Using MODFLOW to Model Riparian Wetland Shallow Groundwater and Nutrient Dynamics in an Appalachian Watershed
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
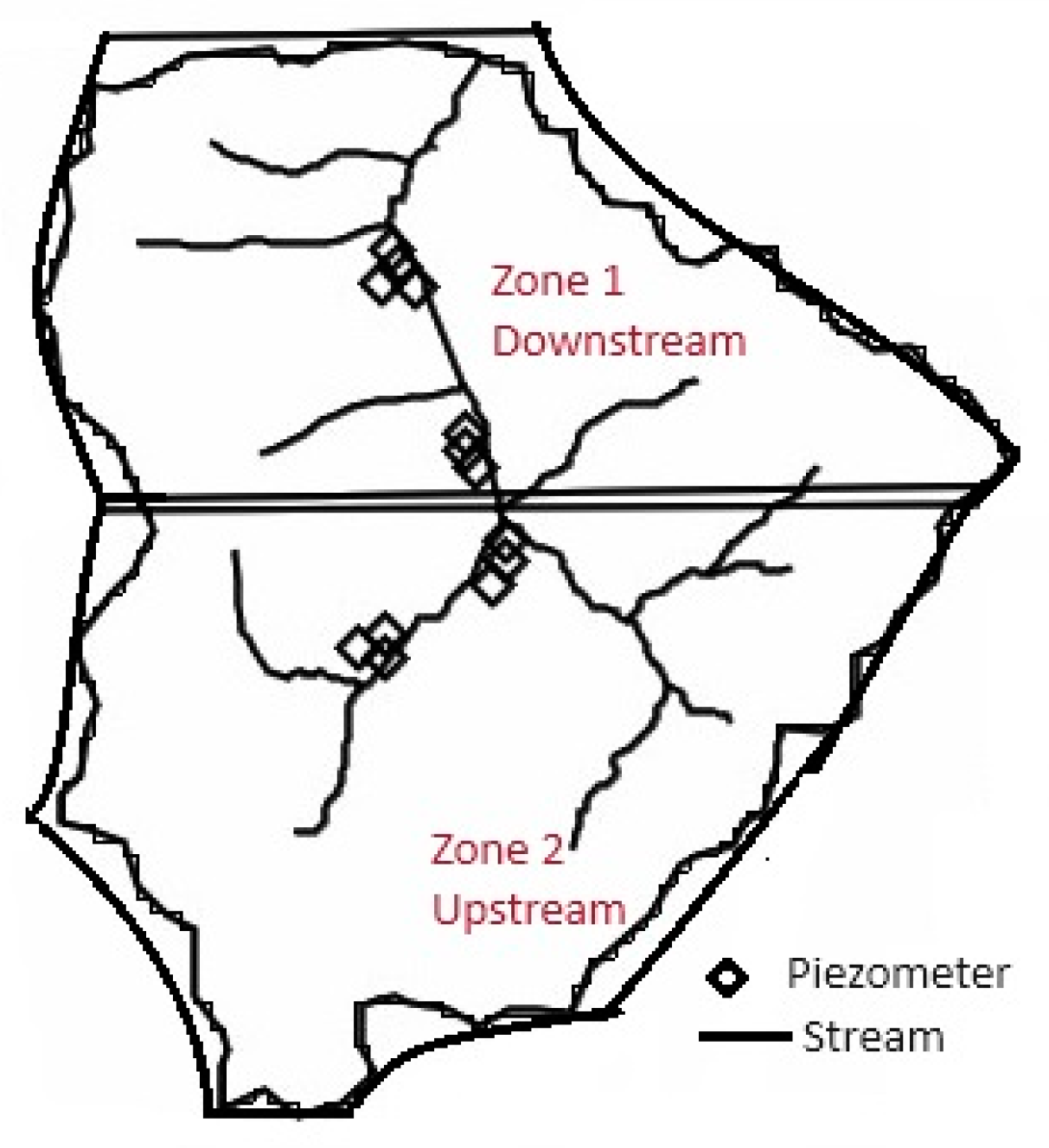
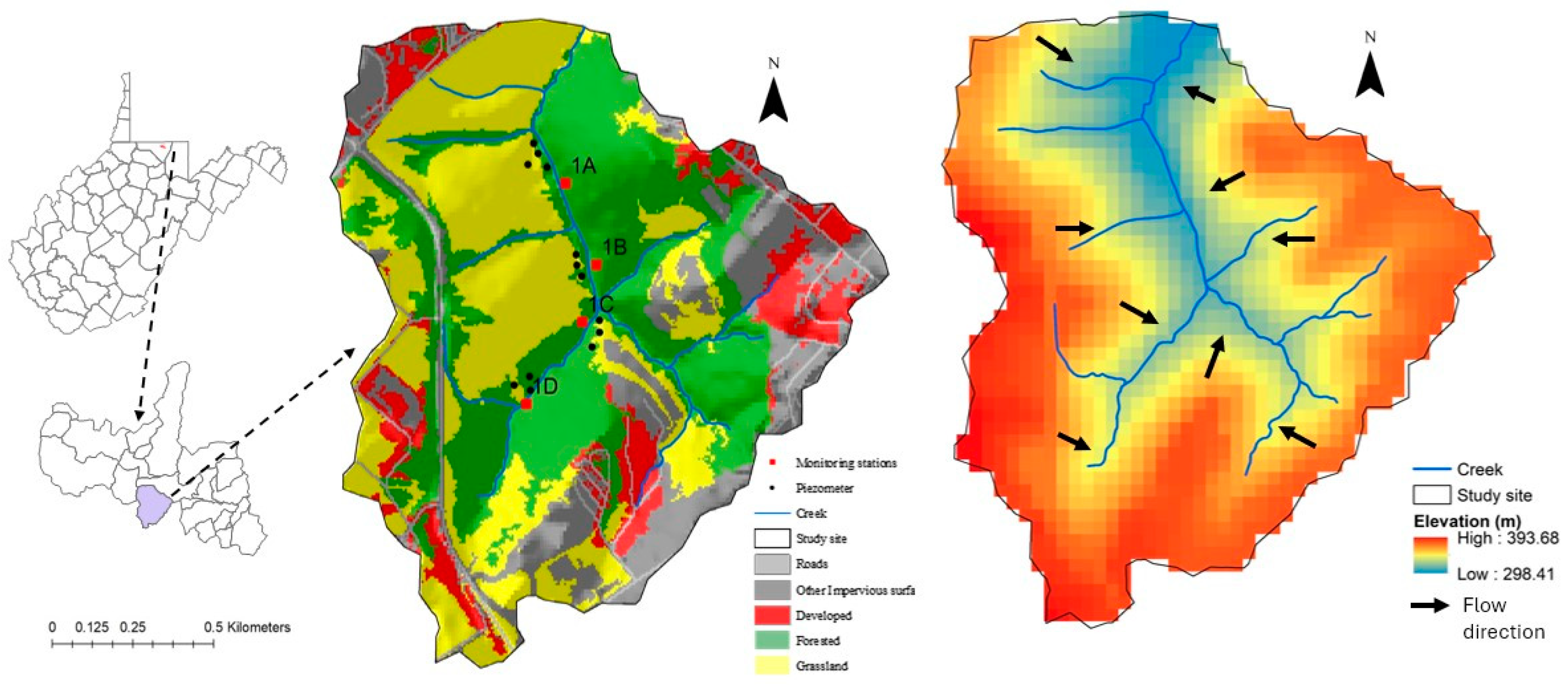
2.1. Study Area
2.2. SGW Flow Model Description and Parameterization
2.3. SGW Flow Model Calibration and Validation Procedures
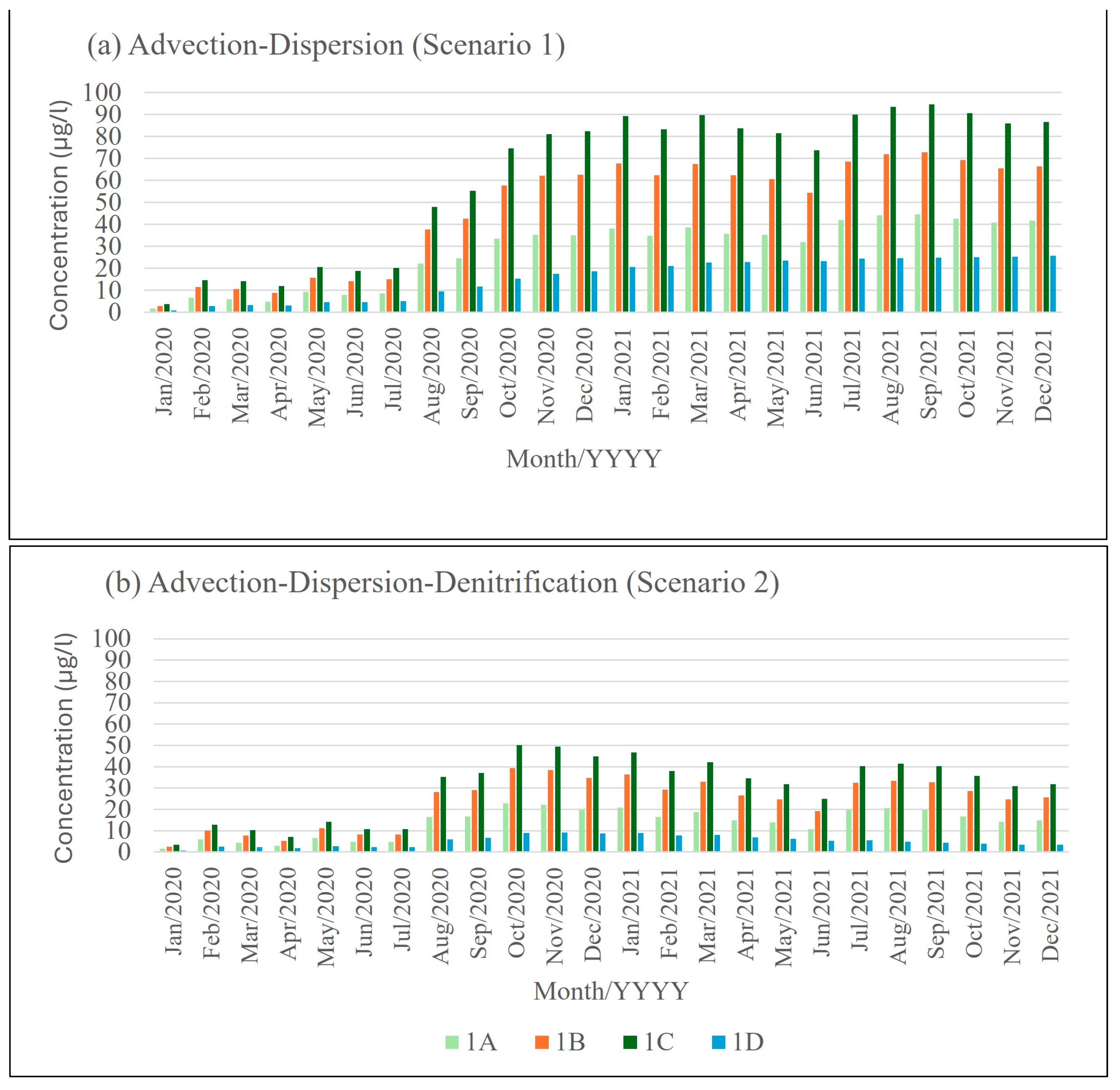
2.4. Nutrient Transport Scenario
3. Results and Discussion
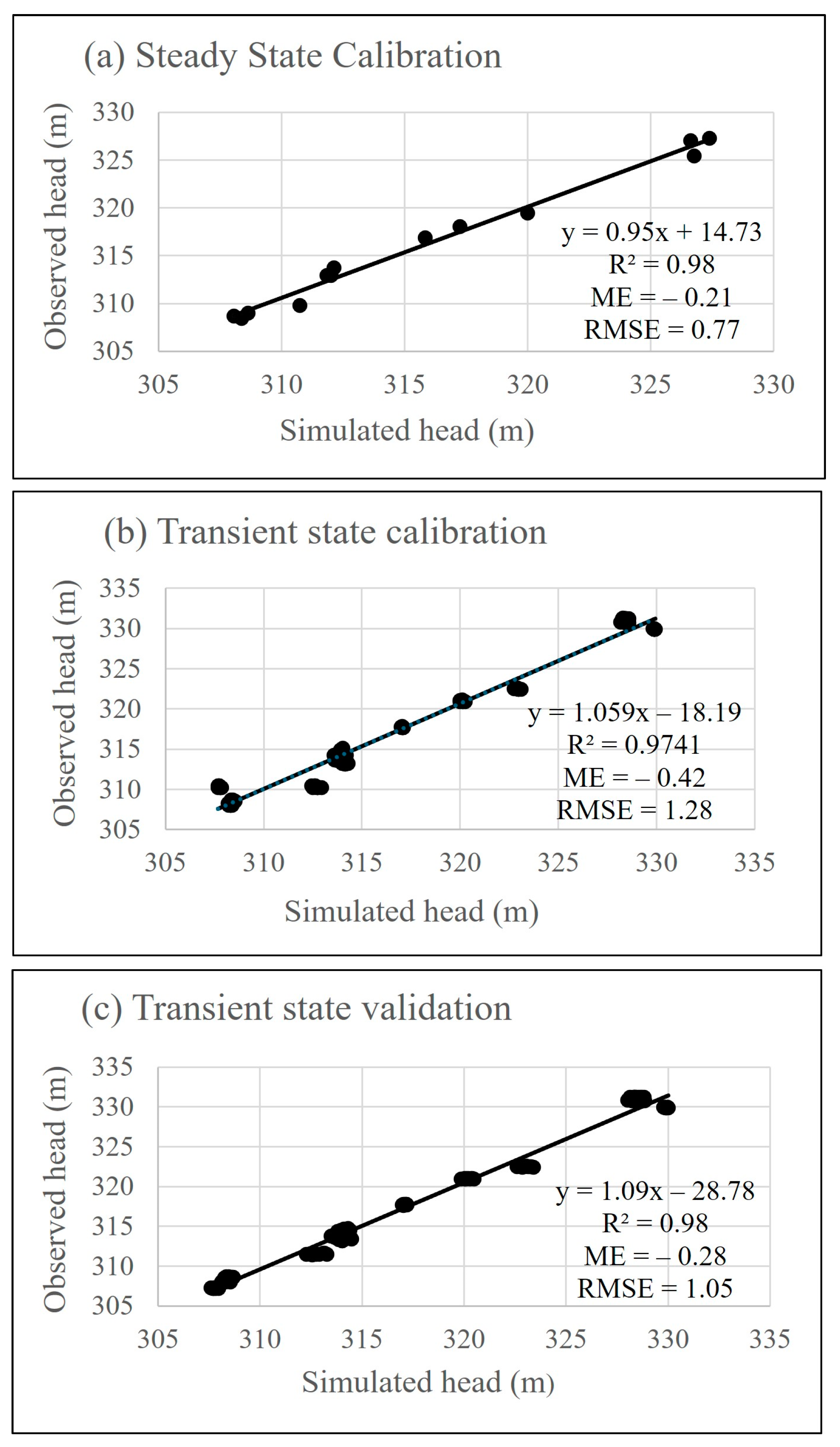
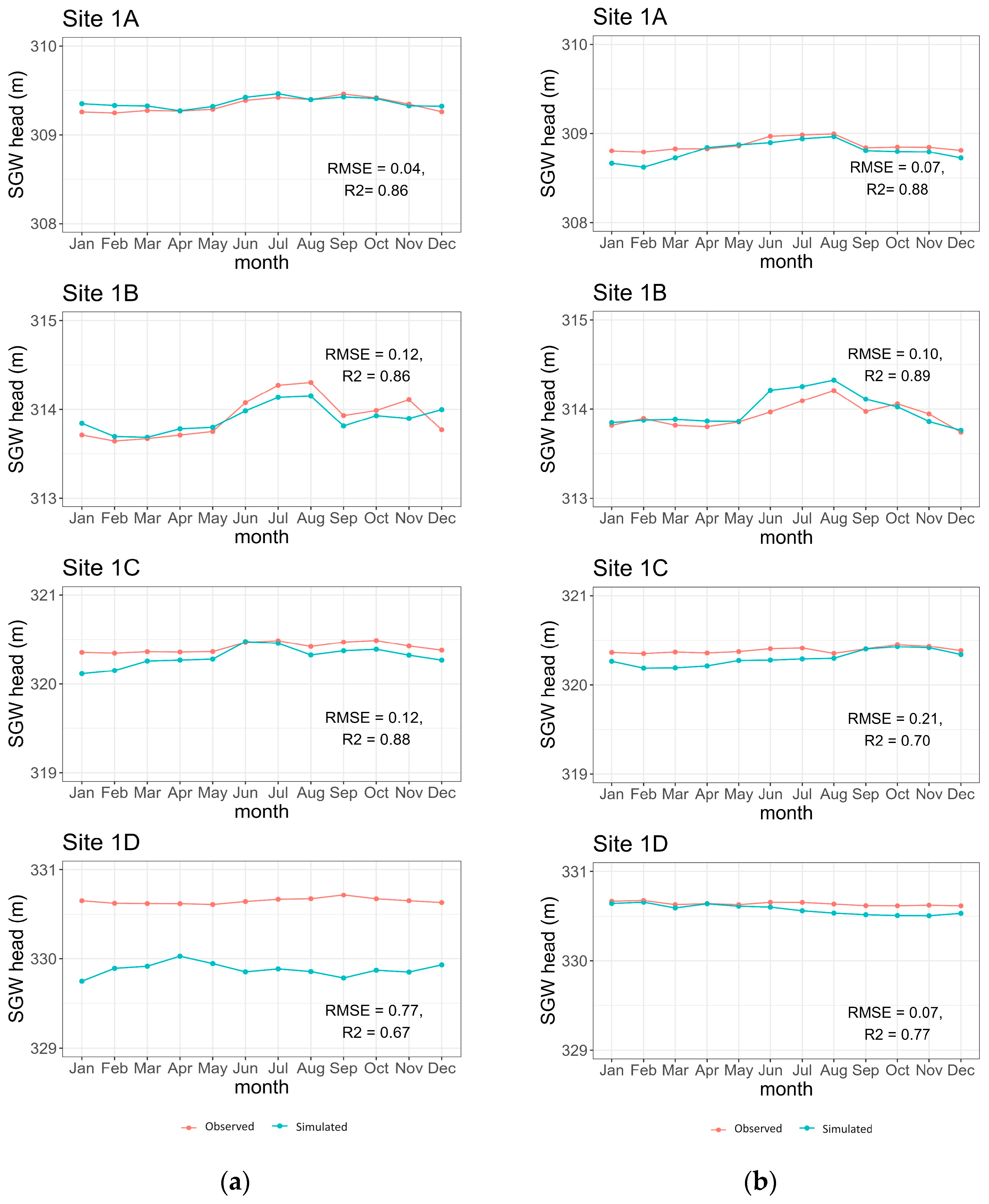
3.1. Calibration and Validation
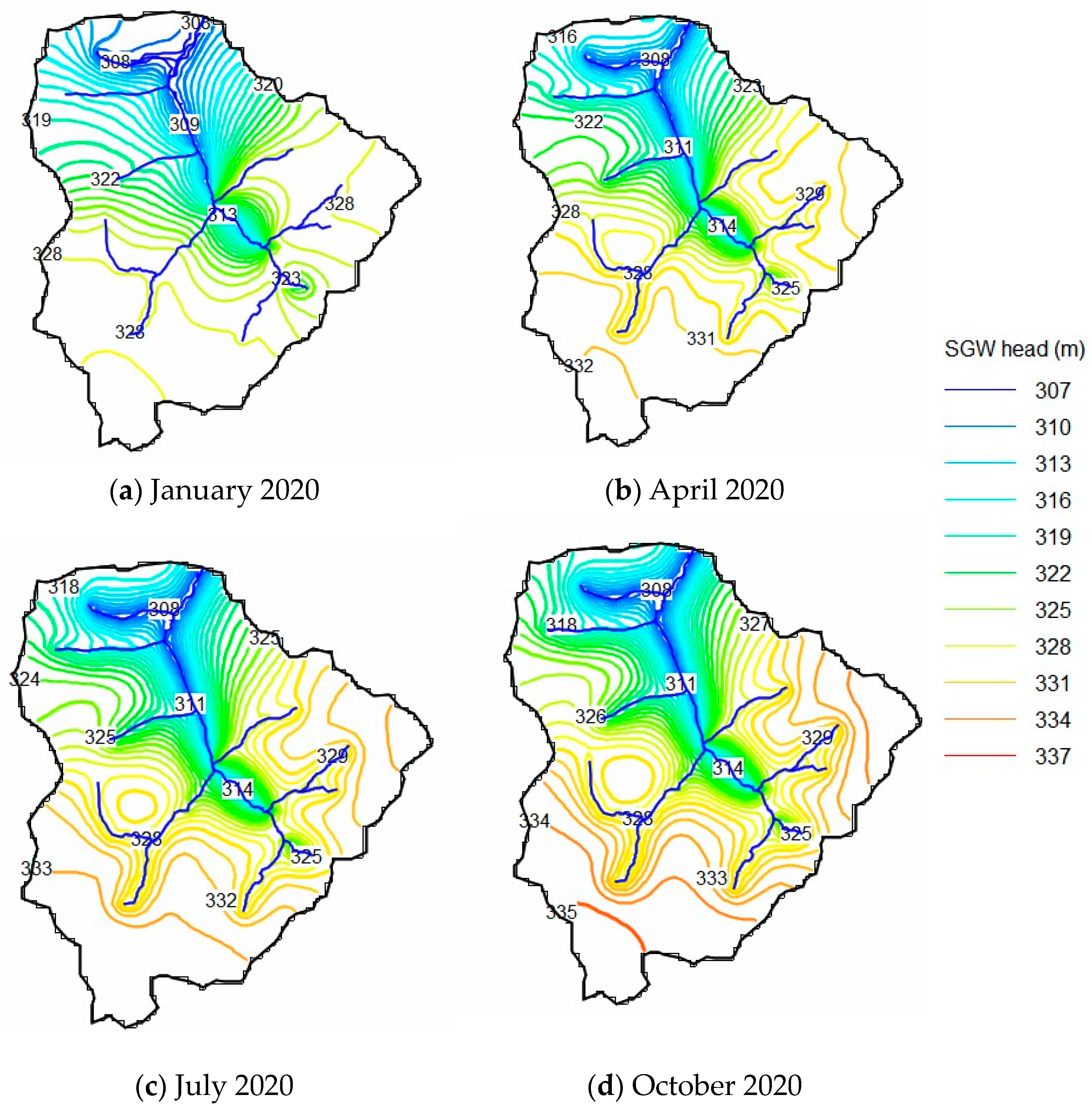
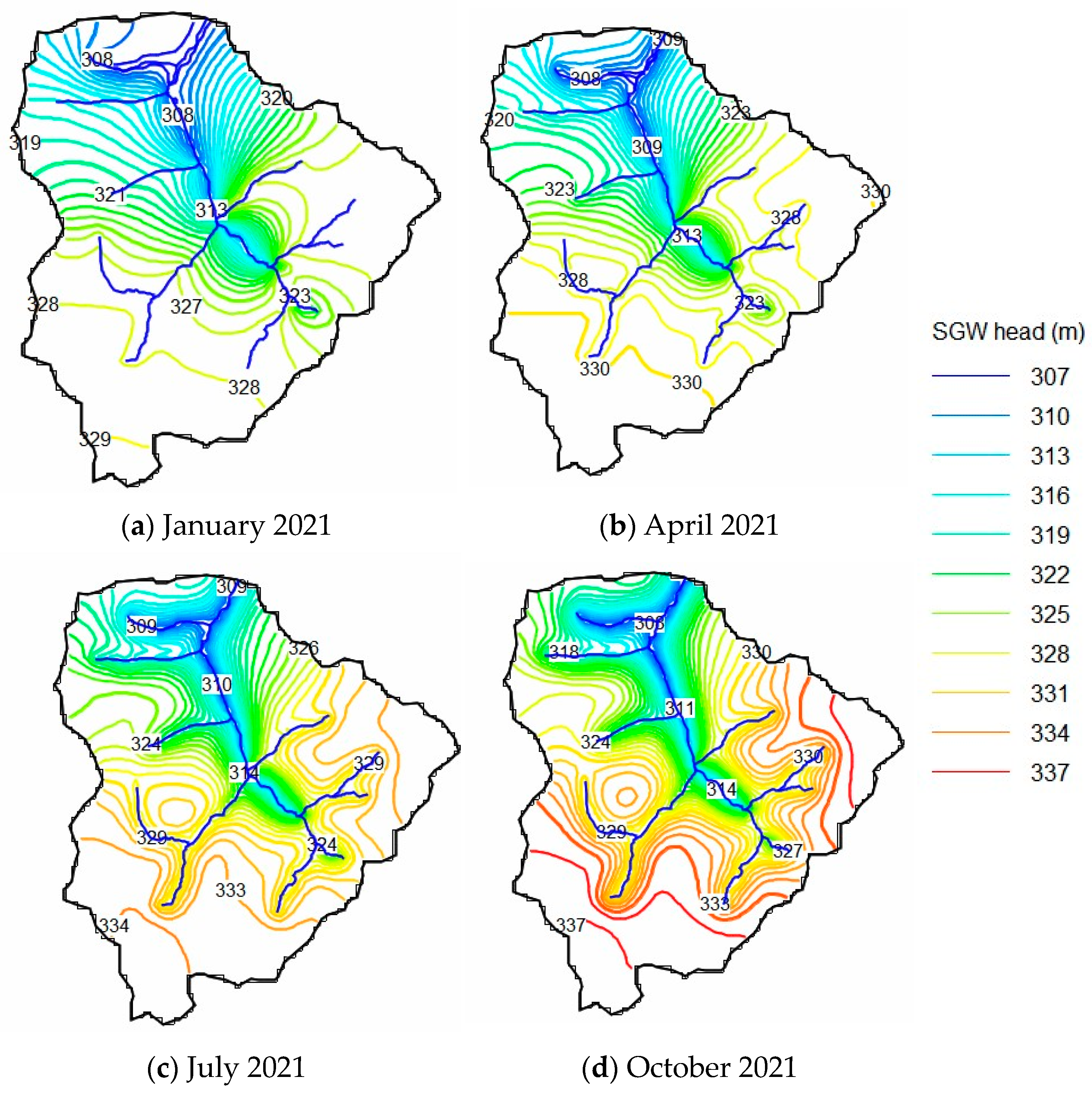
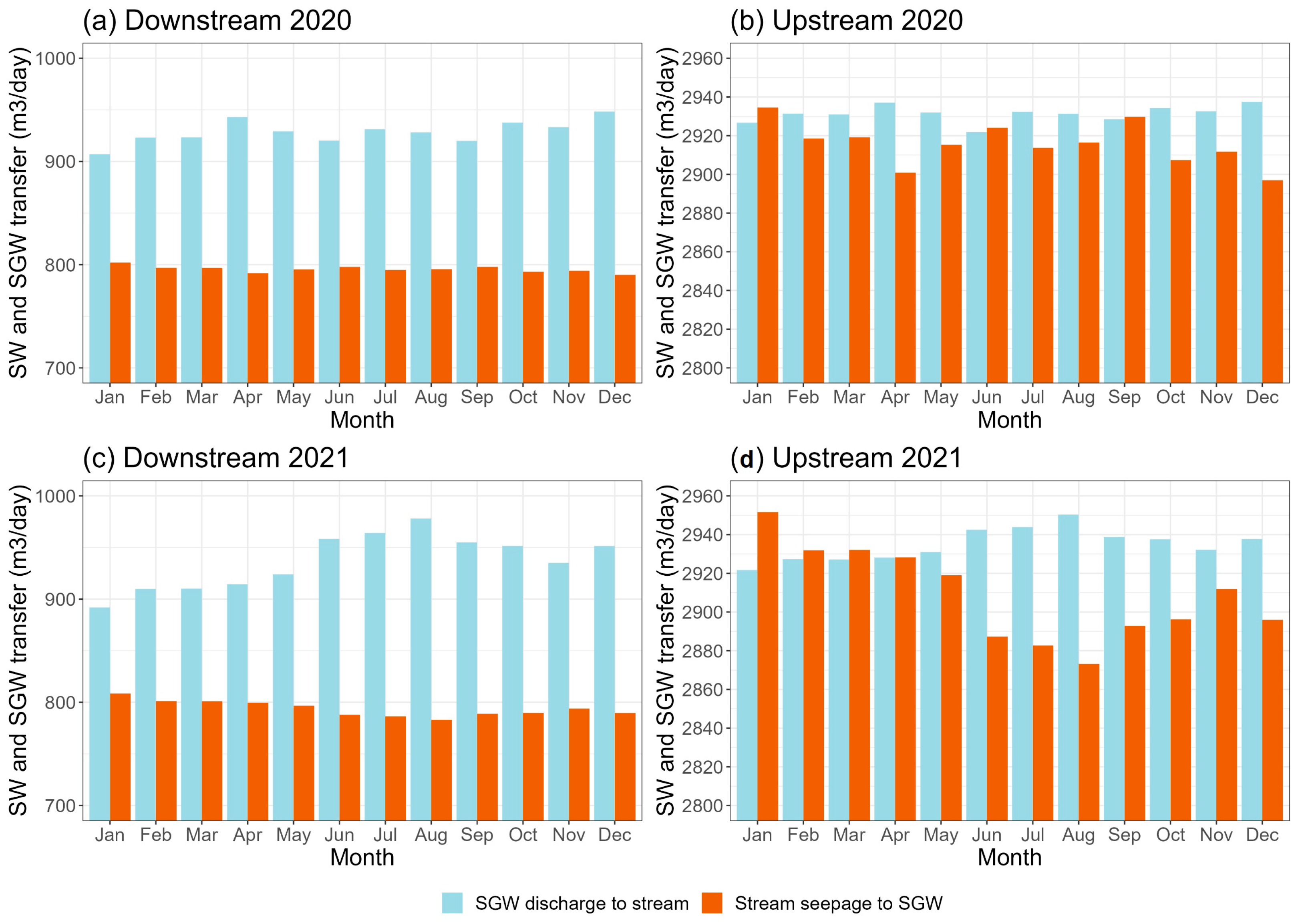
3.2. SGW Simulated Head and Stream-SGW Interaction
3.3. Nutrient Transport
3.4. Limitations and Implications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hare, D.K.; Helton, A.M.; Johnson, Z.C.; Lane, J.W.; Briggs, M.A. Continental-Scale Analysis of Shallow and Deep Groundwater Contributions to Streams. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Wu, W.; Hu, K.; Li, W. The Effects of Land Use Change and Irrigation Water Resource on Nitrate Contamination in Shallow Groundwater at County Scale. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.A.; Stefan, H.G. Shallow Groundwater Temperature Response to Climate Change and Urbanization. J. Hydrol. 2009, 375, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, O.V.; Barr, A.D.; Donn, M.J. Effect of Urbanisation on the Water Balance of a Catchment with Shallow Groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2013, 485, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C. Review on Groundwater as a Source of Nutrients to the Great Lakes and Their Tributaries. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions between Groundwater and Surface Water: The State of the Science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, S. A Review on the Research Advances in Groundwater–Surface Water Interaction with an Overview of the Phenomenon. Water 2023, 15, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleckenstein, J.H.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Boano, F. Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions: New Methods and Models to Improve Understanding of Processes and Dynamics. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, P.; Hubbart, J.A. Potential of MODFLOW to Model Hydrological Interactions in a Semikarst Floodplain of the Ozark Border Forest in the Central United States. Earth Interact. 2014, 18, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kurylyk, B.L.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; Caissie, D.; McKenzie, J.M. Shallow Groundwater Thermal Sensitivity to Climate Change and Land Cover Disturbances: Derivation of Analytical Expressions and Implications for Stream Temperature Modeling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2469–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, S.D.; Kucharik, C.J.; Foley, J.A. Impact of Changing Land Use Practices on Nitrate Export by the Mississippi River. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Bailey, R.T.; Records, R.M.; Wible, T.C.; Arabi, M. Comprehensive Simulation of Nitrate Transport in Coupled Surface-Subsurface Hydrologic Systems Using the Linked SWAT-MODFLOW-RT3D Model. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 104242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Biogeochemical Dynamics I: Nitrogen Cycling in Wetlands. In The Wetlands Handbook; Maltby, E., Barker, T., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 213–227. ISBN 978-0-632-05255-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hefting, M.M.; Clement, J.-C.; Bienkowski, P.; Dowrick, D.; Guenat, C.; Butturini, A.; Topa, S.; Pinay, G.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. The Role of Vegetation and Litter in the Nitrogen Dynamics of Riparian Buffer Zones in Europe. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, P.; Hubbart, J.A. Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrient Concentrations in an Ozark Forested Riparian Zone of the Central USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6577–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay, W.G.; Gallagher, D.L.; Simmons, G.M. Groundwater discharge and its impact ON surface water quality IN a chesapeake bay inlet 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1992, 28, 1121–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y. Estimation of Shallow Groundwater Discharge and Nutrient Load into a River. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 38, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.-I.; Koh, D.-C.; Cho, B.-W.; Jung, Y.-Y. Nutrient Dynamics in Stream Water and Groundwater in Riparian Zones of a Mesoscale Agricultural Catchment with Intense Seasonal Pumping. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 261, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, L.; Abiven, S.; Martin, C.; Durand, P.; Beaujouan, V.; Molénat, J. Effect on Nitrate Concentration in Stream Water of Agricultural Practices in Small Catchments in Brittany: II. Temporal Variations and Mixing Processes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, B.; Springer, P.; Fohrer, N. Variability of Water Quality in a Riparian Wetland with Interacting Shallow Groundwater and Surface Water. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 2009, 172, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlović, I.; Posavec, K.; Larva, O.; Marković, T. Numerical Groundwater Flow and Nitrate Transport Assessment in Alluvial Aquifer of Varaždin Region, NW Croatia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 41, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaeian, S.; Ketabchi, H.; Ebadi, T. Investigation on Quantitative and Qualitative Changes of Groundwater Resources Using MODFLOW and MT3DMS: A Case Study of Hashtgerd Aquifer, Iran. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 4679–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, L.; Alberti, L.; Mazzon, P.; Formentin, G. Transient Flow and Transport Modelling of an Historical CHC Source in North-West Milano. Water 2019, 11, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbaugh, A.W. MODFLOW-2005: The U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model—The Ground-Water Flow Process. 2005. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/publication/tm6A16 (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Brunner, P.; Simmons, C.T.; Cook, P.G.; Therrien, R. Modeling Surface Water-Groundwater Interaction with MODFLOW: Some Considerations. Ground Water 2010, 48, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Wang, P.P. MT3DMS: A Modular Three-Dimensional Multispecies Transport Model for Simulation of Advection, Dispersion, and Chemical Reactions of Contaminants in Groundwater Systems; Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program; Documentation and User’s Guide; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 1999; pp. 1–40.
- Jazi, R.S.; Eckstein, Y. Simulation of Groundwater Flow System in Alluvium and Fractured Weathered Bedrock Zone: Sand Lick Watershed, Boone County, West Virginia, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Geological Survey, Washington Water Science Center; Kozar, M.D.; McCoy, K.J. Use of modflow drain package for simulating inter-basin transfer of groundwater in abandoned coal mines. JASMR 2012, 1, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boettner, F.; Clingerman, J.; McIlmoil, R.; Hansen, E.; Hartz, L.; Hereford, A.; Vanderberg, M.; Arano, K.; Deng, J.; Strager, J.; et al. An Assessment of Natural Assets in the Appalachian Region: Water Resources; Appalachian Regional Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; 76p.
- Abesh, B.F.; Hubbart, J.A. A Comparison of Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity (Ksat) Estimations from Pedotransfer Functions (PTFs) and Field Observations in Riparian Seasonal Wetlands. Water 2023, 15, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abesh, B.F.; Anderson, J.T.; Hubbart, J.A. Surface Water (SW) and Shallow Groundwater (SGW) Nutrient Concentrations in Riparian Wetlands of a Mixed Land-Use Catchment. Land 2024, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, Z.A. Development of Multi-Catchment Rating Curves for Streams of Appalachian Mixed-Land-Use Watersheds: Preliminary Results; West Virginia University Libraries: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gootman, K.S.; Hubbart, J.A. Characterization of Sub-Catchment Stream and Shallow Groundwater Nutrients and Suspended Sediment in a Mixed Land Use, Agro-Forested Watershed. Water 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbart, J.A.; Kellner, E.; Zeiger, S.J. A Case-Study Application of the Experimental Watershed Study Design to Advance Adaptive Management of Contemporary Watersheds. Water 2019, 11, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, E.; Hubbart, J.; Stephan, K.; Morrissey, E.; Freedman, Z.; Kutta, E.; Kelly, C. Characterization of Sub-Watershed-Scale Stream Chemistry Regimes in an Appalachian Mixed-Land-Use Watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.L.; Charles, H.D.; Sponaugle, K.; Cole, C.; Ammons, J.T.; Gorman, J.; Childs, F.D.; Soil Conservation Service. Soil Survey of Marion and Monongalia Counties, West Virginia. 1982. Available online: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GOVPUB-A57-PURL-LPS105834/pdf/GOVPUB-A57-PURL-LPS105834.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Soil Survey Geographic Database (SSURGO). Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/resources/data-and-reports/soil-survey-geographic-database-ssurgo (accessed on 28 January 2023).
- Kozar, B.M.D.; Mathes, M.V. Aquifer-Characteristics Data for West Virginia; Water Investigations Report 01-4036; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2001.
- Winston, R.B. ModelMuse: A Graphical User Interface for MODFLOW-2005 and PHAST; Techniques and Methods 6—A29; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2009; 52p.
- Abesh, B.; Liu, G.; Vázquez-Ortega, A.; Gomezdelcampo, E.; Roberts, S. Cyanotoxin Transport from Surface Water to Groundwater: Simulation Scenarios for Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2022, 48, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.P.; Woessner, W.W.; Hunt, R.J. Applied Groundwater Modeling: Simulation of Flow and Advective Transport; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Andualem, T.G.; Demeke, G.G.; Ahmed, I.; Dar, M.A.; Yibeltal, M. Groundwater Recharge Estimation Using Empirical Methods from Rainfall and Streamflow Records. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 37, 100917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. Local Climatological Data (LCD). 2010. Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/land-based-station/local-climatological-data (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Solinst. Solnist Levelogger Pressure Transducer. 2020. Available online: https://www.solinst.com/products/products-dataloggers.php (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Harbaugh, A.W. A Computer Program for Calculating Subregional Water Budgets Using Results from the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Three-Dimensional Finite-Difference Ground-Water Flow Model; Open-File Report 90-392; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1990.
- Solinst. Solinist Levelogger Junior Edge Pressure Transducers. 2020. Available online: https://www.solinst.com/onthelevel-news/water-level-monitoring/water-level-datalogging/levelogger-data-critical-for-water-and-leachate-management-at-a-queensland-landfill/ (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Behera, A.K.; Pradhan, R.M.; Kumar, S.; Chakrapani, G.J.; Kumar, P. Assessment of Groundwater Flow Dynamics Using MODFLOW in Shallow Aquifer System of Mahanadi Delta (East Coast), India. Water 2022, 14, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, R.; Nassery, H.R.; Ebadi, T. Numerical Modeling of Groundwater Flow and Nitrate Transport Using MODFLOW and MT3DMS in the Karaj Alluvial Aquifer, Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Wilson, B.N.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R.; Arnold, J.G.; Gowda, P.H. Hydrologic and Water Quality Models: Use, Calibration, and Validation. Lebensversicherungsmedizin 2012, 55, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.C.; Banta, E.R.; Harbaugh, A.W.; Anderman, E.R. MODFLOW-2000, the U.S. Geological Survey Modular Ground-Water Model; User Guide to the Observation, Sensitivity, and Parameter-Estimation Processes and Three Post-Processing Programs; Open-File Report 2000-184; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2000; 209p.
- Bedekar, V.; Morway, E.D.; Langevin, C.D.; Tonkin, M.J. MT3D-USGS Version 1: A U.S. Geological Survey Release of MT3DMS Updated with New and Expanded Transport Capabilities for Use with MODFLOW; Techniques and Methods 6—A53; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2016.
- Wang, Y.; Shao, M.; Liu, Z.; Horton, R. Regional-Scale Variation and Distribution Patterns of Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivities in Surface and Subsurface Layers in the Loessial Soils of China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 487, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Han, J.; Lin, J.; Dai, Y.; Liu, P. Identification of Surface Water—Groundwater Nitrate Governing Factors in Jianghuai Hilly Area Based on Coupled SWAT-MODFLOW-RT3D Modeling Approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Nitrate Migration and Transformation in Low Permeability Sediments: Laboratory Experiments and Modeling. Water 2023, 15, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conan, C.; Bouraoui, F.; Turpin, N.; de Marsily, G.; Bidoglio, G. Modeling Flow and Nitrate Fate at Catchment Scale in Brittany (France). J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 2026–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.T.; Baù, D.A.; Gates, T.K. Estimating Spatially-Variable Rate Constants of Denitrification in Irrigated Agricultural Groundwater Systems Using an Ensemble Smoother. J. Hydrol. 2012, 468, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HACH. DR3900 Laboratory Spectrophotometer for Water Analysis|Hach USA. 2020. Available online: https://au.hach.com/spectrophotometers/dr3900-laboratory-spectrophotometer-for-water-analysis/family?productCategoryId=22218653565 (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- HACH. TNTplus Vial Chemistries. 2020. Available online: https://www.hach.com/products/chemistries/tntplus (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- HACH. Hach Company TNTplus 835/836 Nitrate Method 10206 Spectrophotometric Measurement of Nitrate in Water and Wastewater. 2013. Available online: https://cdn.bfldr.com/7FYZVWYB/at/wv5rq9452s3bkwxh28xbwjm/EPA_Method_10206_Hach_Nitrate_TNTplus_835_836_for_Water___WW.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2021).
- Winston, R.B. GW_Chart Version 1.30; Software Release; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Pollock, D.W. User Guide for MODPATH Version 7—A Particle-Tracking Model for MODFLOW; Open-File Report 2016-1086; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2016.
- Tripathi, M.; Yadav, P.K.; Chahar, B.R.; Dietrich, P. A Review on Groundwater–Surface Water Interaction Highlighting the Significance of Streambed and Aquifer Properties on the Exchanging Flux. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, B.M.; Nedaw, D.; Birhanu, B.; Gigar, A.G. Application of SWAT and MODFLOW Models for Characterization of Surface–Groundwater Interaction in the Modjo River Catchment, Central Ethiopia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bernard-jannin, L.; Grusson, Y.; Sauvage, S.; Arnold, J.; Id, R.S.; Miguel, S. Using SWAT-LUD Model to Estimate the Influence of Water Exchange and Shallow Aquifer Denitrification on Water and Nitrate Flux. Water 2018, 10, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korom, S.F. Natural Denitrification in the Saturated Zone: A Review. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1657–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triska, F.J.; Kennedy, V.C.; Avanzino, R.J.; Zellweger, G.W.; Bencala, K.E. Retention and Transport of Nutrients in a Third-order Stream in Northwestern California: Hyporheic Processes. Ecology 1989, 70, 1893–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
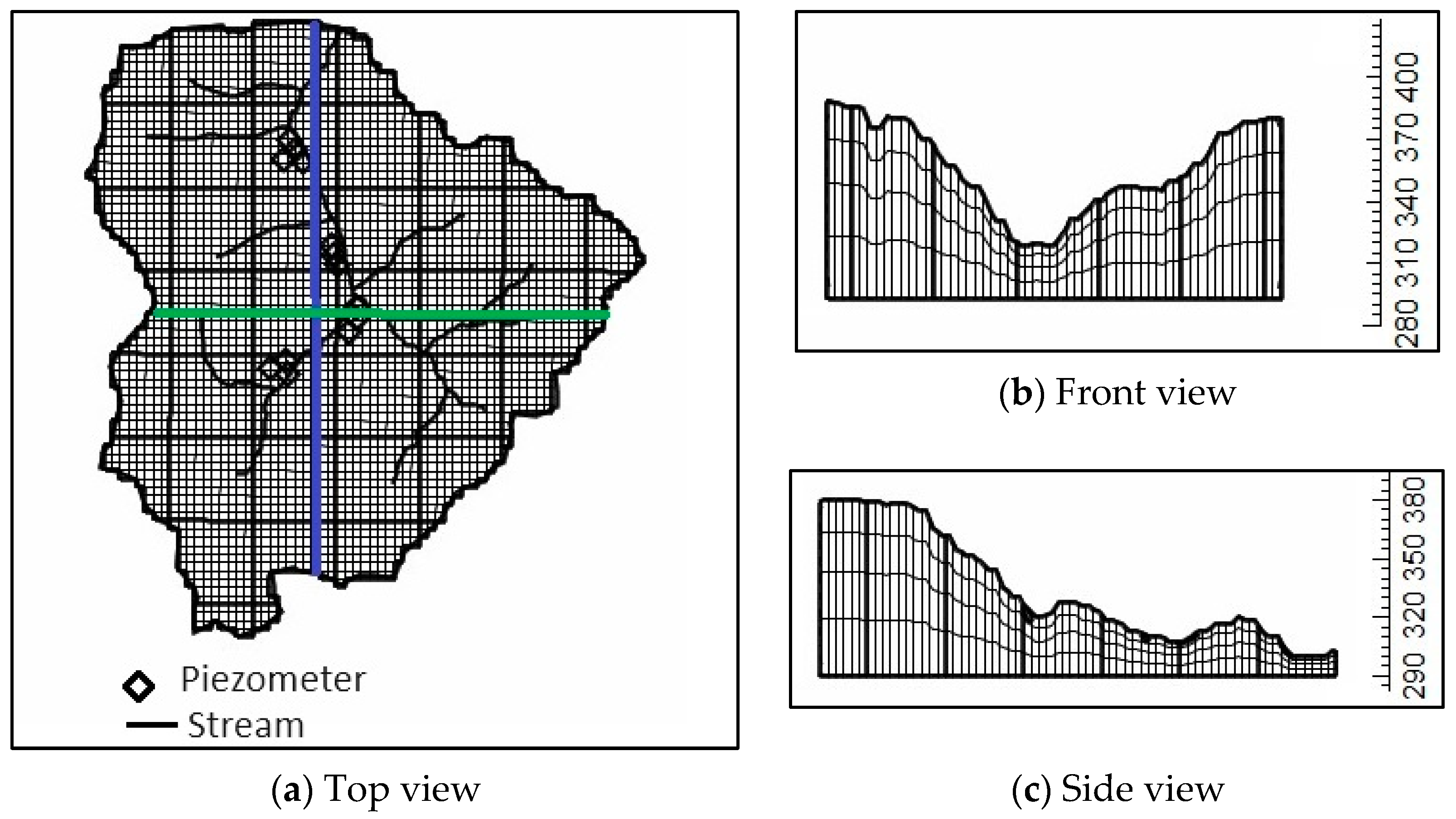

| Model Parameters | Range | Fitted Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid properties | Rows | — | 74 |
| Columns | — | 67 | |
| Layers | — | 4 | |
| Cell width along rows | — | 12 | |
| Cell width along columns | — | 12 | |
| Hydrological properties | Hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | 0.0038–38 | 0.38, 0.38, 0.58, 1.28 |
| Specific Storage | 1 × 10−3–9.5 × 10−4 | 0.013, 0.001, 0.001, 0.001 | |
| Specific yield (m−1) | 0.01–0.46 | 0.02, 0.01, 0.01, 0.01 | |
| Recharge rate (m/d) | 5–20% of Precipitation | 20% of precipitation | |
| Stream-bed hydraulic conductivity (m/d) | 0.038–50 | 10 | |
| Stream width (m) | — | 2 | |
| Stream-bed thickness (m) | — | 1 |
| Parameter (Unit) | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Advection | Simulation type | Third Order TVD |
| Dispersion | Longitudinal dispersivity (m) | 5 |
| Horizontal transverse dispersivity ratio | 0.5 | |
| Vertical transverse dispersivity ratio | 0.05 | |
| Porosity | Layer 1, 2, 3, 4 | 0.8, 0.5, 0.4, 0.4 |
| Chemical reaction | Reaction rate (day−1) | 0.07 |
| Model | ME | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steady state calibration | −0.21 | 0.77 | 0.98 |
| Transient state calibration | −0.42 | 1.28 | 0.97 |
| Transient state validation | −0.28 | 1.05 | 0.98 |
| Site | Piezometer | Travel Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|
| 1A | PA_1A (19 m) | 820 |
| PB_1A (21 m) | 680 | |
| PC_1A (55 m) | >1095 | |
| PD_1A (16 m) | 80 | |
| 1B | PA_1B (28 m) | 780 |
| PB_1B (27 m) | 770 | |
| PC_1B (18 m) | 730 | |
| 1C | PA_1C (40 m) | 1080 |
| PB_1C (80 m) | >1095 | |
| PD_1C (24 m) | 840 | |
| 1D | PA_1D (43 m) | >1095 |
| PC_1D (31 m) | >1095 | |
| PB_1D (8 m) | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abesh, B.F.; Anderson, J.T.; Hubbart, J.A. Using MODFLOW to Model Riparian Wetland Shallow Groundwater and Nutrient Dynamics in an Appalachian Watershed. Water 2024, 16, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131772
Abesh BF, Anderson JT, Hubbart JA. Using MODFLOW to Model Riparian Wetland Shallow Groundwater and Nutrient Dynamics in an Appalachian Watershed. Water. 2024; 16(13):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131772
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbesh, Bidisha Faruque, James T. Anderson, and Jason A. Hubbart. 2024. "Using MODFLOW to Model Riparian Wetland Shallow Groundwater and Nutrient Dynamics in an Appalachian Watershed" Water 16, no. 13: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131772
APA StyleAbesh, B. F., Anderson, J. T., & Hubbart, J. A. (2024). Using MODFLOW to Model Riparian Wetland Shallow Groundwater and Nutrient Dynamics in an Appalachian Watershed. Water, 16(13), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16131772








