Use of Machine Learning and Indexing Techniques for Identifying Industrial Pollutant Sources: A Case Study of the Lower Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
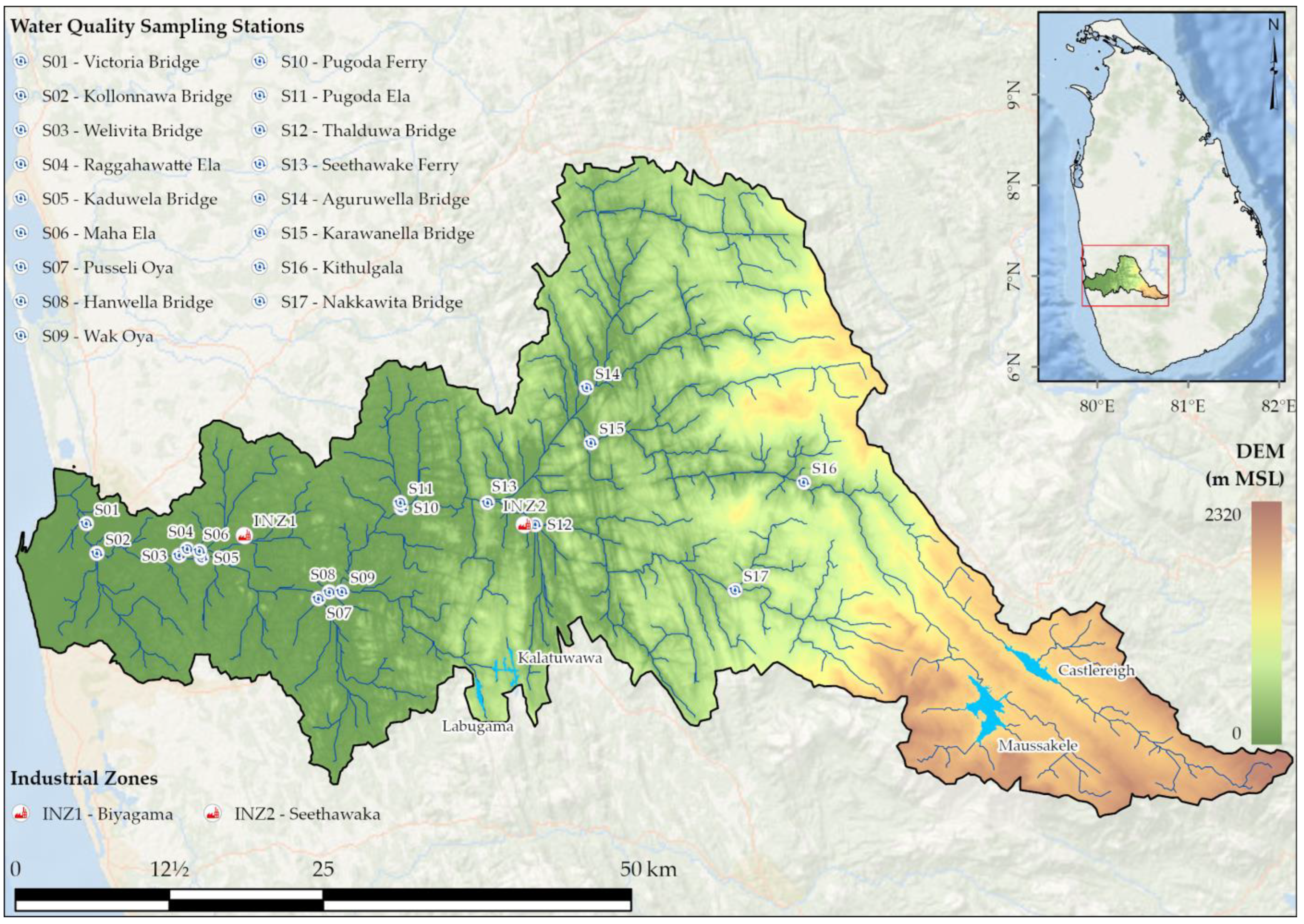
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Overall Research Methodology
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Machine Learning Approach: Unsupervised Learning
2.4.1. Factor Analysis (FA)
2.4.2. Self-Organising Map
2.5. Indexing Approach: Industrial Pollution Index (IPI)
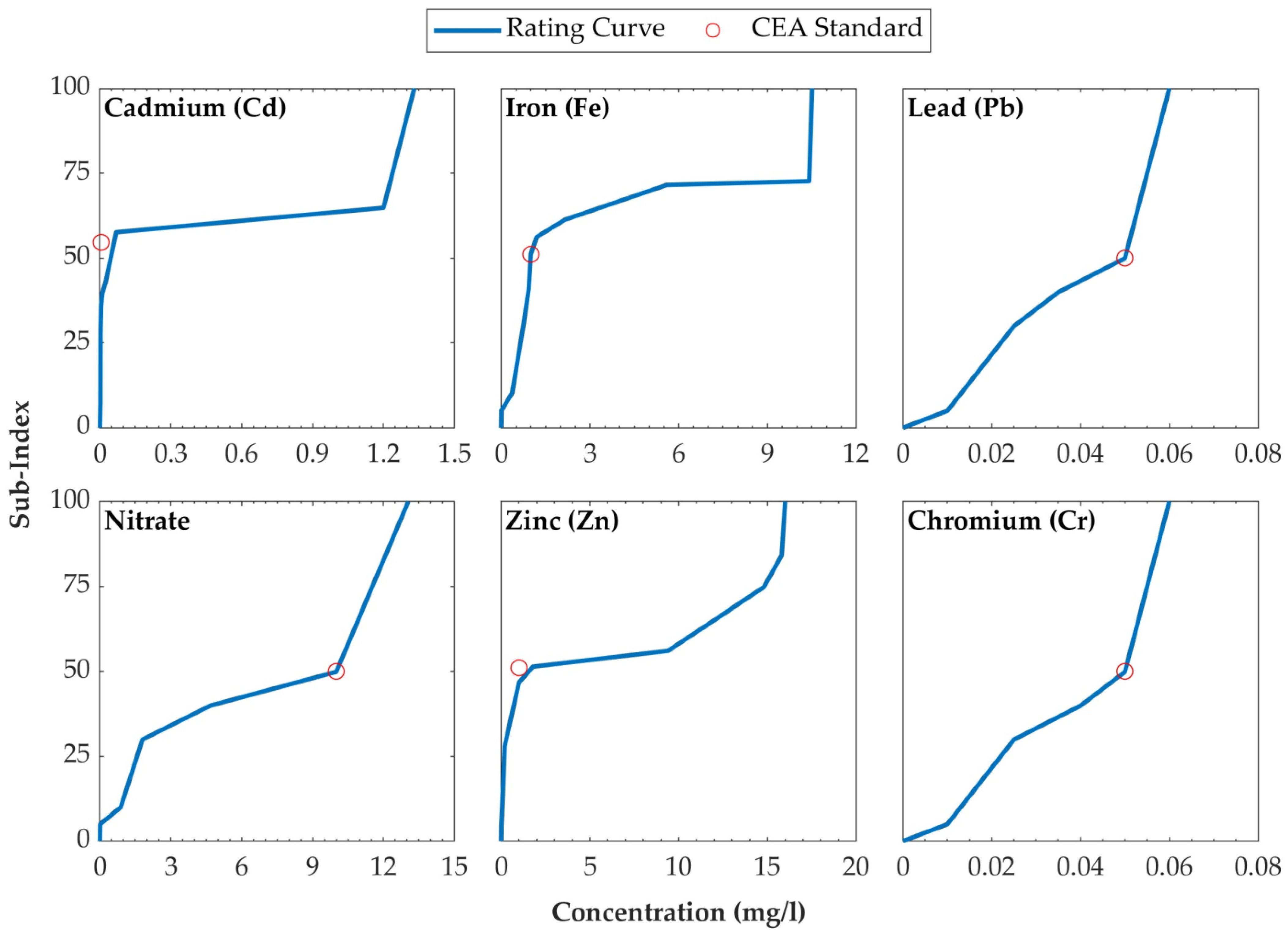
2.5.1. Parameter Identification and Sub-Indexing
2.5.2. Parameter Weighting
Random Forest (RF) Model
Rank Order Centroid (ROC) Method
2.5.3. Parameter Aggregation and Classification
Long Short-Term Memory Artificial Neural Network (LSTM-ANN)
2.6. Objective Functions
3. Results
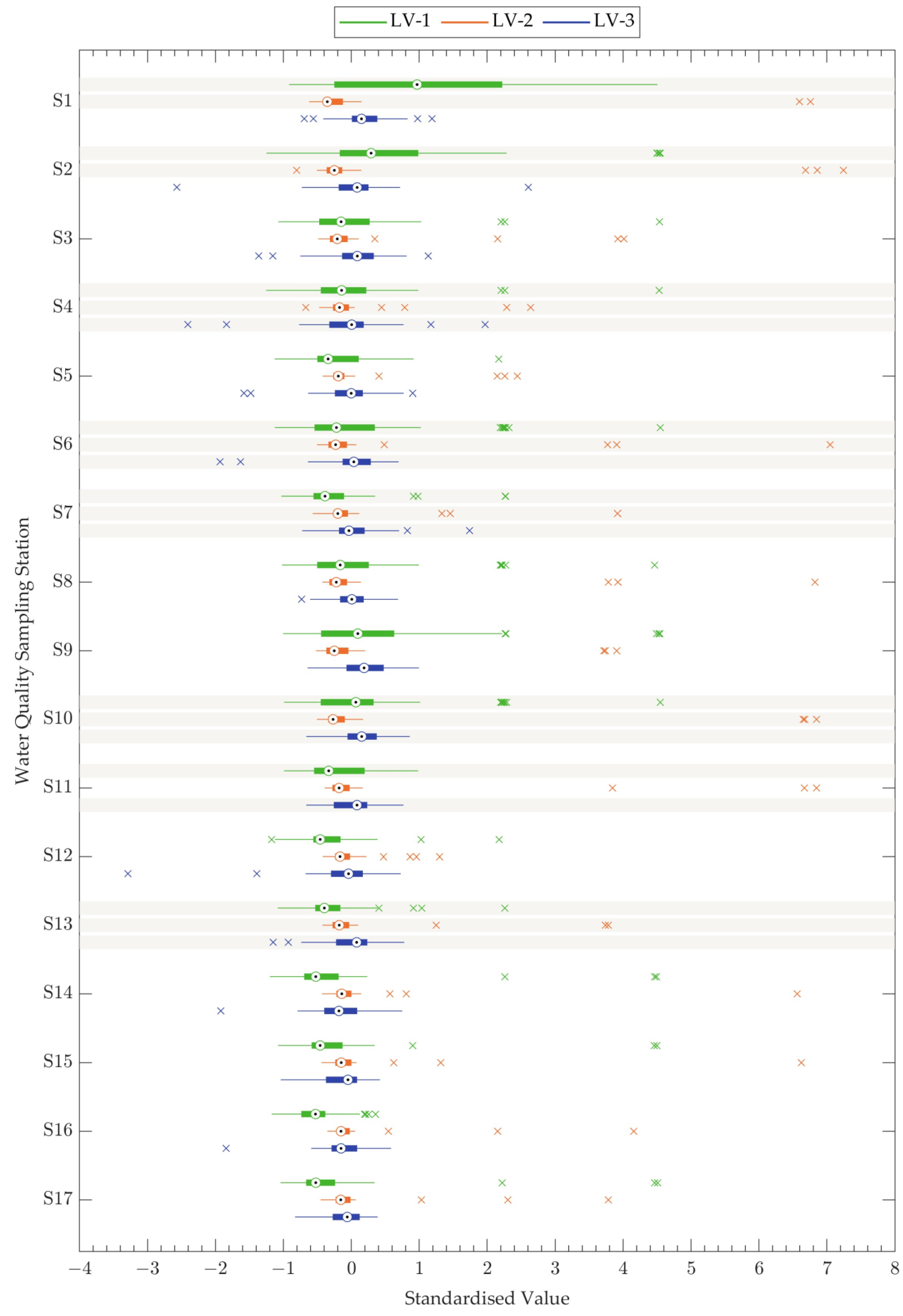
3.1. Unsupervised Learning Approach
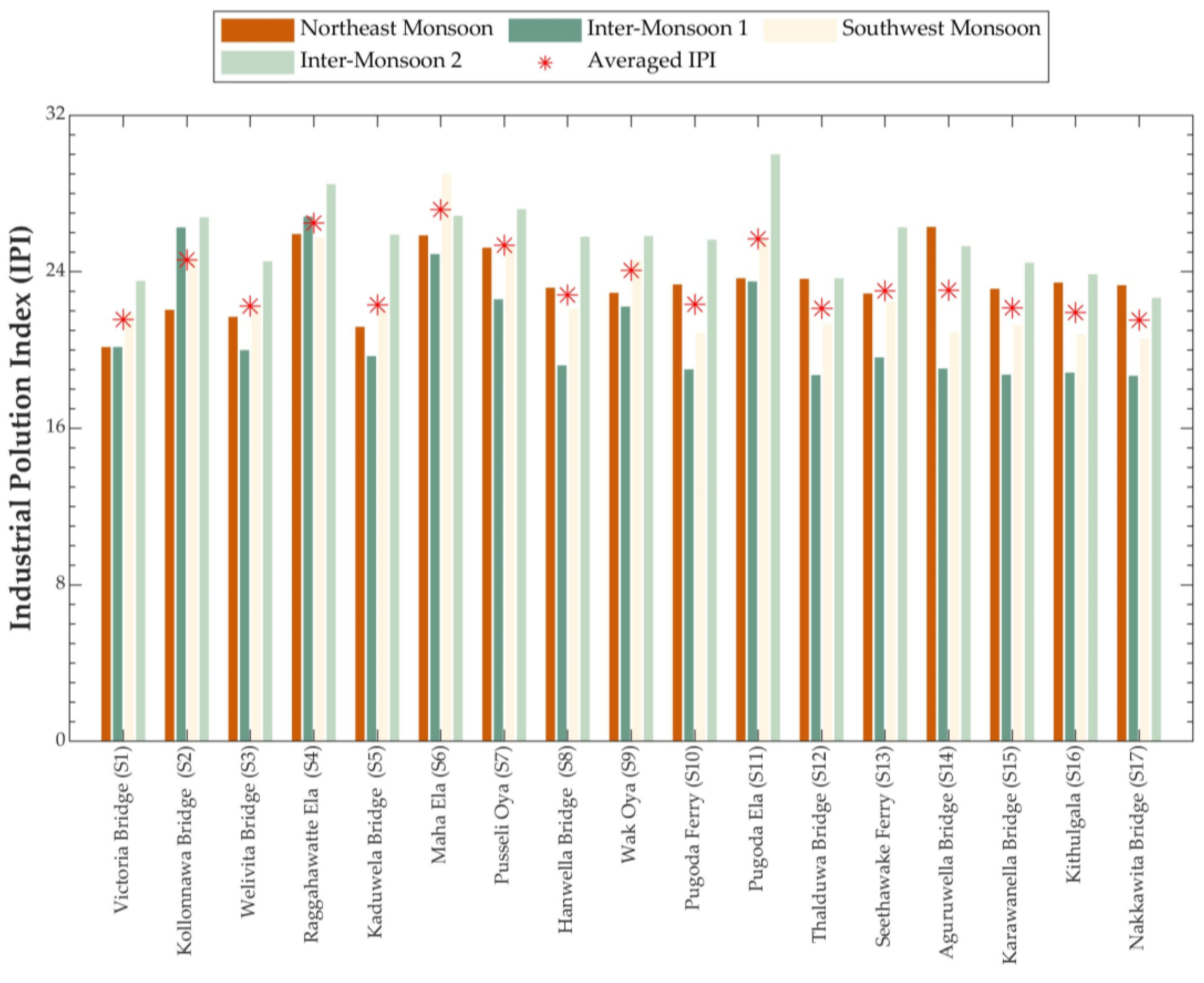
3.2. Industrial Pollution Index (IPI)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Central Environmental Authority Guidelines
- (1)
- Category A shall be water that requires simple treatment for drinking.
- (2)
- Category B shall be bathing and contact recreational water.
- (3)
- Category C shall be water suitable for aquatic life.
- (4)
- Category D shall be water sources that are required to undergo a general treatment process for drinking.
- (5)
- Category E shall be water suitable for irrigation and agricultural activities.
- (6)
- Category F shall be water with minimum quality but that does not fall into categories A to E
| Parameter | Category A | Category B | Category C | Category D | Category E | Category F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3− as N | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | - | 10 |
| Pb | 0.05 | - | 0.002 | 0.05 | - | - |
| Cd | 0.005 | - | 0.005 | 0.005 | - | 5 |
| Fe | 1 | - | - | 2 | - | - |
| Cr | 0.05 | - | 0.02 | 0.05 | - | 0.05 |
| Zn | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 24 |
References
- WHO. A Global Overview of National Regulations and Standards for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; ISBN 978-92-4-151376-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wear, S.L.; Acuña, V.; McDonald, R.; Font, C. Sewage Pollution, Declining Ecosystem Health, and Cross-Sector Collaboration. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 255, 109010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, A. Persistent Degradation: Global Water Quality Challenges and Required Actions. One Earth 2022, 5, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN-Water. Summary Progress Update 2021: SDG 6—Water and Sanitation for All; UN-Water: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner, M.; Bader, H.P.; Scheidegger, R. Modeling the Contribution of Point Sources and Non-Point Sources to Thachin River Water Pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4902–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Mulla, S.I.; Bilal, M.; Bharagava, R.N. Environmental and Health Hazards of Textile Industry Wastewater Pollutants and Its Treatment Approaches. In Handbook of Environmental Materials Management; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fořt, J.; Kobetičová, K.; Böhm, M.; Podlesný, J.; Jelínková, V.; Vachtlová, M.; Bureš, F.; Černý, R. Environmental Consequences of Rubber Crumb Application: Soil and Water Pollution. Polymers 2022, 14, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, N.T.; Can, L.D.; Nhan, N.T.; Schmalz, B.; Luu, T. Le Influences of Key Factors on River Water Quality in Urban and Rural Areas: A Review. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 8, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawari, G.; Kumar, N.; Sarkar, S.; Frank, A.L.; Daga, M.K.; Singh, M.M.; Joshi, T.K.; Singh, I. Human Health Risk Assessment Due to Heavy Metals in Ground and Surface Water and Association of Diseases with Drinking Water Sources: A Study from Maharashtra, India. Environ. Health Insights 2022, 16, 11786302221146020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, U.; Mumtaz, R.; Anwar, H.; Shah, A.A.; Irfan, R.; García-Nieto, J. Efficient Water Quality Prediction Using Supervised Machine Learning. Water 2019, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.; Kim, M.; Won, H.; Min, B.; Choi, H. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies Machine-Learning-Based Water Quality Management of River with Serial Impoundments in the Republic of Korea. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, H.; Wu, B.; Ye, L. Eco-Environment & Health A Review of the Application of Machine Learning in Water Quality Evaluation. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, M.P.; Solano Donado, F. Identifying and Estimating the Location of Sources of Industrial Pollution in the Sewage Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Qu, L.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K.; Huang, H. Distribution and Source Analysis of Heavy Metal Pollutants in Sediments of a Rapid Developing Urban River System. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; An, Z.; Wang, S. Analysis and Evaluation of the Source of Heavy Metals in Water of the River Changjiang. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barati Moghaddam, M.; Mazaheri, M.; Mohammad Vali Samani, J. Inverse Modeling of Contaminant Transport for Pollution Source Identification in Surface and Groundwaters: A Review. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 15, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Kumari, P.; Bano, S.; Kumari, S. Ground Water Quality Evaluation near Mining Area and Development of Heavy Metal Pollution Index. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseinzadeh, E.; Khorsandi, H.; Wei, C.; Alipour, M. Evaluation of Aydughmush River Water Quality Using the National Sanitation Foundation Water Quality Index (NSFWQI), River Pollution Index (RPI), and Forestry Water Quality Index (FWQI). Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 54, 2994–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaouzas, I.; Kapetanaki, N.; Mentzafou, A.; Kanellopoulos, T.D.; Skoulikidis, N. Heavy Metal Contamination Status in Greek Surface Waters: A Review with Application and Evaluation of Pollution Indices. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.K.; Sharma, S.; Patel, A.; Dixit, G.; Shah, E. Comprehensive Evaluation of Microalgal Based Dairy Effluent Treatment Process for Clean Water Generation and Other Value Added Products. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, A.K.; De Maio, M. Estimation of Heavy Metal Contamination in Groundwater and Development of a Heavy Metal Pollution Index by Using GIS Technique. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, J.P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Martens, W.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Development of a Hybrid Pollution Index for Heavy Metals in Marine and Estuarine Sediments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Wu, Q.T.; Shinde, D.; Huang, C.H. Assessment of Seasonal Variations in Surface Water Quality. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3800–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinalzadeh, K.; Rezaei, E. Determining Spatial and Temporal Changes of Surface Water Quality Using Principal Component Analysis. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, H.; Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y.; Soylu, E.N. Assessment of Water Quality of Streams in Northeast Turkey by Water Quality Index and Multiple Statistical Methods. Environ. Forensics 2021, 22, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Lenz, O.K.; Azad, A.K.; Ara, M.H.; Rahman, M.; Hassan, N. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Variations in Water Quality of Shailmari River, Khulna (Bangladesh) Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, K.; Liao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, P.; Wang, Z.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M. Evaluation of Spatial-Temporal Variations and Trends in Surface Water Quality across a Rural-Suburban-Urban Interface. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 8036–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, S.P.; He, L.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Yue, Y.; Zeng, H.; Xu, N. Assessing Water Quality in the Pearl River for the Last Decade Based on Clustering: Characteristic, Evolution and Policy Implications. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Tepe, Y.; Taş, B. Assessment of Stream Quality and Health Risk in a Subtropical Turkey River System: A Combined Approach Using Statistical Analysis and Water Quality Index. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhassan, A.M.; Wan Zainon, W.M.N. Review of Feature Selection, Dimensionality Reduction and Classification for Chronic Disease Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 87310–87317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, P.; Sivakumar, V. Application of K-Means and Hierarchical Clustering Techniques for Analysis of Air Pollution: A Review (1980–2019). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badillo, S.; Banfai, B.; Birzele, F.; Davydov, I.I.; Hutchinson, L.; Kam-Thong, T.; Siebourg-Polster, J.; Steiert, B.; Zhang, J.D. An Introduction to Machine Learning. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 871–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topp, S.N.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Jensen, D.; Simard, M.; Ross, M.R.V. Research Trends in the Use of Remote Sensing for Inland Water Quality Science: Moving towards Multidisciplinary Applications. Water 2020, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kushawaha, J.; Chauhan, J.S.; Sharma, S.; Singh, P. Water Pollutants: Sources and Impact on the Environment and Human Health. In Sensors in Water Pollutants Monitoring: Role of Material; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaweli Authority of Sri Lanka. Annual Report 2017; Ministry of Mahaweli Development and Environment: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2017.
- Mahagamage, M.G.Y.L.; Manage, P.M. Water Quality Index (CCME-WQI) Based Assessment Study of Water Quality in Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Environ. Nat. Resour. 2014, 1, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Narangoda, C.; Amarathunga, D.; Dangalle, C.D. Evaluation of Water Quality in the Upper and Lower Catchments of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water Pract. Technol. 2023, 18, 716–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations (UN). World Population Prospects 2024; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-92-1-148373-4. [Google Scholar]
- Manage, P.; Mahagamage, Y.L.; Ajward, R.; Amaratunge, S.; Amarathunga, V.I. The Need for Proper Management Leading to the Sustainability of the Kelani River and Its Lower Basin. J. Water Land Dev. 2020, 47, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Environmental Authority. Annual Report 2021; Central Environmental Authority: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hemachandra, C.K.; Pathiratne, A. Assessing Toxicity of Two Industrial Zone Effluents Reaching Kelani River, Sri Lanka. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2018, 46, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, H.M.; Alam, S.T.; Hasan, M.; Yameogo, D.D.S.; Kannan, A.D.; Rahman, A.; Kwon, M.J. Phosphorous in the Environment: Characteristics with Distribution and Effects, Removal Mechanisms, Treatment Technologies, and Factors Affecting Recovery as Minerals in Natural and Engineered Systems. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20183–20207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, N. Factor Analysis as a Tool for Survey Analysis. Am. J. Appl. Math. Stat. 2021, 9, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuero, A.G.; Sayago, A.; González, A.G. The Correlation Coefficient: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, M.; Al-Shebany, M.; Sarhan, S. Artificial Neural Network: A Brief Overview. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2014, 4, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Treshansky, A.; McGraw, R.M. Overview of Clustering Algorithms. Enabling Technol. Simul. Sci. V 2001, 4367, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, M.G.H.; Engelbrecht, A.P.; Salman, A. An Overview of Clustering Methods. Intell. Data Anal. 2007, 11, 583–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhabi, D.K.; Mensah, P.K.; Asare, N.K.; Pulumuka-Kamanga, T.; Ouma, K.O. Adapted Water Quality Indices: Limitations and Potential for Water Quality Monitoring in Africa. Water 2023, 15, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Alappat, B.J. Selection of the Appropriate Aggregation Function for Calculating Leachate Pollution Index. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2004, 8, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, S.; El Najjar, P.; Ouaini, N.; El Rayess, Y.; El Azzi, D. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): History, Models, Attempts and Perspectives; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 22, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Hallock, D. A Water Quality Index for Ecology’s Stream Monitoring Program; Washington State Department of Ecology: Olympia, Greece, 2002.
- Casillas-García, L.F.; de Anda, J.; Yebra-Montes, C.; Shear, H.; Díaz-Vázquez, D.; Gradilla-Hernández, M.S. Development of a Specific Water Quality Index for the Protection of Aquatic Life of a Highly Polluted Urban River. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Rahman, A.; Nash, S.; Diganta, M.T.M.; Sajib, A.M.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Olbert, A.I. Marine Waters Assessment Using Improved Water Quality Model Incorporating Machine Learning Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaya, M.S.; Abba, S.I.; Abdu, A.M.; Tukur, A.I.; Saleh, M.A.; Esmaili, P.; Wahab, N.A. Estimation of Water Quality Index Using Artificial Intelligence Approaches and Multi-Linear Regression. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2020, 9, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Yuan, W.; Gao, M.; Wu, J.; Han, Z. Groundwater Quality Assessment Based on the Random Forest Water Quality Index—Taking Karamay City as an Example. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Rahman, A.; Olbert, A.I. Development of a Water Quality Index Model—A Comparative Analysis of Various Weighting Methods. In Proceedings of the Mediterranean Geosciences Union Annual Meeting, Instanbul, Turkey, 25–28 November 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Kuang, J.; Lin, C.; Xiao, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. An Alternative to Laboratory Testing: Random Forest-Based Water Bodies. Water 2021, 13, 3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.A.; Kalakech, A.; Steiti, A. Random Forest Algorithm Overview. Babylon. J. Mach. Learn. 2024, 2014, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, G.; Scornet, E. A Random Forest Guided Tour. Test 2016, 25, 197–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, T.; Waghmare, A.V.; Singh, V.P.; Ramu, M.; Patnana, N.; Meena, V.P.; Azar, A.T.; Hameed, I.A. Investigation of Rank Order Centroid Method for Optimal Generation Control. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syeed, M.M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Karim, M.R.; Uddin, M.F.; Hasan, M.; Khan, R.H. Surface Water Quality Profiling Using the Water Quality Index, Pollution Index, and Statistical Methods: A Critical Review. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2023, 18, 100247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Umar, K.; Md Yusuff, M.S.; Anees, M.T.; Qadir, A.; Almanasir, Y.K.A. Modification of the Water Quality Index (Wqi) Process for Simple Calculation Using the Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (Mcdm) Method: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A Review of Water Quality Index Models and Their Use for Assessing Surface Water Quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouri, L.; Bashar Al-Moufti, M. Selection of Suitable Aggregation Function for Estimation of Water Quality Index for the Orontes River. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 142, 109290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C. A Transdisciplinary Review of Deep Learning Research and Its Relevance for Water Resources Scientists. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 8558–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y. A Review of Artificial Neural Network Techniques for Environmental Issues Prediction. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2021, 145, 2191–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, A.; Thamrin, N.M.; Ali, M.S.A.M.; Misnan, M.F.; Yassin, A.I.M. Water Quality Prediction Using Lstm-Rnn: A Review. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 2022, 17, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayissa, Y.A.; Tadesse, T.; Svoboda, M.; Wardlow, B.; Poulsen, C.; Swigart, J.; Van Andel, S.J. Developing a Satellite-Based Combined Drought Indicator to Monitor Agricultural Drought: A Case Study for Ethiopia. GIScience Remote Sens. 2019, 56, 718–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Dixit, J. Assessment of Landslide Susceptibility for Meghalaya (India) Using Bivariate (Frequency Ratio and Shannon Entropy) and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (AHP and Fuzzy-AHP) Models. All Earth 2022, 34, 179–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R. Performance Evaluation of Hydrological Models: Statistical Significance for Reducing Subjectivity in Goodness-of-Fit Assessments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makubura, R.; Meddage, D.P.P.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Pandey, M.; Rathnayake, U. A Simplified Mathematical Formulation for Water Quality Index (WQI): A Case Study in the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Fluids 2022, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, M.H.M.A.S.V.; Sanjaya, K.; Atapaththu, K.S.S.; Yapa Mudiyanselage, A.L.W.Y.; Masakorala, K.; Widana Gamage, S.M.K. Quantitative Prediction of Toxin-Producing Aphanizomenon Cyanobacteria in Freshwaters Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 1364–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvinda, K.M.; Pathiratne, A. Biomarker Responses of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Exposed to Polluted Water from Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka: Implications for Biomonitoring River Pollution. Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ranasinghe, P.N.; Siriwardana, Y.P.S.; Wanasinghe, V.R. Heavy Metal Pollution in Drainage Network of Colombo City and Suburbs of Sri Lanka. Chin. J. Geochem. 2006, 25, 84–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, P.; Lu, K.; Tantai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X. Catena Seasonal Changes in Water Quality and Its Main in Fl Uencing Factors in the Dan River Basin. Catena 2019, 173, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwyanjalee, G.R.; Premarathne, W.A.P.J. Impact of Rainfall on the Water Quality of a Tropical River: Based on the Nilwala River in the Southern Province of Sri Lanka between March and October 2019. Water Pract. Technol. 2024, 19, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, A.; Babel, S. Science of the Total Environment Microplastics and Heavy Metals in a Tropical River: Understanding Spatial and Seasonal Trends and Developing Response Strategies Using DPSIR Framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 897, 165405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Quantiles | For a Subset of Observations Lower than the Standard Limit | For a Subset of Observations Higher than the Standard Limit |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||
| 0.1 | ||
| 0.8 | ||
| 0.95 | ||
| 0.99 | ||
| 1 | 100 |
| Percentile Range | Pollution Type |
|---|---|
| 0–20 | Very Low Pollution |
| 20–40 | Low Pollution |
| 40–60 | Moderate Pollution |
| 60–80 | High Pollution |
| 80–100 | Extreme Pollution |
| Parameter | Latent Variable 1 | Latent Variable 2 | Latent Variable 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrate | −0.08 | 0.63 | −0.12 |
| Cr | 0.01 | −0.04 | 0.04 |
| Pb | −0.13 | 0.64 | 0.16 |
| Cd | 0.81 | −0.08 | 0.11 |
| Fe | 0.82 | −0.16 | −0.04 |
| Zn | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.30 |
| Cumulative Variance (%) | 31.5 | 51.4 | 68.5 |
| Eigen Value | 1.89 | 1.19 | 1.03 |
| Parameter | Parameter Importance (RF) | Parameter Weight (ROC) |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.525 | 0.245 |
| Fe | 0.148 | 0.232 |
| Zn | 0.154 | 0.218 |
| Cr | 0.073 | 0.109 |
| Pb | 0.055 | 0.107 |
| Nitrate | 0.045 | 0.089 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wijayaweera, N.; Gunawardhana, L.; Bamunawala, J.; Sirisena, J.; Rajapakse, L.; Patabendige, C.S.; Karunaweera, H. Use of Machine Learning and Indexing Techniques for Identifying Industrial Pollutant Sources: A Case Study of the Lower Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water 2024, 16, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192766
Wijayaweera N, Gunawardhana L, Bamunawala J, Sirisena J, Rajapakse L, Patabendige CS, Karunaweera H. Use of Machine Learning and Indexing Techniques for Identifying Industrial Pollutant Sources: A Case Study of the Lower Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water. 2024; 16(19):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192766
Chicago/Turabian StyleWijayaweera, Nalintha, Luminda Gunawardhana, Janaka Bamunawala, Jeewanthi Sirisena, Lalith Rajapakse, Chaminda Samarasuriya Patabendige, and Himali Karunaweera. 2024. "Use of Machine Learning and Indexing Techniques for Identifying Industrial Pollutant Sources: A Case Study of the Lower Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka" Water 16, no. 19: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192766
APA StyleWijayaweera, N., Gunawardhana, L., Bamunawala, J., Sirisena, J., Rajapakse, L., Patabendige, C. S., & Karunaweera, H. (2024). Use of Machine Learning and Indexing Techniques for Identifying Industrial Pollutant Sources: A Case Study of the Lower Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water, 16(19), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16192766








