Heterogeneous Interaction Effects of Environmental and Economic Factors on Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Green Efficiency of Water Resources
2.2. Spatial Autocorrelation
2.3. Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression
2.4. Geographical Detector Model
2.5. Data Sources
3. Results
3.1. The Spatial Variation Characteristics of the Green Efficiency of Water Resources
3.2. Spatial Agglomeration Features
3.3. Global Driving Factors Influencing the Green Efficiency of Water Resources
3.4. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Influence of Driving Factors
3.5. Spatial Heterogeneity of Interactions between Driving Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Interactive Relationship Description
| Description | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1∩X2) > Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Bivariate enhanced |
| q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Nonlinear enhanced |
| q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independent |
| q(X1∩X2) < Min(q(X1), q(X2)) | Nonlinear weakened |
| Min(q(X1), q(X2)) < q(X1∩X2) < Max(q(X1), q(X2)) | Univariate weakened |
References
- Johnson, N.; Revenga, C.; Echeverria, J. Managing water for people and nature. Science 2001, 292, 1071–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Pittock, J.; Davis, R.; Williams, J.; Fu, G.; Warburton, M.; Udall, B.; McKenzie, R.; Yu, X.; Che, N. Global insights into water resources, climate change and governance. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Peng, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, H.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y. The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China. Nature 2010, 467, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Kong, F.Z.; Zhan, C.S. Assessment of water resources carrying capacity in Tianjin City of China. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 857–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, J.; Deng, W. Land use/cover changes, the environment and water resources in Northeast China. Environ. Manag. 2005, 36, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. China’s water scarcity. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3185–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Piao, S.; Wang, S.; Ciais, P.; Zeng, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X.; et al. Revegetation in China’s Loess Plateau is approaching sustainable water resource limits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z. Industrial water pollution, water environment treatment, and health risks in China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X. Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Xie, M.; Cheng, W.; Shu, Q. A study on the effects of regional differences on agricultural water resource utilization efficiency using super-efficiency SBM model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yin, K.; Liu, Z.; Cao, T. Spatial and temporal differences in the green efficiency of water resources in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and their influencing factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, Z.; Xu, C. Environmental regulation and regional green water resources efficiency improvement: An empirical analysis based on the Yangtze river economic belt. World 2020, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; He, J.; Wang, L. Inter-provincial water resources utilization efficiency and its driving factors considering undesirable outputs: Based on SE-SBM and Tobit model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Xue, H. Research on green total factor water efficiency of Chinese industry under environmental resource constraints. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Xie, B. A study on the dynamic evolution and spatial spillover effects of industrial green water resources efficiency: The Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example. Resour. Ind. 2020, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E. Geographically weighted regression: A method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geogr. Anal. 1996, 28, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; Fotheringham, S.; Charlton, M. Geographically weighted regression. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. D Stat. 1998, 47, 431–443. [Google Scholar]
- Páez, A.; Farber, S.; Wheeler, D. A simulation-based study of geographically weighted regression as a method for investigating spatially varying relationships. Environ. Plan. A 2011, 43, 2992–3010. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Li, L.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Pang, Q.; Zeng, X. Spatial differentiation of agricultural water resource utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt under changing environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M. Geographically Weighted Regression: The Analysis of Spatially Varying Relationships; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Crespo, R.; Yao, J. Geographical and temporal weighted regression (GTWR). Geogr. Anal. 2015, 47, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Yang, W.; Kang, W. Multiscale geographically weighted regression (MGWR). Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2017, 107, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, Y. Mapping the increased minimum mortality temperatures in the context of global climate change. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polykretis, C.; Alexakis, D.D. Spatial stratified heterogeneity of fertility and its association with socio-economic determinants using Geographical Detector: The case study of Crete Island, Greece. Appl. Geogr. 2021, 127, 102384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. Network DEA: A slacks-based measure approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 197, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Li, L.; Song, Y. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengquan, Z.; Yuanlong, H.; Teng, Q.; Jun, L.I.; School, B.; University, H. Green use efficiency of industrial water resources considering unexpected output based on SBM-Tobit regression model. J. Econ. Water Resour. 2019, 37, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Lei, Y.; Yao, H.; Ge, J.; Liu, L. Estimation and influencing factors of agricultural water efficiency in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 93–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, C.W.; Lam, N.S.N.; Quattrochi, D.A. A comparison of local variance, fractal dimension, and Moran’s I as aids to multispectral image classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Xu, W.; Ledwith, V. Use of local Moran’s I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 398, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiefelsdorf, M.; Boots, B. A note on the extremities of local Moran’s Iis and their impact on global Moran’s I. Geogr. Anal. 1997, 29, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, C.; Liu, F. Interprovincial two-stage water resource utilization efficiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichstein, J.W.; Simons, T.R.; Shriner, S.A.; Franzreb, K.E. Spatial autocorrelation and autoregressive models in ecology. Ecol. Monogr. 2002, 72, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boots, B.; Tiefelsdorf, M. Global and local spatial autocorrelation in bounded regular tessellations. J. Geogr. Syst. 2000, 2, 319–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, P.H.; Thill, J.C.; Issel, M. Spatial autocorrelation statistics of areal prevalence rates under high uncertainty in denominator data. Geogr. Anal. 2019, 51, 354–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhou, A.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y. Estimating Regional PM2.5 Concentrations in China Using a Global-Local Regression Model Considering Global Spatial Autocorrelation and Local Spatial Heterogeneity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.M. The application of local measures of spatial autocorrelation for describing pattern in north Australian landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. Quantile local spatial autocorrelation. Lett. Spat. Resour. Sci. 2019, 12, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, B.D.; Islam, S.M.N. Ordinary least-squares regression. In The SAGE Dictionary of Quantitative Management Research; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- Horrace, W.C.; Oaxaca, R.L. Results on the bias and inconsistency of ordinary least squares for the linear probability model. Econ. Lett. 2006, 90, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, R. The analysis of two-stage sampling data by ordinary least squares. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1987, 82, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotheringham, A.S.; Charlton, M.E.; Brunsdon, C. Spatial variations in school performance: A local analysis using geographically weighted regression. Geogr. Environ. Model. 2001, 5, 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Oshan, T.M.; Wolf, L.J. Measuring bandwidth uncertainty in multiscale geographically weighted regression using Akaike weights. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 2020, 110, 1500–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Brunsdon, C.; Charlton, M.; Harris, P. Geographically weighted regression with parameter-specific distance metrics. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017, 31, 982–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Smith, J.P.; Fotheringham, A.S. Targeting the spatial context of obesity determinants via multiscale geographically weighted regression. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2020, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshan, T.M.; Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J.; Fotheringham, A.S. mgwr: A Python implementation of multiscale geographically weighted regression for investigating process spatial heterogeneity and scale. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Fotheringham, A.S.; Li, Z.; Oshan, T.; Kang, W.; Wolf, L.J. Inference in multiscale geographically weighted regression. Geogr. Anal. 2020, 52, 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Su, Y.; Wu, K. Identifying the determinants of housing prices in China using spatial regression and the geographical detector technique. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.-F. Optimal discretization for geographical detectors-based risk assessment. GISci. Remote Sens. 2013, 50, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoutsos, T.; Frantzeskaki, N.; Gekas, V. Environmental impacts from the solar energy technologies. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.-m.; Wen, Z.-g. Review and challenges of policies of environmental protection and sustainable development in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 88, 1249–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Du, S. Dynamic change and spatial overflow of water resources green efficiency: A case study on Yangtze river economic zone. Resour. Ind. 2021, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, J.; Liu, L.; Shi, M. Impacts of water works investment on water resources green efficiency in Yangtze river economic zone. Resour. Ind. 2022, 24, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal pattern and influencing factors of green efficiency of water resources in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Tao, W.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, X. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influencing factors of China’s urban water resource utilization efficiency from the perspective of sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 338, 130649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik-Zada, E.R.; Ferrari, M. Environmental Policy Stringency, Technical Progress and Pollution Haven Hypothesis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik-Zada, E.R.; Gatto, A. The puzzle of greenhouse gas footprints of oil abundance. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 75, 100936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.; Wang, Y.; An, M.; Wang, L. Spatial-temporal evolution of wate resources green efficiency and potential of water-saving and emission-abating in cities along Yangtze river economic belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2023, 32, 692–705. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Liu, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F. Spatial differences and influencing factors of urban water utilization efficiency in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 890187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xue, Y.; Lan, Y.; Fu, Y. Agricultural water utilization efficiency in China: Evaluation, spatial differences, and related factors. Water 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xiaohua, Y.; Dehui, B.; Yajing, C.; Yan, L.; Zixing, Y.; Kaiwen, W. A novel approach for quantifying water resource spatial equilibrium based on the regional evaluation, spatiotemporal heterogeneity and geodetector analysis integrated model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 424, 138791. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Fotheringham, A.S. Computational improvements to multi-scale geographically weighted regression. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 1378–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, Z.; Han, Y.; Cong, P. Assessing Spatial Heterogeneity of Factor Interactions on PM2.5 Concentrations in Chinese Cities. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

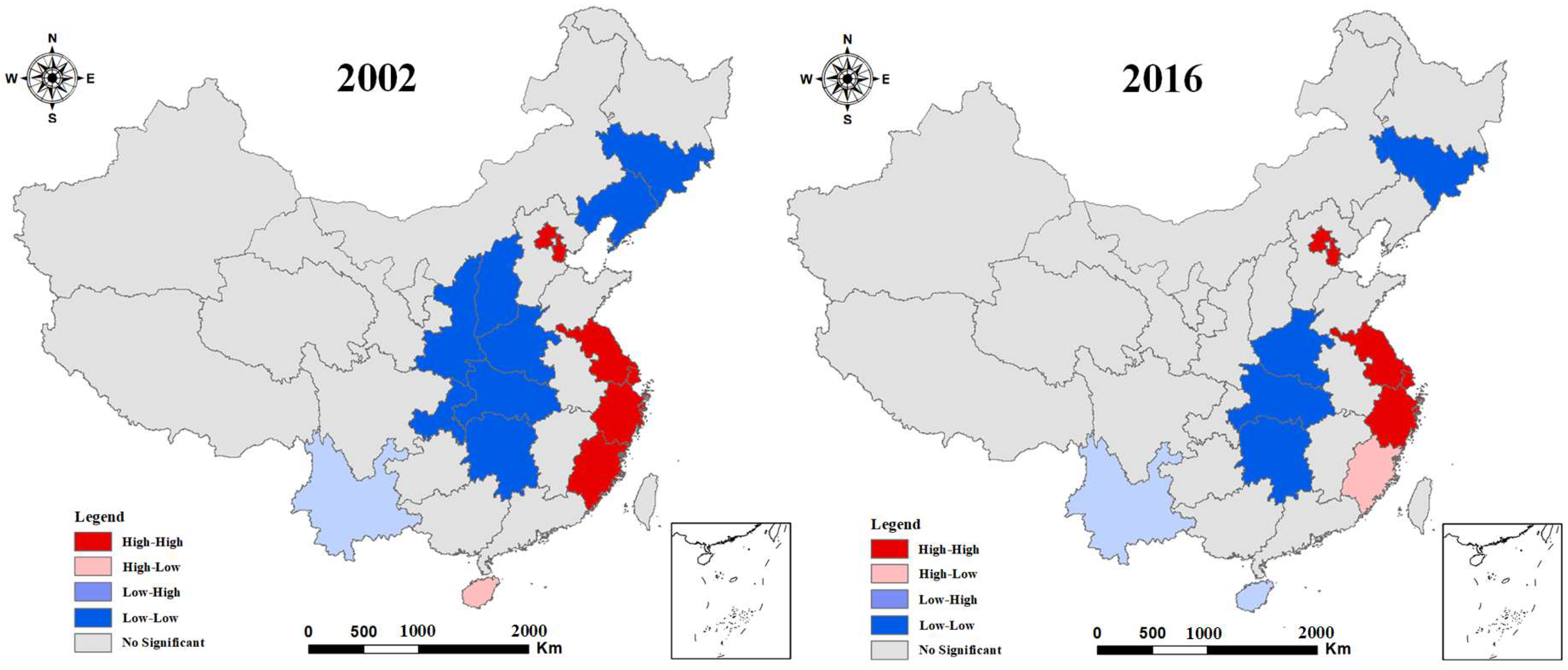
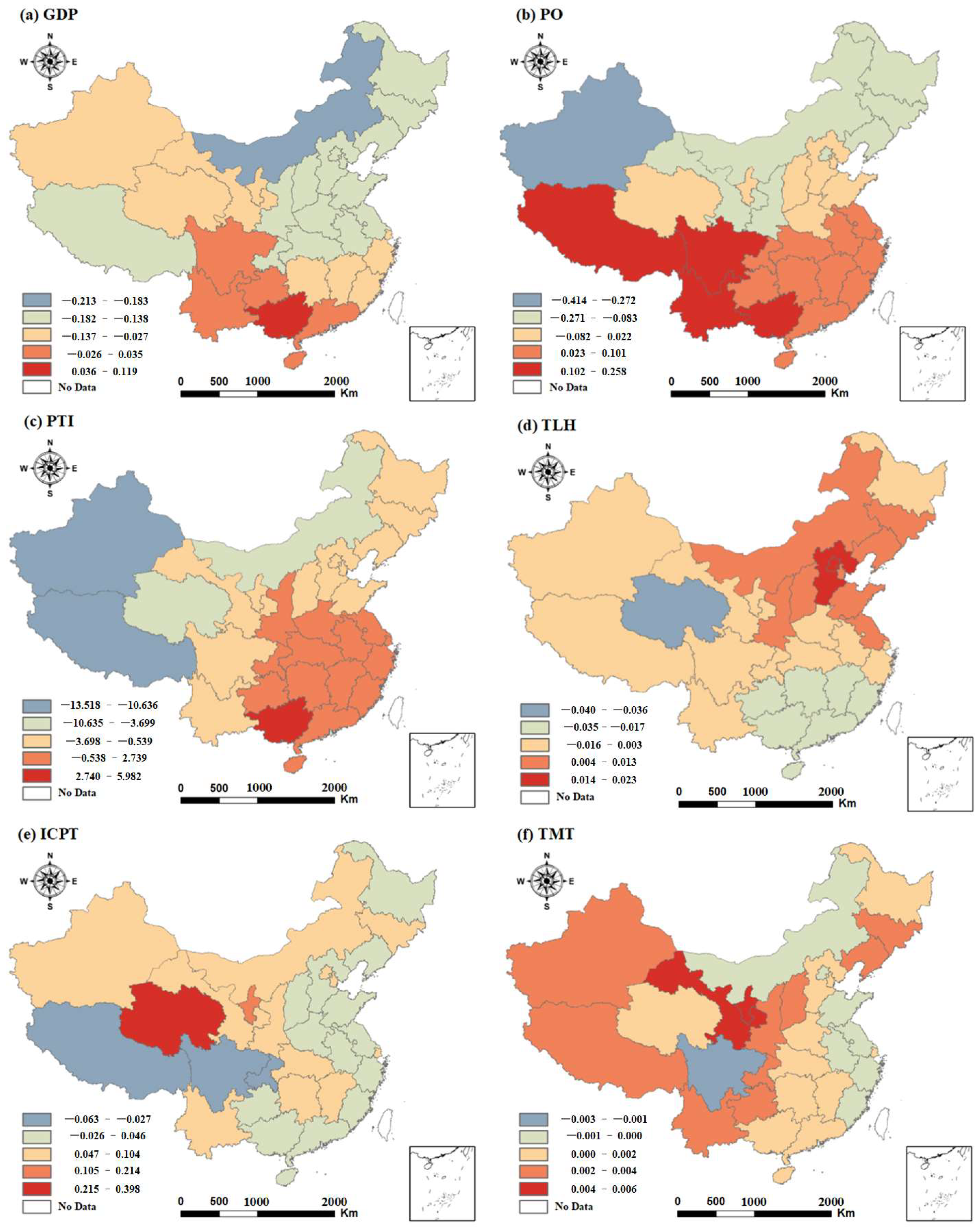

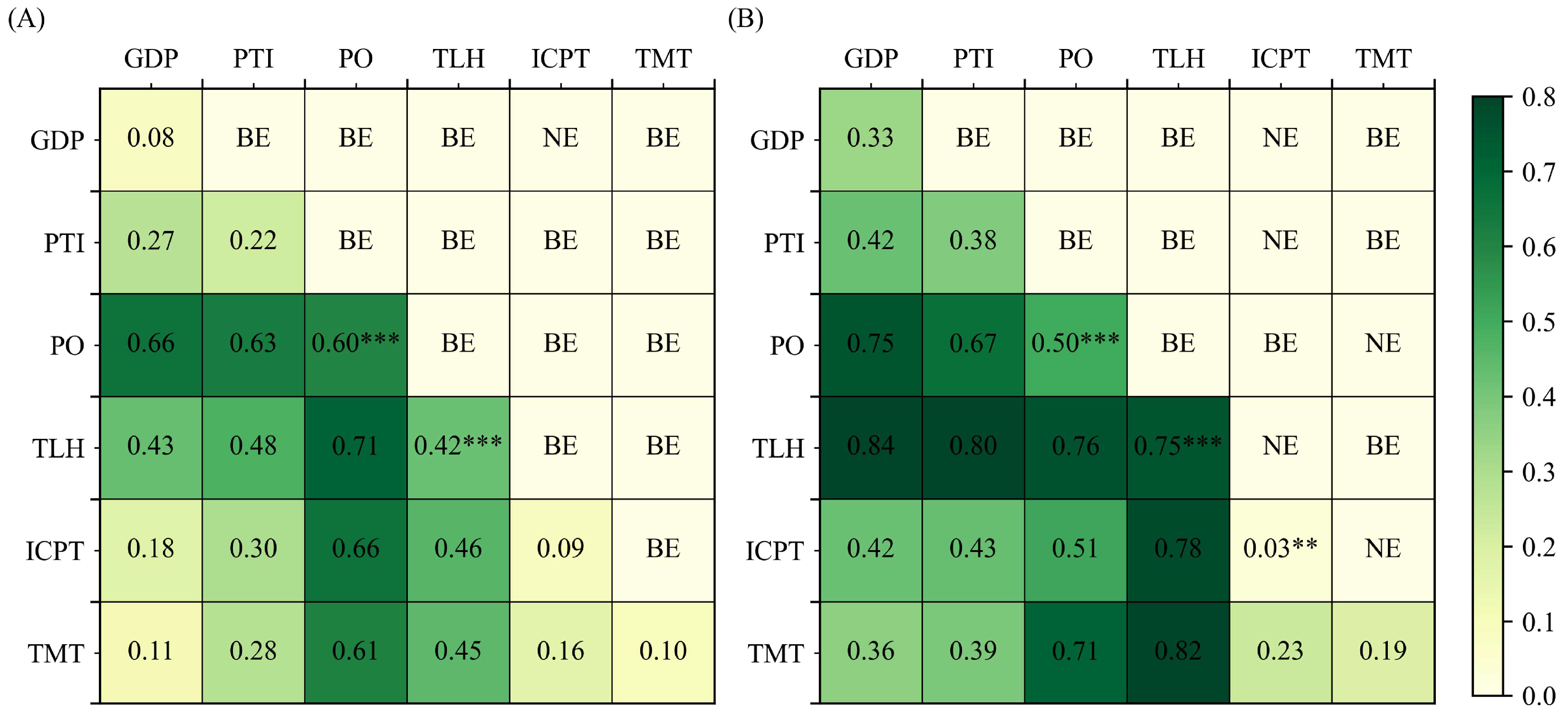

| Factor | Variable Description | Abbreviation | Spatial Resolution | Data Sources |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Socioeconomic | ||||
| Economic level | GDP per capita | GDP | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Industrial structure | Proportion of tertiary industry | PTI | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Population size | Population | PO | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Water use structure | Industrial water consumption | IWC | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Agricultural water consumption | AWC | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) | |
| Transportation infrastructure | Total length of highways | TLH | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Environment | ||||
| Pollution degree | COD discharged | COD | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Environmental protection input | Investment completed in pollution treatment | ICPT | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Technology | ||||
| Technology conversion rate | Technology market turnover | TMT | Provincial level | China Statistical Yearbook (CSY) |
| Variable | 2002 | 2016 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | VIF | Coefficient | VIF | |
| Intercept | 9.195 ** | 2.372 | 9.631 * | 1.799 |
| GDP | −0.083 *** | 1.508 | 0.005 *** | 1.692 |
| PTI | −0.594 *** | 2.669 | −0.060 *** | 1.103 |
| PO | 0.011 *** | 3.827 | 0.118 *** | 1.042 |
| TLH | 0.008 ** | 1.467 | 0.025 *** | 1.365 |
| ICPT | 0.040 *** | 1.041 | 0.072 *** | 1.052 |
| TMT | 0.001 *** | 1.282 | 0.003 ** | 1.394 |
| Models | R2 | Adjusted R2 | AIC | AICc | RSS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS-2002 | 0.643 | 0.618 | 585.424 | 599.136 | 84.250 |
| MGWR-2002 | 0.807 | 0.772 | 520.003 | 527.804 | 61.459 |
| OLS-2016 | 0.715 | 0.679 | 535.791 | 542.261 | 76.620 |
| MGWR-2016 | 0.862 | 0.834 | 477.206 | 483.290 | 58.943 |
| Variable | 2002 | 2016 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Median | Bandwidth (km) | Min | Max | Median | Bandwidth (km) | |
| Intercept | 8.192 | 9.504 | 8.733 | 30 | 8.860 | 9.935 | 9.247 | 28 |
| GDP | −0.213 | 0.119 | −0.097 | 397 | −0.182 | 0.298 | 0.011 | 383 |
| PTI | −13.518 | 5.982 | −0.682 | 418 | −6.272 | 5.580 | −0.142 | 402 |
| PO | −0.414 | 0.258 | 0.003 | 365 | −0.305 | 0.597 | 0.104 | 361 |
| TLH | −0.040 | 0.026 | 0.002 | 493 | −0.032 | 0.630 | 0.011 | 510 |
| ICPT | −0.063 | 0.398 | 0.028 | 181 | −0.031 | 0.484 | 0.062 | 166 |
| TMT | −0.005 | 0.006 | −0.001 | 572 | −0.003 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 549 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shen, W.; Zhang, Y. Heterogeneous Interaction Effects of Environmental and Economic Factors on Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China. Water 2024, 16, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202902
Jin Y, Zhang H, Shen W, Zhang Y. Heterogeneous Interaction Effects of Environmental and Economic Factors on Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China. Water. 2024; 16(20):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202902
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yuhao, Han Zhang, Weiping Shen, and Yucheng Zhang. 2024. "Heterogeneous Interaction Effects of Environmental and Economic Factors on Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China" Water 16, no. 20: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202902
APA StyleJin, Y., Zhang, H., Shen, W., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Heterogeneous Interaction Effects of Environmental and Economic Factors on Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China. Water, 16(20), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16202902






