The Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Phytoplankton and the Impact of Environmental Factors in a Harbor-Construction-Formed Reservoir
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
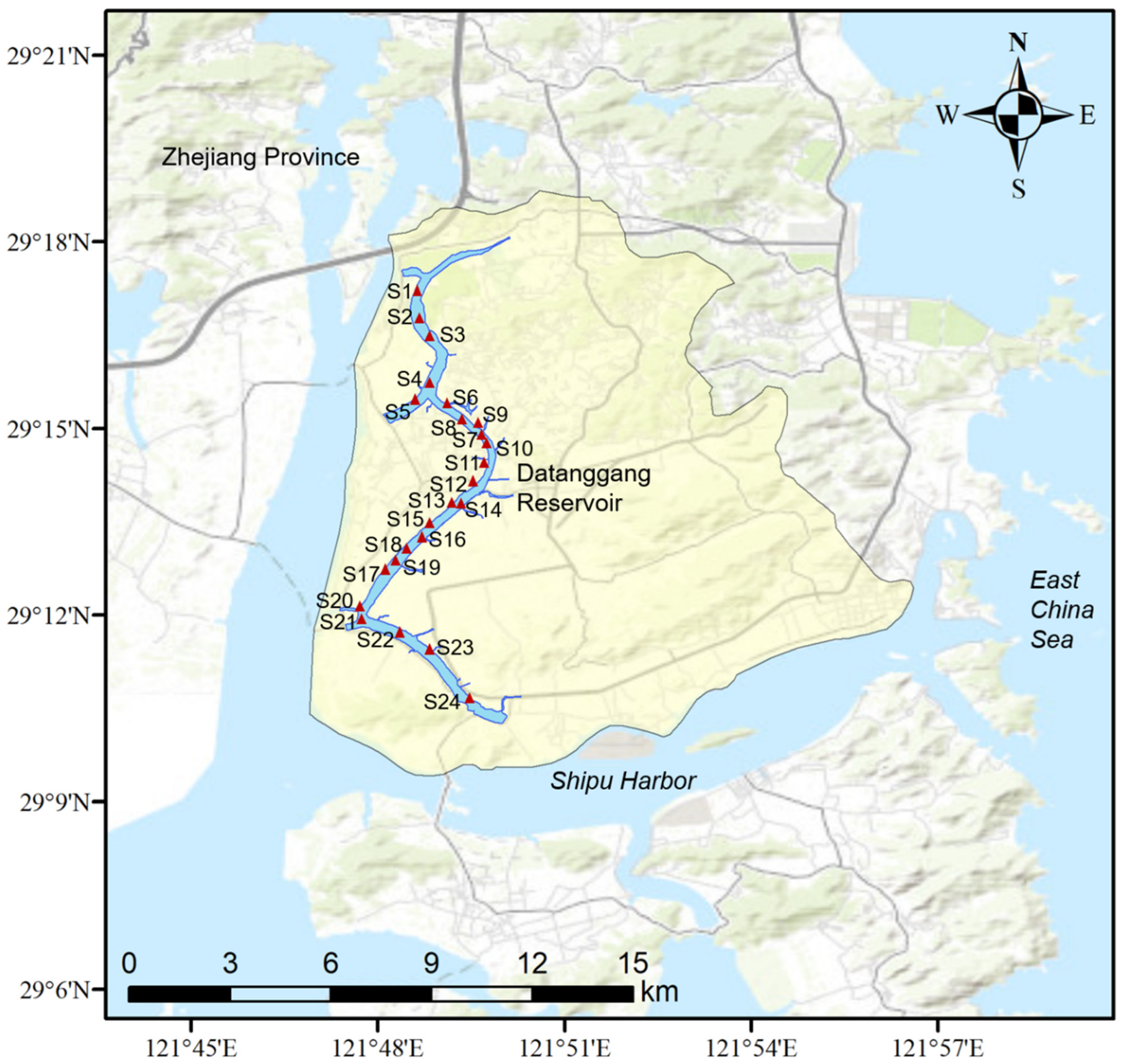
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Analysis of Field Samples
2.3. Data Analysis
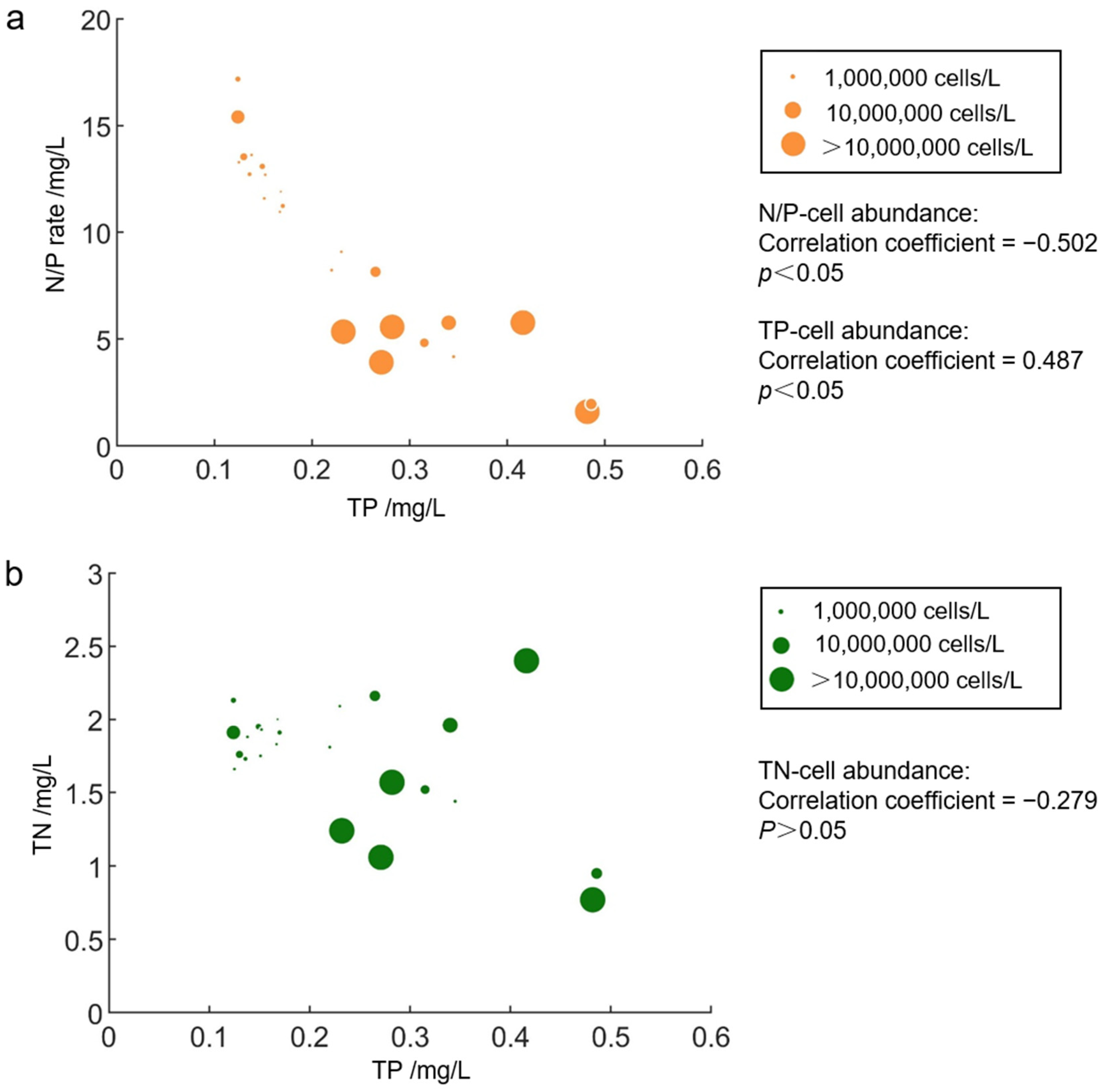
3. Results
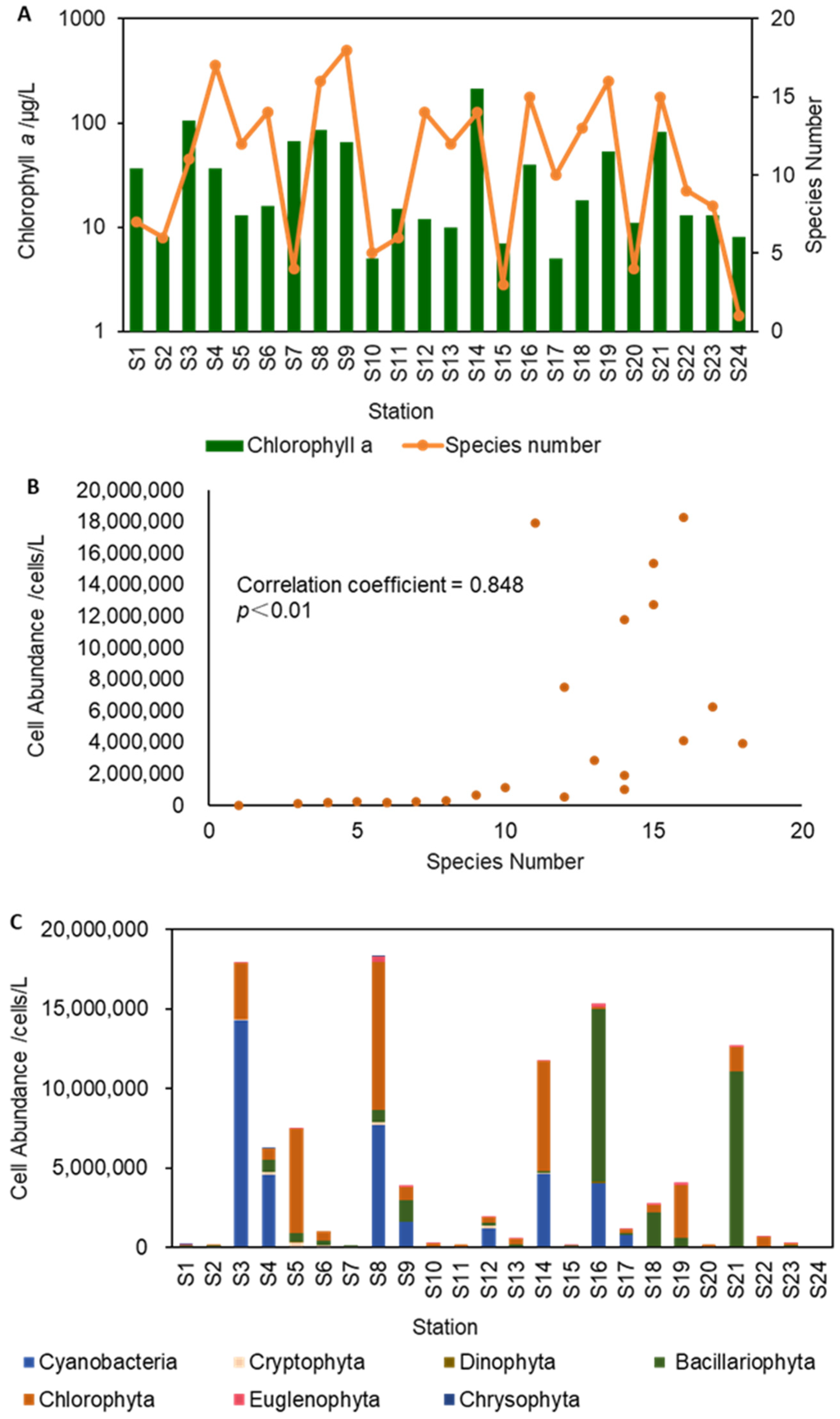
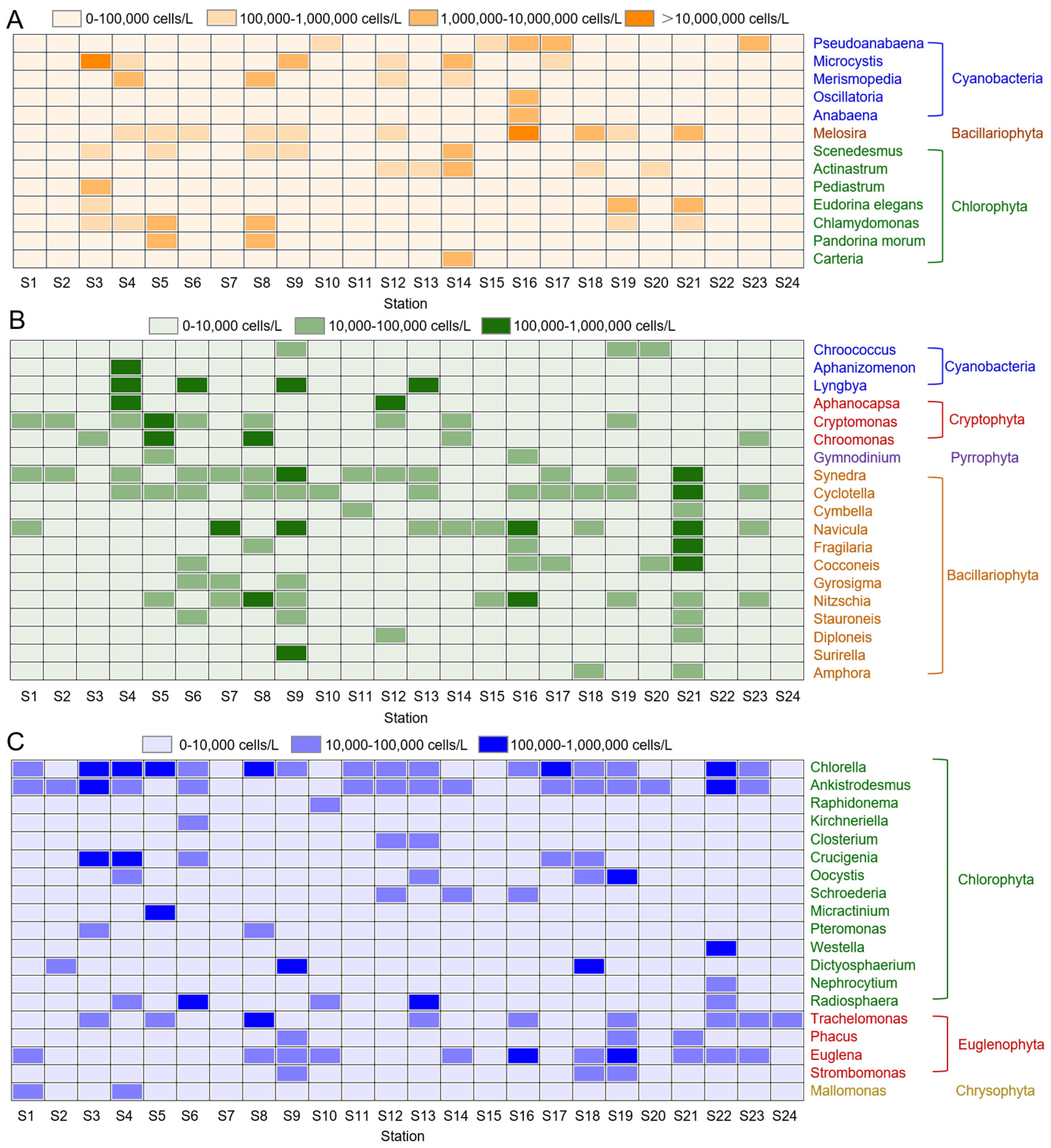
3.1. Phytoplankton Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Spatial Variability in Physicochemical Parameters of Water
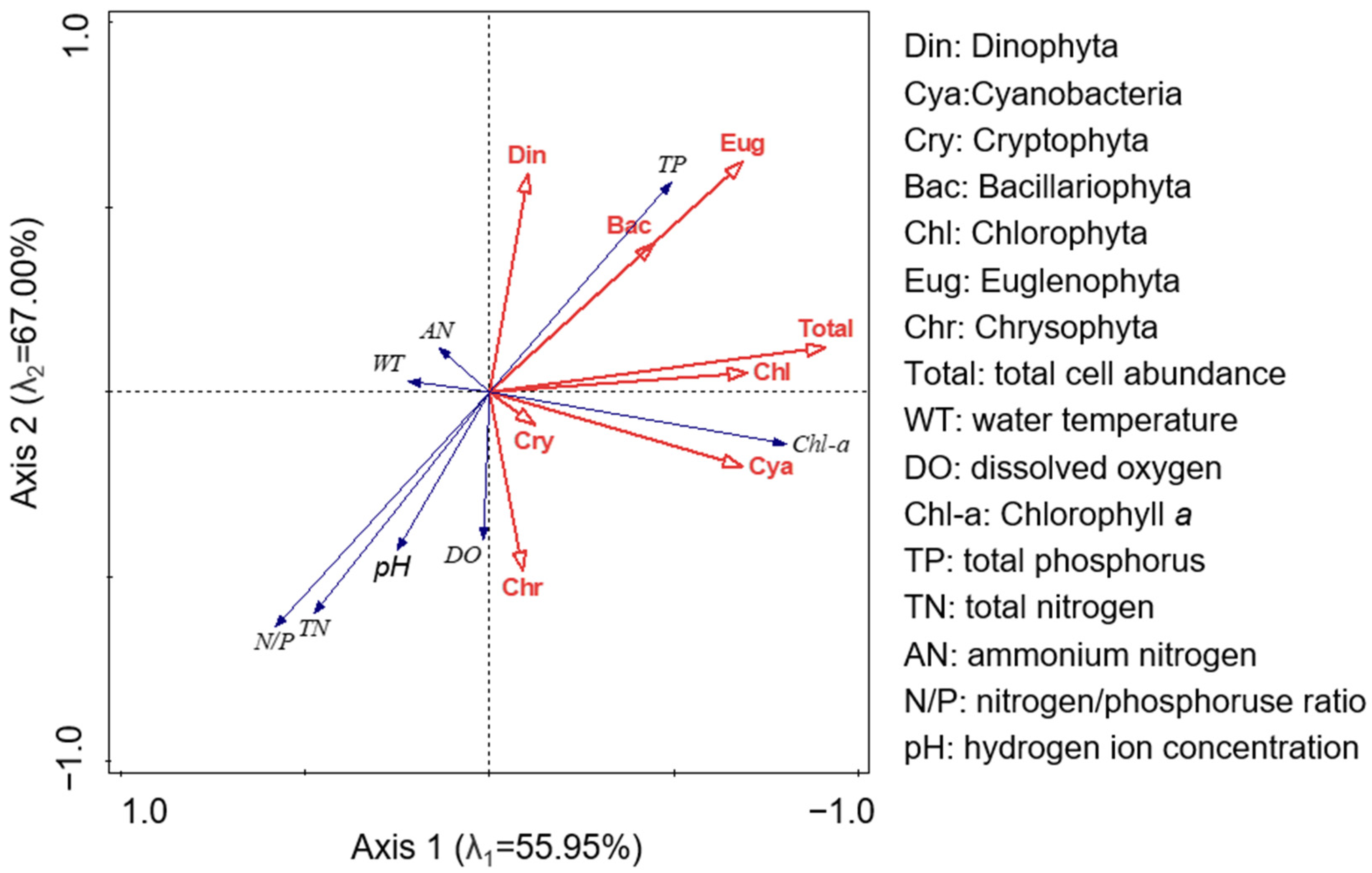
3.3. Relationship between Phytoplankton Distribution and Physicochemical Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Several Algae Caused Single or Multiple Algal Blooms in Different Areas of Continuous Water
4.2. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Phytoplankton Distribution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Almond, R.E.A.; Grooten, M.; Juffe Bignoli, D.; Petersen, T. Living Planet Report 2022–Building a Naturepositive Society; WWF: Gland, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- GlobalHAB. Global Harmful Algal Blooms, Science and Implementation Plan; SCOR (Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research): Newark, DE, USA; IOC: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; Maccormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful Cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romo, S.; Fernández, F.; Ouahid, Y.; Barón-Sola, Á. Assessment of microcystins in lake water and fish (Mugilidae, Liza sp.) in the largest Spanish coastal lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.C.; Lv, S.H.; Liang, Y.B. Harmful algal blooms in the coastal waters of China. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Glibert, P.M., Berdalet, E., Burford, M.A., Pitcher, G.C., Zhou, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 309–316. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Liu, G.X.; Zhou, G.J.; Mei, H.; Hu, Z.Y. Peridinium polonicum, a new record of freshwater toxic Dinoflagellate from China. Plant Sci. J. 2018, 26, 454–457, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Roset, J.; Gibello, A.; Aguayo, S.; Domínguez, L.; Álvarez, M.; Fernández-Garayzabal, J.F.; Zapata, A.; Muñoz, M. Mortality of rainbow trout (Oncorynchus mykiss (Walbaum)) associated with freshwater dinoflagellate bloom (Peridinium polonicom (Woloszynska)) in a fish farm. Aquac. Res. 2002, 33, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, C.A.; Moura, A.D.N. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shi, X.L.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Shi, L.M.; Qin, B.Q. Long-term dynamics and drivers of phytoplankton biomass in eutrophic Lake Taihu. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.M.; Qin, B.Q.; Paerl, H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ma, J.R.; Chen, Y.W. Earlier and warmer springs increase Cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms in subtropical Lake Taihu, China. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakhmalniy, A.F.; Wasser, S.P.; Nevo, E.; Kapitanchuk, L.M. New variety of Peridinium gatunense Nygaard f. kinnereta Krachmalny (Dinophyta) from Lake Kinneret (Israel). Int. J. Algae 2014, 24, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.T.; O’Dell, K.; Smith, V.H. Water quality trends in lake Tohopekaliga, Florida, USA: Responses to watershed management. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1994, 30, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo, S.; Villena, M.; Sahuquillo, M.; Soria, J.; GimÉNez, M.; Vicente, E.; Miracle, M. Response of a shallow Mediterranean lake to nutrient diversion: Does it follow similar patterns as in northern shallow lakes? Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, T.J.S.; Maris, T.; Soetaert, K.; Conley, D.J.; Van Damme, S.; Meire, P.; Middelburg, J.J.; Vos, M.; Struyf, E. A macro-tidal freshwater ecosystem recovering from hypereutrophication: The Schelde case study. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Shu, T.; Jeppesen, E.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y. Restoration of a subtropical eutrophic shallow lake in China: Effects on nutrient concentrations and biological communities. Hydrobiologia 2013, 718, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utermöhl, H. Zur Vervollkommung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. Mitteilungen. 1958, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sournia, A. Phytoplankton Manual; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus-Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Former State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989. (In Chinese)
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Former State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- HJ/T 91-2002; Technical Specifications Requirements for Monitoring of Surface Water and Waste Water. Former State Environmental Protection Administration of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Lv, S.C.; Li, X.H.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.J.; Zhou, T.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Lin, K.X.; Liu, L.S. Autochthonous sources and drought conditions drive anomalous oxygen-consuming pollution increase in a sluice-controlled reservoir in eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, S.S.; Chakraborty, B.; Chaudhuri, P. Comparison of multivariate distributions using quantile–quantile plots and related tests. Bernoulli 2014, 20, 1484–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joanes, D.N.; Gill, C.A. Comparing measures of sample skewness and kurtosis. Statistician 1998, 47, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christia, C.; Giordani, G.; Papastergiadou, E. Assessment of ecological quality of coastal lagoons with a combination of phytobenthic and water quality indices. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary production of the biosphere: Integrating terrestrial and oceanic components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, R.T.; Hilting, A.K. History of the study of plankton productivity. In Phytoplankton Productivity: Carbon Assimilation in Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems; Williams, P.J., Thomas, D.N., Reynolds, C.S., Eds.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 2002; pp. 16–43. [Google Scholar]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Qian, K. Photosynthesis, carbon acquisition and primary productivity of phytoplankton: A review dedicated to Colin Reynolds. Hydrobiol. 2020, 848, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: Paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Lim, W.A.; Lu, D.D.; Dai, X.F.; Orlova, T.; Iwataki, M. Harmful algal blooms and associated fisheries damage in East Asia: Current status and trends in China, Japan, Korea and Russia. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandrino, E.S.; Paerl, H.W. Determining the potential for the proliferation of the harmful cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in Currituck Sound, North Carolina. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, M.; Raymond, F.; Levesque, A.; Thaler, M.; Mohit, V.; Audet, M.; Corbeil, J.; Culley, A. Communities of phytoplankton viruses across the transition zone of the St. Lawrence Estuary. Viruses 2018, 10, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Kuroda, H.; Setou, T.; Okazaki, M.; Yamatogi, T.; Hirae, S.; Ishida, N.; Yoshida, K.; Mitoya, Y. Exceptional red-tide of fish-killing dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi promoted by typhoon-induced upwelling. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 219, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Geng, H.X.; Yu, R.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, Q.C.; Kong, F.Z.; Zhou, M.J. Distribution of Alexandrium pacificum cysts in the area adjacent to the Changjiang River estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.; Daugbjerg, N.; Henriksen, P. Comparative study of Gymnodinium mikimotoi and Gymnodinium aureolum, comb. nov. (=Gyrodinium aureolum) based on morphology, pigment composition, and molecular data. J. Phycol. 2003, 36, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toebe, K.; Alpermann, T.J.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Molecular discrimination of toxic and non-toxic Alexandrium species (Dinophyta) in natural phytoplankton assemblages from the Scottish coast of the North Sea. Eur. J. Phycol. 2013, 48, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Fukushima, T. Impacts of long-term increase in silicon concentration on diatom blooms in Lake Kasumigaura, Japan. Ann. Limnol.-Int. J. Lim. 2014, 50, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, M.; Rahbary, S.H.; Shamsaii, M. Determination of optimum concentration of Diuron for the growth and bloom of the algae (Scenedesmus obliquus) in in Vitro condition. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2014, 13, 739–747. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowska, N.; Szelag-Wasielewska, E. Toxic picoplanktonic cyanobacteria-review. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1497–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormas, K.A.; Gkelis, S.; Vardaka, E.; Moustaka-Gouni, M. Morphological and molecular analysis of bloom-forming Cyanobacteria in two eutrophic, shallow Mediterranean lakes. Limnologica 2011, 41, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.; Santiago-Vazquez, L.; Paul, V. Toxin release in response to oxidative stress and programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The persistence of cyanobacterial (Microcystis spp.) blooms throughout winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Li, W.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Gao, G. Cyanobacterial bloom management through integrated monitoring and forecasting in large shallow eutrophic Lake Taihu (China). J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernat-Quesada, F.; Alvaro, M.; Garcia, H.; Navalon, S. Impact of chlorination and pre-ozonation on disinfection by-products formation from aqueous suspensions of Cyanobacteria: Microcystis aeruginosa, Anabaena aequalis and Oscillatoria tenuis. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, N. The predominant phytoplankton of Pseudoanabaena holding specific biosynthesis gene-derived occurrence of 2-MIB in a drinking water reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 19134–19142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Sivonen, K.; Rouhiainen, L.; Fewer, D.P.; Liu, B. Genome-derived insights into the biology of the hepatotoxic bloom-forming cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. Strain 90. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.P.; Li, S.C.; Chai, W.B.; Chen, Y.W. A newly recorded cyanobacterial species in water blooms occurred in Lake Poyang-Merismopedia convoluta Breb. Kützing. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 643–646, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Blokker, P.; Schouten, S.; van den Ende, H.; de Leeuw, J.W.; Hatcher, P.G.; Sinninghe Damsté, J.S. Chemical structure of algaenans from the fresh water algae Tetraedron minimum, Scenedesmus communis and Pediastrum boryanum. Org. Geochem. 1998, 29, 1453–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.X.; Xing, W.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Liu, G.X.; Hu, Z.Y. Analysis of mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes in two volvocine algae: Eudorina elegans and Eudorina cylindrica (Volvocaceae, Chlorophyta). Eur. J. Phycol. 2019, 54, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Takeshita, S.; Sudo, R. Microcosm system study on the formation and control of water-bloom. Jpn. J. Water Pollut. Res. 1988, 11, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rhee, G.-Y. A continuous culture study of phosphate uptake, growth rate and polyphosphate in Scenedesmus sp. J. Phycol. 1973, 9, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.M.; Davis, T.W.; Burford, M.A.; Gobler, C.J. The rise of harmful Cyanobacteria blooms: The potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.; Smith, V. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keck, F.; Lepori, F. Can we predict nutrient limitation in streams and rivers? Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Joyner, A.R.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Qin, B.; Scott, J.T. Mitigating Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. The nitrogen and phosphorus dependence of algal biomass in lakes: An empirical and theoretical analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1982, 27, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Bracken, M.E.S.; Cleland, E.E.; Gruner, D.S.; Harpole, W.S.; Hillebrand, H.; Ngai, J.T.; Seabloom, E.W.; Shurin, J.B.; Smith, J.E. Global analysis of nitrogen and phosphorus limitation of primary producers in freshwater, marine and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugdale, R.C.; Goering, J.J. Uptake of new and regenerated forms of nitrogen in primary productivity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1967, 12, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, R.W.; Marino, R. Nitrogen as the limiting nutrient for eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems: Evolving views over three decades. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, T.R.; Peele, E.R.; Ammerman, J.W.; Harding, L.W. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton in Chesapeake Bay. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 82, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, M.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Rudek, J.; Bates, P.W. Regulation of estuarine primary production by watershed rainfall and river flow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 93, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudek, J.; Paerl, H.W.; Mallin, M.A.; Bates, P.W. Seasonal and hydrological control of phytoplankton nutrient limitation in the Lower Neuse River Estuary, North Carolina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 75, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Paerl, H.W. Nitrogen transformations differentially affect nutrient-limited primary production in lakes of varying trophic state. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2019, 4, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; He, Z.L.; Yang, Y.G.; Stoffella, P.J.; Philips, E.J.; Charles, A.P. Nitrogen versus phosphoruslimitation of phytoplankton growth in Ten Mile Creek, Florida, USA. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Scott, J.T.; McCarthy, M.J.; Newell, S.E.; Gardner, W.S.; Havens, K.E.; Hoffman, D.K.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. It takes two to tango: When and where dual nutrient (N & P) reductions are needed to protect lakes and downstream ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10805–10813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, W.T.; Lehman, J.T. The effect of changes in the nutrient income on the condition of Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1981, 26, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.M.; Wurtsbaugh, W.A. Control of Lacustrine Phytoplankton by Nutrients: Erosion of the Phosphorus Paradigm. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2008, 93, 446–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, R.W. The limiting factor concept. What Stops Growth? Lakeline 2001, 21, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G. Variations in productivity of Goose and hypereutrophic Sylvan lakes, Indiana. Invest. Indiana Lakes Streams 1966, 7, 147–184. [Google Scholar]
- Dzialowski, A.R.; Wang, S.H.; Lim, N.C.; Spotts, W.W.; Huggins, D.G. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in central plains reservoirs, USA. J. Plankton Res. 2005, 27, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.A.; Watson, S.B.; McCauley, E. Predicting Cyanobacteria dominance in lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1905–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; Lin, K.; Wang, R.; Lv, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, L. The Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Phytoplankton and the Impact of Environmental Factors in a Harbor-Construction-Formed Reservoir. Water 2024, 16, 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192813
Hu X, Lin K, Wang R, Lv S, Liu Y, Wang Y, Luo Y, Zhou T, Liu L. The Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Phytoplankton and the Impact of Environmental Factors in a Harbor-Construction-Formed Reservoir. Water. 2024; 16(19):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192813
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xiaokun, Kuixuan Lin, Rui Wang, Shucong Lv, Yunlong Liu, Yu Wang, Yan Luo, Tianpeng Zhou, and Lusan Liu. 2024. "The Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Phytoplankton and the Impact of Environmental Factors in a Harbor-Construction-Formed Reservoir" Water 16, no. 19: 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192813
APA StyleHu, X., Lin, K., Wang, R., Lv, S., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Luo, Y., Zhou, T., & Liu, L. (2024). The Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Phytoplankton and the Impact of Environmental Factors in a Harbor-Construction-Formed Reservoir. Water, 16(19), 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192813






