Abstract
Common or European carp (Cyprinus carpio) were eliminated from Lake Winona during a 1973 lake reclamation project. Multiple efforts to prevent their return and eliminate spawning opportunities have failed. Carp have remained in the lake for the past 50 years, but more recent observations of spawning activity in the lake suggest that their numbers have increased. We used shoreline electrofishing data from Lake Winona (2005–2021), along with carp abundance and effects models, to estimate the abundance of carp in Lake Winona, and to evaluate the need for future carp management within the lake. Carp size (mean TL = 614 mm, mean weight = 3.42 kg) did not differ between eastern and western basins, but densities were three times higher in the western basin (105 compared to 34 fish/hectare), and carp had significantly higher relative weights in the western (117%) versus the eastern (107%) basin. Carp biomass estimates for the eastern (116 kg/hectare) and western (360 kg/hectare) basins suggest that the lake may soon experience significant declines in macrophyte cover and other ecological damage associated with that loss. With an estimated adult carp population of >6900 fish and a carp biomass (23,750 kg) 1.5 times greater than the biomass of all carp killed during the 1973 reclamation, carp management activities (e.g., fish removal and spawning migration barriers) should be initiated soon to protect the Lake Winona game fish community.
1. Introduction
Common or European carp (Cyprinus carpio) have been introduced to many continents outside of their native range and occur throughout much of the continental USA [1,2,3,4]. Although prized as a game fish in many localities [5,6,7,8,9], they are considered invasive in many regions of the world [10], competing with native fishes, destroying aquatic macrophytes, impairing water quality, and impacting waterfowl use of rivers, lakes, and reservoirs [11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. To protect and/or restore native aquatic habitats and communities, considerable money and effort is being expended to manage or eliminate carp from systems that they have invaded [18,19,20]. Novel approaches to assess populations, direct spawning migrations, and corral, remove, and kill carp have been used successfully [18,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29], while still sustaining populations and spawning migrations of native species [30,31].
Carp have caused problems in some lakes for many decades. In systems where predators (e.g., bluegill Lepomis macrochirus and yellow perch Perca flavescens) of carp eggs and larvae are abundant, carp populations typically do not reach levels that can cause harm to their aquatic habitats [24,32,33,34,35,36]. However, if carp have access to wetlands with few to no bluegills or yellow perch (due to periodic winterkill events), they can spawn and recruit successfully [33,35,36,37]. Adult carp often migrate in masses to these spawning wetlands during spring [26,30,31,32,38,39], before returning to their home lake for the remainder of the year [13,39]. Young carp remain and grow in the wetlands for a year or two before they also migrate to the lake(s) where adults reside [24,39,40]. Wherever carp have access to spawning wetlands, their numbers can increase dramatically, and they may cause significant damage to macrophyte beds and the communities (e.g., invertebrates, fish, and waterfowl) that depend on them [11,12,15].
Common carp were eliminated from Lake Winona, an urban floodplain lake in southeastern Minnesota, USA, in 1973 by treatment with rotenone during a lake reclamation project, but they re-entered the lake from the Mississippi River the following year when equipment designed to exclude them malfunctioned [41]. Carp have remained in the lake for the past 45 years, but recent electrofishing carp catch rates and observations of carp spawning activity in the lake, along with reduced numbers of bluegill, suggest that carp numbers might be increasing. Consequently, we used historical catch data and a series of more recent investigations to estimate the abundance of carp in Lake Winona and evaluate the need for future carp management within the lake.
2. Study Area and History
Lake Winona is a hypereutrophic, 129 ha urban lake in southeastern Minnesota, USA (Figure 1). The lake originated as a natural side channel of the Mississippi River, but it has been modified extensively during the past 170 years by repeated dredging, filling of fringe wetlands to create parklands, and rerouting urban storm sewers (42 km of storm sewers draining 650 ha of urban lands directly or indirectly into the lake) and a local creek into the lake [41]. The lake consists of two basins (eastern [93 ha] and western [36 ha]) separated by a road causeway and connected only by a single 3.5-meter diameter concrete arched culvert (Figure 1). The lake drains from the eastern basin into the Mississippi River via an engineered drainage canal (3.5 km long; County Ditch #4) and connects upstream from the western basin via another canal (3.9 km long; County Ditch #3) to Bollers Lake, a shallow natural lake and wetland complex, and Gilmore Creek, which flows through Bollers Lake before following the canal route to Lake Winona (Figure 1).
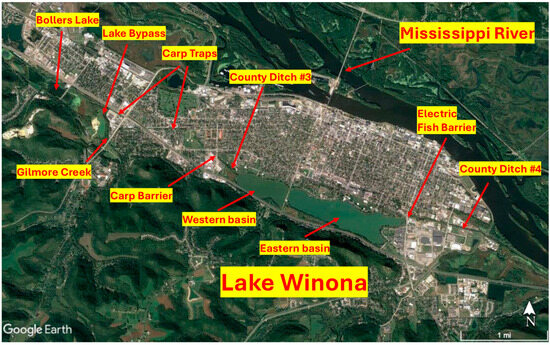
Figure 1.
Aerial photo of Lake Winona, Minnesota, USA, and connecting waterways. Locations of various common carp control structures are indicated.
Up until the mid-1960s, Lake Winona supported a fair game fish community (largemouth bass Micropterus nigricans, bluegill Lepomis macrochirus, black crappie Pomoxis nigromaculatus, northern pike Esox lucius, and yellow perch Perca flavescens), but severe winters during 1964–65 and 1968–69 led to drastic oxygen depletion, eliminating most game fish and leading to the invasion and/or population increases of less desirable nuisance fish species such as carp, buffalo (Ictiobus cyprinellus and Ictiobus bubalus), and gizzard shad (Dorosoma cepedianum) from the Mississippi River [41]. Winterkills continued and cleanups involving 100,000 kg of dead fish (with carp typically comprising 15% of the total) became a common practice after spring ice-out. By 1973, aquatic macrophytes had been eliminated, water transparency declined precipitously, and a lack of oxygen at the lake bottom led to a rapidly expanding layer of organic ooze that eliminated aquatic insects [41].
Beginning in 1973, efforts were initiated to reclaim the lake as a sport fishery [41]. The existing fish community was eliminated by chemical treatment with rotenone, and an electric weir and bar screens were installed on the lake outlet (Figure 1) to prevent reinvasion by undesirable fish species; six aerators were installed to prevent die-offs from a lack of oxygen, and game fish were stocked by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Unfortunately, carp re-invaded the lake from the Mississippi River the following year (1974) when the electric barrier malfunctioned, and an improperly installed bar screen was undercut by strong outflow currents [41].
Although carp were unable to spawn successfully in Lake Winona due to its high population of carp egg-eating bluegill [41,42], they moved through the lake, up the upper canal, and spawned in Bollers Lake [41]. A controlled winter freeze-out of Bollers Lake (accomplished by bypassing the creek around the lake via an engineered gate and valve system, allowing the lake to freeze to the bottom, as seen in Figure 1) killed off the young carp, preventing them from eventually moving downstream into Lake Winona. To prevent carp from accessing Boller Lake each year to spawn, two carp traps and a single carp barrier were installed in 1982 in the connecting canal to intercept carp during their migrations (Figure 1). Although initially successful at preventing carp from reaching Bollers Lake, the carp traps and barrier regularly became clogged with trash washed into the system via storm sewers, leading to the eventual removal of both traps and the barrier [41].
Since carp trap and barrier removal, carp have been observed migrating from Lake Winona to Bollers Lake in small numbers, and adult carp (but no juveniles) have been captured regularly in Lake Winona. Carp have also been observed spawning in macrophyte beds in both basins of Lake Winona during multiple years. Young-of-year carp have been captured near Bollers Lake, both upstream from the lake in Gilmore Creek and downstream in the canal connecting to Lake Winona. Concurrently, bluegill abundance in Lake Winona has declined significantly since a 1999–2001 lake dredging project [43,44], increasing the potential for the survival of carp eggs and larvae spawned in the lake.
3. Methods
3.1. Historical Data
We obtained historical carp catch data for Lake Winona from the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources LakeFinder Lake Survey Results (https://www.dnr.state.mn.us/lakefind/showreport.html?downum=85001100 [accessed on 15 August 2024]). Catch records, based on fish management surveys with overnight sets of standardized trap nets (double frame, 1.2 × 1.8 m, 1.9 cm mesh, 12.2 m lead; set perpendicular to shore in water <2.4 m deep) and gill nets, were available for 21 dates between 1953 and 2021. These data were examined to assess potential changing patterns in carp abundance during the period that included pre-reclamation, post-reclamation, and more recent times.
3.2. Field Work
Common carp (Figure 2) were collected multiple times from both the eastern (13 collections) and western (11 collections) basins of Lake Winona during autumns (September–October) from 2005 to 2021 by shoreline electrofishing (boat-mounted Smith-Root VVP-15B electrofisher). Electrofishing runs were timed (typically 10 to 35 min) as the boat paralleled the shoreline in shallow (2 to 3 m) water, and all carp encountered were counted. During some collections, carp were weighed (g wet mass) individually on a top-loading balance at the end of each run for use in estimating the total carp biomass and assessing the carp size distribution. During 2018, 30 carp from the western basin and 14 carp from the eastern basin were weighed and measured (mm total length [TL]) to determine fish condition. After measurements, all carp were returned to the lake alive.

Figure 2.
Typical adult common carp collected by shoreline electrofishing in Lake Winona, Minnesota, USA.
3.3. Data Analyses
Carp abundances from each electrofishing run were standardized (fish/h) to produce catch rates and analyzed in two ways. First, catch rates were compared between the two basins with a standard t test after log10-transforming catch data to address normality concerns. Second, catch rates were analyzed across years with simple linear regression applied to each basin separately. Again, catch rates were log10-transformed prior to analysis.
Carp population densities and biomass were calculated separately for each basin of Lake Winona. First, shoreline electrofishing catch rates were used to calculate carp densities (carp/hectare) with the relationship developed for Minnesota lakes [23]:
Density (fish/hectare) = (4.71 × fish/h) + 3.04
Next, the fish wet mass was compared between the basins (using a standard t test) to determine whether the mean fish size differed between the basins. Basin-specific densities were then converted into biomass estimates (kg/hectare) by multiplying the basin densities by the average fish mass (kg).
For carp collected during 2018, the wet mass and TL were used to calculate a relative weight (Wr) for each fish as a measure of fish condition. The relative weight (Wr) formula used was as follows:
where W was the wet mass of the fish in g and Ws was the standard wet mass for a fish of the same TL (in mm) [45]. The standard wet mass was determined for each carp with the following equation [46]:
Wr = 100 × (W/Ws),
log10Ws = 2.920 × log10TL − 4.639
The relative weights of carp were compared between the basins with a standard t test.
4. Results
Historical trap net and gill net catch rates of common carp in Lake Winona suggest that carp populations were higher in the lake in 1953 than during the past 40 years (Figure 3). Unfortunately, no surveys were conducted during the 19-year period surrounding the year of the lake reclamation. Regardless, trap net and gill net data did not indicate any major change in the carp population since 1980.
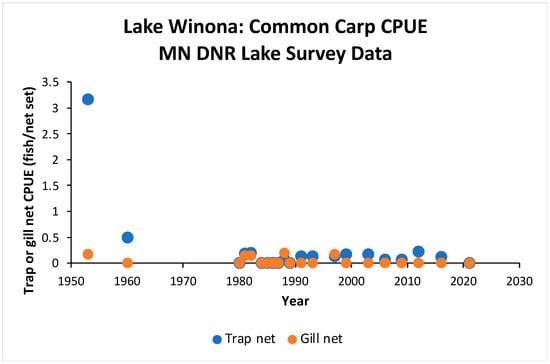
Figure 3.
Trap net and gill net catch rates (catch per unit effort, CPUE) of common carp during lake fisheries surveys of Lake Winona by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources (MN DNR), 1953–2021.
The catch rates of common carp differed significantly (t14 = 2.29, p= 0.040) between the eastern and western basins, with rates twice as high in the western basin (Table 1). Although there was a tendency for catch rates to increase in both basins of the lake between 2005 and 2021 (Figure 4), the increase was significant in the eastern basin (slope: t11 = 3.64, p = 0.004), but not in the eastern basin (slope: t9 = 0.028, p = 0.786). The mean catch rates across all the years corresponded to carp densities of 34 fish/hectare in the eastern basin and 105 fish/hectare in the western basin (Table 1).

Table 1.
The mean (SD) electrofishing catch rates (fish/h) and densities (fish/hectare) of common carp in the eastern and western basins of Lake Winona, 2005–2021. N is the number of electrofishing runs. The results of a t test comparing log10-transformed catch rates between the basins are included.
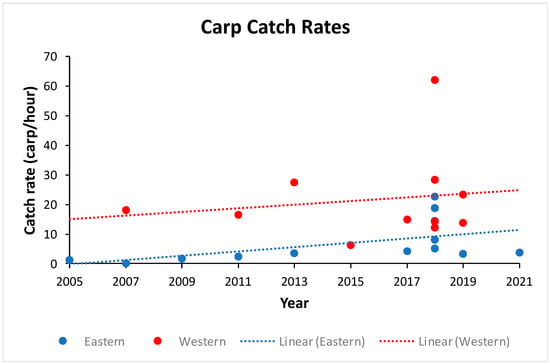
Figure 4.
Shoreline electrofishing catch rates of common carp in eastern and western basins of Lake Winona, Minnesota, USA, from 2005 to 2021. Best-fit linear regression lines are shown for each basin. See Results for regression statistics.
During seven years between 2007 and 2018, 113 carp (20 from the eastern basin and 93 from the western basin) were weighed. Carp ranged in wet mass from 1.19 kg to 8.05 kg, with the majority between 2.1 and 4.5 kg (Figure 5). Mean ± SD carp masses were 3.2 ± 1.3 kg for the eastern basin and 3.5 ± 1.2 kg for the western basin. Because the mean carp mass did not differ significantly (t111 = 0.89, p = 0.374) between the basins, data were combined to produce an overall mean carp mass of 3.4 ± 1.2 kg per fish for Lake Winona.
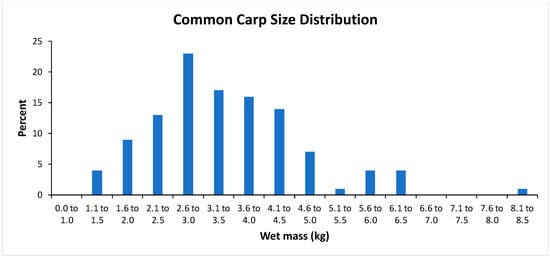
Figure 5.
Wet mass size distribution of common carp collected from Lake Winona, Minnesota, USA, from 2007 to 2018.
The carp condition based on relative weight was excellent in both basins during 2018. Carp had mean (±SD) relative weights of 117% (±15%) in the western basin and 107% (±13%) in the eastern basin. Carp relative weights in the western basin were significantly higher (t42 = 2.08, p = 0.043) than those in the eastern basin.
Based on shoreline catch rates in Lake Winona and the average mass of individual carp within the system, the average areal biomass of carp was estimated at 116 kg/ha in the eastern basin and 360 kg/ha in the western basin (Figure 6). This translates into 12,960 kg of carp (approximately 3811 fish) in the eastern basin and 10,790 kg of carp (approximately 3173 fish) in the western basin. Combined, the two basins were estimated to hold 6984 adult carp weighing a collective 23,750 kg.
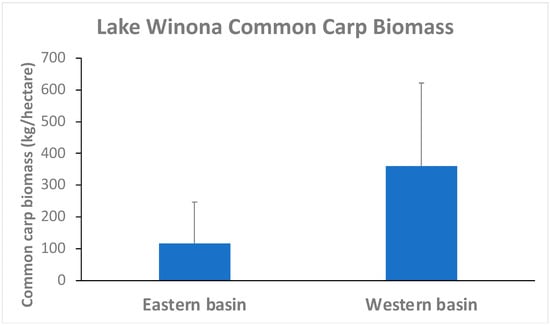
Figure 6.
Mean (SD) common carp biomass estimates for eastern and western basins of Lake Winona, Minnesota, USA, based on shoreline electrofishing 2005–2021.
5. Discussion
It has been more than 50 years since the Lake Winona reclamation project eliminated common carp from the system and took steps to prevent their return. Although carp quickly reinvaded the lake due to unexpected equipment problems, the status of their population was largely unknown. This study discovered four important characteristics of Lake Winona’s carp population. First, the carp population appears to be comprised entirely of adult fish. Second, catch rates indicate that carp densities are three times higher, and carp are in better condition in the western basin than in the eastern basin. Third, the western basin population appears to be remaining stable, whereas the eastern basin population continues to increase. Finally, the carp biomass in the western basin far exceeds the level considered potentially damaging to a lake ecosystem.
Lake Winona’s carp population is lacking in fish < 1 kg (young-of-year carp), and fish < 2 kg (most likely yearling, or non-mature carp) represent only a small proportion, indicating that few young carp exist in the system. A proportional lack of small or young carp within a lake population has been reported previously [26,32,40]. Even though carp have been observed spawning in Lake Winona, the existing population of bluegill [42,43,44] is apparently large enough to serve as effective egg predators [24,32,33,34,35,36], preventing few, if any, young carp from being produced within the lake itself. However, young carp likely recruit into the Lake Winona population via the canal connecting the western basin of Lake Winona with Bollers Lake, where migratory carp from Lake Winona probably spawn [41]. Young carp apparently rear successfully in the bluegill-free wetlands that comprise much of Bollers Lake [41], eventually moving downstream to Lake Winona to feed and grow as they mature. Previous fisheries surveys of Bollers Lake after natural winterkills or rotenone treatments have noted the presence of hundreds to thousands of carp, but fish size (juvenile versus adult) was not noted [41]. Low numbers of young carp recruited [41] to Lake Winona, even on an irregular basis (e.g., only a few times per decade) [32], should be sufficient to maintain or even expand the lake’s carp population, given the longevity of adult carp [26,32,47,48]. Migratory spawning behavior and the downstream movement of older juveniles is common in many populations of carp that reside in interconnecting aquatic habitats [13,20,30,31,32,38,39].
The higher density and better condition of common carp in the western versus the eastern basin of Lake Winona highlights several characteristics of the Lake Winona system. Carp reinvaded the eastern basin of the lake in 1974 from the Mississippi River, but they spread quickly to the western basin [41]. However, to spawn, adult carp from both basins need to exit the western basin through the upstream canal to reach Bollers Lake and return post-spawn to Lake Winona along the same route. Any young carp recruitment to Lake Winona from Bollers Lake would also first enter the western basin of Lake Winona. With the single small culvert connecting the two lake basins potentially serving as a bottleneck to fish movements between the basins [44], it seems probable that higher carp densities could develop in the western basin. However, based on our calculations (with the eastern basin being over twice as large as the western basin), both basins hold 3000+ adult carp, with the eastern basin possibly containing ~20% more carp than the western basin. Even though carp in both basins are in excellent condition, the significantly higher relative weights of carp in the western basin suggest that this basin is a better feeding area for adult carp than the other basin. Similar differences in relative weights between the basins of Lake Winona have been reported for both bluegill and largemouth bass (Micropterus nigricans) [44]. Information on the age structures of carp in both basins would contribute to a better understanding of the possible movements of the species between the basins.
We suspected that carp populations in both the basins of Lake Winona had been increasing during the past 20 years, based on more frequent collections of carp and observations of increased spawning activity within the lake (N. Mundahl, personal observations). Although historical trap net catch rates did not indicate any increase in carp abundances in Lake Winona since 1980, our electrofishing catch rates indicated that carp numbers in both basins appeared to be trending upward, especially in the eastern basin. Trap nets may not provide a very good estimate of adult carp abundance, as carp are known to be cautious (not risk-taking) about new objects in their environment and tend to avoid or escape from different types of visible set nets, especially when in groups [27,49,50]. Less-visible gill nets are effective at capturing carp in other systems throughout Minnesota [15], but they only captured five carp across 21 lake surveys between 1950 and 2021 in Lake Winona. In contrast, shoreline electrofishing has been proven to accurately estimate common carp abundances in systems similar to Lake Winona [23]. Although the gradual increases in carp catch rates observed in Lake Winona do not appear as threatening as the extremely rapid increase in carp numbers reported in other systems [12,33], they are still worrisome when considered in the context of the current carp densities within Lake Winona.
The estimated carp biomass in both the eastern (116 kg/ha) and western (360 kg/ha) basins of Lake Winona are equal to or exceed the levels (50 to 100 kg/ha) considered potentially damaging to lake ecosystems [15,24,51,52]. When the carp biomass exceeds 50 kg/ha, aquatic macrophyte cover declines precipitously, plant richness becomes suppressed, and non-native plant species may become dominant [11,12,15,24]. Even if carp can be subsequently removed from a system, the recovery of the macrophyte community may be prolonged and/or incomplete without significant intervention(s) [16].
The macrophyte community within the littoral regions of Lake Winona (approximately 70% of total lake area) [43] is dominated by non-native and highly invasive curly-leaf pondweed (Potomageton crispus) from ice-out through June and by non-native Eurasian watermilfoil (Myriophyllim spicatum) and native coontail (Ceratophyllum sp.) from July through ice-on. Other native submersed (sago pondweed, Stuckenia pectinata, and Canada waterweed, Elodea canadensis) and emergent (yellow pond-lily, Nuphar variegatum, and American lotus, Nelumbo lutea) species are present, but less common (N. Mundahl, personal observation, [41,53]). Carp do not appear to have significantly reduced Lake Winona’s macrophyte coverage during recent years, even though spawning activities occur in curly-leaf pondweed stands and carp tend to forage in milfoil and coontail beds. The tissue toughness (i.e., high fiber content) of coontail and the chemical deterrents present in sago pondweed make them more resistant to and less preferred by foraging carp [54], although another study [11] reported that coontail was reduced significantly by carp. Non-native Eurasian watermilfoil and curly-leaf pondweed also appear to be resistant to or not preferred by carp, as another Minnesota lake with a carp biomass similar to Lake Winona required chemical treatment to manage the non-native macrophytes, even in the presence of carp [19]. Given these factors, Lake Winona appears to have a macrophyte community dominated by non-preferred or carp-resistant species that, at least on a total coverage basis, has so far maintained itself in the presence of a high carp biomass. The sustainability of this current situation is unknown, as the macrophyte communities in so many lake systems within the southern Minnesota region have already been decimated by carp [15,24].
The current estimated biomass of carp in Lake Winona (23,750 kg) exceeds by 50% the biomass (15,727 kg) of carp removed via chemical treatment of the lake during the 1973 reclamation project [41]. Consequently, the lake’s carp population may be at its highest level since the active fisheries management of the system began in the 1950s. Lake Winona’s game fisheries had improved significantly after the 1999–2001 partial dredging of the eastern basin, with improved size structures, better predator-to-prey balance, and excellent fish condition [43]. However, bluegill in Lake Winona have recently displayed a significant decline in condition, especially in the western basin [44], an indicator of change in the system [55] that may be linked to the abundance of carp.
Lake Winona is currently listed as an impaired water body by the Minnesota Pollution Control Agency due to its elevated levels of total phosphorus [56]. To manage phosphorus levels, local governmental agencies and consultants have recommended a series of projects to reduce phosphorus inputs from the watershed by controlling and removing phosphorus from runoff, and to reduce the recirculation of phosphorus already in the system through alum treatments to prevent phosphorus in sediments from entering the water column [57]. Because carp foraging can interfere with the success of alum treatments [19,58], a thorough assessment and management of Lake Winona’s carp population will be needed prior to any alum applications [57].
The recommended next steps for the management of carp in Lake Winona [57] include the following: (1) installing PIT tags in a representative number of carp from each basin to aid in conducting mark-recapture population estimates and documenting spawning migrations; (2) assessing the effectiveness of using baited box nets to capture and remove carp from the lake; (3) analyzing carp age structures to better focus management approaches (different strategies for old-dominated versus young-dominated populations); and (4) blocking both upstream spawning migrations of adult carp and downstream recruiting movements of juvenile fish with electric barriers. Although these efforts will be expensive [57], the active management of common carp in both basins of Lake Winona will likely be necessary to protect a valuable game fish community [43] that is specifically focused toward younger and older anglers, and others not able to safely access the nearby Mississippi River [41].
Author Contributions
N.D.M. developed the concept for the paper. All authors participated in field work and data analyses. N.D.M. wrote the original draft manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Fish collections were carried out under special permits (Numbers 12769, 14055, 15585, 17021, 18903, 20320, 21933, 23668, 28374, and 20310) from the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, Division of Fish and Wildlife, Section of Fisheries, and were conducted with the approval of the Winona State University Animal Care and Use Committee (1310071-2). This research complied with all ethical standards.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Winona State University limnology students and several friends and coworkers for assisting with fish collections.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, D.S.; Gilbert, C.R.; Hocutt, C.H.; Jenkins, R.E.; McAllister, D.E.; Stauffer, J.R., Jr. Atlas of North American Freshwater Fishes; North Carolina Biological Survey Publication #1980-12; North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Page, L.M.; Burr, B.M. A Field Guide to Freshwater Fishes: North America North of Mexico; Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Berra, T.M. Freshwater Fish Distribution; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, B.; Befus, B.; Berryman, J. Carp on the Fly: A Flyfishing Guide; Bower House: Denver, CO, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, C.; Clifford, K.; Paisley, T. A Century of Carp Fishing; Carptalk Enterprises: Newport, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Raat, A.J.P. Analysis of angling vulnerability of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., in catch-and-release angling ponds. Aquac. Fish. Manag. 1985, 16, 171–187. [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus, R.; Mehner, T. Socio-economic characterization of specialized common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) anglers in Germany, and implications for inland fisheries management and eutrophication control. Fish. Res. 2003, 61, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlinghaus, R. Voluntary catch-and-release can generate conflict within the recreational angling community: A qualitative case study of specialized carp, Cypinus carpio, angling in Germany. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2007, 14, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, G. Common carp as an invasive species. In Carp Habitat, Management and Diseases; Sanders, J.D., Peterson, S.B., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Crowl, T.A. Effects of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) on macrophytes and invertebrate communities in a shallow lake. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sullivan, G.; Sorensen, P.W. Effects of a rapidly increasing population of common carp on vegetative cover and waterfowl in a recently restored midwestern shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 2009, 632, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.H.; Tracey, S.R.; Hartmann, K.; Patil, J.G. Exploiting seasonal habitat use of the common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in a lacustrine system for management and eradication. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilizzi, L.; Tarkan, A.S. Experimental evidence for the effects of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) on freshwater ecosystems: A narrative review with management directions for Turkish inland waters. LIMNOFISH-J. Limnol. Freshw. Fish. Res. 2015, 1, 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Beck, M.W.; Cross, T.K.; Koch, J.D.; Bartodziej, W.M.; Sorensen, P.W. Biological invasion by a benthivorous fish reduced the cover and species richness of aquatic plants in most lakes of a large North American ecoregion. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopik, J.M.; Newman, R.M. Transplanting aquatic macrophytes to restore the littoral community of a eutrophic lake after removal of common carp. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2018, 34, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huser, B.J.; Bajer, P.G.; Kittelson, S.; Christenson, S.; Menken, K. Changes to water quality and sediment phosphorus forms in a shallow, eutrophic lake after removal of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Inland Waters 2022, 12, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, M.E.; Pierce, C.L.; Stewart, T.W.; Grummer, S.E. Strategies to control a common carp population by pulsed commercial harvest. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2012, 32, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartodziej, W.; Sorensen, P.W.; Bajer, P.G.; Pilgrim, K.; Blood, S. A Minnesota story: Urban shallow lake management. LakeLine 2017, 37, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, J.; Dunham, J.; Bellmore, J.R.; Lyons, D. Modeling control of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in a shallow lake-wetland system. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 27, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Chizinski, C.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Using the Judas technique to locate and remove wintertime aggregations of invasive common carp. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2011, 18, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulhanek, S.A.; Leung, B.; Ricciardi, A. Using ecological niche models to predict the abundance and impact of invasive species: Application to the common carp. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. Using boat electrofishing to estimate the abundance of invasive common carp in small midwestern lakes. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2012, 32, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G. A decade of common carp research and management in Minnesota. LakeLine 2017, 37, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, J.R.; Sauey, B.W.; Amberg, J.J.; Bajer, P.G. Assessing the efficacy of corn-based bait containing antimycin-a to control common carp populations using laboratory and pond experiments. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.W.; Bajer, P.G. Case studies demonstrate that common carp can be sustainably reduced by exploiting source-sink dynamics in Midwestern lakes. Fishes 2020, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piczak, M.L.; Bzonek, P.A.; Pratt, T.C.; Sorensen, P.W.; Stuart, I.G.; Theÿsmeÿer, T.; Mandrak, N.E.; Midwood, J.D.; Cooke, S.J. Controlling common carp (Cyprinus carpio): Barriers, biological traits, and selective fragmentation. Biol. Invasions 2023, 25, 1317–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, S.E.; Lhewa, P.; Rundquist, K.; Schultz, S.; Levers, L.; Smanski, M.J. Perceptions on the genetic biocontrol of invasive carp. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G. Common Carp Management: Acoustic Conditioning in Common Carp to Accelerate Removal and Reduce Cost; Minnesota Aquatic Invasive Species Research Center, University of Minnesota: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2024; Available online: https://maisrc.umn.edu/carp-biocontrol (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Chizinski, C.J.; Bajer, P.G.; Headrick, M.E.; Sorensen, P.W. Different migratory strategies of invasive common carp and native northern pike in the American Midwest suggest an opportunity for selective management strategies. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2016, 36, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, N.; Miner, J. Environmental cues of spawning migration into a confined wetland by northern pike and common carp in Lake Erie: Identifying fine-scale patterns. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2022, 42, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. Recruitment and abundance of an invasive fish, the common carp, is driven by its propensity to invade and reproduce in basins that experience inter-time hypoxia in interconnected lakes. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Chizinski, C.J.; Silbernagel, J.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Variation in native micro-predator abundance explains recruitment of a mobile invasive fish, the common carp, in a naturally unstable environment. Biol. Invasions 2012, 14, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson-Reinemer, D.K.; Chick, J.H.; VanMiddlesworth, T.D.; VanMiddlesworth, M.; Casper, A.F. Widespread and enduring demographic collapse of invasive common carp (Cyprinus carpio) in the Upper Mississippi River system. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.R.; Bajer, P.G. A small native predator reduces reproductive success of a large invasive fish as revealed by while-lake experiments. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Ghosal, R.; Mselko, M.; Smanski, M.J.; Lechelt, J.D.; Hansen, G.; Kornis, M.S. Biological control of invasive fish and aquatic invertebrates: A brief review with case studies. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2019, 10, 227–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Parker, J.E.; Cross, T.K.; Venturelli, P.A.; Sorensen, P.W. Partial migration to seasonally-unstable habitat facilitates biological invasions in a predator-dominated system. Oikos 2015, 124, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penne, C.R.; Pierce, C.L. Seasonal distribution, aggregation, and habitat selection of common carp in Clear Lake, Iowa. Trans. Am. Fish Soc. 2008, 137, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banet, N.V.; Fieberg, J.; Sorensen, P.W. Migration, homing and spatial ecology of common carp in interconnected lakes. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2022, 31, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechelt, J.D.; Kocian, M.J.; Bajer, P.G. Low downstream dispersal of young-of-year common carp from marshes into lakes in the Upper Mississippi River region and its implications for integrated pest management strategies. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2017, 8, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fremling, C.R.; Heins, G.A. A Lake Winona Compendium: Information Concerning the Reclamation of an Urban Winter-Kill Lake at Winona, Minnesota, 2nd ed.; Winona State University: Winona, MN, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Melnytschuk, C.; Spielman, D.K.; Harkins, J.P.; Funk, K.; Bilicki, A.M. Effectiveness of bowfin as a predator on bluegill in a vegetated lake. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1998, 18, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundahl, N.D.; Hoisington, J. Game fish response to dredging of a eutrophic urban lake in Minnesota. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2020, 37, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkelman, M.L.; Mundahl, N.D. Growth and condition of largemouth bass (Micropterus nigricans) and bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) in a Minnesota, USA, lake with separate dredged and non-dredged basins. Limnol. Rev. 2024, 24, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, K.L.; Kruse, C.G. Condition. In Analysis and Interpretation of Freshwater Fisheries Data; Guy, C.S., Brown, M.L., Eds.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2007; pp. 423–471. [Google Scholar]
- Bister, T.J.; Willis, D.W.; Brown, M.L.; Jordan, S.M.; Neumann, R.M.; Quist, M.C.; Guy, C.S. Proposed standard weight (Ws) equations and standard length categories for 18 warmwater nongame and riverine fish species. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2000, 20, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelps, Q.E.; Edwards, K.R.; Willis, D.W. Precision of five structures for estimating age of common carp. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2007, 27, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.R.; Watkins, C.J.; Quist, M.C. Evaluation of hard structures used to estimate age of common carp. Northwest Sci. 2016, 90, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.R.; Wisby, W.J. Net avoidance behavior of carp and other species of fish. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1964, 21, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntingford, F.A.; Andrew, G.; Mackenzie, S.; Morera, D.; Coyle, S.M.; Pilarczyk, M.; Kadri, S. Coping strategies in a strongly schooling fish, the common carp Cyprinus carpio. J. Fish Biol. 2010, 76, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilizzi, L.; Tarkan, A.S.; Copp, G.H. Experimental evidence from causal criteria analysis for the effects of common carp Cyprinus carpio on freshwater ecosystems: A global perspective. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2015, 23, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechelt, J.D.; Bajer, P.G. Elucidating the mechanism underlying the productivity-recruitment hypothesis in the invasive common carp. Aquat. Invasions 2016, 11, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skawinski, P.M. Aquatic Plants of the Upper Midwest: A Photographic Field Guide to Our Underwater Forests; P.M. Skawinski: Wausau, WI, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Provenza, F.D. Mechanisms of resistance of freshwater macrophytes to herbivory by invasive juvenile common carp. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxmeier, R.J.H.; Aday, D.D.; Wahl, D.H. Examining interpopulational variation in bluegill growth rates and size structures: Effects of harvest, maturation, and environmental variables. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency. Minnesota’s Impaired Waters List; Minnesota Pollution Control Agency: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.pca.state.mn.us/air-water-land-climate/minnesotas-impaired-waters-list (accessed on 17 August 2024).
- Barr Engineering. Lake Winona Water Quality Improvement Plan: A Targeted, Prioritized, and Measurable Implementation Plan to Effectively Restore Lake Winona; Barr Engineering: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huser, B.J.; Bajer, P.G.; Chizinski, C.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Effects of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) on sediment mixing depth and mobile phosphorus mass in the active sediment layer of a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 2016, 763, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).