Abstract
Drought is one of the most frequent types of natural disasters in the world, and it has been classified into several different categories. Generally, meteorological drought is considered to be the beginning of a drought disaster, while socio-economic drought is the possible ultimate result. However, controversy remains around the main impact factors in the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought over the past decades. In this study, a comprehensive investigation of the 2022 drought event in the city of Lishui, China was conducted to build a model for analyzing the main impact factors in the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought. The results showed that the 2022 drought event had a great impact on the city’s socio-economic activities. According to governmental reports on socio-economic drought and basic information on water sources, a random forest attribution analysis model was built. The model demonstrated a great performance in distinguishing whether a socio-economic drought had occurred, with an accuracy of 0.9935, a true positive rate of 0.9489 and a false positive rate of 0.0021. Additionally, the variables related to water sources—including drainage area, covered population and daily water supply volume—were found to be more important than the other variables related to meteorological conditions in the model, meaning that the capacity of water sources is the main impact factor in the propagation between meteorological drought and socio-economic drought. In other words, it is feasible to prevent the propagation of meteorological drought to socio-economic drought through water conservancy engineering construction.
1. Introduction
With the rapid growth of global water demand as well as climate change, drought, as one of the most common types of natural disasters, is posing a challenge to the safety of socio-economic development [1,2]. Over the past few decades, a number of researchers have proposed a series of drought indices to identify, evaluate and predict drought events, such as the standardized precipitation index (SPI) and the Palmer drought severity index (PDSI) [3,4,5]. Generally, drought is divided into four categories, i.e., meteorological drought, hydrological drought, agricultural drought and socio-economic drought, between which a natural propagation chain is formulated [6,7]. When precipitation falls below a specific threshold, meteorological drought occurs first, and the deficiency of precipitation further leads to a decrease in runoff and soil moisture, triggering hydrological drought and agricultural drought, which may have an impact on the safety of the water supply and food production, ultimately resulting in socio-economic drought. However, due to the influence of human activities, the natural propagation chain of drought is becoming increasingly inapparent [8,9]. For example, reservoirs can store excess water during the wet season for use in the dry season, which means that meteorological drought may not necessarily lead to hydrological, agricultural or socio-economic drought [10,11]. To be more specific, meteorological drought occurs naturally and is scarcely affected by human activities. However, it is feasible to prevent meteorological drought from propagating to socio-economic drought through various methods, such as a reasonable layout of water conservation projects and reservoir regulation [12,13]. Therefore, it is of great significance to understand the main impact factors of drought propagation under human activities in order to evaluate the impact of drought [14,15].
Many previous studies have investigated the propagation between different categories of drought, along with its impact factors, but most of these studies have focused on large spatial scales with low resolution, such as large basins, counties and even globally [16,17,18,19]. There is still a lack of research on the impact factors of drought propagation at a detailed resolution in relatively small areas; as such, many research results serve only as a reference for large-scale drought countermeasures, while playing a limited role at a small scale [20,21]. However, the proportion of water conservancy engineering with the ability to influence large areas is quite small in the drought prevention system. Most water conservancy engineering can only affect the local area, which makes many large-scale research findings impractical. Furthermore, compared to large-scale droughts, small-scale droughts are generally more frequent and may have a more severe impact on the local area. Therefore, it is meaningful to strengthen the research on small-scale droughts. Although the development of hydrometeorological simulations and remote sensing provides an opportunity to evaluate meteorological, hydrological and agricultural droughts in small areas and the propagation between them, it is still quite difficult to study small-scale socio-economic droughts and the impact factors in their propagation due to the limitations of measured data on the impact of droughts on socio-economic activities [22,23].
In this study, an attribution analysis of the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought was conducted based on a detailed practical survey of an extreme drought disaster in 2022 in the city of Lishui, China. In order to identify the main impact factors that led to the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought, large amounts of in situ data, including information about precipitation, water sources and socio-economic activities affected by the drought, were employed to build a random forest model. The results of this study contribute to improving our understanding of the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought, and they can be used as a reference for government managers when formulating construction plans for water conservation projects. In the next section, we present an overview of the study area and data sources. The methodology of this study is detailed in Section 3. Section 4 describes the results and discussion, and the conclusions are provided in Section 5.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
The city of Lishui is located in Zhejiang Province, southeastern China, with an area of 17,324 km2. The city is mainly characterized by mountainous terrain, accounting for 88.4% of its total area. Additionally, the city receives a large amount of precipitation every year. Due to the mountainous terrain and abundant precipitation, Lishui is the source of several large rivers, meaning that the city has abundant water resources and good water quality. However, as a typical area influenced by the monsoon climate, the precipitation and runoff in Lishui are unevenly distributed throughout the year and undergo significant interannual changes. The annual runoff is mainly concentrated from March to June, accounting for 56% of the total annual runoff. The location and a digital elevation model (DEM) of the city of Lishui are shown in Figure 1.
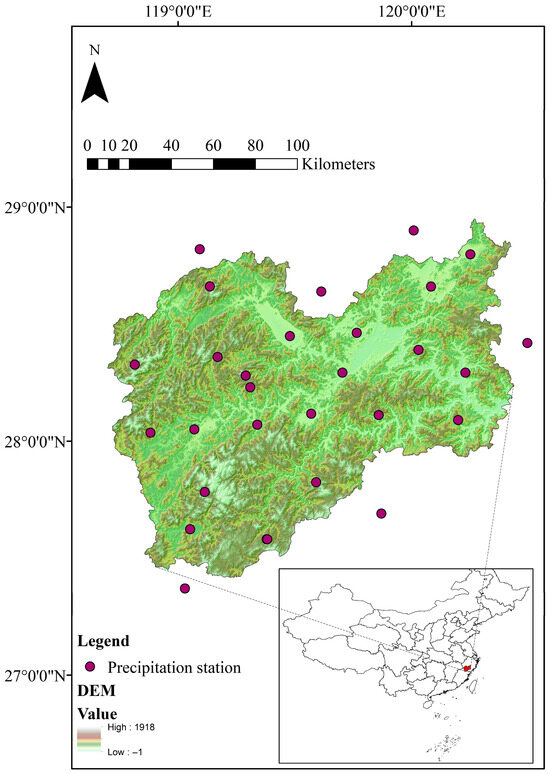
Figure 1.
Location and DEM of the city of Lishui.
Although Lishui has abundant high-quality water resources, the city still faces several severe problems in water supply due to the limitations of its terrain and climate. The undulating mountainous terrain limits the water supply range of large-scale water sources, resulting in a large number of remote villages in mountainous areas relying on small ponds or rivers as their water sources, which are greatly affected by the weather. In addition, due to the rapid socio-economic development of Lishui over the past decade, the water demand in some areas has also sharply increased, leaving the water supply capacity of the original water sources in these areas insufficient. In general, drought has posed a major threat to the safety of the water supply system in Lishui. There is, therefore, an urgent need to characterize the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought, to support the formulation of future plans for Lishui.
Lishui suffered from an extreme drought event from July to October 2022. The average precipitation in the city during these four months was 212.9 mm, 63.3% less than the multi-year average for the same period, and it was especially low in September and October, where it was 80.0% and 87.3% less than the multi-year average for the same period, respectively. This serious lack of precipitation led to water supply crises in many areas. Over 1 million people experienced water supply restrictions due to the drought, causing a huge socio-economic impact.
2.2. Data Sources
In this study, the supply area for each water source was selected as the research unit (i.e., each water source corresponded to a research unit), and whether the water supply security was affected by the drought in 2022 was used as the basis for determining the occurrence of socio-economic drought. For the analysis of the meteorological drought, socio-economic drought and the propagation between them in Lishui during 2022, three main types of data were employed, i.e., the long-term precipitation, the water sources and the socio-economic drought condition of each research unit.
The precipitation was determined from the observation data recorded at ground stations in and around Lishui. The locations of the precipitation ground stations used in this paper are shown in Figure 1, and the time series of the precipitation data is from 1991 to 2022. Since the locations of the ground stations do not coincide with the water sources, the precipitation data of each water source were determined based on the principle of geographic proximity. Additionally, the areal precipitation used in this study was calculated via Thiessen polygons based on the data from the ground stations. The basic information about water sources consisted of the water source type, active capacity (AC), drainage area (DA), covered population (CP) and actual water supply volume (AWSV). For a specific water source, AC (m3) is the actual storage capacity of the water source that can be used to regulate runoff, while DA (km2) is the catchment area above the water source. CP is the population supplied by the water source, and AWSV is the actual daily water supply of the water source (m3/d). Note that all of the water sources were divided into three different types based on their total capacity: reservoirs (total capacity more than 100 thousand m3), ponds (total capacity from 10 thousand m3 to 100 thousand m3) and rivers (total capacity less than 10 thousand m3). Furthermore, the AWSV values were calculated based on the average daily water supply volumes for the water sources from 2017 to 2021, so as to avoid the influence of the serious drought event in 2022. The basic information about the water sources was obtained from the dataset provided by the Water Conservancy Bureau of Lishui, and the drought condition data were collected from reports by the local government. The location and CP of the water sources are shown in Figure S1.
3. Methodology
3.1. Drought Indices
The standardized precipitation index (SPI) was selected to identify the meteorological drought events and evaluate their severity [24,25]. The SPI can be calculated based on the long-term precipitation data through the following equation:
where denotes the random variable of precipitation for a specific period, which obeys a certain distribution with a cumulative distribution function (CDF) of , while is the inverse CDF of the standard normal distribution.
Through Equation (1), it can be seen that the key to calculating the SPI is to determine the distribution of precipitation, i.e., . In this study, four different continuous distributions (i.e., Weibull distribution, gamma distribution, log-normal distribution and exponential distribution) were used to fit the distribution of precipitation, and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was employed to select the best distribution. Additionally, it is worth noting that the distribution of precipitation over different timescales at each ground station was estimated by the above method separately.
The severity of meteorological drought can be assessed by the value of the SPI and divided into seven different levels. The classification standards of the SPI are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Classification standards of meteorological drought through the SPI.
Reports from the local government were used to determine whether socio-economic drought had occurred, rather than using a specific drought index. A research unit (i.e., water source) was considered to have experienced a socio-economic drought if it suffered a water supply crisis during a specific period according to the local government reports.
3.2. Analysis Model
A random forest (RF) model was employed in this study as the analysis model to identify the key impact factors leading to the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought. RF is a statistical learning model composed of multiple decision trees and has been widely used in classification and regression analysis [26,27]. Here, the variables based on precipitation and basic information for each research unit were used as the inputs, while the occurrence or nonoccurrence of a socio-economic drought in the research unit was used as the output. The input variables were divided into two different categories: The first category was precipitation, including the SPI on different time scales, annual average precipitation (AAP), no-rain days (ND) and longest no-rain period (LNP). All of these variables were obtained from the precipitation data and used to reflect the meteorological conditions over different time scales. According to the reports from the local government, the 2022 drought in Lishui lasted for four months (from July to October); therefore, the SPI on the scale of one month to four months was employed as the input in this study. The second category was water source data, consisting of CP, AWSV, AC and DA and representing the conditions of water sources and water demand. The output of the RF model was 1 or 0, representing the occurrence or nonoccurrence of socio-economic drought, respectively. Due to the large range of variables used in this paper (including CP, AWSV, AC and DA), the natural logarithms of these variables were used in the subsequent analysis rather than the real values, in order to avoid problems from values of varying scale. Detailed information about the input and output variables can be found in Table 2. In addition, since the number of samples in which socio-economic drought occurred was significantly smaller than the number in which it did not occur, the borderline synthetic minority oversampling technique (B-SMOTE) was used to oversample the samples from the minority category in order to better train the RF model [28].

Table 2.
Information about the input and output variables of RF.
B-SMOTE is a commonly used oversampling method for imbalanced sample sets; it uses only minority-class samples on the boundary to synthesize new samples, thereby improving the class distribution of the sample set. This method divides the minority samples into three categories (Safe, Danger and Noise), and it only oversamples the samples listed as Danger in the minority sample set. The specific explanations of these three categories are as follows:
Safe: More than half of the samples around the selected sample are minority-class samples.
Danger: More than half of the samples around the selected sample are majority-class samples. The samples in this category are considered to be the samples on the boundary.
Noise: The selected sample is surrounded by majority-class samples.
Here, let represent a minority-class sample listed as Danger. The B-SMOTE method can be conducted via the following steps:
Step 1: Select nearest neighbors of from all samples of the minority class.
Step 2: Randomly select a sample from these neighbors and generate a random value between 0 and 1; thus, a new sample can be synthesized as follows:
Step 3: Repeat Step 2 until the number of samples is enough.
Furthermore, 5-fold cross-validation is used to avoid overfitting, and the Bayesian optimization method was used to determine the parameters of the RF model. More detailed information about RF and B-SMOTE can be found in the work of Yang et al. [29].
3.3. Evaluation Indicators
To examine the accuracy of the RF model, several different evaluation indicators were used in this study, including accuracy, true positive rate (TPR), false positive rate (FPR), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and area under the ROC curve (AUC) [30].
The confusion matrix was the basis for calculating the above indicators [31]. The meanings of the variables in a confusion matrix are as follows:
True positive (TP): The true class of the sample is positive, and the result of the model is also positive.
False negative (FN): The true class of the sample is positive, but the model identifies it as negative.
False positive (FP): The true class of the sample is negative, but the model identifies it as positive.
True negative (TN): The true class of the sample is negative, and the model result is also negative.
Once the numbers of occurrences for the various situations in the confusion matrix are determined, the above evaluation indicators can be calculated by the following equations:
All three of these indicators are positive, i.e., a larger value indicates a better model. The ROC curve is a graphical plot that illustrates the relationship between TPR and FPR at different threshold values. The AUC is the area under the ROC curve and is used to measure the classifiers’ performance. The range of AUC is [0, 1], and the AUC value of a theoretical perfect classifier is 1. In other words, classifiers with AUC values closer to 1 have better performances.
To identify the main impact factors in the RF model, first, the importance of each variable in a specific tree is calculated by summing the changes in the target function due to the splits in this variable and then dividing the sum by the total number of branch nodes. In this study, the minimization of Gini’s diversity index (GDI) was used as the target function, and the change in the target function was the difference between the GDI for the parent node and the total GDI for the two children. The GDI for a node can be calculated as follows:
where is the number of the classes, and is the probability of class .
Then, the importance of a specific variable in the RF model can be obtained by averaging the importance of this variable in all trees.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Survey of the Water Supply System in Lishui
As the first step of this study, a comprehensive survey of the water supply system for Lishui was conducted including basic information about water sources. According to the statistical data from the local government, there are a total of 3141 water sources at different scales in Lishui, covering over 2.51 million people. Figure 2 illustrates the distribution of the types of water source projects with different thresholds for CP. From the perspective of the total number, the proportion of rivers is significantly greater than those of the other two types. However, as shown in Figure 2b–f, the proportions of reservoirs and ponds gradually expand with the increase in the CP thresholds, indicating a positive relationship between the CP and AC of the water sources. Overall, the water sources in the water supply system of Lishui are quite diverse, with several large urban water supply units and numerous small rural water supply units, meaning that Lishui provided a comprehensive sample set for this study.
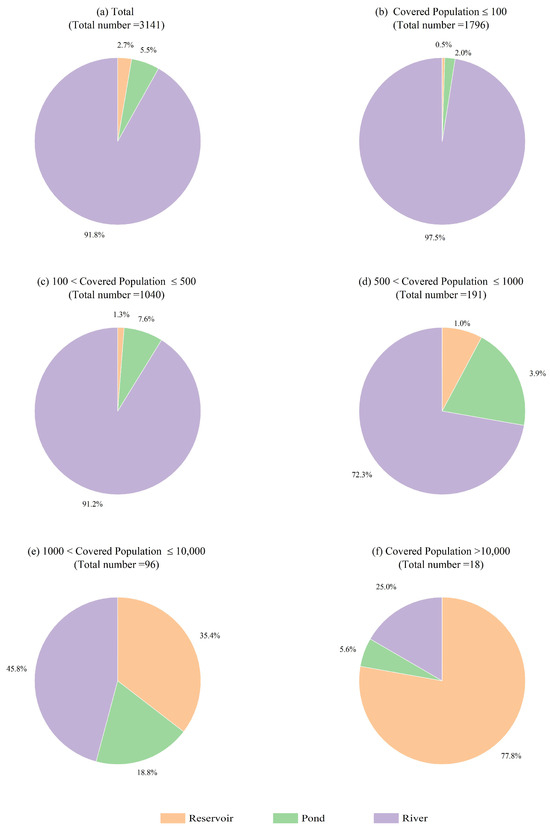
Figure 2.
Type distribution of the water sources in Lishui. (a) Total; (b) CP ≤ 100; (c) 100 < CP ≤ 500; (d) 500 < CP ≤ 1000; (e) 1000 < CP ≤ 10,000; (f) CP > 10,000.
Histograms for the LCP and LAWSV of the water sources are presented in Figure 3. Generally, regional water consumption (i.e., AWSV) is highly correlated with the regional population (i.e., CP). However, the LCP values are mostly concentrated between 3 and 6 in Figure 3a, while the majority of the LAWSV values are between 3 and 4 in Figure 3b. The main reason for this difference is that the per capita water consumption varies in different areas covered by various water sources. In other words, if the per capita water consumption of each water source is the same, there must be a linear relationship between LCP and LAWSV, which means that the histograms for the two variables are consistent. Therefore, it was necessary to employ LCP and LAWSV as two different independent input variables in this study. Additionally, it can also be seen in Figure 3 that there is a large number of small water sources with small CP and AWSV in Lishui, which are used for the water supply in remote mountainous villages that are not covered by large water sources.
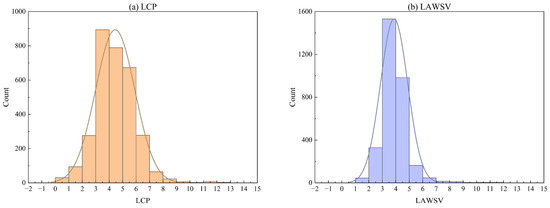
Figure 3.
Histograms of LCP and LAWSV for different water sources. (a) LCP; (b) LAWSV.
4.2. Survey on the 2022 Drought Event in Lishui
According to the long-term SPIs, based on the areal precipitation in Lishui at different scales, as shown in Figure 4, the city historically experienced several severe meteorological drought events. Detailed information about the SPIs at different scales for the meteorological drought event from July to October 2022 is presented in Table 3. Note that the regional SPIs were calculated based on the areal precipitation by using the Thiessen polygon method. It can be seen from Figure 4 and Table 3 that the meteorological drought in Lishui was most severe in October, followed by September, while July and August were comparatively less severe. The severity of meteorological drought slightly weakened as time continued, but the minimum values of SPIs at different time scales were still below −1.5, indicating severe drought.
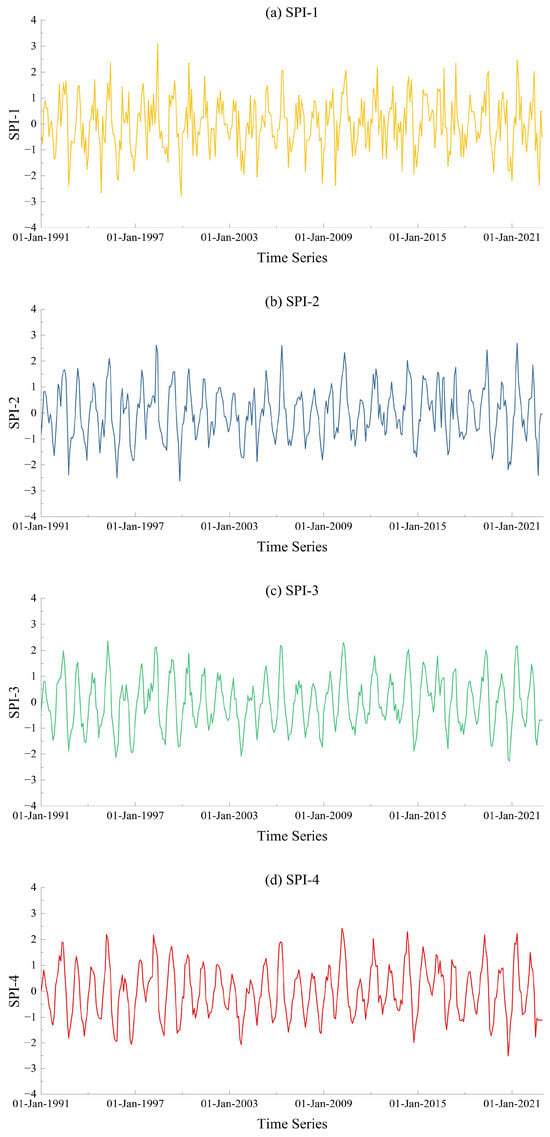
Figure 4.
Long-term SPI at different scales in Lishui: (a) SPI-1; (b) SPI-2; (c) SPI-3; (d) SPI-4.

Table 3.
SPI at different scales in Lishui from July to October 2022.
In addition, the spatiotemporal distribution of the meteorological drought in Lishui during 2022 is presented in Figure 5 through SPI-1 and administrative divisions. Lishui is divided into nine districts, and all of the districts experienced an extreme meteorological drought in 2022. However, the spatiotemporal distribution of the drought was not consistent. From Figure 5, it can be seen that the northern areas of Lishui first experienced moderate drought in July, while the remaining areas were still in a near-normal condition. The drought disappeared in August, and all of the areas were in the near-normal condition. However, the drought index rapidly declined in the following two months, indicating a fast deterioration of the meteorological drought situation in the city. In September, extreme drought occurred in the southeast and southwest parts of the city, and most of the other parts experienced severe drought. Finally, the entire city, except the northeast part, suffered from extreme drought in October. The spatiotemporal distribution of the drought also indicates that the most severe meteorological drought in Lishui during 2022 occurred in October, and that all areas of the city were affected by the drought.
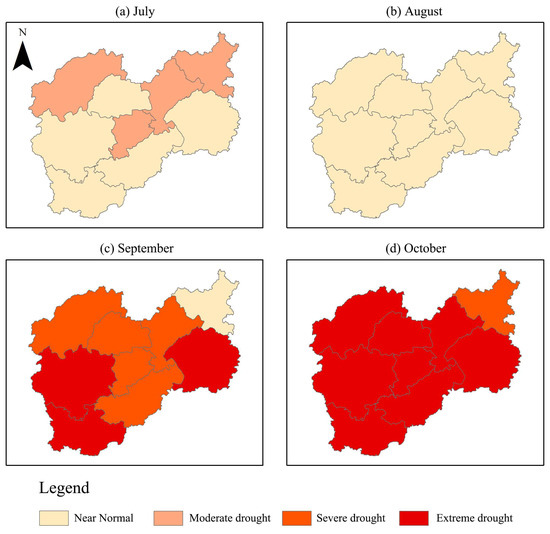
Figure 5.
Spatiotemporal distribution of meteorological drought in Lishui during 2022.
According to the statistical reports from the local government, there were 276 research units that suffered from water supply problems—i.e., experienced socio-economic droughts in Lishui from July to October 2022—involving a covered population of 105,241. In this study, we conducted statistical tests on the types, LCP and LAWSV of the water sources that suffered socio-economic drought. As shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7, the research areas with relatively large LCP and river-type water sources were more prone to socio-economic drought. The main reasons for this phenomenon are that (1) the river-type water sources have a very limited active capacity, causing them to be greatly affected by precipitation, and (2) the relatively large population results in a large regional water demand. The insufficient active capacity of water sources and large water demand jointly led to the occurrence of socio-economic drought in these research areas.
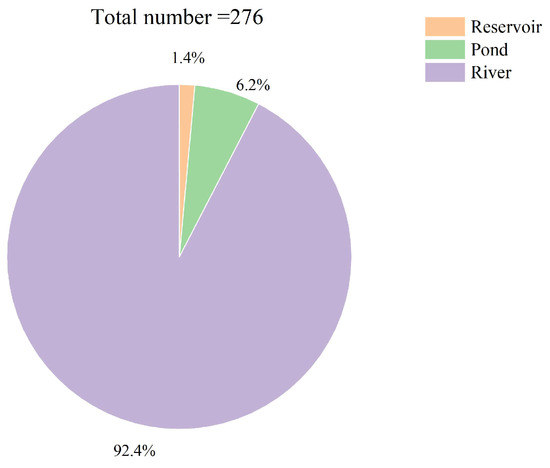
Figure 6.
Type distribution of the water sources that experienced socio-economic drought in 2022.
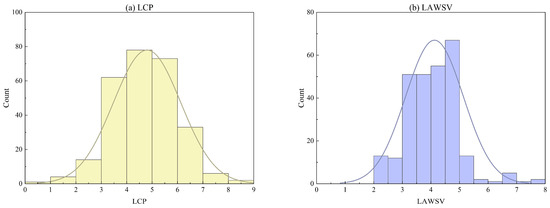
Figure 7.
Histograms for LAWSV and LCP of the water supply projects that experienced socio-economic drought in 2022. (a) LCP; (b) LAWSV.
4.3. Analysis of Main Impact Factors
The above practical survey proved that the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought is closely related to the conditions of water sources. Therefore, an RF model was established as a classifier based on different kinds of data for attribution analysis of the main impact factors in drought propagation. The inputs of the RF model were all of the variables listed in Table 2 for the 3141 water sources, and the output was whether socio-economic drought occurred. To examine the performance of the model, several evaluation indicators were calculated, as presented in Table 4 and Figure 8. The accuracy, TPR and AUC of the model were 0.9935, 0.9489 and 0.9995, respectively, while the FPR was only 0.0021. The low FPR and the high accuracy, TPR and AUC imply that the RF model exhibits good performance as a classifier, thus support its use to analyze the importance of different variables in drought propagation.

Table 4.
Evaluation indicators for the RF model.
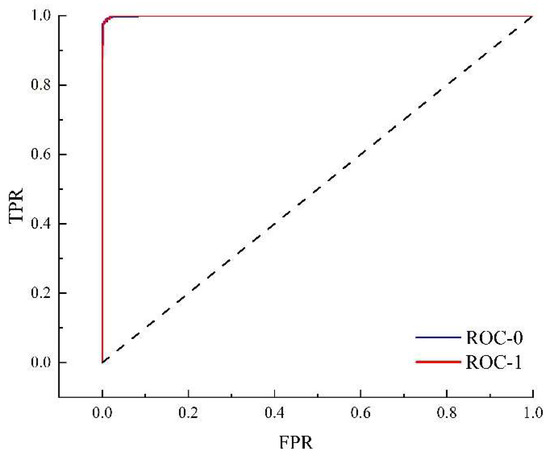
Figure 8.
ROC curve for the RF model. The dotted line is the 1:1 goodness fit line.
The importance of different variables in the RF model is shown in Figure 9. The LDA, LAWSV and LCP of the water sources play the most important role in the model. The variables based on precipitation, including SPIs, ND, LNP and AAP, are less important than the variables related to water sources, implying that the main impact factors causing socio-economic drought are the project capacities of the water supply system, rather than the meteorological conditions. To be more specific, the variables based on meteorological conditions, such as SPI and no-rain days, can be used as signals of the occurrence of meteorological drought, but whether such meteorological drought will lead to socio-economic drought mainly depends on the situation of the water sources. In addition, it is worth noting that the importance of LAC is significantly less than that of LDA. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the majority of water sources in Lishui are rivers, which usually have a very small LAC and are relatively close, resulting in the limited role of LAC in the RF model.
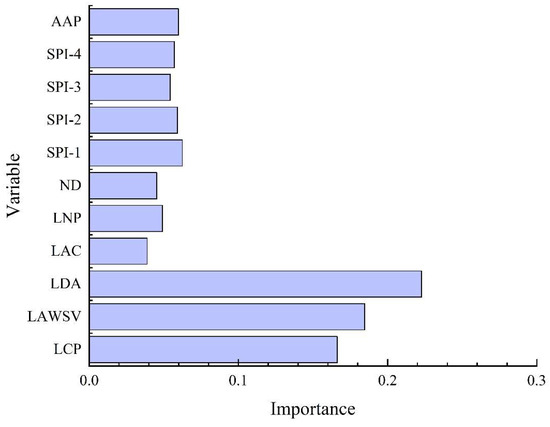
Figure 9.
Importance of the different input variables in the RF model.
4.4. Relationships between the Main Impact Factors
In practice, it is commonly believed that there are relationships between the variables of water sources, especially between LCP and LAWSV. To be more specific, an increase in LCP will lead to an increase in LAWSV, and a greater LAWSV means a demand for more water resources, which is related to LDA and LAC. According to the results in Figure 9, the LCP, LAWSV and LDA are the three most important variables in the RF model. Therefore, the relationships between these three variables were analyzed in this study. Figure 10 shows a clear relationship between LCP and LAWSV, while the correlations between LDA and the other two variables are poor. In Figure 10a, it can be seen that the growth rate of LAWSV increases with the growth of LCP and becomes stable when the LCP exceeds a certain threshold, indicating that the per capita water consumption varies in different areas. To be more specific, the growth rate of LAWSV is slower when the LCP is small, while the growth rate of LAWSV increases as the LCP increases. The water sources with a small LCP usually serve remote rural areas, with very limited industry. On the other hand, the water sources with a large LCP are mostly used for urban areas with dense and developed industry. Differences in industrial water consumption are the main reason for the different per capita water consumption levels in different areas.
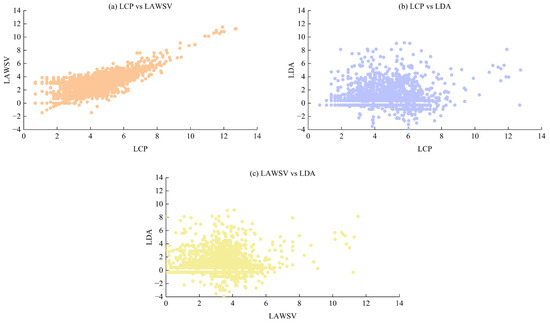
Figure 10.
The relationship between LCP, LAWSV and LDA: (a) LCP vs. LAWSV; (b) LCP vs. LDA; (c) LAWSV vs. LDA.
4.5. Limitations and Future Work
In this study, the main impact factors in the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought were identified and analyzed based on a practical survey in the city of Lishui, China. As with all scientific research, this study had several limitations. First, due to a lack of practical investigations producing detailed data on socio-economic drought, the data concerning the study area in the study period were limited. Fortunately, the large number of water sources in Lishui provided more than 3000 samples for the attribution analysis. However, further efforts are needed to generate more robust evidence, to verify the results of this study. Another main limitation of this study was the lack of a comprehensive comparison with large-scale areas. However, it is very difficult to collect detailed information about socio-economic drought in a large area, especially for small water sources. Beyond this, in a final limitation, since the input variables of the RF model were not completely independent, interaction between the input variables may have affected the results and conclusions of this study.
With the intensification of human activities and climate change, drought will stand as one of the major threats to future socio-economic development. It is, therefore, of great importance to identify and understand the main impact factors in the propagation between different types of droughts. In this regard, the development of remote sensing can provide new variables for the analysis of drought propagation. Additionally, the explosion of machine learning provides new methods for attribution analysis and understanding the interactions between different input variables. In that context, it is expected that a better understanding of the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought can be achieved.
5. Conclusions
As a city with over 3000 different water sources, Lishui provides a good sample area in which to observe the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought. In this study, a detailed investigation of a severe drought event in Lishui during 2022 was conducted based on in situ data and governmental reports. Furthermore, an RF model was established to analyze the main impact factors in the propagation from meteorological drought to socio-economic drought. The results showed that the level of the drought event experienced by Lishui from July to October 2022 ranged between severe and extreme according to the meteorological drought indices (i.e., SPI) at different time scales. A total of 276 water sources were reported to have suffered from water supply problems that impacted socio-economic activities. Most of these water sources were rivers. To identify the main impact factors in the propagation from metrological drought to socio-economic drought, an RF model was employed for attribution analysis. The model showed a great performance in the evaluation of its accuracy, proving that it can effectively distinguish whether socio-economic drought has occurred in different areas based on input variables related to water sources and meteorology. The model indicates that variables related to water sources, including LCP, LDA and LAWSV, are more important than meteorological variables and SPIs in drought propagation.
In conclusion, although the occurrence of meteorological drought is one of the most important causes of socio-economic drought, the propagation between these two different types of drought is controlled by regional water conservation projects and the water supply system. In other words, it is possible to prevent meteorological drought from transforming into socio-economic drought through water conservancy engineering construction, and the RF model built in this paper can serve as a reference for determining the engineering scale. Furthermore, in contrast to research on large areas, one of the defining characteristics of this study was its inclusion of a large number of small water supply units with low CP and AWSV, which are generally ignored in large-scale research, in the analysis carried out. It is also worth noting that the LDA, LAWSV and LCP were found to be the most important impact variables, rather than the LAC. A larger LAC usually represents a water source that can store more water in order to prevent drought, but this may not be necessary for small water supply units with limited water demand. In other words, it is more cost-effective to increase the LDA through water division projects than to construct water sources with a large LAC for small water supply units.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16101426/s1, Figure S1: Locations and covered populations of water sources in Lishui.
Author Contributions
C.C.: Methodology and Writing—Original Draft. C.W.: Software and Investigation. J.W. (Jing Wang): Data Curation and Investigation. H.W.: Methodology and Validation. R.W.: Software, Formal Analysis and Visualization. L.F.: Resources, Project Administration and Funding Acquisition. J.W. (Jinhua Wen): Supervision, Conceptualization and Writing—Review and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was jointly supported by the Research Program of the Department of Water Resources of Zhejiang Province (Nos. RB2107, RC2139, RA2102, ZIHE21Q003, ZIHE21Z002, ZIHE22Q014, ZIHE21Q004); the Applied Basic Public Research Program and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LGF22E090007); the Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No.LZJWY23E090008); the Key Research and Development Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2023C03134); the Technology Demonstration Project of the Chinese Ministry of Water Resources (No. SF202212); and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. LZJWY23E090009).
Data Availability Statement
Since most data used in this paper was collected by a practical survey and the authors did not receive the authorization to share the data, we are sorry that we cannot share the research data of this paper.
Acknowledgments
This study benefited from socio-economic data and basic information about water conservancy projects provided by the Water Conservancy Bureau and public water supply enterprises. Furthermore, the methods used in this paper benefited from MATLAB, and the authors are grateful to the developers of the software. The authors are also grateful to the reviewers of the manuscript for their constructive comments and useful suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; van der Schrier, G.; Jones, P.D.; Barichivich, J.; Briffa, K.R.; Sheffield, J. Global warming and changes in drought. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Fu, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, B. Three-dimensional-based global drought projection under global warming tendency. Atmos. Res. 2023, 291, 106812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, N.; Wada, Y. Human and climate impacts on the 21st century hydrological drought. J. Hydrol. 2015, 526, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W. The Palmer Drought Severity Index: Limitations and Assumptions. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1984, 23, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nengcheng, C.; Ronghui, L.; Xiang, Z.; Chao, Y.; Xiaoping, W.; Linglin, Z.; Shengjun, T.; Wei, W.; Deren, L.; Dev, N. Drought propagation in Northern China Plain: A comparative analysis of GLDAS and MERRA-2 datasets. J. Hydrol. 2020, 588, 125026. [Google Scholar]
- Meresa, H.; Murphy, C.; Donegan, S. Propagation and Characteristics of Hydrometeorological Drought Under Changing Climate in Irish Catchments. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD038025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Jonsson, E.; Todorović, A.; Tootoonchi, F.; Stenfors, E.; Grabs, T. Future drought propagation through the water-energy-food-ecosystem nexus—A Nordic perspective. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Xu, C.; Menzel, L.; Yuan, F.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Separating the effects of climate change and human activities on drought propagation via a natural and human-impacted catchment comparison method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigatu, Z.; You, W.; Melesse, A. Drought Dynamics in the Nile River Basin: Meteorological, Agricultural, and Groundwater Drought Propagation. Romete Sens. 2024, 16, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, S.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z. A New Perspective on Drought Propagation: Causality. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y. The Three Gorges Dam has weakened the drought propagation process in the Yangtze River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 632, 130875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X.; Leng, G.; Su, Z.; Lv, J.; Yu, Z.; Yi, P. Altered drought propagation under the influence of reservoir regulation. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apurv, T.; Sivapalan, M.; Cai, X. Understanding the Role of Climate Characteristics in Drought Propagation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 9304–9329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ertsen, M.; Svoboda, M.; Hafeez, M. Propagation of Drought: From Meteorological Drought to Agricultural and Hydrological Drought. Adv. Meteorol. 2016, 2016, 6547209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Zhang, B.; Gu, Q.; He, Z.; Zheng, R. Drought propagation characteristics across China: Time, probability, and threshold. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Gu, X.; Cai, H. Quantitative analysis of vegetation drought propagation process and uncertainty in the Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apurv, T.; Cai, X. Drought Propagation in Contiguous U.S. Watersheds: A Process-Based Understanding of the Role of Climate and Watershed Properties. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cai, H.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shi, H. Propagation of meteorological to hydrological drought for different climate regions in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 283, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hao, Z.; Singh, V.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F. Drought propagation under global warming: Characteristics, approaches, processes, and controlling factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Miao, C.; Gou, J.; Wu, J.; Jiao, W.; Song, Y.; Xu, D. Spatiotemporal characteristics of meteorological to hydrological drought propagation under natural conditions in China. Weather Clim. Extremes 2022, 38, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Yin, G.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F. Evaluation of Drought Propagation Characteristics and Influencing Factors in an Arid Region of Northeast Asia (ARNA). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos Brandão Raposo, V.; Costa, V.A.F.; Rodrigues, A.F. A review of recent developments on drought characterization, propagation, and influential factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 165550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavitis, C.; Alexandris, S.; Tsesmelis, D.; Athanasopoulos, G. Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece. Water 2011, 3, 787–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Singh, V.P.; Bai, Y. SPI-based evaluation of drought events in Xinjiang, China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyralis, H.; Papacharalampous, G.; Langousis, A. A Brief Review of Random Forests for Water Scientists and Practitioners and Their Recent History in Water Resources. Water 2019, 11, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Ouarda, T. Regional hydrological frequency analysis at ungauged sites with random forest regression. J. Hydrol. 2021, 594, 125861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Wang, W.; Mao, B. Borderline-SMOTE: A New Over-Sampling Method in Imbalanced Data Sets Learning. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2005, 3644, 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Shen, X.; Yang, F.; Anagnostou, E.; He, K.; Mo, C.; Seyyedi, H.; Kettner, A.; Zhang, Q. Predicting Flood Property Insurance Claims over CONUS, Fusing Big Earth Observation Data. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E791–E809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centor, R.; Schwartz, J. An Evaluation of Methods for Estimating the Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve. Med. Decis. Mak. 1985, 5, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Carrasco, A.; Martín, A.; de Las Heras, A. The impact of class imbalance in classification performance metrics based on the binary confusion matrix. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 91, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).