Abstract
Sandbars are an integral part of the alluvial river’s geophysical system due to these rivers’ wide sediment availability and varied transport capacity. The sandbars’ evolution and translation considerably influence the stability of the riverbank. However, while designing the riverbank protection structures (RBPS), the impact of such sandbars is often overlooked, as the evolution of such bars is quite uncertain in terms of location, amplitude, and translation. This study evaluates the localized impact of sandbars on bank protection structures in two types of alluvial rivers: meandering (Ganges) and braided (Brahmaputra-Jamuna), utilizing time series satellite images, hydraulic characteristics, and numerical modeling. We found that sandbar development initiates width adjustment in both meandering and braided rivers when the ratio of width to depth surpasses 90. In the case of meandering rivers, riverbank erosion mostly occurs as a result of the presence of alternate bars or point bars. Sandbars in a meandering river (Ganges) can lead to an approximate 18% increase in flow depth. The depth-averaged velocity is anticipated to rise by approximately 29%, and the tractive force may increase by a factor of 1.6. On the other hand, the braided river (the Brahmaputra-Jamuna) underwent significant bank erosion due to the presence of both free unit and hybrid types of bars. In such rivers, the depth of the flow may experience a notable increase of 18%, while the depth-averaged velocity undergoes an approximate increase of 50%, and the tractive force has the potential to grow by a factor of 5.3. Consequently, we recommend allowing the natural evolution of sandbars while preserving the riverbank (where needed only) through RBPS, considering these additional loads.
1. Introduction
Riverbank stability is governed by the equilibrium of motive and resistive forces associated with the most critical failure mechanism [1,2]. Sandbars affect motive and resistive forces by altering the flow–sediment regime of a particular reach. These bars may interact with instream engineering features, enhance bank erosion, and impact navigability [3,4,5]. The formation and development of bars are considered a precursor morpho-dynamic process for the formation of meandering or braiding [3,6,7,8]. Therefore, the sandbar translation considerably influences bed evolution and bank stability. However, while designing the riverbank protection structures (RBPS), the impact of such sandbars is frequently overlooked, as the development of such bars is quite uncertain regarding location, amplitude, and translation (e.g., [9,10]). As most of the streams are either meandering or braided, they have a tendency to form bars [11]. Additional load coming from the formation of such bars on RBPS needs to be quantified.
During the last five decades, extensive fieldwork [12,13], laboratory experiments (e.g., [14,15,16]), theoretical analyses (e.g., [11,17,18,19]), and numerical modeling (e.g., [20,21,22,23]) contributed to our understanding of river bar formation and behavior. Any sandbar’s spatial dimensions are comparable to the channel width, and amplitudes may be scaled with the depth of flow at the time of bank full discharge [5]. Fluvial bars may be classified as forced bars (appearing locally) or periodic bars (appearing regularly in sequences; the hydraulic properties are essentially similar). At the same time, according to the formation type, the bars may be grouped as unit and compound bars with many channels going through them [24,25]. In general, local geometry or discontinuity produces forced bars [22]. There are a few examples of forced bars: eddy bars at locations where flows separate, confluence bars at the intersections of tributaries, and point bars within the inner bends of winding rivers. These bars often rely on the existence of forcing, and their magnitude is proportionate to the forcing. Point bars are considered stable or steady bars since they do not move inside the channel shape [26]. Previous experiments confirmed that sediment-transporting straight channels can develop free bars in periodic patterns and that channels with bank erosion can change to a meandering pattern with fixed bars at each bend (point bars) [26,27,28]. A rise in channel curvature causes the suppression of free bars in straight channels, turning them into fixed bars [7]. Both theory and studies imply that the creation of free bars is governed by a channel width–depth ratio threshold, and that they may be induced by increasing the width, although issues about cause and effect in connection to channel widening remain unsolved [29]. Periodic bars, classified as free (named as mid-channel bars as well) and hybrid bars, are formed by the morpho-dynamic instability of the riverbed. Their physical parameters, such as bar length, celerity, growth rate, and mode, can be predicted using linear and nonlinear bar theories [11,18,19,28,30,31], but limitations exist. The actual bar height and pool depth cannot be reliably predicted by either linear or nonlinear theories [5]. In contrast, braided rivers frequently feature hybrid bars that have fixed positions due to localized pushing of at least one bar in the sequence [32]. The primary bar properties of these types of bars are connected to the flow’s width-to-depth ratio as well. Periodic bars are normally not visible if the width-to-depth ratio is less than around 10, and channels become braided when the width-to-depth ratio exceeds about 50 [5]. The wavelengths of hybrid alternating bars are 10–15 times wider than the channel width. Free bars have wavelengths that are two to three times shorter when the width-to-depth ratio is equal [5]. Similar to the point or free bars, the interaction of the bar with the channel widening or narrowing process during the evolvement or migration period remains unsolved in the literature. This study attempted to fill some of these gaps. On the other hand, as bars act as ecologically important fluvial or riparian habitats, their restoration is a prevalent objective in river rehabilitation initiatives (e.g., [33]).
Therefore, considering them during the RBPS design should be an essential approach to sustainable river management, but this accrued knowledge was not easily applicable to design engineers or river managers. There are no general guidelines on how to deal with the design variable, i.e., depth, velocity, or scouring, when the bars are available or favorable conditions of bar development exist in the design site, as per our knowledge [5]. However, there is evidence that the formation and growth of the sandbar affects the bank stability. For example, Inoue et al. [34] investigated the bedrock re-exposure by sandbar formation and channel curvature of Ishikari River, where the local bedrock erosion has led to insufficient depth of bridge piers and damage to revetments. Performing a laboratory experiment, they concluded that the bankside bedrock re-exposer has a direct and complicated link with the formation of sandbars (alternate bars and double-row bars). Both the sandbar wave heights and length increased with the redistribution of bankside sediment and in addition to continuous sediment supply from upstream. Yamaguchi et al. [35] demonstrated that the installation of revetment alters the characteristics of point bars, even the meandering pattern of the river. Nakagawa et al. [36] also showed that the intensity of the flow around the termination of Sirajganj hardpoint in Brahmaputra-Jamuna is closely related to the evolution of the nearby sandbars.
Therefore, this research quantifies the localized impact of sandbars on RBPS in two types of alluvial rivers in Bangladesh: meandering (Ganges) and braided (Brahmaputra-Jamuna). Our focus is on the rivers’ most downstream portions, which have an elevation of less than 200 m MSL and are known as the low-land reaches. In general, bank protection structures tend to be designed based on the severity of specific return period floods, such as 100-year floods. We hypothesized that the formation and migration of sandbars would affect this design condition. The specific objectives were first to understand the bar–channel interaction in relation to the bank erosion, and then to determine how much hydraulic load is imposed during an extreme flood because of the presence of sandbars.
2. Study Area
As the study area, a part of the Ganges and Brahmaputra-Jamuna Rivers was considered, as shown in Figure 1. The distinct plan form of meandering and braiding is clearly visible in Figure 1A,B in the case of the Ganges and Brahmaputra-Jamuna, respectively. Though both rivers originate at a similar elevation to the Himalayas, nearly 5000 m above the mean sea level (MSL), the Ganges shows a considerable shift in gradient between the highlands and the plain. The slope in the Himalayas is nearly 0.0128, and it drops to about 0.000005 for the last 1300 km, as shown in Figure 1 (bottom subfigure) [37,38,39]. We focused only on 11 km (where the RBPS exists) of the 2500 km-long Ganges near Bangladesh’s Rajbari district, which lies in a low-slope zone (shown by point A in Figure 1). The discharge of this part of the river varies from 500 m3/s to 80,000 m3/s [40]. The total suspended sediment load varies from 380 kg/s to 97, 510 kg/s (at the Hardinge bridge measurement location, shown in Figure 1). The sediment size varies from 0.13 mm to 0.17 mm [40,41,42]. The Ganges is an alluvial river in the study region; therefore, the upstream bed and banks may serve as sediment sources for the river [40]. Furthermore, in the upstream portion of the river, various tributaries join the Ganges and may operate as a possible sediment source, in addition to local bank erosion and scouring [39,40]. On the other hand, the Brahmaputra-Jamuna enters into the low-land after flowing around 1600 km. The study reach of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River was also 11 km, near Islampur. The slope of the river in this region is nearly 0.000008. The discharge varies in this section between 5000 m3/s and 110,000 m3/s [41,42,43,44]. The sediment size varies from 0.15 mm to 0.304 mm [41,42,43]. The suspended sediment load varies from 2 kg/s to 712,871 kg/s, with the average of 35,395 kg/s [41]. The Brahmaputra-Jamuna River, similar to the Ganges, is an alluvial river in the specified area. In addition to the bed and banks, local erosion and the erosion of upstream bars contribute to the sediment supply of the river. In the study reach, the Ganges River is 2.7 km wide, while the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River is 14.71 km wide. The current RBPS lengths of these sections were 6.7 km for the Ganges and 14.4 km for the Brahmaputra-Jamuna (Figure 1). Our field investigation in the year 2022 confirmed that the construction and alignment of RBPS were on an ad hoc basis based on erosion protection priorities.
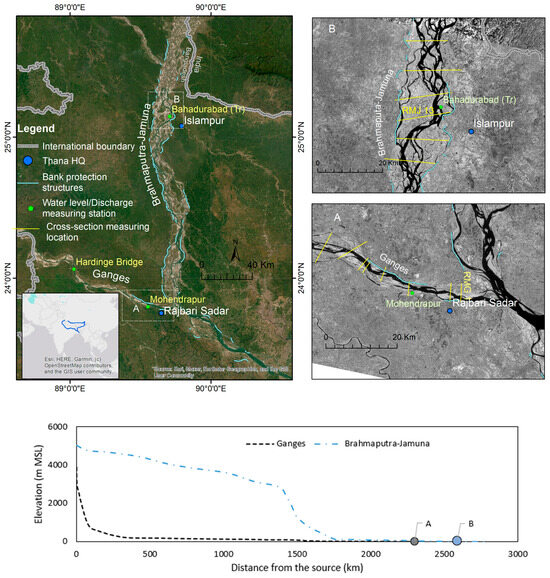
Figure 1.
Study areas for (A) Ganges and (B) Brahmaputra-Jamuna. The bottom figure shows the longitudinal profile of the river’s valley from source to sink.
3. Methodology
In this study, we used time series satellite imagery (Landsat) from 1973 to 2022, river hydraulic data from 2000 to 2022 measured by the Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB), and numerical modeling to determine how much the RBPS is impacted by the existence of sandbars. First, the long-term (almost 50 years) interaction between the bar and channel was studied to better understand the river’s inherent hydro-morphological properties. The riverbank erosion was then scaled over a relatively short period of time (12 years), and the influence of the sandbar was evaluated in relation to the rivers’ other hydraulic characteristics. The effect of a sandbar on RBPS was calculated using numerical modeling of an extreme hydrologic event. From the recent image analysis, a scenario known as the ‘base condition (Mbs or Bbs)’, in which there is no bank erosion, and the reach is less influenced by the sandbar, was identified. Similarly, when the study reach was influenced by a sandbar and met high bank erosion, it was characterized as the ‘extreme bar condition (Mex or Bex)’, as illustrated in Table 1. By comparing these two conditions, the additional load on RBPS was calculated. The next sections detail the methodology.

Table 1.
Cases considered in this study.
3.1. Satellite Image Analysis
Analyzing historical satellite images to evaluate the channel and bar shifting pattern is a common practice. Landsat Thematic Mapper (TM) and Landsat 1–5, 7, 8, and 9 were used to investigate a 49-year shifting pattern of the studied rivers. For the long-term change detection, the decadal interval was focused on, but for the short-term, the change of every year was calculated. The Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) has been proven to be an effective approach to identifying riverbank lines that have higher moisture content [45,46,47,48]. The NDWI usually ranges between −1 and 1, and it was calculated using Equation (1) (according to [49]). Usually, the positive values indicate water bodies because of the higher reflectance of the near infrared (NIR) band than the GREEN band, whereas negative NDWI values indicate vegetation and others:
However, the old and new sand deposition have posed some uncertainty while delineating the riverbank, as well as the included bar area. It should be noted that places with recent soil deposition contain more moisture than other regions near a riverbank. These places have been identified as being part of the river because either the river was running through that region recently or that area was inundated with water during periods of high river flow. The river or channel width, bar length, and width were also determined from these image analyses. It should be noted that here, the channel width signifies the channel where the bar appeared. It can be equal to the full river width or smaller than it, as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
Definition sketch of channel width and bar width.
3.2. Time Series Hydraulic Data Analysis
The BWDB usually measures the river cross-section of the Ganges and Brahmaputra-Jamuna at 4 km to 6 km intervals in the early monsoon period (April–May). The cross-section data from the years 2000 to 2022 that lie within the study reach were analyzed to determine several hydraulic properties, such as bar amplitude, river width, and depth. Besides this, the time series discharge and water level data were analyzed for the numerical model boundary setup, calibration, and validation purposes.
3.3. 2D Numerical Simulation
3.3.1. Governing Equations
Delft3D, an open-source program with a flow version of 4.00.01.000000, was used to simulate the numerical model (Lesser et al. [49] provides further information about Delft3D). This section provides a concise overview of the hydro-morphology model. Partially based on Navier–Stokes’ equations for incompressible free surface flow, the model applies Boussinesq approximations to solve two-dimensional, depth-averaged, shallow-water equations in the hydrodynamics section.
The continuity equation (Equation (2)) was used to compute the conservation of mass:
Equation (3) demonstrates the conservation of momentum in the x-direction:
The conservation of momentum in the y-direction is demonstrated by Equation (4):
where is water surface elevation with respect to a datum (here in m PWD), and are the depth-averaged velocity in the x and y directions, respectively (m/s), represents water depth (m), denotes kinetic eddy viscosity (m2/s), represents the Manning’s coefficient (sm−1/3), and is the acceleration due to gravity (m/s2).
The sediment transport (advection–diffusion equation) is calculated by Equation (5):
In this case, stands for horizontal diffusivity and for the mass sediment concentration (kg/m3). The unit area of sediment source terms is denoted by . Both the turbulent kinetic energy, , and the dissipation, , which reflect shear stresses at the bed, surface, and in the flow, are generated by the production terms in the turbulence model, which was employed for turbulence closure. The numerical model’s sediment transport calculations were based on [50].
The bedload transport rate, , was computed by Equation (6):
In this context, stands for the specific density of the sediment particle, (), denotes the particle size, and denote the bed shear stress and critical bed shear stress, respectively, and represents the ratio between the total bed roughness and the grain-related bed roughness. The dimensionless particle parameter is denoted by . By applying the mass-balance equation [51] using Equation (7), the bed elevation was calculated:
Here, is porosity, and are the bedload transport vectors, represents the bed change, upward and downward suspended sediment transport flux near the bed are denoted by represents the morphological acceleration factor to reduce the computational time step to adapt the morphology. The summation of the bed changes, , resulted in the total bed variation in one-time step:
Here, represents the total considered size fraction.
For the erosion of nearby dry cells along the bank or bar, a technique developed by Roelvink et al. [52] was applied. A wet cell’s erosion flux can be (partially) redistributed to the dry cells around it. One way to express the actual fraction of erosion in an edge, (Equation (9)), is by comparing the maximum fraction of erosion, , with the user-defined water depth () in the wet cell, at which the edge will be reallocated from the wet cells to the surrounding dry cell(s):
where represents the minimum threshold flow depth for reallocating the erosion in a dry cell.
3.3.2. Model Schematization and Boundary Conditions
For the Ganges, the model domain was 11,000 m-long and began 5.9 km upstream of Rajbari Sadar. The domain’s overall width was 2700 m. As shown in Figure 3, the reach was discretized using 36,864 cells, with an average cell size of 35 m × 20 m. The Brahmaputra-Jamuna model was nearly 11 km-long, beginning at 1.9 km from Bahadurabad Station of Islampur. The domain’s average width was 14.71 km, and the entire domain was discretized with 20,412 cells, with each cell measuring 90 m × 70 m. For bathymetry and RBPS, the measured river cross-sections (measured in May 2022, where the bathymetry was measured at regular intervals of 500 m in the longitudinal direction and 5 m in the cross-sectional direction) were used. The 100-year return period flood was used as the model boundary, as shown in Figure 4, which was collected from [9]. For both of the cases, the hydrograph’s shape represented the flood discharge in 1998, which was the last extreme flood in the recent past. The other parameters of the simulation are listed in Table 2.
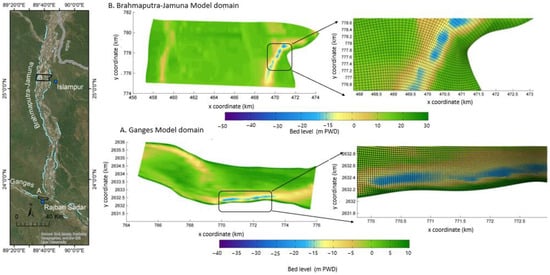
Figure 3.
Grid and bathymetry were used in the models. BWDB commonly refers levels to the Public Works Datum (PWD), which is 0.46 m below the MSL.
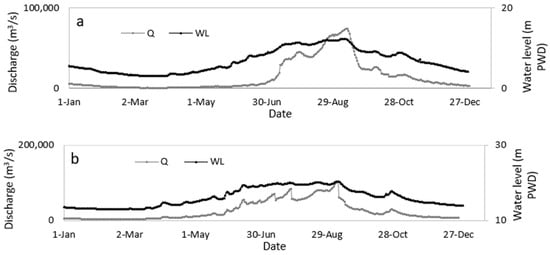
Figure 4.
The boundary conditions used in the models. (a) Ganges model and (b) Brahmaputra-Jamuna model.

Table 2.
The paraments used in the simulations.
3.3.3. 2D Numerical Model Validation
The numerical model was validated using measured data from BWDB. For validation, the flood year 2022 was used. The Bahadurabad Station (where measured discharge and water level data were available, locations are shown in Figure 1) falls within the model domain in the case of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna model. As a result, the model was validated using these data. In the case of the Ganges, however, only water level data (from the Mohendrapur Station) were available. The evaluation statistics are shown in Table 3: Nash–Sutcliffe model efficiency coefficient (NSE), root mean square error (RMSE) observations, standard deviation ratio (RSR), and coefficient of determination, R2. These values were within the acceptable range of the hydrodynamic model [53,54,55].

Table 3.
Validation parameters measured for water level and discharge data.
This figure depicts that the model can reproduce the sediment load pattern efficiently. Figure 5 shows the comparison of simulated and measured bed levels. In Ganges (Figure 5a), the minimum measured (measured in May 2023) bed level was −17.3 m PWD, whereas the simulated bed level was found as −19.3 m PWD. In the simulated bed, another small channel was observed after 1500 m. As the simulated bed represents the bed five months earlier than the measured one, this channel might be closed during the dry season sedimentation. In Brahmaputra-Jamuna (Figure 5b), the bed level of the measured deepest channel was 6 m PWD, whereas the simulated bed level was 2.39 m PWD. Similar to Ganges, there were time differences between the end of simulation and measured data of the next year.
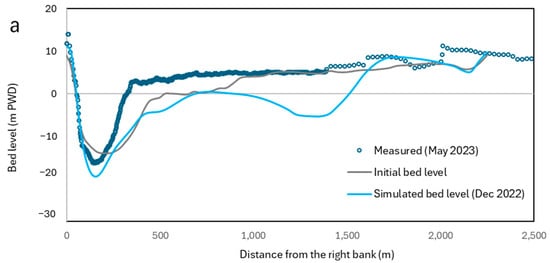
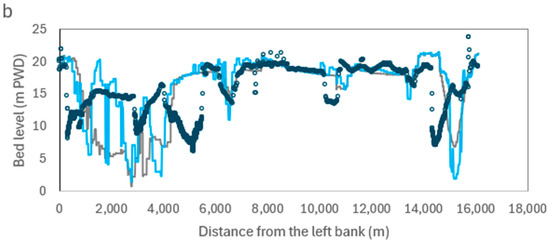
Figure 5.
The comparison of simulated and measured bed levels. (a) Ganges and (b) Brahmaputra-Jamuna.
4. Results
4.1. Channel-Bar Dynamics and Bank Erosion
4.1.1. Meandering River: Ganges
The long-term channel planform analysis is shown in Figure 6. This figure reveals that the confluence of Ganges and Brahmaputra-Jamuna shifted toward the southeast direction of nearly 13.2 km during this time. During the confluence shifting process, the Ganges experienced several types of bars in our study area. The point, free (unit and mid-channel), and alternate bars are common (Figure 7 and Figure 8). From the year 2000 to 2022, the channel width–depth ratio varied from 147 to 374. Mostly, free unit bars and alternate bars were observed during that period in the study reach of the Ganges. The free unit bars were observed when the channel width–depth ratio was less than 220 and disappeared or merged with the increase in the channel width–depth ratio (Figure 9a). At the same time, alternate bars were detected when the channel width–depth ratio ranged from 170 to 374. Alternate bars cause greater bank erosion (Figure 8; yearly bank erosion rate is shown in Table S1). Figure 9 depicts the interaction between bank erosion and bar channel parameters, demonstrating that when the bar width to channel width ratio surpassed 0.6, higher bank erosion rates were found. At those times, relatively high-amplitude (>2 m) bars were observed (Figure 9b). Bars of such amplitude can be found in some lower bar/channel width ratios, but no substantial rate of bank erosion was observed at such times.
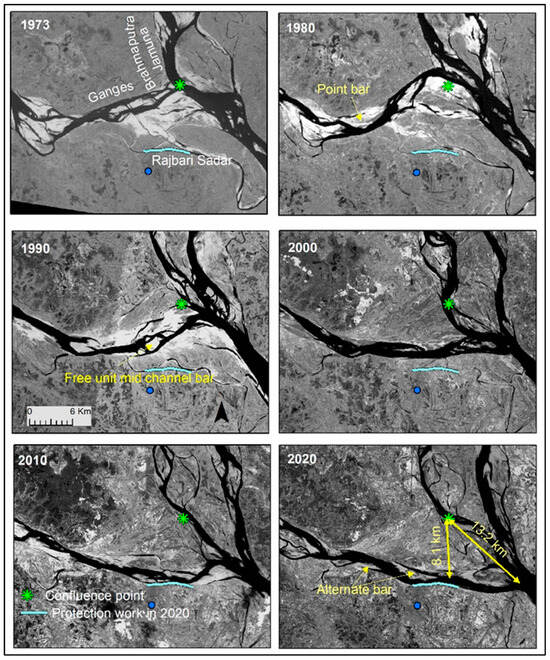
Figure 6.
Planform changes of Ganges around the study area for the last five decades, derived from Landsat images.
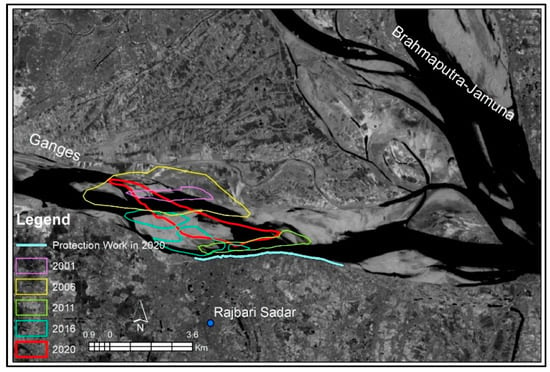
Figure 7.
The changes in bar alignment for the last two decades. The background satellite image is the Landsat image, dated February 2023.
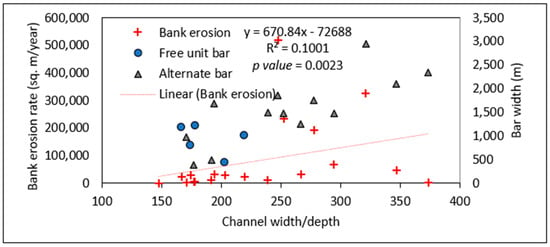
Figure 8.
The relationship between channel width, bar width, and bank erosion of Ganges reach.
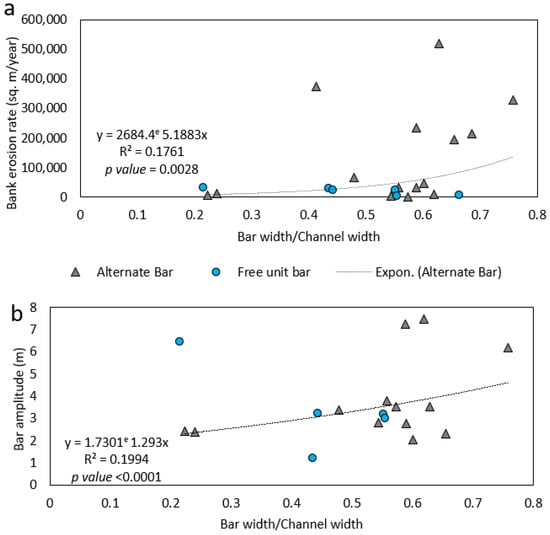
Figure 9.
The relationship between the bank erosion and bar–channel properties of Ganges reach. (a) relationship between bar-channel width ratio to bank erosion (b) relationship between bar-channel width ratio to bar amplitude.
4.1.2. Braided River: Brahmaputra-Jamuna
Figure 10 and Figure 11 shows the long-term and short-term planform change of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River within our study reach. During the early 1970s, in this section, one single channel dominated. However, two dominant main channels were observed in the 1990s. In the 2010s, the reach became a single-channel-dominated reach again. During the whole process, free bars (unit and mid-channel type) and hybrid bars (compound type) appeared near the bank protection structure. The braided belt widened to nearly 3.8 km during this time. Figure 12 shows the interrelationship between the channel’s width (considered channel, where the current RBPS exits), bar width, and bank erosion. During the study period, the channel’s width–depth ratio varied between 91 and 443, and the hybrid bar was seen in the lower width–depth ratio of the channel. It is evident from this figure that with the increments of the channel width–depth ratio, the bank erosion rate increased, which signified the blockage of the channel by new bars. Similar to the Ganges, with the increment of the channel width–depth ratio, the width of the free bar seemed to be decreased, but it was the opposite in the case of hybrid bars (Figure 12). However, with a lower width–depth ratio, the tendency of the free bar was more frequent, but with the increment of the width–depth ration, hybrid compound bars emerged. With the increment of bar width/channel width, the bank erosion increased (Figure 13a; yearly bank erosion rate is shown in Table S1). We found no definite relationship between bar amplitude and bar width to channel width in the case of the free bar, but in the case of the compound bar, the amplitude became higher as it grew larger (Figure 13b). For a free bar, the amplitude never goes above 5 m. Basically, if the bar remains after that, it usually merges with another bar to form a compound one.
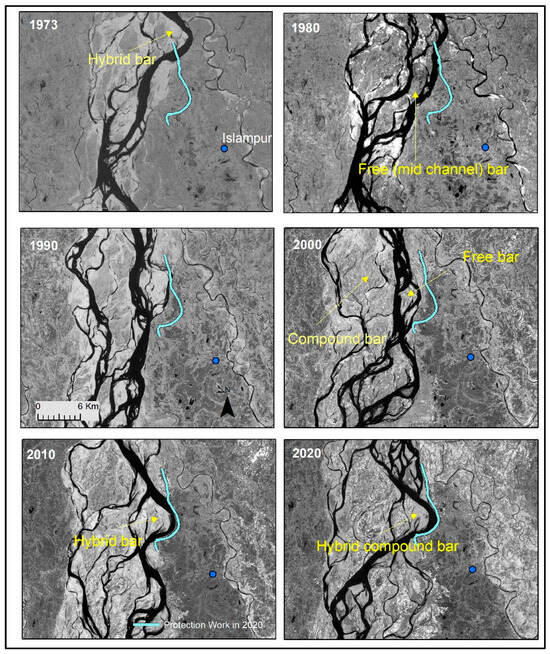
Figure 10.
Planform changes of Brahmaputra-Jamuna around the study area for the last five decades, derived from Landsat images.
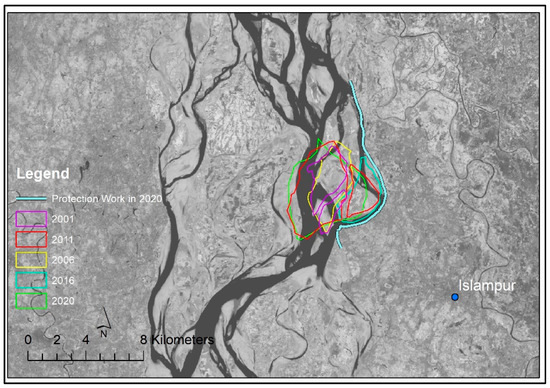
Figure 11.
The changes in bar alignment in the study have reached off the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River over the last two decades. The background satellite image is the Landsat image, dated February 2023.
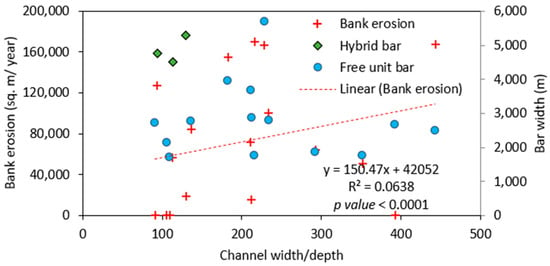
Figure 12.
The relationship between channel width, bar width, and bank erosion of Brahmaputra-Jamuna.
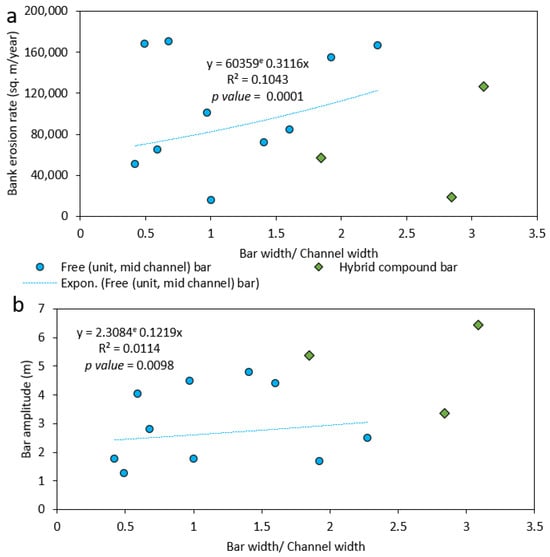
Figure 13.
The relationship between bank erosion and bar–channel properties of Brahmaputra-Jamuna reach. (a) relationship between bar-channel width ratio to bank erosion (b) relationship between bar-channel width ratio to bar amplitude.
4.2. Hydraulic Impact of Sandbar
4.2.1. Hydraulic Impact of Sandbar in Ganges Reach
Figure 14 shows the results of the flow depth, depth-averaged velocity during the peak discharge, and end of the monsoon season bed level changes for the Ganges River. The maximum flow depth in Mbs conditions was 50 m, while in Mex, it was 47.6 m. However, the maximum depth occurred near the confluence of two channels, not along the RBPS location in the case of Mbs. The maximum depth along the RBPS was 29.7 m for Mbs and 35.3 m for Mex. The average depth along the model domain in both cases was about 12.7 m. In both cases, the maximum depth-averaged velocity was around 4.7 m/s. The depth-averaged velocity along the RBPS in the case of Mbs was 2.8 m/s, but it was 3.6 m/s in Mex. In the instance of Mex, due to channel curvature, another point bar was also generated. Along the RBPS, the highest scour level was estimated to be –16.98 m PWD for Mbs and −23.94 m PWD for Mex. The hydraulic loads exerted on RBPS in base and extreme bar conditions are summarized in Table 4. The maximum shear stress applied to RBPS was 5.62 and 8.92 N/m2 for Mbs and Mex, respectively.
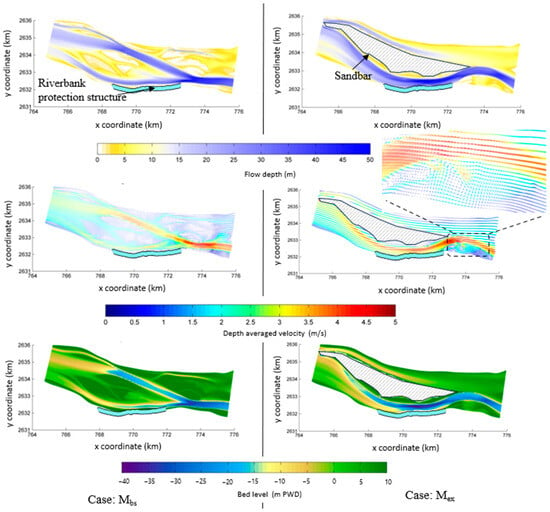
Figure 14.
The distribution of (top) flow depth, the (middle) velocity at the peak discharge, and the (bottom) bed level change under the MBS and MEX scenarios at the Ganges.

Table 4.
The hydraulic load exerted on RBPS in base and extreme bar conditions of Ganges reach.
4.2.2. Hydraulic Impact of Sandbar in Brahmaputra-Jamuna Reach
In the Brahmaputra-Jamuna, during peak discharge, the river depth in the braided channel ranged from 3 to 50 m, with an average depth of 10 m, while in the braided plain or bar, it ranged from 0.05 to 3 m, with an average depth of 1.64 m (Figure 15). In the case of Bex, the depth of flow was more than 50 m in the channel. Along the RBPS, the maximum depth was found to be 32.2 m and 38.2 m in the case of Bbs and Bex, respectively. During peak discharge, the channel’s maximum velocity was 3.11 m/s, with an average velocity of 1.1 m/s, while it was nearly 5 m/s in the Bex case. This shows that after such a large flood, the average bed scouring was 2.65 m, with a maximum scour of nearly 46.57 m. Along the RBPS, the maximum velocity was observed at 1.8 m/s in Bbs, but it was 2.5 m/s in Bex. The shear stress exerted on RBPS was 13.1 N/m2 in the case of Bbs and 69.0 N/m2 in the case of Bex (Table 5).
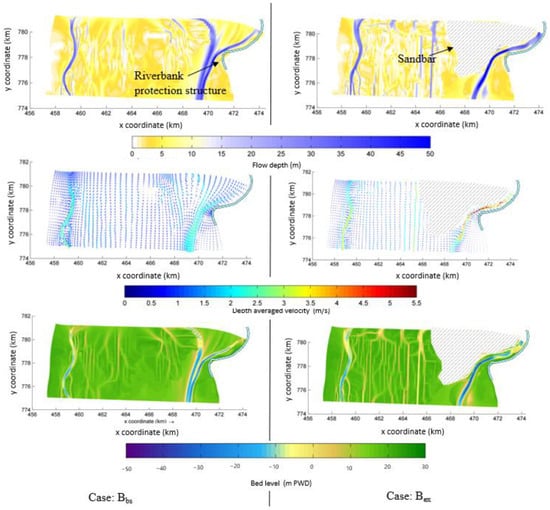
Figure 15.
The distribution of (top) flow depth, the (middle) velocity at the peak discharge, and the (bottom) bed level change under the Bbs and Bex scenarios at Brahmaputra-Jamuna.

Table 5.
The hydraulic load exerted on RBPS in base and extreme bar conditions of Brahmaputra-Jamuna reach.
5. Discussion
Protecting the riverbank from erosion through structural interventions is challenging for the wide rivers of Bangladesh. The implementation of numerous structural interventions that have proven successful in other regions of the world has been unsuccessful in Bangladesh due to the erratic behavior of the rivers in this area [56]. Here, in this paper, we found that for the wide rivers in low-lands, the formation and evolution of several types of bars introduced additional load to the RBPS and quantified such loads for an extreme condition. There are lots of examples where the evolution of bars affects the stability of riverbanks (e.g., [56,57,58,59,60]). Due to the initiation of sandbars, width adjustment happens, which eventually leads to bank erosion in many exposed regions [61,62]; for example, the failure of RBPS of the Ganges study reach in 2021. Typically, along the main rivers of Bangladesh, the RBPS are constructed to withstand floods of a 100-year return period. The highest discharge in 2021 reached a magnitude of only 45,491 m3/s, which corresponds to approximately 60% of flow of a 100-year return period floods. BWDB [9] and local communities reported that the failure could be attributed to the formation of an alternate sandbar. A similar phenomenon was also observed during the failure of Brahmaputra-Jamuna RBPS at Kulkandi, Islampur [9]. This investigation confirmed similar results, as shown in Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 12 and Figure 13, which demonstrated a positive correlation between bank erosion and channel-bar features. Despite the coefficient of determination indicating a low value, the trend can be considered statistically significant, as the p-value (determined by Student’s t-test) was less than 0.05. We found that bars’ evolution affects the banks in both meandering and braided rivers when the width–depth ratio exceeds 90. However, bank erosion occurred even at very high width–depth ratios (>300). Fluvial erosion, deposition, and bank failure are the fundamental processes of width adjustment [56]. In the instance of the Lower Yellow River, Li et al. [63] found that the braided width grew as the number of braided bars increased, and bank erosion was closely connected with such process adjustment.
The Mbs and Bbs results shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15 and Table 4 and Table 5 represent the design condition of RBPS according to the BWDB6. Comparing these cases with the Mex and Bex, it was evident that the presence of a sandbar increased the flow depth (18% for both of the reaches) and velocity (29% for Ganges and 50% for Brahmaputra-Jamuna) and, consequently, resulted high bed scouring and thus affected the stability of RBPS. BWDB [42] yielded similar results when evaluating Ganges cross-sections. They observed in the Ganges (within the study reach of this paper) that between 2013 and 2019, additional scouring of about 12.5 m occurred when a sandbar was present. We found nearly 7 m of additional scouring if a sandbar was present in the case of Ganges. Nakagawa et al. [36] investigated the cross-sections of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna in Sirajganj (located downstream of the study area) and observed a similar phenomenon. They observed roughly 6 m of additional scour as sandbars appeared in the reach. Similar scouring was also observed in our study as well. The vortex system they observed was also seen near the end of the sandbar in both Mex and Bex cases (Figure 16), which impinged the flow toward the bank and caused uneven sedimentation, or vice versa. However, due to the three-dimensional nature of the vortex phenomena and the utilization of a two-dimensional numerical model in this study, certain constraints existed. Furthermore, even at moderate velocities, the fine bed and bank materials were eroded by the flowing water in the delta region because the soils mostly consist of easily erodible, poorly graded sands and silts. The scouring caused by floodwaters’ high velocity is quite profound [56]. During the monsoon, river discharge can vary as much as 20 times, and water levels may rise as much as 7 m between the dry and wet seasons in the study reach (see Figure 4) [9,45,64]. When hydrostatic confining force, pore water pressure, and gravity all work together during the water-rising period, localized tensile stress concentration may cause RBPS to fail. This process may initiate severe bank failure events, particularly during the flood period [65]. However, we did not consider such a process in this study.
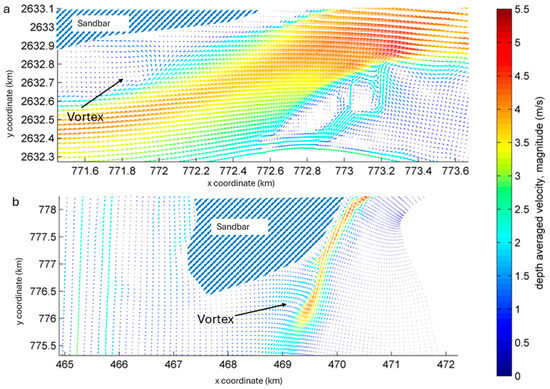
Figure 16.
The generation of vortex flow generated near the sandbar: (a) Ganges and (b) Brahmaputra-Jamuna.
The bars create velocity and sediment concentration variation in rivers, serving as ecological hotspots for diverse fauna and flora [66]. Through the field investigation of Brahmaputra-Jamuna bars, Rahman et al. [67] showed that during the wet season, multiple channels emerged within a bar or connected two second- or third-level channels. These channels, with velocities ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 m/s, serve as breeding grounds for several endangered species. Ock et al. [68] found that restoring gravel bars can promote hyporheic exchange and retention of suspended particulate organic matter, refresh bed materials to improve substrate permeability, and expand the area where water has been absorbed in shallow waters. As a result, the development of sandbars should also be permitted from an ecological standpoint. As the periodic bars do not form with very smaller width-to-depth ratios (below about 10) [5], the river width shortening should not be allowed to reach such a threshold in the study reach. However, being a land-hungry country, the widening of rivers many times needs to be controlled by RBPS in some densely populated areas, i.e., cities. In that case, the evolution of the sandbar should be considered in structural design. Conventionally, BWDB usually follows the design manual [69], which was updated in 2021 [70]. However, in the design consideration of revetment (or RBPS), the provision for the sandbars was overlooked. However, numerous RBPS failures have occurred when the design condition was not exceeded, such as the failure of the Islampur RBPS in 2021 [9]. In many design manuals, the Pilarczyk [71] approach is recommended for estimating riprap roughness using the protective element size (e.g., CC-block size) of RBPS. We urge that while using this method, the depth-averaged flow velocity and flow depth be updated, along with the possibility of sandbar commencement, if the river’s width–depth ratio exceeds 90.
6. Conclusions
Sandbars are an essential component of the river’s dynamics. They can deviate the flow and sediment transport direction toward the bank, so the additional load generated by these bars should be considered when designing the RBPS. Bars’ evolution affects the banks in both meandering and braided rivers when the width–depth ratio exceeds 90. In the case of meandering rivers (Ganges), riverbank erosion was found mostly due to the presence of alternate bars. The presence of sandbars in a meandering river can cause the flow depth to increase by roughly 18%. The depth-averaged velocity is expected to increase by approximately 29%, and as a result of the presence of alternate bars, the tractive force may increase by 1.6 times in the case of a meandering river. The braided one (Brahmaputra-Jamuna) showed substantial bank erosion due to the existence of both free unit and hybrid types of bars. In such a river, the flow depth may increase by 18%, while the depth-averaged velocity may increase by around 50%. In a braided river, the tractive force may increase by 5.3 times. Therefore, for wide low-land rivers, natural evolution of such sandbars can be allowed by considering the additional loads in RBPS during the design phase.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16172523/s1, Table S1: Yearly riverbank erosion rate of the studied reaches.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.; methodology, S., H.M.M. and I.J.N.; software, S., H.M.M. and I.J.N.; validation, S., H.M.M. and I.J.N.; formal analysis, S., H.M.M. and I.J.N.; investigation, S., H.M.M., I.J.N. and M.M.R.; resources, A.K.M.S.I.; data curation, H.M.M. and I.J.N.; writing—original draft preparation, S.; writing—review and editing, S., H.M.M., I.J.N., A.K.M.S.I., M.M.R. and G.M.T.I.; visualization, S., H.M.M., I.J.N., A.K.M.S.I., M.M.R. and G.M.T.I.; supervision, A.K.M.S.I.; project administration, A.K.M.S.I.; funding acquisition, A.K.M.S.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the project entitled, ‘An Investigation on the Causes of Embankment Failure (CEF) and Recommendations for Sustainable Solution’, carried out by the Institute of Water and Flood Management (IWFM) of Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET). The authors would like to acknowledge the access to observed water level, discharge, and bathymetric data from the Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Thorne, C.R.; Tovey, N.K. Stability of composite river banks. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1981, 6, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-H.; Wei, H.-Y.; Wu, S.-B. Experimental study on the bank erosion and interaction with near-bank bed evolution due to fluvial hydraulic force. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2015, 30, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redolfi, M. Free Alternate Bars in Rivers: Key Physical Mechanisms and Simple Formation Criterion. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2021WR030617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, N.; Rodrigues, S.; Bustillo, V.; Bréhéret, J.G.; Tassi, P.; Jugé, P. Interactions between flow structure and morphodynamic of bars in a channel expansion/contraction, Loire River, France. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2850–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosato, A.; Mosselman, E. An Integrated Review of River Bars for Engineering, Management and Transdisciplinary Research. Water 2020, 12, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredsøe, J. Meandering and braiding of rivers. J. Fluid Mech. 1978, 84, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubino, M.; Seminara, G. Free–forced interactions in developing meanders and suppression of free bars. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 214, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Wen, S. Bar dynamics in a sandy braided river: Insights from sediment numerical simulations. Sediment. Geol. 2020, 396, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BWDB. An Investigation on the Causes of Embankment Failure and Recommendations for Sustainable Solutions; Final Report, Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB); Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2023.
- WBIWD. Guidelines for Riverbank Protections & Anti-Sea Erosion Work in West Bengal. lst Amendment; Government of West Bengal Irrigation & Waterways Department (WBIWD), 2019. Available online: https://wbxpress.com/files/2022/05/501-IFC.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- Parker, G. On the cause and characteristic scales of meandering and braiding in rivers. J. Fluid Mech. 1976, 76, 457–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J. Mid-channel bar growth and its relationship to local flow strength and direction. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1996, 21, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L.; Ashworth, P.J.; Bristow, C.S.; Roden, J. Three-Dimensional Sedimentary Architecture of a Large, Mid-Channel Sand Braid Bar, Jamuna River, Bangladesh. J. Sediment. Res. 2003, 73, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.E. How do gravel-bed rivers braid? Can. J. Earth Sci. 1991, 28, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egozi, R.; Ashmore, P. Experimental analysis of braided channel pattern response to increased discharge. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2009, 114, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P. Morphology and Dynamics of Braided Rivers; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Muramoto, Y. Experimental Study on Stream Channel in Alluvial Rivers. Bull. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. 1982, 32, 49–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, S.; Parker, G.; Sawai, K. Bend theory of river meanders. Part 1. Linear development. J. Fluid Mech. 1981, 112, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeaux, P.; Seminara, G. A unified bar-bend theory of river meanders. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 157, 44–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhans, M.G.; van den Berg, J.H. River channel and bar patterns explained and predicted by an empirical and a physics-based method. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Cao, Z.; Liu, H.; Pender, G. Numerical modelling of alternate bar formation, development and sediment sorting in straight channels. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 555–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duró, G.; Crosato, A.; Tassi, P. Numerical study on river bar response to spatial variations of channel width. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 93, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordier, F.; Tassi, P.; Claude, N.; Crosato, A.; Rodrigues, S.; Van Bang, D.P. Numerical Study of Alternate Bars in Alluvial Channels With Nonuniform Sediment. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 2976–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurman, F.; Kleinhans, M.G. Bar dynamics and bifurcation evolution in a modelled braided sand-bed river. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 1318–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.P.; Church, M.; Wooldridge, C.L.; Hickin, E.J. Morphology and evolution of bars in a wandering gravel-bed river; lower Fraser river, British Columbia, Canada. Sedimentology 2009, 56, 709–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooke, J.M.; Yorke, L. Channel bar dynamics on multi-decadal timescales in an active meandering river. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 1910–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y. Bar and channel formation. In River Meandering; Ikeda, S., Parker, G., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 417–462. [Google Scholar]
- Colombini, M.; Seminara, G.; Tubino, M. Finite-amplitude alternate bars. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 181, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchi, R.; Zolezzi, G.; Tubino, M. Modelling mid-channel bars in meandering channels. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2010, 35, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S. Prediction of Alternate Bar Wavelength and Height. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struiksma, N.; Olesen, K.W.; Flokstra, C.; De Vriend, H.J. Bed deformation in curved alluvial channels. J. Hydraul. Res. 1985, 23, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, D.; Crosato, A.; Tassi, P. Numerical experiments to explore bar management by channel width variations. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Rohde, S.; Schütz, M.; Kienast, F.; Englmaier, P. River widening: An approach to restoring riparian habitats and plant species. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 1075–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Ushiyama, T.; Asahi, K.; Yonemoto, M. An Experimental Study on the Bedrock Re-Exposure by Sandbar Formation and Channel Curvature. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Kyuka, T. A Hydraulic Model Experiment on the Relationship between Sediment Low-Water Revetment or Spur Dikes. In Proceedings of the 38th IAHR World Congress, Panama City, Panama, 1–6 September 2019; pp. 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Zhang, H.; Baba, Y.; Kawaike, K.; Teraguchi, H. Hydraulic characteristics of typical bank-protection works along the Brahmaputra/Jamuna River, Bangladesh. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2013, 6, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishwakarma, K.; Wang, G.-X.; Zhang, F.; Adhikari, S.; Karki, K.; Ghimire, A. Hydrochemical characterization and irrigation suitability of the Ganges Brahmaputra River System: Review and assessment. J. Mt. Sci. 2022, 19, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.A. Geologic framework and environmental status of the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 826–836. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A. Large Rivers: Geomorphology and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.M. Numerical Simulation of Bed Level Changes of the Ganges. Master’s Thesis, Department of Water Resources Engineering, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- BWDB. Hydroinformatics & Flood Forecasting Circle Bangladesh Water Development Board. Available online: http://www.hydrology.bwdb.gov.bd/index.php?pagetitle=home&id=75 (accessed on 12 July 2024).
- BWDB. Morphological Changes of River Ganges over the Last Seven Years (2013 to 2019); River Morphology Processing Branch, Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2020. Available online: http://www.hydrology.bwdb.gov.bd/img_upload/ongoing_project/782.pdf (accessed on 7 June 2024).
- FAP 24. Flood Action Plan (FAP); Special Report 9, River Survey Project; Flood Plan Coordination Organization, Government of Bangladesh: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1996.
- Shampa; Roy, B.; Hussain, M.M.; Islam, A.S.; Rahman, M.A.; Mohammed, K. Assessment of Flood Hazard in Climatic Extreme Considering Fluvio-Morphic Responses of the Contributing River: Indications from the Brahmaputra-Jamuna’ s Braided-Plain. GeoHazards 2022, 3, 465–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI A Normalized Difference Water Index for Remote Sensing of Vegetation Liquid Water from Space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, S. An automated approach in estimation and prediction of riverbank shifting for flood-prone middle-lower course of the Subarnarekha river, India. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2021, 19, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Cai, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, X. Remotely sensed trajectory analysis of channel migration in Lower Jingjiang Reach during the period of 1983-2013. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16241–16256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Gan, T.Y.; Baki, A.B.M. Assessing morphological changes of the Ganges River using satellite images. Quat. Int. 2013, 304, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, G.; Roelvink, J.; van Kester, J.; Stelling, G. Development and validation of a three-dimensional morphological model. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 883–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijn, L.C. Principles of Sediment Transport in Rivers, Estuaries and Coastal Seas; Aqua Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Exner, F.M. On the interaction between water and sediment in rivers. Akad. Wiss. Wien. Math. Naturwiss. Klasse 1925, 134, 165–204. [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink, D.; Lesser, G.; van der Wegen, M. Evaluation of the Long Term Impacts of an Infiltration BMP Drexel E-Repository and Archive (iDEA). In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on HydroScience and Engineering College of Engineering, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–13 September 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoben, W.J.M.; Freer, J.E.; Woods, R.A. Technical note: Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash-Sutcliffe and Kling-Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 4323–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijai, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Yapo, P.O. Status of a Utomatic Calibration For Hydrologic Models: Comparison With Multilevel Expert Calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Oberhagemann, K.; Haque, A.M.A.; Thompson, A. A century of riverbank protection and river training in bangladesh. Water 2020, 12, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, J.; Watanabe, K.; Saito, N. Study on the Behavior of Sandbar in a River Channel at the Babamegawa River. Int. J. Geomate 2021, 20, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Ito, A. Development of a meandering channel caused by the planform shape of the river bank. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2014, 2, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.P.; Galeazzi, C.P.; Best, J.; Ianniruberto, M.; Prado, A.H.D.; Janikian, L.; Mazoca, C.E.M.; Tamura, L.N.; Nicholas, A. Morphodynamics and depositional architecture of mid-channel bars in large Amazonian rivers. Sedimentology 2024, 71, 1591–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigg, M.A.; Carr, A.B.; Smith, M.W.; Tshimanga, R.M. Measuring Geomorphological Change on the Congo River Using Century-Old Navigation Charts. In Congo Basin Hydrology, Climate, and Biogeochemistry: A Foundation for the Future; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2022; pp. 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASCE. River Width Adjustment I: Processes and Mechanisms. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 881–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASCE. River Width Adjustment II: By the ASCE Task Committee on Hydraulics, Bank Mechanics. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1998, 124, 903–917. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.; Kong, L.; Ji, Q.; Li, L.; Chen, F. Geomorphic adjustments of channel bars in the braided reach of the lower Yellow river from 1986 to 2018. Catena 2024, 236, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.H.; Thorne, C.R.; Aktar, M.N.; Ferdous, R. Morpho-dynamics of the Brahmaputra-Jamuna River, Bangladesh. Geomorphology 2014, 215, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xia, J.; Deng, S.; Han, Z. Bank erosion under the impacts of hydraulic erosion, river stage change and revetment protection in the Middle Yangtze River. Geomorphology 2024, 448, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tockner, K.; Paetzold, A.; Karaus, U.; Claret, C.; Zettel, J. Ecology of Braided Rivers; Special Publication-International Association of Sedimentologists 36; 2006; pp. 339–359. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781444304374.ch17 (accessed on 7 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Islam, T.G.M.; Sarker, M.H.; Choudhury, S.M.; Ahmed, M. Hydraulic Profiling of Important Fish. Habitats of the Jamuna River; Final Report; Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ock, G.; Gaeuman, D.; McSloy, J.; Kondolf, G.M. Ecological functions of restored gravel bars, the Trinity River, California. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BWDB. Standard Design Manual; Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 1993; Volume 1.
- BWDB. Design Guidelines for River Bank Protection Work; Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB): Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2021.
- Pilarczyk, K.W. Coastal Protection: Design of Seawalls and Dikes incl. Overview of Revetments; Rijkswaterstaat, Road and Hydraulic Engineering Division Van der Burghweg 1: Delft, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).