Abstract
Since the 1970s, comprehensive control measures on soil erosion in the headwater region of the Loess Plateau have been carried out. Quantitative evaluation of the benefits of soil and water conservation measures during extreme rainstorms is of great significance for the comprehensive management of the catchments. In this study, a systematic modeling methodology for evaluating the effects of soil and water conservation measures on sediment reduction was developed based on a distributed soil erosion model (DSEM). Taking the Chabagou basin in the Loess Plateau as the study area, the tested DSEM was used to simulate soil erosion and sediment yield during an extreme rainstorm under two scenarios, the uncontrolled condition and the controlled condition with soil and water conservation measures implemented. The results showed that DSEM could successfully simulate soil and water losses and evaluate the effects of soil and water conservation measures during extreme storm events. The evaluated results showed that each soil and water conservation measure had the specific function of sediment reduction. And under rainstorm conditions, the effect of engineering measures on sediment reduction was greater than that of forest and grass measures.
1. Introduction
The Loess Plateau is one of the regions with the most severe soil erosion in the world. Due to climate change, the rainfall patterns on the Loess Plateau have changed, resulting in an increase in precipitation intensity and more uneven precipitation regions. As a result, soil erosion on the Loess Plateau is more susceptible to erosion [1]. Soil erosion is one of the most significant forms of land degradation throughout the world, and it is triggered by human-kind activities, affecting the available water resources, the biota, and soil fertility [2,3,4]. As one of the most serious soil erosion regions in the world, the Loess Plateau region, with a total area of 0.64 million km2, is located in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin in northern China, suffering from a soil loss rate even higher than 10,000 t.km2/a. The severe soil erosion in the Loess Plateau region not only causes local soil quality degradation, which affects agricultural activities, the safety of hydroengineering projects, ecological restoration, and environmental protections [5] but also causes sedimentation in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, making the Yellow River a world-famous “overhanging River”, where the elevation of the river channel is higher than the land surface behind the artificial levees [6].
To control the soil erosion in this typical region with a subtropical climate, soil and water conservation measures have been practiced in some tributary drainage basins since the 1970s. Especially since 2000, with the implementation of afforestation and the construction of check dams, soil and water conservation has been greatly enhanced. As of 2015, there are a total of 56,422 silt dams in the controlled areas above Tongguan Hydrological Station, including 5658 large dams, 11,248 medium dams, and 39,516 small dams [7]. Numerous studies have indicated that the soil and water conservation measures had an obvious effect of reducing sediment and effectively curbing the continuous development of soil erosion. Observation suggested that there had been a significant decline in the sediment load in the upper and middle reaches of the Yellow River due to soil and water conservation measures [8,9,10,11]. The measured sediment discharge in the Yellow River of Tongguan station decreased from an average of 15.9 million tons in 1919~1959 to an average of 2.78 million tons in 2000~2013, and the sediment reduction rate reached 82.5% [12,13,14]. Since the 1980s, many studies have been devoted to evaluating the effect of soil and water conservation on sediment reduction at an inter-annual time scale. However, only a few studies are related to sediment reduction by specific soil and water conservation measures under rainstorm events, which is crucial for precise watershed management.
To evaluate the benefits of specific soil and water conservation measures, traditional methods include the “watershed hydrological approach” and “observation approach” [15,16,17]. The “hydrological approach” refers to using the hydrological data measured at the watershed scale in the base period (namely, without soil and water conservation measures) to establish the empirical model for predicting sediment yields and then substitute the rainfall regime of the target period for evaluation into the established model for the base period and to calculate the reduction in sediment yield in the target period using the gross soil and water conservation measures. In the Chinese Loess Plateau, the 1970s could usually be taken as the base period for when soil and water conservation measures had not been implemented [18]. However, the effect of individual measures on sediment reduction cannot be evaluated by this method. And furthermore, the limited hydrological dataset was available in most watersheds before the 1970s. The “observation approach” is used to determine the sediment reduction per unit area of the land with or without soil and water conservation measures, by analyzing the sediment reduction data observed in runoff experimental plots in different regions. Multiplying the sediment reduction rate and the land area of individual measures, the sediment reduction by the individual measure can be obtained. However, the scale conversion of the sediment reduction index from the experimental plot to the watershed has not been solved.
In recent years, with the development of remote sensing and GIS technology, the combination of GIS and advanced in situ observations has gradually made the distributed hydrological model at the watershed scale to be applied in the evaluation of soil and water conservation measures implemented in basins. The distributed watershed hydrological model could better represent the spatial variations of underlying surfaces than most of the conceptual lumped models [19]. At present, the distributed watershed hydrological models widely applied abroad include USLE, RUSLE, WEPP, SWAT, LISEM, WATEM/SEDEM, etc. The objects simulated by these models were mostly gentle slopes, but there are a large number of steep slopes distributed on the Loess Plateau. Due to the significant differences in erosion patterns between steep and gentle slopes, directly applying these models will result in significant errors [20,21]. So, the objectives of this study are (1) to establish and to test the distributed soil erosion model in the middle reach of the Yellow River and (2) to evaluate the sediment reduction effects of individual and gross soil and water conservation measures during an extreme storm event by the distributed watershed soil erosion model.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in the Chabagou creek (latitude 109°47′ E, longitude37°31′ N; See Figure 1) and covers an area of 201 km2 with Caoping hydrometric station as its outlet. The Chabagou creek is a second-order tributary of the Wudinghe River and a third-order tributary of the Yellow River. It has a monsoon climate with mean annual precipitation of between 200 and 600 mm, which predominantly occurs from June to September. The rainfall in these 3 months often accounts for 60~70% of total annual precipitation, and most of the rainfall events have high intensity with extremely high and coarse sediment yield, so soil erosion predominately occurs in this period. The average hourly temperature varies between −18 °C and 38 °C, with the highest temperature observed in July and the lowest temperature in January. The soils are mainly composed of mountain gray loamy soil, gray loess soil, and loamy soil, all of which are typical representative soil types of the Loess Plateau. These soils are loosely compacted and susceptible to water erosion [22]. The rainstorms were characterized by short and high intensity as well as the concentrated Hortonian flow, which made the loess soil surface steep-gullied.
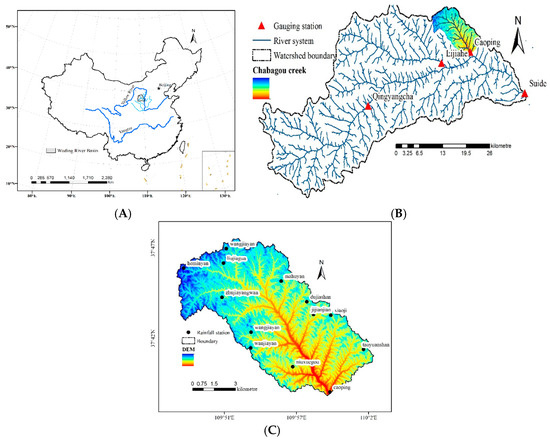
Figure 1.
(A) The location of the Wudinghe basin (gray shading) in the middle reaches of the Yellow River basin, China. (B) Location of the Dalihe watershed (color shading) in the Wudinghe basin. (C) An overview of the Chabagou creek.
In this study, a catastrophic rainstorm (From 8:00 p.m. on 25 July to 8:00 a.m. on 26 July 2017) occurred in the Wudinghe basin, the first tributary of the Yellow River in Northern Shaanxi Province. The rainstorm center was mainly concentrated in the Dalihe Basin, the first tributary of the Wudinghe basin. The rainstorm center happened at Zhaojiabian rainfall station with a precipitation of 252.3 mm within 12 h. The precipitation of all 34 rainfall stations exceeded 100 mm, of which 10 rainfall stations even exceeded 200 mm. Precipitation above 50 mm covered 97% of the Dalihe basin area, and precipitation over 100 mm covered 66% of the Dalihe basin (Figure 2).
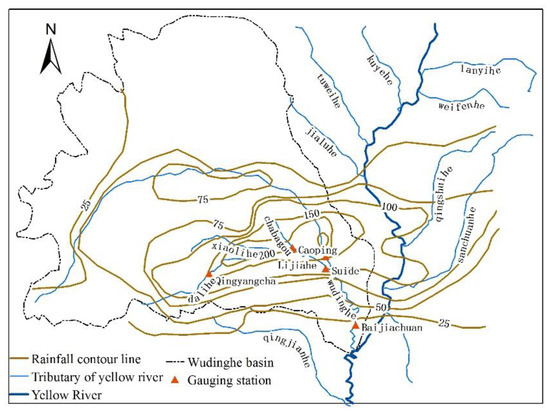
Figure 2.
Rainfall equivalent line of the “26 July 2017” event in the middle reaches of the Yellow River.
This heavy rainstorm caused a super flood in the Wudinghe basin. The peak discharge at 5:05 am on July 26 at Suide station of Dalihe basin was 3160 m3/s, exceeding the maximum discharge of 2450 m3/s in 1960 when the observation data were available. At the same time, the sediment concentration of the flood was also high in the basin. For example, the sediment concentration of the Baijiachuan hydrological station in the Wudinghe basin reached 872 kg/m3, and that of the Suide hydrological station in the Dalihe basin reached 849 kg/m3. The sediment concentration of the Caoping hydrological station in the Chabagou catchment, the tributary of the Dalihe basin, was 270 kg/m3, and the total amount of sediment yield above this hydrological station was 86.6 thousand tons (Figure 3) [23].
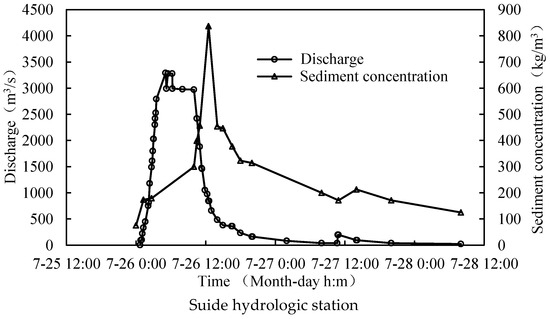
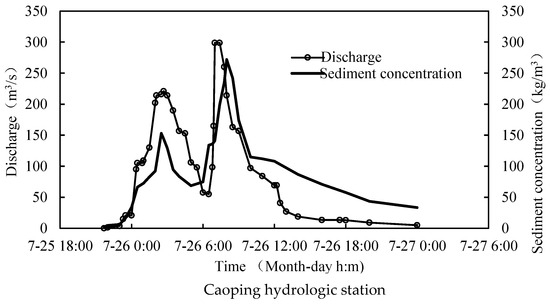
Figure 3.
Stream flow dynamic during the extreme event in Suide and Caoping hydrologic station.
2.2. Set up of Base Year and the Extreme Storm Year
Before 1980, the Chabagou creek was intensively cultivated except for steep areas. For instance, the percent of the cultivated land area was as high as 65%, among which the percent of land area steeper than 20° was as high as 68%. Watershed management for soil conservation was not extensively implemented in that period. In contrast, the basin was under intensive soil conservation after 1980, especially the full implementation of the project of Grain for Green in 2000, a large number of hydrologic engineering works, such as check dams, intercepted large quantities of sediment [24]. The double cumulative curve analysis method is often used to determine the turning point when soil and water conservation measures have a significant impact on sediment yield and runoff [25]. By analyzing the double cumulative curves of annual precipitation, sediment yield, and runoff in Chabagou creek, the turning point of the Chabagou creek was also in the 1970s. Considering the earliest available remote sensing image to interpret the watershed land use, the year 1978 is determined as the base year, and the year 2017, when the extreme rainstorm event on 26 July 2017 occurred, is considered the extreme storm year.
2.3. Data Preparation
There were thirteen rainfall stations and one hydrological station in the Chabagou creek (Figure 1). The precipitation and rainfall processes of the single rainfall event in 1960–1978 at the pre-changed period of 13 rain gauge stations inside the watershed were obtained from the Bureau of Hydrology, Yellow River Conservancy Commission. Runoff and sediment data of all the hydrological stations at each single rainfall event were also provided by this institute and were used to calibrate the soil erosion model in this study. Notably, the precipitation, runoff, and sediment dynamic of the extreme rainstorm “26 July 2017 event” was also obtained from this institute.
Land use and land cover in 1978 was obtained by interpreting the Landsat TM image, and land use and land cover in 2017 was obtained by interpreting the GF-2 image combined with field investigation. Land use and land cover were classified into ten categories: forestland, high-cover grassland, medium-cover grassland, low-cover grassland, residential land, barren land, arable land, road, terrace, and check dam land.
2.4. Soil Erosion Model Description
In this study, the soil erosion evolution process during the extreme flood event was simulated using the distributed soil erosion model (DSEM) independently developed by the Yellow River Institute of Hydraulic Research (Authorized by National Copyright Administration of the People’s Republic of China with the certificate number of 2011SR017739). The distributed erosion model is a DEM-based surface runoff and sediment yield model. The catchment was represented as a matrix of cells formed through the discretization of the catchment using square grids. The cell topographic properties, such as DEM, land use, and roughness, for each discretized cell of the catchment were extracted and analyzed based on GIS. The model comprised four main components: runoff generation, soil erosion, watershed flow concentration, and sediment transport. The runoff and sediment yield are coupled. That is to say, according to the runoff depth, flow velocity in each time step of each grid, the flow discharge, and the sediment yield in each period are calculated for the grid based on the runoff generation and overland flow model. So, the DEM-based model can be used to simulate the runoff and sediment processes and their spatiotemporal distribution. The overall framework of the model is shown in Figure 4.
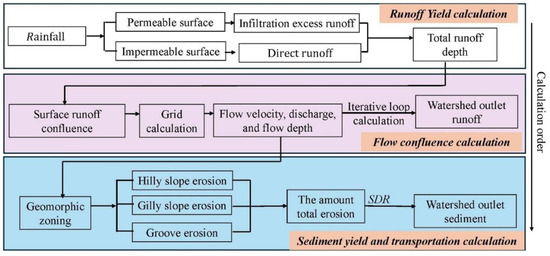
Figure 4.
The framework of DSEM.
2.4.1. Runoff Generation Calculation
(1) Runoff Yield calculation
The calculation of runoff yield is divided into two parts: runoff on impermeable surfaces and runoff on permeable surfaces. For the impermeable surface, rainfall minus evapotranspiration is the yield of runoff. Due to the gully region of the Loess Plateau being located in an arid area, the main mode of runoff generation is infiltration excess. For the permeable surface, the runoff yield depends on the comparative relationship between rainfall intensity and infiltration intensity. The Horton infiltration model is employed because of its physical basis and simplicity. The Horton infiltration model is as follows:
where is the potential infiltration rate (m/min) when the soil surface receives unlimited water supply (mm/min); is maximum infiltration rate (mm/min); is initial infiltration rate (mm/min); t is infiltration time (min); and k is a coefficient that changes with the soil, calibrated by measured data.
(2) Flow confluence calculation
The isochronous method is mainly used to calculate surface runoff. When using the isochronous method to calculate surface runoff, the first step is to calculate the transition time from the center point of the flow generation grid to the outlet of the river channel. The convergence time is as follows:
where is convergence time of each grid, min; is velocity constant, which includes the influence of factors such as roughness and hydraulic radius on the flow; is the length of the flow path from each grid to the outlet of the river channel, m. S is the slope of the flow path from each grid to the outlet of the river channel, ‰. is the runoff velocity, which is calculated using Manning’s formula, m/s.
The isochronous method to calculate surface runoff is as follows:
where is the net rainfall on the ground in the i-th period, mm; ,, … is the area between each isochronous line, m2.
2.4.2. Sediment Yield and Transportation Calculation
Catchments in the hilly gully region of the Loess Plateau displayed clear vertical zoning from the slope top to the valley bottom. The profile is divided into the hilly slope, the gully slope, and the gully bottom (Figure 5) [26]. The calculation formulas of soil erosion in the different topographic units are deduced by means of the energy balance principle [27].
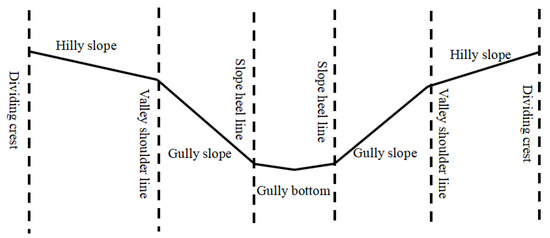
Figure 5.
Illustration of types of erosion on the Loess Plateau.
- (1)
- Hilly slope erosion
The soil erosion of the hilly slope Er can be written as
where is the runoff depth in the hilly slope, mm; is the slope of the hilly, ‰; is the slope of the hilly in degree; is the sediment particle size; mm; is the friction coefficient taking 0.047; and are the bulk density of dry sediment and wet sediment, respectively, g/cm3; is the average velocity of surface flow in the hilly slope, m/s; is a dimensionless coefficient calibrated by measured data; and is the width of the hilly slope, m.
- (2)
- Gilly slope erosion
The soil erosion of the gully slope Eg can be written as
where is water depth in the gully; is the slope of a gully in ‰; is slope of a gully in degree; is the average velocity of surface flow in gully slope, m/s; is a dimensionless coefficient calibrated by measured data; and is the width of the gully slope, m. Other parameters are the same as above.
- (3)
- Gully erosion
The soil erosion of the gully Ec can be written as
where is gravitational acceleration, m/s2; is the average velocity of surface flow in the gully, m/s; is shear stress, ; is bulk density of dry sediment, g/cm3; is runoff depth, mm; J is the channel gradient; is a non-dimensional coefficient and calibrated using measured data.
- (4)
- Sediment yield
The total erosion E is obtained by adding up :
The sediment yield in the watershed is calculated using the sediment delivery ratio (SDR) of the single rainfall [28].
where SDR is the sediment delivery ratio; is the time when the maximum rainfall occurs during a rainfall process, min; is the rainfall duration, min; is the peak discharge, m3/s; is the runoff; m3; is the watershed area; km2; is the specific gravity of water; kg/m3; is the volume density of the sediment-laden flow, ; is the sediment concentration, kg/m3; is the sediment bulk density, kg/ m3; and , and are the calibrated parameters.
2.5. Method to Evaluate the Benefits of Soil and Water Conservation Measures
After calibration of the DSEM with a satisfied performance (R2 = 0.85, NSE = 0.57, Figure 6) for sediment yields during the observation period of 1960–1980, simulations of two specific scenarios were designed in order to evaluate the impacts of the conservation measures on soil erosion in the flood event on 26 July 2017 based on the DSEM.
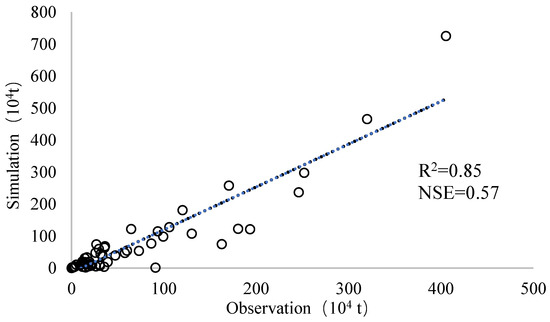
Figure 6.
Model calibration results.
W1: the potential soil erosion based on the calibrated distributed soil erosion model with the observed rainfall on 26 July 2017 and the underlying surface in 1978 was conducted.
W2: the control soil erosion with the observed rainfall on 26 July 2017 and the underlying surface in 2017, excluding the reservoir influences in the gully.
Based on the first scenario simulation result, combining the observation of sediment discharge of the Caoping hydrological station on 26 July 2017 (Ws), the difference between W1 and Ws (W1 − Ws) was used to estimate the changed magnitude of sediment reduction caused by the implementation of the soil and water conservation measures:
Based on the second scenario simulation result and the observation of sediment discharge of the Caoping hydrological station on 26 July 2017 (Ws), the impact of gully channel control measures, such as check dams and reservoirs on soil erosion, was analyzed. For the small watershed in the hilly gully region, the sediment production and transportation would reach balance in a short time. Thus, the difference between W2 and Ws (W2 − Ws) was used to represent the changed magnitude of the sediment reduction by gully channel engineering measures.
The sediment reduction in the slope control measures () can be obtained by reducing from , and the contribution of the slope control measures variation and channel engineering measures can be quantitatively estimated using the following equations:
where and represent the contributions of total soil and water conservation measures, channel engineering measures, and slope control measures in relation to the year 1978, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. Land Use and Vegetation Cover Dynamic
From the remote sensing images in different periods, land use structure was observed. Among the ten land use types, arable land and terraces changed dramatically during the entire study period (Table 1, Figure 7). From 1978 to 2017, in the total study area (201 km2), the area of arable land decreased significantly, while the area of grassland increased sharply. In particular, the area of medium-cover grassland increased obviously. In 1978, the arable land was 114.33 km2, accounting for 56.88% of the study area. The medium-cover grassland was 59.87 km2, accounting for 29.79% of the area of the basin. However, in 2017, the arable land was 39.96 km2, accounting for 19.88% of the area of the study area. The medium-cover grassland was 106.87 km2, accounting for 53.17% of the area of the basin. The effect of returning farmland to the forest (grass) has been remarkable in the last 30 years. Furthermore, since 1983, the Chabagou catchment has been listed as a key control area of the Wudinghe basin, where the construction of terraces, afforestation, and grass planting on the arable land had been implemented. It is noted that the area of the terrace increased from 0 to 21.17 km2 (Table 1), which caused distinct differences in the landforms.

Table 1.
Area and percentage of land use type in the Chabagou catchment (km2).
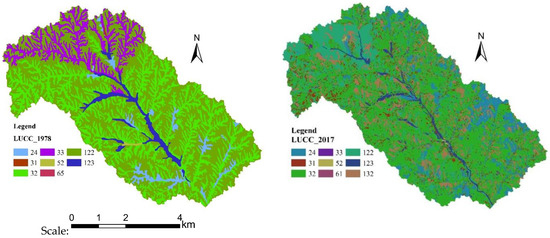
Figure 7.
Land use distribution in different periods in the Chabagou catchment. Note: road refers to the main road with cement.
Fractional Vegetation Cover (FVC) is an important index used to measure the vegetation status. The FVC of the Chabagou catchment in different periods was calculated using the dimidiate pixel model (Figure 8). As shown in Figure 6, from 1978 to 2017, the FVC of the Chabagou catchment was significantly improved. The average FVC was 19% and 68% in the years 1970 and 2017, respectively. Compared with the vegetation coverage in 1978, the vegetation coverage increased by 257% in 2017.
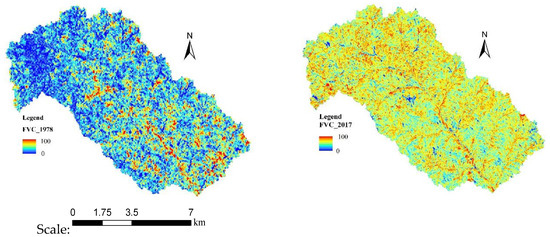
Figure 8.
Vegetation coverage distribution in different periods in the Chabagou catchment.
3.2. Sediment Yield Responses to the Extreme Storm under Different Underlying Surfaces
Based on the land use and vegetation coverage in 1978, the runoff and sediment yield process of the “26 July 2017” rainstorm under the underlying surface conditions in 1978 was simulated by the DSEM (Figure 9). The measured runoff and sediment yield process were recorded on 26 July 2017, and the simulated runoff and sediment yield process of the extreme rainstorm under the underlying surface conditions was used for comparison and calculation. Compared with the runoff process of the untreated underlying surface representing 1978, the measured maximum discharge in 2017 had been reduced by 57%, the runoff had been reduced by 34%, and the flood peak occurrence time had been delayed by 4.5 h. Meanwhile, the measured maximum sediment transport rate had been reduced by 65%, the sediment yield had been reduced by 80%, and the sediment peak occurrence time was delayed by about 2 h. The sediment reduction magnitude by the soil and water conservation measures was greater than that of runoff reduction.
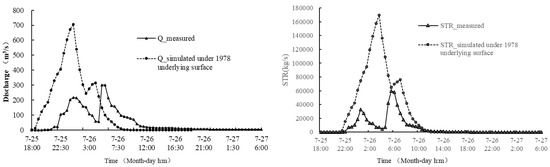
Figure 9.
The measured and simulated runoff (left) and sediment yield (right) processes. Note: Q is discharge, and STR is sediment transport rate.
Utilizing the soil erosion model DSEM, the spatial distribution of eroded thickness was obtained. Then, the sediment yield of the “26 July 2017” rainstorm under the underlying surface in 1978 was calculated based on the spatial distribution of the eroded thickness. The results of the model calculation showed that the sediment yield under the underlying surface in 1978 in the case of the occurrence of the event “26 July 2017” was 4.131 million tons. In order to evaluate the sediment reduction effect of the forest, grass, terrace measures, and gully blocking engineering measures, respectively, the sediment yield of the “26 July 2017” extreme rainstorm on the underlying surface condition without considering check dam interception in 2017 were calculated. The model calculated result was 2.749 million tons. The spatial distributions of eroded depth are displayed in Figure 10.
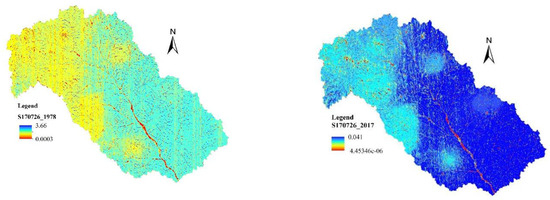
Figure 10.
Spatial distribution of eroded depths in Chabagou watershed in different periods.
3.3. Sediment Reduction Benefits of Check Dam Measures under the Extreme Rainfall Event
The simulated sediment yields of the “26 July 2017” extreme rainstorm under the untreated underlying surface in 1978 and the latest underlying surface without considering the check dam in 2017s were 4.131 million tons (equal to 22091 tons km−2) and 2.749 million tons (equal to 14,701 tons km−2), respectively. And the measured sediment flux of Caoping hydrologic station (outlet of the Chabagou catchment) in the “26 July 2017” extreme rainstorm was 0.866 million tons (equal to 4631 tons km−2); thus, it is stated that the check dams in the channel intercepted 1.883 million tons based on Equation (12). In total, according to Equations (11)–(16), the total sediment reduction by the ensemble of soil and water conservation measures was 3.265 million tons (equal to 17,460 tons km−2). Among the total sediment reduction, slope conservation measures such as forests, grasses, and terraces reduced sediment yield of 1.382 million tons (equal to 7390 tons km−2). The sediment reduction rates of channel engineering and the slope conservation measures were 57.7% and 42.3%, respectively.
When simulating the sediment yield during the typical extreme rainstorm under the different conditions in the base year condition and the extreme storm year in 2017, the spatial distribution of soil erosion of the base year and the extreme storm year were both obtained. Based on the grid computing function of the ArcGIS, the spatial distribution of the total sediment reduction on the slope surface was obtained. Then, based on the zonal statistics function in spatial analysis tools of ArcGIS and the specific locations of the soil and water conservation measures in 2017, the sediment reduction by different soil and water conservations was calculated (Table 2). As shown in Table 2, under the condition of the “26 July 2017” extreme rainstorm, compared to the natural sediment yield, the sediment reduction by the afforestation was 3%, the grass plantation reduced 33.9% of sediment yield, the terracing reduced 4.5% of sediment yield and other measures reduced 0.9% of sediment yield in the Chabagou catchment.

Table 2.
Sediment reduction by different soil and water conservation measures during the “26 July 2017” rainstorm.
4. Discussion
China implemented a series of soil and water conservation (SWC) projects on the Chinese Loess Plateau, which significantly changed the patterns of soil erosion, sediment transport, and deposition. As a result, the sediment flux of the Yellow River, which once was the largest among the global rivers, has been reduced by approximately 85% in the past 60 years [13]. The sediment reduction effects of soil and water conservation measures were due to the changes in sediment sources, vegetation, terraces, and silt fractions in the Loess Plateau watershed.
As early as 1998, many ecological restoration measures following policies such as Grain for Green, prohibiting grazing, mountain closing, and so on were implemented in the Chabagou watershed. From 1978 to 2017, the vegetation coverage in the Chabagou watershed increased from 19% to 68%. Previous researchers found that forests and grasses measures of soil and water conservation improved soil properties, such as soil texture, bulk density, water stable aggregate content, organic matter content, and permeability [29,30]. Therefore, these soil and water conservation engineering measures greatly altered the runoff and sediment transport process on the slope and in the gullies [31]. As vegetation coverage increased, vegetation interception capability, soil porosity, and soil water infiltration increased, and ultimately the surface runoff decreased significantly. Previous studies also showed that when the rainfall intensity is up to 10–15 mm/h, surface runoff begins to occur on the slope under less vegetation coverage. With the increase in vegetation coverage, the critical rainfall intensity to produce surface runoff increased to even 30 mm/h in the Kuyehe basin, which is near this study site [32]. It is noted that extreme rainstorms like the “26 July 2017” event could trigger much stronger soil erosion than usual, and the control measures should continuously focus on this type of storm event.
In terms of specific soil and water conservation measures, it is suggested that terracing measures by changing the slope morphology, shortening the slope length, lowering the slope, and increasing water infiltration accounted for 15% of the total area of the Chabagou watershed. Normally, the terraces could protect the soil under the storms of a 20-year return period. However, the return period of 200 years for the storm on 26 July 2017 [33] could destroy the terraces or even accelerate the soil erosion [34]. Therefore, terraces only had a relatively small sediment reduction effect in the “26 July 2017” rainstorm. For the sediment reduction effect of check-dams, the sediment retention by the dams and the subsequent erosion reduction by elevated baseline were involved. As of 2017, there were 134 dams in the Chabagou watershed, including 45 small dams, 59 medium dams, and 30 key dams. Although 30% of the dams had already been filled up, the remaining 94 dams still played an important role in blocking sediment during the rainstorm. When the check dams were filled up, the slope gradient of the gully slope was reduced within the control area or drainage area of the check dams; therefore, the gully incision, slope collapse, and land sliding could be restrained or eliminated to a certain extent. It is reasonable that the sediment carrying capacity could sharply decrease when the stream flow enters the relatively flat alluvial fan within the reservoirs above the check dams. The check dams performed important roles in regulating the soil erosion in the Loess Plateau region, especially with over 50% contributions to sediment reduction even during extreme storm events. The other soil and water conservation measures in the Wuding River Basin during the July 26 rainstorm were also quantified based on field investigation and hydrological analysis. It is suggested that forest and grass vegetation and terrace had only limited effects on sediment reduction under extreme storms, which might be more useful under normal rainfall conditions; meanwhile, check dams had a greater effect on sediment reduction when encountering heavy rainstorms like “26 July 2017” event.
Moreover, soil and water conservation measures not only have ecological effects on reducing sediment but also have tremendous ecosystem service value (ESV). Soil conservation investment, as an active investment activity, was the primary driving force for guiding human ecological construction of soil and water conservation. Comprehensive measures for soil and water conservation, such as afforestation and blockading, affected the structure and layout of land use, thereby affecting the regional ecological environment and ESV. For example, it was estimated that from 2010 to 2015, the afforestation and construction of terraces in Henan Province created an ESV of CNY 12.267 billion [35,36].
The application of the DSEM method provided objective and useful results for evaluating the effects of specific soil and water conservation measures for an extreme rainstorm in this study; however, the DSEM constructed in this article is only applied in the small watersheds. In the future, attention should be paid to the application of the model in large watersheds covering an area of over a thousand square kilometers to continuously improve its applicability. And more tests should be completed in future studies under the context of global warming and increasing extreme rainstorms.
5. Conclusions
Under the context of global warming and increasing extreme rainstorms, this paper intended to evaluate the impacts of the various soil and water conservation measures on soil erosion under the extreme rainstorms in a typical Loess Plateau basin, Chabagou watershed where the land use and vegetation coverage had changed greatly from 1978 to 2017 due to implementing a large amount of soil and water conservation measures. The results showed that the newly built distributed soil erosion model (DSEM) could simulate runoff and sediment under different scenario simulations and was feasible to evaluate the impacts of soil and water conservation measures on soil erosion. In terms of the extreme rainstorm that occurred on 26 July 2017, the simulated sediment yield of the Chabagou watershed under the non-treated condition was 22,091 tons/km2. After nearly 50 years of comprehensive management with various soil and water conservation measures being implemented, the sediment yield had been reduced sharply up to 17,460 tons/km2 with a reduction rate of 79.02%.
Of all the sediment reductions, 57.7% of sediment in the Chabagou watershed was intercepted by channel engineering, such as check dams, and was 3% by afforestation, 33.9% by grass plantation, 4.5% by terracing, and 0.9% by other measures. Under extreme rainstorms, each soil and water conservation measure had a certain effect on sediment reduction, and channel engineering measures (such as check dams) played the most important role under extreme rainstorm conditions; check dams could further reduce sediment yield even after being filled up.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W. and P.X.; methodology, L.W. and Z.W.; software, X.H.; validation, L.W. and X.H.; formal analysis, Z.W.; investigation, X.H.; resources, X.H.; data curation, L.W.; writing—original draft preparation, L.W.; writing—review and editing, L.W. and Z.W.; visualization, X.H.; supervision, P.X.; project administration, L.W. and P.X.; funding acquisition, L.W. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Inner Mongolia Open bidding for selecting the best candidates Project (150000243033210000057) and the National Natural Science Foundation (U2243212).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author due to (specify the reason for the restriction).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jing, K.; Li, F.X. Effect of global climatic warning on the erosion and sediment yield on the Loess Plateau. Geogr. Res. 1993, 12, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Munoz-Rojas, M.; Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; De la Rosa, D.; Abd-Elmabod, S.K.; Anaya-Romero, M. Qrganic carbon stocks in Mediterranean soil types under different land uses (Southern Spain). Solid Earth 2012, 3, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Noble, A.D.; Chartres, C. Adapting to climate change by improving water productivity of soil in dry areas. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendse, F.; van Ruijven, J.; Jongejans, E.; Keesstra, S. Loss of plant species diversity reduces soil erosion resistance. Ecosystems 2015, 18, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.C.; Lu, K.X.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.Y. Impact of soil and water conservation on soil organic carbon content in a catchment of the middle Han River, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6503–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.Y. Ecological environment problems and countermeasures on the Loess Plateau. Agric. Econ. Probl. 2002, 3, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Y.; Gao, Y.F.; Ma, S.B.; Dong, G.T. Sediment reduction of warping dams and its timeliness in the Loess Plateau. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2018, 49, 145–155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.D.; Wu, Z.; Jia, L.L.; Pang, G.W. Vegetation change and its influence on runoff and sediment in different landform units, Wei River, China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 141, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Gao, G.Y.; Fu, B.J. Changes in streamflow and sediment load in the catchments of the Loess Plateau, China, a review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 2–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Jiang, X.H.; Sun, H.T.; Xu, H.Y.; Bo, X.Z.; Li, L.L. Driving forces of nature and human activities on water and sediment changes in the middle reaches of the Yellow River in the past 100 years. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2450–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z. Effect of soil and water conservation measures on the reduction of runoff and sediment load in a loess hilly-gully region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 76, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, C.C.; Liu, J.H.; Wei, J.H.; Xue, H.; Li, T.J. Analyses on the variation of vegetation coverage and water/sediment reduction in the rich and coarse sediment area of the Yellow River basin. J. Sediment Res. 2006, 4, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.H.; Zhang, X.M. Loess Plateau soil erosion governance and runoff-sediment variation of Yellow River. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2020, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.W.; Hou, L.L.; Li, L.Q. Great achievements in sediment reduction and water demand of sediment transport in the feature of the Yellow River management. China Water 2021, 21, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Li, Z.; Ran, D.C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Inquiring into the method of calculating the benefits of runoff and sediment reducing by soil and water conservation sloping measures. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 1998, 18, 43–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yao, W.Y. Discussion on the calculation method for water and sediment reduction benefits of soil and water conservation in the Yellow River Basin. Yellow River 1993, 5, 10–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.Q.; Chen, G.X. Study on calculation methods of benefits of water and soil conservation. J. Hohai Univ. 1999, 27, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.Q.; Gao, J.N.; Luo, H. Changes and implications of the relationship between rainfall, runoff and sediment load in the Wuding River basin on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2019, 175, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.Q.; Chen, G.X. Application of physical conceptual model in evaluating the benefits of water and soil conservation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 9, 62–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.L.; Fang, H.Y. Research progress in WaTEM/SEDEM model and its application prospect. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 13, 85–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.L.; Huo, A.D.; Zhu, X.H.; Jiang, C. Review of research processes in soil erosion prediction model on the Loess Plateau. Appl. Chem. Ind. 2019, 48, 902–912. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.C.; LI, X.; Dong, Y.H. Ecological stoichiometry characteristics and physical-chemical properties of soils at different latitudes on the Loess Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 870–879. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.D.; Lu, G.Y.; Gong, L. Analysis of the characteristics of July 26, 2017 rainstorm and flood in Wuding River Basin. Yellow River 2018, 40, 25–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.G.; Li, R.K.; He, J.J. Sediment delivery across multiple spatio-temporal scales in an agriculture watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2015, 12, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Guan, X.J. The causes of runoff variation based on double cumulative curve analysis method. J. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 1, 204–210. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.H.; Cai, Q.G.; Zhang, G.Y.; Chen, N.; Liu, H.; Feng, J.L. Soil erosion and sediment yield of physiognomyZanations of small watershed in Loess Hilly and Gully Region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.Y.; Chen, J.R.; Qin, F. Study on the distributed forecast model of soil loss in sandy area of Yellow River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 22, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L.; Yao, W.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yang, J.S. Modelling Sediment Delivery Ratio of Single Rainfall Events in Hilly-gullied Loess Region Based on Hydrologic Elements. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 31, 28–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Olson, K.R.; Gennadiyev, A.N.; Jones, R.L. Erosion patterns on cultivated and reforested hillslopes in Moscow region, Russia. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.M.; Yao, W.Y. Calculation Method of Water and Sediment Reduction for Soil and Water Conservation; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994; pp. 72–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.B.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.W. Characteristics of typical rainfall-runoff on different vegetation types in the river basin in the upper Jialiang river. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 24, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Qi, L.; Ma, M.W.; Chen, R.X. Analysis of“July 26”rainstorm return period of Suide Station in 2017. Yellow River 2018, 40, 11–14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Chen, Y.X.; Bai, L.C. Investigation on soil erosion in small watersheds under “7.26” extreme rainstorm in Zizhou County, Northern Shaanxi Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 37, 338–344. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H.; Jin, S.Y.; Gao, Y.J.; Gao, W.Y. Analysis of the effect of water and soil conservation measures on storm water and sediment reduction of the flood on July 26, 2017. Yellow River 2017, 39, 22–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tu, W.; Wu, J.W.; Ma, L.H.; Feng, Z. Soil and water conservation measures drive the change of landuse landscape pattern in the village. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 147–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.T.; Wang, Q.Y.; He, M.Z.; Zheng, Z.H. Influence of Soil and Water Conservation Investment on the Agricultural Economy and Ecosystem Service Value in Henan Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 265–275. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).