Abstract
Systematic and scientific assessments on heavy metal pollution are greatly important to protecting the coastal eco-environment. In this paper, the spatial distribution, pollution degree, ecological toxicity and possible sources of eight heavy metal elements collected from the 126 marine and 715 terrestrial surface sediments surrounding Dingzi Bay were analyzed by obtaining concentration measurements. The results revealed that the concentrations of heavy metals followed a pattern: inner bay > terrestrial areas > outer bay. Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Hg were found to accumulate in fine particles (<0.063 mm), while As showed an association with specific particles (>0.25 mm and <0.016 mm). Spatial pollution patterns varied from non-polluted to low pollution levels overall, with localized contamination by individual elements. In addition to natural sources, four types of anthropogenic pollution were identified in the marine and terrestrial settings. Agricultural pollution, characterized by As predominance, exerted profound effects on both terrestrial and marine environments. Industrial pollution, featuring Hg dominance, was widespread in land environment and predominantly linked to atmospheric deposition. Traffic pollution, marked by elevated Pb and Cd, was concentrated around factories and densely populated areas. Maritime pollution, comprising Hg, Cr, Cd, and Zn, primarily occurred in the nearshore areas outside the bay. The findings of this study provide scientific data to the authorities in charge of sustainable coastal zone management in the South Yellow Sea.
1. Introduction
The coastal zone is a crucial interface connecting land and sea, and it is also a densely populated area and highly impacted by human activities [1,2]. In the process of geological evolution, the sediments in the coastal zone serve as carriers and sinks for the migration, transformation, and cycling of various elements [3]. The development and changes in the coastal zone are not only constrained by natural factors such as land, ocean, and climate, but also directly and profoundly influenced by large-scale human production activities [4]. In recent years, with the rapid economic development and urbanization in coastal areas, intensified industrial, mining, and agricultural activities, as well as the accumulation of pollutants from various human activities such as sewage discharge, have made environmental issues in the coastal zone increasingly prominent [5,6,7].
HMs (heavy metals) are a type of pollutant that is characterized by their accumulation and persistence [8]. They can remain in water and sediment environments for long periods of time and have strong biological activity and toxicity [9,10]. They can harm organisms through processes such as bioaccumulation and biomagnification in the food chain [11]. As a result, HMs have become important pollutants that impact marine environments [12]. Sediments, as a crucial carrier of pollutants, can indicate pollution characteristics in marine areas and reflect the long-term impacts of natural factors and human activities on marine environments [13,14]. Therefore, conducting investigations and environmental quality assessments of HM pollution in coastal sediments is of great significance for understanding the current status of HM pollution, as well as the influences of natural environmental processes and human activities in the area.
Dingzi Bay, located in the Shandong Peninsula, is a significant semi-enclosed bay. However, in recent years, the bay has been impacted by human activities, resulting in a decline in water quality, loss of coastal wetlands, and a decrease in biodiversity [15,16]. Previous studies have analyzed the distribution and pollution levels of HMs in the sediments of Dingzi Bay, but there are limitations in understanding the complete process of HM pollution from its sources to the marine environment [17,18]. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct a comprehensive investigation of HMs in both terrestrial and marine environments in the Dingzi Bay region. In this study, we will use high-resolution sampling to explore Dingzi Bay and the surrounding land. The objectives of this research are to evaluate HM pollution in both land and sea, identify potential sources of pollution in the region, and determine the extent of influence from each source. This research will provide guidance to the government in effectively preventing and controlling sediment HM pollution in the study area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study area is situated in Dingzi Bay and its surrounding regions (Figure 1). Dingzi Bay is bordered by Jimo, Jiaozhou, Laiyang, and Haiyang along the Yellow Sea coast. The tidal pattern is characterized by regular semidiurnal tides and the water depth in Dingzi Bay is primarily shallower than 5 m. Extensive reclamation for aquaculture and salt flats has significantly altered the water body of Dingzi Bay, leading to reduced tidal inflow, diminished sediment-carrying capacity, and the accumulation of silt and sand in the inner bay [15,19]. The adjacent region is primarily composed of cropland and woodland, hosting numerous industrial parks.
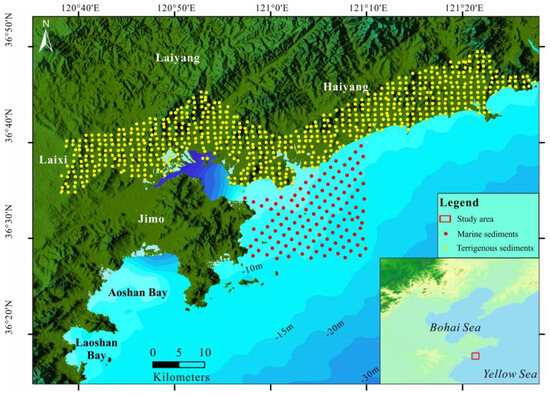
Figure 1.
Distribution of sampling sites.
The development of this region has attracted significant national and local attention, aligning with the Blue Economic Zone of the Shandong Peninsula and resulting in the designation of Dingzi Bay as a new maritime city. The primary development strategy for this area encompasses key aspects such as marine conservation, leisure and tourism, port infrastructure, and land allocation for industrial and urban utilization [20].
2.2. Collection of Samples
A total of 126 seabed surface sediment samples and 715 terrestrial sediment samples were collected (Figure 1). The box samplers were employed for marine sampling, with the top 2–3 cm of sediment being collected for experimental analysis. For terrestrial sites, stainless steel shovels were employed to collect surface sediment with a thickness of 0–3 cm. Subsequently, all samples were stored in self-sealing polyethylene bags and maintained at a low temperature (4 °C). They were then expeditiously transported to the sample repository for preservation.
2.3. Analysis Method
2.3.1. Grain-Size Analysis
Marine samples were pretreated with 10% H2O2 to digest organic matter. Excess H2O2 solution was removed through heating and evaporation, followed by the addition of 0.5% sodium hexametaphosphate to achieve complete sample dispersion. The mixture was analyzed using a laser particle size analyzer (Mastersize-2000, Malvern Instruments Ltd., Malvern, UK). Subsequently, the data were used to calculate the proportion of particle sizes ranging from 0–0.001 mm, 0.001–0.002 mm, 0.002–0.004 mm, 0.004–0.008 mm, 0.008–0.016 mm, 0.016–0.032 mm, 0.032–0.063 mm, 0.063–0.125 mm, 0.125–0.25 mm, 0.25–0.5 mm, 0.5–1 mm, 1–2 mm, and >2 mm.
2.3.2. HMs in Sediments
After samples were dried and ground, an appropriate quantity of each sample underwent microwave digestion with HNO3-HF-HClO4. The resulting solution was transferred to PTFE crucibles and further evaporated on an automatic temperature-controlled hotplate at 300 °C until nearly dry, adding 0.1 mL of HF. Subsequent heating continued until the solution achieved a viscous liquid state. The solution was diluted to 25 g with 2% HNO3 solution, and then 5g aliquot of the mixture was further adjusted to 20 g.
After the pre-treatment phase, the analysis of HMs was conducted. Elements Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn were quantified by an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS, X7, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), meanwhile, As and Hg contents were determined by atomic fluorescence spectrometry (AFS,9750, Beijing Haiguang Instrument Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The HMs recovery process adhered to stringent quality assurance and control protocols. Certified national standard reference materials (GBW07343, GBW07344, GBW07333, and GBW07308) were employed to evaluate experimental accuracy and precision. Duplicates and blank samples were utilized for quality control. Results for reference materials exhibited less than 10% variability, and replicate samples demonstrated relative standard deviations below 10%. Method detection limits were 0.07, 1.0, 0.2, 2.0, 1.0, 0.02, 0.1, and 0.002 mg kg−1 for Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, and Hg, respectively, ensuring reliable analytical performance.
2.3.3. HM Pollution Evaluation Indices
In the evaluation of HM elements within the study area, the chosen pollution indices must possess specific attributes: precision in scale, minimal limitations, efficient outcomes, and applicability to both sea and terrestrial samples. To comprehensively assess HM contamination in the study area, commonly used single and combined indices were employed [21], including the Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo), Contamination Factor (CF), Modified Contamination Degree (mCd), and Pollution Load Index (PLI). This selection enhances the objectivity and accuracy of the assessments [22]. The background value (BV) for assessment was derived from the soils of Shandong Province [23]. The basis for classification using these indices and associated descriptions is as follows:
Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo)
The Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo), proposed by Müller [24], was calculated using the formula:
where is the concentration of a metal in the sample; is the geochemical background concentration of the metal. The interpretation of Igeo values is categorized as follows: Igeo < 0, unpolluted; 0 ≤ Igeo ≤ 1, unpolluted to moderately polluted; 1 < Igeo ≤ 2, moderately polluted; 2 < Igeo ≤ 3, moderately to heavily polluted.
Contamination Factor (CF)
CF, proposed by Hakanson [25], was calculated using the equation:
where is the concentration of a metal in the sample; is the background or reference concentration. Interpretation of CF values includes: CF < 1, Low contamination factor; 1 ≤ CF < 3, Moderate contamination factor; 3 ≤ CF < 6, Considerable contamination factor; CF ≥ 6, High contamination factor.
Modified Contamination Degree (mCd)
The Modified Contamination Degree (mCd) quantifies contamination levels at specific locations [26], and was calculated using the formula:
where n is the number of pollutants considered; is the concentration of a metal in the sample; is the background or reference concentration. mCd values are interpreted as follows: mCd < 1.5, no to very low pollution; 1.5 ≤ mCd < 2, low pollution; 2 ≤ mCd < 4, moderate pollution; 4 ≤ mCd < 8, high pollution.
Pollution Load Index (PLI)
The Pollution Load Index (PLI) is a composite index that considers multiple pollutants, offering a holistic view of pollution [27], and is the geometric mean of the CF values for all pollutants considered. The formula for PLI is:
where n is the number of pollutants considered; are the enrichment factor for each pollutant at that location. PLI values are interpreted as follows: PLI ≤ 1, no pollution; 1 < PLI < 2, low pollution; 2 ≤ PLI < 3, moderate pollution; PLI ≥ 3, heavy pollution.
2.3.4. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
Normality tests and correlation analysis were conducted with Python 3.11.4. Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) via EPA PMF 5.0 was employed to explore potential sources of HM pollution in soil and sediment. The model requires input files containing the concentrations of elements (C) along with their respective uncertainties (Unc). The Unc for elements Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni, and Zn were calculated using Equations (5) and (6), while the Unc for elements As and Hg were computed following Equation (7):
If C ≤ MDL, Unc = 5/6 × MDL
Unc = CV × C,
Here, MDL is the method detection limit and EF is the error fraction. In this study, the EF was replaced by relative standard deviation and CV is the coefficient of variation of standard material.
A weight of evidence approach [28] determined that four factors were appropriate for terrestrial samples and three factors for marine samples.
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations of HMs in Land and Bay
The concentrations (µg/g) of HMs in Dingzi Bay and its surrounding terrestrial areas are outlined in Table 1. On the coastal land, the mean concentrations were in descending order: Cr (50.54) > Zn (43.94) > Ni (24.48) > Pb (23.24) > Cu (19.88) > As (9.09) > Cd (0.10) > Hg (0.019). In the outer section of Dingzi Bay, the concentrations maintained the same sequence: Cr (60.95) > Zn (46.42) > Ni (21.46) > Pb (15.30) > Cu (11.49) > As (8.38) > Cd (0.08) > Hg (0.016). For most HMs (Ni, Cu, As, and Cd), the mean values followed the pattern: inner bay > terrestrial areas > outer bay. In the Dagu River, the same pattern was also found, where HMs at the estuary were consistently higher than inland [11]. HMs in the terrestrial area accumulated as the river entered the inner bay and subsequently dispersed to the outer bay. Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Pb, and Hg in the outer Dingzi Bay consistently had lower concentrations than in the South Yellow Sea [29]. However, As (both inside and outside the bay) exhibited higher concentrations than South Yellow Sea’s 7.64 µg/g, Laoshan Bay’s 7.11 µg/g, and Jiaozhou Bay’s 6.12 µg/g [11,29,30].

Table 1.
Concentrations of HMs in Dingzi Bay and adjacent area(µg/g).
In the outer section of Dingzi Bay, the coefficients of variation (CVs) were Cr (0.218) < Ni (0.221) < Pb (0.225) < As (0.275) < Zn (0.306) < Cu (0.405) < Hg (0.438) < Cd (0.529). On the coastal land, the CVs were Pb (0.431) < Cr (0.502) < As (0.535) < Ni (0.619) < Cu (0.698) < Cd (0.704) < Hg (0.743) < Zn (0.774). Each element exhibited a higher CV on the coastal land than in the bay, indicating a more pronounced human impact on the terrestrial environment compared to the marine environment.
According to the China Marine Sediment Quality Standard [31], among the 126 sampling sites in Dingzi Bay, 126 (Cu), 126 (As), 126 (Cd), 126 (Pb), 126 (Hg), 125 (Zn), and 121 (Cr) sites met Class I standards, signifying suitability for marine aquaculture, natural and endangered species conservation areas, beach bathing areas, and recreational activities. Additionally, five sites with Cr concentrations and one site with As concentrations met Class 2 standards, making them suitable for general industrial water use areas and coastal scenic tourist areas.
3.2. Relationship between HMs and Grain Size
Normality tests show that the data on particle size and HM do not follow a normal distribution. Consequently, Spearman’s rank correlation was employed to measure the strength and direction of variables. The correlation coefficients among elements in various particle fractions of marine samples are illustrated in Figure 2. Elements, including Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Hg, displayed analogous geochemical behaviors, demonstrating a positive correlation with fractions smaller than 0.063 mm (p ≤ 0.01). Conversely, a negative correlation was evident, with grain sizes exceeding 0.25 mm. In essence, finer sediments tended to exhibit higher concentrations of these HMs compared to coarser sediments within the specified size range. Traditional views suggest that finer sediments harbor higher HMs due to the larger surface area-to-volume ratio of particles with smaller grain sizes, thereby exhibiting enhanced adsorption capacity [32,33].
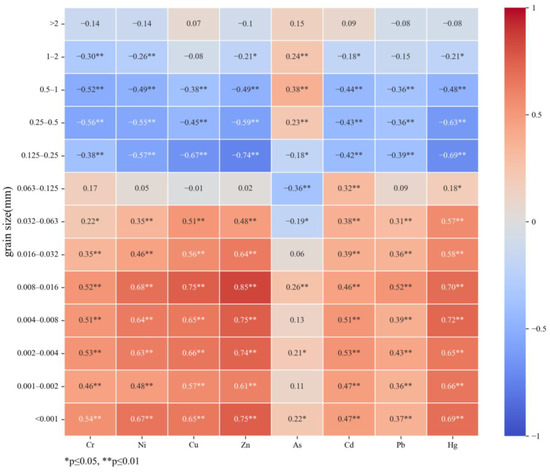
Figure 2.
Spearman’s correlation matrix among HMs and grain size.
In contrast to other elements in this study, As, the sole non-metallic element, manifested distinct geochemical behavior. It displayed weak positive correlations with particle fractions larger than 0.25 mm and finer than 0.016 mm. The enrichment of As in fine particles can be attributed to their higher adsorption capacity, whereas its presence in coarse particles may have greater environmental significance. Some studies propose that coarser particles may exhibit comparable or even higher HMs than finer particles due to prolonged residence time in a particular location, as larger particles, with an extended residence time in a specific area, potentially have more time to form oxide coatings [32,34]. It is believed that coarser particles may provide a better record of anthropogenic inputs.
An intriguing observation was that the p-values associated with the correlation between the 0.063–0.125 mm fraction and HMs surpassed the thresholds of 0.01 or 0.05. This created a distinct boundary in the research findings, where the upper and lower sides of the grain size spectrum corresponded to different correlations. Consequently, when investigating the relationship between grain size and elements, caution should be exercised to avoid narrow size ranges. For instance, studying the geochemical behavior of elements solely within the 0–0.063 mm or greater than 0.125 mm ranges may yield one-sided conclusions.
3.3. Assessment of Pollution
Utilizing mCd and PLI, a comprehensive assessment was conducted for both the terrestrial and bay areas. The results from the two indices all indicated that both the land and bay regions were situated in an unpolluted to low-polluted status (Table 2).

Table 2.
Assessment of pollution in land and bay.
Single indices pollution analyses were further conducted, using Igeo and CF as two key indicators. The results of Igeo and CF values mutually corroborated (Figure 3). In the bay area, Igeo and CF values for individual HMs were ordered as follows (means): Igeo-Cr (−0.62) > Igeo-As (−0.69) > Igeo-Ni (−0.94) > Igeo-Zn (−0.96) > Igeo-Pb (−1.28) > Igeo-Cd (−1.49) > Igeo-Cu (−1.57) > Igeo-Hg (−0.97), CF-Cr (0.98) > CF-As (0.93) > CF-Ni (0.78) > CF-Zn (0.77) CF-Pb (0.62) > CF-Cd (0.53) > CF-Cu (0.50) > CF-Hg (0.44). These results collectively indicated that the HM status within the bay was predominantly characterized by an unpolluted or non-enriched state. However, certain bay sites revealed a moderately polluted status for As and Cd. The sites exhibiting moderate pollution for As were situated closer to the coastline, while locations with moderate Cd pollution were located in the southernmost part of the study area.
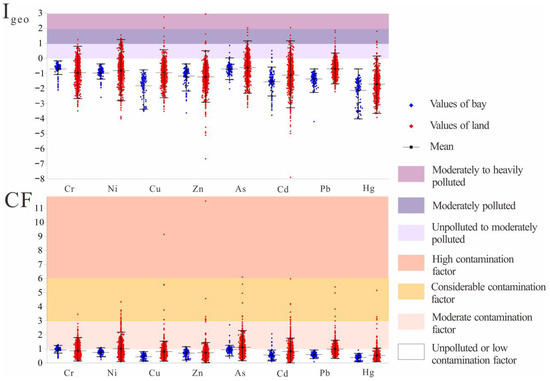
Figure 3.
The Igeo and CF values of bay and land.
Igeo and CF values on land were ordered as follows (means): Igeo-As (−0.52) > Igeo-Pb (−0.70) > Igeo-Ni (−0.79) > Igeo-Cu (−0.87) > Igeo-Cr (−0.94) > Igeo-Cd (−1.09) > Igeo-Zn (−1.14) > Igeo-Hg (−0.97), CF-As (1.04) > CF-Pb (0.92) > CF-Ni (0.86) > CF-Cu (0.82) > CF-Cr (0.78) > CF-Cd (0.71) > CF-Zn (0.68) > CF-Hg (0.45). The Igeo and CF values on land indicated that most HMs were in an unpolluted or non-enriched state, with As showing a low enrichment status. However, certain sites on land exhibited element pollution, with all eight HMs present. Although Cr pollution was inconspicuous, the study revealed that sites with Cr pollution mostly accompany Ni and Cu pollution (Figure 4a–c). According to the sampling information, areas designated as cropland and woods gathered sites with high Igeo and CF values for Cu, As, Cd, and Hg. Notably, a site (TY2904) near the synthetic playground showed Cd contamination. Zn exhibited higher Igeo and CF values in cultivated lands and road greenbelt. High outliers of Igeo-Pb and CF-Pb were relatively sparse (Figure 4g), some identified in sites located around industrial land and residential zones.
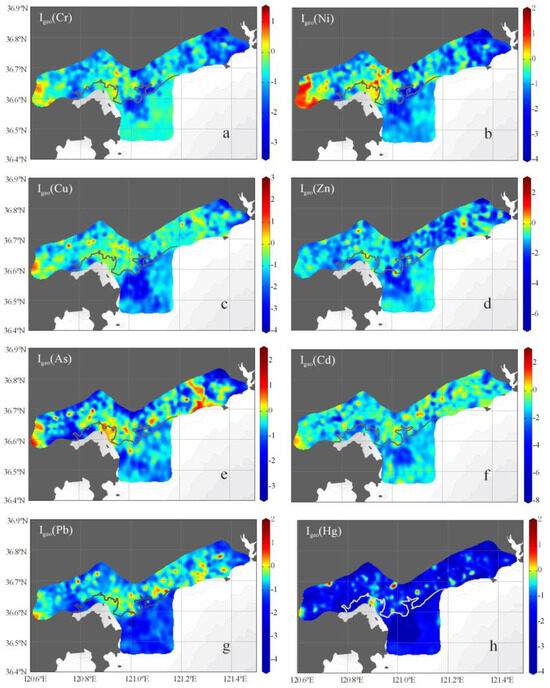
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of the Igeo values for HMs ((a) the distribution of Igeo(Cr); (b) the distribution of Igeo(Ni); (c) the distribution of Igeo(Cu); (d) the distribution of Igeo(Zn); (e) the distribution of Igeo(As); (f) the distribution of Igeo(Cd); (g) the distribution of Igeo(Pb); (h) the distribution of Igeo(Hg)).
HMs are naturally present in the environment, with each region exhibiting unique elemental background values. Therefore, spatial assessments of HM concentrations without proper treatment cannot provide meaningful insights. Numerous studies have made significant contributions to spatial distribution investigations using various pollution indices [35,36,37,38]. Localized elevations in Igeo and CF for certain elements suggested spot-source pollution within the research area, providing quantitative assessments of HMs resulting from human activities [39].
The Igeo values of the inner bay were ranked as follows: Cd (0.71) > As (0.45) > Ni (0.10) > Pb (−0.01) > Cr (−0.03) > Cu (−0.12) > Zn (−0.27) [18]. These values were consistently higher than those observed in the outer bay and land. Notably, in the Wulong River basin (located on the north bank of the bay), the spatial distribution of Igeo values for Zn, As, and Cd exhibited a strong continuity with Liu’s results [18] (Figure 4d–f). The land spatial distribution of Cu and Pb showed a limited connection with the inner bay (Figure 4c,g), suggesting a substantial elemental transport between Dingzi Bay and land, mainly through the Wulong River.
3.4. Factor Apportionment and Contributions
To obtain quantifiable insights into the sources of HMs, we applied the PMF model to analyze marine and terrestrial datasets separately. In the marine dataset (Figure 5a), three factors (labeled as Factor 1, Factor 2, and Factor 3) were identified, contributing 9.6%, 61.2%, and 29.2%, respectively. Factor 1 was characterized by a major contribution of As, constituting 42.99% of the element sum. Factor 2 showed substantial contributions from Pb, Cr, Ni, and Zn. Meanwhile, Factor 3 was primarily shaped by the major contribution of Hg, accounting for 65.97%.
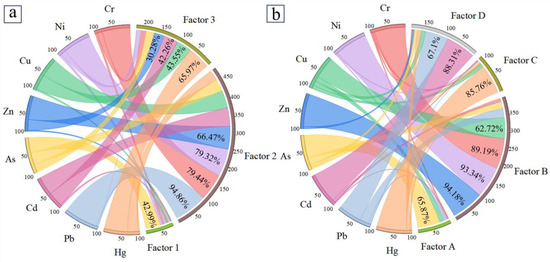
Figure 5.
Source profiles resolved by PMF model ((a) factors in bay, (b) factors in land).
In the terrestrial dataset (Figure 5b), four factors (labeled as Factor A, Factor B, Factor C, and Factor D) were identified, contributing 11.8%, 49.5%, 14.0%, and 24.7%, respectively. Factor A was dominated by the substantial contribution of As (65.87%), while Factor B encompassed notable contributions from Zn, Ni, Cr, and Cu. Factor C indicated a pollution source primarily dominated by Hg (85.76%). Finally, Factor D was primarily characterized by the contributions of Cd and Pb, constituting 88.31% and 67.1%, respectively.
The results of the Spearman’s correlation analysis for bay and land samples exhibited slight differences (Figure 6). Marine samples exhibited robust positive correlations among most elements (r > 0.40), except for As with others, Cd with Pb, and Hg with Pb, which exhibited negative or weak positive correlations with other elements. Terrestrial samples showed strong positive correlations among most elements (r > 0.41), except for the weak correlations observed between Cd and other elements, Hg and other elements, and As with Zn. These slight differences indicate that, while the marine and terrestrial environments share common sources of elements, each environment also possesses unique sources of pollution.
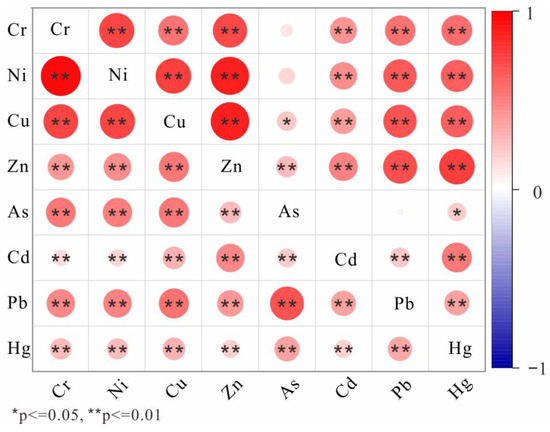
Figure 6.
Spearman’s correlation matrix among HMs (top right side is in bay, bottom left side is in land).
In the Spearman’s correlation results (Figure 6), As exhibited weak correlations with other HMs in the marine environment, suggesting a pollution source predominantly dominated by As, corresponding to Factor A, constituting 42.99% As in the source. In the terrestrial region, Factor A was also predominantly characterized by As. Previous studies have documented that As in terrestrial areas primarily originates from agricultural activities [40,41]. Elevated Igeo-As values, notably occurring in cropland and woodland, served as evidence supporting this perspective. Cropland areas, often subjected to intensive agricultural practices, see frequent use of pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers that contribute to As accumulation. Similarly, woodland areas, despite being less intensively managed, may accumulate As due to the application of livestock manure and other organic fertilizers, which are common in sustainable forestry practices. Long-term agricultural activities and green management practices can lead to significant As buildup in the soil [42,43]. Sumiahadi and Acar’s research [44] suggests that improper agricultural practices may elevate soil erosion rates. If the eroded sediment contains HMs, downstream water bodies and aquatic organisms could be exposed to agricultural pollutants from the land [45]. Therefore, Factor 1 in the bay also received As inputs from land-based Factor A. Concurrently, the thriving aquaculture industry in Dingzi Bay, which involves the use of fungicides, algaecides, and phosphorus fertilizers, could introduce agriculturally derived As into the marine environment [41,46]. This indicates that Factor 1 in the bay area and Factor A in the terrestrial region can be interpreted as agricultural pollution. Factor 2 and Factor B constituted 61.2% and 49.5% of their respective environments, being the factors with the highest proportions in each setting. These factors were characterized by significant contributions from Zn, Ni, Cr, and Cu. The Cr-Ni group is identified as primarily natural, given that rocks like basalt exhibit high concentrations of Zn, Cu, and Ni, and shale contains substantial quantities of Zn, Cu, Mn, and other elements [47]. Within the marine environment, 94.86% of Pb was attributed to Factor 2, and in the outer region of Dingzi Bay, all sampled sites indicated an absence of Pb pollution (Figure 3). Natural processes, such as geological weathering, wave erosion, and dissolution, play roles in releasing Pb from the earth’s crust into the marine surroundings [48]. Furthermore, the proportions of other elements in Factor 2 and Factor B closely corresponded to BV, reinforcing their classification as natural sources. Hg exhibited weak correlation with other HMs on land (Figure 6), indicating the presence of an independent source of Hg, in accordance with Factor C. Substantial research has demonstrated that Hg can function as an independent pollutant [49,50,51], owing to its unique physicochemical properties and environmental behavior [52]. Hg serves as an indicative element for atmospheric deposition, primarily due to its extensive long-range transport within the atmosphere resulting from human activities [53]. Anthropogenic Hg emissions, stemming from activities such as fossil fuel combustion, mining, mineral processing, and chlor-alkali production, significantly contribute to the release of Hg into the atmosphere [51,54,55]. Shandong Province, characterized by its significant industrial and coal-dependent land use, is the third-largest economy in China and a crucial area for coal management. It accounts for approximately one-tenth of China’s total energy consumption [56]. The industrial coal consumption in this region leads to substantial Hg emissions into the atmosphere. Consequently, Factor C was identified as industrial pollution. Factor D was distinguished by the predominant loading of Cd and Pb. Previous research suggests that pollutants like Pb and Cd can be linked to the wear of tires, brakes, and linings, as well as the corrosion of lubricating oil and fuel additives [57,58,59]. Despite the gradual phase-out of leaded gasoline in recent years, the current fuel contains only trace amounts of lead, and lead emissions now primarily originate from wear rather than fuel combustion. Moreover, discarded tires are frequently used as infill material for synthetic track and turf, containing a range of organic pollutants and metal oxides such as CdO and PbO [60], which can either volatilize into the air or permeate into rainwater. The site adjacent to a synthetic track (TY2904), which had found elevated Cd concentrations, also confirmed this viewpoint. Therefore, the presence of Cd and Pb in Factor D was attributed to traffic pollution. Factor 3 was primarily composed of Hg, Cu, Cd, and Zn. Similar to Hg, the origin of Cd can be attributed to the combustion of fossil fuels [51]. In the marine environment, Cu is often associated with ship antifouling coatings, while Zn is utilized in anticorrosive materials for ship cargo holding [61]. Dingzi Bay lacks large internal ports, only featuring small fishing harbors. However, it is externally connected to the Yellow Sea, which undergoes substantial maritime transportation activities, leading to the inevitable release of HMs into the bay. Beyond the bay, Shang et al. [62] identified maritime pollution in the Yellow Sea attributed to ports and shipyards in the coastal area.
3.5. Sources Spatial Impact Range
Excluding natural sources, four main pollution sources were identified in the study area: agricultural pollution, industrial pollution, traffic pollution, and maritime pollution. To assess the spatial impact of these pollution sources, the contribution of each factor in the study area was investigated. The average contribution of each pollution factor was normalized to 1. Sites with values greater than 1 were collected, and the results are presented in Figure 7.
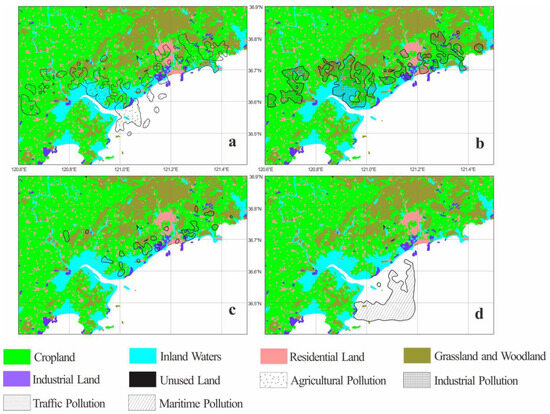
Figure 7.
Sources spatial impact range and land use type ((a) agricultural pollution impact range; (b) industrial pollution impact range; (c) traffic pollution impact range; (d) maritime pollution impact range).
Agricultural pollution was the most widespread contamination in the study area, extending beyond the terrestrial environment into the marine environment (Figure 7a). The distribution of agricultural pollution largely coincided with land-use types, concentrating primarily in cropland and inland waters, and gradually diminishing as it extends towards the Yellow Sea. The predominant land-use type is cropland; additionally, substantial portions of the original coastline have been developed into aquaculture farms and salt fields, serving as significant contributors to the extensive agricultural pollution observed. The study results above suggested As, as the major contributor to agricultural pollution, with the As concentration in Dingzi Bay surpassing the levels found in all adjacent water bodies. The pervasive presence of agricultural pollution raises concerns about its potential impact on the local population’s health, given the carcinogenic nature of inorganic As compounds to humans [63]. Strategies were recommended to incentivize farmers to adopt environmentally friendly production methods, emphasizing substantial reductions in potentially polluting input [64].
Industrial pollution was also prevalent in the terrestrial environment (Figure 7b). The study above indicated that Hg was dominant in industrial pollution, and the primary transport pathway for Hg is the atmosphere. Airborne Hg is transported over long distances and eventually redistributed in terrestrial and marine systems [65]. Therefore, Hg is generally not indicative of in situ deposition, and as a result, the sources of industrial pollution were not strictly localized around industrial land. The study area is characterized by numerous rivers, including the Wulong River, Baisha River, and Jituan River. The transport and mixing processes within these rivers also contribute to the expanded impact range of industrial and other types of pollution. Therefore, despite the low proportion of industrial land in the study area, a wide distribution of industrial pollution was still detected. Industrial activities release substantial quantities of toxic and hazardous substances such as soot, sulfur dioxide, HMs, persistent organic pollutants, etc., causing more severe harm than other forms of pollution [66]. With the ongoing acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, there is an increasing need for ecological restoration, monitoring, and the risk management of polluted sites, which should garner heightened attention [67].
Traffic pollution was sparsely scattered in the study area, indicating a low level of traffic pollution. An intriguing observation emerged: despite the presence of a highway in the study area, traffic pollution did not concentrate around the highway; instead, it tended to accumulate near village and town roads. This phenomenon was ascribed to the low traffic volume and reduced frequency of braking on the highway. In contrast, village and town roads are often in proximity to industrial land and densely populated residential areas, subject to heavy and stop-and-go traffic. This dynamic vehicular movement accelerates the wear and tear of brake pads and tires, thereby amplifying traffic pollution [57,68].
Maritime pollution in Dingzi Bay was observed in the external area of the bay (Figure 7d), corresponding to the maritime traffic patterns. Owing to sedimentation, the internal section of Dingzi Bay has lost its navigational conditions. In contrast, the adjacent Yellow Sea is home to major ports such as Qingdao Port, Rizhao Port, and Weihai Port, among others, contributing to active maritime activities. Wang et al. [69] analyzed the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Dingzi Bay, revealing lower PAHs within the bay compared to the Yellow Sea. The elevated PAHs in the outer part were mainly due to the combustion of coal and biomass required for navigation. This served as evidence that maritime pollution in Dingzi Bay was primarily sourced from the outer sea.
4. Conclusions
This study conducted a comprehensive analysis of the spatial distribution characteristics, pollution levels of eight HMs (Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, and Hg), pollution sources, and contamination range in Dingzi Bay and its surrounding terrestrial areas. The concentrations of most HMs exhibited a gradient, with the highest levels observed in the inner bay, followed by the terrestrial region, and the lowest levels in the outer bay. A strong continuity was observed between the terrestrial area and the inner bay, indicating the transport of HMs from the terrestrial region into the inner bay through Wulong River, subsequently dispersing to the outer bay. The correlation coefficients among elements in various particle fractions were investigated, revealing that Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, and Hg tended to accumulate in fine sediments, while As tended to load in particle fractions larger than 0.25 mm and finer than 0.016 mm. A comprehensive assessment of Dingzi Bay and its adjacent regions revealed an overall spatial pollution pattern, ranging from no pollution to very low pollution. However, localized instances of single-element pollution were found. The results of the PMF analysis identified four pollution sources: agricultural, industrial, traffic, and maritime pollution. Agricultural pollution, characterized primarily by As, exhibited a concentration in cropland and the inner part of the bay. Industrial pollution sources, characterized by Hg, were not strictly localized around industrial land due to their association with atmospheric migration. Traffic emissions impacted the levels of Cd, Pb, and Zn in the environment, primarily concentrated in areas with dense factories and residential populations. Maritime activities influenced concentrations of Hg, Cd, Cu, and Zn, mainly distributed in the offshore areas beyond the bay.
The findings of this study underscore the pressing necessity for integrated coastal zone management strategies that comprehensively address terrestrial and marine pollution sources. The intricate transport mechanisms of pollutants from land to sea highlight the interconnectivity of these ecosystems, emphasizing the imperative for holistic environmental policies.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, Y.L.; Investigation, X.G., J.S., Q.W., H.W., Y.C. and W.W.; Resources, X.G.; Writing—original draft, Y.L.; Writing—review & editing, S.Y.; Funding acquisition, X.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by China Geological Survey projects (Nos. DD20243132, DD20230073, DD20230412, DD20211578, DD20211553).
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study are openly available in Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11581999.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mandal, A.; Ghosh, A.; Saha, R.; Bhadury, P. Seasonal variability of modern benthic foraminifera assemblages in a mangrove ecosystem from northeast coastal Bay of Bengal. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN. International Policy Framework for Blue Carbon Ecosystems: Recommendations to Align Actions across International Policy Processes for the Conservation and Restoration of Coastal Blue Carbon Ecosystems; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, S. Ecological Functions and Biogenic Element Cycling Roles of Marine Sediment/Particles. CCAMLR Sci. 2017, 24, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Silliman, B.R. Climate Change, Human Impacts, and Coastal Ecosystems in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1021–R1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios-Yunes, D.; Tiano, J.C.; van Rijswijk, P.; De Borger, E.; van Oevelen, D.; Soetaert, K. Long-term changes in ecosystem functioning of a coastal bay expected from a shifting balance between intertidal and subtidal habitats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2023, 254, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, R.K.; Keyzer, L.M.; van de Velde, S.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Bouma, T.J. Climate change mitigation by coral reefs and seagrass beds at risk: How global change compromises coastal ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Han, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y. Impacts of anthropogenic discharge on distribution, mass budget, and long-term risk of total mercury in coastal region: A case study of the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shahawi, M.S.; Hamza, A.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Al-Saggaf, W.T. An overview on the accumulation, distribution, transformations, toxicity and analytical methods for the monitoring of persistent organic pollutants. Talanta 2010, 80, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, M. Biological effects of heavy metals: An overview. J. Environ. Biol. 2005, 26, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Bharagava, R.N.; More, N.; Yadav, A.; Zainith, S.; Mani, S.; Chowdhary, P. Heavy metal contamination: An alarming threat to environment and human health. Environ. Biotechnol. 2019, 2019, 103–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yin, P.; Chen, X.; Cao, K. Distribution, enrichment and transport of trace metals in sediments from the Dagu River Estuary in the Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. Minerals 2019, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kalamdhad, A. Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil, Plants, Human Health and Aquatic Life. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ip, C.C.M.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Wai, O.W.H.; Li, Y.-S. Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Li, J.; Luo, X.; Fu, T.; Chen, O.; Yang, Q. Identification of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments under long-term reclamation: Ecological toxicity, sources and implications for estuary management. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, H.; Feng, A. Research on Marine Functional Zoning of Dingzi Bay based on Resources and Environmental Evolution. KMI Int. J. Marit. Aff. Fish. 2013, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y. Geomorphic change in Dingzi Bay, East China since the 1950s: Impacts of human activity and fluvial input. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Pan, J.F.; Wang, M. Trace elements distribution and ecological risk assessment of seawater and sediments from Dingzi Bay, Shandong Peninsula, North China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Ecological and environmental risks of heavy metals in sediments in Dingzi Bay, South Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhan, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Impact of climate change and human activities on the runoff and sediment load discharged into the sea from mountainous rivers during the last 60 years: A case study of Wulong River in Southern Jiaodong Peninsula. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2012, 43, 891–899. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- The State Council of China. The State Council of China, National Marine Functional Zoning (2011–2020); The State Council of China: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad Ahirvar, B.; Das, P.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, M. Perspectives of heavy metal pollution indices for soil, sediment, and water pollution evaluation: An insight. Total Environ. Res. Themes 2023, 6, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Hou, K.; Ren, W.; Qu, W.; Chen, Y. Distribution characteristics, source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yellow River, China. Catena 2022, 216, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Dai, J.; Hu, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Background Values of Soil Geochemistry in Shandong Province. Shandong Land Resour. 2018, 32, 39–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg, L.A.; Meng, Q.; Yee, D.; Greenfield, B.K. Evidence for photochemical and microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in San Francisco Bay sediment. Chemosphere 2014, 106, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, K.; Yin, P.; Gao, F.; Chen, X. Composition, distribution and enrichment of trace metals in sediments from the muddy area off the southern Shandong Peninsula in the Northwestern South Yellow Sea of China since 10,000 years. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Du, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, E.; Yan, W. Source and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Laoshan Bay, South Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18668—2002; SBQTS. Marine Sediment Quality. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 242–245.
- Martinčić, D.; Kwokal, Ž.; Branica, M. Distribution of zinc, lead, cadmium and copper between different size fractions of sediments I. The Limski Kanal (North Adriatic Sea). Sci. Total Environ. 1990, 95, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomons, W.; Förstner, U. Sediments and the Transport of Metals. In Metals in the Hydrocycle; Salomons, W., Förstner, U., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984; pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.K.; Hasnain, S.I.; Banerjee, D.K. Grain size and geochemical partitioning of heavy metals in sediments of the Damodar River–a tributary of the lower Ganga, India. Environ. Geol. 1999, 39, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, W. Identification of factors controlling heavy metals/metalloid distribution in agricultural soils using multi-source data. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, V.B.; Hollas, C.E.; Bortoli, M.; Manosso, F.C.; de Souza, D.Z. Heavy metal contamination in soils of a decommissioned landfill southern Brazil: Ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Qiuhua, L.; Kuang, P.; Han, M.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, J. Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE) and Toxic Risk Index (TRI) Analysis of the Heavy Metals in Sediments of Hongfeng Reservoir, Southwest China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 3463–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, R.; Lin, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H. Multivariate statistical analysis of potentially toxic elements in the sediments of Quanzhou Bay, China: Spatial relationships, ecological toxicity and sources identification. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Shan, B.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, W. Heavy metal pollution of the surface sediments in a typical clean river system of Haihe Basin. Acta Sci. Circum. 2015, 35, 2860–2866. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, B.; Lin, G. Arsenic (As) contamination in sediments from coastal areas of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhao, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B.; Han, Z.; Huang, H.; Fan, Z. Determination of priority control factors for the management of soil trace metals based on source-oriented health risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chheang, L.; Limsuwan, P.; Thongkon, N.; Sriwiriyarat, T.; Thanasupsin, S.P.J.W. Ecological Risk Assessment and Source Contributions of Heavy Metals in the Sediment of the Chan Thnal Reservoir, Kampong Speu, Cambodia. Water 2023, 15, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cai, L.; Wen, H.; Luo, J. Characterizing pollution and source identification of heavy metals in soils using geochemical baseline and PMF approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumiahadi, A.; Acar, R. Soil Erosion in Indonesia and Its Control. In Proceedings of the International Symposium for Environmental Science and Engineering Research 2019, Konya, Turkey, 25–27 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir Ahmad, N.S.B.; Mustafa, F.B.; Muhammad Yusoff, S.Y.; Didams, G. A systematic review of soil erosion control practices on the agricultural land in Asia. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2020, 8, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in the surface seawater of the Yellow River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Dumat, C. A comparison of technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 182, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Wang, L.; Jiang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. Effects of Human Activities on the Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk and Sources of PTEs in Coastal Sediments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Wang, H.; Han, B.; Rao, Y.; Gong, H.; Zhang, W.; Gu, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S.; Huang, H. Coastal sediment heavy metal pollution under multifaceted anthropogenic stress: Insights based on geochemical baselines and source-related risks. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Shahab, A.; Ye, F.; Wei, G.; Li, J.; Deng, L. Source-specific ecological risk assessment and quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Pearl River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 179, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, S.N.; Cheng, I.; Gratz, L.E.; Weiss-Penzias, P.; Zhang, L. An updated review of atmospheric mercury. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, V. A new approach for indexing groundwater heavy metal pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 87, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckley, C.S.; Gustin, M.; Marsik, F.; Miller, M.B. Measurement of surface mercury fluxes at active industrial gold mines in Nevada (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Li, X.; Chen, W. High-resolution risk mapping of heavy metals in soil with an integrated static-dynamic interaction model: A case study in an industrial agglomeration area in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131650. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y. Strategy on China’s regional coal consumption control: A case study of Shandong province. Energy Policy 2018, 112, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yang, S.; Han, H.; Bai, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, Q. Is biomagnetic leaf monitoring still an effective method for monitoring the heavy metal pollution of atmospheric particulate matter in clean cities? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, P.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Gong, L.; Xia, S. Spatial distribution, source identification, and risk assessment of heavy metals in riparian soils of the Tibetan plateau. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 116977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szwalec, A.; Mundała, P.; Kędzior, R.; Pawlik, J. Monitoring and assessment of cadmium, lead, zinc and copper concentrations in arable roadside soils in terms of different traffic conditions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Reinhard, M. Environmental and Health Impacts of Artificial Turf: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2114–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, J. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in surface sediments of Luoyuan Bay, Fujian. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Yang, M.; Han, Z.; Chen, X. Distribution, contamination assessment, and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments from the south of the North Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 196, 115577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sohn, M. Aquatic arsenic: Toxicity, speciation, transformations, and remediation. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrington, G.; Nfa, L.W.; Parkinson, R.; Redman, M.; Winder, L. Agricultural Pollution: Environmental Problems and Practical Solutions; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pirrone, N.; Cinnirella, S.; Feng, X.; Finkelman, R.B.; Friedli, H.R.; Leaner, J.; Mason, R.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Stracher, G.B.; Streets, D.G.; et al. Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5951–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. Heavy metal pollution in China: Origin, pattern and control. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2003, 10, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C.; Cao, X.; Chen, C.; Cui, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Johnson, A.C.; et al. Ecology of industrial pollution in China. Ecosyst. Health Sustain. 2020, 6, 1779010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limo, J.; Paturi, P.; Mäkinen, J. Magnetic biomonitoring with moss bags to assess stop-and-go traffic induced particulate matter and heavy metal concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 195, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Han, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Z. Distribution, source, and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface sediments from Dingzi Bay, China. J. Sea Res. 2023, 193, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).