Geochemical Assessment of Heavy Metal Distribution in Bug River Sediments, Poland: The Impacts of Urbanization and Agricultural Practices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area
2.2. River Sediment Sampling and Analytical Procedures
2.3. Assessment of Sediment Contamination
2.4. Spatial Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Concentration of Metals in the Surface Sediments of the Bug River Catchment Area
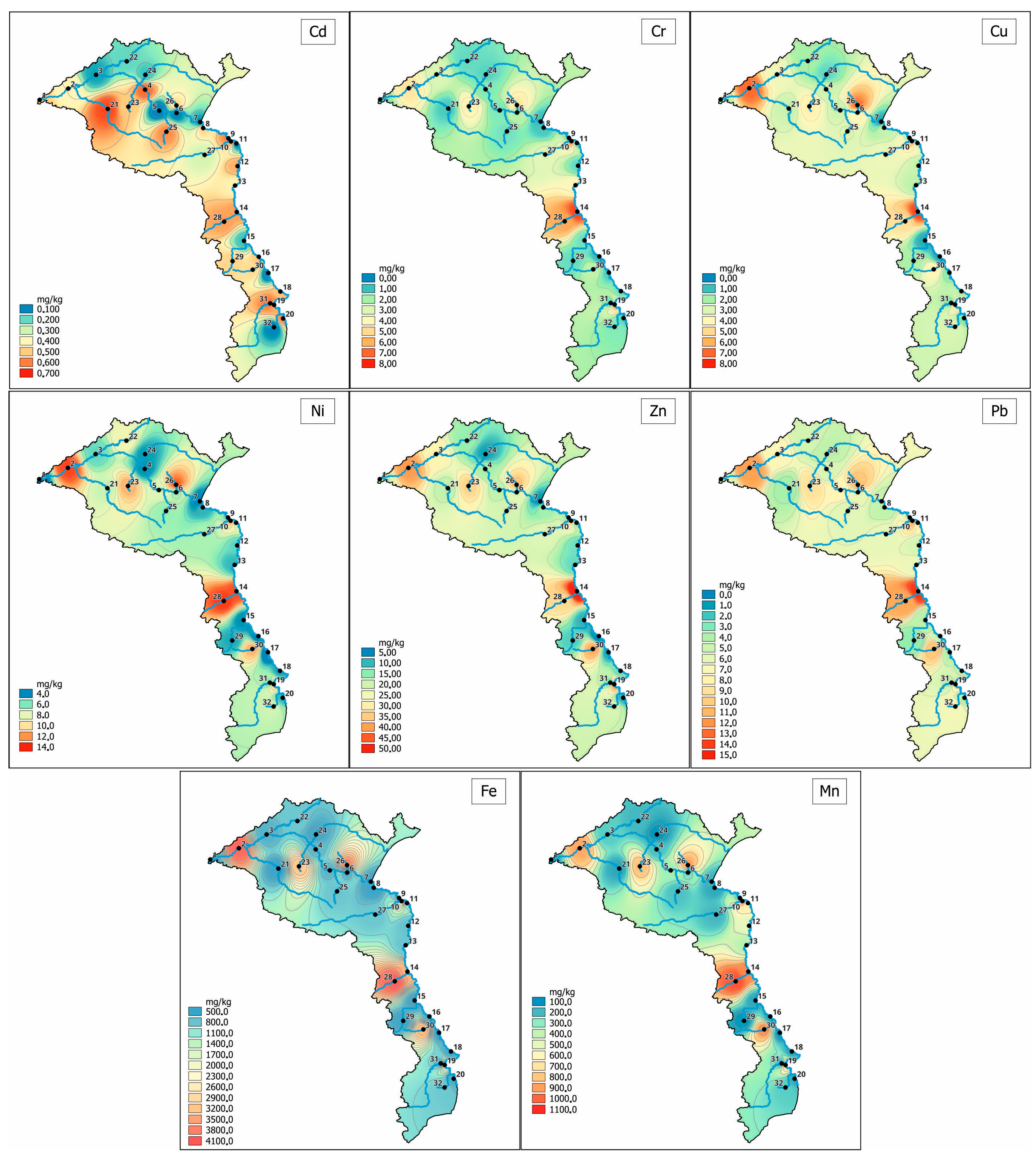
3.2. Spatial Variability in Heavy Metals in the Surface Sediments of the Bug River and Its Tributary Systems
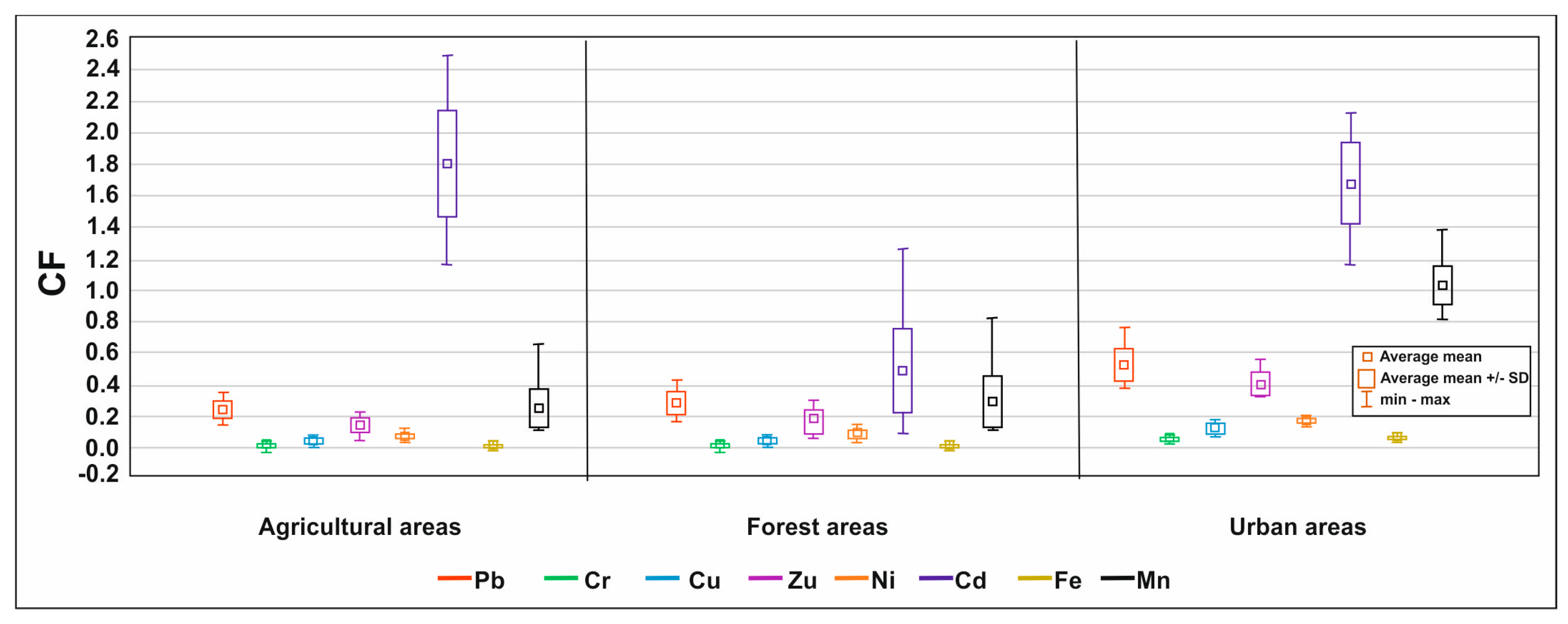
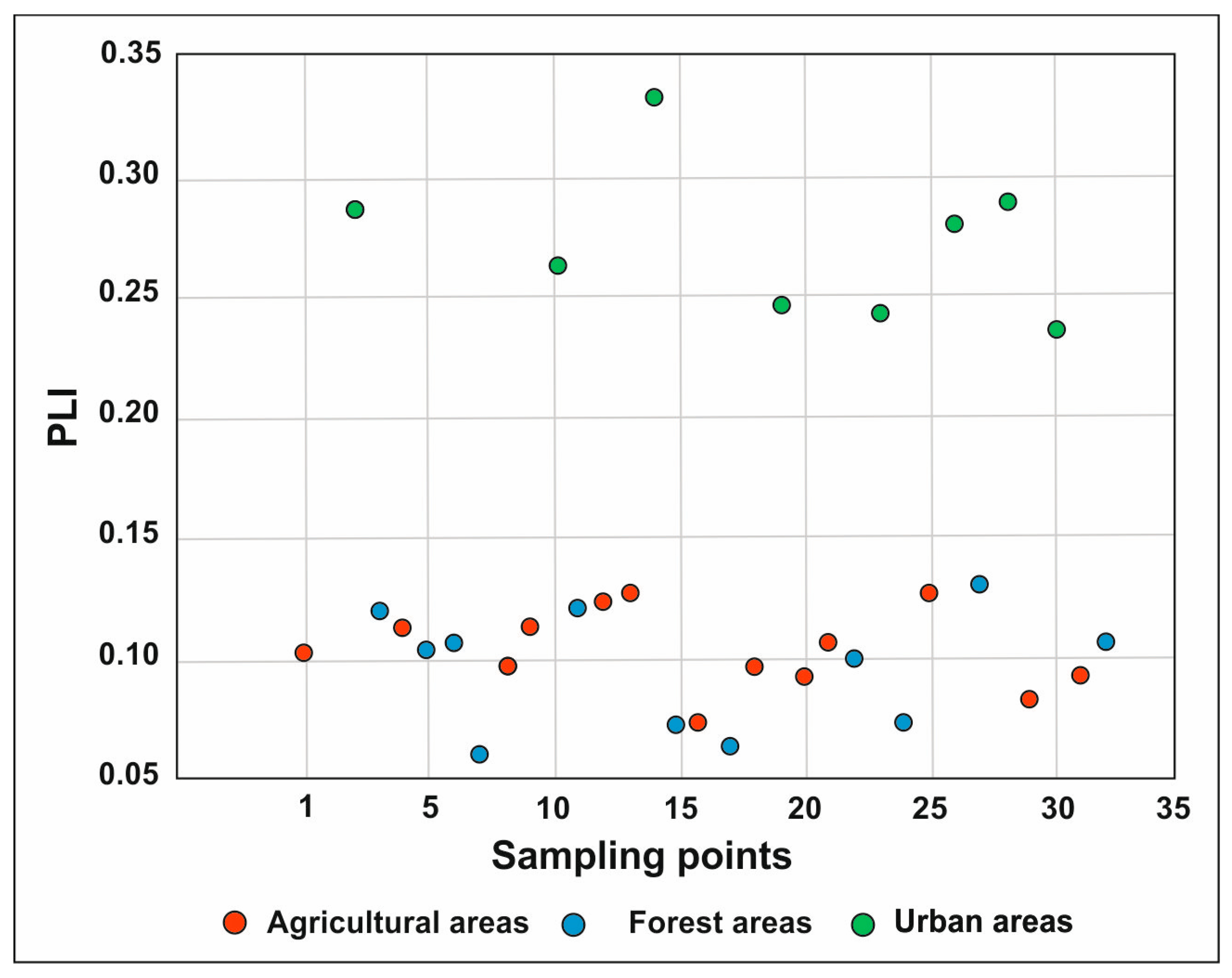
3.3. Indices of Heavy Metal Pollution of the Bug River’s Surface Sediments
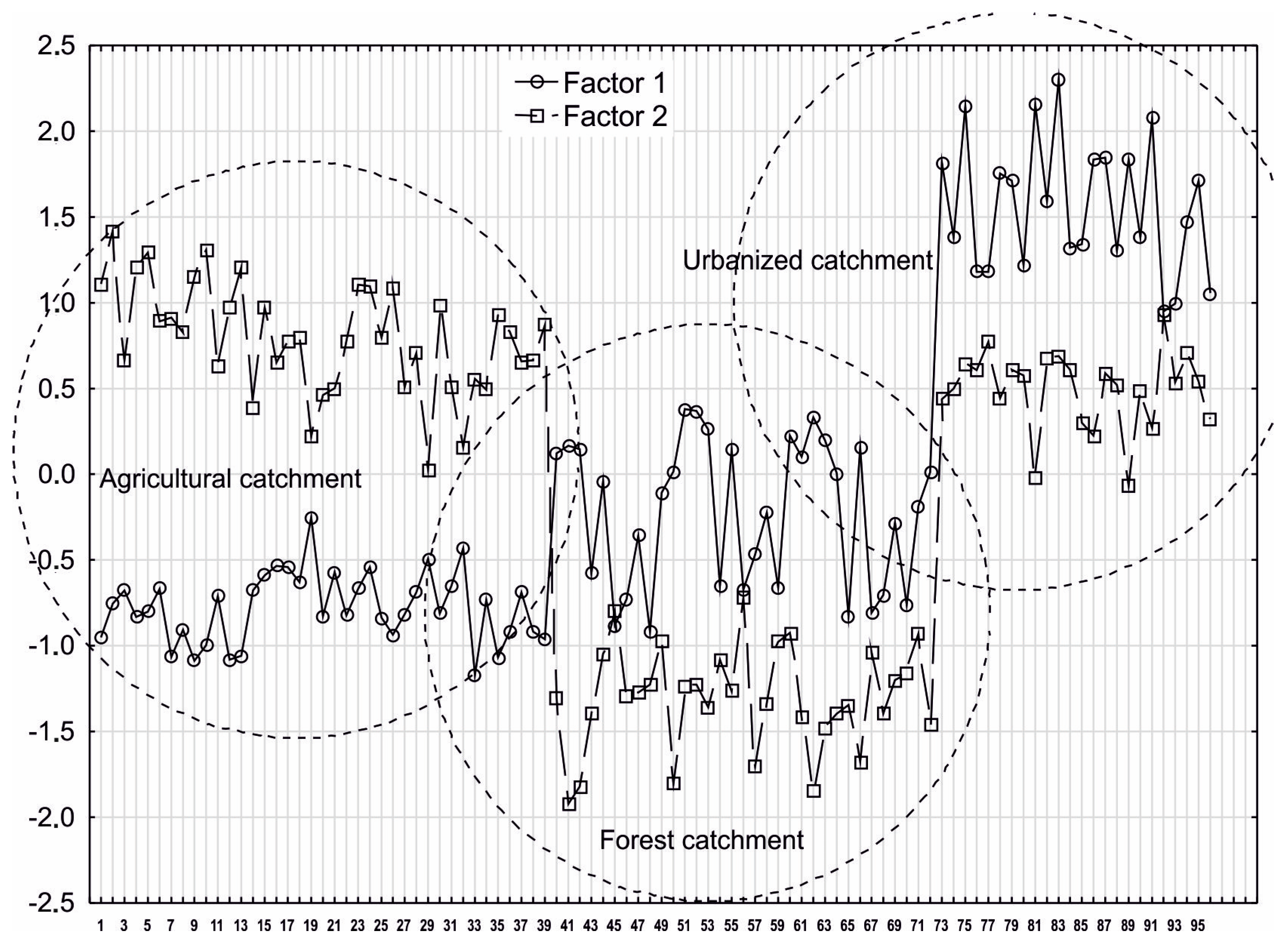
3.4. Identification of Sources of Pollution via Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, P. Levels and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of tidal fats along the North Jiangsu coast, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustaoğlu, F.; Islam, M.S. Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: A preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 113, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.P. Trace Metals in Aquatic Systems; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; p. 440. [Google Scholar]
- Skorbiłowicz, E. Assessment of heavy metals contents in surface sediments of Bug River. J. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 15, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sidoruk, M.; Cymes, I. Effect of water management technology used in trout culture on water quality in fish ponds. Water 2018, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Ren, B. Trends and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake sediments from 1970 to 2018. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 257, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sidoruk, M.; Cymes, I.; Kobus, S. Impact of trout breeding in a cascade water flow technology on water quality. J. Elem. 2020, 25, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Fan, D.; Liu, M.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y. Source identifcation, geochemical normalization and infuence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Prada, L.; García-Ordiales, E.; Roquńí, N.; Gil, J.A.G.; Loredo, J. Geochemical distribution of selected heavy metals in the Asturian coastline sediments (North of Spain). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 156, 111263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, M.; Bakhshi, K.; Zarei, A.; Hoseinzadeh, E.; Gholizadeh, A. Soil pollution indices and health risk assessment of metal(loid)s in the agricultural soil of pistachio orchards. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ordiales, E.; Loredo, J.; Covelli, S.; Esbri, J.M.; Millan, R.; Higueras, P. Trace metal pollution in freshwater sediments of the world’s largest mercury mining district: Sources, spatial distribution, and environmental implications. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, F.; Huang, X. Spatial and seasonal characteristics of dissolved heavy metals in the east and west Guangdong coastal waters, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Saha, N.; Molla, A.; Al-Reza, S. Assessment of Anthropogenic Infuence on Heavy Metals Contamination in the Aquatic Ecosystem Components. Water, Sediment, and Fish. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Qin, B.; Li, W.; Gao, G. Growth and Community Composition of Submerged Macrophytes in Lake Taihu (China): Assessment of Changes in Response to Sediment Characteristics. Wetlands 2016, 37, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, H.; Baiyinbaoligao; Hu, H.; Khan, M.Y.A.; Wen, J.; Chen, L.; Tian, F. Future projection of seasonal drought characteristics using CMIP6 in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, S.; Neven, C.; Stanislav, F.B.; Ali, K.M.; Mihri, H. Contamination assessment of ecotoxic metals in recent sediments from the Ergene River, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J. Heavy metals in river sediments: Contamination, toxicity, and source identification—A case study from Poland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Duodu, G.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G. Infuence of land use confgurations on river sediment pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.B.; Matin, A.; Sarker, M.S.I. Assessment of heavy metal pollution, distribution and source apportionment in the sediment from Feni River estuary, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, A.; Singh, P.K.; Sharma, Y.C. Metallic contamination of global river sediments and latest developments for their remediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorbiłowicz, M.; Skorbiłowicz, E.; Tarasiuk, U.; Falkowska, M. Studies of heavy metal content in bottom sediments and aquatic plants near treated wastewater discharge. Geology Geoph. Environ. 2017, 43, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Feng, T. Metals and metalloids distribution, source identifcation, and ecological risks in riverbed sediments of the Jinsha River, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 205, 106334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojakowska, I. Criteria for assessing the pollution of water sediment. Prz. Geol. 2001, 49, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lis, J.; Pasieczna, A. Geochemical Atlas of Polond 1:2 500 000; Polish Geological Institute: Warszawa, Poland, 1995; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Bojakowska, I.; Sokołowska, G. [Geochemical classes of purity of aquatic sediments] Geochemiczne klasy czystości osadów wodnych. Prz. Geol. 1998, 46, 49–54. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Turekian, K.K.; Wedepohl, K.H. Distribution of the Elements in Some Major Units of the Earth’s Crust. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1961, 72, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Schwermetalle in den sedimenten des Rheins, Veranderungen Seit 1971. Umschau 1979, 79, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the Assessment of Heavy-Metal Levels in Estuaries and the Formation of a Pollution Index. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyon, M.A.H.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Likuku, A.S.; Mmolawa, K.B.; Gaboutloeloe, G.K. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment and degree of contamination around the copper-nickel mine in the Selebi Phikwe region, Eastern Botswana. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2013, 1, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ren, B.; Hursthouse, A.S.; Zhou, Y. Trace metal pollution in topsoil surrounding the Xiangtan Manganese mine area (South-central China): Source identification, spatial distribution and assessment of potential ecological risks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadi, S.A.; Mohammadi, A.; Khosravi, R.; Zarei, A. Distribution, exposure, and human health risk analysis of heavy metals in drinking groundwater of Ghayen County, Iran. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 13127–13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acksel, A.; Giani, L.; Stasch, C.; Kühn, P.; Eiter, S.; Potthoff, K.; Regier, T.; Leinweber, P. Humus-rich topsoils in SW Norway—Molecular and isotopic signatures of soil organic matter as indicators for anthropo-pedogenesis. Catena 2019, 172, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.W.; Gunn, J.M.; Dixit, S.S. Sediment trace metal profiles in lakes of Killarney Park, Canada: From regional to continental influence. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 130, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, D.E.; Akinci, G. Effect of sediment size on bioleaching of heavy metals from contaminated sediments of Izmir Inner Bay. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 1784–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoğlu, S.; Karaer, F. Relationships of Heavy Metals in Waterand Surface Sediment with Different Chemical Fractions in Lake Uluabat, Turkey. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2016, 25, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Wen, J. Evaluation of physicochemical and heavy metals characteristics in surface water under anthropogenic activities using multivariate statistical methods, Garra River, Ganges Basin, India. Environ. Eng. Res. 2021, 26, 200280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oost, K.V.; Cerdan, O.; Quine, T.A. Accelerated sediment fluxes by water and tillage erosion on European agricultural land. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegari Mehr, M.; Shakeri, A.; Amjadian, K.; Khalilzadeh Poshtegal, M.; Sharifi, R. Bioavailability, distribution and health risk assessment of arsenic and heavy metals (HMs) in agricultural soils of Kermanshah Province, west of Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, L.C.; Tiecher, T.; de Oliveira, J.S.; Andreazza, R.; Inda, A.V.; de Oliveira Camargo, F.A. Sediment pollution in margins of the Lake Guaíba, Southern Brazil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: Insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese. Greece. Geoderma 2014, 221–222, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghavi, M.; Darvishiyan, M.; Momeni, M.; Momeni, M.; Eslami, H.; Fallahzadeh, R.A.; Zarei, Z. Ecological risk assessment of trace elements (TEs) pollution and human health risk exposure in agricultural soils used for saffron cultivation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Huang, S.; Deng, L.; Ji, B. A Critical Review of the Effectiveness of Biochar Coupled with Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Soil Cadmium Immobilization. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Gani, K.M.; Chakrapani, G.J. Spatial and temporal variations of physicochemical and heavy metal pollution in Ramganga River—A tributary of River Ganges, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayrat, A.; Eziz, M. Identification of the spatial distributions, pollution levels, sources, and health risk of heavy metals in surface dusts from Korla, NW China. Open Geosci. 2020, 12, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckeman, T.; Gossiaux, L.; Guimont, S.; Sirguey, C.; Lin, Z. Cadmium mass balance in French soils under annual crops: Scenarios for the next century. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahoor, I.; Mushtaq, A. Water pollution from agricultural activities: A critical global review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Milke, J.; Gałczyńska, M.; Wróbel, J. The Importance of Biological and Ecological Properties of Phragmites Australis (Cav.) Trin. Ex Steud., in Phytoremendiation of Aquatic Ecosystems-The Review. Water 2020, 12, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Pérez, A.M.; Álvarez-Vázquez, M.A.; De Ula-Álvarez, E.; de Blas, E. Environmental Assessment of Trace Metals in San Simon Bay Sediments (NW Iberian Peninsula). Minerals 2020, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Shan, B.; Sun, D. Spatial Distribution, Potential Risks and Source Identification of Heavy Metals in the Coastal Sediments of the NorthernBeibu Gulf, South China Sea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabadayi, F.; Cesur, H. Determination of Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Co, Cd and Mn in road dusts of Samsun City. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 168, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, F.; Cattaruzza, E.; Gonella, F.; Rampazzo, G.; Valotto, G. Characterization of road dust collected in Traforo del San Bernardo highway tunnel: Fe and Mn speciation. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6459–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamiec, E.; Jarosz-Krzemińska, E.; Wieszała, R. Heavy metals from non-exhaust vehicle emissions in urban and motorway road dusts. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Y.A.; Gani, K.M.; Chakrapani, G.J. Assessment of surface water quality and its spatial variation. A case study of Ramganga River, Ganga Basin, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaram, B.S.; Suryawanshi, P.V.; Bhanarkar, A.D.; Rao, C.V.C. Heavy metals contamination in road dust in Delhi city. India Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 3929–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Li, H.; Jones, K.C.; Martin, F.L. Understanding and harnessing the health effects of rapid urbanization in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landre, A.L.; Winter, J.G.; Helm, P.; Hiriart-Baer, V.; Young, J. Metals in Lake Simcoe sediments and tributaries: Do recent trends indicate changing sources? J. Great Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Yang, M.; Wang, X. Environmental Health and Ecological Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Coastal Cities of Estuarine Bay—A Case Study of Hangzhou Bay, China. Toxics 2020, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzal, Y.; Bárbulescu, A.; Howari, F.; Al-Taani, A.A.; Iqbal, J.; Xavier, C.M.; Sharma, M.; Dumitriu, C.S. Assessment of Metals Concentrations in Soils of Abu Dhabi Emirate Using Pollution Indices and Multivariate Statistics. Toxics 2021, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorbiłowicz, E.; Skorbiłowicz, M.; Rogowska, W. Temporal and spatial changes in metal contents of arable soils in the Bug river catchment in 1995–2015 (Poland). Int. J. Conserv. Sci. 2022, 13, 895–914. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, G.; Ramasamy, V.; Meenakshisundaram, V.; Venkatachalapathy, R.; Ponnusamy, V. Influence of mineralogical and metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, M.S.; Bakar, M.A.; Akhtar, A.; Hossain, M.B.; Ali, M.M.; Islam, M.S. Metal contamination in surface water and sediment of the Meghna River, Bangladesh. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2017, 8, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciazela, J.; Siepak, M.; Wojtowicz, P. Tracking metal contamination in a complex river-oxbow lake system: Middle Odra Valley, Germany/Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, S.M.D.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Rume, T.; Mohinuzzaman, M. Assessing heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Shitalakhya River, Bangladesh, using pollution evaluation indices and geo-spatial analysis. Pollution 2016, 2, 299–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Negrete-Bolagay, D.; Figueroa, F.; Zamora-Ledezma, F.; Ni, M.; Alexis, F.; Guerrero, V.H. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopchak, I.; Kalko, A.; Basiuk, T.; Pinchuk, O.; Gerasimov, I.; Yaromenko, O.; Shkirynets, V. Assessment of surface water pollution in Western Bug River within the cross-border section of Ukraine. J. Water Land Dev. 2020, 46, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Połeć, K.; Grzywna, A. Influence of Natural Barriers on Small Rivers for Changes in Water Quality Parameters. Water 2023, 15, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, T.; Xiao, J.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Dong, L. Major ion and dissolved heavy metal geochemistry, distribution, and relationship in the overlying water of Dongting Lake. China Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 laying down rules on the making available on the market of EU fertilising products and amending Regulations (EC) No. 1069/2009 and (EC) No. 1107/2009 and repealing Regulation (EC) No. 2003/2003. 25.6.2019. L 170/1.
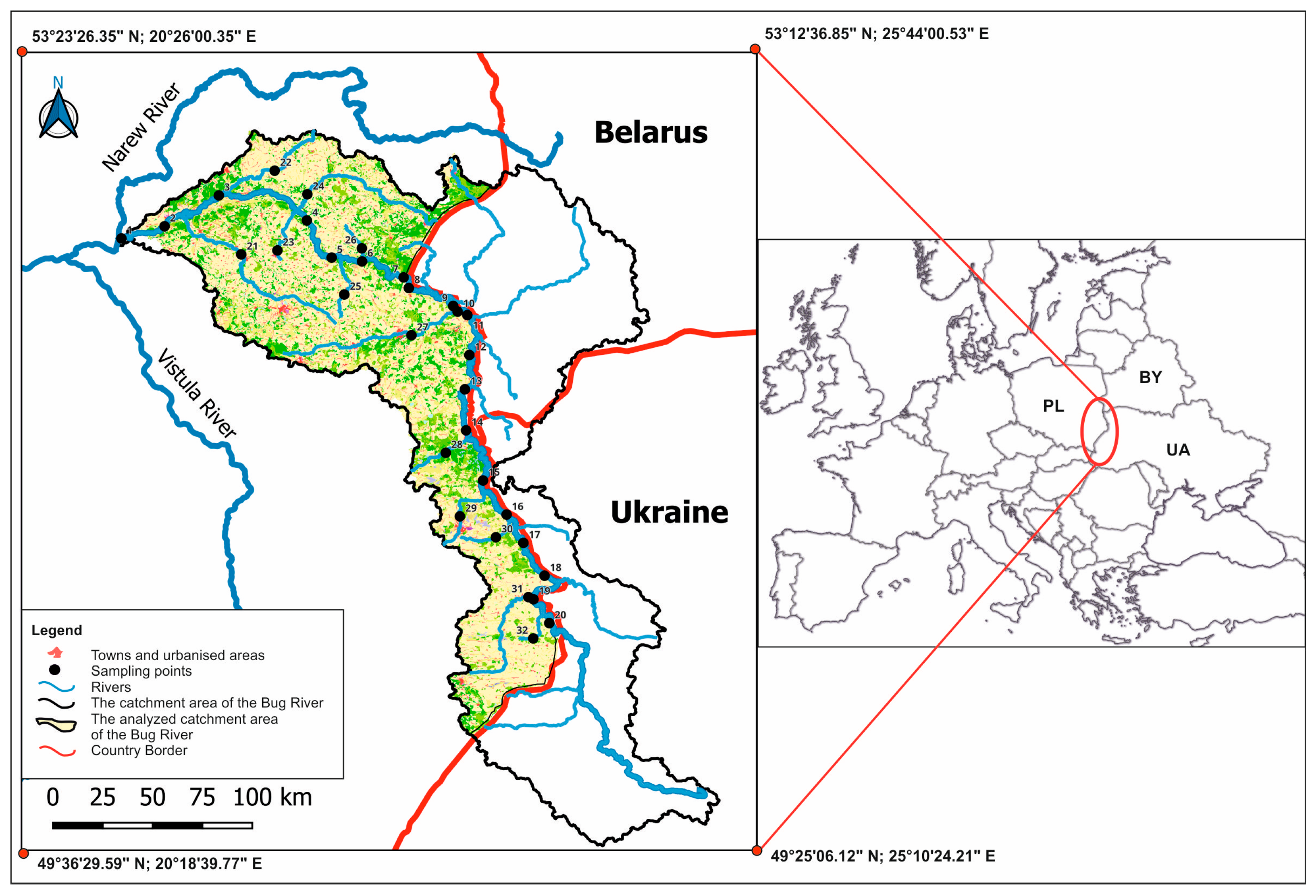

| Type of Land Use | Sampling Points | Sampling Point Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Urban areas | 2 10 14 19 23 26 28 30 | Points situated within densely populated urban areas: Wyszków (26.965 inhabitants), Włodawa (13.535), Hrubieszów (18.212), Siemiatycze (15.169). Points were situated along roads traversing smaller towns adjacent to both single- and multifamily residential structures as well as service buildings, including sewage treatment plants. |
| Forest areas | 3 5 6 7 11 15 17 22 24 27 32 | Points situated within extensive forest complexes, encompassing naturally significant areas protected under the Natura 2000 program (Sobiborski Landscape Park, Podlaska Switzerland Reserve, Oak Meadow Nature Reserve) |
| Agricultural areas | 1 4 8 9 12 13 16 18 20 21 25 29 31 | Points near areas to be cultivated |
| Parameter | λ [nm] | R2 | LoD [mg/kg] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cadmium | 228.8 | 0.998 | 0.08 |
| Lead | 217.3 | 0.996 | 0.05 |
| Chromium | 357.9 | 0.993 | 0.31 |
| Mercury | 324.7 | 0.999 | 0.02 |
| Zinc | 213.9 | 0.997 | 0.25 |
| Nickel | 232.0 | 0.997 | 0.40 |
| Iron | 248.3 | 0.999 | 0.09 |
| Manganese | 279.5 | 0.996 | 0.17 |
| Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) | Contamination Factor (CF) | Pollution Load Index (PLI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | Sediment Quality | Value | Sediment Contamination | Value | Pollution Status |
| Igeo ≤ 0 | Uncontaminated | CF < 1 | low | PLI = 0 | Perfection |
| 0 < Igeo < 1 | Uncontaminated to moderately contaminated | ||||
| 1 < Igeo < 2 | Moderately contaminated | 1 ≤ CF < 3 | moderate | 0 < PLI ≤ 1 | Only baseline levels of pollution |
| 2 < Igeo < 3 | Moderately to strongly contaminated | 3 ≤ CF< 6 | considerable | PLI > 1 | Deterioration of sediment quality |
| 3 < Igeo < 4 | Strongly contaminated | CF ≥ 6 | very high | ||
| 4 < Igeo < 5 | Strongly to extremely contaminated | ||||
| Igeo ≥ 5 | Extremely contaminated | ||||
| Conductivity | OM | pH | Fe | Mn | Ni | Zn | Cr | Cu | Pb | Cd | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGB | 47,200 | 850 | 68 | 95 | 90 | 45 | 20 | 0.3 | |||
| LGB | n.a. | n.a. | 5 | 48 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 0.5 | |||
| urban area n = 24 | |||||||||||
| min | 512.00 | 0.33 | 6.87 | 1659.33 | 701.25 | 9.74 | 32.15 | 2.35 | 3.62 | 7.73 | 0.35 |
| max | 1003.00 | 1.11 | 7.32 | 4852.11 | 1182.01 | 14.26 | 53.94 | 8.13 | 8.05 | 15.36 | 0.64 |
| average ± SD | 766.17 sł ±151.16 | 0.75 pr ±0.29 | 3264.04 łm ±786.27 | 882.61 no ±96.81 | 12.00 ij ±1.40 | 38.75 gh ±6.35 | 5.29 cd ±1.63 | 5.65 ef ±1.28 | 10.67 ab ±1.95 | 0.50 l ±0.08 | |
| CV (%) | 19.73 | 39.44 | 24.09 | 10.98 | 11.63 | 16.39 | 30.87 | 22.73 | 18.31 | 15.50 | |
| agricultural area n = 39 | |||||||||||
| min | 298.00 | 0.81 | 6.99 | 492.36 | 110.08 | 3.59 | 5.11 | 0.87 | 0.67 | 3.01 | 0.35 |
| max | 615.00 | 2.69 | 8.22 | 941.02 | 563.29 | 8.45 | 21.48 | 4.61 | 3.61 | 7.18 | 0.75 |
| average ± SD | 442.64 s ±74.04 | 1.24 p ±0.46 | 654.39 ł ±119.04 | 220.40 n ±100.72 | 5.31 i ±1.03 | 14.45 g ±4.14 | 1.54 c ±0.77 | 2.25 e ±0.65 | 5.04 a ±1.01 | 0.54 k ±0.10 | |
| CV (%) | 16.73 | 37.32 | 18.19 | 45.70 | 19.37 | 28.67 | 50.05 | 29.01 | 20.01 | 18.45 | |
| forest area n = 33 | |||||||||||
| min | 318.00 | 2.78 | 7.22 | 501.14 | 120.99 | 3.12 | 6.95 | 0.87 | 0.55 | 3.45 | 0.03 |
| max | 695.00 | 4.01 | 8.26 | 1110.25 | 704.81 | 8.99 | 28.94 | 3.99 | 4.15 | 8.63 | 0.38 |
| average ± SD | 484.33 ł ±95.60 | 3.48 pr ±0.44 | 719.12 m ±160.35 | 252.35 o ±137.52 | 6.12 ij ±1.77 | 16.34 h ±6.63 | 1.78 d ±0.77 | 2.35 f ±1.07 | 5.86 ab ±1.44 | 0.15 kl ±0.08 | |
| CV (%) | 19.74 | 12.77 | 22.30 | 54.49 | 28.91 | 40.56 | 43.47 | 45.55 | 24.52 | 54.90 | |
| entire catchment n = 96 | |||||||||||
| min | 298.00 | 0.33 | 6.87 | 492.36 | 110.08 | 3.12 | 5.11 | 0.87 | 0.55 | 3.01 | 0.03 |
| max | 1003.00 | 4.01 | 8.26 | 4852.11 | 1182.01 | 14.26 | 53.94 | 8.13 | 8.05 | 15.36 | 0.75 |
| average ± SD | 537.85 ±169.38 | 1.79 ±1.10 | 1329.05 ±1194.15 | 396.94 ±303.88 | 7.26 ±3.10 | 21.18 ±11.67 | 2.56 ±1.90 | 3.13 ±1.76 | 6.73 ±2.72 | 0.40 ±0.20 | |
| CV (%) | 31.49 | 61.17 | 89.85 | 76.56 | 42.75 | 55.10 | 74.11 | 56.01 | 40.38 | 50.90 | |
| Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn | Ni | Cd | Fe | Mn | OM | pH | Conductivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 1.00 | ||||||||||
| Cr | 0.86 | 1.00 | |||||||||
| Cu | 0.88 | 0.85 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| Zn | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.93 | 1.00 | |||||||
| Ni | 0.88 | 0.79 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Cd | 0.10 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 1.00 | |||||
| Fe | 0.86 | 0.76 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.25 | 1.00 | ||||
| Mn | 0.89 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.90 | 0.21 | 0.93 | 1.00 | |||
| OM | −0.35 | −0.39 | −0.40 | −0.38 | −0.36 | −0.80 | −0.45 | −0.44 | 1.00 | ||
| pH | −0.75 | −0.69 | −0.75 | −0.80 | −0.76 | −0.03 | −0.75 | −0.72 | 0.26 | 1.00 | |
| Conductivity | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.15 | 0.70 | 0.72 | −0.34 | −0.70 | 1.00 |
| Variable | Factor 1 | Factor 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.94 | 0.09 |
| Cr | 0.87 | 0.19 |
| Cu | 0.92 | 0.19 |
| Zn | 0.92 | 0.18 |
| Ni | 0.93 | 0.14 |
| Cd | 0.04 | 0.96 |
| Fe | 0.90 | 0.23 |
| Mn | 0.92 | 0.21 |
| OM | −0.27 | −0.91 |
| pH | −0.86 | 0.01 |
| Conductivity | 0.79 | 0.13 |
| (%) var. | 70 | 15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skorbiłowicz, E.; Ofman, P.; Skorbiłowicz, M.; Sidoruk, M.; Tarasiuk, U. Geochemical Assessment of Heavy Metal Distribution in Bug River Sediments, Poland: The Impacts of Urbanization and Agricultural Practices. Water 2024, 16, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111573
Skorbiłowicz E, Ofman P, Skorbiłowicz M, Sidoruk M, Tarasiuk U. Geochemical Assessment of Heavy Metal Distribution in Bug River Sediments, Poland: The Impacts of Urbanization and Agricultural Practices. Water. 2024; 16(11):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111573
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkorbiłowicz, Elżbieta, Piotr Ofman, Mirosław Skorbiłowicz, Marcin Sidoruk, and Urszula Tarasiuk. 2024. "Geochemical Assessment of Heavy Metal Distribution in Bug River Sediments, Poland: The Impacts of Urbanization and Agricultural Practices" Water 16, no. 11: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111573
APA StyleSkorbiłowicz, E., Ofman, P., Skorbiłowicz, M., Sidoruk, M., & Tarasiuk, U. (2024). Geochemical Assessment of Heavy Metal Distribution in Bug River Sediments, Poland: The Impacts of Urbanization and Agricultural Practices. Water, 16(11), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16111573







