Abstract
Lake Taihu, a subtropical shallow lake in the Yangtze River Basin, is the third-largest freshwater lake in China. It serves not only as a crucial source of drinking water and an ecological resource but also holds significant economic, tourism, and fisheries value. Phytoplankton, a vital component of aquatic ecosystems, plays a critical role in nutrient cycling and maintaining water structure. Its community composition and concentration reflect changes in the aquatic environment, making it an important biological indicator for monitoring ecological conditions. Understanding the impact of water quality on phytoplankton is essential for maintaining ecological balance and ensuring the sustainable use of water resources. This paper focuses on Lake Taihu, with water samples collected in February, May, August, and November from 2011 to 2019. Using quantile regression, a robust statistical analysis tool, the study investigates the heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton and seasonal variations. The results indicate significant seasonal differences in water quality in Lake Taihu, which substantially influence phytoplankton, showing weakly alkaline characteristics. When phytoplankton concentrations are low, pondus hydrogenii (pH), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), water temperature (WT), and conductivity significantly affect them. At medium concentrations, COD, TP, TN, and WT have significant effects. At high concentrations, transparency and dissolved oxygen (DO) significantly impact phytoplankton, while TP no longer has a significant effect. These findings provide valuable insights for policymakers and environmental managers, supporting the prevention and control of harmful algal blooms in Lake Taihu and similar aquatic systems.
1. Introduction
Phytoplankton, as a crucial component of aquatic communities, play an essential role in nutrient cycling and shaping water structure within aquatic ecosystems [1]. These microorganisms are fundamental to the aquatic food web, serving as primary producers that convert inorganic compounds into organic matter through photosynthesis. Their community composition can significantly reflect changes in the water environment, making them vital bioindicators for monitoring ecological conditions and assessing water body health [2,3]. Water quality profoundly influences the ecological dynamics of freshwater systems, particularly in nutrient-rich lakes, where increased nutrient levels can lead to excessive phytoplankton growth [4]. Lake Taihu, the third-largest freshwater lake in China, has experienced severe eutrophication, resulting in frequent harmful algal blooms [5,6]. These blooms have far-reaching consequences, including oxygen depletion and the production of toxins that affect aquatic life and human health. The deterioration of water quality in Lake Taihu poses significant threats to local biodiversity, water supply, and public health [7]. Therefore, understanding the heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton is crucial for managing and mitigating these ecological issues. Comprehensive research on this topic can provide valuable insights for policymakers and environmental managers, helping them maintain ecological balance and ensure the sustainable use of water resources. Such knowledge is essential for developing effective strategies to combat eutrophication and preserve the integrity of freshwater ecosystems.
In recent years, numerous studies have analyzed the relationship between water quality parameters and phytoplankton using a variety of statistical methods from different perspectives. Previous research in this field has extensively emphasized the complex relationship between nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus) and phytoplankton. Magumba et al. [8] conducted an in-depth study of water quality data from 396 lakes across 18 European countries, utilizing panel models to explore the relationships among chlorophyll-a, TP, and TN. Their findings indicated that the concentration of chlorophyll-a could be controlled by reducing TP levels rather than TN levels, although this effect might be offset by historical chlorophyll-a concentrations. Zhang et al. [9] modeled phytoplankton biomass data from Lake Okeechobee using generalized linear models and random forest algorithms, revealing that TN is the most significant factor influencing phytoplankton biomass. Xu et al. [10] conducted a detailed study on the water quality of Lake Tai, examining the seasonal thresholds of TN and TP on phytoplankton. Roberto et al. [11] carried out a comprehensive study on global lakes, primarily investigating the impact of TP on chlorophyll-a, while also examining the influence of physical factors on lakes. Additionally, many studies have demonstrated the close relationship between TP, TN, and phytoplankton [12,13,14,15,16]. Beyond TP and TN, other studies have explored the relationship between water quality and phytoplankton from various angles, including the influence of temperature, light, and other trace nutrients. Smith et al. [17] used random forest algorithms to model the phytoplankton community in agricultural irrigation ponds, investigating the predictive roles of three sets of water quality parameters: physicochemical, organic, and nutrient components. Meng et al. [3] analyzed the composition of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities using relative abundance, density, and biomass, employing distribution matrix temperature and bipartite network methods to study the seasonal characteristics of their nested patterns and interaction networks. However, traditional statistical modeling methods, typically used to estimate the average impact of water quality on phytoplankton biomass, often fail to capture the inherent complexity and heterogeneity of these relationships, especially under varying environmental conditions. Quantile regression offers a robust alternative by allowing researchers to explore how water quality impacts different concentrations of phytoplankton across various quantiles of the phytoplankton distribution. This approach is particularly useful in ecological studies where the effects of explanatory variables may vary at different points of the response variable distribution, providing a more nuanced understanding of the data [18,19].
Despite extensive research on the distribution characteristics of phytoplankton and their influencing factors across various lakes, rivers, and water bodies, significant gaps remain in this field. First, most studies have primarily focused on analyzing the mean effects of water quality or other factors on phytoplankton, without providing a comprehensive analysis of their distribution. Second, the majority of research has examined heterogeneity primarily from a seasonal perspective, neglecting the investigation of heterogeneity at the level of phytoplankton concentration. To address these gaps, this study employs quantile regression to analyze the heterogeneous effects and seasonal variations of water quality on phytoplankton in Lake Taihu. By examining the impact of various water quality parameters, including nutrient levels, WT, and pH, across different quantiles, this study aims to offer a more detailed understanding of the complex interactions between water quality and phytoplankton, as well as the effects of heterogeneity. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: (1) a comprehensive analysis of recent water quality and phytoplankton conditions in Lake Taihu, with an in-depth exploration of the heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton; (2) an investigation into the complex interactions between water quality and phytoplankton from two perspectives—seasonal changes and concentration variations—providing valuable insights for managing lake ecosystems not only seasonally but also during different pollution periods; and (3) as the third-largest freshwater lake in China, the analysis of the relationship between water quality and phytoplankton in Lake Taihu is not only significant for improving the aquatic environment of the lake but also offers a reference for the management of freshwater lakes worldwide.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Lake Taihu, situated in the southern part of the Yangtze River Delta in China, is the third-largest freshwater lake in China, following Lake Poyang and Lake Dongting. Straddling Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces, the lake’s specific coordinates range from E to E longitude and N to N latitude. It is bordered by Wuxi in Jiangsu to the north, Huzhou in Zhejiang to the south, Changzhou and Yixing in Jiangsu to the west, and Suzhou in Jiangsu to the east. Lake Taihu covers a total area of 2427.8 km2, with a water surface area of 2338.1 km2, a shoreline length of 393.2 km, a length of approximately 68.5 km from north to south, and a width of about 56 km from east to west. The lake has an average depth of 1.9 m, reaching a maximum depth of 2.6 m, classifying it as a shallow lake. Lake Taihu’s average annual outflow is 7.5 billion cubic meters, and it has a storage capacity of 4.4 billion cubic meters. The watershed’s annual average water resource volume is 17.6 billion cubic meters, supporting urban and rural water supply for over 20 million people in cities such as Wuxi, Suzhou, and Shanghai. The lake is interconnected with numerous rivers and ports, with more than 50 major inflow and outflow rivers. It also contains more than 50 islands of various sizes. The surrounding terrain is generally flat, dominated by lakes and wetlands, while its western and southwestern sides feature hilly and mountainous areas, and the eastern side comprises plains and a network of waterways. The nutritional status of Lake Taihu generally exhibits a trend towards eutrophication. The phytoplankton community in Lake Taihu is predominantly composed of cyanobacteria, particularly the genus Microcystis. Due to the high degree of eutrophication, the coastal areas of Wuxi along Lake Taihu have frequently experienced cyanobacterial blooms during the summer in recent years, significantly affecting water quality. The chemical composition of Lake Taihu primarily includes dissolved inorganic salts, nutrients, dissolved gases, and organic matter. The pH of the lake typically ranges from 7.5 to 9.0, indicating a mildly alkaline condition, which is related to the balance of the carbonate system in the water. Ecologically, Lake Taihu is a habitat for a diverse array of aquatic organisms, including various species of fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants. As a significant natural ecosystem and economic region, the protection and management of Lake Taihu are crucial not only for the improvement of the local ecological environment but also for the sustainable development of the Yangtze River Delta region [20,21].
2.2. Data Sources
The data for this study were sourced from National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (https://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 11 February 2022)). We selected a representative subset of this data for analysis. In this study, samples were collected from 32 designated sampling sites (Figure 1) distributed across Lake Taihu. The sampling was systematically conducted over a nine-year period, spanning from 2011 to 2019. To capture seasonal variations and ensure comprehensive temporal coverage, samples were taken during the months of February, May, August, and November each year. These specific months were selected to represent winter, spring, summer, and autumn, respectively, allowing for the analysis of seasonal dynamics in water quality and ecological parameters. The consistent temporal and spatial sampling framework provides a reliable dataset for assessing the heterogeneous effects of lake water environments on phytoplankton.
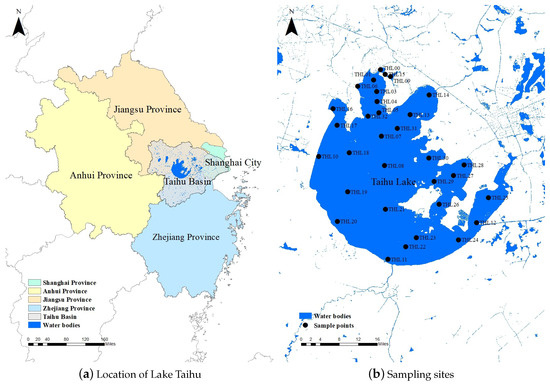
Figure 1.
Location of Lake Taihu in China and sampling sites in Lake Taihu.
2.3. Statistical Method
This study employed the R programming language for data processing and analysis. Initially, missing values in the dataset were filled using linear interpolation within the same site. Subsequently, the data were log-transformed, and the log-transformed data were utilized for statistical analysis. In the univariate analysis, we examined the relationships between phytoplankton and water quality variables using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, univariate linear regression, and univariate quantile regression [22]. To explore the heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton, quantile regression was primarily employed, and its results were compared with those from linear regression. Additionally, ANOVA and quantile regression were used to investigate the seasonal heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton. The software packages used in this study include zoo 1.8-12 [23], pastecs 1.4.2 [24], corrplot 0.94 [25], quantreg 5.97 [26], and ggplot2 3.5.1 [27].
Since quantile regression [22,28,29] is a key tool in the data analysis of this study, we provide a brief overview of this method. Traditional regression models focus on modeling the conditional expectation of the dependent variable given the independent variables. In contrast, quantile regression models the conditional quantiles of the dependent variable given the independent variables. While traditional regression models capture only the central tendency of the dependent variable, quantile regression allows for inferences about the entire conditional distribution of the dependent variable. Let y be dependent variable and be independent variables. The -th conditional quantile, , of y given X is defined as , where is the conditional distribution function of y given X. Then, the quantile regression model can be defined as
where is the coefficient of the quantile regression model. Quantile regression has been widely used in environmental science and ecology [19,30,31] because of its robustness in modeling with outliers or heavy tail quantile data and its ability to analyze data more comprehensively.
3. Results
3.1. Univariate Analysis of Phytoplankton and Water Quality
Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics for the phytoplankton and eight water quality parameters in Lake Taihu, including the minimum, maximum, mean, standard deviation, skewness, and kurtosis. The results shown in Table 1 provide a general overview of the water quality in Lake Taihu. The water quality of Lake Taihu predominantly exhibits weak alkalinity, and there is considerable variability in the fluctuations of various water quality parameters. Additionally, the skewness and kurtosis indicate that the variables do not follow a normal distribution. Based on the data preprocessing methods referenced in existing literature [11,32], we log-transformed the data for subsequent analysis.

Table 1.
Univariate descriptive statistical analysis of phytoplankton and water quality parameters.
Figure 2 displays the Pearson correlation coefficient matrix for the pairwise relationships between phytoplankton and eight water quality parameters in Lake Taihu. The results in Figure 2 reveal that phytoplankton exhibits the strongest correlation with COD (Pearson’s R = 0.55), followed by TP (Pearson’s R = 0.44), both of which are positive correlations. At the same time, we can also find some other interesting conclusions, such as a significant negative correlation between WT and DO (Pearson’s R = −0.60), and a significant positive correlation between TP and COD (Pearson’s R = 0.76). However, it is important to note that these coefficients represent only linear relationships between pairs of variables and do not fully capture the comprehensive impact of water quality on phytoplankton. A more thorough analysis will be provided in subsequent sections.
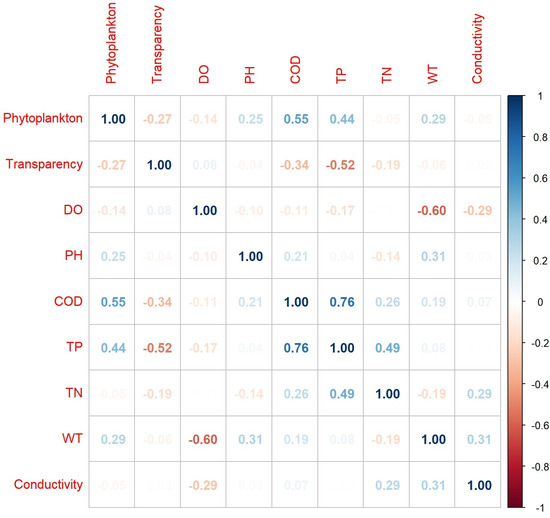
Figure 2.
Pearson correlation coefficient matrix between phytoplankton and each water quality parameters. Blue indicates the positive correlation, and red indicates the negative correlation.
Figure 3 presents the results of univariate ordinary linear regression and univariate quantile regression, with phytoplankton as the dependent variable and each water quality variable as the independent variable. The figure includes scatter plots showing the relationships between phytoplankton and eight water quality variables, along with the fitted lines for both univariate linear regression and univariate quantile regression, as well as the corresponding significance test results.

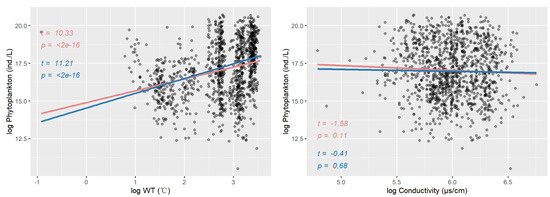
Figure 3.
Scatter plot between phytoplankton and eight water quality variables. The fitting lines of univariate linear regression and univariate quantile regression () and the t-value and p-value of the significance test are shown. Pink indicates the linear regression results, and blue indicates the quantile regression results.
The results of the ordinary linear regression indicate that there are significant relationships between phytoplankton and the variables transparency, DO, pH, COD, TP, and WT (). However, there are no significant relationships between phytoplankton and TN () or conductivity (). In contrast, the results of the quantile regression show significant relationships between phytoplankton and transparency, DO, pH, COD, TP, TN, and WT (), but not with conductivity (). This suggests that, compared to traditional ordinary linear regression, quantile regression is capable of uncovering more detailed information from the data. However, it should be noted that we only established a univariate regression model here, and the quantile regression is only established under . The analysis results are not sufficient to fully reveal the relationship between phytoplankton and water quality.
3.2. Heterogeneous Effects of Water Quality on Phytoplankton under Different Quantiles
Table 2 presents the modeling results of linear regression and quantile regressions at quantile levels ranging from 0.1 to 0.9, with phytoplankton as the dependent variable and eight water quality variables as the independent variables. The table provides the coefficient estimates, standard errors, and significance test results for each model.

Table 2.
Quantile regression and linear regression results with phytoplankton as the dependent variable and (log-transformed) water quality as the independent variable. Quantile regression results are shown under to .
The linear regression results indicate that pH, COD, TP, TN, WT, and conductivity significantly affect phytoplankton (). The quantile regression results show that at lower quantile levels (), the findings are similar to those of the linear regression, with pH, COD, TP, TN, WT, and conductivity having significant impacts on phytoplankton (). However, starting from , discrepancies between the quantile regression and linear regression results emerge. At the median quantile levels (), COD, TP, TN, and WT remain significant (), while pH () and conductivity () no longer significantly affect phytoplankton. At higher quantile levels, the right-skewed nature of the data results in varying outcomes across different quantiles. Nonetheless, some insights can still be gleaned from the high quantile levels. At and , transparency significantly influences phytoplankton (), whereas TP no longer has a significant effect (), a nuance that linear regression cannot capture.
Overall, from both the quantile and linear regressions, we observe that COD, TN, and WT consistently have a significant impact on phytoplankton, indicating that these three variables are the primary factors influencing phytoplankton dynamics.
Figure 4 illustrates the quantile regression coefficients at various quantile levels, along with the coefficients from the linear regression. This figure clearly demonstrates the variation in coefficients across different quantiles and their relationship with the linear regression coefficients.
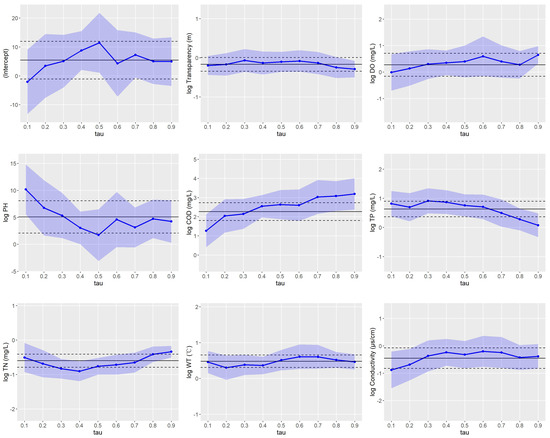
Figure 4.
Quantile regression coefficient plot under different quantiles. Blue line indicates quantile regression coefficients, Blue shade indicates the confidence intervals under different quantiles, and Black indicates linear regression coefficient and confidence interval.
3.3. Heterogeneous Effects of Water Quality on Phytoplankton under Different Seasons
Figure 5 displays violin plots of phytoplankton distribution across different seasons. Analyzing the results shown in Figure 5 reveals that the distribution of phytoplankton varies significantly between seasons. In the spring, summer, and autumn seasons, phytoplankton exhibit a pronounced right-skewed distribution, with the concentration of phytoplankton in summer being higher than in the other seasons.
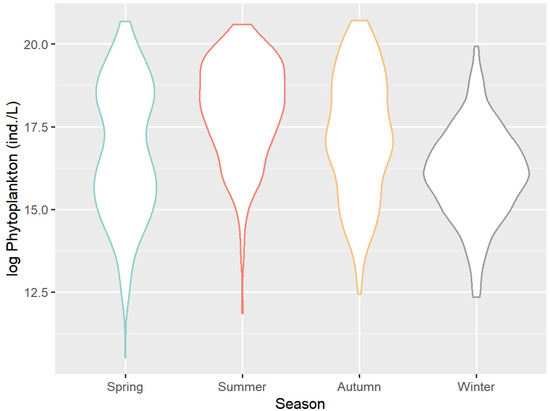
Figure 5.
Violin plot of phytoplankton distribution under different seasons.
Table 3 presents the descriptive statistics and analysis of variance (ANOVA) results for phytoplankton and eight water quality variables across different seasons. Although the data have been log-transformed, valuable insights can still be obtained.

Table 3.
The mean and standard deviation of phytoplankton and eight (log-transformed) water quality variables under different seasons, as well as the F-value of ANOVA and the corresponding p-value.
Analysis of the results in Table 3 reveals significant seasonal differences () for phytoplankton, DO, pH, COD, TP, TN, and WT. This indicates that phytoplankton, along with the six water quality parameters—DO, pH, COD, TP, TN, and WT—exhibit significant seasonal variations. Consequently, the impact of water quality on phytoplankton may differ across seasons. However, no significant seasonal differences were found for transparency () and conductivity ().
In spring, the primary influencing factors are DO, COD, and TP. In summer, at higher quantiles, the main influencing factors are DO, pH, and COD, while at lower quantiles, they shift to TP, TN, and conductivity. During autumn, the primary factors are COD, TP, TN, and conductivity, with TP showing a significant impact only at the median quantile. In winter, the main factors include transparency, DO, pH, COD, temperature, and conductivity, with transparency showing a significant impact only at high quantiles, and conductivity not being significant at low quantiles.
Figure 6 presents the coefficient plots from the quantile regression analysis across different seasons. The detailed modeling results are provided in the Supplementary Materials. The results indicate that the impact of water quality on phytoplankton shows both similarities and heterogeneity across different seasons.
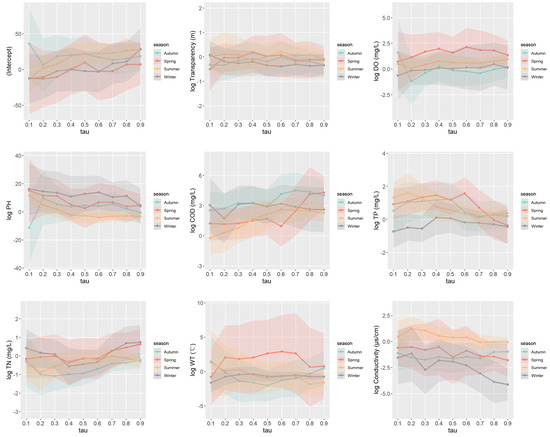
Figure 6.
Quantile regression coefficient plot under different seasons.
4. Discussion
4.1. Basic Characteristics of Phytoplankton and Water Quality in Lake Taihu
Phytoplankton is one of the important indicators for assessing the ecological status and eutrophication of Lake Taihu [33]. Establishing robust statistical models that elucidate the relationship between water quality and phytoplankton dynamics can provide crucial scientific guidance for lake management policies [34]. Data analysis reveals that phytoplankton concentrations vary dramatically, ranging from a minimum of ind./L to a maximum of ind./L, with a mean concentration of ind./L (Table 1). This substantial variability underscores the complex interplay of environmental factors affecting phytoplankton populations, which is consistent with previous findings [35]. However, our study goes further by quantifying the skewness (2.6538) and kurtosis (7.8996), revealing that phytoplankton concentrations are not only highly variable but also heavily skewed and leptokurtic (Table 1). This indicates a higher frequency of extreme values compared to a normal distribution, suggesting that extreme values are more frequent than in a normal distribution. These findings align with the characteristic patterns observed in eutrophic systems, where nutrient influxes can trigger abrupt and intense phytoplankton blooms [36,37,38].
The water quality parameters of Lake Taihu exhibit significant variability, which plays a critical role in determining the ecological dynamics of the lake, particularly the behavior of phytoplankton populations [39]. Consistent with earlier research [40], we observed a strong correlation between COD and phytoplankton, further confirmed in this study (Pearson’s R = 0.55, Figure 2). COD values exhibit extreme variability in Lake Taihu, ranging from 2.38 mg/L to 24.19 mg/L, with a high mean of 4.5366 mg/L and a very high kurtosis of 29.4605 (Table 1). While univariate analysis reveals a significant correlation between TP and phytoplankton (Pearson’s R = 0.44, Figure 2), TN does not exhibit a clear correlation or impact (Pearson’s R = −0.05, Figure 2). However, our study diverges from some earlier research by identifying a significant effect of TN on phytoplankton through univariate quantile regression (, Figure 3). This suggests that, despite the lack of a linear correlation, high nitrogen levels may still contribute to phytoplankton proliferation under specific conditions. These findings highlight that high phosphorus levels and nitrogen pollution both play a role in eutrophication and the growth of phytoplankton, consistent with recent studies [11,41,42]. The differences observed in the effects of TN between our study and previous research may be due to differences in the analytical methods used or variations in environmental conditions across different regions of Lake Taihu.
4.2. Heterogeneous Effects of Water Quality on Phytoplankton in Lake Taihu
Using a traditional linear regression model, we found that phytoplankton is primarily influenced by pH, COD, TP, TN, WT, and conductivity (Table 2), consistent with findings from previous studies [43,44]. However, traditional linear regression only models the conditional mean of the dependent variable given the independent variables, failing to comprehensively analyze the conditional distribution of the dependent variable [29]. This limitation has led to the inability of many existing studies to fully explore the distribution characteristics of phytoplankton, and the presence of eutrophication in lakes may significantly impact the robustness of the regression model. Quantile regression is a statistical model that can model the conditional quantiles of the dependent variable, allowing us to explore the heterogeneous influencing factors of phytoplankton at different concentrations [45]. Given the right-skewed distribution of phytoplankton, it is crucial to study the influencing factors at lower concentrations (), which is essential for the daily management of the Taihu Lake ecosystem. The analysis results indicate that at low concentrations, the main influencing factors are pH, COD, TP, TN, WT, and conductivity.
Most phytoplankton adapt to neutral to slightly alkaline water environments, so pH has a positive effect on phytoplankton [46]. However, in this study, pH did not exhibit a significant impact at the median quantile levels (), suggesting that its influence may be more nuanced than previously thought. Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is a comprehensive indicator reflecting the degree of organic and reducing inorganic pollution in the water [47], directly relating to phytoplankton growth. TP is a limiting nutrient element for phytoplankton growth [48]. An appropriate amount of phosphorus promotes the growth and reproduction of phytoplankton, but excessive phosphorus leads to eutrophication, causing a massive proliferation of phytoplankton, especially algae, forming algal blooms. However, at higher quantile levels (), TP does not show a significant impact, indicating that TP is no longer a primary factor affecting phytoplankton when eutrophication occurs. This contrasts with the findings of earlier studies that emphasize TP as a key driver of phytoplankton growth across all conditions, and suggests that other factors might become more influential in heavily eutrophic environments. The divergence in the impact of TP at different quantile levels could be due to variations in the study’s environmental context or differences in the analytical approach, highlighting the complexity of nutrient dynamics in eutrophic systems. Another possible reason is that as phytoplankton concentrations increase, phytoplankton may also play a role in shaping the aquatic environment. This environmental formation function could lead to changes in their light and nutrient requirements, resulting in different impact relationships compared to those observed at lower concentrations.
TN is a critical nutrient for phytoplankton growth [49], and excessive nitrogen generally promotes the proliferation of phytoplankton, particularly algae. However, our findings reveal that TN has a negative impact on phytoplankton, which contrasts with the typical understanding. This negative effect may be attributed to the toxicity of ammonia nitrogen, an imbalanced nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio, or the detrimental effects of eutrophication. Water temperature is a crucial physical factor affecting the metabolic activities of phytoplankton [50]. Warmer temperatures can enhance the metabolic activity and growth rate of phytoplankton. Conductivity reflects the total amount of dissolved salts in the water, and changes in conductivity can influence the growth environment of phytoplankton [51]. Moderate conductivity facilitates the absorption of essential minerals and nutrients by phytoplankton, thereby influencing their growth. Nevertheless, conductivity does not show a significant impact at the median quantile levels (), suggesting that its influence may be limited or overshadowed by other factors under certain conditions. Transparency, which indicates the depth of light penetration in the water [52], and DO, which is vital for the respiration of aquatic organisms and the decomposition of organic matter [53], only show significant effects at higher concentrations of phytoplankton. This pattern suggests that the influence of these factors becomes more pronounced in environments with dense phytoplankton populations, likely due to increased competition for light and oxygen.
4.3. Seasonal Variations in the Impact of Water Quality on Phytoplankton in Lake Taihu
The water quality factors of Lake Taihu exhibit significant seasonal variations, profoundly influencing the growth and distribution of phytoplankton, demonstrating seasonal heterogeneity [54]. In spring, rising air temperatures lead to an increase in WT, creating favorable conditions for the reproduction and growth of phytoplankton [55]. During this period, DO levels are generally sufficient, which supports the active proliferation of phytoplankton. In summer, WT reach their annual peak, resulting in the highest metabolic activity of phytoplankton [56]. Under high-temperature conditions, DO levels in the water may decrease due to enhanced biological respiration and decomposition activities, reducing populations of oxygen-sensitive phytoplankton species. Summer also marks the peak period for algal blooms, with increased concentrations of COD and nutrients (TP and TN), potentially leading to eutrophication.
As autumn approaches, WT begin to decline, slowing the growth rate of phytoplankton. Reduced rainfall during autumn typically leads to increased water transparency, and DO levels tend to rise [57]. During this time, the concentrations of TP and TN stabilize, promoting the steady growth of phytoplankton. In winter, decreasing air temperatures cause WT to reach its annual minimum, significantly reducing the metabolic activity of phytoplankton and their population numbers. The lower temperatures result in increased DO levels, alleviating the oxygen demand pressure on phytoplankton. Winter water transparency is generally high but limited by shorter daylight hours and lower light intensity, restricting phytoplankton photosynthesis. Additionally, COD and nutrient (TP and TN) concentrations are relatively low, and conductivity may also decrease, reflecting reduced levels of dissolved substances in the water [58].
These seasonal dynamics align with findings from previous studies, but our analysis further highlights how specific water quality factors, such as WT and DO, differentially affect phytoplankton across seasons, potentially leading to variations in species composition and abundance. The differences observed between seasons can be attributed to the complex interplay between temperature, nutrient availability, and other environmental factors, underscoring the need for season-specific management strategies to address the challenges of eutrophication and algal blooms.
Our findings have significant implications for the development of policies and management plans aimed at preventing and controlling harmful algal blooms in Lake Taihu and other aquatic systems. Based on our research, we suggest that management strategies should be tailored to different phytoplankton concentration levels. At the same time, based on our findings, this study can support the ecological zoning management of Lake Taihu, particularly by providing a scientific basis for the refined regional classification and management of cyanobacterial blooms. For example, policies could include stricter nutrient input limits during periods of high phytoplankton concentrations and more robust monitoring programs during low concentrations. Additionally, improving water treatment processes to address both organic and nutrient pollution can help mitigate the adverse effects of eutrophication. Seasonal monitoring programs are also recommended to better understand and manage the dynamic changes in water quality and phytoplankton populations throughout the year.
5. Conclusions
This study employed quantile regression to investigate the heterogeneous effects of water quality parameters on phytoplankton in Lake Taihu. The analysis revealed that the relationships between water quality factors—such as WT, DO, COD, TP, TN, conductivity, and transparency—and phytoplankton abundance exhibit heterogeneity across different levels of phytoplankton concentration. At higher quantiles, factors such as DO and transparency play a more significant role, underscoring their importance in maintaining baseline levels of phytoplankton. Conversely, at lower quantiles, nutrients (TP and TN) have a more pronounced effect on phytoplankton growth, highlighting the critical need for managing nutrient inputs to prevent algal blooms. Additionally, we analyzed the seasonal heterogeneous effects of water quality parameters on phytoplankton, providing further insights into their seasonal dynamics. In conclusion, the heterogeneous effects of water quality on phytoplankton emphasize the necessity of a multifaceted management approach in Lake Taihu. By addressing the specific influences of various water quality factors at different levels of phytoplankton abundance, more effective and targeted strategies can be developed to enhance water quality and ecological health. Future research should continue to explore these dynamic relationships, particularly under varying environmental and anthropogenic pressures, to provide scientific foundations for sustainable lake management practices.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16182570/s1, Table S1: Quantile regression results in spring. Table S2: Quantile regression results in summer. Table S3: Quantile regression results in autumn. Table S4: Quantile regression results in winter.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z.; methodology, L.W. and S.L.; software, L.W. and S.L.; validation, Y.C. and W.G.; formal analysis, L.W. and S.L.; investigation, S.M. and Z.Y.; resources, Q.L.; data curation, S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.W.; writing—review and editing, L.W. and S.L.; visualization, L.W., Q.L. and S.L.; supervision, Q.L. and Y.Z.; project administration, Y.Z. and Z.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. and Q.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Key Research and Development Program of China, project no. (2021YFC3201004) and National Natural Science Foundation of China no. (42107507).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgment for the data support from “National Earth System Science Data Center, National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (https://www.geodata.cn (accessed on 11 February 2022))”. The author sincerely thanks the anonymous reviewers and the editor for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| TP | total phosphorus |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| WT | water temperature |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| pH | pondus hydrogenii |
References
- Lobus, N.V.; Kulikovskiy, M.S. The co-evolution aspects of the biogeochemical role of phytoplankton in aquatic ecosystems: A review. Biology 2023, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wei, J.; Pei, H. Variation of phytoplankton communities and their driving factors along a disturbed temperate river-to-sea ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Zhao, R.; Qiu, X.; Liu, S. Nested Patterns of Phytoplankton and Zooplankton and Seasonal Characteristics of Their Mutualistic Networks: A Case Study of the Upstream Section of the Diannong River in Yinchuan City, China. Water 2023, 15, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Downing, J.A. Relationship of chlorophyll to phosphorus and nitrogen in nutrient-rich lakes. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Loiselle, S.A.; Zhu, L.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R. Distribution and incidence of algal blooms in Lake Taihu. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; Hall, N.S.; Rossignol, K.L.; Joyner, A.R.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B. Nutrient limitation dynamics examined on a multi-annual scale in Lake Taihu, China: Implications for controlling eutrophication and harmful algal blooms. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Xu, P.; Wu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y. Environmental issues of lake Taihu, China. In Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes with Special Reference to Lake Taihu, China; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Magumba, D.; Maruyama, A.; Takagaki, M.; Kato, A.; Kikuchi, M. Relationships between chlorophyll-a, phosphorus and nitrogen as fundamentals for controlling phytoplankton biomass in lakes. Environ. Control Biol. 2014, 51, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhi, M.; Zhang, Y. Combined Generalized Additive model and Random Forest to evaluate the influence of environmental factors on phytoplankton biomass in a large eutrophic lake. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 130, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gaoa, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, R.; Filazzola, A.; Mahdiyan, O.; Shuvo, A.; Blagrave, K.; Ewins, C.; Moslenko, L.; Gray, D.K.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Relationships of total phosphorus and chlorophyll in lakes worldwide. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Tang, H.J.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, C.S.; Wang, X.L. Increased nutrient loads from the Changjiang (Yangtze) River have led to increased harmful algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wan, L.; Zhao, L. Effect of nutrient level on phytoplankton community structure in different water bodies. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Liao, J.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y. The threshold responses of phytoplankton community to nutrient gradient in a shallow eutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Heathcote, A.J.; Kendall, D.L.; Downing, J.A. Phytoplankton taxonomic compositional shifts across nutrient and light gradients in temperate lakes. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhong, F.; Cui, N.; Cheng, S. Increasing phytoplankton-available phosphorus and inhibition of macrophyte on phytoplankton bloom. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Wolny, J.L.; Hill, R.L.; Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y. Examining the relationship between phytoplankton community structure and water quality measurements in agricultural waters: A machine learning application. Environments 2022, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornaroli, R.; Cabrini, R.; Zaupa, S.; Bettinetti, R.; Ciampittiello, M.; Boggero, A. Quantile regression analysis as a predictive tool for lake macroinvertebrate biodiversity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, E.E.O.; Aluko, O.A. Heterogeneous effects of industrialization on the environment: Evidence from panel quantile regression. Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 2021, 59, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B. Lake Taihu, China: Dynamics and Environmental Change; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 87. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Jia, Z.; Liu, K.; Wang, G. Temporal and spatial distributions and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in western Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R. Quantile Regression; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Zeileis, A.; Grothendieck, G. zoo: S3 Infrastructure for Regular and Irregular Time Series. J. Stat. Softw. 2005, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosjean, P.; Ibanez, F.; Etienne, M. Pastecs: Package for analysis of space-time ecological series. R Package Version 2018, 1, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V.; Levy, M.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zemla, J. Package ‘Corrplot’. Statistician 2017, 56, e24. [Google Scholar]
- Koenker, R.; Portnoy, S.; Ng, P.T.; Zeileis, A.; Grosjean, P.; Ripley, B.D. Package ‘Quantreg’. 2018. Available online: https://cloud.r-project.org/web/packages/quantreg/index.html (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenker, R.; Bassett, G., Jr. Regression quantiles. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1978, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regression, Q. Handbook of Quantile Regression; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. Probabilistic water demand forecasting using quantile regression algorithms. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, S.; Mohammadi Ghaleni, M. Revealing accuracy in climate dynamics: Enhancing evapotranspiration estimation using advanced quantile regression and machine learning models. Appl. Water Sci. 2024, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiades, L. Size scaling patterns of species richness and carbon biomass for marine phytoplankton functional groups. Mar. Ecol. 2017, 38, e12454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Xu, Y.; Ruan, A. Spatial and temporal patterns of phytoplankton community succession and characteristics of realized niches in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 243, 117896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Kong, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z. Towards the comprehensive water quality control in Lake Taihu: Correlating chlorphyll a and water quality parameters with generalized additive model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Yu, H. Phytoplankton functional groups succession and their driving factors in a shallow subtropical lake. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2020, 35, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouraï, L.; Logez, M.; Laplace-Treyture, C.; Argillier, C. How do eutrophication and temperature interact to shape the community structures of phytoplankton and fish in lakes? Water 2020, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Su, H.; Wang, J.; Xie, P.; Chen, F. Eutrophication and predation mediate zooplankton diversity and network structure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, S133–S145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Gu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, H.; Shen, R.; Jeppesen, E. The role of top-down and bottom-up control for phytoplankton in a subtropical shallow eutrophic lake: Evidence based on long-term monitoring and modeling. Ecosystems 2020, 23, 1449–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.; Cheng, S. Phytoplankton community structure and water quality assessment in an ecological restoration area of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Shi, Z.; Feng, L. Temporal and spatial variations of chemical oxygen demand in Lake Taihu, China, from 2005 to 2009. Hydrobiologia 2011, 665, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenken, T.; Brandenburg, K.M.; Van de Waal, D.B. Long-term nutrient load reductions and increasing lake TN: TP stoichiometry decrease phytoplankton biomass and diversity in a large shallow lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2023, 68, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Zhang, T.; Fan, J.; Li, C.; Xiong, K. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in the Pearl River, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 42242–42253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.L.; Sand-Jensen, K.; Borum, J.; Geertz-Hansen, O. Phytoplankton, nutrients, and transparency in Danish coastal waters. Estuaries 2002, 25, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.K.; Mohan, D.; Rai, A.K. Predicting phytoplankton growth and dynamics in relation to physico-chemical characteristics of water body. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 202, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusiana, E.D.; Arsad, S.; Buwono, N.R.; Putri, I.R. Performance of Bayesian quantile regression and its application to eutrophication modelling in Sutami Reservoir, East Java, Indonesia. Ecol. Quest. 2019, 30, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Archilla, A.I.; Moreira, D.; López-García, P.; Guerrero, C. Phytoplankton diversity and cyanobacterial dominance in a hypereutrophic shallow lake with biologically produced alkaline pH. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharagava, R.N.; Saxena, G.; Mulla, S.I. Introduction to industrial wastes containing organic and inorganic pollutants and bioremediation approaches for environmental management. In Bioremediation of Industrial Waste for Environmental Safety: Volume I: Industrial Waste and Its Management; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, D.; Nwankwegu, A.S.; Lai, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, K.; Wei, J.; Norgbey, E. Study on nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in Xiangxi Bay of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Nakano, S.i. The crucial influence of trophic status on the relative requirement of nitrogen to phosphorus for phytoplankton growth. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, S.; Niu, X. Effect of water temperature on the dynamic behavior of phytoplankton–zooplankton model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2020, 378, 125211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xiong, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, G. Lakes-scale pattern of eukaryotic phytoplankton diversity and assembly process shaped by electrical conductivity in central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiad163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, T.; Sadchikov, A. The Phase of High Transparency and the Chemistry of Pond Water. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2022, 92, 3170–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. Phytoplankton, dissolved oxygen and nutrient patterns along a eutrophic river-estuary continuum: Observation and modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Salmaso, N.; Jeppesen, E.; Qin, B.; Zhang, Y. The relative importance of weather and nutrients determining phytoplankton assemblages differs between seasons in large Lake Taihu, China. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 81, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of nutrients, temperature and their interactions on spring phytoplankton community succession in Lake Taihu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Peng, Y.; Qian, X.; Xiao, L. Spatial and seasonal patterns of size-fractionated phytoplankton growth in Lake Taihu. J. Plankton Res. 2014, 36, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.X. Seasonal dependency of controlling factors on the phytoplankton production in Taihu Lake, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Ji, X.; Hu, W. Characteristics of phytoplankton production in wet and dry seasons in hyper-eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).