The Synergistic Power of Rosehip Seed Powder and Aluminum Chloride in Steel Industry Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Steel and Iron (IS) Industry Wastewater Collection and Characterization
2.2. RSP Coagulant Preparation
2.3. Chemicals
2.4. Experiment Procedures
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
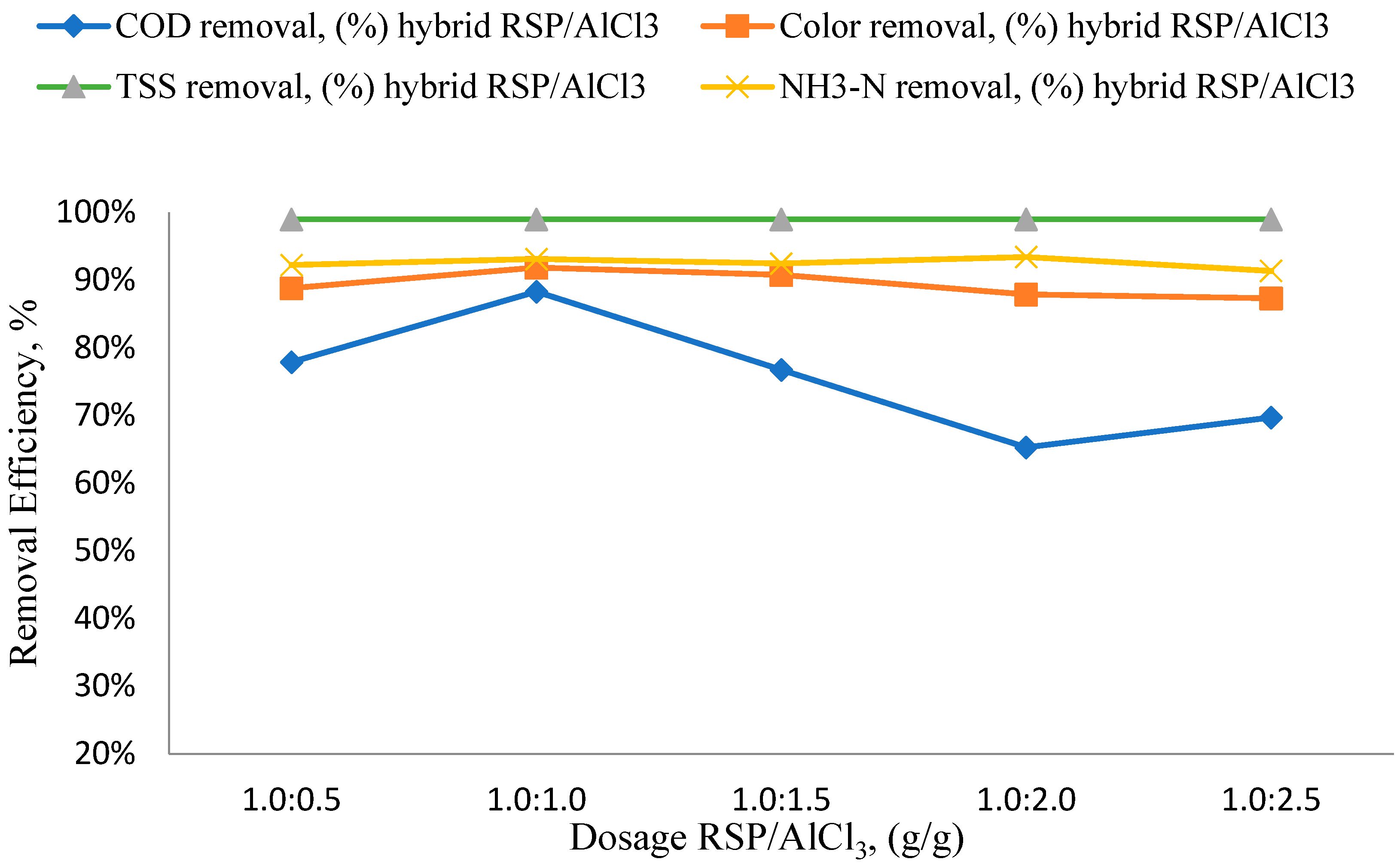
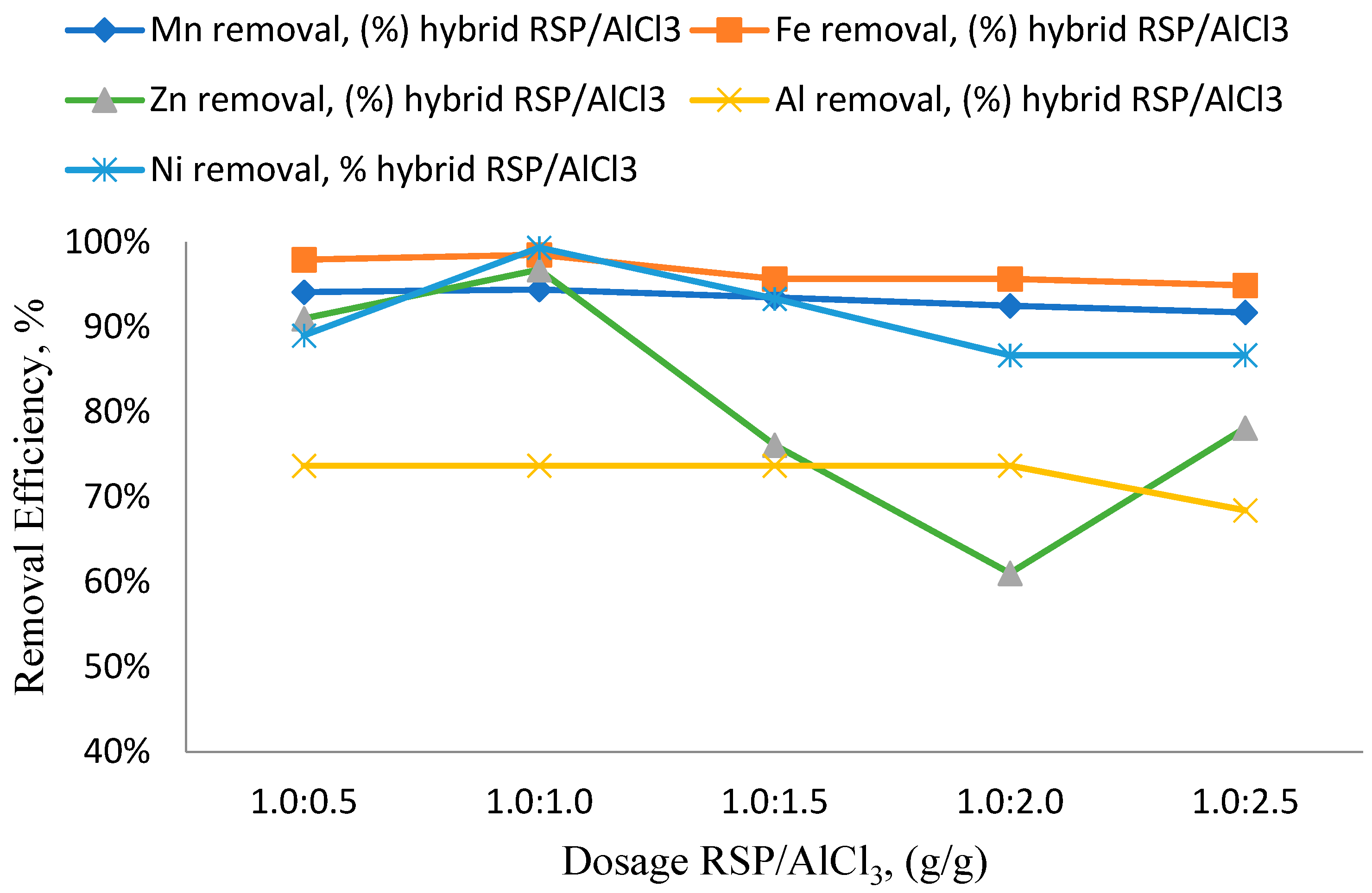
3.1. RSP/AlCl3 Dosage Effects
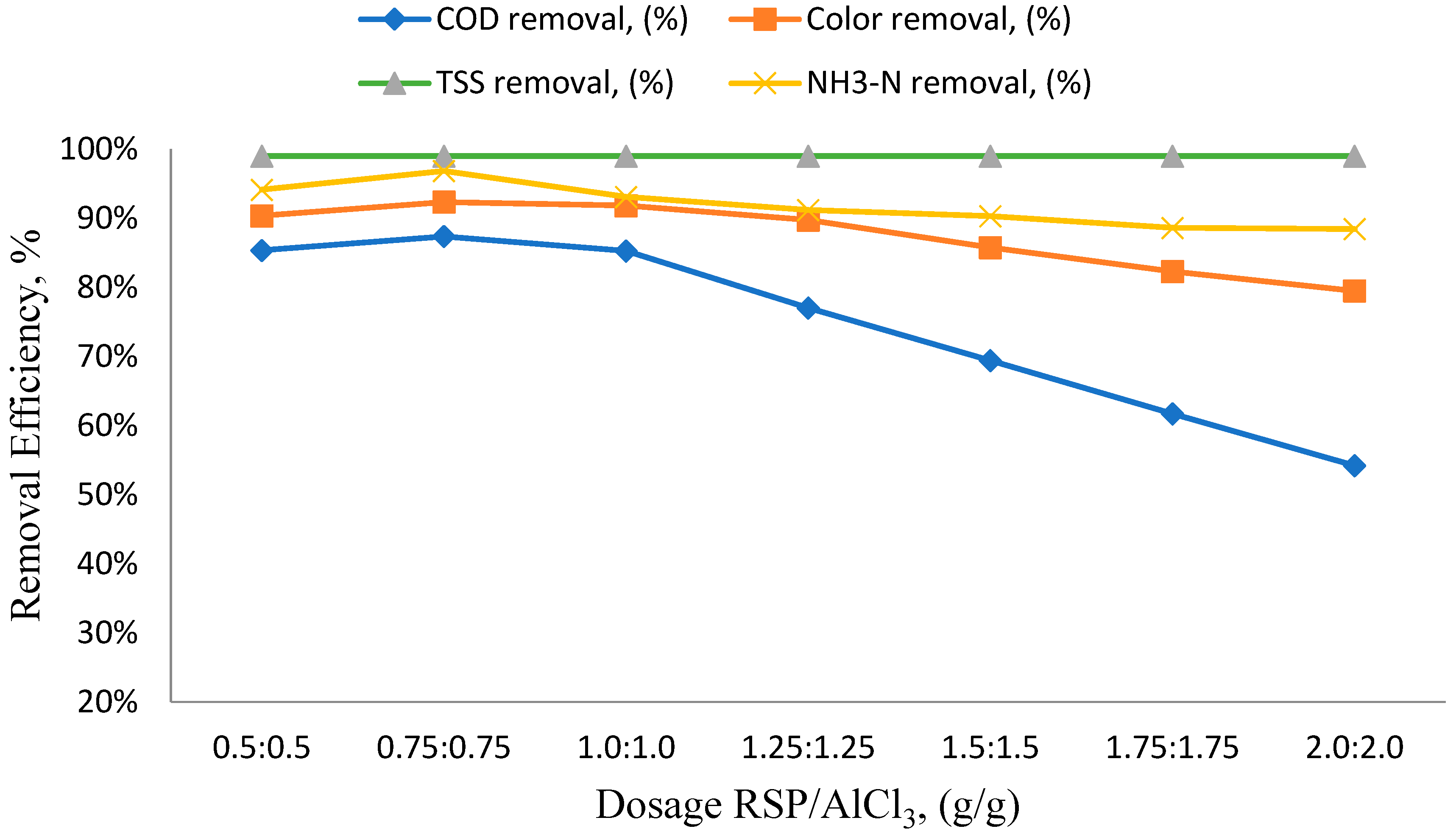
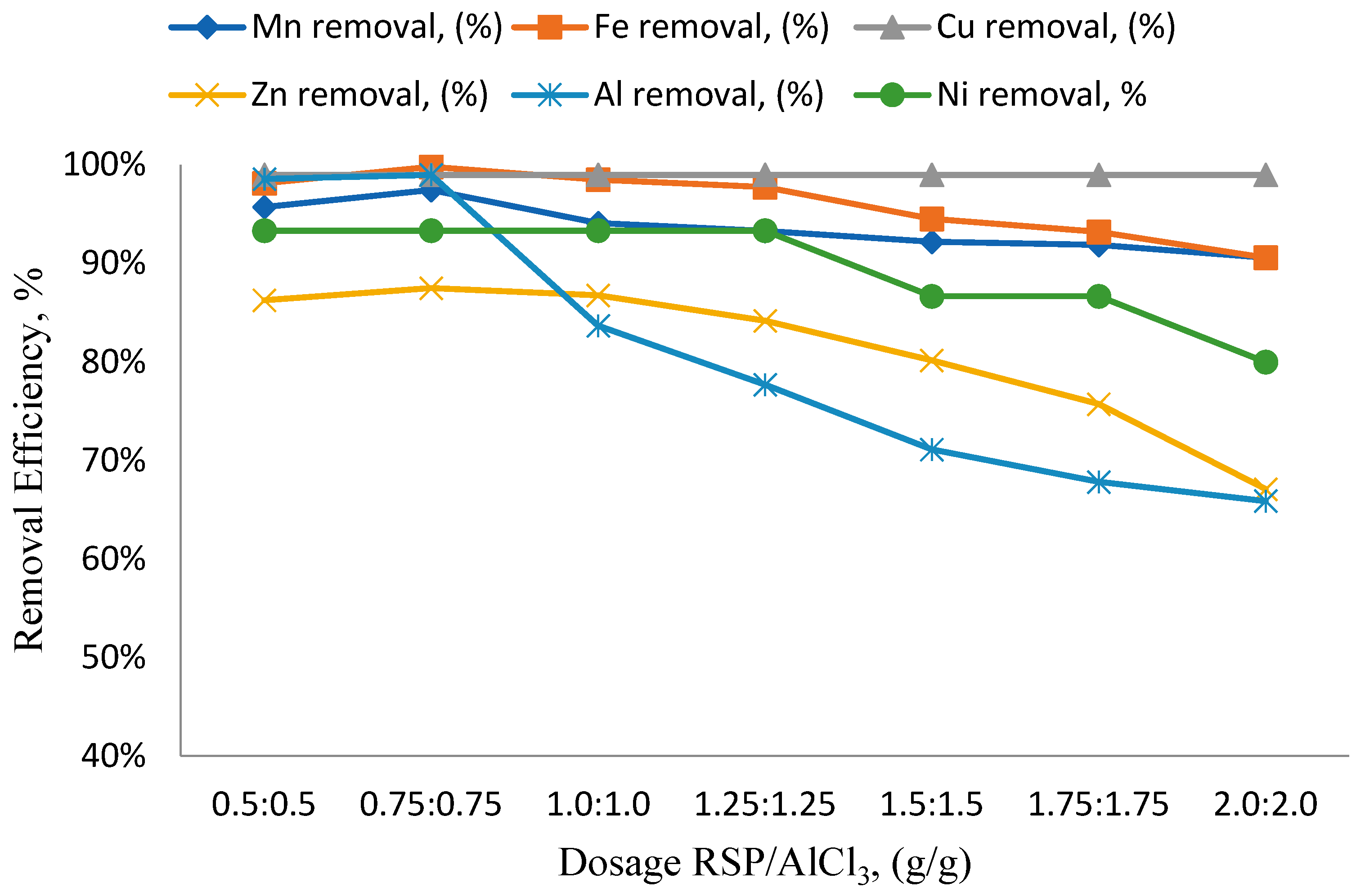
3.2. Effects of Different RSP/AlCl3 Hybrid Natural and Chemical Coagulant Ratios on Particular Parameters
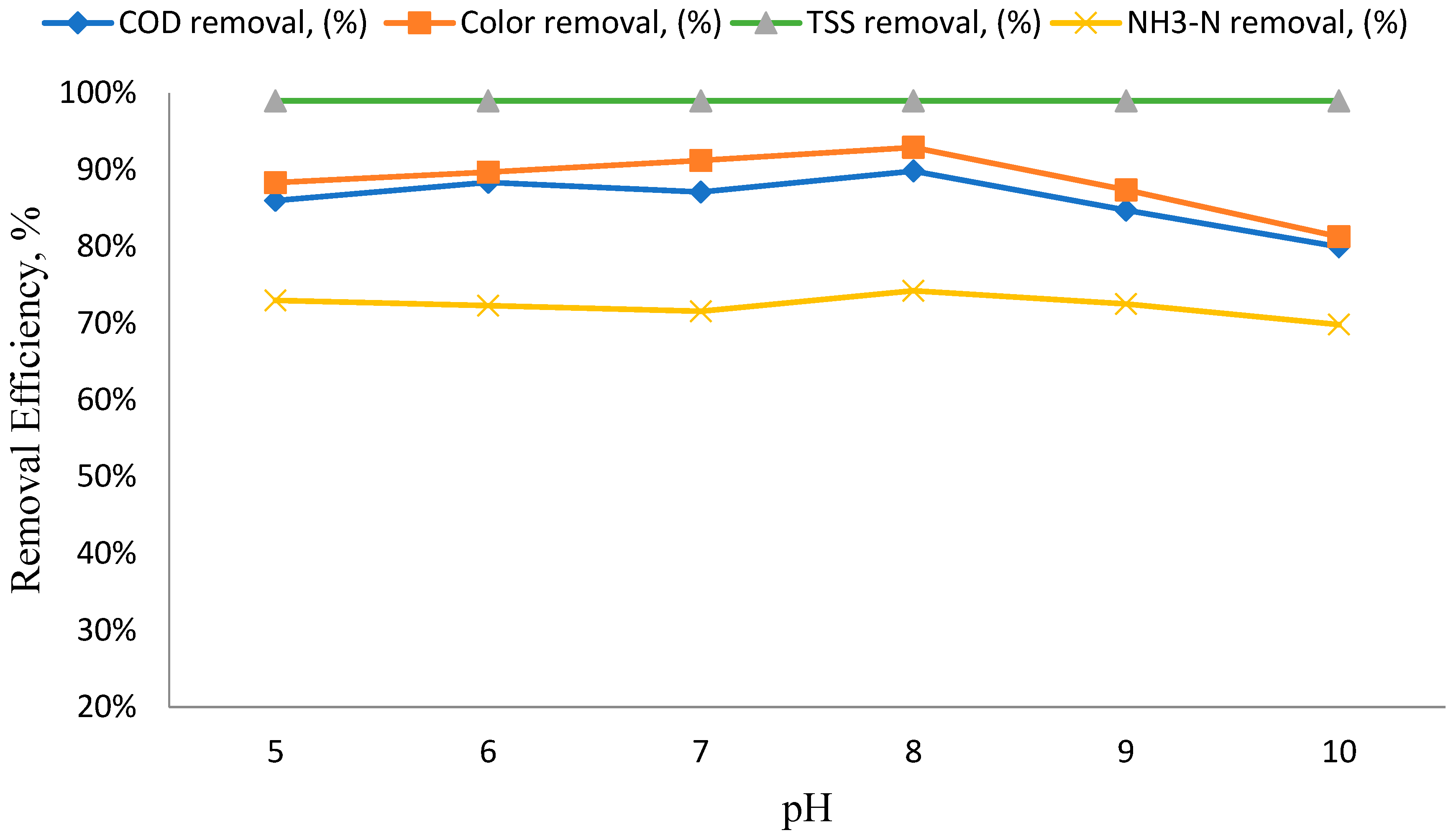
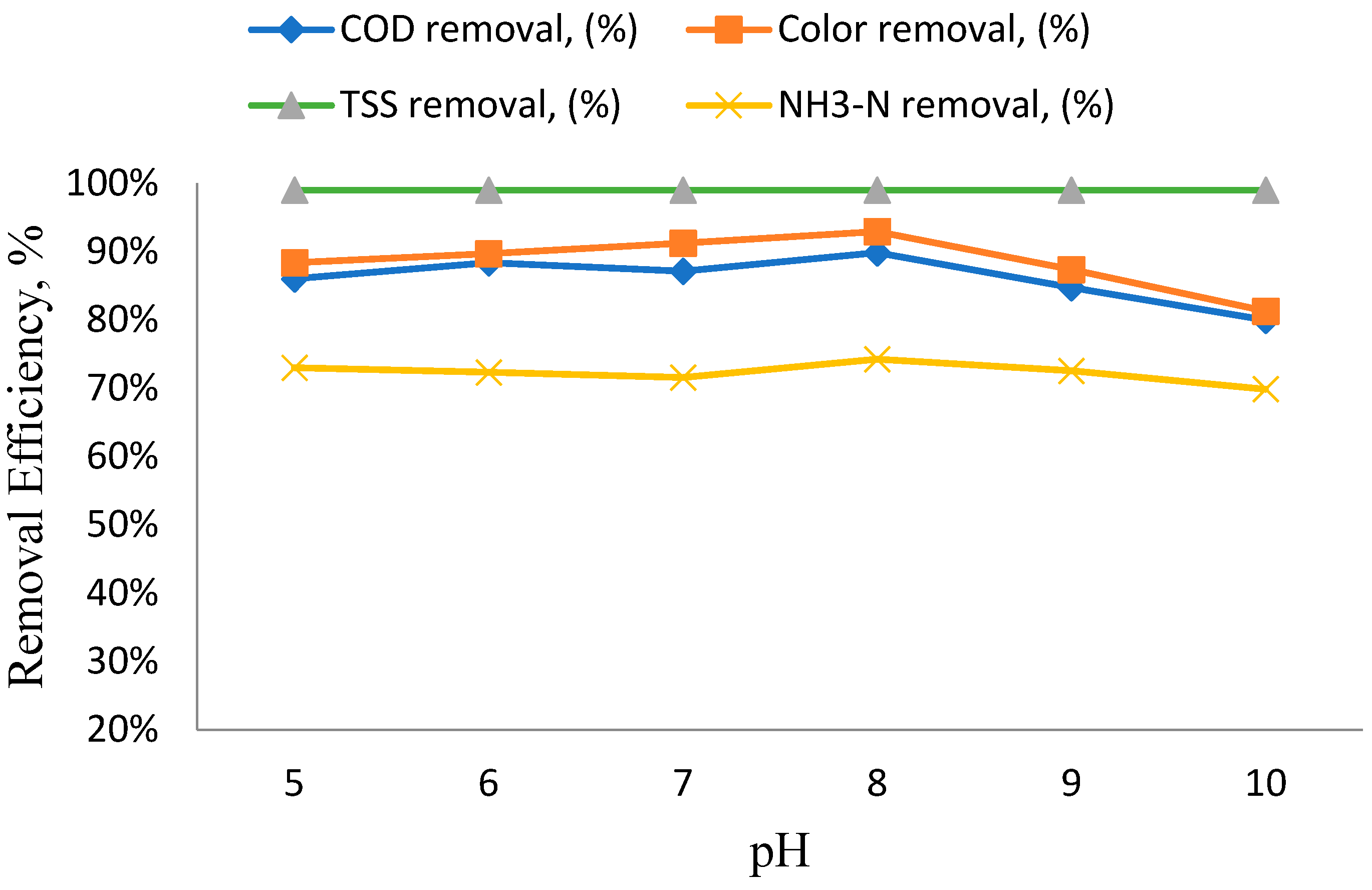
3.3. The Impact of pH Variation on the Efficiency of Removing Specific Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu Amr, S.S.A.; Abujazar, M.S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Albahnasawi, A.; Omer, F. Heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater using date seeds powder and aluminum chloride-based hybrid natural/chemical coagulation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 318, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Fatihah, S.; Bashir, M.J.K. Recent Advancements in Plant-Based Natural Coagulant Application in the Water and Wastewater Coagulation-Flocculation Process: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Global Nest J. 2022, 24, 687–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Alzghoul, T.M.; Amr, S.A.; Bangalore Ramu, M.; Nassani, D.E. Bibliometric Insights into Car Wash Wastewater Treatment Research: Trends and Perspectives. Water 2024, 16, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Abu Amr, S.S.; Fatihah, S.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Ibrahim, E. The Effectiveness of Rosehip Seeds Powder as a Plant-Based Natural Coagulant for Sustainable Treatment of Steel Industries Wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 270, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, E.; Muñoz-Meneses, R.A.; Marín, L.; Mora, M.; Tabares, J.A.; Manotas-Albor, M.; Rodríguez, L.A.; Diosa, J.E.; Mosquera-Vargas, E. Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Submicron Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Particles Synthesized from Industrial Steel Waste. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2023, 288, 116170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Sheen, O.S.; Ng, C.A.; Abujazar, M.S.S.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Abu Amr, S.S. Advanced Treatment of Palm Oil Mill Effluent Using Thermally Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Separations 2022, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, B.; Kumar, S.; Nand, S.; Azad, I.; Bharagava, R.N.; Romanholo Ferreira, L.F.; Dutta, V. Wastewater Generation and Treatment by Various Eco-Friendly Technologies: Possible Health Hazards and Further Reuse for Environmental Safety. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Comprehensive Utilization of Steel Slag: A Review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, R.; Xia, W.; Nie, Y.; Kong, Y.; Jia, B.; Li, S. Emulsified Oil Removal from Steel Rolling Oily Wastewater by Using Magnetic Chitosan-Based Flocculants: Flocculation Performance, Mechanism, and the Effect of Hydrophobic Monomer Ratio. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchaiyappan, A.; Sarangapany, S.; Saksakom, Y.A.; Devipriya, S.P. Feasibility Study of a Point of Use Technique for Water Treatment Using Plant-Based Coagulant and Isolation of a Bioactive Compound with Bactericidal Properties. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullayev, E.; Vakili, A.H.; Amr, S.S.A.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D. Navigating heavy metal removal: Insights into advanced treatment technologies for wastewater: A review. Global Nest J. 2024, 260, 06247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Amr, S.S.; Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaağaç, S.U.; Mahfud, R.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Hamad, R.J.A. Application of Plant-Based Natural Coagulant for Sustainable Treatment of Steel and Iron Industrial Wastewater, Karabuk, Turkey. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 287, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristianto, H. Recent Advances on Magnetic Natural Coagulant: A Mini Review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2021, 10, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinejad, M.H.; Bina, B. Application of Moringa Oleifera Coagulant Protein as Natural Coagulant Aid with Alum for Removal of Heavy Metals from Raw Water. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 116, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiviskä, T.; Santos, S.C.R. Purifying Water with Plant-Based Sustainable Solutions: Tannin Coagulants and Sorbents. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, A.K.; Salama, R.S.; Mostafa, M.M.M. Natural-Based Coagulants/Flocculants as Sustainable Market-Valued Products for Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Review of Recent Developments. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 19335–19355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Li, T.; Chang, X.; Ma, K.; You, W.; Tan, C. Successful Prediction for Coagulant Dosage and Effluent Turbidity of a Coagulation Process in a Drinking Water Treatment Plant Based on the Elman Neural Network and Random Forest Models. Environ. Sci. 2023, 9, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemile, O.O.; Eze, N.E.; Ogedengbe, K. Effectiveness of Moringa Oleifera and Blends of Both Alum and Moringa as Coagulant in the Treatment of Dairy Wastewater. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1036, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzani, D.; Handajani, M.; Notodarmojo, S.; Helmy, Q.; Kardiansyah, T. The Synthesis and Use of Bio-Based Flocculant from Boehmeria Nivea in Coagulation-Flocculation and Direct Flocculation of Kaolin Suspension. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bouaidi, W.; Libralato, G.; Tazart, Z.; Enaime, G.; Douma, M.; Ounas, A.; Yaacoubi, A.; Lofrano, G.; Carotenuto, M.; Saviano, L.; et al. Nature-based Coagulants for Drinking Water Treatment: An Ecotoxicological Overview. Water Environ. Res. 2022, 94, e10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veli, S.; Arslan, A.; Isgoren, M.; Bingol, D.; Demiral, D. Experimental Design Approach to COD and Color Removal of Landfill Leachate by the Electrooxidation Process. Environ. Chall. 2021, 5, 100369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ran, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D. Evaluation of electro-oxidation of biologically treated landfill leachate using response surface methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramavandi, B.; Farjadfard, S. Removal of Chemical Oxygen Demand from Textile Wastewater Using a Natural Coagulant. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi Keerthi, D.; Mukunda Vani, M. Optimization Studies on Decolorization of Textile Wastewater Using Natural Coagulants. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owodunni, A.A.; Ismail, S. Revolutionary Technique for Sustainable Plant-Based Green Coagulants in Industrial Wastewater Treatment—A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Liu, S.; Chow, C.W.K.; Drikas, M.; Amal, R.; Lim, M. Understanding Effects of Water Characteristics on Natural Organic Matter Treatability by PACl and a Novel PACl-Chitosan Coagulants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.E.; Zazo, J.A.; Pliego, G.; Bidóia, E.D.; Moraes, P.B. Electrochemical oxidation of landfill leachate in a flow reactor: Optimization using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5831–5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaağaç, S.U.; Abujazar, M.S.S.; Amr, S.S.A.; Fatihah, S.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Ibrahim, E. The Potential Use of Olive Seeds Powder as Plant-Based Natural Coagulant for Sustainable Treatment of Industrial Wastewater. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 270, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, M.; Asaithambi, P.; Befekadu, A.; Alemayehu, E. Chemical oxygen demand removal from wet coffee processing wastewater using indigenous natural coagulants: Optimization through response surface methodology. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharati Fard, M.; Hamidi, D.; Alavi, J.; Jamshidian, R.; Pendashteh, A.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Saline Oily Wastewater Treatment Using Lallemantia Mucilage as a Natural Coagulant: Kinetic Study, Process Optimization, and Modeling. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 163, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, P.; Mbugua, D.M.; Pell, A.N. Analysis of Condensed Tannins: A Review. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2001, 91, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, S.F.F.S.; Abdul Aziz, H.; Mohd Omar, F.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D. Sludge performance in coagulation-flocculation treatment for suspended solids removal from landfill leachate using Tin (IV) chloride and Jatropha curcas. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 4716–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Industrial Wastewater Parameters | Units | Results |
|---|---|---|
| pH | -- | 8 |
| Color | Pt-Co | 865.6 |
| TSS | mg/L | 110 |
| COD | mg/L | 840.24 |
| NH3-N | mg/L | 42.8 |
| Manganese “Mn” | mg/L | 6.27 |
| Iron “Fe” | mg/L | 5.30 |
| Zinc “Zn” | mg/L | 5.44 |
| Aluminum “Al” | mg/L | 0.38 |
| Nickel “Ni” | mg/L | 0.15 |
| Parameters | Method |
|---|---|
| pH | pH meter |
| Color (Pt-Co) | SM 2120 C |
| TSS (mg/L) | SM 2540 D |
| COD (mg/L) | ASTM D1252-A |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11732 |
| Manganese “Mn” (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11885 |
| Iron “Fe” (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11885 |
| Zinc “Zn” (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11885 |
| Aluminum “Al” (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11885 |
| Nickel “Ni” (mg/L) | TS EN ISO 11885 |
| Process | COD Removal (%) | Color Removal (%) | TSS Removal (%) | NH3-N Removal (%) | Mn Removal (%) | Fe Removal (%) | Zn Removal (%) | Ni Removal, (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSP (1 g) | 86.1% | 82.9% | 99.0% | 79.0% | 85.7% | 90.7% | 90.6% | 78.0% |
| AlCl3 (1 g) | 87.80% | 84.00% | 99.00% | 88.60% | 88.70% | 91.50% | 91.70% | 88.80% |
| RSP/AlCl3 (0.75:0.75 g/g) | 88.29% | 91.85% | 99.00% | 93.11% | 94.3% | 98.5% | 96.70% | 99.30% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abujazar, M.S.S.; Karaagaç, S.U.; Amr, S.S.A.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Albahnasavi, A.; Nassani, D.E. The Synergistic Power of Rosehip Seed Powder and Aluminum Chloride in Steel Industry Wastewater Treatment. Water 2024, 16, 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192770
Abujazar MSS, Karaagaç SU, Amr SSA, Alazaiza MYD, Albahnasavi A, Nassani DE. The Synergistic Power of Rosehip Seed Powder and Aluminum Chloride in Steel Industry Wastewater Treatment. Water. 2024; 16(19):2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192770
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbujazar, Mohammed Shadi S., Sakine Ugurlu Karaagaç, Salem S. Abu Amr, Motasem Y. D. Alazaiza, Ahmed Albahnasavi, and Dia Eddin Nassani. 2024. "The Synergistic Power of Rosehip Seed Powder and Aluminum Chloride in Steel Industry Wastewater Treatment" Water 16, no. 19: 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192770
APA StyleAbujazar, M. S. S., Karaagaç, S. U., Amr, S. S. A., Alazaiza, M. Y. D., Albahnasavi, A., & Nassani, D. E. (2024). The Synergistic Power of Rosehip Seed Powder and Aluminum Chloride in Steel Industry Wastewater Treatment. Water, 16(19), 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192770










