Abstract
Coralligenous bioconstructions are biogenic calcareous formations developing at low irradiance on littoral rocky cliffs or on the deeper sub-horizontal bottom in the Mediterranean Sea. Unusually shallow coralligenous banks on the sandy coast of Sinuessa (Mondragone City, Gulf of Gaeta, SW Italy) were investigated. Their communities and the surrounding biogenic detritus were characterized. Geophysical and acoustic data revealed the presence of coralligenous banks between 7.5 and 15 m depth, showing constant thickness and sub-horizontal geometry, incised by sub-perpendicular channels. Sediment deposits ranging from silty sands to bioclastic gravel occur in the area. The biogenic detritus of the soft bottom sampled around the coralligenous banks is highly heterogeneous. Through the thanatocoenosis analysis of macrozoobenthos, different biocenoses were detected, among which the coralligenous and photophilic habitats are mainly represented, followed by the well-calibrated fine sands and the relit sands. A total of 16 different species and 10 epimegabenthic morphological groups (MGs) were detected on the coralligenous banks, of which 4 are included in European regulation for threatened species. The density of epimegabenthic organisms has an average of 10.34 ± 5.46 individuals or colonies/100 m2. Cladocora caespitosa is the dominant species, with a height of 17 ± 5 cm. This and other structuring species (SS) were larger in size in the sampled sites than in the literature data. Overall, coralligenous had a “medium” health status, with 52% of the individuals or colonies in healthy conditions, compared to 47% with epibiosis phenomena and 1% with entanglement. Longlines were the most common anthropogenic litter, with a density of 2/100 m2. Ad hoc monitoring programs and conservation measures would be desirable to protect and guarantee the well-being of these sensitive and rare shallow bioconstructions.
1. Introduction
Coralligenous bioconstructions are calcareous formations of biogenic origin, produced by the accumulation of crustose coralline algae (Corallinophycidae, Rhodophyta), which grow in dim light conditions, in benthic environments [1]. The irradiance reaching the sea floor defines the depth range for the formation of coralligenous frameworks. According to Ballesteros [2], coralligenous communities can develop at solar irradiances from 3% to 0.05% of the surface irradiance. On vertical slopes, the minimum depth is about 20 m, but it can be much lower (e.g., 12 m) in areas where coralligenous communities thrive in highly turbid waters near river mouths) [1]. On flat substrata, coralligenous banks frequently occur in the mesophotic zone, where rhodolith beds mostly thrive at 30–75 m depth [3,4,5,6,7], with the deepest occurrences in very clear waters at 130–170 m [8,9].
Two main types of coralligenous structures have been described: coralligenous assemblages over littoral rocky cliffs and coralligenous banks or platforms on continental shelves [10]. Banks are primarily built over a sub-horizontal substrate and display a very articulated three-dimensional structure with numerous ravines, and a thickness ranging from 0.5 to 4 m [11]. These banks (coralligène de plateau) develop from the coalescence of coralline algal nodules, known as rhodoliths or maërl, and are usually surrounded by a sedimentary substrate [12].
Coralligenous bioconstructions are considered hotspots of biodiversity in the Mediterranean Sea and benthic habitats of high conservation interest [13,14]. They are important ecosystems supporting a wide variety of marine species including algae, fishes, corals, bryozoans, sponges, and other invertebrates [15,16]. They also provide ecosystem services of social and economic relevance [17,18].
The ecological relevance of coralligenous banks and the risks posed by human activities like pollution, overfishing, and coastal urbanization make conservation efforts for these ecosystems crucial. Protecting these habitats is essential for preserving marine biodiversity and ecosystem health. Recently, the EU Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD; [19]) has led to an increase in the mapping of coralligenous habitats. Coralligenous assemblages are regarded as “special habitat types” that require monitoring and characterization as part of the MSFD’s mission to improve the environmental status of the European seas.
The presence of submerged coralligenous banks in the inner shelf off the coast of Sinuessa (Mondragone City, Gulf of Gaeta, SW Italy), surrounded by mixed bioclastic–siliciclastic deposits on the seafloor predominantly characterizing the Gulf of Gaeta, has only been recently identified through geomorphological and paleoenvironmental studies [20,21,22]. Pennetta et al. [23] and Aiello et al. [24] have reported that the banks at Sinuessa are characterized by a rocky substrate represented by spotted Campanian Ignimbrite [11,25]. However, there are no available biological and ecological studies on the presence of coralligenous bioconstructions on these banks. The occurrence of such banks at shallow depths (above 15 m) and in an area mostly characterized by a sandy substrate is particularly uncommon. Hence, the aim of this study is to characterize the macrobenthic and epimegabenthic components of the coralligenous communities of these shallow banks and the adjacent bioclastic–siliciclastic deposits.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Gulf of Gaeta, along with the Northern Campania Plain on land, forms one of the major sedimentary basins along the coastal zone of the Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea. It is bounded by the Aurunci mountains to the north, the Roccamonfina volcano to the east, and the Campi Flegrei volcanic district to the south [23,26]. The study area, known as Sinuessa, is included in the “Mondragone” Geological Sheet (n 429) at a 1:50,000 scale. Sinuessa is located on the inner continental shelf of the Gulf of Gaeta and corresponds to a ~7.5 km long and 1.5 km wide strip of seafloor, elongated parallel to the coastline. This area is characterized by relatively rough seafloor morphology, with water depths ranging from ~7.5 m to 15 m. Sinuessa is located offshore the southwestern foot of Mt. Massico, which represents a NE–SW elongated horst dividing the Garigliano and Volturno river coastal plains. The continental margin features NE–SW and NW–SE normal faults that displace the Quaternary sedimentary prograding successions [27,28,29,30], composed of siliciclastic and volcanoclastic deposits [31,32,33] (Figure 1).
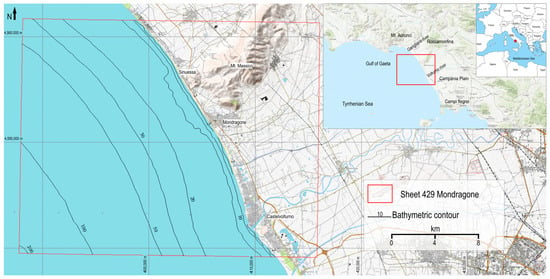
Figure 1.
Study area located in the Gulf of Gaeta (central Tyrrhenian Sea).
The Volturno river contributes to the accumulation of terrigenous sediment at its mouth, due to the hydrodynamic and morphological conditions of the area [34]. This sedimentation process significantly influences the distribution of the macrobenthos sampled in the loose seafloor deposits of the Gulf [35]. Additionally, anthropogenic activities, particularly fish farming facilities, have been linked to alterations in the structure of the soft bottom [36].
Similarly, the Garigliano River introduces freshwater input that affects a very large stretch of coast, to the north and south of its mouth, extending up to 15 km offshore [37]. Anthropogenic disturbances primarily associated with agricultural activities in the surrounding plains and urban settlements have been observed in this area [34]. Coastal waters are impacted by high concentrations of heavy metals and organic pesticides from agricultural sources, as well as microbiological contamination from urban wastewater discharge [38,39,40]. Additionally, fishing activities exert a moderate impact on the marine ecosystem [41,42,43].
2.2. Geophysical Acquisition and Processing
The study area was investigated within the activities planned by the Institute of Marine Science of Naples (CNR-ISMAR) for the geological and geothematic mapping of the Sinuessa banks (sheet n. 429; CARG project) at 1:50,000 scale (Figure 1) [44].
High-resolution bathymetric data and sediment samples were collected in an area of about 28 km2, located in front of Mt. Massico, in the depth range of 5.5–25 m.
Two multibeam echosounders were used: a Kongsberg EM 2040-C (https://www.kongsberg.com/discovery/seafloor-mapping/EM2040C-MkII/ (accessed on 14 May 2024)) and an R2 Sonic 2020-V (https://r2sonic.com/products/sonic-2020/ (accessed on 14 May 2024)), with a pole mounted on vessels equipped for hydrographic services. The inertial systems Kongsberg SeaPath130 and Applanix PosMV ensured time synchronization for positioning data from dual antenna receivers and vessel movement data from motion sensors. The synchronized position, ship heading, and motion data were transmitted to the acquisition software Sis—Seafloor Information System ver. 5 and QPS Qinsy ver. 9.4. During both surveys, an SV probe and an SV profiler yielded sound velocity values near the multibeam transducers and along the water column, required for a proper depth computation.
The survey lines were planned and traveled to have a 25–50% overlap between adjacent swaths to achieve very high-resolution seafloor coverage. Sound velocity profiles were collected twice a day in the surveyed area to calculate refractive indices along the water column.
Bathymetric data were processed using the Teledyne Caris Hips&Sips ver. 9.0 and QPS Qimera ver. 2.5 software by applying quality filters and performing a supervised data de-spiking; tide data collected by the National Tidegauge Network (https://www.mareografico.it/it/stazioni.html (accessed on 30 June 2021)) were applied to the dataset to set up the real depth.
A reflectivity dataset was also collected by means of a Klein 2000 side-scan system (https://www.oicinc.com/klein-2000.html (accessed on 16 April 2024)). The side-scan acquisition covered the entire 429-sheet CARG project (Figure 1) to a depth of 30 m, unlike the multibeam survey. The lines were spaced to provide 20% adjacent data coverage and the fish were positioned approximately 10 m from the bottom, with the vessel’s 3 knot acquisition speed. In the Sinuessa banks, enclosed in a depth range of 5 to 16 m, the acquisition range was 75 m per channel. The data were processed using SieView ver 5.0 of the MogaSoftware©. The processing workflow included navigation data smoothing, geometric and radiometric corrections [45], and exporting the acoustic mosaic in georeferenced TIFF format.
2.3. Analysis of the Macrozobenthic Thanatocoenoses of Biogenic Detritus
The sediments were sampled in 53 stations, using a 20 l Van Veen grab (0.1 m2 sample area), to characterize the macrozoobenthic thanatocoenoses. Samples were dried and sieved with mesh sizes ranging from 0.5 mm to 63 µm.
The taxonomic identification of thanatocoenoses, particularly on bivalve and gastropod molluscs, was carried out on 14 sampling stations within three sectors (Northernmost, Central, and Southernmost) close to the shallow coralligenous bioconstructions. Through their determination, Pérès and Picard [10] biocenoses were identified to characterize the soft bottom of the study area. For each sample, intact shells and bioclastic fragments were identified, where possible, at the species level.
2.4. Analysis of the Coralligenous Bioconstructions
Based on the bathymetric and geomorphological surveys of the area, seven transects were conducted using a Remotely Operated Vehicle (SEAMOR Steelhead ROV; https://rsaqua.co.uk/product/seamor-steelhead-rov/ (accessed on 22 April 2024)), equipped with an HD (high definition) navigation camera with an Ultra Short Base Line (USBL) underwater positioning system interfaced with the on-board navigation system, which allows establishing in real time the exact position and depth of the ROV. The vehicle is equipped with two spotlights and two laser pointers, spaced 13 cm apart, used for measuring the frame area and the size of the organisms. The ROV moves 0.5–1 m above the seafloor, with a speed of about 0.3–0.4 knots and a field of view width of 0.5 m.
The coralligenous community composition and the species richness of sessile taxa were estimated. The density, dominance, and health status of the epimegabenthic organisms, described as “structuring species” (SS) in the MSFD (2008/56/CE), were evaluated. The presence of “priority” species listed in Annex II of the EU Habitats Directive 92/43/EEC [46], the species subject to specific conservation plans in the Barcelona Convention [47,48], and the threatened species reported in the Global Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature [49] were also considered. Morphometry was calculated as the average height of erect and massive species and compared with the few data available in the literature.
Furthermore, the impact of fishing gear was calculated as the density of gear lost on the sea bottom, while the epimegabenthic health status (coralligenous quality: bad, medium, good, or optimum, CBQI Index [50]) was evaluated as the percentage of colonies/individuals out of the total population that exhibit epibiosis/necrosis phenomena or are covered/entangled by fishing gear.
Finally, 12 bioconstruction samples were randomly collected by scuba diving between 5 and 12 m, refrigerated, and promptly observed under a stereomicroscope (LEICA EZ4 W) to corroborate taxonomic identification from ROV videos.
3. Results
3.1. Geomorphology
The processed bathymetric data were exported to create a high-resolution image of the investigated seafloor. The final 0.25 × 0.25 m grid cell DTM covers about 28 km2 in a water depth range of 5–25 m below sea level (Figure 2a).
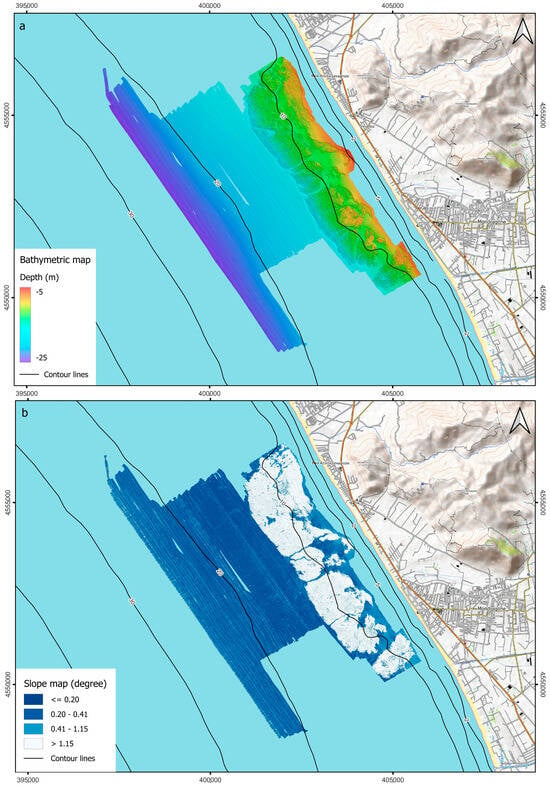
Figure 2.
(a) Shaded relief map and (b) slope map with bathymetric contour of the DTM.
The surveyed area shows an almost flat morphology interrupted by an articulated biogenic hard substrate, the Sinuessa banks, between 7.5 and 15 m depth. The coralligenous banks cover an area of about 11 km2 and rise from the seafloor for about 1–2 m. They present an elongated shape, ~7.5 km long and 1.5 km wide, developing parallel to the coastline from which it is 450 m away at its closest point. The resulting slope map (Figure 2b) shows values greater than 1.15° up to a depth of 15 m on the hard substrate, which is limited by almost sub-vertical flanks, and values between 0.5° and 0.15°, typical for the inner continental shelf environment, toward offshore.
The acoustic mosaic of the Sinuessa banks, with a pixel resolution of 1 m and details of the mosaic with a pixel resolution of 20 cm, is shown in Figure 3. The areas shown in black are characterized by the presence of coarse material, most of which consists of biogenic detritus, as evidenced by the sampling carried out in this area. Acoustic facies of high roughness with the presence of shadows and medium/high reflectivity are also evident in the mosaic, characteristic of the entire coralligenous of the Sinuessa banks. Medium-reflectivity and low-reflectivity facies, i.e., gray areas and white areas, respectively, on the acoustic mosaic can be observed in the area toward offshore, which has a homogeneous morphology and increasingly finer-grained sand deposits. The coralligenous banks are incised by channels sub-perpendicular to the coastline, some with a straight course, others meandering (Figure 2a and Figure 3). The incisions develop from about 7 m depth, varying in depths between 80 cm and 2 m and in width between 20 m and 100 m. The acoustic mosaic shows that the channels are filled with fine sand and silt (as evidenced also by the seafloor sampling), with a substantial lack of coarse-grained material that characterizes instead both the areas with articulated hard substrate and the lower parts of some channels (Figure 3).
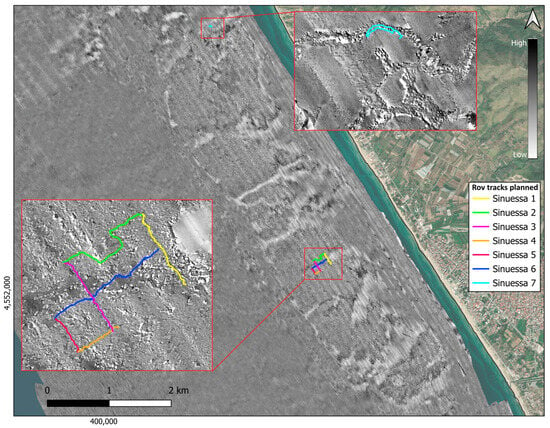
Figure 3.
Acoustic mosaic derived from side data processing (1 m pixel resolution) in grayscale (high values correspond to high reflectivity). The two insets show details of the acoustic mosaic (20 cm pixel resolution) and the planned ROV transects.
3.2. Sedimentology and Thanatocoenoses of Biogenic Detritus
Sediments collected in the study area (Figure 4) are primarily composed of very fine sand (Mz: 3.4 to 4.5 phi) and poorly sorted sandy silt (Mz: 4.9 to 6.3 phi). Samples G33, G37, G36, and G27 from the northern area and G01, G02, and G10 from the southern area, collected at a depth of ca. 10 m, are instead composed of sandy gravel (Mz: −1.5 to −1.4 phi) and very coarse/coarse gravelly sand (Mz: −0.1 to 0.6 phi). These are moderately sorted, with an abundant bioclastic content, and partly characterized by abraded and well-rounded bioclasts and lithoclasts of a yellowish-brown color (Figure 5a,d,f).
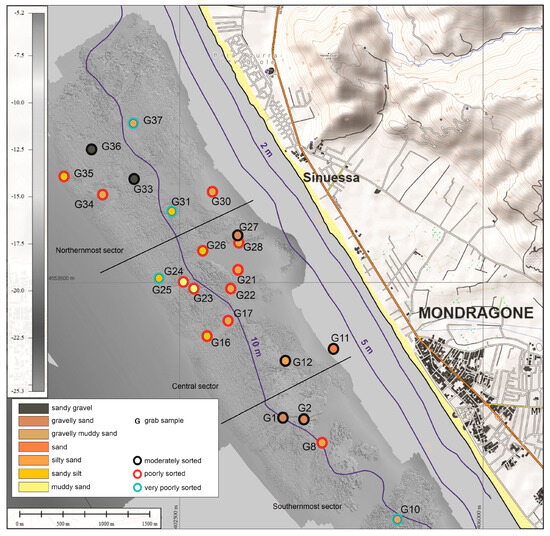
Figure 4.
Morphobathymetric map with sample location, grain size, and sorting of marine sediments.
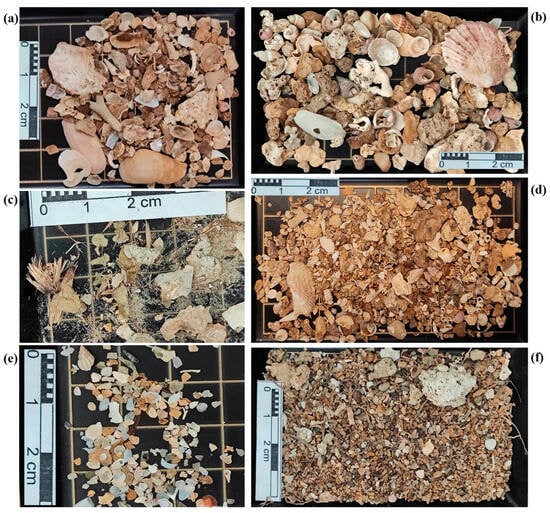

Figure 5.
Examples of biogenic detritus sampled in proximity to the coralligenous bioconstructions of the study area, composed of bivalve and gastropod shell fragments (a–f), with bryozoan (a) and vegetal (c,f) fragments.
The biogenic detritus (Table 1; Figure 5), sampled at about 10 m depth, close to the bioconstructions, reveals the presence of both coralligenous and photophilic assemblages, as well as the well-calibrated fine sand biocenosis and relict sands.

Table 1.
List of identified taxa from fragments and integral shells, sampled in 14 stations closely related to the investigated coralligenous bioconstructions, related to three sampling sectors (North, Central, South). “x” represents the presence.
In the northernmost sector of the investigated area, the sampled stations G33 and G34, located very close to the bioconstructions, are characterized by species typical of hard bottoms, as well as coralligenous habitat, such as the bivalves Lithophaga lithophaga (Linnaeus, 1758), Chama gryphoides (Linnaeus, 1758), and Striarca lactea (Linnaeus, 1758) (Figure 5a). At the same time, the taxonomical identification of intact shells, as well as shell fragments, highlights the occurrence of the photofilic biocenosis, represented by the gastropods Gibbula ardens (Salis Marschlins, 1793), Rissoina bruguieri (Payraudeau, 1826), and by Bittium spp. and Tricolia spp. (Figure 5b). They are species typically associated with algal turf and seagrasses, whose presence is also corroborated by the vegetal fiber of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, 1813 (Figure 5c,f) in stations G35 and G37. In this latter station, the very smooth and brown biogenic fragments belonging to both bivalves and gastropods occurred (Figure 5d). Nevertheless, the thanatocoenosis analyses also highlighted the presence of typical species of well-calibrated fine sand biocenosis, such as the “accompanying species” like Tritia varicosa (W. Turton, 1825), as well as the presence of Varicorbula gibba (Olivi, 1792), a “preferential characteristic species” of unstable soft bottom biocenosis. In addition, together with mollusk fragments, some Foraminifera and fragments of erected bryozoans (Figure 5a) were found.
The biogenicdetritus, coming from the central sector of the investigated area, always close to the bioconstructions (stations G21, G22, G23, and G26), reveals a similar compositional design to the thanatocoenosis of coralligenous and photophilic assemblages found in previous stations. For the latter, in addition to the genera Bittium and Jujubinus, another bioindicator species that was detected is Smaragdia viridis (Linnaeus, 1758), whose habitat is primarily related to seagrasses. Other shell fragments identified concern T. varicosa, of well-calibrated fine sand biocenosis; the genus Caecum, characteristic of sandy and muddy-sandy soft bottoms; and V. gibba, of unstable soft bottoms biocenosis. Also, foraminifers and brachiopods occurred. Together with these identified macrozoobentonic species, very smooth and brownish shell fragments were found in the study area.
Always in the central sector of the investigated area, in the sampling stations G12, G16, and G17, the thanatocoenoses suggest the occurrence of well-calibrated fine sand biocenosis, due to the presence of “characteristic species” like Peronidia albicans (Gmelin, 1791) and “accompanying species” such as Spisula subtruncata (da Costa, 1778) and T. varicosa (Figure 5e). In addition, in G12, the occurrence of gastropod Turritellinella tricarinata (Brocchi, 1814) is valuable, being a representative species of sandy muddy bottom, known at low bathymetry as “littoral sands with pelitic content” or “relict sands” [51]. Soft bottom also occurred in station G8, in the southernmost part of the investigated area, close to the coralligenous bioconstructions. Here, T. tricarinata, together with the Clausinella fasciata (da Costa, 1778) shell fragments corroborate the presence of relict sands.
Finally, always in the southernmost sampling sector, close to the coralligenous bioconstructions, stations G1 and G2 are characterized by coralligenous and photophilic assemblages, as well as detected in stations sampled in the northernmost part of the study area. All taxa detected concern the sampled size >500 µm, while in the smallest size dimensional classes, until 63 µm, the samples are composed of indeterminate shell fragments intermixed in a fine sandy matrix.
3.3. Coralligenous Assemblages
ROV transects (Sinuessa_1-Sinuessa_7, in Figure 6 and Figure 7) represent the investigated sites for the bio-ecological analyses (S_01–S_07). The first six transects were followed using a grid pattern on the coralligenous bioconstruction, crossing the biogenic detritus (black area). The last transect (Sinuessa_7) was acquired in an area to the north to verify a structure of probable anthropogenic origin.
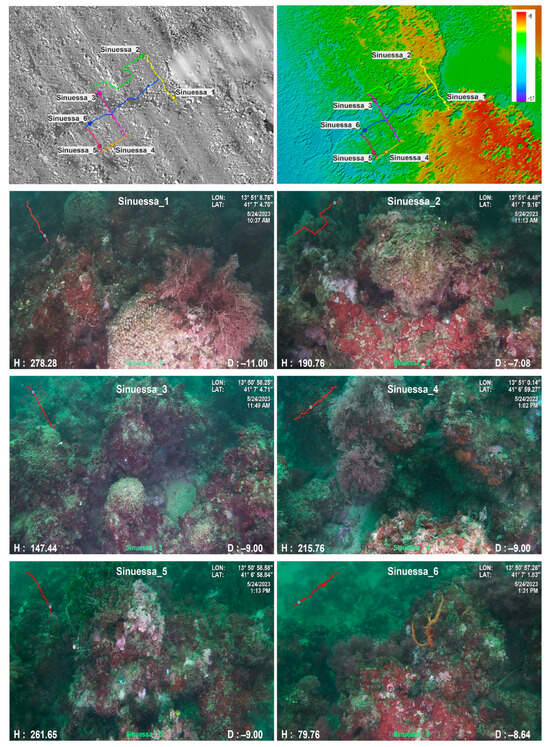

Figure 6.
ROV images of the Sinuessa_1–6 transects of the coralligenous bioconstructions.
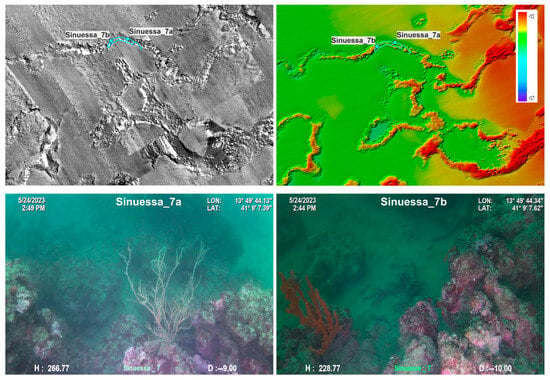
Figure 7.
ROV image of the Sinuessa_7 transect of the coralligenous bioconstructions.
Video ROV investigated an area of about 800 m2 at depths ranging from 5 to 16 m. The coralligenous bioconstructions are usually 1–2 m thick and distributed on a flat surface of sandy and detrital bottom.
A total of 16 different species and other 10 epimegabenthic morphological groups (MGs, proxy of the species when a lower taxonomic identification is not possible—sensu [49]) were detected among flora and sessile fauna (Table 2). The greatest number of species identified belonged to 3 Phyla: Rhodophyta, Porifera, and Cnidaria. Some of these taxa are sciaphilic, typical of coralligenous assemblages (Ballesteros, 2006), such as the crustose coralline algae Lithophyllum spp., Mesophyllum spp., and Peyssonnelia spp., and the sponges of the genus Axinella; otherwise, some photophilic taxa were observed, such as the Cnidaria Eunicella singularis (Esper, 1791) and Cladocora caespitosa (L., 1767).

Table 2.
List of species and morphological groups (MGs) found at each site. Density (number of individuals or colonies/100 m2) of structuring species (*) was calculated. “x” represents the presence.
Out of the total species found (16), seven structuring species (SS) were detected, of which four are included in European regulations for threatened species. In particular, an average of 15 ± 2 species, of which 4 ± 1 structuring, were identified at each site (S_01–S_07). S_07 was the site with the highest values of both total species number (17) and structuring species number (6) (Figure 8).
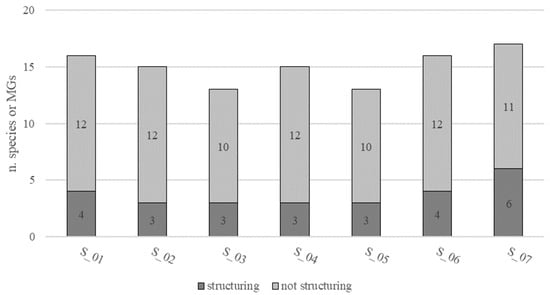
Figure 8.
Species richness as number of structuring and not structuring species or morphological groups (MGs) at each site (S_01–S_07).
The density of epimegabenthic organisms among the structuring species was estimated and ranged from 5 to 20 individuals or colonies/100 m2, with an average of 10.34 ± 5.46 individuals or colonies/100 m2, in the total study area (Figure 9). C. caespitosa was the dominant species, accounting for 93.93% in the density calculation, followed by Axinella cannabina (Esper, 1794) (2.98%), A. polypoides (Schmidt, 1862) (1.88%), Leptogorgia sarmentosa (Esper, 1791) (0.94%), and E. singularis (0.27%) (Figure 10).
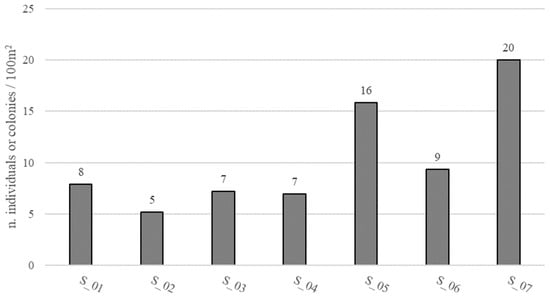
Figure 9.
Density (number of individuals or colonies/100 m2) of epimegabenthic structuring species at each site (S_01–S_07).
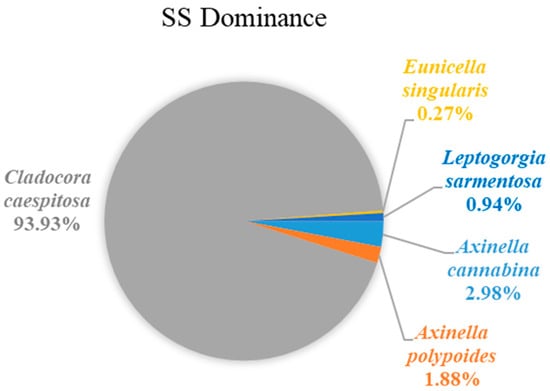
Figure 10.
Dominance (%) of epimegabenthic structuring species in the study area.
Axinella cannabina had a height ranging from 20 to 30 cm, with an average of 25 ± 7 cm; the only specimens of A. polypoides and L. sarmentosa measured were 40 and 35 cm, respectively; finally, C. caespitosa was 17 ± 5 cm high, with a minimum of 8 cm and a maximum of 35 cm (Figure 11).
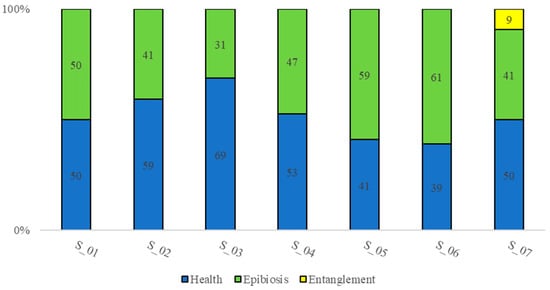
Figure 11.
The percentage of epimegabenthic structuring species in health status and damaged (epibiosis, entanglement, necrosis phenomena were not observed).
Epimegabenthic structuring species were in a “medium” health status (52%), ranging from 39% to 69% of the individuals or colonies in healthy conditions in the total population. Epibiosis was the main cause of organisms’ degradation (47%), ranging between 31% and 61%. Epibionts were mostly represented by calcareous red algae. Entanglement represents the second cause of degradation (1%) and it was detected in only 9% of species in transect S_07. Necrosis phenomena were not observed (Figure 11).
Among the anthropogenic marine litter found on the sea bottom, longlines were the most common ones, with a density of 2/100 m2. Other anthropogenic litter occasionally detected were tangles of longlines and nets, plastic debris, and other undetermined objects (Table 3).

Table 3.
Type and density (number of debris/100 m2) of anthropogenic litter (debris) found in the investigated area.
4. Discussion
Geophysical data provided an unprecedented, detailed overview of the Sinuessa banks and the channels that run through it, relics of a submerged drainage network, incised in the subaerial environment during the last glacial episode [23]. The relief areas show a constant thickness and sub-horizontal geometry and can be defined as a “tabular bank” according to the categorization of coralligenous morphotypes proposed in [52]. The rough morphology is associated with the presence of coralligenous bioconstructions and the occurrence of bioclastic gravel deposits, while the surrounding areas and the incised channels show an acoustic response associated with silty sands [53,54,55,56].
Understanding the taxonomic composition of the biotic component of an ecosystem, referred to as “biocenosis” (sensu Pérès and Picard), is crucial to assess the ecosystem functioning. In the Mediterranean Sea, benthic biocenoses are classified on bathymetry, sediment type, and plant and animal communities. The biogenic detritus around the coralligenous banks highlights the occurrence of a highly heterogeneous soft bottom. Through the thanatocoenosis analyses, carried out on the intact shells and on identifiable fragments of gastropod and bivalve mollusks, it was possible to detect different biocenoses, among which the biocenoses of photophilic algae and of coralligenous are mainly represented, since the assemblages were characterized by the sciaphilous and byssate bivalve species and macrograzer gastropods, respectively. In addition, two other biocenoses increase the heterogeneity of the investigated area: the well-calibrated fine sands, suggesting the occurrence of water currents on the soft bottom, together with relict sands [51], and the terrigenous muddy bottoms, where the reduction in water current on the soft bottom permits the increase in pelitic matrix, with the presence of the gastropod T. tricarinata.
The ROV investigations revealed the unexpected occurrence of macrobenthic and epimegabenthic components of the coralligenous communities commonly living at greater depths. These communities create a three-dimensional hotspot of benthic biodiversity in a wide area mostly characterized by a sandy bottom. This finding is even more interesting since these coralligenous platforms (i.e., on a horizontal bottom) occur at very shallow depths. Indeed, coralligenous banks are usually recorded at a minimum depth of ~20 m [1], while here at the Sinuessa they are already present starting from ~5 m depth.
The very shallow depths of these banks are likely due to the presence of the two mouths of the Volturno and Garigliano rivers and their several secondary channels, causing large sediment input that leads to high water turbidity and eutrophication phenomena for several kilometers along the shore [37].
The impact of a high sedimentation rate determines low values of both abundance and species richness, with an alteration of the structure of the soft-bottom benthic community [35]. Moreover, several studies in this area have demonstrated that there has been a general ecological deterioration of benthic communities due to chemical, toxic and genotoxic pollution of river waters, with a decrease in diversity and species richness, and dominance of few more tolerant species [40,57,58]. However, these studies refer to the vagile faunal component living in the sediments close to the two river mouths, while the hard-bottom sessile communities were never investigated until now. Our results show, conversely, that the biocenoses of coralligenous bioconstructions seem to benefit from the high turbidity and eutrophic waters. The communities of these banks result in high heterogeneity and richness, being composed of both photophilic and sciaphilic taxa, probably due to the high variability of environmental factors (e.g., light, temperature, water movements, and sedimentation rates) of the coastal water due to the intermittent inputs from the river mouths.
The coralligenous banks here investigated were composed of a relatively rich community of 26 species and MGs. Many of these taxa are considered structuring ones by the MSFD and some of them are also protected by other European regulations. In particular, Axinella cannabina (Esper, 1794) and A. polypoides (Smidt, 1862) are “Endangered” on the IUCN Red List and are included in Annex II of the SPA/BIO Protocol of the Barcelona Convention and Annex II of the Berne Convention. Eunicella singularis is “Near Threatened” on the IUCN Red List and C. caespitosa is listed in Annex II of the SPA/BIO Protocol of the Barcelona Convention. Regarding the latter species, of considerable relevance are the large dimensions of the colonies found in these marine assemblages, reaching a maximum height of 35 cm. Indeed, C. caespitosa usually has a size ranging from 7 to 13 cm [59,60,61], with a maximum of 31 cm recorded in the Columbretes Islands Nature and Marine Reserve, Spain [62]. Because of the high biodiversity that they support, these coralligenous banks might provide valuable ecosystem services of social and economic relevance, hosting species of commercial interest (provisioning services) and contributing to climate regulation through carbon sequestration and stock (regulating services) [16,17,18].
Erect and massive organisms of the epimegabenthic fauna represent particularly sensitive species to anthropogenic pressures and they are used as indicators of environmental conditions [63,64,65,66]. More in-depth studies on the biology and ecology of these species may improve their knowledge and allow a better protection of the habitats in which they thrive. For example, very few ecological studies on the epimegabenthic sponge A. cannabina are available in the scientific literature and most of them are focused on its distribution, density, and coverage [67,68,69,70,71], while morphometric data are still scarce and could not be compared to the data of this study. Axinella polypoides and Leptogorgia sarmentosa measured 40 and 35 cm, respectively, while some records reported an average of 10 ± 4 cm for the former [72] and 27 ± 18 cm for the latter [73]. Finally, C. caespitosa was particularly high at Sinuessa, i.e., 17 ± 5 cm (ranging from 8 to 35 cm), compared to the literature (15 ± 11 cm) [59,60,61,62] (Figure 12).
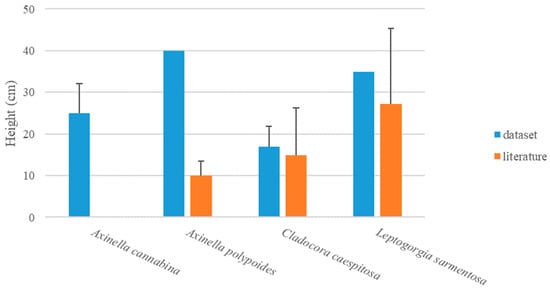
Figure 12.
Height (cm) ± SE of epimegabenthic structuring species in the study area (dataset), compared with literature data.
These data can be useful to evaluate the impact of anthropogenic activities, such as fishing, on these sensitive species and their communities.
Several anthropogenic activities, including fishing, pollution, the introduction of alien species, and climate change, pose a threat to benthic communities [15,74,75,76]. Erect or branching organisms like Cnidaria, Porifera, and Bryozoa are the most vulnerable to fishing gear, since they can be easily entangled, damaged, and overturned [77,78,79]. Longlines are the main gear impacting the epimegabenthic organisms of coralligenous habitats. Fishing activities have the potential to seriously reduce species diversity [80,81]. These impacts may result in structural and functional modifications, trophic web alterations, and transmission of inorganic and organic contaminants to the food web, ultimately harming human well-being [82].
The medium health status (sensu [50]) of the coralligenous banks, mostly evaluated by the percent of epibiosis and entanglement on epimegabenthic structuring species, reflects the presence of some pressures acting on the communities. Although the entanglement by fishing gear is clearly linked to anthropogenic activities, the epibiosis phenomena, which are the main stressors in the study area, may be also directly attributable to human activities. Epibiosis can be the consequence of mechanical damages causing tissue necrosis [15,83,84] and colonization of the structuring species, acting as a secondary substratum, by less complex ones.
These findings are particularly important for the management and conservation of the Sinuessa banks. Coralligenous habitat is prominently featured in the Council of the European Union (EC) No. 1967/2006, which addresses sustainable fishery management in the Mediterranean Sea. This regulation extends to all Natura 2000 sites, special protected areas, and Specially Protected Areas of Mediterranean Interest. Coralligenous is also classified among the “special habitat types” within the MSFD (2008/56/EC), which also recognizes “seafloor integrity” as a key indicator for assessing marine environmental health. Despite its ecological significance, Mediterranean coralligenous habitats are poorly known and are currently labeled as “Data Deficient” in the European IUCN Red List of marine habitats [85].
The discovery of peculiar very shallow coralligenous bioconstructions, along a coast characterized by sandy–muddy bottoms for several tens of kilometers, requires urgent conservation measures to protect such a relevant hotspot of biodiversity, in an area strongly urbanized. Further monitoring programs and ad hoc sampling for dating these coralligenous banks may unveil the formation rate of these bioconstructions and give more insights into how the photophilous and sciaphilous species vary over time.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.F.; Validation, F.M.; Investigation, F.F., L.D., F.M., F.R. and R.T.; Data curation, G.D.M., L.D., S.I., F.M., F.R. and R.T.; Writing—original draft, F.F., G.D.M., L.D., S.I. and F.R.; Writing—review & editing, R.S., G.F.R. and M.S.; Supervision, R.S., G.F.R. and M.S.; Project administration, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported by the funds of Regione Campania and ISPRA—Istituto Superiore per la Protezione e la Ricerca Ambientale (CARG Project—Geological Map of Italy, 1:10,000 and 1:50,000 scale).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to ISPRA for the coordinating role in the CARG Project. We thank the Captains and Crew of the M/B Lighea of ISPRA, M/B Idrosfera S.N.C., and the M/B Enviroconsult S.r.l. for their help and continuous support during all the operations of data acquisition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ballesteros, E. Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: A synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2006, 44, 123–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, E. Els Vegetals i la Zonació Litoral: Espècies, Comunitats i Factors que Influeixen en la Seva Distribució; Arxius Secció Ciències 101; Institut d’Estudis Catalans: Barcelona, Spain, 1992; pp. 1–616. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, M.S.; Amado Filho, G.M.; Kamenos, N.A.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R.; Steller, D.L. Rhodoliths and rhodolith beds. In Research and Discoveries: The Revolution of Science through SCUBA; American Academy of Underwater Sciences: Mobile, AL, USA, 2013; pp. 143–155. [Google Scholar]
- Rendina, F.; Kaleb, S.; Caragnano, A.; Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R.; Roviello, V.; Falace, A. Distribution and characterization of deep rhodolith beds off the Campania coast (SW Italy, Mediterranean Sea). Plants 2020, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendina, F.; Buonocore, E.; di Montanara, A.C.; Russo, G.F. The scientific research on rhodolith beds: A review through bibliometric network analysis. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, S.; Di Martino, G.; Romagnoli, C.; Tonielli, R. Seabed classification around Lampione islet, Pelagie Islands Marine Protected area, Sicily Channel, Mediterranean Sea. J. Maps 2019, 15, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, S.; Ferraro, L.; Innangi, M.; Di Martino, G.; Giordano, L.; Bracchi, V.A.; Tonielli, R. Linosa island: A unique heritage of Mediterranean biodiversity. J. Maps 2024, 20, 2297989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, R.; Pastor, X.; Torriente, A.; Garcia, S. Deep-sea coralligenous beds observed with ROV on four seamounts in the western Mediterranean. In Proceedings of the 1st Mediterranean Symposium on the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Others Calcareous Bio-Concretions, Tabarka, Tunis, 15–16 January 2009; pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Romagnoli, B.; Grasselli, F.; Costantini, F.; Abbiati, M.; Romagnoli, C.; Innangi, S.; Di Martino, G.; Tonielli, R. Evaluating the distribution of priority benthic habitats through a remotely operated vehicle to support conservation measures off Linosa Island (Sicily Channel, Mediterranean Sea). Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2021, 31, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, J.; Picard, J.M. Nouveau manuel de bionomie benthique de la mer Méditerranée. Recl. Trav. Stn. Mar. D’endoume 1964, 31, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Laborel, J. Marine Biogenic Constructions in the Mediterranean; Scientific Reports of Port-Cros National Park 13; 1987; pp. 97–126. Available online: https://www.portcros-parcnational.fr/sites/portcros-parcnational.fr/files/260a5f3a0255b4e119d609e159a59187.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Pérès, J.; Picard, J.M. Les corniches calcaires d’origine biologique en Méditerranée Occidentale. Recl. Trav. Stn. Mar. D’endoume 1952, 4, 2–33. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrosso, G.; Abbiati, M.; Badalamenti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Belmonte, G.; Cannas, R.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Bertolino, M.; Bevilacqua, S.; Bianchi, C.N.; et al. Mediterranean bioconstructions along the italian coast. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2018, 79, 61–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Impact of fishing activities on different coralligenous assemblages of Gulf of Naples (Italy). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2018, 98, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Rendina, F.; Sandulli, R.; Russo, G. Coralligenous assemblages: Research status and trends of a key mediterranean biodiversity hotspot through bibliometric analysis. Ecol. Quest. 2024, 35, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Tonin, S. Economic value of marine biodiversity improvement in coralligenous habitats. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 85, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, E.; Donnarumma, L.; Appolloni, L.; Miccio, A.; Russo, G.F.; Franzese, P.P. Marine natural capital and ecosystem services: An environmental accounting model. Ecol. Model. 2020, 424, 109029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E.C. MSFD 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, of 17 June 2008, establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework directive). Off. J. Eur. Comm. 2008, L164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Corrado, G.; Amodio, S.; Aucelli, P.P.C.; Pappone, G.; Schiattarella, M. The Subsurface Geology and Landscape Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain, Italy: Interplay between Tectonics and Sea-Level Changes during the Quaternary. Water 2020, 12, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, G.; Donadio, C.; Pennetta, M.; Schiattarella, M.; Valente, A. Pliocene to Quaternary morphotectonic evolution of the Gaeta Bay, Tyrrhenian coastal belt, central Italy: A review. Quat. Int. 2022, 638–639, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Amato, V.; Aucelli, P.P.; Barra, D.; Corrado, G.; Di Leo, P.; Di Lorenzo, H.; Jicha, B.; Pappone, G.; Parisi, R.; et al. Multiproxy study of cores from the Garigliano Plain: An insight into the Late Quaternary coastal evolution of Central-Southern Italy. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclim. Palaeoecol. 2021, 567, 110298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennetta, M.; Stanislao, C.; D’Ambrosio, V.; Marchese, F.; Minopoli, C.; Trocciola, A.; Valente, R.; Donadio, C. Geomorpho-logical features of the archaeological marine area of Sinuessa in Campania, southern Italy. Quat. Int. 2016, 425, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Barra, D.; Collina, C.; Piperno, M.; Guidi, A.; Stanislao, C.; Saracino, M.; Donadio, C. Geomorphological and paleoenvironmental evolution in the prehistoric framework of the coastland of Mondragone, southern Italy. Quat. Int. 2018, 493, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Got, H.; Laubier, L. Prospection sysmique au large des Albères: Nature du substrat originel du coralligène. Vie Et Milieu 1968, 19, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- De Pippo, T.; Donadio, C.; Pennetta, M.; Petrosino, C.; Terlizzi, F.; Valente, A. Coastal hazard assessment and mapping in Northern Campania, Italy. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, G.; Marsella, E.; Sacchi, M. Quaternary structural evolution of Terracina and Gaeta basins (Eastern Tyrrhenian margin, Italy). Rend. Lince Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2000, 11, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffardi, C.; Barbato, R.; Vigliotti, M.; Mandolini, A.; Ruberti, D. The Holocene Evolution of the Volturno Coastal Plain (Northern Campania, Southern Italy): Implications for the Understanding of Subsidence Patterns. Water 2021, 13, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannace, P.; Milia, A.; Torrente, M.M. 4D geologic evolution in the Gaeta Bay sedimentary infill (Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea). GeoActa 2013, 12, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Milia, A.; Torrente, M.M.; Russo, M.; Zuppetta, A. Tectonics and crustal structure of the Campania continental margin: Relationships with volcanism. Miner. Pet. 2003, 79, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alteriis, G.; Fedi, M.; Passaro, S.; Siniscalchi, A. Magneto-seismic interpretation of subsurface volcanism in the Gaeta Gulf (Italy, Tyrrhenian Sea). Ann. Geophys. 2006, 49, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.; Meo, A.; Aiello, G.; Senatore, M.R. The Neapolitan Yellow Tuff record in the Gaeta Gulf (Eastern Tyrrhenian margin, Southern Italy). Adv. Geosci. 2024, 63, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misuraca, M.; Budillon, F.; Tonielli, R.; Di Martino, G.; Innangi, S.; Ferraro, L. Coastal Evolution, Hydrothermal Migration Pathways and Soft Deformation along the Campania Continental Shelf (Southern Tyrrhenian Sea): Insights from High-Resolution Seismic Profiles. Geosciences 2018, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, O.; Niccolai, I.; Bianchil, C.N.; Tucci, S.; Morri, C.; Veniale, F. An environmental investigation of a marine coastal area: Gulf of Gaeta (Tyrrhenian Sea). In Sediment/Water Interactions, Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium 1989; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zurlini, G.; Bedulli, D. Associazioni macrobentoniche del Golfo di Gaeta e loro relazione con i fattori ambientali. In Un Esempio di Analisi Ecologica del Sistema Marino Costiero da Capo Circeo all’Isola d’Ischia; Zurlini, G., e Damiani, V., Eds.; ENEA: Serie Simposi, Roma, 1983; pp. 185–208. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzola, A.; Mirto, S.; La Rosa, T.; Fabiano, M.; Danovaro, R. Fish-farming effects on benthic community structure in coastal sediments: Analysis of meiofaunal recovery. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgente, R.; Di Maio, A.; Pessini, F.; Ribotti, A.; Bonomo, S.; Perilli, A.; Alberico, I.; Lirer, F.; Cascella, A.; Ferraro, L. Impact of freshwater inflow from the Volturno river on coastal circulation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, B.; Monini, M.; Salamone, M.; Pellicanò, R.; Di Bartolo, I.; Guida, M.; La Rosa, G.; Fusco, G. Environmental surveillance of human enteric viruses in wastewaters, groundwater, surface water and sediments of Campania Region. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 38, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, E.; Montuori, P.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Di Duca, F.; Giovinetti, M.C.; Provvisiero, D.P.; Cavicchia, C.; Triassi, M. Spatiotemporal estimation of heavy metals pollution in the Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, southern Italy: Distribution, risk assessment and loads. Chem. Ecol. 2022, 38, 327–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, P.; De Rosa, E.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Di Duca, F.; Provvisiero, D.P.; Nardone, A.; Triassi, M. Polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in water and sediment from Volturno River, Southern Italy: Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, R.; Vigliotti, M.; Prevedello, L.; Sprovieri, M.; Ruberti, D. An integrated approach to environmental quality assessment in a coastal setting in Campania (Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 70, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triassi, M.; Nardone, A.; Giovinetti, M.C.; De Rosa, E.; Canzanella, S.; Sarnacchiaro, P.; Montuori, P. Ecological risk and estimates of organophosphate pesticides loads into the Central Mediterranean Sea from Volturno River, the river of the “Land of Fires” area, southern Italy. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 678, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, C.; Virgili, M.; Bargione, G.; Petetta, A.; De Marco, R.; Punzo, E.; Lucchetti, A. Impact on macro-benthic communities of hydraulic dredging for razor clam Ensis minor in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonielli, R.; Innangi, S.; Contiero, M.; Di Martino, G.; Molisso, F.; Monti, L.; Conti, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Papasodaro, F.; Sacchi, M. Preliminary Results from New Data Acquisition off the Inner Shelf of Gulf of Gaeta, Eastern Tyrrhenian Sea, for the Geological Mapping of Sheet N° 429 Mondragone, 1:50.000 Scale (Carg Project). In Proceedings of the Geohab 2022, Venice, Italy, 16 May 2022; p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Beaudoin, J.; Clarke, J.E.; Van den Ameele, E.J.; Gardner, J.V. Geometric and radiometric correction of multibeam backscatter derived from Reson 8101 Systems. In Proceedings of the Canadian Hydrographic Conference, Toronto, ON, USA, 28–31 May 2002; p. 242. [Google Scholar]
- E.C. Council Directive 92/43/EEC (Habitat Directive) of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. As amended by the Accession Act of Austria, Finland and Sweden. Off. J. Eur. Comm. 1992, L1, 135. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Action Plan for the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Other Calcareous Bio-Concretions in the Mediterranean Sea; RAC/SPA: Tunis, Tunisia, 2008; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Action Plan for the Conservation of the Coralligenous and Other Calcareous Bio-Concretions in the Mediterranean Sea; RAC/SPA: Athens, Greece, 2017; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, Version 2022-2; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2023; ISSN 2307-8235. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 2 September 2024).
- Ferrigno, F.; Russo, G.; Sandulli, R. Coralligenous Bioconstructions Quality Index (CBQI): A synthetic indicator to assess the status of different types of coralligenous habitats. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 82, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brambati, A.; Ciabatti, M.; Fanzutti, G.P.; Marabini, F.; Marocco, R. A new sedimentological textural map of the Northern and Central Adriatic Sea. Boll. Oceanol. Teor. Appl. 1983, 1, 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Bracchi, V.A.; Basso, D.; Marchese, F.; Corselli, C.; Savini, A. Coralligenous morphotypes on subhorizontal substrate: A new categorization. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 144, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, J.; Brown, C. Correlation of sidescan backscatter with grain size distribution of surficial seabed sediments. Mar. Geol. 2005, 214, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, G.; Tonielli, R.; Di Martino, G.; Innangi, S.; Simeone, S.; Parnum, I.M. Relationships between multibeam backscatter, sediment grain size and Posidonia oceanica seagrass distribution. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micallef, A.; Le Bas, T.P.; Huvenne, V.A.; Blondel, P.; Hühnerbach, V.; Deidun, A. A multi-method approach for benthic habitat mapping of shallow coastal areas with high-resolution multibeam data. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 39–40, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innangi, S.; Innangi, M.; Di Febbraro, M.; Di Martino, G.; Sacchi, M.; Tonielli, R. Continuous, High-Resolution Mapping of Coastal Seafloor Sediment Distribution. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, M.; Lavorgna, M.; Nardelli, A.; Parrella, A. Integrated environmental assessment of Volturno River in South Italy. Sci. Total. Environ. 2004, 327, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, L.; Bonomo, S.; Alberico, I.; Cascella, A.; Giordano, L.; Lirer, F.; Vallefuoco, M. Live benthic foraminifera from the Volturno River mouth (central Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Rend. Lince Sci. Fis. E Nat. 2018, 29, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunino, S.; Pitacco, V.; Mavrič, B.; Orlando-Bonaca, M.; Kružić, P.; Lipej, L. The ecology of the Mediterranean stony coral Cladocora caespitosa (Linnaeus, 1767) in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea): A 30-year long story. Mar. Biol. Res. 2018, 14, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.; Cefalì, M.; Movilla, J.; Vergotti, M.; Linares, C. The endangered coral Cladocora caespitosa in the Menorca Biosphere Reserve: Distribution, demographic traits and threats. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 240, 106626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrototaro, F.; Tursi, A.; Logrieco, A.; Chimienti, G. Preliminary assessment of Cladocora caespitosa population at Tremiti Islands Marine Protected Area (Southern Adriatic Sea). In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Valletta, Malta, 4–6 October 2023; pp. 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kersting, D.K.; Linares, C. Cladocora caespitosa bioconstructions in the Columbretes Islands Marine Reserve (Spain, NW Mediterranean): Distribution, size structure and growth. Mar. Ecol. 2012, 33, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolloni, L.; Ferrigno, F.; Russo, G.; Sandulli, R. β-Diversity of morphological groups as indicator of coralligenous community quality status. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 109, 105840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.C.; Rützler, K. Biodiversity and abundance of sponges in a Caribbean mangrove: Indicators of the environmental quality. Smithson. Contrib. Mar. Sci. 2009, 38, 151–172. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.J.; Biggerstaff, A.; Bates, T.; Bennett, H.; Marlow, J.; McGrath, E.; Shaffer, M. Sponge monitoring: Moving beyond diversity and abundance measures. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 78, 470–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, N.R.; Foster, S.D.; Hill, N.A.; Marzloff, M.P.; Barrett, N.S. Temporal and spatial variability in the cover of deep reef species: Implications for monitoring. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalas, E.; Tsirtsis, G.; Castritsi-Catharios, J. Distribution and ecology of Demospongiae from the circalittoral of the islands of the Aegean Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Hydrobiologia 2003, 499, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, C.; Voultsiadou, E.; Chintiroglou, C. Sublittoral megabenthos along cliffs of different profile (Aegean Sea, Eastern Mediterranean). Belg. J. Zool. 2006, 136, 69. [Google Scholar]
- Gerovasileiou, V.; Voultsiadou, E. Sponge diversity gradients in marine caves of the eastern Mediterranean. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2016, 96, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, G.; Mercurio, M.; Pierri, C.; Longo, C. Three-dimensional habitat-forming species in scleractinian mesophotic ecosystems along the Apulian coast (Italy). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Milazzo, Italy, 3–5 October 2022; pp. 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez, G.; Pierri, C.; Coccia, I.; Longo, C.; Marzano, C.N.; Mercurio, M. Insights into the impact of marine litter on coralligenous structuring species in Apulia (Italy). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Milazzo, Italy, 3–5 October 2022; pp. 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Coppari, M.; Gori, A.; Viladrich, N.; Saponari, L.; Canepa, A.; Grinyó, J.; Olariaga, A.; Rossi, S. The role of Mediterranean sponges in benthic–pelagic coupling processes: Aplysina aerophoba and Axinella polypoides case studies. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2016, 477, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, F.; Bo, M.; Bava, S.; Faimali, M.; Bavestrello, G. Shallow-water sea fans: The exceptional assemblage of Leptogorgia sarmentosa (Anthozoa: Gorgoniidae) in the Genoa harbour (Ligurian Sea). Eur. Zool. J. 2018, 85, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, G.-R.; Post, E.; Convey, P.; Menzel, A.; Parmesan, C.; Beebee, T.J.C.; Fromentin, J.-M.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Bairlein, F. Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 2002, 416, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, F.; Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Sandulli, R.; Fulvio, G. Anthropic pressure due to lost fishing gears and marine litter on different rhodolith beds off the Campania Coast (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Ecol. Quest. 2020, 31, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendina, F.; Bouchet, P.J.; Appolloni, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R.; Kolzenburg, R.; Putra, A.; Ragazzola, F. Physiological response of the coralline alga Corallina officinalis L. to both predicted long-term increases in temperature and short-term heatwave events. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 150, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.R.; Althaus, F.; Schlacher, T.A.; Williams, A.; Bowden, D.A.; Rowden, A.A. The impacts of deep-sea fisheries on benthic communities: A review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73 (Suppl. S1), i51–i69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Bo, M.; Ravanetti, G.; Enrichetti, F.; Coppari, M.; Cappanera, V.; Venturini, S.; Cattaneo-Vietti, R. Evidences of fishing impact on the coastal gorgonian forests inside the Portofino MPA (NW Mediterranean Sea). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 187, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Rendina, F.; Donnarumma, L.; Russo, G.F.; Sandulli, R. Red coral (Corallium rubrum) populations and coralligenous characterization within “Regno di Nettuno MPA” (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Eur. Zool. J. 2020, 87, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S.; Hoey, A.S.; Wilson, S.K.; Messmer, V.; Graham, N.A. Changes in biodiversity and functioning of reef fish assemblages following coral bleaching and coral loss. Diversity 2011, 3, 424–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrigno, F.; Appolloni, L.; Donnarumma, L.; Di Stefano, F.; Rendina, F.; Sandulli, R.; Russo, G.F. Diversity loss in coralligenous structuring species impacted by fishing gear and marine litter. Diversity 2021, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolillo, M.; di Lorenzo, B.; Farcomeni, A.; Bo, M.; Bavestrello, G.; Santangelo, G.; Cau, A.; Mastascusa, V.; Cau, A.; Sacco, F.; et al. Distribution and assessment of marine debris in the deep Tyrrhenian Sea (NW Mediterranean Sea, Italy). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 92, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, M.; Canese, S.; Fourt, M.; Bo, M.; Innocenti, C.; Goujard, A.; Daniel, B.; Angeletti, L.; Taviani, M.; Aquilina, L.; et al. Coral forests and Derelict Fishing Gears in submarine canyon systems of the Ligurian Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 178, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPA/RAC-UNEP/MAP. Interpretation Manual of Marine Habitat Types in the Mediterranean Sea; SPA/RAC: Tunis, Tunisia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).