Distribution and Comprehensive Risk Evaluation of Cr, Cd, Fe, Zn, and Pb from Al Lith Coastal Seawater, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
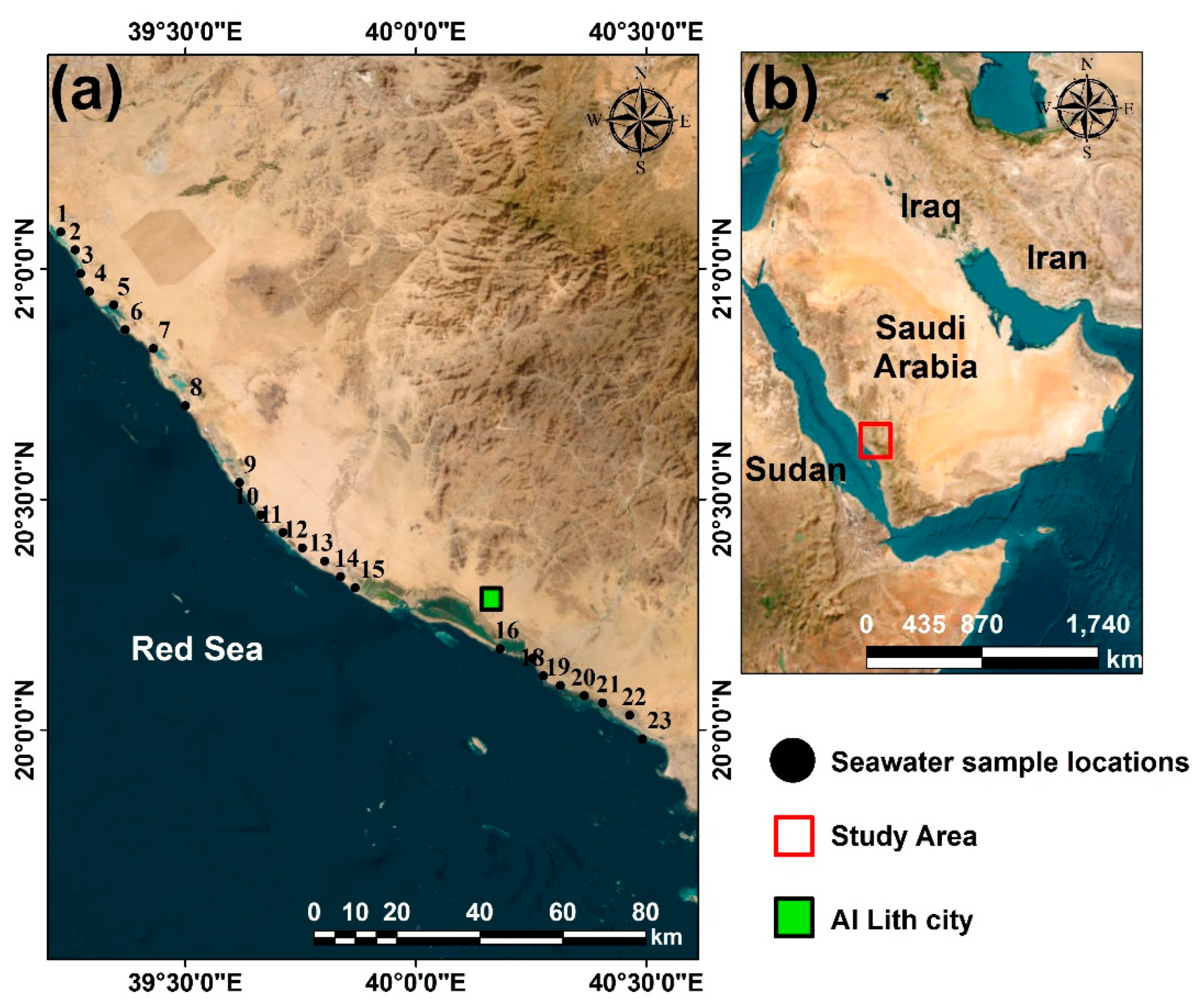
2.1. Study Area and Analytical Methods
2.2. Pollution Indices and Multivariate Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
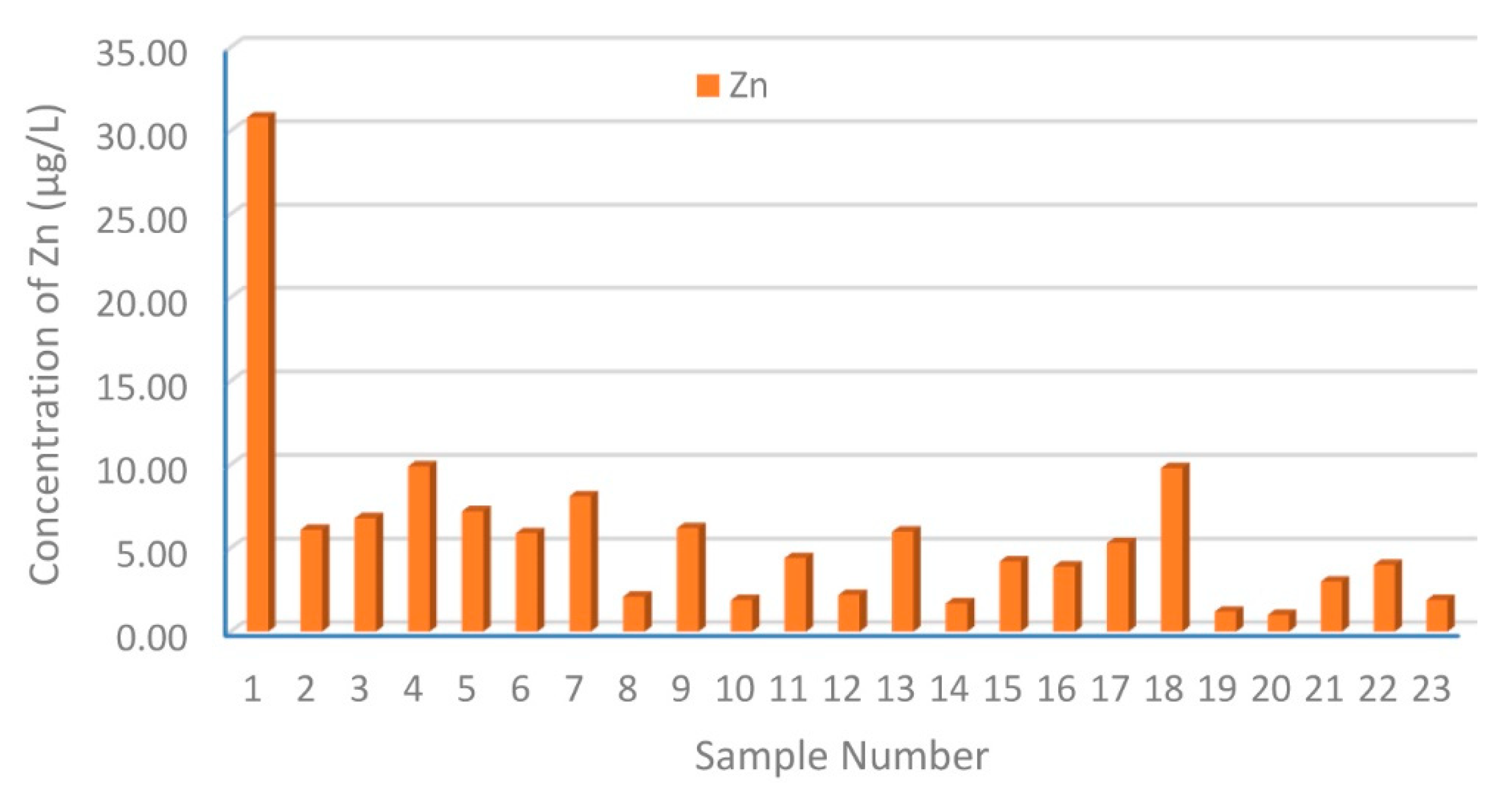
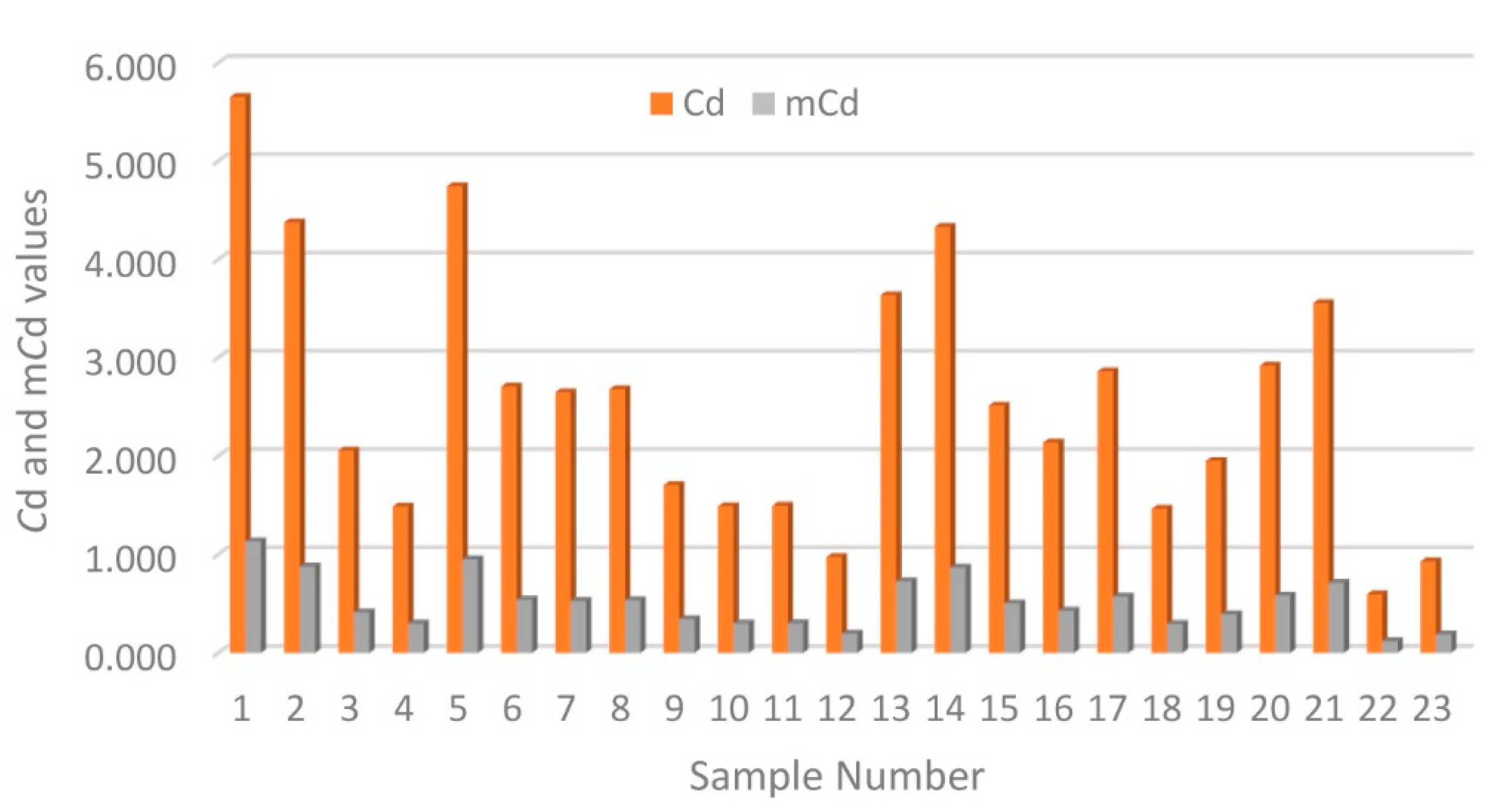
3.1. Distribution and Contamination Assessment of HMs
3.2. Ecological Assessment of HMs
3.3. Potential Sources of HMs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Zou, X.; Feng, Z.; Hao, Z.; Gao, J. Distribution and transport of heavy metals in estuarine–inner shelf regions of the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Er-Ramy, N.; Nachite, D.; Anfuso, G.; Williams, A.T. Coastal Scenic Quality Assessment of Moroccan Mediterranean Beaches: A Tool for Proper Management. Water 2022, 14, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pásková, M.; Štekerová, K.; Zanker, M.; Lasisi, T.T.; Zelenka, J. Water pollution generated by tourism: Review of system dynamics models. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.G.; Li, J. Impact of environmental regulations on industrial structure upgrading: An empirical study on Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azdem, D.; Mabrouki, J.; Moufti, A.; El Hajjaji, S.; Fatni, A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in seawater in Agadir coastline, Morocco. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 317, 100129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athar, M.; Vohora, S.B. Heavy Metals and Environment; New Age International: Delhi, India, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiq, H.B.; Ajaz, M.; Rasool, S.A. Bacterial and toxic pollutants in lakes of river Indus. Pak. J. Bot. 2011, 43, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar]
- Hader, D.-P.; Helbling, E.W.; Villafane, V.E. Anthropogenic Pollution of Aquatic Ecosystems; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; 426p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Interactions of trace metals and different marine food chains. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 243, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffan, J.J.; Brevik, E.C.; Burgess, L.C.; Cerdà, A. The effect of soil on human health: An overview. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadin, H.; Ashizawa, A.; Stevens, Y.; Llados, F.; Diamond, G.; Sage, G.; Quinones, A.; Bosch, S.; Swarts, S. Toxicological Profile for Lead, Atlanta (GA): Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (US); Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nishijo, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Suwazono, Y.; Nogawa, K.; Kido, T. Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: A nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e015694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, N.B.E.; El-Fiky, A.A.; Mostafa, A.R.; Al-Mur, B.A. Metal pollution records in core sediments of some Red Sea coastal areas, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 155, 509–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Lee, O.O.; Qian, P.-Y.; Wang, W.-X. Sponges and sediments as monitoring tools of metal contamination in the eastern coast of the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sofyani, A.A.; Marimuthu, N.; Wilson, J.J. A rapid assessment of Scleractinian and non-Scleractinian coral growth forms along the Saudi Arabian coast, Red Sea. J. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 13, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandour, I.M.; Basaham, S.; Al-Washmi, A.; Masuda, H. Natural and anthropogenic controls on sediment composition of an arid coastal environment: Sharm Obhur, Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahal, A.Y.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Qaysi, S.I.; Al-Hashim, M.H.; Al-Dossari, A. Environmental Risk Assessment and Sources of Potentially Toxic Elements in Seawater of Jazan Coastal Area, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mur, B.A.; Quicksall, A.N.; Al-Ansari, A.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of heavy metals in coastal core sediments from the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Oceanologia 2017, 59, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, M.; Qurban, M.A.B.; Krishnakumar, P.K. Metal Contamination Assessment in the Sediments of the Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. In Oceanographic and Biological Aspects of the Red Sea; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; El-Sorogy, A.; Al-Kahtany, K.; Madkour, H. Status of trace metals in surface seawater of Sharm Al-Kharrar lagoon, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M. Pollution assessment of the Red Sea-Gulf of Aqaba seawater, northwest Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sorogy, A.S.; Youssef, M.; Al-Hashim, M.H. Water Quality Assessment and Environmental Impact of Heavy Metals in the Red Sea Coastal Seawater of Yanbu, Saudi Arabia. Water 2023, 15, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.A.; Mesaed, A.A. The Role of the Geologic and the Geomorphologic Factors in the Formation of Some Geotourism Sites of Saudi Arabia. In Geotourism in the Middle East; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 193–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shanti, G. Geology of the Arabian Shield; Ministry of Agriculture, and Water: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 1993.
- Hussein, M.T.; Lashin, A.; Al Bassam, A.; Al Arifi, N.; Al Zahrani, I. Geothermal power potential at the western coastal part of Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 26, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, H. Guidelines for Groundwater Sampling. 2005. Available online: http://www.limpopo.riverawarenesskit.org/limpoporak_com/index.htm (accessed on 25 April 2019).
- Yidana, S.M.; Ophori, D.; Banoeng-Yakubo, B. Groundwater quality evaluation for productive uses—The Afram Plains area, Ghana. J. Irrig. Drain Eng. 2008, 134, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; ElKashouty, M.; Bob, M. Impact of rapid urbanization and tourism on the groundwater quality in Al Madinah city, Saudi Arabia: A monitoring and modeling approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.A.; Hamdona, S.; Shakweer, L.; El Saharty, A. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface and bottom water along the eastern part of the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simou, A.; Mrabet, A.; Abdelfattah, B.; Bougrine, O.; Khaddor, M.; Allali, N. Distribution, ecological, and health risk assessment of trace elements in the surface seawater along the littoral of Tangier Bay (Southwestern Mediterranean Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 202, 116362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, M.V.; Praveena, S.M.; Chidambaram, S.; Nagarajan, R.; Elayaraja, A. Evaluation of water quality pollution indices for heavy metal contamination monitoring: A case study from Curtin Lake, Miri City, East Malaysia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1987–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kahtany, K.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Heavy metal contamination of surface seawaters in Abu Ali Island, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- Al-Hashim, M.H.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Alshehri, F.; Qaisi, S. Environmental Assessment of Surface Seawater in Al-Uqair Coastline, Eastern Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taani, A.A.; Batayneh, A.; Nazzal, Y.; Ghrefat, H.; Elawadi, E.; Zaman, H. Status of trace metals in surface seawater of the Gulf of Aqaba, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, T.; Alfaifi, H.; El-Sorogy, A. Metal pollution in Al-Khobar seawater, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shriadah, M.A.; Okbah, M.A.; El-Deek, M.S. Trace metals in the water columns of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 153, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S. Assessment of seawater pollution of the Al-Khafji coastal area, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.M.; Neary, J.P. Water quality for ecosystem and human health. In United Nations Environment Programme Global Environment Monitoring System/Water Programme; GEMS Burlington: Burlington, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gad, M.; El-Safa, M.M.A.; Farouk, M.; Hussein, H.; Alnemari, A.M.; Elsayed, S.; Khalifa, M.M.; Moghanm, F.S.; Eid, E.M.; Saleh, A.H. Integration of Water Quality Indices and Multivariate Modeling for Assessing Surface Water Quality in Qaroun Lake, Egypt. Water 2021, 13, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqarawy, A.; El Osta, M.; Masoud, M.; Elsayed, S.; Gad, M. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance and Water Quality Indices to Assess Groundwater Quality for Drinking in Arid Regions, Saudi Arabia. Water 2022, 14, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, D.; Zheng, B.; Fang, Y.; Shen, G.; Liu, H. Distribution and pollution assessment of trace metals in seawater and sediment in Laizhou Bay. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, B.; Bodis, D.; Lahermo, P.; Rapant, S.; Tarvainen, T. Application of a groundwater contamination index in Finlandand Slovakia. Environ. Geol. 1997, 36, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lateef, K.H. Evaluation of Groundwater Quality for Drinking Purpose for Tikrit and Samarra Cities using Water Quality Index. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2011, 58, 472–481. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.G.; Aly, A.A.; Aldhumri, S.A.; Al-Barakaha, F.N. Hydrochemical and Quality Assessment of Groundwater Resources in Al-Madinah City, Western Saudi Arabia. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Kumari, S. Heavy metal pollution index of ground water of an abandoned open cast mine filled with fly ash: A case study. Mine Water Environ. 2008, 27, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Saxena, A.; Shukla, S.; Sekar, S.; Senapathi, V.; Wu, J. Environmental contamination by heavy metals and associated human health risk assessment: A case study of surface water in Gomti River Basin, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 56105–56116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bartolomeo, A.; Poletti, L.; Sanchini, G.; Sebastiani, B.; Morozzi, G. Relationship among parameters of lake polluted sediments evaluated by multivariate statistical analysis. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.H.; Gad, M.; Khalifa, M.M.; Elsayed, S.; Moghanm, F.S.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Danish, S.; Datta, R.; Moustapha, M.E.; El-Safa, M.M.A. Environmental Pollution Indices and Multivariate Modeling Approaches for Assessing the Potentially Harmful Elements in Bottom Sediments of Qaroun Lake, Egypt. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, R.S.; Shah, M.H.; Shaheen, N.; Khalique, A.; Manzoor, S.; Jaffar, M. Multivariate analysis of selected metals in tanneryeffluents and related soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 122, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Duan, Z.; Liu, G.; Kalla, P.; Scheidt, D.; Cai, Y. Evaluation of the Possible Sources and Controlling Factors of Toxic Metals/Metalloids in the Florida Everglades and Their Potential Risk of Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9714–9723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Luo, Q.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, J. Identification of the long-term variations of groundwater and their governing factors based on hydrochemical and isotopic data in a river basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements of Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Abingdon, UK, 2011; p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Rai, D.K.; Pandey, R.S.; Sharma, B. Analysis of some heavy metals in the riverine water, sediments and fish from river Ganges at Allahabad. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 157, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, J.; Vargas, G.; Sifeddine, A.; Ortlieb, L.; Guiñez, M. Distribution and enrichment evaluation of heavy metals in Mejillones Bay (23_S), Northern Chile: Geochemical and statistical approach. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.B.; Padhi, R.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Satpathy, K.K. Distribution and ecological- and health-risk assessment of heavy metals in the seawater of the southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, L.H.; Boutaleb, A.; Berdous, D. Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollution in the polymetallic district of Kef Oum Teboul (El Kala, Northeast Algeria). Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Ahmad, N.; Mashiatullah, A. Heavy metals contamination and ecological risk assessment in surface sediments of Namal Lake, Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, Q. The application of electrochemical technologies in water and wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 176, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lofrano, G.; Brown, J. Wastewater management through the ages: A history of mankind. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5254–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Index | Value | Contamination Level |
|---|---|---|
| CF | CF < 1 | Low contamination factor |
| 1 ≤ CF <3 | Moderate contamination factor | |
| 3 ≤ CF < 6 | Considerable contamination factor | |
| CF ≥ 6 | Very high contamination factor | |
| Cd | Cd < 4 | Low contamination degree |
| Cd = 4–8 | Moderate contamination degree | |
| Cd > 8 | Very high contamination degree | |
| mCd | <1.5 | Uncontaminated |
| 1.5 ≤ mCd < 2 | Slightly contaminated | |
| 2 ≤ mCd < 4 | Moderately contaminated | |
| 4 ≤ mCd < 8 | Moderately to heavily contaminated | |
| 8 ≤ mCd < 16 | Heavily contaminated | |
| 16 ≤ mCd < 32 | Severely contaminated | |
| mCd ≥ 32 | Extremely contaminated | |
| HPI | HPI < 5 | Low pollution |
| HPI = 5–10 | Medium pollution | |
| HPI > 10 | High pollution |
| References | Cr | Fe | Zn | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present study | 0.268 | 0.197 | 6.616 | 0.284 | 0.59 |
| Jazan coastline, Saudi Arabia [17] | 1.28 | - | 1.04 | 2.27 | 0.06 |
| Sharm Al-Kharrar lagoon, Saudi Arabia [20] | 0.26 | - | 4.19 | 0.28 | 0.06 |
| Red Sea-Gulf of Aqaba, Saudi Arabia [21] | 0.26 | 1.81 | 5.51 | 1.31 | 0.05 |
| Yanbu coastline, Red Sea, Saudi Arabia [22] | 0.72 | 0.983 | 1.67 | 0.28 | 0.31 |
| Maximum admissible concentration [35] | 50.0 | 200 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 3.00 |
| Al-Uqair coastline, Saudi Arabia [36] | 9.64 | 6.13 | 6.72 | 0.26 | 0.05 |
| Gulf of Aqaba, Saudi Arabia [37] | 0.96 | 15.255 | 3.32 | 0.20 | 0.03 |
| Al-Khobar, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia [38] | 1.38 | 3.54 | 16.21 | 0.04 | 0.11 |
| Gulf of Aqaba [39] | - | 1.78 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.57 |
| Al-Khafji, Arabian Gulf, Saudi Arabia [40] | 0.70 | 0.99 | 1.53 | 0.28 | 0.07 |
| S.N. | CF Values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Fe | Pb | Zn | |
| 1 | 3.000 | 0.058 | 0.0003 | 1.053 | 1.540 |
| 2 | 3.400 | 0.059 | 0.0001 | 0.612 | 0.305 |
| 3 | 1.000 | 0.059 | 0.0006 | 0.656 | 0.340 |
| 4 | 0.330 | 0.055 | 0.0002 | 0.604 | 0.495 |
| 5 | 4.030 | 0.066 | 0.0001 | 0.286 | 0.360 |
| 6 | 2.200 | 0.062 | 0.0003 | 0.149 | 0.295 |
| 7 | 1.770 | 0.067 | 0.0007 | 0.409 | 0.405 |
| 8 | 2.370 | 0.074 | 0.0003 | 0.132 | 0.105 |
| 9 | 1.000 | 0.067 | 0.0005 | 0.326 | 0.310 |
| 10 | 1.130 | 0.075 | 0.0012 | 0.185 | 0.095 |
| 11 | 1.030 | 0.076 | 0.0008 | 0.164 | 0.220 |
| 12 | 0.700 | 0.075 | 0.0005 | 0.086 | 0.110 |
| 13 | 3.030 | 0.074 | 0.0012 | 0.226 | 0.300 |
| 14 | 3.670 | 0.074 | 0.0012 | 0.503 | 0.085 |
| 15 | 2.100 | 0.082 | 0.0011 | 0.120 | 0.210 |
| 16 | 1.770 | 0.004 | 0.0013 | 0.170 | 0.195 |
| 17 | 2.500 | 0.004 | 0.0016 | 0.088 | 0.265 |
| 18 | 0.870 | 0.085 | 0.0019 | 0.021 | 0.490 |
| 19 | 1.830 | 0.004 | 0.0011 | 0.052 | 0.060 |
| 20 | 2.700 | 0.085 | 0.0017 | 0.081 | 0.050 |
| 21 | 3.370 | 0.004 | 0.0018 | 0.032 | 0.150 |
| 22 | 0.370 | 0.004 | 0.0017 | 0.023 | 0.200 |
| 23 | 0.730 | 0.044 | 0.0021 | 0.054 | 0.095 |
| Min. | 0.330 | 0.004 | 0.0001 | 0.021 | 0.050 |
| Max. | 4.030 | 0.085 | 0.0021 | 1.053 | 1.540 |
| Aver. | 1.970 | 0.054 | 0.0010 | 0.284 | 0.331 |
| Cr | Cd | Fe | Zn | Pb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | ||||
| Cd | −0.175 | 1 | |||
| Fe | −0.326 | 0.228 | 1 | ||
| Zn | 0.099 | −0.019 | −0.347 | 1 | |
| Pb | 0.214 | −0.176 | −0.596 ** | 0.738 ** | 1 |
| Component | ||
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | |
| Cr | 0.445 | −0.568 |
| Cd | −0.329 | 0.681 |
| Fe | −0.782 | 0.159 |
| Zn | 0.757 | 0.497 |
| Pb | 0.903 | 0.250 |
| % of Variance | 46.10 | 22.41 |
| Cumulative % | 46.10 | 68.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, T.; El-Sorogy, A.S.; Al-Kahtany, K. Distribution and Comprehensive Risk Evaluation of Cr, Cd, Fe, Zn, and Pb from Al Lith Coastal Seawater, Saudi Arabia. Water 2024, 16, 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131923
Alharbi T, El-Sorogy AS, Al-Kahtany K. Distribution and Comprehensive Risk Evaluation of Cr, Cd, Fe, Zn, and Pb from Al Lith Coastal Seawater, Saudi Arabia. Water. 2024; 16(13):1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131923
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Talal, Abdelbaset S. El-Sorogy, and Khaled Al-Kahtany. 2024. "Distribution and Comprehensive Risk Evaluation of Cr, Cd, Fe, Zn, and Pb from Al Lith Coastal Seawater, Saudi Arabia" Water 16, no. 13: 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131923
APA StyleAlharbi, T., El-Sorogy, A. S., & Al-Kahtany, K. (2024). Distribution and Comprehensive Risk Evaluation of Cr, Cd, Fe, Zn, and Pb from Al Lith Coastal Seawater, Saudi Arabia. Water, 16(13), 1923. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131923






