Abstract
Anaerobic digestion (AD) is a biological process that breaks down organic matter in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas and nutrient-rich digestate. Various reactor designs and mixing strategies are well-established in AD processes, each with their own advantages and benefits. The presented study summarizes and investigates the state of the art of AD in domestic wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in an Austrian alpine region, with a primary focus on finding similarities among the most efficient plants regarding digester design, mixing approaches, and biogas production. By combining surveys and detailed field studies in cooperation with 34 WWTPs, the study provides a comprehensive overview of common AD practices, reactor shapes, and inherent mixing methods, highlighting their potential regarding energetic efficiency and biogas production. The results of the survey reveal qualitative trends in efficient AD design alongside detailed quantitative data derived from the supervised in-field optimization studies. Notably, one of the studies demonstrated energetic savings of 52% with no decrease in biogas production, achieved by transitioning from gas injection to mechanical agitation. Redundant impeller-based overmixing was also practically investigated and demonstrated in another field study. After optimization, the adaptations also resulted in energy savings of 30%, still proving sufficient substrate mixing with biomethane potential analysis. In conclusion, this research emphasizes the economic and environmental importance of energy-refined practices and optimized processes while highlighting the sustainability of AD, particularly for large domestic WWTPs but also for different comparable applications.
1. Introduction
The transition to renewable energy sources and the optimization of energy efficiency in existing processes are becoming increasingly important due to the rising levels of greenhouse gas emissions, namely carbon dioxide (CO2) [1]. Among today’s various green and renewable methods, anaerobic digestion (AD) of organic matter represents a significant and important energy source both because of environmental and economic reasons. Biogas, the end product of the complex decomposition processes in AD, can be utilized in multiple ways: it can be combusted onsite as a short-term energy source, refined and injected into the gas grid, or used as an efficient long-term energy storage solution [2]. Consequently, AD plays an increasingly important role in the context of climate-neutral energy management. This is also reflected in the fact that AD is integrated in in almost every wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). However, while certain AD designs and mixing strategies have been well-established within the AD context, the processes are often prone to inefficient operation due to the difficulties in process monitoring. For evaluation of the AD process, laboratory experiments, computer-aided simulations, and in-field experiments are promising tools to help in understanding and optimizing the individual AD processes [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. However, besides these supportive tools, a pivotal share in efficient AD operation is often contributed by the long-time experience of plant operators. Hence, to harness the full potential of AD for energy transition, a comprehensive theoretical understanding of the processes and parameters involved is as essential as the consideration and implementation of practical recommendations provided by plant supervisors.
In detail, AD involves the generation of biogas from biodegradable substances within large-scale reactors. AD requires a specific environment for the utilized microorganisms and thorough mixing to ensure continuous and efficient biogas production [13]. The resulting biogas typically consists of approximately 60% methane (CH4), 40% CO2, and small amounts of hydrogen (H2), sulfide, and other trace gasses [14]. Industrial large-scale AD plants are capable of generating up to 5000 m3 biogas per day [15,16,17], as also presented within this study. The exothermic combustion of CH4 converts it into energy and less climate-damaging CO2, providing a dual benefit of energy recovery from organic residues and reduced CH4 emissions [18]. However, AD can also contribute to unwanted CH4 emissions due to gas losses. While CH4 emissions may occur along the WWTPs, the majority originate from the sludge line [19,20]. In preliminary studies to this work, CH4 emissions from an Austrian WWTP serving 260,000 population equivalents (PEs) were estimated to be approximately 25 g CH4 per PEs per year, accounting for over a quarter of the plant’s emission footprint. Therefore, optimizing AD is necessary to maximize the potential of organic waste disposal and energy recovery, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The fundamental operational design of AD towers is usually similar to continuously operated and stirred large-scale bioreactors [21]. These continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTRs) are simple and efficient in both design and operation, enabling continuous feeding and withdrawal of digestate. CSTRs are well-suited for treating homogeneous substrates and maintaining stable operating conditions. However, they require relatively long hydraulic retention times (HRTs) to achieve sufficient organic matter degradation [22]. Consequently, volumetric biogas production rates are generally lower compared to other designs, such as anaerobic sequencing batch reactors (ASBRs). Batch cycle-based AD systems, such as ASBR, offer higher flexibility in feeding and substrate types [23,24]. While these systems achieve high levels of organic matter removal and biogas production efficiency, they are associated with higher energy requirements and more complex system control. Anaerobic fixed film reactors (AFFRs) utilize fixed media (e.g., plastic or ceramic materials) to support microbial growth, thereby increasing the surface area available for digestion [25]. AFFRs have shorter HRT and higher organic loading rates compared to suspended growth systems but may become clogged or require periodic replacement. Up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors employ dense sludge blankets to retain microbial biomass and facilitate AD [26]. UASB reactors exhibit relatively high volumetric biogas production rates and can tolerate high organic loading rates [27]. However, these reactors require a careful control of influent characteristics and hydraulic conditions to prevent sludge washout or stratification. Additionally, UASB reactors are sensitive to temperature fluctuations and variations in substrate composition.
The geometric design of AD towers is influenced by technical, economic, and practical considerations and aims to achieve efficient substrate digestion, biogas production, and optimal system performance [7,28,29]. The structure of AD towers depends on several factors, including specific design requirements, available space, and operational influencing factors, resulting in significant variability in physical configurations [30]. Common AD system designs typically employ vertical or horizontal cylindrical configurations due to their high structural stability, simple construction, and efficient space utilization [7,31,32,33]. Vertical designs are prevalent due to their capacity and ease of access for maintenance, though this often requires specialized equipment. Horizontal designs are often partially installed underground for thermal insulation. Cylindrical AD reactors usually feature a conical tapering at the bottom to facilitate sludge removal [17]. Egg-shaped reactors are also common in AD, most often combined with mechanical agitators or impellers inside draft tubes [34,35,36]. More complex shapes, such as quadratic, rectangular, or spherical, are less common due to distinct disadvantages [16,17]. Rectangular tanks, for example, allow for a better utilization of construction space and simpler construction but suffer from constricted hydrodynamics, creating dead zones and uneven flow distribution that necessitate additional mixing equipment [37]. The corners are especially prone to decreased hydrodynamics, resulting in low mixing and potentially unprocessed organic matter [38]. In some designs, quadratic AD towers can be partitioned for multi-stage digestion processes [39]. Spherically designed AD towers, while less optimal for space utilization, offer excellent volume-to-surface area ratios, promoting uniform temperature distribution and efficient mixing [16,17]. Their structural integrity allows them to withstand internal pressures effectively. Custom or hybrid designs combining elements of different geometric shapes could be employed to meet specific site requirements and operational needs, though these are associated with higher upfront and potential operational costs. For structural reasons, AD towers are almost exclusively constructed of concrete [40]. To enhance operational control, AD towers can be designed in pairs, which provides the possibility of serial or parallel operation depending on the situation [41]. When possible, serial operation can increase gas output; however, parallel operation may be beneficial when high amounts of substrate or external influences (e.g., low temperature) are overloading one single AD tower.
AD systems encompass various technical processes, and the overall energy requirement for an AD tower arises from the sum of the individual operational units. The primary energy-consuming aspects of AD operation include mixing, feedstock pumping, temperature control, and auxiliary processes such as monitoring and control equipment [16,42,43]. Maintaining proper feedstock pumping and recirculation, as well as mixing and agitation within the AD tower, is crucial for supporting microbial activity, ensuring uniform substrate distribution, and preventing solids settlement [6]. Besides mixing, AD processes are temperature-sensitive, with optimal microbial activity occurring within a specific temperature range. Energy is required to maintain consistent temperatures, particularly in colder climates or during cold seasons. The ideal temperature for AD depends on the specific types of microorganisms involved in the process and the substrate [24,44,45]. AD is typically operated within the mesophilic temperature range of 25 °C to 40 °C, which is most suitable for a wide range of common anaerobic bacteria and archaea. Thermophilic AD (50 °C to 65 °C) accelerates the digestion process, resulting in faster degradation of organic matter and higher biogas production rates compared to mesophilic digestion [22,46]. However, thermophilic AD requires more energy for heating and is more sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Psychrophilic AD operates at temperatures below 25 °C and is suitable for certain low-temperature environments or feedstocks, though it has slower reaction rates and lower biogas yields [47].
Optimizing mixing in AD is crucial for maintaining uniform conditions within the reactor, enhancing biogas production through increased microbial activity, and, ideally, decreasing energy demand [5,8,9,48,49]. Several approaches to improve mixing have been investigated in recent studies and are applied in new well-planned AD systems. However, implementation in existing AD systems is difficult since most systems are continuously operated. Uninterrupted operation is often essential, and adjustments or maintenance are associated with significant structural and economic challenges. Hydrodynamics and energy demand for mixing can be assessed through experiments in existing plants, laboratory trials, or numerical simulations [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. The choice of mixing method, which significantly impacts energy consumption, should be based on the substrate and AD tower geometry. The energy consumption of the mixing stage can account for up to 50% of the overall energy balance of an AD plant [50,51]. Each mixing approach offers individual advantages and disadvantages dependent on the application and the AD design. Hence, various distinct mixing approaches are established for AD mixing [15,16,17,52]. The main mixing approaches include pumped recirculation, mechanically induced mixing with an agitator or mixing with an impeller inside a draft-tube, and gas injection-based designs [4,8,17,28,35,40,52]. Internal hydraulic mixing via pumped recirculation, the most fundamental approach, is typically achieved using the inlet feed. In CSTR, the inlet feed supplies necessary nutrients and manages the reactor concentration and temperature. Within the AD context, pumped recirculation is primarily utilized for providing fresh substrate, enhancing sludge mixing, and maintaining mesophilic temperature conditions within the reactor. Depending on the fluid properties as well as the reactor design, a powerful sludge recirculation can be sufficient for fluid intermixing throughout the reactors [35]. However, AD mixing that relies solely on sludge recirculation is seldom and rather an exception. More commonly, a combination of pumped recirculation and additional external mixing is applied. External mixing methods in AD primarily involve mechanical agitation or gas-induced mixing. Mechanical mixing devices vary significantly in design. Multi-stage propeller devices induce mixing near the mixing segments, breaking up solid clusters with increased shear [6], while helical, slower-rotating devices provide more uniform and gentle mixing throughout the reactor [43,53]. High agitation diameters are often preferred due to the increased mixing associated with higher circumferential velocity but are linked to higher physical strain in the devices. While higher shear forces improve sludge dewaterability, they can create a non-ideal environment for sensitive microorganisms [6]. Especially in the context of large-scale AD mixing, the thorough and often-cited studies of Wu et al. have demonstrated that mechanical mixing offers the best ratio of mixing intensity to power consumption [3,54]. Besides large agitation devices, fast rotating impellers with a small diameters are also used in combination with draft tubes to induce sludge mixing [35,55]. Although impeller mixing inside draft tubes is a form of mechanical agitation, it is often considered a distinct mixing approach. Impellers lift sludge through a draft tube from the bottom to the top of the reactor, a method often employed in reactors with tapering bottoms, such as egg-shaped geometries. Draft tube mixing with impellers in reactors with a wide bottom diameter may lead to increased dead volumes near the wall regions [35]. However, when specifically designed and harmonized with the reactor geometry, circulation patterns can result in energy-efficient and uniform mixing [34,36]. This effect is pronounced in egg-shaped designs due to the curvature of the wall and can be further enhanced by aligning the sludge recirculation inlet with the reactor wall curvature [35,36]. Besides mechanical mixing, gas-induced mixing is another major approach in AD reactors. Given the anoxic conditions necessary for biogas production, the induced gas is typically biogas, taken from within the AD system [3,56,57]. High nozzle-driven velocities lift the gas to the top, resulting in sludge mixing and a dispersion of solids and particle clusters. The energy required for gas induction depends on factors such as AD tower height, sludge viscosity, and density. However, gas nozzles are prone to fouling and require more maintenance compared to mechanical agitators [58]. Mechanical agitation offers cost-effective and consistent mixing, ensuring a uniform distribution of microorganisms and nutrients throughout the reactor [16]. In contrast, gas-induced mixing is stated to provide aided microbiological activity due to more thorough mixing, but is generally less uniform and has higher operational costs [56,59]. This leads to a consideration of operating costs and the sufficiency of the induced mixing.
To estimate mixing efficiency in existing systems or during the planning stages of new plants, experimental tests on reference plants can help in predicting hydrodynamics. Furthermore, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling is a promising tool for optimizing reactor design and mixing strategies, as it can predict flow patterns and identify poorly mixed regions without implementing changes in the real plant [4,7,8,32,38,56,60,61]. Computer-aided simulations are also very useful for estimating the required mixing power and energetic demand. The overall energy demand in AD towers can be reduced with energy recovery systems such as heat exchangers to prevent energy losses [62]. Monitoring and controlling operating variables like power consumption, rotational speed, and fluid velocities can optimize mixing efficiency in real-time. Overmixing, which is often applied in good faith to ensure a sufficient distribution of components, can negatively impact biogas production and overall plant efficiency. Depending on the substrate composition, mixing too vigorously can lead to decreased biogas production [63]. Adjusting mixing intensity through the rotational speed, mixing depth, and dynamic operation mode can prevent overmixing and match the characteristics of the feedstock [51,64]. However, too low and insufficient mixing is also counterproductive and can lead to decreased microbial activity and the settlement of solids, reducing the usable volume and necessitating costly cleanouts [65]. It can also cause short-circuit flows and dead zones, compromising CH4 yield and sludge digestion, resulting in undigested organic matter and therefore reduced gas production. This is stated in a study showing that biogas can be trapped in low mixed zones [66]. Since dynamic velocity control is often linked with operational difficulties, intermittent mixing can be applied to control the induced amount of mixing. For individual cases, intermittent mixing has been reported to reduce the energy demand for mixing by up to 30% while still maintaining constant biogas production rates [51,67,68]. Regarding the impact of intermittent mixing, it has been proven that different mixing intensities promote different methogenesis. In detail, intermittent mixing results in a beneficial balance of mixing-dependent acetotrophic and hydrogenotrophic methagonesis, leading to overall increased microbial activity [69]. Subsequently, intermitted mixing is reported to both reduce the energetic demand as well as improve biogas production when implemented properly [51]. This results in a more economic AD operation with minimized potential dead zones, promoted fluid circulation, and reduced energy waste.
All the mentioned mixing strategies and approaches in reactor design are common and well-established in anaerobic AD towers. However, for today’s standards, some of the static and conventional methods may be less efficient compared to modern, study-refined techniques and mixing strategies. Specifically, unnecessary and avoidable overmixing, which can be attributed to an inefficient operation of AD towers, must be critically examined as it leads to increased costs and partially unutilized methane potential. To assess the integral efficiency of AD systems, both the output in terms of gas quality and production as well as the input in terms of operational costs, maintenance (e.g., evacuation to remove sediments), and required investments need to be considered. In order to evaluate certain trends in the complex AD framework, this study investigates a wide array of differently designed AD towers in existing WWTPs in an alpine region in Austria. Both with a wide-ranging questionnaire-based survey, as well as with direct cooperation with the WWTPs, a comprehensive summarization of AD data is collected and provided within this study. The novel characteristics and distinguishing features of this study lie in the extensive data collection achieved through a combined approach of in-depth field studies, surveys, and the direct exchange of experience and information with plant operators, encompassing a wide range of plant dimensions, reactor geometries, and mixing methods. Because of the wide-spanning and thorough data from field investigations and experimental trials, this work offers significant practical relevance and can serve as a basis and benchmark for more in-depth analyses, such as numerical studies. In detail, AD specific data such as plant characteristics, gas production, energy demand and additional advantages, and disadvantages of specific plants and approaches are carefully summarized, curated, and presented in an anonymous form, ensuring data protection. This study covers a wide range of well-established and state-of-the-art reactor geometries, inherent mixing approaches, sludge rates, and an overall scale of plants ranging from small local communities to larger cities. The primary focus is to highlight similarities between efficient plants in order to provide recommendations for either optimizing existing plants or for the planning stage of new plants. By combining the conducted survey with supervised field studies and laboratory analyses, the outcoming results offer valuable insights into the interplay between mixing strategies and biogas production efficiency, with the decisive factor of direct practical recommendations and feedback of plant operators. Besides qualitative guidelines on efficient plant designs, the conducted field studies also underline the potential energetic savings of optimization studies. Thus, this study can be seen as a broad set of recommendations for plant operators, applicable not only in the field of AD but also in comparable technical processes where hydrodynamics and particularly complex large-scale mixing tasks are important.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Operator Survey with AD-Specific Questionnaire
To evaluate AD processes in the studied WWTPs, a specifically tailored questionnaire was developed and employed to gather relevant integral data. Key aspects covered in the questionnaire included geometric design, size (AD volume VAD) and dimensions, mixing strategies, operational parameters, and fluid characteristics specific to the AD process. Additionally, biogas production rates, energy requirements, and optional plant-specific details were among the targeted aspects of inquiry. Since the survey responses highlighted that the AD sludge volume and biogas rate fluctuate over time, operators were requested to provide averaged AD volume and gas rate values that approximate the actual parameters for plant classification. With a response rate of 76%, questionnaire data from 34 plants were gathered and are presented in an anonymized form to ensure data privacy for the individual plants included in this study. Within the 34 plants, additional and more detailed field studies were conducted in cooperation with the plant operators. However, not all returned questionnaires were fully completed, as some parameters, such as specific power and energetic requirements, were not consistently monitored by all plant operators—or they were subject to data protection regulations (e.g., specific geometric dimensions such as diameter and height, as well as biogas utilization) and therefore cannot be published. The detailed questions included the following:
- Name
- City
- Structural information: amount of AD towers, AD volume (m3), geometric shape, bottom geometry
- Operational information: serial, parallel or dynamic control
- Substrate information: %TS, organic dry matter (ODM), co-Substrate (yes/no)
- Mixing information: Approach and required power and energetic demand
- Biogas production (m3)
- Energetic processing of the produced biogas
2.2. Investigation of AD Parameters with In-Depth Field Studies
In addition to the wide-ranging comprehensive data collection through the questionnaire, specific plants undergo detailed investigation and monitoring in this study. Energy, biogas rate, and additional sludge-related data are collected through monitoring and experimental investigations. Biogas production is indicated with the CH4 yield, which is the amount of produced CH4 given in normed cubic meters per year (a) (Nm3 CH4/a). The performance of the digester is monitored with specific CH4 productivity and expressed with gas volume per day (d) and AD volume (Nm3 CH4/d m3). It reflects the efficiency in producing CH4. The extent to which the organic material in the substrate is broken down during the AD process is given with the percentage of degree of organic degradation (DOD). The amount of organic material fed into the AD towers is defined as the organic loading rate (OLR) and monitored as kilograms of ODM per AD volume per day (kg ODM/m3 d). It is a crucial parameter for optimizing the digestion process and preventing overloading of the digester. With the OLR and the AD volume, the overall annual amount of organic matter (OM) can be derived and is expressed in kg ODM/a. Specific gas production (SGP) is expressed using the CH4 yield divided by the OM (Nm3 CH4/kg ODM). Regarding sludge properties, key parameters such as sludge density ρ (kg m−3), dynamic viscosity η (Pa s), dry matter DM (%), and ODM are determined. ODM represents the dried organic portion of substrate that is available for the microorganisms to decompose during the AD process, crucial for biogas production and yield. Higher ODM levels generally indicate greater gas potential but require specific handling for mixing and logistics caused by specific rheology (e.g., high viscosity of the sludge). ODM quantification involves drying and oxidizing the substrate, with the resulting ODM calculated by subtracting the remaining inorganic material from the dried sample. Parameters such as overall DM and total solids concentration (%TS) are also important for sludge classification in AD, influencing gas production and especially hydrodynamics. Finally, HRT (in d) indicates the duration that the substrate remains in the digesters, is critical for determining the efficiency of the digestion process, and was also collected for the individual plants.
2.3. Measurement of Biomethane and Residual Gas Potential
In the experimental setup focusing on mixing studies, both the biomethane potential (BMP) and residual gas potential (RGP) were assessed as they represent key indicators in the determination of AD efficiency. BMP indicates the maximum CH4 yield achievable from a specific organic substrate under complete anaerobic conditions, whereas RGP evaluates the remaining biodegradability of partially pre-degraded samples containing unprocessed organic matter [47,70,71]. BMP, RGP as well as SGP are usually given in normed cubic meter per kg of ODM (Nm3 CH4/kg ODM) or per ton (t) ODM for large-scale applications (Nm3 CH4/t ODM). Conducted under controlled laboratory conditions, the assessments involve placing digestate, supplemented with excess nutrients and microorganisms, into laboratory reactors. The subsequent measurement of biogas production over a predefined period occurs at an average mesophilic temperature (37 °C ± 1 °C). BMP determination employs the state-of-the-art automatic methane potential test system (AMPTS) over a 21-day duration, while RGP is assessed using eudiometer tubes over 10 days (Figure 1).
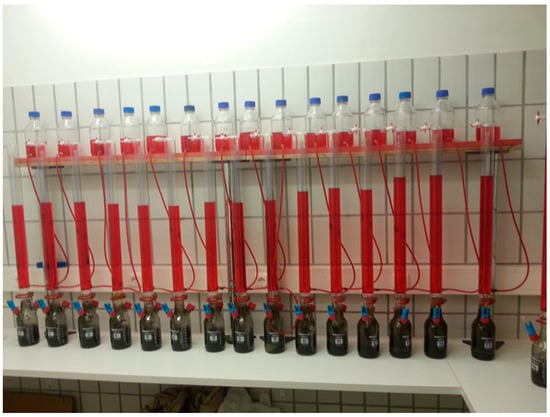

Figure 1.
Laboratory setup for evaluation of the RGP in specific sludge samples using eudiometric tubes.
To ensure the integrity of experimental evaluations, samples are extracted either from the fresh substrate or the recirculation pipe, thereby mitigating potential falsification from fresh substrate influence. Laboratory analysis includes determining the DM and ODM content of these samples. Subsequently, 600 g of sludge undergo AD for 10 days at 37 °C, with the produced gas collected, measured for volume, and filtered to remove CO2 and other trace gasses. Gas volumes are then standardized into norm-gas volumes (norm cubic meter: Nm3) using Equation (1) (while V0 represents the normed gas volume (Nm3), V the measured gas volume (m3), p the measured pressure (Pa), p0 the Norm-pressure of 101,300 Pa, pw vapor-pressure of 5622 Pa of water at 308.15 K, T the gas temperature of 308.15 K, and T0 the norm temperature of 273.15 K) [72]. This methodology enables the precise assessment of both BMP and RGP, providing valuable insights into both the AD efficiency and mixing evaluation.
2.4. Measurement of the Power Demand for Mixing
Within the detailed in-field experiments, the energy demand of 8 operational plants was experimentally monitored using a Fluke Energy Logger 1732 v2.3. Three-phase current voltage (V), current (I), apparent (S), reactive (Q), and active power (P) were measured. Data post-processing was conducted using Fluke Energy Analyze Plus v3.11.2 software. The energy demand of motor engines driving mechanical agitation, impellers, and gas-inducing units was monitored continuously for up to 24 h. Additionally, the energy demand of recirculation pumps was recorded. Measurements were taken at electric distribution boards or directly at technical installations. Linear averaged active power was used for comparing the energetic requirements of the plants. The specific power demand Φ was calculated using the required power demand P (W) and the overall AD volume VAD (m3) according to Equation (2) and is a common indicator used to describe the required volumetric power in W m−3 for the individual mixing approaches in relation to the AD volume [36,69,73,74]. Additional information such as the associated mixing method and origin of the data are described in the indices of Φ (e.g., ΦMixing,Survey). Moreover, energy consumption trends over different operational periods are analyzed to identify potential optimization opportunities. The collected data provides valuable insights into the energy performance of AD systems, aiding in the development of energy-efficient designs and operational strategies.
2.5. Comparison of Gas Injection and Mechanical Agitation in a Cylindrical AD Tower
To highlight differences in the applicability of gas injection and mechanical agitation in cylindrical AD towers, both mixing approaches are investigated in detail in a real-life situation in cooperation with Plant 1. Energetic demand and biogas production were monitored after (Plant 1A) and before (Plant 1B) the conversion from gas injection to mechanical agitation using a propeller-based design. The experimentally measured power demand of the individual mixing approaches was compared to the overall gas composition and production as well as to the SGP, considering the additional impact of season-dependent variables such sludge composition and ODM.
2.6. Investigation of Impeller-Induced Draft Tube Mixing in an Egg-Shaped AD Tower
To highlight the hydrodynamic and energetic impact of additional impeller mixing, coupled with pumped recirculation, a detailed investigation in cooperation with Plant 2 was conducted. The study examined the plant’s performance both with and without additional impeller-induced draft tube mixing. Throughout two distinct representative cases, both power consumption and biogas production were monitored, providing comprehensive data on the system’s efficiency before and after terminating impeller operation. Moreover, to gauge the efficacy of the remaining pumped recirculation-induced mixing in isolation, BMP was assessed in a laboratory setting for the used substrate and compared to the produced gas of the AD towers. This allowed for an evaluation of whether mixing achieved solely through recirculation mechanisms suffices for optimal biogas production.
3. Results
3.1. Data Evaluation of Survey and Field Studies
The results of the conducted survey and field studies were curated and presented in an anonymized form, providing a plant and mixing specific summarization. The prevalence of different reactor designs and mixing approaches derived from the survey are summarized in Table 1, along with their associated AD volume, operation mode, biogas production, and required specific power for external mixing and internal pumped recirculation.

Table 1.
Survey data set collected with an AD-specific questionnaire of 34 individual plants. Frequency of reactor geometry and mixing approach are displayed in Figure 2.
A graphical summarization is displayed in Figure 2a,b for both the frequency of the geometric reactor shape and the AD mixing approaches, respectively. It is noted that the majority of the investigated plants (55%) employ a cylindrical-based reactor geometry. While evaluating the investigated cylindrical AD towers in this manuscript and in the recent literature, no specific recommended diameter–height ratio can be generalized, but in general AD towers tend to be designed vertically with a larger height than diameter. Besides the simple and well-tested cylindrical shapes, egg-shaped AD designs (26%) were also common and widely used as the state-of-the-art in AD design within this study. While again no specific ratio in geometry is widely applied, most egg-shaped reactors are used in combination with draft tube mixing or aligned inlet configuration [3,35]. Quadratic (9%) and rectangular tanks (3%) are more commonly utilized for smaller AD volumes. While truncated cone geometries (7%) relate to a distinct tapered reactor design, most cylindrical AD towers also offer a tapered contour at the bottom to decrease dead zones.
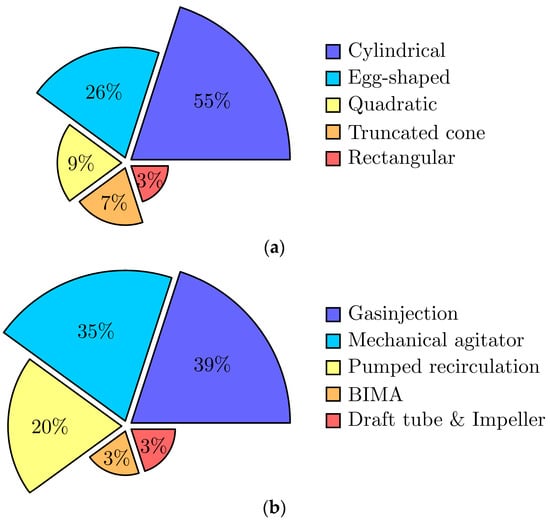
Figure 2.
Approaches in state-of-the-art AD design for reactor design (a) and mixing (b).
Regarding mixing, the frequency of the most common approaches is highlighted in Figure 2b. Mechanical agitation as well as gas injection in conjunction with additional pumped recirculation are the most prominent mixing approaches with 35% and 39%, respectively. While impeller mixing with draft tubes, in general, is a well-established approach [35,36,75], it was less commonly observed in the investigated geographic area of WWTPs, with only two plants employing this approach within this study. Furthermore, within this study, one of the two plants employing draft tube mixing in combination with an impeller terminated its operation to assess its impact on overall mixing. Notably, one of the investigated plants was using a sophisticated biogas-induced mixing arrangement (BIMA). While BIMA is similar to gas-induced mixing methods, no additional energy is required for gas pumping, since the intermixing of the sludge is achieved solely with the pressure formed during the AD process. Both the serial and parallel modes of operation for two or more AD towers are common depending on both the substrate and operational properties. The possibility of dynamic operation was underlined as an important consideration in the overall design of AD plants by direct feedback in the field studies.
The curation of energetic data has highlighted that most energy is required in the pumped recirculation, followed by the internal mixing approaches. The pumped recirculation is used for pumping of the feedstock, temperature control, and also for mixing. As displayed in Figure 3, for 20 of 26 plants that have provided energetic information, the specific energy required for recirculation is higher than for the internal mixing approach.
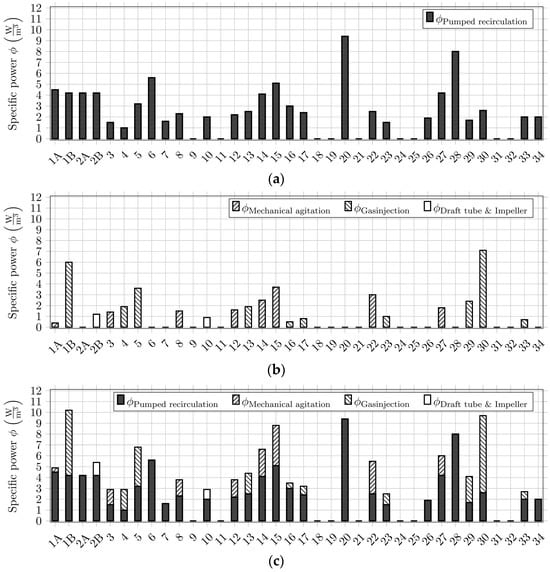
Figure 3.
Breakdown of specific power demand for the individual plants required for pumped recirculation (a), additional external mixing (b), and the sum of both if a combined approach is used (c). Plants 2A, 6, 7, 20, 26, 28, and 34 are exclusively mixed with pumped recirculation.
This is related to the rheology of the sludge as well as to maintaining a certain substrate level and mesophilic temperature inside the AD towers. Regarding the specific power of internal mixing, gas injection and mechanical agitation do not show a specific trend that can be linked to the AD volume or to the mixing method itself. It has to be noted that, especially with gas-induced mixing, plant operators have stated a tendency to using an intermittent operation of the gas injection in order to save energy. In particular, the detailed investigation of Plant 1 shows a severe reduction in energetic demand after the transition to the more cost-effective mechanical agitation (1A), as compared to the prior utilized gas injection (1B). It is also highlighted that the rather seldom-used rectangular and especially quadratic-shaped AD towers are predominantly used in combination with gas-induced mixing and a lower AD volume. This is reasoned with a better applicability of gas-inducing segments at the bottom of the AD towers. Specifically, the corners in the square geometry can lead to increased dead zones, which are particularly poorly mixed, especially with mechanical agitators. The more detailed data gathered in the field studies conducted in cooperation with plant operators are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Data set collected during field studies in cooperation with individual plant operators. RGP is derived from laboratory experiments. Required specific power demand is determined experimentally using a Fluke Energy Logger 1732 v2.3 and may deviate from survey-collected data displayed in Table 1.
The AD temperature (TAD), HRT, OLR, DOD, and RGP are displayed for the individual plants. It is shown that all plants are within the mesophilic temperature range. Plant 8 and Plant 5 show the lowest RGP while also having the highest HRT. In comparison to energetic data provided by the plant operators in Table 1, Table 2 shows small deviations in the experimentally measured required power. The deviations as well as the DOD are displayed in Figure 4. In addition to determining the DOD of the organic dry matter, the RGP of the digested sludge derived from the field studies in cooperation with the different plants is highlighted in Figure 5. The RGP indicates how much biogas can still be produced after further incubation of the partially digested sludge and can be seen as a measure of the remaining degradable substances in the sludge (thus, the degree of stabilization). The investigated RGP values generally ranged between 50 and 80 Nm3 CH4/t ODM. In this range, similar to the case of DOD rates, no correlation between the mixing energy input and the RGP was observed. At Plant 8, a significantly lower RGP is documented compared to the other plants. Besides Plant 5 with a single AD, Plant 1 also showed a lower RGP. These digesters were also operated in serial mode at the time of sampling, but periodically switched to parallel operation due to foaming problems. The sludge age at Plant 1 was also significantly lower compared to Plant 8 at the time of sampling for RGP determination. These data suggest that serial operation with a sufficiently high sludge age can lead to optimal degradation results.
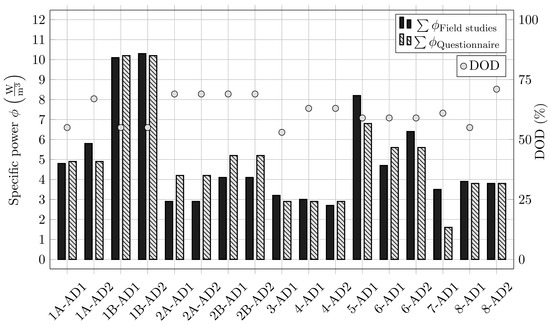
Figure 4.
Comparison of the power rating provided by plant operators and of the measured in-field power demand using a Fluke Energy Logger 1732 v2.3. DOD is also highlighted for the specific AD towers.
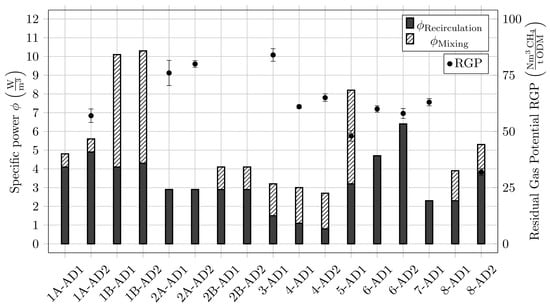
Figure 5.
Comparison of specific power demand required for mixing and recirculation using experimentally determined data displayed in Table 2. RGP is additionally displayed for individual AD towers. Note that for serial operation mode, RGP is only given for final AD stage.
3.2. Field Comparison of Gas Injection and Mechanical Agitation in a Cylindrical AD
To assess the suitability of different mixing approaches, specifically regarding the power consumption, energetic demand, and biogas production, Plant 1 was investigated both during operation with mechanical agitation and previously with gas-induced mixing. To determine the required energetic demand, recorded energy data after transitioning to mechanical agitation (1A) were compared to the energetic data of the previous gas injection method (1B). Table 3 illustrates that the energetic demand in Plant 1 was significantly higher when using gas-injected mixing compared to mechanical agitation. Additionally, the comparison of biogas production rates revealed a notable difference after the conversion to mechanical agitation.

Table 3.
Detailed data of in-depth field study regarding transition from gas injection to mechanical agitation in cooperation with Plant 1.
In detail, the conducted transition increased the CH4 yield by 33.8% while reducing the required energy demand for external mixing by 93.79%. However, it is crucial to note that the associated AD volume, OLR, and CH4 productivity were also higher under mechanical agitation conditions (case A). Therefore, for the comparison of biogas, the SGP should be considered. Furthermore, measurement insecurity, especially in large-scale applications, need to be considered. Nevertheless, energy-related findings hold huge potential for optimizing energy consumption in similar plant setups.
3.3. Field Study Regarding Impact of Impeller Mixing in an Egg-Shaped AD
Evaluation of the survey has indicated that the utilization of impeller mixing within a draft tube is relatively uncommon within the investigated region. Further investigation and exchange of the experience with plant operators has revealed that impeller mixing is indeed less favored due to mechanical abrasion associated with the high velocities generated by small-diameter impellers and solids in the sludge. Additionally, the intense shear forces within the draft tube can lead to foam formation, thereby reducing gas efficiency. The hydrodynamics of impeller mixing necessitate specific reactor geometries, such as a truncated cone or egg-shaped designs, to enhance mixing due to the vertical circulation flow fields [34,35]. The long-term study of impeller operation inside a draft tube within this study has highlighted the disadvantages regarding mechanical durability. The high rotational speed associated with impeller mixing leads to pronounced abrasive effects that potentially damage the impeller blades, especially in comparison to slow rotating mechanical agitators with a larger diameter. It was observed that the mechanical stress on the impeller, caused by solids within the AD tower, resulted in severe abrasive effects on the impeller geometry. Subsequently, the maintenance and repair of the mixing equipment represent substantial costs and prolonged downtime for the AD tower.
To examine the necessity of additional impeller mixing, a detailed investigation was conducted at Plant 2 to assess the potential issue of overmixing. As demonstrated in Table 2 (data of 2A and 2B), the required specific power for mixing ∑ΦF.E decreased per AD from 4.1 W m−3 to 2.9 W m−3 due to the termination of the additional impeller mixing through a draft tube. This results in a short-term reduction in the required mixing power demand of approximately 30%. The monitored biogas remained constant before and after the transition, with no significant fluctuations throughout the period of one year. The SGP provided by the plant was 445 Nm3 CH4/t ODM. To ensure the sufficiency of the AD mixing induced solely via pumped recirculation, the BMP determined in laboratory experiments compared to the plant’s gas production is displayed in Figure 6. Evaluation of the gas production from the AD mixed solely with recirculation is displayed for 11 samples that were taken over a span of 16 weeks and digested under ideal laboratory conditions to estimate the BMP. Fluctuations in the samples, as highlighted in Figure 6, are attributed to a less ideal intermixing of primary and excess sludge when the samples were taken.
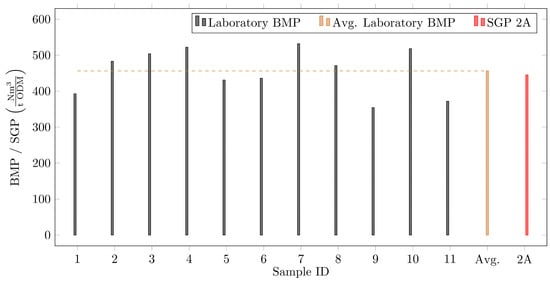
Figure 6.
Laboratory evaluation of the BMP and SGP for Plant 2 after termination of impeller mixing.
The comparison shows good agreement between the BMP derived through the ideal lab-scale AD (avg. laboratory BMP = 456 Nm3 CH4/t ODM) and the SGP of the real AD towers (SGP of Plant 2A = 445 Nm3 CH4/t ODM). Small deviations between the gas potentials highlight sufficient intermixing and thorough processing of the organic matter. Regarding biogas production, sludge mixing based solely on recirculation was proven to be sufficient, and additional impeller mixing was deemed unneeded for this specific case. Regarding settlement and the long-term maintenance of the AD towers, the ongoing study did not reveal significant alterations in the hydrodynamic behavior of solid particles within the investigated period. The available AD volume is regularly determined using tracer-based tests. As highlighted in Figure 7, the available AD volume is shown for specific time points before and after impeller shutdown, as well as after complete AD evacuation.
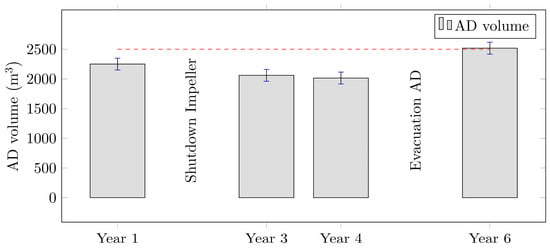
Figure 7.
Investigation of sediment behavior after impeller termination. While no significant change in available AD volume was detected while terminating impeller, complete regeneration of AD volume is shown after complete sediment evacuation.
The results indicate that the steady and continuous decrease in usable AD volume was not impacted significantly by the termination of the impeller. These findings suggest that overmixing mitigation strategies, such as terminating the draft tube, can effectively reduce energy demand without adversely affecting biogas production or the hydrodynamics. The results of this in-field study highlight the potential benefits of re-evaluating mixing strategies in WWTPs to optimize both operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Further research is warranted to generalize these findings across different plant configurations and operational conditions as well as to assess the long-term implications on system performance and maintenance. Therefore, the investigated plant has terminated the impeller mixing and solely relies on a pumped recirculation after the hydrodynamics and potential overmixing were highlighted.
4. Discussion
The results of the field investigations and survey-based AD studies highlight that while there is a general trend in geometric AD designs and mixing approaches, the operational strategies of most plants investigated in this study rely on individual operators’ expertise and manual intervention when specific parameters change during the AD process. While the structural AD design of new plants—regarding the overall volume, shape, and operation mode—is generally based on existing reference plants with a similar PE, the task of digester mixing is often outsourced and planned by external parties. Despite the proven significance of dynamic operation (e.g., intermittent mixing) in several studies [43,67,68,76,77], the majority of the implemented mixing approaches of the investigated plants are designed statically for one single operating point, providing limited flexibility to adapt to changing process properties. This leads to a less ideal harmonization of the mixing approach with the constantly changing operational conditions of the specific plants and subsequently to either overmixing or insufficient mixing. While the specific design of AD has been the subject of many scientific optimization studies [8,12,49,76,78,79], practical AD design and operation are often constricted on the operators’ experience and prevailing habits. This can lead to black-box thinking and subsequently inefficient operation and increased expenses, as stated by the operators of several of the investigated plants.
Regarding the structural design of AD, this survey-based study has highlighted a predominance in cylindrical design followed by egg-shaped AD towers. This is reasoned with less ideal hydrodynamics or space efficiency when using rectangular or spherical AD designs, respectively. Scientific investigations regarding optimized hydrodynamics in the context of AD also show a predominantly preferred utilization of cylindrical AD geometries [7,17,32,33,53,80]. The cylindrical shape is favored because of simple construction, good hydrodynamics, and reasonable space utilization. Deeper analyses of scientific publications in recent decades have also shown a continuous growth in publications regarding egg-shaped AD designs [17,31,34,35,36,81,82]. This is due to the fact that the curved geometry offers a promising investigation template when harmonized with specific mixing approaches and feedstock inlet configurations [34,35]. The pumped recirculation can especially offer a beneficial impact on hydrodynamics when properly aligned with the reactors’ curvature.
As highlighted both in the study results and in feedback by the plant operators, the possibility of a dynamic operation of multiple AD towers can significantly help to increase the overall system efficiency by enabling targeted responses to changes in fluid properties or external influences on the AD process. The serial mode of operation is stated to lead to a higher gas production rate by providing different and specifically tailored environmental conditions in each tower [41,43]. The resulting optimized activity of specific microorganisms at different stages of digestion has a beneficial impact on the gas rate. However, the first-stage digester needs to be capable of handling the amount of substrate. According to the feedback of the AD operators, cold temperatures combined with high amounts of co-substrate can result in foaming layers, decreasing the efficiency of AD towers by inhibiting gas release and disrupting the microbial community. Parallel operation is favored when processing large amounts of sludge or different types of substrate that require individual mixing strategies [83].
Regarding mixing, gas injection and mechanical agitation are demonstrated to be the most frequently implemented approaches according to the survey (Figure 2b). This is consistent with the trend observed in scientific studies, which report an increased frequency of 62% for mechanical agitation and 19% for both gas injection and pumped recirculation, as summarized by Caillet et al. [12]. According to Table 1, the sum of the specific power ∑ΦSurvey required for pumped recirculation and optional additional mixing spans from 1.6 W m−3 to 10.2 W m−3, with the share of ΦPumped Recirculation being higher than ΦMixing for 20 of 34 plants. Therefore, the investigated plants are in the range of the general recommendation of the United States Environmental Protection Agency [74], with 5–8 W m−3 for digester mixing, which is often cited in studies addressing AD mixing [36,69,73]. However, this recommendation does not account for fluid properties (e.g., non-Newtonian behavior) or the digester design. In particular, the comprehensive studies of Wu et al. [3] report similar ranges in specific power, with 4.11 W m−3, 5.0 W m−3, and 5.9 W m−3 for mechanical mixing, gas-induced mixing, and a pumped recirculation, respectively. Regarding draft tube mixing, similar values are reported between approximately 4 W m−3 and 12 W m−3 [55,75,84]. The inserted specific power significantly relies on the basic AD design and fluid properties. Lower values are also reported as sufficient for mixing in specific cases without compromising hydrodynamics, as shown by Grazia Leonzio [85] with 1.9 W m−3 to 2.7 W m−3 exclusively using a pumped recirculation, Xinxin et al. [86] with 0.5 W m−3 and Oates et al. [7] with 0.3 W m−3 for mechanical agitation, or by Dapelo and Bridgeman [58] with 1 W m−3 for gas-induced mixing. However, certain process variables can have a drastic impact on the calculated specific power, as exemplified in the studies of Soroush et al. [80] using 50 W m−3 due to a relatively low AD volume and Li et al. [56], reporting ranges from 21 to 131 W m−3 due to very high %TS concentrations. This underlines the fact that the recommendation of 5–8 W m−3 is only a rough guideline, and individual AD specific consideration of the induced specific mixing power is highly important.
It was noted that some of the provided energetic data of the answered surveys deviates from the experimentally measured energetic demands derived from the field studies, as highlighted in Figure 4. This can be mainly attributed to the fact that the plant operators provide annual averaged data, while the experimental measurements were conducted for a maximum of 24 h.
Direct contact with the surveyed plants has revealed that there is a tendency to transition from gas-inducing methods to mechanical agitation due to a potential decrease in maintenance and operational costs. This was furthermore reasoned with a better dynamic control regarding changing sludge properties and hydrodynamics. This, however, necessitates the implementation of dynamic motor control for the respective mixing approach to specifically adapt to the continuously changing operational conditions and, therefore, prevents insufficient or too-intense mixing. The comparison between gas mixing and mechanical mixing is also a continuously debated topic in scientific studies [11,12,87]. Most plants investigated rely on static speed control, especially when operating mechanical agitation devices. Retrofitting a dynamic control of the rotational speed is often not possible because of static gear shifts. Therefore, the exclusive implementation of a new dynamic mixing strategy is often associated with problematic downtimes and high expenses. Static motor controls usually only allow for changing the direction of rotation, which is useful for preventing clogging of the rotating stirring devices. Dynamic regulation of the rotational speed would allow for optimizing the induced mixing depending on changes in the substrate or reactor volume. It was noted that when a dynamic velocity control is not possible, plant operators tend to implement intermittent mixing as also implemented in several optimization studies [51,67,68,77]. The short-term result is a decrease in operational costs due to lower required mixing power, but it also can increase the biogas production, since different bacteria show specific microbial activity at certain mixing intensities. The potential negative effects of overmixing were also proven in laboratory experiments in previous studies [51,64,88].
Within this study, inefficient mixing was investigated and subsequently confirmed for two individual cases. Changes in the mixing stage were implemented for Plants 1 and 2 during the field study. As presented in Table 3, the transition from gas injection to mechanical agitation decreased the required energetic demand for external mixing by almost 94%. The specific mixing power required for gas injection before the transition is documented in Table 1 with ΦMixing, Survey = 6 W m−3. This is consistent with the aforementioned typical values recommended for thorough digester mixing [3,69,73,74]. The combined required specific power demand of mixing and pumped recirculation ∑ΦSurvey is subsequently reduced by 52% from 10.2 W m−3 to 4.9 W m−3. At the same time, according to the data in Table 3, gas production was also affected. The gas production between both cases increased significantly from 1,680,250 m3 to 2,248,200 m3 for case A. However, both the OLR and the AD volume were higher in case A, with 2.3 kg ODM/m3 d and 8552 m3 compared to 1.9 kg ODM/m3 d and 8217 m3 in the previous case B. Even after considering the change in OLR and AD volume, this still results in a slightly increased SGP of 0.313 Nm3 CH4/kg ODM for case A compared to 0.295 Nm3 CH4/kg ODM for case B. The comparison of the associated SGPs shows good accordance with values found in the literature ranging between 0.1 and 0.5 Nm3 CH4/kg ODM [89,90]. Although an increase in gas production can be derived from the data, it is necessary to critically assess this due to large-scale measurements and associated uncertainties in the determination of gas parameters. However, the transition from gas injection to mechanical agitation, which subsequently decreased the required energetic demand, definitely did not impact the gas production negatively. This indicates that for this specific case, the gas injection additional to the pumped recirculation was unneeded and a mechanical agitator with lower power consumption was sufficient. Therefore, it can be stated that the efficiency of the plant was significantly increased.
For Plant 2, the redundancy of impeller mixing inside the egg-shaped reactors was confirmed by the field experiments, since the used pumped recirculation was demonstrated to be sufficient for complete digestion of the organic matter without increasing RGP values. According to Table 2, the specific power demand ∑ΦF.E between cases 2A and 2B was reduced by 30% by terminating the impeller-induced mixing. The ΦPumped Recirculation F.E. of 2.9 W m−3, again, in the common range associated with specific power required for pumped recirculation, is demonstrated to be sufficient according to the absence of observed changes in biogas production, as indicated by the BMP comparison of ideally processed substrate derived from laboratory BMP trials with the monitored SGP of Plant 2A (Figure 6). Notably, the comparison of the SGP of Plant 2A, employing only pumped recirculation, with the BMP derived under ideal conditions shows nearly identical values (avg. laboratory BMP = 456 Nm3 CH4/t ODM, SGP of 2A = 445 Nm3 CH4/t ODM). This indicates a very efficient AD as compared to common values found in the literature, where the SGP is usually only 85–95% of the BMP [71,91]. The range is also very comparable to common BMP values, which are strongly dependent on the used sludge composition [92,93,94,95,96]. While impeller mixing has been reported to be efficient, especially in combination with curved egg-shaped geometries [35,36], the presented results demonstrate that for this individual case with pumped recirculation, additional mixing is deemed as redundant. Therefore, the plant’s operators ultimately decided to terminate the impeller-induced mixing and since then only rely on mixing through pumped recirculation. The efficiency of mixing with pumped recirculation could further be improved by a reduction in dead zones by dynamically changing the position of the suction of the sludge intake and occasional drainage of the bottom sludge [35,36,81].
The optimization of the mixing stage was successful in both cases, leading to the assumption that there is much more potential for optimizing each of the remaining plants. However, AD in domestic WWTPs is a continuous process that is very difficult to shut down, especially if plant operators run on full capacity and do not have the opportunity to temporarily terminate one of multiple available digesters. This underlines the importance of careful planning when designing new AD towers or implementing changes in existing plants. In particular, a dynamic control of the mixing approach [43,67,68,76,77] as well as the possibility to easily switch between parallel and serial operation modes [41,43] was a reoccurring recommendation by the plant operators in the direct exchange of know-how and operational experience. The possibility of dynamic process control by manipulating mixing variables can improve the plant’s efficiency and prevent overmixing. While no correlation between the mixing approach and RGP was proven, the operation mode seems to impact the overall RGP. When using serial operation, each AD tower can be tailored specifically to the requirements for optimal AD and gas production. Particularly, Plant 8 showed a decreased RGP when operated in serial. The reduction in RGP is substantial both for the plants efficiency and sustainability in operation, since both CO2 and CH4 are greenhouse gases.
In summary, the investigations and the direct contact with AD operators have revealed that while AD operation and mixing are extensively studied in scientific research, there remains a stigma around overmixing AD towers, which leads to the acceptance of disadvantageous results, such as higher operational costs or decreased microbial activity [51,63,64]. This is related to the fact that most of the time there is no possibility to monitor the mixing of opaque sludge in optically non-accessible AD towers. While real-time mixing monitoring is possible at laboratory scales with sophisticated measurement approaches [5,10,97] which are not practical for constant real-scale live-monitoring, the implementation of a simple dynamic mixing control would be sufficient to enable the possibility of alternating the mixing intensity by simultaneously evaluating the gas production and process-related AD phenomena such as foaming, sedimentation, and RGP. On the basis of Plant A and B, it was shown that even little changes in the mixing stage can drastically decrease energy requirements and subsequently increase the plants’ energetic efficiency. This, however, requires individual consideration of the investigated plants’ design and operation conditions. In general, cylindrical shapes are favored because of their simplicity in both operation and construction [31,32,33]. Coupled with dynamic internal pumped recirculation and also an additional dynamic mechanical agitation, the complex mixing process can be adapted to changing process or fluid properties if necessary. Depending on the volume and space, a parallel or serial AD setup can increase capacity or gas production [41,43]. The final determination of the optimal mixing intensity remains a crucial objective, which can be achieved through the implementation of dynamic mixing control, which subsequently helps to reduce costs and minimize the potential for residual gas.
5. Conclusions
The presented combined evaluation of AD plants using surveys and field studies provides a comprehensive summary of the state-of-the-art in AD design and mixing strategies, and it highlights potential optimization points for similar existing systems and comparable technical applications. It was highlighted that besides cylindrical reactor geometries, the variable operation of two or more AD towers with a dynamic mixing strategy is the most favored approach within the investigated region. Regarding mixing, a tendency towards mechanical agitation was noticed, which is related to better control, lower operational costs, and easier maintenance compared to gas injection and especially impeller-driven draft tube mixing. Two specific field studies demonstrated practically that AD systems might often be operated in a habit-driven and potentially inefficient manner by evaluating induced mixing and optimizing it regarding energetic demand and gas-related efficiency. In both cases, the operational power demands for mixing were reduced by 52% and 30%, respectively. Besides plant-specific optimization, the survey, and especially the direct contact with plant operators, highlighted which AD designs are frequently used and identified common operational problems. Furthermore, prevention methods and practical recommendations for common AD phenomena are presented. It is notable that the inefficient operation of AD most often contributed to difficulties in the process monitoring, especially regarding the hydrodynamics. Therefore, there is significant potential for optimization within the AD context, which can reduce operational and maintenance costs, as well as investment costs, with proper planning in the design phase. Applied refinement of AD processes, as presented in this study, can help increase gas production and decrease gas losses and operational expenses, positioning AD as an indispensable green energy source. The conducted optimizations not only hold economic value because of decreased energetic costs, but also have environmental impact because of the reduction in RGP associated with greenhouse gas emissions. In conclusion, this study underscores the importance of continuous improvement and optimization in AD systems to enhance their efficiency and sustainability as a green energy source.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.N., M.P., M.M. and W.R.; methodology, T.N., S.D.-W., C.E., M.P., M.M., T.S. and J.W.; software, S.D.-W. and T.N.; validation, T.N., S.D.-W. and C.E.; formal analysis, T.N., S.D.-W. and C.E.; investigation, T.N., W.R., M.M. and M.P.; resources, M.M., M.P. and W.R.; data curation, T.N., T.S. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, T.N., M.M., T.S. and J.W.; writing—review and editing, T.N., T.S., M.M., J.W., M.P. and W.R.; visualization, T.S., T.N. and J.W.; supervision, W.R., M.P. and M.M.; project administration, W.R. and M.M.; funding acquisition, W.R. and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Austrian Federal Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, Regions and Water Management, grant number B801259.
Data Availability Statement
Due to data protection, data will be made available in an anonymized form upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Simon Draxl-Weiskopf was employed by the company BioTreaT GmbH. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Letcher, T. Global Warming, Greenhouse Gases, Renewable Energy, and Storing Energy. In Storing Energy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Grangeiro, L.C.; de Almeida, S.G.C.; de Mello, B.S.; Fuess, L.T.; Sarti, A.; Dussán, K.J. Chapter 7-New Trends in Biogas Production and Utilization. In Sustainable Bioenergy; Rai, M., Ingle, A.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 199–223. ISBN 978-0-12-817654-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B. CFD Simulation of Gas and Non-Newtonian Fluid Two-Phase Flow in Anaerobic Digesters. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3861–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. CFD Investigation of Turbulence Models for Mechanical Agitation of Non-Newtonian Fluids in Anaerobic Digesters. Water Res. 2011, 45, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuner, T.; Meister, M.; Pillei, M.; Koch, M.; Rauch, W. Numerical and Experimental Flow Investigation Using Ultrasonic PIV for Optimizing Mechanically Agitated Lab-Scale Anaerobic Digesters. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 264, 118129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Neuner, T.; Hupfauf, S.; Arthofer, A.; Ebner, C.; Rauch, W.; Bockreis, A. Impact of Impeller Design on Anaerobic Digestion: Assessment of Mixing Dynamics, Methane Yield, Microbial Communities and Digestate Dewaterability. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 406, 131095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, A.; Neuner, T.; Meister, M.; Borman, D.; Camargo-Valero, M.; Sleigh, A.; Fischer, P. Modelling Mechanically Induced Non-Newtonian Flows to Improve the Energy Efficiency of Anaerobic Digesters. Water 2020, 12, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuner, T.; Meister, M.; Pillei, M.; Rauch, W. Optimizing Mixing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digesters with High Total Solids Concentrations Using Validated CFD Simulations. Biochem. Eng. J. 2024, 208, 109320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebranchu, A.; Delaunay, S.; Marchal, P.; Blanchard, F.; Pacaud, S.; Fick, M.; Olmos, E. Impact of Shear Stress and Impeller Design on the Production of Biogas in Anaerobic Digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, P.A.; Lacroix, R.; Bertrand, F.; Choplin, L.; Brito-De La Fuente, E. Mixing of Non-Newtonian Viscous Fluids with Helical Impellers: Experimental and Three-Dimensional Numerical Studies. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 1992, 286, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sasidhar, K.B.; Somasundaram, M.; Ekambaram, P.; Arumugam, S.K.; Nataraj, G.; Murugan, M.A. A Critical Review on the Effects of Pneumatic Mixing in Anaerobic Digestion Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Bastide, A.; Adelard, L. Advances in Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of Anaerobic Digestion Process for Renewable Energy Production: A Review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 6, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Lauwers, J.; Degreve, J.; Helsen, L.; Lievens, B.; Willems, K.; Dewil, R. Anaerobic Digestion in Global Bio-Energy Production-Potential and Research. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4295–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, V.; Sridharan, N.V.; Feroskhan, M.; Vaithiyanathan, S.; Subramanian, B.; Tsai, P.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Lay, C.H.; Wang, C.T.; Ponnusamy, V.K. Biogas Production and Its Utilization in Internal Combustion Engines—A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 186, 518–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Radetic, B. Anaerobic Digestion, Important Aspects Regarding Digester Design and Sludge Mixing Systems. In Handbook of Water and Used Water Purification; Lahnsteiner, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2024; pp. 737–749. ISBN 978-3-319-78000-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yagna Prasad, K. Gas Mixing in Anaerobic Sludge Digestion. In Handbook of Water and Used Water Purification; Lahnsteiner, J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–16. ISBN 978-3-319-66382-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Development of Biogas Combustion in Combined Heat and Power Generation. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marañón, E.; Salter, A.M.; Castrillón, L.; Heaven, S.; Fernández-Nava, Y. Reducing the Environmental Impact of Methane Emissions from Dairy Farms by Anaerobic Digestion of Cattle Waste. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ólafsdóttir, S.S.; Jensen, C.D.; Lymperatou, A.; Henriksen, U.B.; Gavala, H.N. Effects of Different Treatments of Manure on Mitigating Methane Emissions during Storage and Preserving the Methane Potential for Anaerobic Digestion. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.V.; Yadav Lamba, B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Chen, W.-H. Sustainable Biogas Production via Anaerobic Digestion with Focus on CSTR Technology: A Review. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 162, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, H.; Wu, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Xu, K.-Q. Performance Comparison of CSTR and CSFBR in Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste with Grease Trap Waste. Energies 2022, 15, 8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraprasertwong, A.; Vichaitanapat, K.; Leethochawalit, M.; Chavadej, S. Three-Stage Anaerobic Sequencing Batch Reactor (ASBR) for Maximum Methane Production: Effects of COD Loading Rate and Reactor Volumetric Ratio. Energies 2018, 11, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, S.M.; Bakare, B.F.; Tetteh, E.K.; Rathilal, S. Sequencing Batch Reactor Performance Evaluation on Orthophosphates and COD Removal from Brewery Wastewater. Fermentation 2022, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Switzenbaum, M.S. Anaerobic Fixed Film Wastewater Treatment. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1983, 5, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pererva, Y.; Miller, C.D.; Sims, R.C. Approaches in Design of Laboratory-Scale UASB Reactors. Processes 2020, 8, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Buttazzoni, M.; Goi, D. Up-Flow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket (UASB) Technology for Energy Recovery: A Review on State-of-the-Art and Recent Technological Advances. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.J.; Hobbs, P.J.; Holliman, P.J.; Jones, D.L. Optimisation of the Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Resources. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7928–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamawand, I. Anaerobic Digestion Process and Bio-Energy in Meat Industry: A Review and a Potential. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, I.M.; Mohd Ghazi, T.I.; Omar, R. Anaerobic Digestion Technology in Livestock Manure Treatment for Biogas Production: A Review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohungbe, M.O.; Dodd, I.C.; Herbert, B.M.J.; Li, H.; Ricketts, L.; Semple, K.T. High Solid Anaerobic Digestion: Operational Challenges and Possibilities. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 268–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhaschandra Singh, T.; Nath Verma, T.; Nashine, P. Analysis of an Anaerobic Digester Using Numerical and Experimental Method for Biogas Production. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 5202–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Pagilla, K.R. Anaerobic Digester Foaming in Full-Scale Cylindrical Digesters–Effects of Organic Loading Rate, Feed Characteristics, and Mixing. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, S.; Sappl, J.; Kumar, P.; Meister, M.; Rauch, W. On the Effect of the Inlet Configuration for Anaerobic Digester Mixing. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, M.; Rezavand, M.; Ebner, C.; Pümpel, T.; Rauch, W. Mixing Non-Newtonian Flows in Anaerobic Digesters by Impellers and Pumped Recirculation. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 115, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. CFD Simulation of Mixing in Egg-Shaped Anaerobic Digesters. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendieta-Pino, C.A.; Garcia-Ramirez, T.; Ramos-Martin, A.; Perez-Baez, S.O. Experience of Application of Natural Treatment Systems for Wastewater (NTSW) in Livestock Farms in Canary Islands. Water 2022, 14, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswantara, A.I.; Daryus, A.; Darmawan, S.; Gunadi, G.G.; Camalia, R. CFD Analysis of Slurry Flow in an Anaerobic Digester. Int. J. Technol. 2016, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Khim, J.; Kim, J.D. Application of a Full-Scale Horizontal Anaerobic Digester for the Co-Digestion of Pig Manure, Food Waste, Excretion, and Thickened Sewage Sludge. Processes 2023, 11, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Construction Materials and Structures of Digesters. In Biogas Technology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 157–199. ISBN 978-981-15-4940-3. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, A.; Hanser, M.; Ebner, C.; Insam, H.; Markt, R.; Hupfauf, S.; Probst, M. Stability of the Anaerobic Digestion Process during Switch from Parallel to Serial Operation—A Microbiome Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corigliano, O.; Iannuzzi, M.; Pellegrino, C.; D’Amico, F.; Pagnotta, L.; Fragiacomo, P. Enhancing Energy Processes and Facilities Redesign in an Anaerobic Digestion Plant for Biomethane Production. Energies 2023, 16, 5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kovács, K.L.; Bagi, Z.; Nyári, J.; Szepesi, G.L.; Petrik, M.; Siménfalvi, Z.; Szamosi, Z. Enhancing Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion by Optimization of Mixing Regimes Using Helical Ribbon Impeller. Fermentation 2021, 7, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiniger, B.; Hupfauf, S.; Insam, H.; Schaum, C. Exploring Anaerobic Digestion from Mesophilic to Thermophilic Temperatures—Operational and Microbial Aspects. Fermentation 2023, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ibrahimi, M.; Khay, I.; El Maakoul, A.; Bakhouya, M. Food Waste Treatment through Anaerobic Co-Digestion: Effects of Mixing Intensity on the Thermohydraulic Performance and Methane Production of a Liquid Recirculation Digester. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Hans, M.; Kumar, S.; Yadav, Y.K. Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion: An Advancement towards Enhanced Biogas Production from Lignocellulosic Biomass. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.S.; Flores-Rodriguez, C.; Torres-Albarracin, L.; da Silva, A.J. Thermochemical Pretreatment for Improving the Psychrophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Coffee Husks. Methane 2024, 3, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, K.; Varma, R.; Vesvikar, M.; Al-Dahhan, M.H. Flow Pattern Visualization of a Simulated Digester. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3659–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terashima, M.; Goel, R.; Komatsu, K.; Yasui, H.; Takahashi, H.; Li, Y.Y.; Noike, T. CFD Simulation of Mixing in Anaerobic Digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2228–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, L.; Conti, F.; Saidi, A.; Sonnleitner, M.; Goldbrunner, M. Modeling Mixing in Anaerobic Digesters with Computational Fluid Dynamics Validated by Experiments. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Harnisch, E.; Schwede, S.; Gerber, M.; Span, R. Different Mixing Modes for Biogas Plants Using Energy Crops. Appl. Energy 2013, 112, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Kuo-Dahab, C.; Chapman, T.; Mei, Y. Anaerobic Digestion, Mixing, Environmental Fate, and Transport. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1210–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameur, H.; Kamla, Y.; Sahel, D. Performance of Helical Ribbon and Screw Impellers for Mixing Viscous Fluids in Cylindrical Reactors. ChemEngineering 2018, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B. CFD Analysis of Mechanical Mixing in Anaerobic Digesters. Trans. ASABE 2009, 52, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroney, R.N.; Colorado, P.E. CFD Simulation of Mechanical Draft Tube Mixing in Anaerobic Digester Tanks. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, K.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J. CFD Simulation and Performance Evaluation of Gas Mixing during High Solids Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 178, 108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesvikar, M.S.; Al-Dahhan, M. Flow Pattern Visualization in a Mimic Anaerobic Digester Using CFD. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 89, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapelo, D.; Bridgeman, J. Euler-Lagrange Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation of a Full-Scale Unconfined Anaerobic Digester for Wastewater Sludge Treatment. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 117, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellinger, A.; Lindberg, A. Biogas Upgrading and Utilisation. IEA Bioenergy Task 2000, 24, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bridgeman, J. Computational Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Sewage Sludge Mixing in an Anaerobic Digester. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2012, 44, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchain, J.; Gabelle, J.-C.; Cockx, A. A Coupled Population Balance Model and CFD Approach for the Simulation of Mixing Issues in Lab-Scale and Industrial Bioreactors. AIChE J. 2013. Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Ghufran, R.; Nasir, Q.; Shahitha, F.; Al-Sibani, M.; Al-Rahbi, A.S. Enhanced Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Solid Poultry Slaughterhouse Waste Using Fixed Bed Digester: Performance and Energy Recovery. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaparaju, P.; Buendia, I.; Ellegaard, L.; Angelidakia, I. Effects of Mixing on Methane Production during Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Manure: Lab-Scale and Pilot-Scale Studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, T.; Nosrati, M.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. Anaerobic Digestion from the Viewpoint of Microbiological, Chemical, and Operational Aspects—A Review. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, P.; Ou, X.; Luo, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, H.; Ge, X.; Li, L. Effect of the Inoculum Mixing Ratio on the Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Reactor Performance and Microbial Community. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, P.J. Minimisation of Energy Input Requirements of an Anaerobic Digester. Agric. Wastes 1979, 1, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Cui, Z.; Hao, J.; Li, G. Effects of Intermittent Mixing Mode on Solid State Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Wastes. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Q.; Jiang, J.; Mei, W. Effect of Optimized Intermittent Mixing during High-Solids Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge: Simulation, Performance, and Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindmark, J.; Thorin, E.; Bel Fdhila, R.; Dahlquist, E. Effects of Mixing on the Result of Anaerobic Digestion: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 40, 1030–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Achinas, V.; Euverink, G.J.W. Chapter 2—Microbiology and Biochemistry of Anaerobic Digesters: An Overview. In Bioreactors; Singh, L., Yousuf, A., Mahapatra, D.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 17–26. ISBN 978-0-12-821264-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.K.; Park, S.C.; Chang, H.N. Biochemical Methane Potential and Solid State Anaerobic Digestion of Korean Food Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 1995, 52, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W.; Perry, R.H. Perry’s Chemical Engineers’ Handbook, 8th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780071422949. [Google Scholar]
- Stukenberg, J.R.; Clark, J.H.; Sandino, J.; Naydo, W.R. Egg-Shaped Digesters: From Germany to the US. Water Environ. Technol. 1992, 4, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Process Design Manual for Sludge Treatment and Disposal; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, K.J.; Nieuwoudt, M.N.; Niemand, L.J. CFD Simulation of Anaerobic Digester with Variable Sewage Sludge Rheology. Water Res. 2013, 47, 4485–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Optimization and Experimental Study of Variable Frequency Intermittent Stirring Strategy for Anaerobic Digestion Based on CFD. Fuel 2024, 355, 129371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Kovács, K.L.; Bagi, Z.; Petrik, M.; Szepesi, G.L.; Siménfalvi, Z.; Szamosi, Z. Significance of Intermittent Mixing in Mesophilic Anaerobic Digester. Fermentation 2022, 8, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldehans, M.G. Optimization of Distillery-Sourced Wastewater Anaerobic Digestion for Biogas Production. Clean. Waste Syst. 2023, 6, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani Abyaneh, E.; Zarghami, R.; Krühne, U.; Rosinha Grundtvig, I.P.; Ramin, P.; Mostoufi, N. Mixing Assessment of an Industrial Anaerobic Digestion Reactor Using CFD. Renew. Energy 2022, 192, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, S.; Noorpoor, A.; Arfaee, M.; Kumar, P.; Rauch, W. CFD Modeling of a Stirred Anaerobic Digestion Tank for Evaluating Energy Consumption through Mixing. Water 2021, 13, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Miot, A.; Jones, B.; Klibert, C.; Pagilla, K.R. A Full-Scale Study of Mixing and Foaming in Egg-Shaped Anaerobic Digesters. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 192, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Singh, N.; Čonka, Z.; Kolcun, M.; Siménfalvi, Z.; Péter, Z.; Szamosi, Z. Critical Analysis of Methods Adopted for Evaluation of Mixing Efficiency in an Anaerobic Digester. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborrino, A.; Catalano, F.; Leone, A.; Bianchi, B. A Real Case Study of a Full-Scale Anaerobic Digestion Plant Powered by Olive By-Products. Foods 2021, 10, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyama, I.D.; Zhai, X.; Wu, B. Influence of Mixing on Anaerobic Digestion Efficiency in Stirred Tank Digesters: A Review. Water Res. 2018, 143, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G. Study of Mixing Systems and Geometric Configurations for Anaerobic Digesters Using CFD Analysis. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liang, J.; Cheng, G.; Pan, R. Study on Side-Entering Agitator Flow Field Simulation in Large Scale Biogas Digester. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 153, 5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergamo, U.; Viccione, G.; Coppola, S.; Landi, A.; Meda, A.; Gualtieri, C. Analysis of Anaerobic Digester Mixing: Comparison of Long Shafted Paddle Mixing vs Gas Mixing. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 1406–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Speece, R.E. Comparative Process Stability and Efficiency of Anaerobic Digestion; Mesophilic vs. Thermophilic. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4369–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolzonella, D.; Pavan, P.; Battistoni, P.; Cecchi, F. Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge: Influence of the Solid Retention Time in the Wastewater Treatment Process. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bres, P.; Beily, M.E.; Young, B.J.; Gasulla, J.; Butti, M.; Crespo, D.; Candal, R.; Komilis, D. Performance of Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Poultry Manure with Fruit and Vegetable Waste and Analysis of Digestate Quality: A Bench Scale Study. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretto, G.; Ardolino, F.; Piasentin, A.; Girotto, L.; Cecchi, F. Integrated Anaerobic Codigestion System for the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and Sewage Sludge Treatment: An Italian Case Study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 95, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Ranade, V. V Enhancing BMP and Digestibility of DAF Sludge via Hydrodynamic Cavitation. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2024, 198, 109733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, G.K.; Chen, L. Comparison on Batch Anaerobic Digestion of Five Different Livestock Manures and Prediction of Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Using Different Statistical Models. Waste Manag. 2016, 48, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, K.; Mansoor Ahammed, M. Development of an Anaerobic Digestibility Index for Organic Solid Wastes. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 187, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsefil, I.C.; Miraloglu, I.H.; Ozbayram, E.G.; Ince, B.; Ince, O. Bioaugmentation of Anaerobic Digesters with the Enriched Lignin-Degrading Microbial Consortia through a Metagenomic Approach. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Üveges, Z.; Damak, M.; Klátyik, S.; Ramay, M.W.; Fekete, G.; Varga, Z.; Csaba, G.; Szekacs, A.; Aleksza, L. Biomethane Potential in Anaerobic Biodegradation of Commercial Bioplastic Materials. Fermentation 2023, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindall, R.; Dapelo, D.; Leadbeater, T.; Bridgeman, J. Positron Emission Particle Tracking (PEPT): A Novel Approach to Flow Visualisation in Lab-Scale Anaerobic Digesters. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2017, 54, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).