Abstract
In this study, the chemical fractions (CFs) of trace metal (TMs) and multiple magnetic parameters were analysed in the sedimentary column from the centre of Lake Taihu. The sedimentary column, measuring 53 cm in length, was dated using 210Pb and 137Cs to be 124 years old. Surface layers of the column were found to contain significantly higher concentrations of Cd, Co, Cu, Pb, Sb, Ti, and Zn than the middle and bottom layers. The sedimentary core contained a substantial amount of ferrimagnetic minerals. Most of the TMs were present in the residual state, except for Mn and Pb. The chemical fractions of Cd exhibited the most significant variation with depth. The pollution load index (PLI) indicated moderate TMs pollution levels in the region, whereas the risk assessment code (RAC) classified Mn as being heavily polluted. Multiple linear regression (MLR) and random forest (RF), support vector machine (SVM), and XGBoost (1.7.7.1) machine learning models were used to simulate the RAC and total concentration of TMs, using physical and chemical indicators and magnetic parameters of the sediments as input variables. The MLR model outperformed RF, SVM, and XGBoost in simulating the CFs and total concentrations of most TMs in the sedimentary column, with R2 up to 0.668 and 0.87. The SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) method reveals that χarm/χ is the dominant factor influencing the RAC of As in the XGBoost models. For the RAC of Co and Cu in RF models, C% and N% exhibit greater contributions.
1. Introduction
Trace metals (TMs) pose a significant threat to lake ecosystems and human health due to their toxicity, persistence, and bioaccumulation [1,2,3]. Lake sediments act as crucial repositories for these contaminants, reflecting the health of aquatic systems and preserving a long-term record of environmental conditions [4,5,6]. The vertical and historical distribution of TMs in sediments not only reveal the current state and historical trends of TM contamination in lakes, but also shed light on the evolution of natural and human-induced inputs to these ecosystems [7,8,9]. Studying the vertical and historical distribution of TMs in lake sediments is essential for accurately assessing the environmental hazards associated with TM pollution [10]. The risk (referred to as ecological risk) that TMs pose to ecosystems mainly depends on their chemical fractions (CFs), not just their total concentration [11]. The CFs of TMs in the sediments significantly affected their mobility, bioavailability, and biotoxicity [12]. Current methods for analysing these CFs are often laborious, expensive, and struggle to identify contamination signatures in complex environments.
Environmental magnetism provides rapid analysis of the scope, extent, source, and history of environmental pollution by testing and analysing the magnetic properties of the research object, and also reveals information on the type, content, and granularity of magnetic minerals reflected in different magnetic parameters [13]. Magnetic methods offer the unique advantages of being highly sensitive, rapid, economical, and non-destructive compared to conventional methods. TMs can either cling to the surface or be incorporated within these magnetic particles [14]. Thus, there is a significant correlation between magnetic concentration parameters and TM concentrations. This strong correlation allows us to use magnetic properties to estimate TM concentrations and risks, making it a valuable tool for screening and monitoring pollution.
This correlation between magnetic properties and TMs holds true for sediments in water bodies. Magnetic minerals often originate alongside TMs, and Fe/Mn oxides further enhance this association by attracting these minerals. Additionally, minerals combined with near-ferrous elements, magnetic bacteria, and even complexes of TMs and these elements all contribute to the overall magnetic signature of the sediment [15,16,17,18]. Studies have confirmed this link. Ma found strong correlations between magnetic parameters and TM concentrations in reservoir sediments near a steel plant [19]. Similarly, Costanzo-Alvarez identified magnetic susceptibility (χfd%) that best reflected changes in pollution levels in a Spanish river [20]. Zhang observed a significant correlation between non-hysteresis remanent magnetisation (χarm) and Cu, Zn, and Pb in Chinese river estuary sediments [21]. However, most research has focused on the total concentration of TMs and the magnetic properties in surface sediments. Less is known about the CFs of TMs and how they relate to magnetic properties across different sediment layers. Further research is required to explore these relationships and their vertical variation throughout the sedimentary column.
Machine learning is a powerful tool that excels at discovering hidden connections in data, learning these connections by analysing a training set and then validating the results using a separate test set. Traditional methods for TM analysis are often slow and labour-intensive, whereas machine learning offers a compelling alternative. By learning the connections between the magnetic parameters of the sediment, physical and CFs, and concentrations of TMs within a training dataset, the model can rapidly predict contamination levels and ecological risks based solely on these readily measurable sediment properties. The multiple linear regression (MLR) model is a machine learning regression algorithm used to predict linear relationships, in a broad sense, between continuous dependent variables and multiple independent variables. Random forest (RF) is an ensemble learning algorithm that excels in both classification and regression tasks by creating numerous decision trees and aggregating their predictions. With superior generalization capabilities, it efficiently handles high-dimensional data. Support vector machine (SVM) is an optimal hyperplane-based model for classification and regression tasks. By determining the hyperplane that maximizes the margin between classes, SVM is adept at handling linear and non-linear data, particularly shining in small-sample datasets. XGBoost, a gradient boosting tree algorithm, enhances model accuracy by iteratively training multiple decision trees and merging their predictions. It thrives with large-scale data and intricate features, showcasing robustness and interpretability. SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis is a robust method for interpreting the outputs of machine learning models. By quantifying the contribution of individual features to the final prediction, SHAP illuminates the underlying decision-making process. The magnitude of SHAP values allows for the identification of the most influential features, enabling targeted model optimization. Moreover, applying SHAP analysis to the entire dataset provides a comprehensive understanding of the model’s dependencies on various features and overall trends. This aids in uncovering hidden patterns, regularities, and potential biases within the data.
Therefore, the objectives of the present study are to (1) determine the sediment age by using 210Pb and 137Cs and to reconstruct the contamination deposition history of TMs in Lake Taihu, (2) analyse the characteristics of the vertical distribution of the CFs of TMs in the sedimentary column, assessing the ecological risk of TMs in the column, and (3) construct a magnetic diagnostic model of CFs using machine learning methods for the rapid identification of ecological risks from TMs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
Taihu Basin is located in the Yangtze River Delta region of China, with a good base of agricultural production, developed industry, and dense population. The average water depth of Lake Taihu is 1.9 m, and the average thickness of sediments throughout the lake is 0.82 m, with a total sediment accumulation of up to 1.915 billion m3. In this study, sedimentary samples were collected in the centre of Lake Taihu, encompassing the largest area and being relatively less affected by anthropogenic siltation, using columnar sludge extractors. The samples were sliced and divided every 1 cm in the field and placed into clean polyethylene airtight bags. The samples were freeze-dried, and the debris, such as stones and shells, was removed. Then, each sample was ball-milled in an agate mortar and pestle, then sieved through 100 mesh for analysis.
2.2. Sample Measurement
2.2.1. Methods for Physicochemical Indexes and Dating of the Sedimentary Column
In this study, the combined dating method using 210Pb and 137Cs was used to date the sedimentary column, and the CRS model was used to calculate the deposition rate of the column. The experimental steps are mainly as follows: The sediment samples, which have been freeze-dried to remove impurities, were first sealed in sample vials for 21 days to reach a relative radio-equilibrium state. Then, a high-purity germanium well-type detector (Ortec GWL-120-15, EG&G Ortec Company, Oak Ridge, TN, USA) was used to measure the specific activities of 137Cs,226Ra, and 210Pb at a γ-energy spectra of 46.5, 351.9, and 661.6 keV, respectively, with a measurement error of less than 5%. The excess 210Pb (210Pbex) was calculated from the difference between the specific activities of 210Pb and 226Ra. The detailed calculation process can be found in the Supporting Information. Methods for determining TOC, TP, N%, and C% for the settling column are provided in Table S2.
2.2.2. Trace Metal Determination
The three-stage, four-step sequential extraction method proposed by the European Community Bureau for Standardised Substances was used for the extraction of the CFs of the TMs. The method classifies TMs into four CFs: exchangeable and carbonate-bound (F1), ferromanganese oxide-bound (F2), organic and sulphide-bound (F3), and residual residue (F4), the first three of which are collectively referred to as the bioeffective forms. The reagents used in the experiments were of superior purity, and the blank liquid extraction was carried out simultaneously. The dried sediment sample weighed 0.8 g. The specific experimental steps and reagents required are shown in Table S1.
For the determination of the total concentration of TMs, it is necessary to reweigh the sample and refer to the extraction method of the residue state in the fourth step. The concentrations of As, Cd, Cr, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, Sb, and Zn were determined using the inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (HJ 803-2016) method, with the detection limits of 0.05, 0.07, 2, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0, 0.7, 2.0, 2.0, 0.3, and 7.0 mg·kg−1, respectively, and the concentration of Hg was determined using the atomic fluorescence method (HJ 680-2013), with the detection limit of 0.002 mg·kg−1. After the completion of the determination of the total concentration of TMs, the sum of the concentrations of the four forms of each TM was calculated to account for the individual total extracted concentration. The sums of the concentrations of HMs in the four CFs were compared with their total concentrations in the sediment measured separately. The results showed that the total recovery rate is greater than or equal to 90%.
2.2.3. Physicochemical Indicators and Magnetic Measurement
A total of 5 g of the freeze-dried sample was weighed, wrapped in cling film, and placed in an 11.15 cm3 cylindrical non-magnetic plastic box for magnetic testing. The low frequency (χlf, 0.47 kHz) and high frequency (χhf, 4.7 kHz) magnetisations of the samples were measured using a Bartington-MS2 magnetisation meter. The samples were demagnetised using a Dtech2000 alternating demagnetiser, with a peak alternating magnetic field of 100 mT and a DC magnetic field of 0.05 mT, and the ARM values were measured using a JR-6A rotating magnetometer to calculate the χarm. The samples were magnetised using an ASCIM-10-30 pulsed magnetisation meter with magnetic fields of 20, 100, 300, and 1000 mT. The corresponding ARMs were measured, and the isothermal remanent magnetisation obtained under a pulsed magnetic field, with a peak value of 1000 mT, was the saturated isothermal remanent magnetization (SIRM). Subsequently, the samples were magnetised in a reversed magnetic field, and the isothermal remanent magnetisation in the reversed magnetic field was measured, with the remaining selected field strengths of −20 mT, −100 mT, and −300 mT, and remanent magnetisation data were obtained as follows: IRM-20, IRM-100, IRM-300, and IRM. The remaining parameters are calculated as follows:
2.3. Pollution Evaluation Methods
The pollution load index (PLI) was used to evaluate the overall regional pollution level and the contribution of TM pollution; the formula is shown in the Supporting Information [22]. The grading of the PLI is shown in Table S3.
The ratio of secondary to primary phase (RSP) is a method used to judge the relative retention time and potential hazard of metals in the local area, based on the distribution pattern of TMs [23]; the formula is as follows:
is the degree of contamination, is the concentration of the extracted state of the secondary phase (F1 + F2 + F3) of sediment TMs, and is the concentration of the residual state of the primary phase (F4) of sediment TMs. The grading criteria of the secondary phase compared with primary phase method are shown in Table S3.
2.4. Ecological Risk Assessment Methodology
The comprehensive potential ecological risk index (RI) integrates the regional background values of TMs [24], toxicity factors, and the sensitivity of the evaluation area to TM contamination, and it can be used to evaluate the hazards produced by the combination of a variety of TMs in sediments. The calculation expression is shown in the Supporting Information.
The risk assessment code (RAC) method evaluates the ecological risk of TMs, based on the proportion of the acid extractable state in the total amount [25], using the following formula:
is the risk index of TMs in sediments; CFi is the concentration of each HM in the CFs (mg·kg−1); the assessment levels are shown in Table S3.
2.5. Machine Learning Methods
The MLR model is a multivariate statistical analysis method used to build ideal equations based on the optimal combination of multiple independent variables (Xn) to predict the dependent variable (Y) [11,12], and its basic form is shown in Equation (6), as follows:
Y is the dependent variable, X1~Xn are the independent variables, b0~bn are the overall regression parameters, and ε is the regression error.
In this study, MLR, RF, SVM, and XGBoost were developed to predict the total concentration of TMs and their associated RAC indices in the Lake Taihu sedimentary column. A total of 13 TMs, including physical and chemical indicators and magnetic parameters, were used as input variables. The total concentration of each TM and its corresponding RAC value served as the output targets. A total of 80% of the data was included in a training set, and 20% was assigned to a test set. In this study, only simulations with an R2 exceeding 0.5 are considered. To further analyse the influence of various factors on RAC values, the SHAP analytical method was employed to investigate the contributions of TOC, C%, N%, TP, and magnetic parameters in the machine learning models.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Sedimentary Column Chronology
The analysis results of 137Cs (Bq/kg) and 210Pbex in the sediment are shown in Figure 1. The maximum value of 137Cs appears at 9 cm in the sedimentary column. Historically, the first peak value of 137Cs should appear in the year 1963 [26]. It is obviously very unreasonable that only 9 cm has been deposited in 57 years. However, 210Pbex decreases exponentially with the increase in depth, indicating a stable sedimentary environment. The age of the sedimentary column is calculated using the CRS model of 210Pbex. The calculation formula can be found in the Supporting Information. The calculation results are shown in Figure S1. The results show that around 18 cm of the sedimentary column appeared in the year 1986, around 28 cm was noted around 1975, and around 34 cm existed in 1965. This is consistent with the research results of others [27]. The sedimentary column revealed a record spanning 124 years (1895–2019), with an average sedimentation rate of 0.75 g per square centimetre per year (g·cm−2·a−1) (Figure 1). Interestingly, the sedimentation rate exhibited a distinct trend, e.g., initially decreasing with depth, then continuously increasing, and finally decreasing again. This pattern significantly differs from observations in the western part of Lake Taihu, potentially due to geographical factors and crustal movements [28,29]. To further explore these changes, we identified turning points in the sedimentation rate at the 10th (approximately 1990) and 30th (approximately 1971) layers. These shifts may be linked to national development policy in China and changes in industrial activity around the lake. Based on these turning points, we divided the sediment core into three layers: the surface layer (layers 1–10, SLs), the middle layer (layers 11–30, MLs), and the bottom layer (layers 31–53, BL).
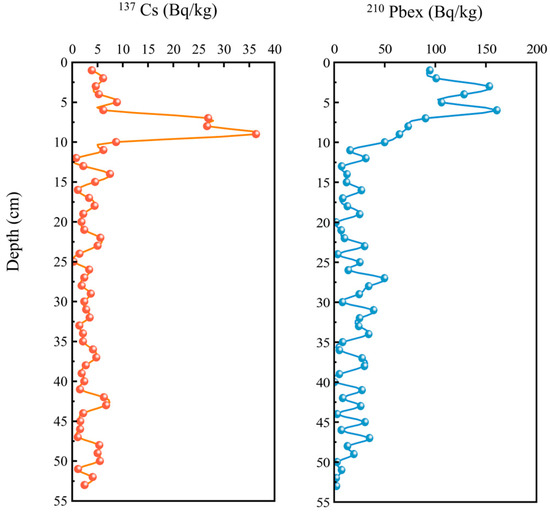
Figure 1.
Vertical distribution of 137 Cs (Bq/kg) and 210 Pbex (Bq/kg) in the sediment.
3.2. Trends in TMs Concentrations, PLI, and RI
3.2.1. Trends in TMs Concentrations
The concentrations of TMs in the sedimentary column are shown in Table S4, and concentrations of TOC, TP, C%, and N% appear in Figure S2. Fe, Ti, and Mn exhibited the highest concentrations. Conversely, Sb, Cd, and Hg displayed the lowest concentrations in the sediment core (Figure 2). Except for Hg and Sb, the concentrations of all TMs were greater than the background values for soils in Jiangsu Province. Compared to other studies, the concentrations of As, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Sb, Ti, and Zn observed in this study were higher than those reported for a reservoir sedimentary column [30]. Additionally, Zn, Pb, and Cr levels exceeded those found in the western Lake Taihu sedimentary column. Compared with surface sediments from other locations in Lake Taihu, the average TMs concentrations in this core fall within a moderate range [31].

Figure 2.
Average concentration of TMs in the sedimentary column.
Vertically, the concentrations of most TMs in the SLs show a gradual decrease with increasing depth (Figure S3). However, As, Cd, and Cu concentrations in layers 6~10 exhibit a slight increase. The MLs display significant fluctuations in As, Cr, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sb, and Zn, while the BLs show relatively stable concentrations. Fe, Mn, and Ti levels also fluctuate considerably in both MLs and BLs. Overall, the SLs exhibit significantly higher concentrations of Cd, Co, Cu, Pb, Sb, Ti, and Zn compared to the MLs and BLs. Conversely, Cr and Mn concentrations are significantly higher in the MLs and BLs, especially in the BLs when compared to the amounts in the SLs.
These observed variations likely stem from changes in the surrounding industrial structure and in national policies. Prior to 1990, China’s industrial focus centred on steel production and electroplating processes [32]. Consequently, Mn and Cr, crucial additives used in these industries, were used in much greater quantities than were other metals. With industrial transformation and evolving national policies, sectors like textile printing and dyeing, chemical production, mechanical processing, and fertilizer/pesticide production have flourished around Lake Taihu. This industrial and agricultural expansion has led to a gradual increase in various TM concentrations within the lake. However, stricter national policies on TM pollution control have mandated stricter discharge standards for key industries, resulting in a decrease in the amount of certain TMs (particularly As, Cd, and Cu) entering Lake Taihu [33].
3.2.2. PLI and RI
The PLI of 13 TMs in the sedimentary column ranged from 1.07 to 1.70, with an average value of 1.28, indicating an overall moderate level of TMs contamination. The results are consistent with those of Zhang [34]. The PLI showed a decreasing trend with increasing depth (Figure 3). The PLI value of the SL was higher than that of the ML and BL, and the PLI value below 15 cm was relatively stable, fluctuating around 1.2. The RI values of trace metals in the first five layers of the sedimentary column are all greater than 300, indicating medium risk. The RI values of trace metals in the sediments from layer 5 to layer 13 gradually decrease with the increase in depth, indicating low risk. After layer 13, the RI value continuously fluctuates between no risk and low risk. The average value of Cd exceeded 40, indicating a moderate pollution level, and the maximum value was 159.9, indicating a high pollution level. The average value of Sb was less than 40, and the maximum value was 97.57. Except for Cd and Sb, the values of the other 11 TMs were all less than 40, indicating no pollution level. The potential ecological risk index indicated that Cd was the main contributor to the ecological risk in the region, which is consistent with the results of others [35].

Figure 3.
Trend of the TMs PLI and RI in sedimentary columns.
3.3. Trends in TM Chemical Fractions
3.3.1. Trends in Chemical Fractions of TMs
Mn and Pb were primarily found in bioavailable fractions (F1 + F2 + F3). Notably, Mn resided mainly in the F1 fraction, suggesting its easy displacement and release by cations like potassium (K⁺), calcium (Ca2⁺), and magnesium (Mg2⁺) [36]. Lead, on the other hand, concentrated in the F2 fraction, was readily soluble in weakly acidic environments, and was susceptible to increased bioavailability due to changes in external conditions [37]. The F4fraction dominated the speciation of As, Co, Cr, Fe, Ni, Hg, Sb, Ti, and Zn. Interestingly, As and Cr exhibited F4 proportions exceeding 80%, aligning with observations noted in the Wushui River [38]. Metals within the F4 fraction are typically incorporated into the crystal lattice of minerals, granting them long-term stability under natural conditions. Consequently, they are unavailable for biological uptake and pose a minimal environmental threat [39]. However, Cd and Cu, despite being predominantly found in F4, also displayed significant bioavailable fractions, indicating a potential environmental risk. The residual Mn primarily occurred in the form of insoluble minerals. Its content variations are primarily influenced by the sources of sediment pollution and diagenetic processes [40]. The percentage of Mn in fraction F4 initially decreases before gradually increasing with depth. This trend might be attributed to the diverse sources of heavy metals during distinct sedimentary episodes. Additionally, as depth increases, pore water reduction could potentially lead to a relative enrichment of F4 Mn. The percentage of Mn in fraction F2 exhibits an initial rise, followed by a decline with increasing depth. Besides pollution sources, redox conditions, organic matter, and bioturbation may also influence this trend. The percentage of Mn in fraction F1 gradually increases with depth, possibly due to diagenetic Mn reactivation. MnO2 dissolves under reducing conditions, releasing Mn2+ ions. These ions diffuse downward through interstitial water, eventually precipitating as carbonates and transitioning into the F4 state [41].
Our findings reveal a depth-dependent transformation of TMs fractions (Figure 4). The F3 fraction of all TMs remains relatively unchanged with increasing depth. This stability is likely due to the requirement of strong oxidizing conditions for their release. The decomposition of organic matter consumes oxygen, resulting in lower oxygen levels in deeper sedimentary layers [42]. Cd exhibited the most significant depth-dependent transformation, primarily converting from bioavailable to residual fractions. The proportion of F1 decreased with depth, while F2 initially decreased but stabilized in the MLs. Conversely, F4 increased rapidly. This pattern suggests that carbonates and phosphates promote the transformation of unstable Cd fractions into more stable forms through complexation and precipitation, consequently reducing Cd bioavailability [43]. Furthermore, surface water temperature and pH exhibit significant fluctuations, and the F2 fraction appears to be particularly sensitive to these variations. This interplay of factors likely drives the gradual transformation of Cd from F1 and F2 fractions into the more stable F4 fraction with increasing depths.

Figure 4.
Changes in the percentage of TM fractions in the sedimentary column with depth.
In the SLs, Co in fractions F1 and F2 undergoes a gradual conversion to F3 and F4. Similarly, Cu in F1 experiences this transition in both SLs and BLs. Pb exhibits a more nuanced transformation, with F1 converting to the F2 and F4 fractions in the SL, while the F2 fraction of Pb transitions to the F4 fraction in the BLs. Cr, Ni, Ti, and Zn exhibit specific fraction patterns in the SLs, becoming more stable in the MLs and BLs. These transformations likely depend on various environmental factors, including water temperature, pH, physical properties of the sediment, and microbial communities [44,45,46].
3.3.2. RSP and RAC
Due to the undetectable level of the F1 state of Ti, its RAC and RSP values were not calculated. The results indicate minimal pollution for As, Cr, Fe, Hg, Ni, Sb, and Zn, with all RSP values below 1. Cd, Cu, and Pb fall under the mild pollution category, while Co exhibits medium pollution levels (Figure 5a). Notably, Mn exhibits the highest RSP value of 5.34, signifying trace pollution. It is worth emphasizing that Mn demonstrates a progressive increase in contamination with depth, unlike other metals. This suggests a shorter retention time and a stronger migration ability for Mn within the sedimentary column, warranting serious attention.
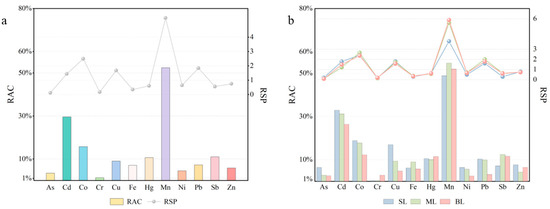
Figure 5.
RSP and RAC for TMs in sedimentary columns: (a) the entire sedimentary column; (b) different depths of the sediment column.
In summary, Cr (1.29%), As (3.44%), Ni (4.51%), Zn (5.84%), Fe (7.09%), Pb (7.28%), and Cu (9.04%) pose low RAC risks. Conversely, Hg (10.68%), Sb (11.02%), Co (15.76%), and Cd (29.62%) exhibit medium RAC risks. Mn stands out with the highest RAC value exceeding 50%, indicating a very high ecological risk (Figure 5a).
The analysis of RAC reveals a gradual decrease in ecological risks for As, Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, and Pb with increasing depth (Figure 5b). Notably, Cd risk transitions from high (SLs and MLs) to medium (BLs). Similarly, Cu and Pb decrease from medium risk (SLs) to low risk (BLs). Conversely, Cr and Hg exhibit increasing ecological risks with depth. Fe, Mn, and Sb show a peak risk in the MLs, exceeding both SLs and BLs. Mn specifically poses a high risk in the SLs, escalating to a very high risk in the MLs and BLs. Interestingly, Zn exhibits the lowest ecological risk within the MLs.
These findings differ from those of Deng [47], in which Cd presented a high risk, while As, Co, Cr, Fe, and Pb displayed low risks, and Cu, Hg, Ni, Sb, and Zn fell under the medium risk category. This discrepancy might be attributed to the current study’s sampling site located in the centre of the lake, further away from industrial areas and consequently, less impacted by pollution.
3.4. Magnetic Properties of the Sedimentary Column
SIRM ranged from 4930.87 × 10−6 to 20,967.14 × 10−6 Am2·kg−1, with an average of 11,084.25 × 10−6 Am2·kg−1. HIRM varied between 98.82 × 10−6 and 386.76 × 10−6 Am2·kg−1, averaging 226.85 × 10−6 Am2·kg−1. The s-ratio, indicating the relative abundance of subferromagnetic and incomplete antiferromagnetic minerals [48,49], ranged from 0.835 to 1.000, with an average of 0.972. This value is slightly higher than that reported by Deng [50], suggesting the dominance of subferromagnetic minerals in the sediments [51,52].
χfd% reflects the content of ultrafine superparamagnetic minerals [53]. χfd% varied from 0.51% to 13.94%, with an average of 1.72%. χarm is influenced by magnetic mineral grain size. χarm ranged from 114.39 × 10−8 to 733.67 × 10−8 m3·kg−1, averaging 317.14 × 10−8 m3·kg−1. The χarm/SIRM ratio varied between 0.13 × 10−3 and 0.44 × 10−3 m·A−1, averaging 0.28 × 10−3 m·A−1. This suggests the dominance of magnetic minerals with pseudo-single-domain (PSD) and multi-domain (MD) grain sizes.
Vertically, SIRM, HIRM, χarm, and χfd% exhibited a stable trend in the SLs, but fluctuated more in the BLs. Notably, χarm and χfd% tended to increase with depth. The s-ratio showed greater fluctuations near the boundary between the SLs and MLs (around layer 10), which coincided with changes in the SIRM/χ ratio. χfd% fluctuated more throughout the MLs and BLs, possibly due to waves [54], while χarm/χ and χarm/SIRM showed increased variability within the MLs (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Trend of magnetic parameters of sedimentary columns (a–i).
Compared to previous studies, the mean values of χfd% and χarm/χ in this study were significantly lower than those reported for the Guangxi Baxianchi Formation [55]. Conversely, the HIRM, s-ratio, and SIRM/χ levels were higher in this study compared to those in the Guangxi Baxianchi Formation. Additionally, χarm/χ results were higher than the values observed in Yunnan’s Heihai Lake [56]. The χarm/SIRM levels were lower than the values observed in the Zhongchen Water Reservoir [19].
3.5. Correlation between CFs of TMs and Environmental Index
To explore the connection between physicochemical indicators, magnetic parameters, and the risk posed by RACs of TMs across the sedimentary column, Spearman correlation analyses were performed for the SLs and BLs (Figure 7). Overall, the correlations between the RACs of the TMs and other parameters were stronger in the SLs than in the MLs and BLs. This suggests that changes in sediment properties with increasing depth influence the overall relationship between TMs and these properties. The most notable changes were observed for TOC, C%, N%, and TP.

Figure 7.
Spearman’s correlation of the RAC of TM with physicochemical indicators and magnetic parameters in the sedimentary column lamellae at different depths: (a) SLs; (b) MLs; (c) BLs.
In the SLs, the TOC, C%, and N% displayed significant positive correlations with the RAC of Cd, while the TOC and N% showed significant negative correlations with the RAC of Co. Additionally, TP had a significant positive correlation with the RAC of Cr, and C% displayed a significant negative correlation with the RAC of Sb. These findings can be explained by the high contents of these elements in the SLs. TOC and C% likely influenced the sequestration and adsorption of Cd, Co, and Sb [57]. N% may have affected the bioconcentration of Cd and Co, while TP facilitated the phosphate precipitation of Cr [58]. As the depth increased, the concentrations of TOC, TP, C%, and N% decreased, leading to the absence of significant correlations with TMs in the MLs and BLs.
The magnetic parameter correlations with TMs also varied with depth. In the SLs, χfd% exhibited a significant negative correlation with the RAC of Cd and a positive correlation with the RAC of Sb. However, this trend was not observed in the MLs and BLs. This suggests that the presence of Cd and Co in the SLs is influenced by finer-grained magnetic minerals [59,60]. The coarser magnetic minerals in the MLs and BLs likely explain the lack of correlation.
Further analysis revealed that χarm, SOFT, SIRM, and HIRM in the surface layer were significantly correlated with the RAC of Cr, Hg, Zn, and several other elements. This indicates that the content and type of magnetic minerals can influence the distribution patterns of these TMs and consequently, their ecological risk. This variation might be attributed to the transformation or dissolution of geomagnetic minerals under waterlogged conditions, leading to the formation of new iron-based minerals like hydroxides and sulphides [61,62,63].
3.6. Results of Machine Learning
The MLR model effectively simulated the total concentrations of various elements, achieving R2 values that ranged from 0.601 for Zn to 0.870 for Cr (Figure S4, Table S6). Notably, the R2 values for As, Co, Cr, Cu, and Fe were all above 0.6, indicating good simulation performance. While the MLR model performed well overall, other models exhibited strengths for specific elements. The RF model excelled at simulating Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, and Ni, achieving particularly high R2 values of 0.792 and 0.962 for Cr and Ni, respectively. The SVM model was best suited for simulating Cr and Mn, while the XGBoost model outperformed the other models in simulating Co, Cr, and Fe.
The MLR model exhibited superior performance in simulating the RAC for As, Cu, Fe, Ni, and Sb, achieving R2 values of 0.552, 0.668, 0.559, 0.626, and 0.617, respectively (Figure 8, Table S7). Notably, the coefficient of N% consistently held the highest absolute value within the regression equation for all six simulated RACs of TMs in the MLR model. This suggests that the content of N% significantly influences the ecological risks associated with these elements within the MLR framework. Variations in sediment nitrogen content significantly influence organic matter mineralization rates. Changes in mineralization rates can induce fluctuations in sediment redox conditions, subsequently affecting the structure and function of microbial communities. Concurrently, alterations in redox conditions can lead to the transformation of residual metals into soluble ionic forms, increasing the bioavailability of trace metals and amplifying their potential ecological risks [64,65]. In comparison, the RF model yielded better RAC simulations for Co and Cu, with respective R2 values of 0.565 and 0.733. The XGBoost model surpassed both other models in simulating the RAC of As, achieving an R2 value of 0.861.

Figure 8.
MLR model fitting curves of physical and chemical indices, magnetic parameters, and RAC of sedimentary columns (a, b, c, d, e and f are the simulation results of As, Co, Cu, Fe, Ni and Sb respectively).
The results for the XGBoost model simulating the RAC of As indicate that χarm/χ possesses the largest absolute SHAP value (Figure 9), signifying its role as the strongest contributor to the RAC of As within the sedimentary column, followed by χfd%. In the RF model simulating the RAC of Co, C% exhibits the largest absolute SHAP value (Figure 10), implying that C has the greatest influence on the RAC of Co in the sedimentary column, followed by N%, χarm/SIRM, TOC, and SIRM/χ. In the RF model simulating the RAC of Cu, N% holds the highest absolute SHAP value (Figure 10), suggesting its dominant role in the RAC of Cu within the sedimentary column.

Figure 9.
SHAP analysis of the XGBoost model.

Figure 10.
SHAP analysis of the RF model.
4. Conclusions
The average sedimentation rate of the 124-year-old (1895–2019) sedimentary column decreases with depth, then increases continuously, before a final decrease. The sedimentary column exhibits the highest concentrations of Fe, Ti, and Mn. Except for As, Cd, and Cu, all other TMs show decreasing concentrations with increasing depth in the SLs. The PLI for TMs indicates moderate overall pollution. The RI values identify the ecological hazard category as moderate. Mn and Pb primarily exist in the bioavailable fractions, while Cd shows the most significant depth-dependent change. Based on the RSP, the sedimentary column exhibits heavy Mn pollution, moderate Co pollution, and slight Cd, Cu, and Pb pollution. The RAC results indicate a high ecological risk for Mn, a medium risk for Hg, Sb, Co, and Cd, and a low risk for Cr, As, Ni, Zn, Fe, Pb, and Cu. Vertically, SIRM, HIRM, χarm, and SOFT exhibit relatively stable values in the surface layer, but fluctuate more in the bottom layer. Conversely, χarm and SOFT values show a gradual increase with depth.
The MLR model excelled at simulating the total concentrations of Cr, Co, Cu, Sb, Ni, Cd, Fe, and Ti in the sedimentary column. It also demonstrated strong performance in regards to the simulation RAC of Cu, Ni, Sb, Fe, and As. The RF model performed the best for simulating the total concentrations of Ni, Cr, Mn, Cu, and Fe in the sedimentary column. Additionally, the RF showed good results for the simulation RAC of Cu and Co. The SVM model was the most effective in simulating the total concentrations of Cr, Mn, Cu, and Fe in the sedimentary column. Finally, the XGBoost model outperformed the other models in simulating the total concentrations of Ni, Cr, Co, and Fe. It also achieved the best simulation RAC for As.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16182604/s1, Figure S1: Variation of TMs concentration with depth; Figure S2: Variation of TOC, TP, C%, and N% of sediments with depth; Figure S3: MLR fitting curves of physical and chemical indicators, magnetic parameters and total TMs in sedimentary columns; Table S1: Experimental steps of extracting trace metal forms by multistage continuous extraction method; Table S2: Analysis method of total organic carbon, total phosphorus and total; Table S3: Evaluation criteria for trace metal evaluation methods; Table S4: Concentrations of trace metals; Table S5: RI and PLI values for trace metals; Table S6: MLR model of total trace metals in sediments; Table S7: MLR model of trace metal risk index (RAC) in sediments.
Author Contributions
H.X.: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing—original draft; T.K.: investigation; L.C. (Liming Chen): investigation; D.L.: investigation, methodology; W.Y.: investigation, methodology; X.Q.: conceptualization, validation; L.C. (Long Chen): methodology; L.D.: validation; H.L.: conceptualization, validation, funding acquisition, resources, writing—review and editing, visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Author Contributions” section when you and the co-authors finish the proofreading.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (grant no. BK20221325), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 42077430), and the Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Water Treatment of Lake Taihu Basin, Ministry of Water Resources (Yk922001-C4).
Informed Consent Statement
All authors approved the final manuscript and the submission to this journal. This research work does not contain any individual person’s data in the form of individual details, images, or videos. This work was based on published literature.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper. On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, F.J.; Zhang, B.J.; Ma, B.; Li, L.Q. Comprehensive ecological risk assessment for heavy metal pollutions in three phases in rivers. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3436–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, J.E.; Boyd, R.S.; Rajakaruna, N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A.J.; Planchart, A. The neurological toxicity of heavy metals: A fish perspective. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 208, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widada, J.; Nojiri, H.; Omori, T. Recent developments in molecular techniques for identification and monitoring of xenobiotic-degrading bacteria and their catabolic genes in bioremediation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 60, 45–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Z. Historical trends of heavy metal contamination and their sources in lacustrine sediment from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake Catchment, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wei, M.; Xiaona, H. Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 4367–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, C.; Huang, X. The porewater nutrient and heavy metal characteristics in sediment cores and their benthic fluxes in Daya Bay, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 124, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Ju, Y.R.; Chen, C.W.; Dong, C.D. Vertical profile, contamination assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in sediment cores of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, Y.; Guo, M.; Gong, X. Sedimentary records of human activities in China over the past two millennia and implications for the Anthropocene: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audry, S.; Schäfer, J.; Blanc, G.; Jouanneau, J.M. Fifty-year sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution (Cd, Zn, Cu, Pb) in the Lot River reservoirs (France). Environ. Pollut. 2004, 132, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman Na, F.; Elzokm, G.M.; Okbah, M.A. Risk assessment and chemical fractionation of selected elements in surface sediments from Lake Qarun, Egypt using modified BCR technique. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Ding, X.; Li, H. Bioaccessibility and health risk assessment of trace metals in Nanjing park dust. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Song, Y.; King, J.W.; Zan, J.; Saylor, J. A review of recent advances in red-clay environmental magnetism and paleoclimate history on the chinese loess plateau. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, J. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties Reactions Occurrence and Uses. Mineral. Mag. 1997, 61, 740–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Ge, C.; Wang, F.; Feng, H. Recent applications of mineral magnetic methods in sediment pollution studies: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Lemckert, C.; Ma, Y. Laboratory and field magnetic evaluation of the heavy metal contamination on Shilaoren Beach, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Su, Y. Magnetism of the Huguangyan Maar Lake sediments, southeast China and its paleoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2014, 395, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; Hu, P.; Duan, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Doberschütz, S.; Mäusbacher, R.; et al. Mechanism of variations in environmental magnetic proxies of lake sediments from Nam Co, Tibet during the Holocene. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1568–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ma, M.; Hu, S.; Cao, L.; Appel, E.; Wang, L. Atmospheric pollution history at Linfen (China) uncovered by magnetic and chemical parameters of sediments from a water reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 204, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo-Álvarez, V.; Devesa-Rey, R.; Aldana, M.; Barral, M.T.; López-Rodríguez, D.; Andrade, B. Magnetic properties of surface sediments as proxies of recent anthropogenic pollution in the Anllóns riverbed (NW Spain). Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Lu, M.; Hutchinson, S.M.; Feng, H. Magnetic approach to normalizing heavy metal concentrations for particle size effects in intertidal sediments in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angulo, E. The Tomlinson Pollution Load Index applied to heavy metal, ‘Mussel-Watch’ data: A useful index to assess coastal pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 1996, 187, 19–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Cai, L.; Wang, G.; Yin, K.; Chen, H.; Zhi, M.L. Comparison of risk assessment based on the various methods of heavy metals in soil: A case study for the typical field areas in the Jianghan Plain. Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 2018, 45, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.K. Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of River Yamuna, India. Water Res. 2004, 38, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.C.; Li, S.J.; Liu, J.F.; Xue, B.; Xia, W.L. Recent sedimentation of this core in southern taihu lake inferred from 137Cs and 210Pb Measurements. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2006, 2, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mo, P.J.; Gao, W.B. Application of 210Pb isotope in dating anthropocene sediments. Adv. Earth Sci. 2024, 39, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, S. One-century sedimentary record of heavy metal pollution in western Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, J.; Babek, O.; Novakova, T. Sedimentary record and anthropogenic pollution of a complex, multiple source fed dam reservoirs: An example from the Nove Mlyny reservoir, Czech Republic. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, H.; Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Jeppesen, E. Reservoirs as high-efficacy sentinels of regional atmospheric pollution and precipitation: Magnetic and chemical evidence from a typical subtropical reservoir in South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 92507–92524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, K.; Xia, J.; Jiao, W.; Niu, Y.; Yu, H. Meta analysis of heavy metal pollution and sources in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, E. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment and its human impact in lacustrine sediments from four lakes in the mid-low reaches of the Yangtze River, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The State Council of the People’s Republic of China. Law of the people’s republic of China on prevention and control of water pollution. Chin. Law Gov. 2004, 37, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Jin, Z.D.; Cao, J.J.; Posmentier, E.S.; An, Z.S. Atmospheric cu and pb deposition and transport in lake sediments in a remote mountain area;northern China. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2007, 179, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Miao, Q.L.; Feng, J.F. Pollution of heavy metals in the bottom mud of Lake Taihu and its assessment of potential ecological risk. J. Nanjing Inst. Meteorol. 2006, 29, 700–705. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Cui, B.; Liu, X. Heavy metal fractions and ecological risk assessment in sediments from urban, rural and reclamation-affected rivers of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminiyan, M.M.; Aminiyan, F.M.; Mousavi, R.; Heydariyan, A. Heavy metal pollution affected by human activities and different land-use in urban topsoil: A case study in Rafsanjan city, Kerman province, Iran. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2016, 5, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Tang, X. Distribution, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in sediments of a headwater of Beijiang river affected by mining in southern China. Toxics 2024, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, K.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, P.; Panda, U.C.; Bhatta, D.; Sahu, K.C. Use of sequential leaching, mineralogy, morphology and multivariate statistical technique for quantifying metal pollution in highly polluted aquatic sediments—A case study: Brahmani and Nandira Rivers, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M. Effects of Organic Carbon Mineralization on Metal Speciation and Distribution in Sediments of the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yantai Coastal Zone Research Institute, Yantai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Berner, R.A. Early Diagenesis: A Theoretical Approach; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Wang, X.L.; Cheng, H.F.; Tao, S. Effects of physical aging processes on the bioavailability of heavy metals in contaminated site soil amended with chicken manure and wheat straw biochars. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custodio, M.; Espinoza, C.; Penaloza, R.; Peralta-Ortiz, T.; Sanchez-Suarez, H.; Ordinola-Zapata, A.; Vieyra-Pena, E. Microbial diversity in intensively farmed lake sediment contaminated by heavy metals and identification of microbial taxa bioindicators of environmental quality. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, M. A new look at models of the combined effect of temperature, pH, water Activity, or other factors on microbial growth rate. Food Eng. Rev. 2021, 14, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, H.; He, X.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, J.; Yan, Z.; Feng, J.; Li, R. Response of bacterial communities to variation in water quality and physicochemical conditions in a river-reservoir system. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, 01541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.G.; Fan, Y.F.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.T.; Qian, X.; Li, M.J.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.H.; Gao, X.; Li, H.M. Exploring the primary magnetic parameters affecting chemical fractions of heavy metal(loid)s in lake sediment through an interpretable workflow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 468, 133859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F. Toward the discrimination of fine-grained ferrimagnets by magnetic measurements in lake and near-shore marine sediments. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1994, 99, 9045–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Roberts, A.P.; Torrent, J.; Horng, C.S.; Larrasoaa, J.C. What do the HIRM and S-ratio really measure in environmental magnetism? Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.G.; Gao, X.; Xia, B.; Wang, J.H.; Dai, Q.; Fan, Y.F.; Wang, S.; Li, H.M.; Qian, X. Improving the efficiency of machine learning in simulating sedimentary heavy metal contamination by coupling preposing feature selection methods. Chemosphere 2023, 322, 138205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijaksana, S.; Yunginger, R.; Hafidz, A.; Mariyanto, M. Magnetic mineral characteristics, trace metals, and REE geochemistry of river sediments that serve as inlets to Lake Limboto, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, F. Environmental magnetism-A personal prospective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 1991, 10, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Qian, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, H.L. Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiyiah, J.; Acheampong, M.A.; Ansa, E.; Kelderman, P. Grain-size analysis and heavy metals distribution in sediment fractions of lake markermeer in the netherlands. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Toxicol. 2014, 2, 160–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, T. The transformation of magnetic minerals in source-sink process for surface sediments of Baxian Tianchi, Guangxi. J. Sun Yat-Sen Univ. 2021, 60, 76–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, T.P.; Zhang, Y.D.; Li, M. Magnetic properties of core sediments from an alpine lake in Southwest China: Implications for glacier melting. J. Paleolimnol. 2022, 67, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Han, H.; Pan, D. Heavy metals in sediments of Yellow Sea and East China Sea: Chemical speciation, distribution, influence factor, and contamination. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 39, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, L.S.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Adsorption-desorption behavior of heavy metals in aquatic environments: Influence of sediment, water and metal ionic properties. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, L. Correlation patterns between magnetic parameters and heavy metals of core sediments in the Yellow River Estuary and their environmental implications. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 160, 111590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstner, U. Sediment dynamics and pollutant mobility in rivers: An interdisciplinary approach. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. 2004, 9, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinowska, A.; Tucholka, P.; Wieckowski, K. Magnetic properties of sediments in a Polish lake: Evidence of a relation between the rock-magnetic record and environmental changes in Late Pleistocene and Holocene sediments. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 129, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, X.; Hesse, P.P.; Lü, B.; Guo, X.; Chen, J. Magnetic properties of loess deposits in Australia and their environmental significance. Quat. Int. 2013, 296, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ding, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X.C.; Xu, Z.X. Seasonal varieties and influential factors of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 4, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.H.; Han, M.X.; Han, J.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zuolipiyamu, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.C. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Inputs on the Degradation of Terrestrial Grass Organic Matter in Saline Lake Sediments. J. Salt Lake Res. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Deepulal, P.M.; Chandramohanakumar, N. Distribution and sources of sedimentary organic matter in a tropical estuary, south west coast of India (Cochin estuary): A baseline study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 66, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).