A Numerical Model of the Pollutant Transport in Rivers with Multi-Layer Rigid Vegetation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
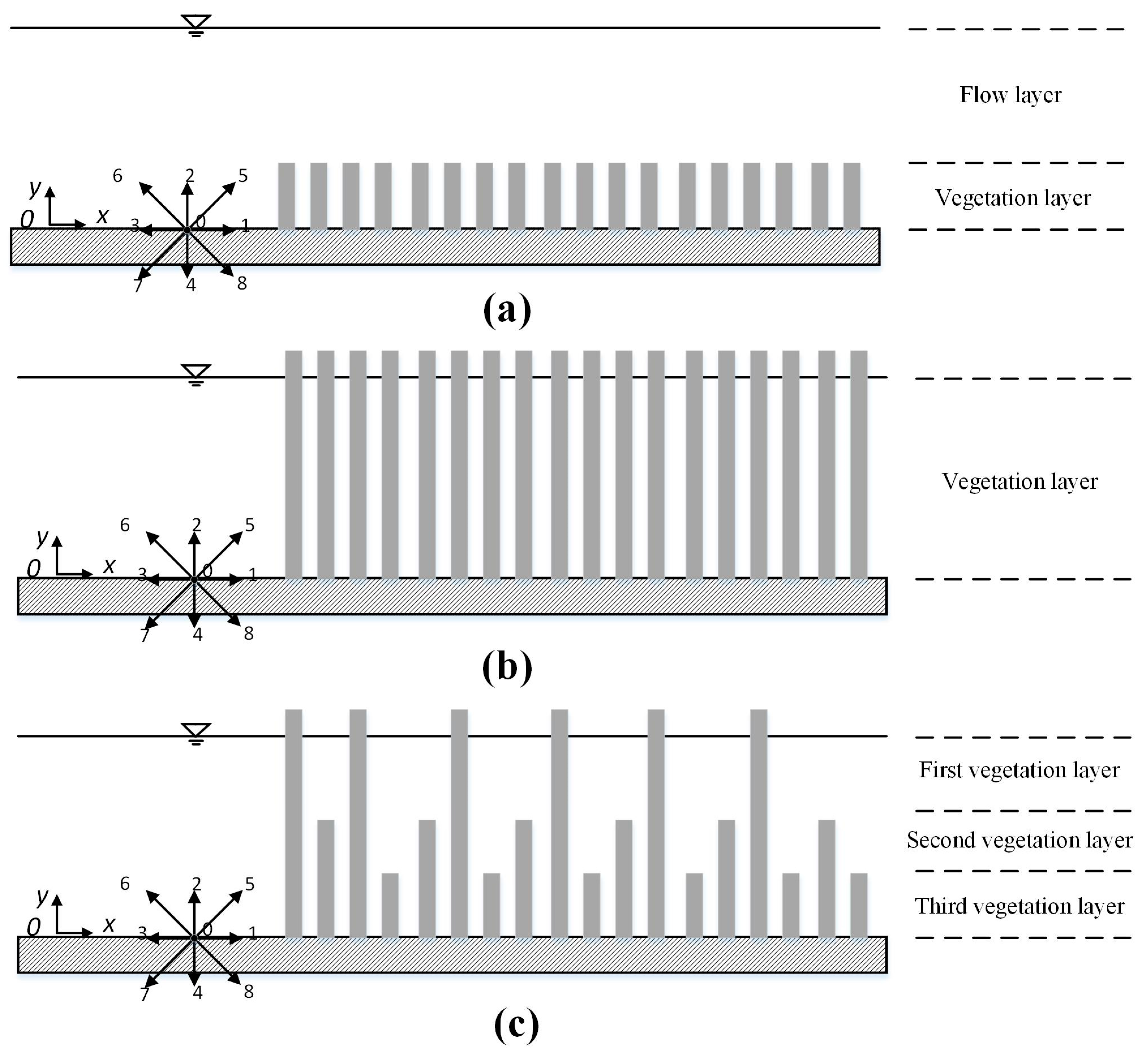
2.1. Numerical Model
2.1.1. Hydraulic Model
2.1.2. Pollution Transport Model
2.2. Validation Data
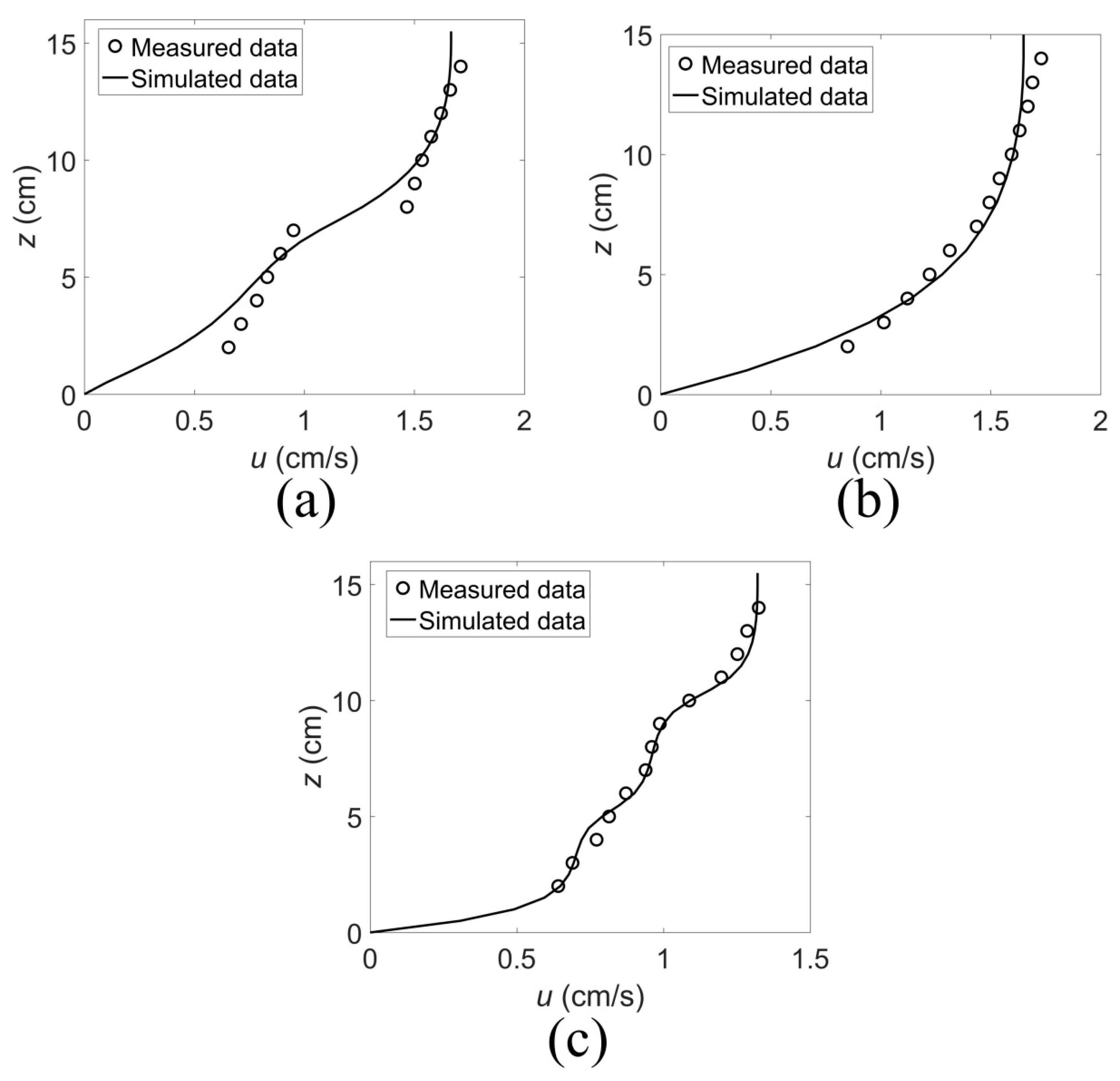
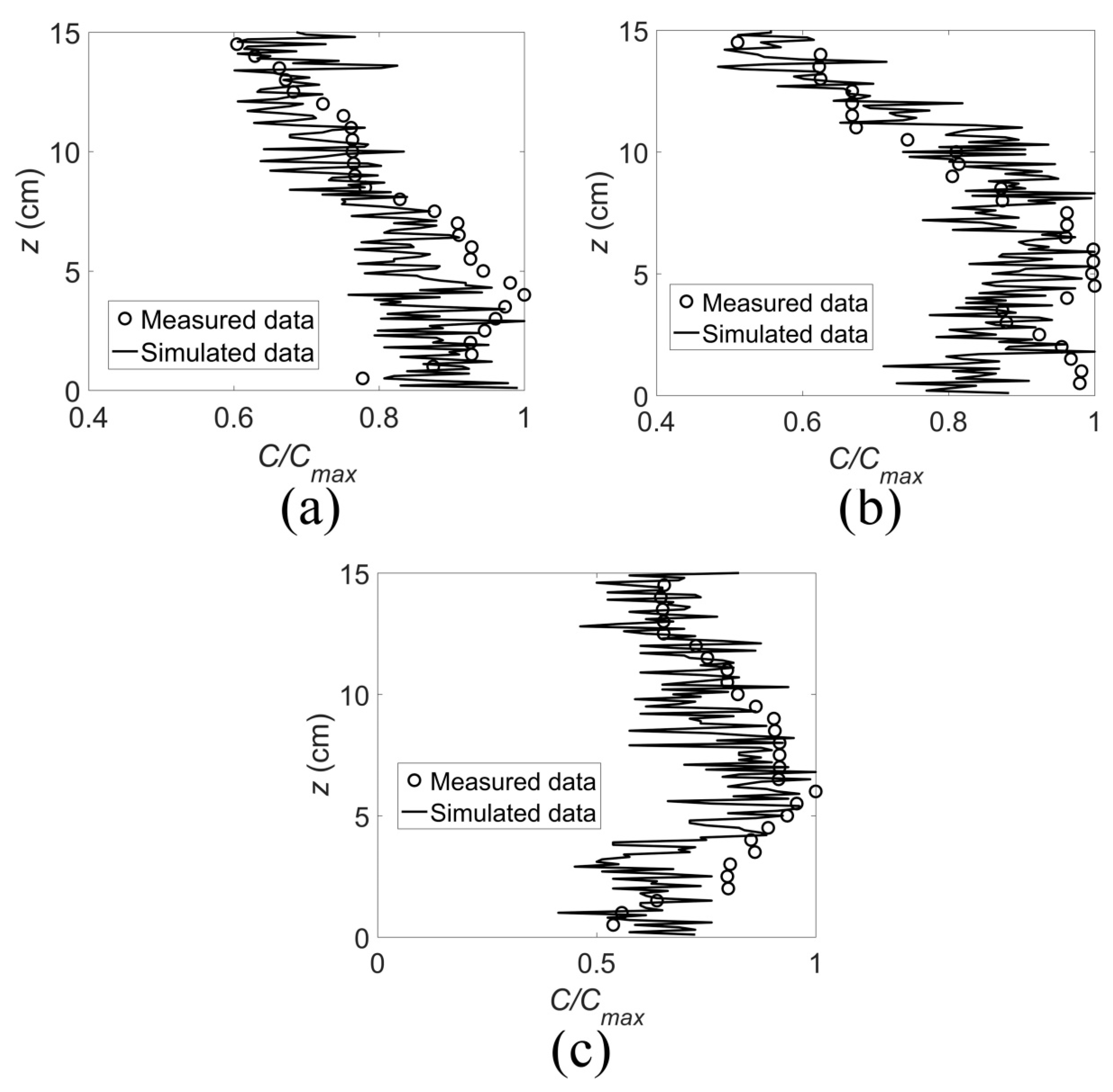
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The distribution pattern of the flow velocity in a multi-layer vegetation flow is related to the number of vegetation layers, and the flow velocity layering is consistent with the number of vegetation layers. For simulating the vertical distribution of the flow velocity in a multi-layer vegetation flow, the drag force of vegetation can be layered according to the number of vegetation layers, which is mainly related to the density of vegetation in different layers. The simulation model has a high simulation accuracy.
- (2)
- The distribution pattern of nutrients in a multi-layer vegetation water flow is related to the number of vegetation layers. The more vegetation layers there are, the more uniform the distribution of nutrient concentrations is. The diffusion of nutrients caused by vegetation is mainly turbulent diffusion and mechanical diffusion. By substituting the diffusion coefficient caused by vegetation into the model, the model simulation has high accuracy.
- (3)
- At the same time, there are also some shortcomings in this research. Firstly, all the validation data come from indoor experiments. The conditions of outdoor river channels are more complex, and the types and arrangements of vegetation are also significantly different from indoor experiments. The organisms and microorganisms in the river channels also have a significant impact on the transport of pollutants. These situations should be further studied in future applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henriques, M.; McVicar, T.R.; Holland, K.L.; Daly, E. Riparian vegetation and geomorphological interactions in anabranching rivers: A global review. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, G.; Chen, Y. Assess river embankment impact on hydrologic alterations and floodplain vegetation. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 97, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelpi, A.; Lapôtre, M.G.; Gibling, M.R.; Boyce, C.K. The impact of vegetation on meandering rivers. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Beall, C.C.; Dixon, M.D.; Illeperuma, N.D.; Sweeney, M.R.; Johnson, W.C. Expansion of woody vegetation on a Missouri River reservoir delta-backwater. Ecohydrology 2022, 15, e2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Chen, W.; Deng, S.; Situ, S.; Chang, M.; Wang, X. Prediction of ozone pollution impacted by vegetation planning in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 309, 119936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Shi, P.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, P.; Ding, S.; Li, J.; Bi, Z.; Wang, X. Vegetation restoration and agricultural management to mitigate nitrogen pollution in the surface waters of the Dan River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 47136–47148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarisamani, A.; Keshavarzi, A.; Hamidifar, H.; Javan, M. Effect of rigid vegetation on velocity distribution and bed topography in a meandering river with a sloping bank. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 8633–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Huang, H. Effects of Emergent Vegetation Patterns on Flow Velocity, Turbulence, and Erosion around River Banks. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2019, 43, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi-Moghadam, M.; Kashefipour, M.; Ebrahimi, N.; Emamgholizadeh, S. Physical and numerical modeling of submerged vegetation roughness in rivers and flood plains. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjoribanks, T.I.; Hardy, R.J.; Lane, S.N. The hydraulic description of vegetated river channels: The weaknesses of existing formulations and emerging alternatives. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2014, 1, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoesser, T.; Kim, S.J.; Diplas, P. Turbulent flow through idealized emergent vegetation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.L.; Prasad, B.S.S.; Sharma, A.; Khatua, K.K. Experimental and numerical analysis of velocity distribution in a compound meandering channel with double layered rigid vegetated flood plains. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2022, 83, 102111. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.J.; Zhao, F.; Mavrommatis, A.; Christodoulou, G.; Stamou, A.; Jia, F.C. Velocity distribution characteristics for rigid vegetation model with spherical canopy: An analytical study adopting multiple mathematical methods. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Mi, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Du, X. An Analytical Solution to Predict the Distribution of Streamwise Flow Velocity in an Ecological River with Submerged Vegetation. Water 2022, 14, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erduran, K.S.; Kutija, V. Quasi-three-dimensional numerical model for flow through flexible, rigid, submerged and non-submerged vegetation. J. Hydroinform. 2003, 5, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.R.; Ai, C.F.; Jin, S. 3-D numerical simulation of curved open channel confluence flow with partially non-submerged rigid vegetation. J. Hydrodyn. 2021, 33, 992–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M.; Ghani, U.; Pasha, G.A.; Ullah, M.K.; Ali, S. 3D numerical investigation of flow behavior in an open channel with uniform and layered vegetation patches under varying submergence conditions. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2024, 15, 102288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chen, X.; Cardenas, M.B.; Liu, X.; Chen, L. Hyporheic exchange driven by submerged rigid vegetation: A modeling study. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2019WR026675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Liu, J.N.; Wu, Y.F.; Ji, C.N. Numerical investigation of the dynamics of flexible vegetations in turbulent open-channel flows. J. Hydrodyn. 2022, 34, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotello, A.; Ielpi, A.; Lapôtre, M.G.A. Vegetation enhances curvature-driven dynamics in meandering rivers. J. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, N.; Tanaka, N. Study on the flow structure around discontinued vertically layered vegetation in an open channel. J. Hydrodyn. 2020, 32, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Shen, H.W.; Chou, Y.J. Variation of roughness coefficients for unsubmerged and submerged vegetation. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1999, 125, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Z. Analytical model of the mean velocity distribution in an open channel with double-layered rigid vegetation. Adv. Water Resour. 2014, 69, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Bai, Y. A numerical model to simulate the vertical velocity distribution in an open channel with double-layered rigid vegetation. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Rahimi, H.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y. Hydraulic characteristics of open-channel flow with partially-placed double layer rigid vegetation. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2021, 21, 317–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, T.; Fernando, H.J.; Rodríguez, R.V. Effects of emergent vegetation on lateral diffusion in wetlands. Water Res. 2004, 38, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, M.; Davari, H.; Shoaei, F. Lateral dispersion in deflected emergent aquatic canopies. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2019, 19, 833–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M. Flow and transport in regions with aquatic vegetation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.L.; Li, C.W.; Shen, Y.M. A 3D non-linear k–ε turbulent model for prediction of flow and mass transport in channel with vegetation. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 34, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dai, H.C. Effect of submerged vegetation on solute transport in an open channel using large eddy simulation. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 97, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.A.; Nezu, I. Large eddy simulation of 3-D flow structure and mass transport in open-channel flows with submerged vegetations. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2010, 4, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yan, G. A lattice Boltzmann model for the Navier-Stokes equation. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2023, 96, 104391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, S.; Di Francesco, S.; Geier, M.; Manciola, P. Forcing for a cascaded lattice boltzmann shallow water model. Water 2020, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorimbert, Y.; Lätt, J.; Chopard, B. Coupling of lattice Boltzmann shallow water model with lattice Boltzmann free-surface model. J. Comput. Sci. 2019, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Shen, D.; Sun, G. Numerical simulation of velocity distribution and pollution retention in flexible submerged vegetated channel. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Yang, L.; Wang, W.J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, T.; Cheng, Y.G. Predicting the vertical low suspended sediment concentration in vegetated flow using a random displacement model. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dai, H.C. Numerical modeling of pollution transport in flexible vegetation. Appl. Math. Model. 2018, 64, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepf, H.M. Drag, turbulence, and diffusion in flow through emergent vegetation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, M.; Zhong, G. Longitudinal and lateral diffusion of solute transport in flow with rigid vegetation. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2020, 32, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Cui, X.Y.; Dong, F.; Peng, W.Q.; Han, Z.; Huang, A.P.; Chen, X.K.; Si, Y. Predictions of bulk velocity for open channel flow through submerged vegetation. J. Hydrodyn. 2020, 32, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Liang, X.; Huai, W.; Wang, Y. Predicting the bulk average velocity of open-channel flow with submerged rigid vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2019, 572, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shan, Y.; Sun, W.; Yan, C.; Yang, K. An open channel with an emergent vegetation patch: Predicting the longitudinal profiles of velocities based on exponential decay. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z. Study of the Impact of Vegetation Direction and Slope on Drag Coefficient. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2018, 42, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, M.C.; Chen, L.; Kyle McKay, S.; Goreham, J.; Acharya, K.; Fischenich, C.; Stone, A.B. Bending of submerged woody riparian vegetation as a function of hydraulic flow conditions. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.X.; Zhang, J.; Katul, G.G.; Cheng, Y.G.; Tang, X.; Wang, W.J. The structure of turbulent flow through submerged flexible vegetation. J. Hydrodyn. 2019, 31, 274–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.A.; Wilson, B.N.; Gulliver, J.S. Drag force parameters of rigid and flexible vegetal elements. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, W.J.; Shi, H.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Tang, X.; Xia, Z. An analytical two-layer model for velocity distribution in open-channel flows with submerged flexible canopies considering multiply fluids mechanics. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xia, Y.; Geng, N.; Qi, Y.; Huang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, L.; Shen, D.; Sun, G.; Xu, C.; et al. Research on oxygen transfer in an aerated flow with emergent vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, G. Concentration distribution of contaminant transport in wetland flows. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M.; Lestel, L.; Carré, C.; Bouleau, G.; Garnier, J.; Mouchel, J.M. Trajectories of river chemical quality issues over the Longue Durée: The Seine River (1900S–2010). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 23468–23484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shan, Y.; Lei, J.; Nepf, H. Floating treatment islands in series along a channel: The impact of island spacing on the velocity field and estimated mass removal. Adv. Water Resour. 2019, 129, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, H.M.; Gurnell, A.M.; Heppell, C.M.; Spencer, K.L. The role of vegetation in the retention of fine sediment and associated metal contaminants in London’s rivers. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalu, T.; Wasserman, R.J.; Magoro, M.L.; Froneman, P.W.; Weyl, O.L. River nutrient water and sediment measurements inform on nutrient retention, with implications for eutrophication. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, D.; Inaba, M.; Yu, N.; Shima, Y.; Ueno, T.; Sei, K.; Fujita, M.; Ike, M. Evaluation of biodegradation potential of organic compounds by river water microorganisms. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
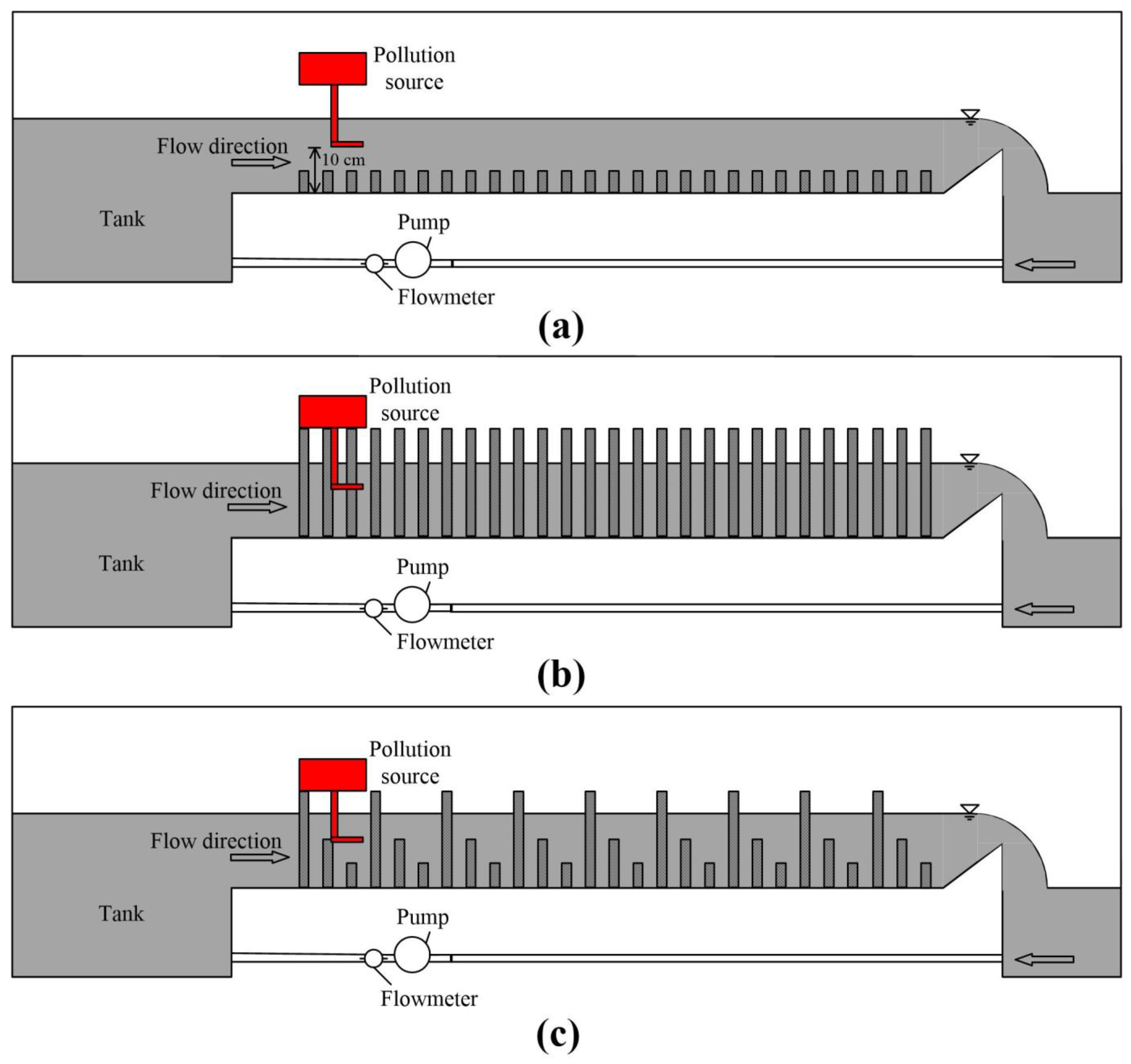
| Treatment | Discharge (L/s) | Vegetation Height (cm) | Stem Number | Vegetation Density | Vegetation Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case A | 0.9 | 5 | 95 | 317 | 8 |
| Case E | 0.9 | 20 | 95 | 317 | 8 |
| Case H | 0.9 | 5 + 10 + 20 | 32 + 32 + 31 | 317 | 8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xuan, W.; Yang, C.; Wu, X.; Shao, Y.; Bai, Y. A Numerical Model of the Pollutant Transport in Rivers with Multi-Layer Rigid Vegetation. Water 2024, 16, 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101397
Xuan W, Yang C, Wu X, Shao Y, Bai Y. A Numerical Model of the Pollutant Transport in Rivers with Multi-Layer Rigid Vegetation. Water. 2024; 16(10):1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101397
Chicago/Turabian StyleXuan, Weidong, Chenggang Yang, Xiang Wu, Yiting Shao, and Yu Bai. 2024. "A Numerical Model of the Pollutant Transport in Rivers with Multi-Layer Rigid Vegetation" Water 16, no. 10: 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101397
APA StyleXuan, W., Yang, C., Wu, X., Shao, Y., & Bai, Y. (2024). A Numerical Model of the Pollutant Transport in Rivers with Multi-Layer Rigid Vegetation. Water, 16(10), 1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101397





