Abstract
In this work, electrical resistivity tomography was carried out together with physical hydrogeology techniques to evaluate the karst aquifer in the northwest region of the Yucatán Peninsula in a study area near the western edge of the Ring of Cenotes of the Chicxulub Crater. In addition, based on a systematic compilation of open-access data of water levels reported for the peninsular aquifer, maps of groundwater isolines and groundwater flows were generated using IDW interpolation, Empirical Bayesian Kriging, and the Flow Net method. From these results, a shallow aquifer is observed, with the presence of heterogeneities such as possible dissolution conduits and/or flooded caverns, approximately 20 m below ground level, formed by the dissolution processes of limestone rocks. On a regional scale, the geomorphological influence of the Ring of Cenotes on groundwater flows was observed. In general, the flow directions observed from these maps coincide with those conceptualized for this region of the peninsular aquifer. Nevertheless, some differences were observed depending on the interpolation method used. Our results contribute to hydrogeological studies carried out in the periphery of this ring, where the vulnerability of the aquifer to anthropogenic contamination has been highlighted due to the intrinsic features of the karst environment.
1. Introduction
The only source of freshwater in the Yucatán Peninsula (YP), México, is obtained through groundwater extraction from a mature karstic aquifer, considered one of the largest in the world. Due to its importance as a source of water for human consumption, all water-consuming activities, and the environment, it is said that the ecosystems and biodiversity of the YP are systems dependent on groundwater. Unfortunately, this aquifer system has a high vulnerability to anthropogenic contamination due to several factors such as the high permeability of the bedrock and the shallow water table with respect to ground level, among many others [1,2,3,4]. In addition, this aquifer is susceptible to salinization due to its marked interaction with seawater [5,6].
Although intense research activity has been carried out during the last three decades, related to the detection of contaminants in the aquifer and their effects and implications on the environment and human health [7,8,9,10], a lot of research is still needed to understand how these contaminants spread within the aquifer [11]. The lack of research on this topic is mainly due to the complexity of the karstic aquifer, which presents a high heterogeneity and anisotropy throughout its extension, so it has been classified by Perry et al. [12] into six hydrogeochemical/physiographic regions that result from a tectonic classification, rock type, sedimentation patterns, and rainfall. These regions are (1) the Chicxulub sedimentary basin, (2) the Ring of Cenotes (RC), (3) the Pockmarked Terrain, (4) the Ticul fault zone, (5) the Holbox Fracture Zone–Xel Ha Zone, and (6) the Evaporite Region [12].
Due to this high heterogeneity and anisotropy, any evaluation that involves the study of the fate and transport of contaminants first requires the development of a conceptual hydrogeological model [13], either at a local and/or regional scale, so it is important to generate cutting-edge scientific knowledge that contributes to the development of conceptual models capable of explaining the complex dynamic behavior of this aquifer system. An invaluable tool to achieve this goal is through the joint application of geophysical and hydrogeological techniques.
Geophysical techniques have been implemented in hydrological research for decades; however, in the last two or three, new methods have been developed that allow for a better characterization of hydrogeological parameters, taking advantage of their relationships with observable geophysical properties [14]. The application of geophysical methods together with hydrogeological techniques, to map features below the surface, has been called hydrogeophysics, which emerges as an interdisciplinary field focused on improving the understanding of hydrological processes using geophysical observations [15]. Although many geophysical techniques can be used, they depend on the depth of the aquifer with respect to the surface. In the case of shallow aquifers, an ideal near-surface geophysics technique is electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), which has already been implemented with success in various areas of the YP [16,17,18,19].
Hydrogeophysical studies constitute a basis for subsequent studies that allow us to understand the transport and dispersion of contaminants in the natural environment. Therefore, to contribute to the hydrogeological studies of the YP karst aquifer, in this work, we present the results of a hydrogeophysical evaluation carried out in a study area near the western periphery of the RC of the Chicxulub Crater, an area of high permeability, with a high density of sinkholes (known locally as cenotes), fractures, and flooded dissolution conduits, around which numerous productive activities (rearing livestock, tourism, etc.) and domestic activities are carried out. These activities generate waste that can infiltrate the aquifer to a greater or lesser extent, altering the quality of groundwater [20,21].
Although numerous studies have been carried out to understand the structure of the RC [22,23], near-surface geophysics studies are scarce, so we hope that our work contributes to the knowledge of the aquifer in this region of the YP and to the conservation efforts of areas on the periphery of the RC.
1.1. Study Area
The study area is located at the geographical coordinates N and W, in the municipality of Maxcanú Yucatán, in the northwest region of the YP, approximately 55 km to the west of Mérida city and 25 km to the east of Celestún, as can be seen in Figure 1. In the same figure, the geophysical transects of ERT are shown.
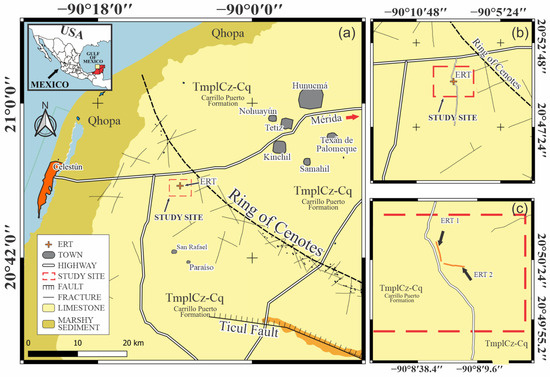
Figure 1.
(a) Location of the hydrogeophysical study site in the northwestern region of the YP, (b) close-up of the study site, and (c) real orientations of ERT transects.
1.2. Geological and Hydrogeological Settings
The geological composition of the region consists of coquinoidal limestones belonging to the Carrillo Puerto formation (TmplCz-Cq), made up of Upper Miocene–Pliocene rocks, as can be seen in Figure 2a,b. In the upper part of this formation, there is a layer of healthy and massive white limestone, with an estimated thickness of several hundred meters and an abundance of macrofossils. This formation has high permeability and secondary porosity due to the high fracturing of the rock matrix and also due to the abundance of cavities and dissolution conduits favored by the dissolution of carbonate rocks [24,25].
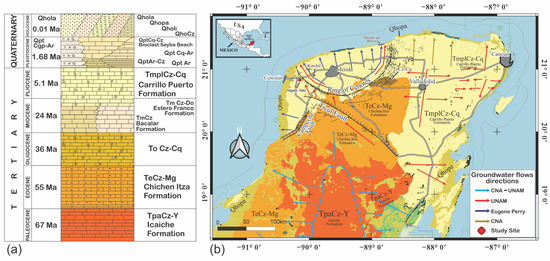
Figure 2.
(a) Classification of the geological formations of the Yucatán Peninsula. (b) Map of surface geology and conceptual regional groundwater flows of the YP. Image modified from [5]. The colors between both figures indicate the respective geological formations. The geological information was obtained from the SGM (01 of 12 of 2007); State Geological-Mining Chart, Campeche, Quintana Roo, Yucatán, SC. 1:500,000.
The Carrillo Puerto formation, as can be seen in Figure 2b, is considered the most important hydrogeological unit in the YP due to its geological characteristics, its large surface area, and also due to the shallowness of the groundwater with respect to the ground level [26]. There is an unconfined karstic aquifer, except for a thin strip parallel to the coast, where there is a semiconfined aquifer developed on unconsolidated Quaternary deposits formed by calcareous sands that can alternate with compacted silty clay deposits (in the wetland area) which overlay a well-consolidated clastic limestone [27,28]. The confined aquifer presents a marked interaction with hydrological forcings such as astronomical and storm tides, and with the effects of precipitation recharge and pumping for groundwater extraction [6]. There is some evidence of the presence of clay lenses in certain areas of the aquifer, but they tend to be local in extension and therefore do not act as significant aquitards [29,30]. The conceptual model of the regional aquifer considers a freshwater lens of variable thickness embedded in a carbonate matrix, floating on top of denser saltwater due to interactions with the sea. The thickness of the freshwater lens varies from a few meters near the coast to approximately 120 m at 90 km inland [30,31]. Several structural and tectonic features influence its regional hydrogeological characteristics, the most important in the study region being the Chicxulub sedimentary basin, the RC, and the Ticul fault [5,12].
As mentioned before, the study site is located on the western periphery of the RC, a regional geomorphological structure that has a high density of cenotes and water bodies called aguadas, which are a product of the dissolution and collapse of carbonate rocks. This ring is approximately 5 km wide and 90 km in radius and has been suggested to be a surface manifestation of the Chicxulub Crater, a deep-buried structure formed by the impact of a meteorite 66 million years ago [22,23]. Superficially, the RC demarcates a boundary between the unfractured limestone inside the ring and the fractured limestone outside [32]. The Mexican Geological Service (SGM) reports a series of fractures in the area formed by its periphery, which together with the great density of sinkholes, make up a very complex network of caverns and dissolution conduits that act as conduction paths for large masses of water.
The RC has been conceptualized as a preferential flow zone, where regional groundwater flows occur due to its geomorphological features. Other indicative characteristics of regional flows have been obtained from hydrogeochemical [33,34] and geophysical studies [16,17], among many others. Then, due to its intrinsic characteristics, groundwater flows that arrive from outside the ring are redirected toward the coastal areas of Celestún (to the west) and Dzilam de Bravo (to the east), which suggests an important hydrogeological feature around the Chicxulub sedimentary basin. Some authors have suggested the hydrogeological isolation of this basin from the rest of the YP [28,35,36,37] while others indicate that there may be flows that cross the RC toward the interior of the sedimentary basin, so the RC would not be an efficient drainage that leads groundwater around its periphery toward discharge points in coastal areas [38]. Figure 2b shows the groundwater flow directions, which were compiled by the Amigos de Sian Ka’an association based on various studies carried out along the YP aquifer by the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Mexico (UNAM), the National Water Commission (CNA or CONAGUA), and by Perry et al. [12], among many others. A more detailed analysis of this compilation can be consulted in the work of Bauer-Gottwein et al. [5].
Although the origin of sinkholes in the YP is due to the geomorphological process called karstification, several hypotheses would explain the initial formation of the RC, related to the tectonic activity of the Cenozoic carbonates deposited after the impact. Some of these formation hypotheses are the faulting reactivated by the post-Eocene–mid-Miocene basin loading [29], the collapse of breccias caused by the consolidation or solution of evaporite components [29], or due to the post-impact hydrothermal activity [39,40]. An existing model considers the presence of geothermal gradients that generated a convective circulation in the sequences of deposited carbonates, which would explain the hypogenic formation (from bottom to top) of the deep sinkholes located in the periphery of the ring [41]. However, as mentioned by Monroy-Ríos [41], despite the widely documented influence of the RC on regional groundwater flows, the influence of the deep crater structure on shallow groundwater flows is unclear.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ERT Measurements
Two ERT surveys were obtained using a SuperSting R1/IP AGI resistivity meter (Advances Geosciences Inc., Austin, TX, USA). For each transect, 36 stainless steel electrodes with a spacing of 5 m were used, covering a total distance of 175 m. The ERT 1 profile, corresponding to the first transect, was made with an approximate north–south orientation, while the ERT 2 profile, corresponding to the second, was carried out with an approximate east–west orientation. Two independent measurements were made on each transect using dipole–dipole (DD) and Wenner (W) electrode arrays. The dipole–dipole array is particularly sensitive to deep variations in lateral resistivity, making it suitable for detecting vertical structures, while the Wenner array has a high vertical resolution, making it suitable for detecting horizontal structures [42]. Before proceeding with the resistivity measurements, contact resistance tests were performed following the criteria established by Advances Geosciences Inc [43] to determine poorly placed electrodes or problems related to the DC current injection. Figure 1c shows the location and real orientation of these transects, which were carried out in February 2022, close to the driest period of the year (from March to April).
2.2. Inverse Modeling of Pseudosections
The real resistivity (2D inverted resistivity) sections of the aquifer were determined from the data of the apparent resistivity sections (pseudosections) measured in the fieldwork through the application of inverse modeling, a standard procedure in many areas of science that consists of determining the value or variation in a physical property by comparing their measurements with predictions of a proposed model [44,45]. Inverse problems present a particularly difficult challenge: no solution is guaranteed to be unique or stable, so different methodologies have been proposed to find an optimal solution to a given problem [46]. In the area of earth sciences, there is a wide variety of software, mostly commercial, that performs data inversion depending on the geophysical method implemented.
In this work, EarthImager 2D “https://www.agiusa.com/agi-earthimager-2d (accessed on 13 July 2024)” was used to invert the results of the apparent resistivity sections. Before proceeding with the inversion process, a data quality analysis was performed following the criteria established by Advances Geosciences Inc. [47] to filter or remove spurious and noisy data. The inversion parameters were those used in a karstic zone of the YP by Zamora-Luria et al. [18], which demonstrated effectiveness in understanding how the fracturing system is related to local hydrogeology. A more detailed description of the inversion process is given in Appendix A.1. It was not necessary to incorporate the topography in the numerical inversion process since the terrain where the measurements were made was flat. Additionally, the depth of investigation of each transect was determined from the inversion process based on the measurements themselves. To compare the quality between the measured and inverted data, different indicators were used: (1) the root mean square or RMS, (2) the L2 norm, and (3) the convergence curve of the numerical inversion process.
To perform the interpretation of real resistivity sections to identify several heterogeneities of the karst aquifer including (a) geological structures such as flooded caverns, dissolution conduits, and fractured limestone matrices; (b) the thicknesses of the vadose or unsaturated zone; (c) the thicknesses of the freshwater lens; and (d) the depth of saline interface, it was necessary to determine resistivity ranges associated with limestones saturated with freshwater, brackish water, and saltwater. For this purpose, the resistivity values reported in several ERT geophysical surveys in the YP were taken [16,17,18,19]. Table 1 presents a summary of the resistivity ranges of limestones that were used for the interpretation of the inverted resistivity sections. It is important to mention that these ranges should not be taken in a literal sense but only as a support guide, since in general they can vary depending on the study area due to the intrinsic petrophysical characteristics of carbonate rocks and the hydrochemical characteristics that define the type of groundwater [48].

Table 1.
Approximate values of the electrical resistivity for limestone rocks.
2.3. Estimation of Effective Porosity by Archie’s Law
The electrical conductivity (inverse of electrical resistivity) of karst aquifers is controlled by the water that saturates the volume of the interconnected pores (interstitial space) as well as by the structure and pore connectivity since in general the resistivity associated with carbonate rocks is too high [49]. In the case of the YP aquifer system, the carbonate rocks below the water table are saturated with freshwater, brackish water, or saltwater, depending on how deep they are from this level, while the rocks above it are found with different grades of saturation, from partially saturated to completely dry. Furthermore, groundwater can be classified into different types of water, which have different concentrations of salts and minerals that change their general properties, including their electrical properties such as their conductivity and resistivity. For this reason, electrical characterization methods such as ERT yield a broad range of resistivity values, so it is essential to know those associated with the different types of rocks that make up the aquifer system, as was mentioned in the previous section.
Archie [50] was a pioneer in the study of the electrical resistivity of saturated rocks and found an empirical relationship between the in situ electrical resistivity and the porosity of porous rock, with the resistivity of the fluid saturating the pore space. This relationship is called Archie’s Law and can be written in terms of resistivity as follows: where , , and are the effective resistivity of the rock, the resistivity of the fluid that saturates the rock, and the effective porosity of the rock sample, respectively. The parameters m and n are the cementation exponent and the tortuosity coefficient, respectively, which depend on the type of rock and its texture, and S is the grade of saturation of the fluid [51,52].
Archie’s Law has been widely used to estimate the porosities of several types of soils and aquifers [53,54,55,56]. In formations where the rocks are completely saturated, , then, solving for , the following expression is obtained: . As can be observed, knowing the resistivity of both the rock and the saturation fluid, as well as the parameters m and a, which characterize the rock sample, it is possible to obtain its effective porosity.
In this work, the previous equation was used to estimate the effective porosity sections of the aquifer along the measured transects, in the saturation zone, i.e., below the water table. In situ rock resistivity was obtained from ERT surveys, while groundwater conductivity was determined in places with access to groundwater using CastAway-CTD equipment (SonTek Xylem, San Diego, CA, USA) with a salinity accuracy of 0.1 PSU and resolution depth of 0.01 m. It is important to mention that in some sites, it is possible to measure vertical profiles of groundwater electrical conductivity (EC), for example in some deep sinkholes, so porosity estimates can take into account the stratification of water masses with depth. However, in this work, only the average groundwater resistivity was considered due to the lack of deep sinkholes within the study site. For m and a, the values associated with carbonate rocks of high permeability from a coastal area of the YP aquifer were used [57].
2.4. Hydrogeology Evaluation
The generation of maps of groundwater isolines from water level data is important in many disciplines, mainly in hydrogeology. There are many classical, deterministic, and geostatistical interpolation methods that have been implemented, some with greater precision than others [58]. In this work, water levels along the YP aquifer system were compiled from the scientific literature and the National Water Commission (CONAGUA) databases, and maps of groundwater isolines were calculated using two methods: Inverse Distance Weighting Interpolation (IDW), which is a deterministic method that has been widely used for many years, and Empirical Bayesian Kriging (EBK), which is a relatively recent method, which has been successfully implemented to evaluate the interannual water table evolution of Guanajuato aquifers [59].
In the IDW method, the water levels reported at different sampling sites are weighted according to the distance to the point where the value of the water table is to be estimated. For this purpose, the following equation is used: where is the average water level at the sampling site i, n is the number of points used in the interpolation process, is the distance between the i and j sites, and p is a weighting exponent that controls how the weight decreases with the separation distance. To perform the IDW interpolation, the QGIS software version 3.16.10 was used, with a recommended value of .
On the other hand, EBK is an improvement on classical geostatistical kriging developed by Krivoruchko and Gribov [60] within the ArcGis—ESRI® software environment “https://www.arcgis.com/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2024)”. The difference with classical kriging methods is that the latter estimates a variogram that is considered the true variogram of the observed data, so they do not explicitly consider the uncertainty of the choice, and as a consequence, they tend to underestimate the standard errors of the predictions. In contrast, EBK creates a spectrum of variograms, so its process accounts for the error introduced by estimating a variogram model in the first place. One of the advantages of this method is that it allows for moderate local and large non-stationarity in the data.
Additionally, from the interpolations of the water levels, maps of regional groundwater flows were generated using the Flow Net method [61], using Surfer® version from Golden Software, LLC “www.goldensoftware.com (accessed on 13 July 2024)”, and the QGIS version 3.34.5 software.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Inverted True Resistivity 2D Sections
Table 2 shows the indicators obtained from the inversion process of the apparent resistivity data for each electrode configuration in each transect using the EarthImager 2D version software. It also shows the indicators of the inversion process considering the joint data of the dipole–dipole and Wenner arrays. All reported values are similar and are within the accepted values for a good-quality inversion [47].

Table 2.
Number of iterations, RMS, and L2 norm values of the inversion process with EarthImager 2D.
Because all inverted sections presented similar characteristics, only the two sections (T1 DD-W and T2 DD-W) where the joint geophysical arrangements were used are shown, as they provide a better definition of the heterogeneity of the karst aquifer, both laterally and vertically.
Figure 3a shows the real resistivity section or ERT 1 profile for the transects with a north–south orientation (T1). The images are presented using the resistivity values on a logarithmic scale, associated with a palette of 64 colors.
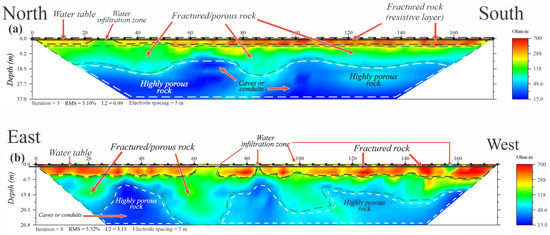
Figure 3.
(a) Interpretation of the real 2D resistivity profiles for transect T1 with a north–south orientation (ERT 1). (b) Interpretation of the real 2D resistivity profiles for transect T2 with an east–west orientation (ERT 2).
We can identify three different zones within this profile. The first zone (from orange to red, between the black dotted lines) represents the layer with the highest resistivity, with an approximate thickness of 4 m, and it is interpreted as a section of fractured limestone that corresponds to the outcrop seen in the field. This outcrop, of extreme hardness, is known locally as laja and is considered a product of the lithification of the original sediments [62]. They could also be attributed to the presence of calcarenites, which may contain silt compact layers that could be confining the aquifer near the surface. Within the same area, regions with yellow and green tones can be interpreted as areas with a highly fractured rock matrix. Therefore, there is a greater infiltration of water into surface sediments when it rains and a major retention of water by capillarity effects, increasing the moisture content in the pore space above the water table [63]. This fact explains the decrease in electrical resistivity values in some places near the surface. The water table for the ERT 1 profile is approximately one meter deep from the surface (the solid black line in Figure 3a), so the rock formation below this level is completely saturated and is related to the different water bodies present in the area.
The second zone (between the green dotted lines) has a resistivity range between 80 and 250 m and can be interpreted as the same fractured limestone with a higher effective porosity, i.e., there is a higher percentage of connected pores completely saturated with freshwater, which explains the decrease in the resistivity values. Unlike the first zone, in this zone, there is no defined thickness, since in some sections along the direction of the transect there are thicknesses of 10 m, while in other sections there are thicknesses of up to 25 m.
The last zone delimited is the one found at the greatest depth (between the white dotted lines). It is easy to identify it since it is distinguished by having a very low resistivity range (15–80 m). In this zone, there is a high percentage of porosity due to karst dissolution, which causes the water content in the pores to be higher, notably decreasing the real resistivity values. According to Table 1, resistivities between 10 and 20 m can be correlated to limestone saturated with brackish water, but in this case, due to the depth at which they occur, they are most likely associated with the presence of caves or dissolution conduits saturated with freshwater, which also tend to lower the effective resistivity. In fact, low resistivity anomalies associated with these possible structures can be identified in this figure. Additionally, this zone also has a variable thickness along the length of the transect.
On the other hand, Figure 3b shows the inverted resistivity section or ERT 2 profile for the transect with an east–west orientation (T2). Three zones with different resistivity ranges along this profile are also identified. The first zone (from orange to red, between the black dotted lines) presents a resistivity range between 350 and 700 m. This layer is the same as that found in the first profile, which is associated with the fractured limestones that outcrop on the surface. Some sections with a high fracturing grade near the surface are also identified, which leads to a greater infiltration of meteoric water. The water table is also located at a depth of 1 m with respect to the surface, so the subsoil is completely saturated below this depth.
The second zone (between the green dotted lines) has a resistivity range between 80 and 350 m. There are irregularities in its thickness due to the effects of karst dissolution, ranging from m in its narrowest part to 30 m in its widest part.
The third delimited zone (from black to blue, between the white dotted lines) presents a low resistivity in a range between 15 and 80 m. Several resistivity discontinuities are observed along this profile, identifying sections of low resistivity isolated from each other. The first of these sections can be observed between 25 and 50 m along the transect and at a depth between 9 and 27 m with respect to the surface and presents a resistivity range between 15 and 20 m. The second section is observed between 70 and 90 m along the transect and at a depth between 15 and 25 m and presents a resistivity range between 25 and 60 m. A third section can also be observed between 110 and 150 m along the transect, with a resistivity range similar to that of the first two sections. However, it is not clear if this last section is connected to the second or is isolated from it. The anomalies with the lowest resistivity are found within these sections, as can be seen in the figure.
A possible explanation for these resistivity anomalies is due to the presence of dissolution conduits oriented perpendicularly (or almost perpendicularly) to the direction of the east–west transect, so the ERT would be identifying their cross-sections. This would also explain the continuity of the third zone in the ERT 1 profile since T1 would be oriented parallel or almost parallel to these possible conduits. They could also be due to the presence of flooded caverns. However, if this were the case, a similar behavior would be observed in both profiles regardless of the direction. This reinforces the interpretation of possible dissolution conduits with orientations close to the north–south direction.
Notably, both inverted resistivity sections present typical characteristics reported for the YP karst aquifer. Given the proximity of the study site to the RC, these characteristics are similar to those obtained by Andrade-Gómez et al. [17], who conducted ERT surveys along the perimeter of the RC. The differences in resistivity between the different zones identified in the ERT1 and ERT2 profiles can be associated with the different resistivity units identified by these authors.
Regarding the thickness of the freshwater lens, it was not possible to determine it through vertical profiles of the groundwater EC due to the lack of deep sinkholes within the study site. However, it was possible to make a moderate estimate from ERT measurements. These were achieved due to two reasons. First, the collection of electrical resistivity values from ERT reported for caves and dissolution conduits flooded with freshwater along the YP aquifer [16,17,18,19,64]. Second, reports from CONAGUA monitoring wells in sites to the west of the RC, toward the Celestún area (thicknesses between 17 and 25 m) and within the Chicxulub sedimentary basin (thicknesses of up to 30 m) [65]. See Appendix A.3 for some of these sites. In general, the thicknesses decrease as the distance from the coast decreases and increases in the opposite directions. Based on the values reported for the thickness of the freshwater lens, and the resistivity values obtained from our ERT profiles, in which the presence of the saline intrusion is not observed up to the measured depths, we estimate a minimum thickness of the freshwater lens of 30 m, which is consistent with the estimated values from other geophysical measurements along the RC [17].
3.2. Effective Porosity Sections
The effective porosity sections were obtained by applying Archie’s Law to the inverted resistivity sections, at depths below the water table (where ), using a cementation exponent and a tortuosity coefficient of and [57], respectively. The groundwater EC was measured with the CastAway probe in two small disused quarries, which were permanently flooded due to their connection with the aquifer, and in a sinkhole; all the sites near the transects and with depths of the water column less than 2 m. The average groundwater resistivity (inverse of the average electrical conductivity) was 4.93 m.
Figure 4 shows the effective porosity sections for both transects (T1 and T2). As can be seen, the porosity varies in a range between 0.1 () and 0.60 (), typical of carbonate rocks with a high grade of karstification [66]. Only subsections close to the possible flooded caverns or dissolution conduits are presented in the image; that is, from 40 to 140 m for the first transect and from 30 to 145 m for the second transect.
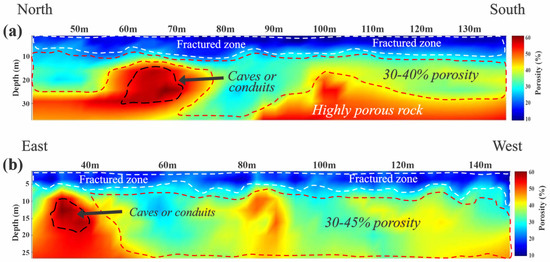
Figure 4.
Effective porosity sections obtained from profiles (a) ERT-1 and (b) ERT-2.
The porosity section corresponding to the ERT 1 profile, with a north–south orientation, clearly presents three zones. The first zone (delimited by the white dotted line) presents the lowest porosity values, in a range from to . The second zone (delimited by the red dotted line) presents higher porosities than the first zone, from to , due to the limestone-dissolution processes. On the other hand, the third zone (color from orange to black, with intermediate red) represents the highest porosity zone of the profile, with values ranging from to . In these areas, some anomalies are identified as possible dissolution conduits or flooded caverns (the area delimited by the black dotted line) with porosities greater than and at a depth of approximately 20 m. The third zone is the one with the highest grade of karstification or carbonate dissolution.
On the other hand, the porosity section corresponding to the ERT 2 profile, with an east–west orientation, also presents three zones. The first zone (delimited by the white dotted line) has a porosity range between and . This area is associated with the surface layer that can be seen in the first porosity section. A second zone is also identified (delimited by the red dotted line), which presents a porosity range between and . Finally, a third zone with porosities greater than is identified. This zone of high porosity can be associated with limestone rocks with a high grade of karstification, in which the presence of dissolution conduits or flooded caverns is observed (the area delimited by the black dotted line).
Additionally, from both images, it can be seen how the effective porosity gradually changes with depth, presenting highly karstified zones along each profile, mainly around the resistivity anomalies. Despite the complicated correlations between porosity and permeability in limestones [67], changes in porosity can be related to the development of permeability, which in carbonate aquifers is due to the variation in groundwater velocity with depth [68]. That is, permeability develops through water circulation and rock dissolution, so in areas where groundwater presents the highest velocities, the highest porosities can occur, e.g., in areas with the presence of caves and/or flooded dissolution conduits. Therefore, saturated zones where there is a higher level of karstification could represent zones or horizons of favored flow due to greater permeability [69].
3.3. Groundwater Flows
Measurements of water levels in the referenced sites were collected from reports in the scientific literature and open-access databases. These measurements cover the entire area of the RC and the northwestern section of the peninsular aquifer, from the Sierrita de Ticul to the north coast of the YP. The measurement sites were collected from the following sources: 10 monitoring sites reported by Canul-Macario et al. [70], with 12 measurements per site taken during the period from March 2013 to December 2015 (in rainy and dry periods); 63 sites in shallow wells reported by Sánchez y Pinto [71], with approximately 4 measurements per site, taken from October 1988 to April 1990; 32 sites registered in the CONAGUA’s Metropolitan Network with 11 measurements per site taken during the period from December 2013 to September 2018; and 70 sites registered in the CONAGUA’s Peninsular Piezometric Network with variable periods and variable measurements per site. It is important to mention that in the absence of information on the measurement sites, we refer generically to water levels for water table measurements in the free aquifer or possible piezometric heights in the semiconfined aquifer of the coastal strip. This last point is not trivial since measurements of hydraulic heads with piezometers in coastal areas can present great uncertainty due to large variations in groundwater density due to a dynamic groundwater environment, with a halocline that can move with the tides [72]. In this case, it is often necessary to convert the water level measured in coastal wells to pressure expressed as an equivalent freshwater head [72]. In our case, we omitted these corrections due to the lack of information from the reported monitoring sites.
The information in the water level database was cleaned and filtered to avoid the duplication of information and to eliminate sites outside the study area. Sites with a separation distance of less than 500 m were averaged due to the low hydraulic gradients reported for the north of the aquifer, which according to some reports present a range between 7 and 10 mm/km [35], while in others present a range between 17 and 25 mm/km [28], depending on the aquifer zone. The total number of sites selected after the filtering process was 129.
Maps of the groundwater isolines were estimated using the average value of the water level for the final 129 sites, following the procedure indicated in Section 2.4, through IDW and EBK interpolation. At this point, the generation of these maps deserves clarification. Strictly speaking, the water levels are representative of the period in which they were measured, so it is not entirely correct to combine data from all sites given the temporality of the sampling. The justification for combining them as a single data set lies in the fact that there is evidence that groundwater levels in the YP aquifer system remain relatively stable for long periods of time [28,73], i.e., they have an almost steady-state behavior. Furthermore, some large aquifers exhibit a steady-state behavior or are very close to it after a given period of time [74,75]. This means that there is a balance of the inflow and outflow of water to the system and therefore the long-term average state of the aquifer system is known. In aquifers with high permeability (and therefore high transmissibility), such as the YP karst aquifer, the transient response to a hydraulic disturbance, e.g., a pumping test, can occur so quickly that the aquifer returns to its stable state after a short period of time. In the case of extreme weather events such as hurricanes or cyclones, water levels may rise, and in some cases, extreme values may occur. [5,76]. However, after a period of resilience, these values tend to return to their steady-state values. Indeed, the estimated recovery time for typical recharge events in the YP karst aquifer can be a few days [30], while for atypical recharge events, it can be a few weeks or a few months [77,78].
Regarding temporal variations in groundwater levels, fluctuations of less than 1 m, associated with prolonged periods of drought, have been reported at distances of 10 km from the north coast of the YP in the Dzilam de Bravo town [79]. Similar variations have also been reported for the northeastern aquifer of the YP, in the Quintana Roo state, where the highest rainfall on the peninsula occurs [80]. On the other hand, the maximum standard deviation of the data reported by Canul-Macario et al. [70] is m at the site called Observatorio, located approximately 32 km from the north coast of the YP, while Sánchez y Pinto [71] reports variations of up to 4 m after a period of intense storms. Based on the analysis of the water level data available per site, and the temporal window of the database, it can be inferred that fluctuations in water levels occur within the same order of magnitude or less in all reported sites and that these levels have remained stable.
The steady-state approximation has already been used in the YP aquifer system as a suitable approximation to numerically model the residence times of contaminants and nitrates in the aquifer from Mérida to Progreso [11], and to simulate groundwater flows in the states of Yucatan [38] and Quintana Roo [80]. This approach, of course, does not take into account anthropogenic effects, which can cause irreversible changes in aquifer behavior due to excessive pumping, nor climate change, which causes changes in temperature and rainfall patterns [81,82].
For the above reasons, and due to the lack of long-term monitoring data in the northwest of the YP aquifer, it was considered as a first approximation that the average water level for selected sites is representative of their behavior in a steady state. Therefore, to understand its regional hydrogeology, the average values at these sites were used (regardless of the time window of each site) to generate the maps of groundwater isolines and to estimate the groundwater flow directions. However, the importance of having groundwater levels statistically representative of the long-term average state of the aquifer system is highlighted.
Maps with the location and average groundwater levels for all selected sites are presented in Figure 5, showing groundwater isolines for both IDW and EBK interpolation methods (see Appendix A.2 for additional information). The sites are indicated with orange, white, and green points for each reference, respectively, whereas water levels are indicated in meters above mean sea level (m a.s.l.). From this figure, it can be seen how the magnitude of the isolines decreases with proximity to the coast. It is also observed that, for the region south of the Sierrita de Ticul, and only for the IDW map, there is a slight variation in their magnitudes over short distances. For the area to the west of the RC, near the study site, a slight deformation of the isolines can be observed. This deformation presents small variations between rainy and dry periods, which has been previously indicated by CONAGUA [65]. This suggests a permanent character in their deformation, which can be associated with the geomorphological influence of the RC.
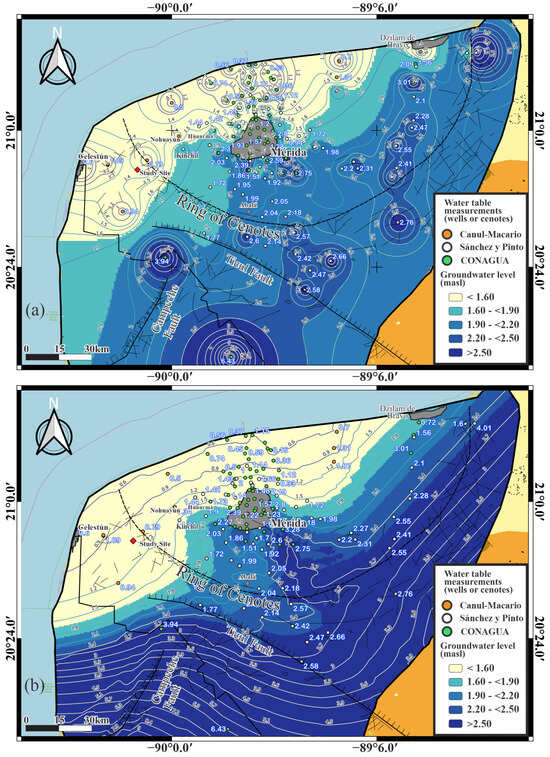
Figure 5.
Groundwater levels for the northwest aquifer of the Yucatán Peninsula considering a steady-state approximation. (a) IDW interpolation with and (b) Empirical Bayesian Kriging.
In the same figure, it can be observed how the coastal areas present water levels below 1 m and how these levels increase as the distance from the coast increases. For the IDW map, some inland zones can be observed where these values drop, which could represent local discharge zones, or it could be an artificial effect due to the interpolation method. In general, many differences can be observed in the groundwater level isolines due to the interpolation process used to generate them. It is important to mention that the EBK method is more precise since it considers the spatial correlation of water level data. However, given the low density of sampling sites in some areas outside the RC, and the inherent heterogeneity of the karst aquifer, the groundwater levels and groundwater flow directions in these areas should be taken with caution. The behavior of the water level isolines obtained with the EBK method, within the Chicxulub sedimentary basin and around the RC, resemble those obtained in numerical simulations by González-Herrera et al. [38].
On the other hand, maps with groundwater flow directions, generated from both interpolation methods, can be seen in Figure 6. It is important to mention some considerations made for the preparation of these maps using the Flow Net method [61]. The development of a Flow Net requires the implicit assumption that the flow is perpendicular to the isolines of the water level, i.e., the porous medium is isotropic, with flow in the direction of decreasing water levels. For an anisotropic medium, the flow lines intersect the isolines at an angle that depends on the degree of anisotropy in the flow plane and the orientation of the hydraulic conductivity tensor. Due to the lack of information on the degree of anisotropy of the karst bedrock, we consider as a first approximation for the analysis of groundwater flow directions that the porous medium is isotropic.
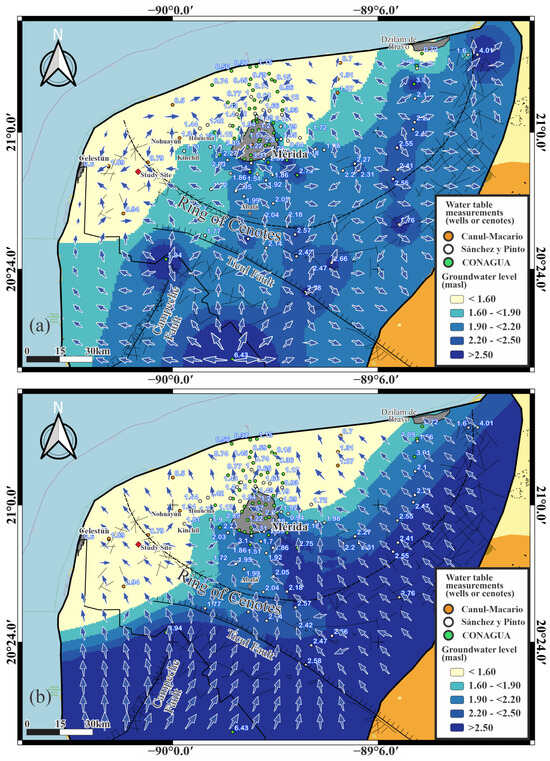
Figure 6.
Groundwater flows on a regional scale for the northwest aquifer of the Yucatán Peninsula considering a steady-state approximation and an isotropic porous medium. (a) IDW interpolation with and (b) Empirical Bayesian Kriging.
Under the isotropic medium assumption, groundwater flow directions are conceptualized perpendicular to the water level isolines and coincide with the directions of the negative hydraulic gradients, which helps a lot for a first hydrogeological interpretation. In fact, it has been reported that in some areas of the YP aquifer, regional hydraulic gradients coincide with the high-permeability directions, which suggests a direct relationship between hydraulic gradients and fracture orientations; in these same areas, groundwater flows have been assumed parallel to hydraulic gradients [30]. However, it must be kept in mind that this is not the general case and that the real groundwater directions can differ significantly when the anisotropy of the medium is taken into account.
The size of the flow vectors shown in Figure 6a,b is proportional to the magnitude of the hydraulic gradient. Then, since it is known that high-permeability areas of the YP karst aquifer have low hydraulic gradients [28,36], the areas of greatest permeability are characterized by having smaller flow vectors. Similarly, high hydraulic gradients may occur in areas where there are sudden changes in permeability along the terrain, or where there are wells close to each other, which may be penetrating different subsystems of the aquifer; so, they can be represented by having larger flow vectors. However, high hydraulic gradients may also occur around recharge areas, or due to abrupt topographic changes. Therefore, in areas with a low land slope or with almost uniform precipitation, high hydraulic gradients are more likely to be due to changes in permeability, e.g., a zone with low permeability in the YP aquifer was observed by Steinich et al. [83] in the vicinity of the town of Abalá near the Sierrita de Ticul, where there is no rain recharge to justify the high water levels measured, so these were necessarily associated with a decrease in the bedrock permeability.
The effect of topography and permeability on the behavior of groundwater flows is an effect well known from the studies carried out by Töth [84] and Freeze and Witherspoon [85]. However, given that large regions of the YP have a relatively flat topography with low slopes, where the aquifer recharge areas do not necessarily coincide with the higher-altitude zones [80], the flow behavior in these regions can be expected to be controlled primarily by the groundwater levels of the recharge areas and by the permeability of the bedrock [85]. Therefore, the topography high of the YP, mainly the Sierrita de Ticul, does not have a dominant influence on the groundwater pattern in the region, as has been pointed out by Back and Hanshaw [86]. The latter can be seen in the map in Figure 5b and Figure 6b, where it is not seen that topography alters appreciably the water level isolines or the flow pattern.
On the western periphery of the RC, a groundwater flow direction toward the northwest of the state following the directions of high fracturing along the edge of the RC (more visible in the EBK map) can be observed. This is consistent with the water level isolines cutting almost perpendicular to the west side of the RC, indicating flows along the perimeter. Groundwater flows can also be observed crossing in the southeastern section of the RC, which is also indicated by the contour isolines from Figure 5a,b. But, in this case, the flow directions change depending on the interpolation method used, which may be a real or an artificial effect due to the low density of the sampling sites used in both interpolation methods for this aquifer’s area. On the other hand, both interpolation methods produce groundwater flows similar to those inside the Chicxulub sedimentary basin. It is possible to observe the presence of parallel flows toward the coasts in some areas of the basin but with smaller hydraulic gradients, which suggests a high permeability [36] that increases as the distance from the coast decreases.
Inland zones where groundwater flows converge can also be identified from both maps in Figure 6. One of these zones corresponds to the city of Mérida. In this case, the flows converge due to the high demand for water resources to meet the needs of a growing population, which altered the direction of groundwater flows [7,30]. The other regional discharge zones are located to the south and southeast of the RC, in areas with a high density of fractures, as can be seen near the city of Ticul. These inland discharge zones could have a geomorphological origin; that is, they could be caused by geological depressions due to the collapse of carbonate rocks by the underground dissolution processes [30]. In the southern part of the RC, and to the north of the Sierrita de Ticul, the groundwater divide can be observed near the Abalá town, as indicated by Steinich et al. [83].
On the other hand, as can be seen from the ERT profiles and porosity sections, anomalies are identified that can be associated with possible dissolution conduits with orientations close to the north–south direction, which coincides with the groundwater flow direction that occurs to the north of the study site, as can be seen in both maps in Figure 6. This coincidence is not entirely by chance, since it has been observed that dissolution conduits tend to develop mainly in the direction of groundwater flows, where the permeability structure has evolved as a consequence of the dissolution of carbonates by the continuous flow of groundwater [30,71,87]. In fact, based on the analysis of well logs, Buckley et al. [69] described the presence of zones of preferential flows at different depths in some areas of the YP aquifer, related to different horizons where a high grade of karstification occurs. However, a confirmation of the real orientations of dissolution conduits would require further geophysical surveys, which is outside the scope of this work, so in this case, it is left only as a real possibility.
It is important to mention that although groundwater flows at a regional scale follow the directions shown in Figure 6, at a local scale, their behavior can be more complicated. This is due to local geological heterogeneities that can modify the flow directions in opposition to those indicated at regional scales, as has been reported in some areas of the YP aquifer [18,30]. Unfortunately, it was not possible to evaluate groundwater flows at a local scale due to the inaccessibility (private land) of the majority of water bodies around the study site. Regarding the groundwater flows, analyzing their directions based on maps created from a water-level-interpolation process is not enough, since these directions can differ significantly from those resulting from groundwater simulation models calibrated with field data, as has been highlighted by Escobedo-Cen [80] for the northeastern aquifer of the state of Quintana Roo. However, they provide a fairly general idea of the behavior of groundwater flow systems.
Finally, although some efforts have already been made to model the northwestern aquifer of the YP [35,38,71], more research is required to generate accurate models that explicitly include geological heterogeneities at different scales, as well as hydrodynamic parameters that change over time due to the evolution of the karst system, e.g., the hydraulic conductivity. This last point is of fundamental importance since the geomorphology and geology of the aquifer are not enough to establish its hydrodynamic behavior, as was pointed out by Kovács [88], who mentions that it is necessary to evaluate the temporal evolution of the aquifer system due to the dissolution of carbonate rocks, which modifies its hydrogeological properties over time.
4. Conclusions
In the study area, there is a shallow aquifer where the water table is approximately one meter deep from the surface. From the interpretation of the real resistivity sections, obtained from the ERT measurements, no indications of the saline intrusion phenomenon were identified, so the freshwater lens has an estimated thickness of at least 30 m.
Similarly, from the ERT measurements, the heterogeneities present in the aquifer were identified. Three units with different ranges of resistivity were observed, which presented different ranges of effective porosity, as can be observed when applying Archie’s Law to the real resistivity 2D sections. The porosities found range from to , which indicates a high grade of fracturing and/or karstification of the bedrock. The presence of possible flooded dissolution conduits with orientations close to the north–south direction was also discussed.
Maps of groundwater flow directions along the northwest section of the YP karst aquifer were estimated from water levels interpolated by two methods, IDW interpolation and EBK. Despite the differences between both methods and the data quality and density of the monitoring sites used to generate the maps, these reproduce qualitatively the conceptual behavior that exists for groundwater flows in some areas of this section of the peninsular aquifer. In particular, it was possible to observe the influence of the RC on the behavior of these flows on a regional scale. The presence of flows that apparently cross the ring in its eastern and southeastern sections was also observed. In addition, in the Chicxulub sedimentary basin, a decrease in the magnitude of the hydraulic gradients is observed as the distance from the coast decreases, indicating regions with limestones of high permeability. There are also areas of discharge inland, possibly associated with excessive pumping or the collapse of limestones, although they could also be due to an interpolation problem due to the low density of points in some areas. In general, groundwater flows are controlled primarily by the water levels and permeability of the karst medium.
Finally, a possible relationship is discussed between the direction of the dissolution conduits near the RC with the direction of the development of permeability, which can be inferred from the ERT, the porosity sections, and the directions of groundwater flows at a regional scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I. and J.C.M.-S.; methodology, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., G.A.-G. and J.H.H.-A.; software, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., J.H.H.-A. and Y.L.; validation, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., J.C.M.-S., C.C.-M., G.A.-G., A.G.-C., J.H.H.-A. and Y.L.; formal analysis, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., J.C.M.-S., C.C.-M., G.A.-G., A.G.-C., J.H.H.-A. and Y.L.; investigation, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., J.C.M.-S., C.C.-M., G.A.-G., A.G.-C., J.H.H.-A. and Y.L.; data curation, J.A.P.-B., L.G.A.-I., G.A.-G. and C.C.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.P.-B. and L.G.A.-I.; writing—review and editing, J.A.P.-B. and Y.L.; visualization, J.A.P.-B. and L.G.A.-I.; project administration, J.A.P.-B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
L.G.A.-I. acknowledges the support of a terminal undergraduate scholarship from CICY. J.A.P.-B., G.A.-G., and A.G.-C. acknowledge the support provided by the Investigadoras e Investigadores por México CONAHCYT program and also UG, CICY, and CIDESI. All the authors acknowledge Biol. Helder Berzunza for their support in the fieldwork and the National Water Commission (CONAGUA), Regional Management of the Yucatán Peninsula, for the support provided for the realization of the present research, the valuable monitoring of the Yucatán Peninsula aquifer, and the database collected during the study period. All the authors appreciate the corrections made by the editor and anonymous reviewers to improve the original manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Details of the Numerical Inversion of Apparent Resistivity Sections
To carry out the inversion process with the EarthImager 2D software, the following parameters recommended by [18] were used: As initial adjustments, voltage values lower than mV were discarded, and apparent resistivity values in a range between and m were considered. For the direct simulation, the finite element method and the Cholesky decomposition with Dirichlet-type boundary conditions were used. The apparent resistivity pseudosection was used as the initial resistivity model. For the inversion stage, a maximum number of 15 iterations and an RMS of were considered.
There are other commercial and/or free software that can numerically invert the resistivity results obtained in the field, which, in principle, should give similar results. For example, Figure A1 shows the results for transects T1 and T2 using ZondRes2D “http://zond-geo.com/english/zond-software/ert-and-ves/zondres2d/ (accessed on 13 July 2024)” and Res2DInv “https://www.geotomosoft.com/downloads.php (accessed on 13 July 2024)” commercial software. For the inversion with them, parameters similar to those used with EarthImager were used. As can be seen from this figure, the results are similar to those described in Section 3.1.
In addition, with the ZondRes2D software, the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm was selected, which is an inversion algorithm that uses the damped least-squares (DLS) method. In this case, only apparent resistivity values between and m were considered. The average of the apparent resistivity values was used as the initial resistivity model. For the inversion stage, a maximum number of 10 iterations and an RMS value of were considered, with an error reduction of . The main use of this last parameter is to avoid overfitting the data, so the inversion stops if the RMS no longer changes significantly from the previous result. For the direct simulation, the program uses the finite element method.
For the Res2DInv, apparent resistivity measurements between and m were considered. The software’s inversion algorithm is based on the smoothness-constrained least-squares method, and the equations are solved using the Gauss–Newton method. Similarly, a maximum number of 10 iterations and an RMS value of were considered, with an error reduction of . As with the ZondRes2D software, the average of the apparent resistivity values is considered as the initial resistivity model. For the direct simulation, the finite element method was used.
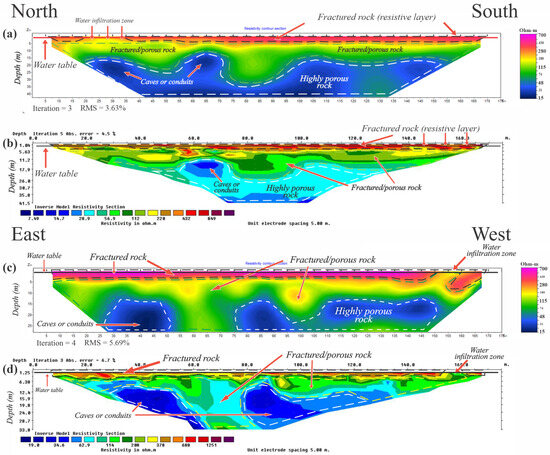
Figure A1.
(a,b) Interpretation of the real 2D resistivity profiles for transect T1 with a north–south orientation (ERT 1) using ZondRes2D and Res2DInv software, respectively. (c,d) Interpretation of the real 2D resistivity profiles for transect T2 with an east–west orientation (ERT 2) using ZondRes2D and Res2DInv, respectively.
Appendix A.2. Additional Information on Interpolation Methods
Figure A2 shows the groundwater isoline images obtained for the cases and , while Figure A3 shows the respective groundwater flow directions. For IDW interpolation, a recommended value of the weight exponent was used to compare with the EBK method. As the value of p increases, the weights of distant points decrease rapidly. If the p value is very high, only the immediate surrounding points will influence the prediction. There is no particular reason to prefer this value; however, the effect of changing the p value must be evaluated for each study case through a statistical cross-validation analysis and by previewing the results. In our case, since the EBK method was statistically validated with field data [59], and is more reliable for estimating water levels, the IDW image was chosen with the parameter p that best approximated the EBK image to the naked eye.
In the case of interpolation with the EBK method, it is important to mention that the model residuals pass the Kolmogorov–Smirnov Normality Test ( with a p-value ). Table A1 shows the calibrated parameters for the final variogram, while Figure A4 presents the cross-validation data and the respective QQ plot of the data.
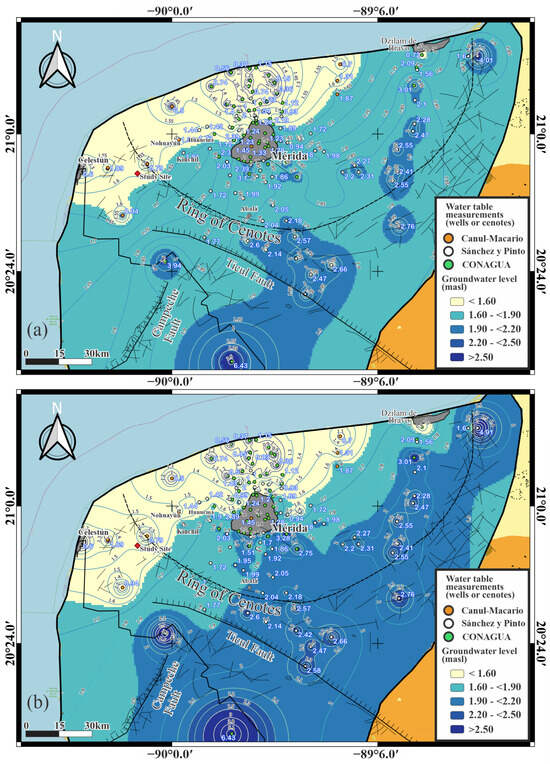
Figure A2.
Groundwater levels for the northwest aquifer of the Yucatán Peninsula considering a steady-state approximation. (a) IDW interpolation with and (b) IDW interpolation with .
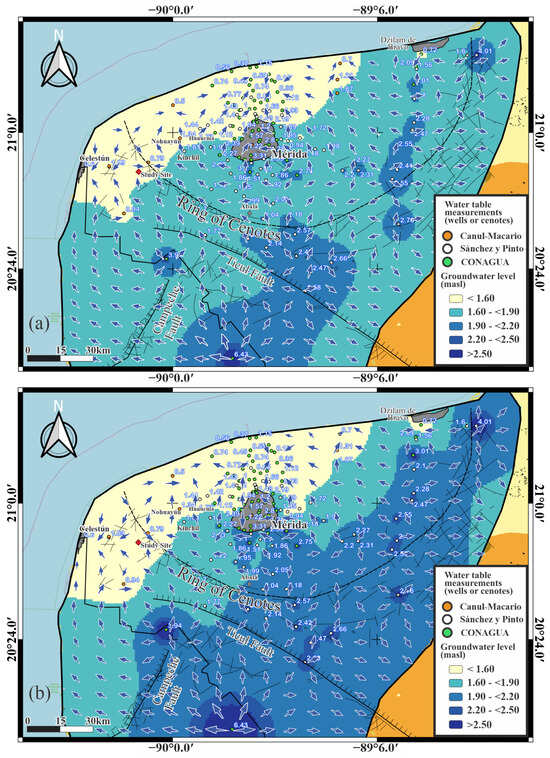
Figure A3.
Groundwater flows on a regional scale for the northwest aquifer of the Yucatán Peninsula considering a steady-state approximation and an isotropic porous medium. (a) IDW interpolation with and (b) IDW interpolation with .

Table A1.
Calibrated parameters for the final semivariogram using the EBK method.
Table A1.
Calibrated parameters for the final semivariogram using the EBK method.
| Subset size | 23 |
| Overlap factor | 1 |
| Number of simulations | 100 |
| Output surface type | Prediction |
| Transformation | Empirical |
| Semivariogram type | K-Bessel Detrended |
| Neighborhood type | Standard Circular |
| Maximum neighbors | 15 |
| Minimum neighbors | 10 |
| Sector type | 1 |
| Angles | 0 |
| Radius | 10,000 |
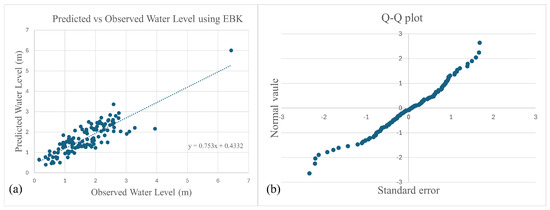
Figure A4.
(a) Cross-validation between observed and predicted water levels and (b) QQ plot of the data.
Appendix A.3. CONAGUA Monitoring Wells
Figure A5 presents a map with the location of three sites with Conagua monitoring wells with the salinity profiles of each one.
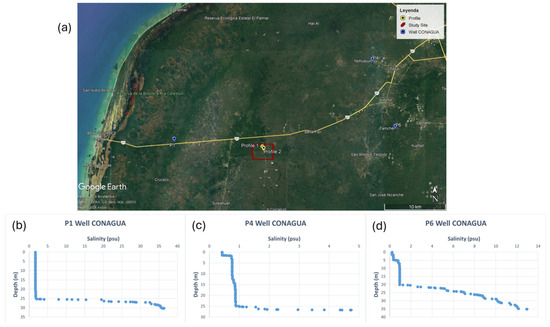
Figure A5.
Location of some sites with CONAGUA monitoring wells. (a) Map of the zone, indicating the study site, and the well sites; (b–d) salinity profiles for wells P1, P4, and P6, respectively.
It can be seen that the thickness of the freshwater lens in these sites is between 20 and 25 m. Given that large masses of groundwater flow on the periphery of the RC, the thickness of the freshwater lens at our study site should be slightly greater than those reported by CONAGUA, which is consistent with our estimated value of 30 m.
However, it is important to note that despite the widely known behavior of the thickness of the freshwater lens, which decreases with distance from the coast and increases inland, CONAGUA detected sites that do not comply with this pattern, as can be seen in profile P6, near the town of Tamchén, south of the town of Kinchil. At this site, the thickness of the freshwater lens is less than at other sites near the coast, and since the halocline is thicker, it would be an indication of hydrogeological heterogeneity at a local scale [89].
References
- Torres-Díaz, M.C.; Basulto-Solís, Y.Y.; Cortés-Esquivel, J.; García-Uitz, K.; Koh-Sosa, A.; Puerto-Romero, F.; Pacheco-Ávila, J.G. Vulnerability and risk assessment of groundwater pollution in Yucatan. Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2014, 1, 189–203. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Duarte, Y.; Bautista, F.; Mendoza, M.E.; Frausto, O.; Ihl, T.; Delgado, C. IVAKY: Índice de la vulnerabilidad del acuífero kárstico Yucateco a la contaminación [IVAKY: Index of the vulnerability of the Yucatecan karst aquifer to contamination]. Rev. Mex. Ing. Química 2016, 15, 913–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gómez, M.; Martínez-Salvador, C.; Moulahoum, A.W.; Liedl, R.; Stefan, C.; Pacheco, J. First Steps into and Integrated Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Approach (IKAV). Groundwater Vulnerability Analysis of the Yucatan Karst, Mexico. Water 2019, 11, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batllori, E.; Canto, S. Vulnerabilidad intrínseca a la contaminación del acuífero kárstico en Yucatán, considerando las anomalías gravimétricas de Bouguer [Intrinsic vulnerability to pollution of the Yucatán karst aquifer, as determined by means of Bouguer gravimetric anomalies]. Boletín Soc. Geológica Mex. 2022, 74, A130921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Gondwe, B.R.N.; Charvet, G.; Marin, L.E.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Merediz-Alonso, G. Review: The Yucatán Peninsula karst aquifer, Mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2011, 19, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canul-Macario, C.; Salles, P.; Espriú, A.H.; Pacheco-Castro, R. Empirical relationships of groundwater head-salinity response to variations of sea level and vertical recharge in coastal confined karst aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, L.E.; Steinich, B.; Pacheco, J.; Escolero, O.A. Hydrogeology of a contaminated sole-source karst aquifer, Mérida, Yucatán, México. Geofísica Int. 2000, 39, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.; Cabrera, A. Groundwater Contamination by Nitrates in the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 5, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco-Rodríguez, A.G.; López, M.I.R.; Casillas, A.D.; León, J.A.A.; Banik, S.D. Impact of pesticides in karst groundwater. Review of recent trends in Yucatan, Mexico. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Sickman, J.O.; Fargher, L.; Herrera-Silveira, J.; Lucero, D.; Oceguera-Vargas, I.; Lamas-Cosío, E.; Robledo-Ardila, P.A. Groundwater Quality in the Yucatan Peninsula: Insights from Stable Isotope and Metal Analysis. Groundwater 2021, 59, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Salvador, C.; Moreno-Gómez, M.; Liedl, R. Estimating Pollutant Residence Time and NO3 Concentrations in the Yucatan Karst Aquifer; Considerations for an Integrated Karst Aquifer Vulnerability Methodology. Water 2019, 11, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, E.; Velazquez-Oliman, G.; Marin, L. The Hydrogeochemistry of the Karst Aquifer System of the Northern Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Int. Geol. Rev. 2002, 44, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresic, N.; Mikszewski, A. Hydrogeological Conceptual Site Models; Taylor & Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, Y.; Hubbard, S. Stochastic Forward and Inverse Modeling: The Hydrogeophysical Challenge: In Hydrogeophysics; Water Science and Technology Library, Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binley, A.; Hubbard, S.S.; Huisman, J.A.; Revil, A.; Robinson, D.A.; Singha, K.; Slater, L.D. The emergence of hydrogeophysics for improved understanding of subsurface processes over multiple scales. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3837–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Nicolás, M.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Canto-Lugo, E.; Huerta-Quintanilla, R.; Ochoa-Sandoval, P. Connectivity in a karst system using electrical resistivity tomography and network theory. Groundwater 2017, 56, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Gómez, L.; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M.; Andrade, J.L.; López, P.Z.; Estrada-Contreras, J. Karstic aquifer structure from geoelectrical modeling in the Ring of Sinkholes, Mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Luria, J.C.; Perera-Burgos, J.A.; González-Calderon, A.; Marin-Stillman, L.E.; Leal-Bautista, R.M. Control of fracture networks on a coastal karstic aquifer: A case study from northeastern Yucatán Peninsula (Mexico). Hydrogeol. J. 2020, 28, 2765–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villela-y-Mendoza, A.; Perez-Flores, M.A.; Ochoa-Tinajero, L.E.; Vargas-Huitzil, E. Applying resistivity (dipole-dipole, Schlumberger, and Wenner) joint inversion to detect endokarst features in Quintana Roo, México. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2021, 106, 103041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanco-Rodríguez, A.G.; Navarro-Alberto, J.A.; Solorio-Sánchez, J.; Mena-Rejón, G.J.; Marrufo-Gómez, J.; Del Valls-Casillas, T.A. Contamination by organochlorine pesticides in the aquifer of the Ring of Cenotes in Yucatán, México. Water Environ. J. 2014, 29, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derriene, M.; Arcega-Cabrera, F.; Velazquez-Tavera, N.L.; Kantún-Manzano, C.A.; Cappela-Vizcaino, S. Sources and distribution of organic matter along the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatan, Mexico: Sterol markers and statistical approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.R.; Pilkington, M.; Connors, M.; Ortiz-Aleman, C.; Chavez, R.E. Size and structure of the Chicxulub crater revealed by horizontal gravity gradients and cenotes. Nature 1995, 376, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Fucugauchi, J.; Camargo-Zanoguera, A.; Pérez-Cruz, L.; Pérez-Cruz, G. The Chicxulub multi-ring impact crater, Yucatán Carbonate platform, Gulf of Mexico. Geofís. Int. 2011, 50, 99–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterlin, J. Reconocimiento geológico preliminar del territorio de Quintana Roo [Preliminary geological reconnaissance of the territory of Quintana Roo]. BoletÍn Asoc. Mex. Geólogos Pet. 1958, 10, 531–564. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, W.C.; Keller, G.; Stinnesbeck, W.; Adatte, T. Yucatán subsurface stratigraphy: Implications and constraints for the Chicxulub impact. Geology 1995, 23, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gil, G.; Graniel-Castro, E. Geología. Biodivers. Desarro. Hum. Yucatán 2000, 10, 531–564. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, E.C.; Swift, J.; Gamboa, J.; Reeve, A.; Sanbon, R.; Marín, L.E.; Villasuso, M. Geological and environmental aspects of surface cementation, north coast, Yucatan, Mexico. Geology 1989, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batllori-Sampedro, E.; González-Piedra, J.I.; Diáz-Sosa, J.; Febles-Patrón, J.L. Caracterización hidrológica de la región costera noroccidental del estado de Yucatán, México [Hydrological characterization of the northwestern coastal region of the state of Yucatán, México]. Investig. Geogr. 2006, 59, 74–92. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, E.; Marin, L.; McClain, J.; Velazquez, G. Ring of Cenotes (sinkholes), northwest Yucatan, Mexico: Its hydrogeologic characteristics and possible association with the Chicxulub impact crater. Geology 1995, 23, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinich, B.; Marin, L.E. Determination of flow characteristics in the aquifer of the Northwestern Peninsula of Yucatan, Mexico. J. Hydrol. 1997, 191, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanshaw, B.B.; Black, W. Chemical mass-wasting of the northern Yucatan Peninsula by groundwater dissolution. Geology 1980, 8, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, K.O.; Ocampo, A.C.; Duller, C.E. Surficial geology of the Chicxulub impact crater, Yucatan, Mexico. Earth Moon Planets 1993, 63, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ceballos, R.; Pacheco-Ávila, J.; Euán-Avila, J.I.; Hernández-Arana, H. Regionalization Based on Water Chemistry and Physicochemical Traits in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatan, Mexico. J. Cave Karst Stud. 2012, 74, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ceballos, R.; Canul-Macario, C.; Pacheco-Castro, R.; Pacheco-Avila, J.; Euán-Ávila, J.; Merino-Ibarra, M. Regional Hydrogeochemical Evolution of Groundwater in the Ring of Cenotes, Yucatán (Mexico): An Inverse Modelling Approach. Water 2021, 13, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, L.E. Field Investigations and Numerical Simulation of Groundwater Flow in the Karstic Aquifer of Northwestern Yucatan, Mexico. Ph.D. Thesis, Northern Illinois University, DeKalb, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, L.E.; Perry, E.C. The hydrogeology and contamination potential of northwestern Yucatán, Mexico. Geofís. Int. 1994, 33, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolero, O.A.; Marin, L.E.; Steinich, B.; Pacheco, J. Delimitation of a hydrogeological reserve for a city within a karstic aquifer: The Merida, Yucatan example. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2000, 51, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Herrera, R.; Sánchez-y-Pinto, I.; Gamboa-Vargas, J. Groundwater-flow modeling in the Yucatan karstic aquifer, Mexico. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Sanchez, J.E.; Urrutia-Fuccugauchi, J. Chicxulub crater post-impact hydrothermal activity—Evidence from Paleocene carbonates in the Santa Elena boreholes. Geofís. Int. 2010, 49, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.L.; Osinski, G.R.; Longstaffe, F.J.; Schmieder, M.; Kring, D.A. Hydrothermal alteration associated with the Chicxulub impact crater upper peak-ring breccias. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Ríos, E. Advancements in Our Understanding of the Yucatán Platform: Sedimentary Geology and Geochemestry, Speleogenesis, Chicxulub Ring of Cenotes, and Tectonic Stability. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.M. An Introduction to Applied and Environment Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Advances Geosciences Inc. The SuperSting with Swift Automatic Resistivity and Ip System —Instructor Manual; Advances Geosciences: Austin, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, S.; Dusseault, M.B.; Nobes, D.C. Inversion techniques applied to resistivity inverse problems. Inverse Probl. 1994, 10, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Verma, G.K. Inversion of Electrical Resistivity Data: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Ecol. Geol. Geophys. Eng. 2015, 9, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aster, R.C.; Borchers, B.; Thurber, C.H. Parameter Estimation and Inverse Problems; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Advances Geosciences Inc. Instruction Manual for EarthImager 2D Version 2.4.2—Resistivity and IP Inversion Software; Advances Geosciences: Austin, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cejudo, E.; Ortega-Almazán, P.J.; Ortega-Camacho, D.; Acosta-González, G. Hydrochemistry and water isotopes of a deep sinkhole in north Quintana Roo, Mexico. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 116, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwer, K.; Eberli, G.P.; Weger, R.J. Effect of pore structure on electrical resistivity in carbonates. AAPG Bull. 2011, 95, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archie, G.E. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics. Trans. AIME. Soc. Pet. Eng. 1942, 146, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.N.; Kenyon, W.E.; Takezaki, H.; Petricola, M.J. Formation factor of carbonate rocks with microporosity: Model calculations. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 1997, 17, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, J.H.; Javaherian, A.; Pishvaie, M.R.; Nabi-Bidhendi, M. An approach to defining tortuosity and cementation factor in carbonate reservoir rocks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2008, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, P.; Clément, R.; Bouvier, C. Monitoring soil water content and deficit using Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT)—A case study in the Cevennes area, France. J. Hydrol. 2010, 380, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwas, S.; Celik, M. Equation estimation of porosity and hydraulic conductivity of Ruhrtal aquifer in Germany using near surface geophysics. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 84, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, D.; Yeboah-Forson, A. Electrical resistivity and porosity structure of the upper Biscayne Aquifer in Miami-Dade County, Florida. J. Hydrol. 2015, 531, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazakis, N.; Vargemezis, G.; Voudouris, K.S. Estimation of hydraulic parameters in a complex porous aquifer system using geoelectrical methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo-Corzo, J.A. Modelación geoestadística de la porosidad y la conductividad hidráulica de un acuífero kárstico costero [Geostatistical modeling of porosity and hydraulic conductivity in a coastal karst aquifer]. Master’s Thesis, Unidad de Ciencias del Agua—Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán, Quintana Roo, Mexico, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shahmohammadi-Kalalagh, S.; Taran, F. Evaluation of the classical statistical, deterministic and geostatistical interpolation methods for estimating the groundwater level. Int. J. Energy Water Resour. 2021, 5, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hernandez, J.H.; Aviles, M.; Knappett, P.S.; Giardino, J.R.; Miranda, R.; Puy, M.J.; Padilla, F.; Morales, J. Empirical Bayesian Kriging method to evaluate inter-annual water-table evolution in the Cuenca Alta del Río Laja aquífer, Guanajuato, México. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, K.; Gribov, A. Evaluation of empirical Bayesian kriging. Spat. Stat. 2019, 32, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, C.W. Applied Hydrogeology, 4 ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Medina, H.; Jiménez-Osornio, J.J.; Álvarez-Rivera, O.; Barrientos-Medina, R.C. The karst of Yucatan: Its origin, morphology and biology. Acta Univ. 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Shen, C.J.; Xin, P.; Song, Z.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A.; Jeng, D.S.; Stagnitti, F.; Lockington, D.A.; Parlange, J.Y. Capillary effect on water table fluctuations in unconfined aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 49, 3064–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo, E.; Acosta-González, G.; Ortega-Camacho, D.; Perera-Burgos, J.A.; Leal-Bautista, R.M. Caracterización hidroquímica y geofísica de una descarga de agua subterránea en Quintana Roo, México [Hydrochemical and geophysical characterization of a groundwater discharge in Quintana Roo, Mexico]. Ecosistemas Recur. Agropecu. 2022, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAGUA. Medición Piezométrica en el Acuífero Costero (litoral Poniente) de la Península de Yucatán, Estado de Yucatán [Piezometric Measurement in the Coastal Aquifer (Western Coast) of the Yucatán Peninsula, State of Yucatán]. 2002. Available online: https://sigagis.conagua.gob.mx/rp20/ (accessed on 13 July 2024).
- Lucia, F.J. Carbonate Reservoir Characterization—An Integrated Approach, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, P.; Cantrell, D.; Zaretskiy, Y.; Jobe, D.; Agar, S.M. Improved quantification of the porosity-permeability relationship of limestones using petrographical texture. Pet. Geosci. 2018, 24, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrande, H.E.; Stringfield, V.T. Development and Distribution of Permeability in Carbonate Aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1971, 7, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.K.; Macdonald, D.; Villasuso, P.M.; Graniel, C.E.; Vázquez, M.J.; Virgilio, J.M. Geophysical logging of a karstic limestone aquifer for hydrogeological purposes at Merida, Yucatan, Mexico. Br. Geol. Survey. Tech. Rep. WD 1994, 94, 194/4C. [Google Scholar]
- Canul-Macario, C.; Salles, P.; Hernández-Espriú, J.A.; González-Herrera, R. Simulación numérica de flujo y transporte de solutos de la porción noroeste del acuífero cárstico Península de Yucatán [Numerical simulation of flow and solute transport of the northwestern portion of the Yucatán Peninsula karstic aquifer]. Química Calid. Contam. Agua 2018, 1, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez y Pinto, I.A. Modelo Numérico del Flujo Subterráneo de la Porción Acuífera N-NW del Estado de Yucatán: Implicaciones Hidrogeológicas [Numerical Model of the Groundwater Flow of the N-NW Aquifer Portion of the State of Yucatán: Hydrogeological Implications]. Master’s Thesis, Universidad Autonoma de Chihuahua, Chihuahua, Mexico, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Costall, A.R.; Harris, B.D.; Teo, B.; Schaa, R.; Wagner, F.M.; Pigois, J.P. Groundwater Throughflow and Seawater Intrusion in High Quality Coastal Aquifers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, W.; Hanshaw, B. Hydrogeochemistry of the Northern of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico with a Section on Mayan Water Practices. In Field Seminar on Water and Carbonate Rocks of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico; Weidie, A.E., Ed.; New Orleans Geological Society: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1974; pp. 53–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, J. Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media; Dover Publications, Inc.: Garden City, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau-Gueutin, P.; Love, A.J.; Vasseur, G.; Robinson, N.I.; Simmons, C.T.; de Marsily, G. Time to reach near-steady state in large aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6893–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escolero, O.; Marin, L.E.; Domínguez-Mariani, E.; Torres-Onofre, S. Dynamic of the freshwater-saltwater interface in a karstic aquifer under extraordinary recharge action: The Merida Yucatan case study. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graniel-Castro, E.; Yam-Caamal, J. Efectos del Huracán Wilma al acuífero de la Península de Yucatán, México [Effects of Hurricane Wilma on the aquifer of the Yucatán Peninsula]. Tecnología Ciencias Agua 2014, 5, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, S.E.; Reinhardt, E.G.; Stastna, M.; Coutino, A.; Werner, C.; Collins, S.V.; Devos, F.; Maillot, C.L. Hurricane Ingrid and Tropical Storm Hanna’s effects on the salinity of the coastal aquifer, Quintana Roo, Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, I.; no Tapia, I.M.; Enriquez, C. Effects of drought and subtidal sea-level variability on salt intrusion in a coastal karst aquifer. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Cen, I.D. Modelación Regional en Estado Estacionario del Acuífero Noreste de Quintana Roo [Regional Modeling in Steady State of the Northeast Aquifer of Quintana Roo]. Master’s Thesis, Unidad de Ciencias del Agua—Centro de Investigación Científica de Yucatán, Quintana Roo, Mexico, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rotzoll, K.; Fletcher, C.H. Assessment of groundwater inundation as a consequence of sea-level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Neupane, S.; Mohanasundaram, S.; Pandey, V.P. Mapping groundwater resiliency under climate change scenarios: A case study of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinich, B.; Olimán, G.V.; Marín, L.E.; Perry, E. Determination of the groundwater divide in the karst aquifer of Yucatán, México, combining geochemical and hydrogeological data. Geofís. Int. 1996, 35, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töth, J. A Theoretical Analysis of Groundwater Flow in Small Drainage Basins. J. Geophys. Res. 1963, 68, 4795–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeze, R.A.; Witherspoon, P.A. Theoretical Analysis of Regional Groundwater Flow. 2. Effect of Water-Table Configuration and Subsurface Permeability Variation. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, W.; Hanshaw, B.B. Comparison of Chemical Hydrogeology of the Carbonate Peninsulas of Florida and Yucatan. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 330–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouves, J.; Viseur, S.; Arfib, B.; Baudement, C.; Camus, H.; Collon, P.; Guglielmi, Y. Speleogenesis, geometry, and topology of caves: A quantitative study of 3D karst conduits. Geomorphology 2017, 298, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, A. Quantitative classification of carbonate aquifers based on hydrodynamic behaviour. Hydrogeol. J. 2021, 29, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batllori-Sampedro, E.A.; Canto-Mendiburu, S.N. Relationship between the Map of Bouguer Anomalies and the Geohydrological Characteristics of the Karst Aquifer of Yucatán. A Review on the Water Vulnerability. J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).