal change in northeast of the Beibu Gulf, China. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2019, 50, 532–542. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; Bao, X.; Shi, M. Study on Circulation and Related Ecological Environment of Beibu Gulf; China Ocean University Press: Qingdao, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Yuan, Y. China Offshore Hydrology; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.H. Preliminary analysis of hydrologic structure and hydrologic feature in the sea region of the Beibu Gulf. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 1987, 4, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Liu, J. The system and pattern of the South China Sea circulation. Ocean Predict. 1993, 10, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Qiu, Z.; Chen, H. Overview of the horizontal circulation in the South China Sea. In Proceedings of the 1980 Symposium on Hydrometeology of the Chinese Society of Oceanology and Limnology; Oceanologia et Limnlolgia Sinica: Qingdao, China, 1982; pp. 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, M.; Ji, L.; Lin, J. Wind, Waves and Currents in the Northern Part of the South China Sea; Ministry of Geology South China Sea Geological Survey Headquarters Comprehensive Research Brigade: Guangzhou, China, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Li, S.; Shi, M. Three-D numerical simulation of wind-driven current and density current in the Beibu Gulf. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2001, 20, 455–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, T. Analysis of the Current and Its Mechanism in the Beibu Gulf. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Yang, J. On the mechanism of the cyclonic circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin in the summer. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z. Numerical Simulation on Seasonal Variation of Ocean Circulation and Its Dynamic Mechanism in the Beibu Gulf. Doctor Dissertation, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.W.; Hou, Y.J.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, F.; Shi, M.C. Analysis of characteristics and mechanism of current system on the west coast of Guangdong of China in summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2005, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Bao, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, F. Analysis on characteristics and mechanism of current system in west coast of Guangdong Province in the summer. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2003, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Beardsley, R.; Cowles, G. An Unstructured Grid, Finite-Volume Coastal Ocean Model (FVCOM) System. Oceanography 2006, 19, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Beardsley, R.C. An Unstructured Grid, Finite-Volume, Three-Dimensional, Primitive Equations Ocean Model: Application to Coastal Ocean and Estuaries. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhou, L.; Bi, C.; Chu, Q. Modeling the westward transversal current in the southern Yellow Sea entrance: A case study in winter 2007. Ocean Dynam 2020, 70, 803–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justic, D.; Wang, L.X. Application of Unstructured-Grid Finite Volume Coastal Ocean Model (FVCOM) to the Gulf of Mexico Hypoxic Zone. In Proceedings of the Oceans 2009 Conference, Biloxi, MS, USA, 26–29 October 2009; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Song, D.; Wang, N.; Ding, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, B.; Bao, X. Baroclinic responses of Qiongzhou Strait throughflow to different forcings. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 308, 108938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellor, G.; Yamada, T. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 851–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagorinsky, J. General circulation experiments with the primitive equations: I. The basic experiment. Mon. Weather Rev. 1963, 91, 99–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.N.M.; Garnier, J.; Billen, G.; Orange, D.; Némery, J.; Le, T.P.Q.; Tran, H.T.; Le, L.A. Hydrological regime and water budget of the Red River Delta (Northern Vietnam). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2010, 37, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xue, H.; Chai, F.; Shi, M. Modeling the circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 979–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, L. Classification of High/Medium/Low Flow Year of the Yangtze River According to Runoff at Datong Station. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2018, 35, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, B. Resource research and application perspective of macroalgae of Beibu Gulf in China. Guangxi Sci. 2014, 21, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liang, W.; Nong, H. Research Report on Coral Reef Resources in the Sea Area of the Weizhou Island; Guangxi Research Centre for Mangrove: Beihai, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T. Strengthened marine heatwaves over the Beibu Gulf coral reef regions from 1960 to 2017. Haiyang Xuebao 2020, 42, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).