Sorption-Based Removal Techniques for Microplastic Contamination of Tap Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods of Sampling and Analyzing Tap Water
2.2. Methodology for Sorption Treatment of Water from Microplastics
- Carbon sorption material (CSM), obtained by carbonizing apricot pits, an annually renewable waste material from plant sources.
- Zeolite sourced from the Chankanaisky zeolite deposit in the Kerbulak district of the Almaty region, Republic of Kazakhstan. This zeolite is a medium-porous material with a brown hue, featuring particle sizes not exceeding 2–4 mm. Its generalized formula is Kx/n [Alx Si Oy2 (x + y)] × pH2O, where K represents alkali and alkaline-earth metal cations, ammonium, etc., p denotes cation charge, y/x = 1:6, and p/x = 1:4.
- A complex comprising activated carbon sorption material (CSM) and ion exchange resins, specifically anionite Ecotar-B and cationite KU-2-8, utilized in household filters for drinking water treatment at a ratio of 1:1:1 (CSM:anionite:cationite).
3. Results and Discussion
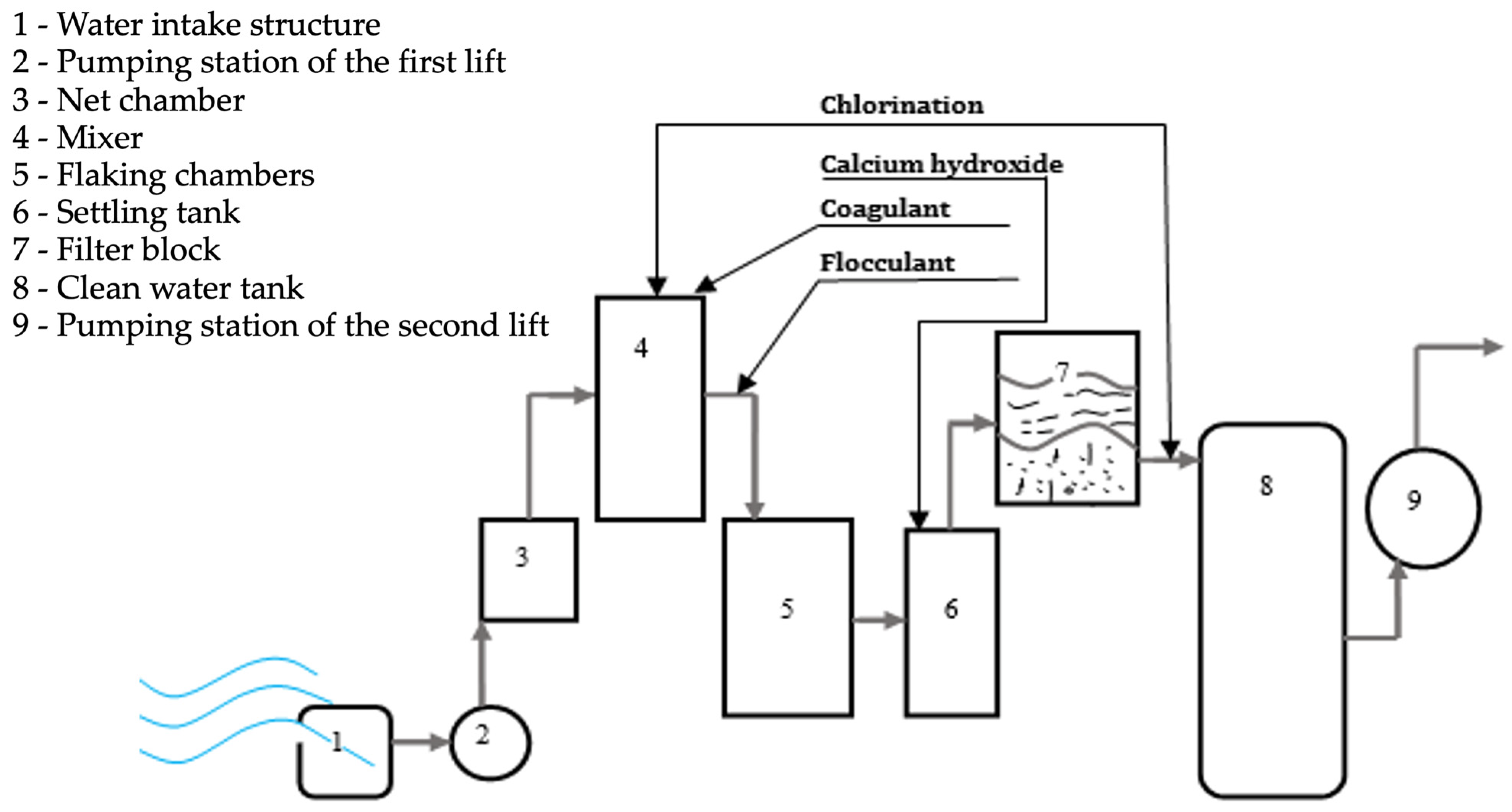
3.1. Analysis of Technological Processes of Water Treatment in Kazakhstan
- Mechanical cleaning: Coarse debris is removed through screening or gridding.
- Settling: Preliminary removal of suspended solids occurs in settling tanks (radial or horizontal).
- Coagulation: Reagents such as iron chloride or aluminum sulfate are used to induce coagulation.
- Flocculation: Aggregation of particles into larger masses for easier removal.
- Alkalization: Water may be alkalinized with a calcium hydroxide solution if necessary.
- Clarification: Large impurities precipitate and settle in settling tanks for 3–4 h after coagulation and flocculation.
- Filtration: Final clarification and removal of bacteria, and small impurities are achieved through rapid filtration. Quartz sand (Kokshetau) or a combination of quartz sand and silica (Almaty) serve as filtering materials.
- Disinfection: Water is disinfected by chlorination to maintain residual free chlorine content in the supplied water at 0.3–0.5 mg/L. Currently, water disinfection is accomplished using sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) solution produced from table salt at electrolysis plants.
- Fluoridation: Fluoride content in drinking water is adjusted at the fluorator unit when it falls below 0.5 mg/L, raising it to a concentration of 0.9–1.2 mg/L. Sodium fluoride is typically used as the reagent.
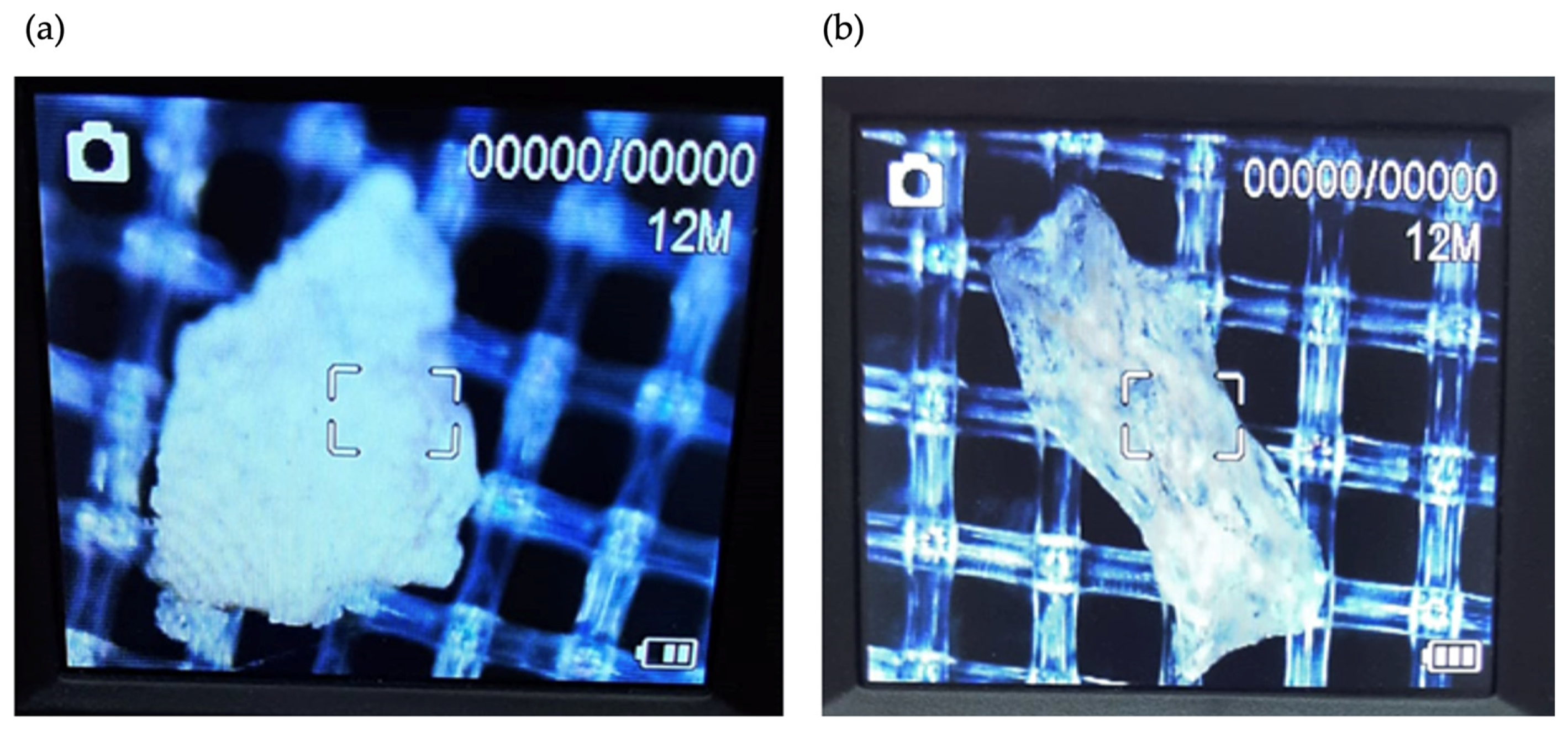
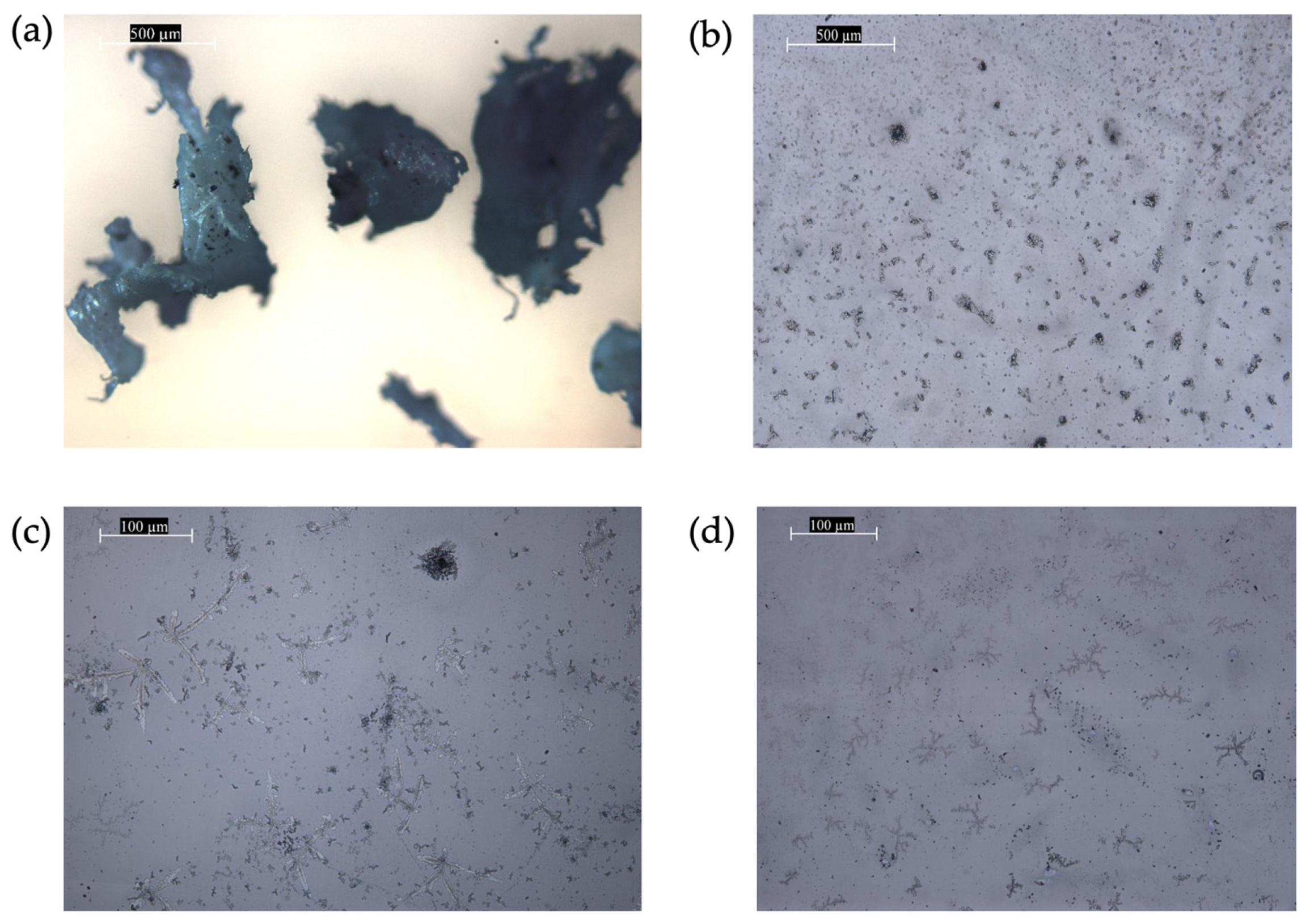
3.2. Microplastics in Tap Water
- Turbidity: Exceedance in 87% of samples (ranging from 1.26 to 6.33 times the maximum allowable concentration).
- Color: Exceedance in 40% of samples (ranging from 1.10 to 1.85 times the maximum allowable concentration).
- Acidity: Exceedance in 20% of samples (ranging from 1.1 to 1.36 times the maximum allowable concentration).
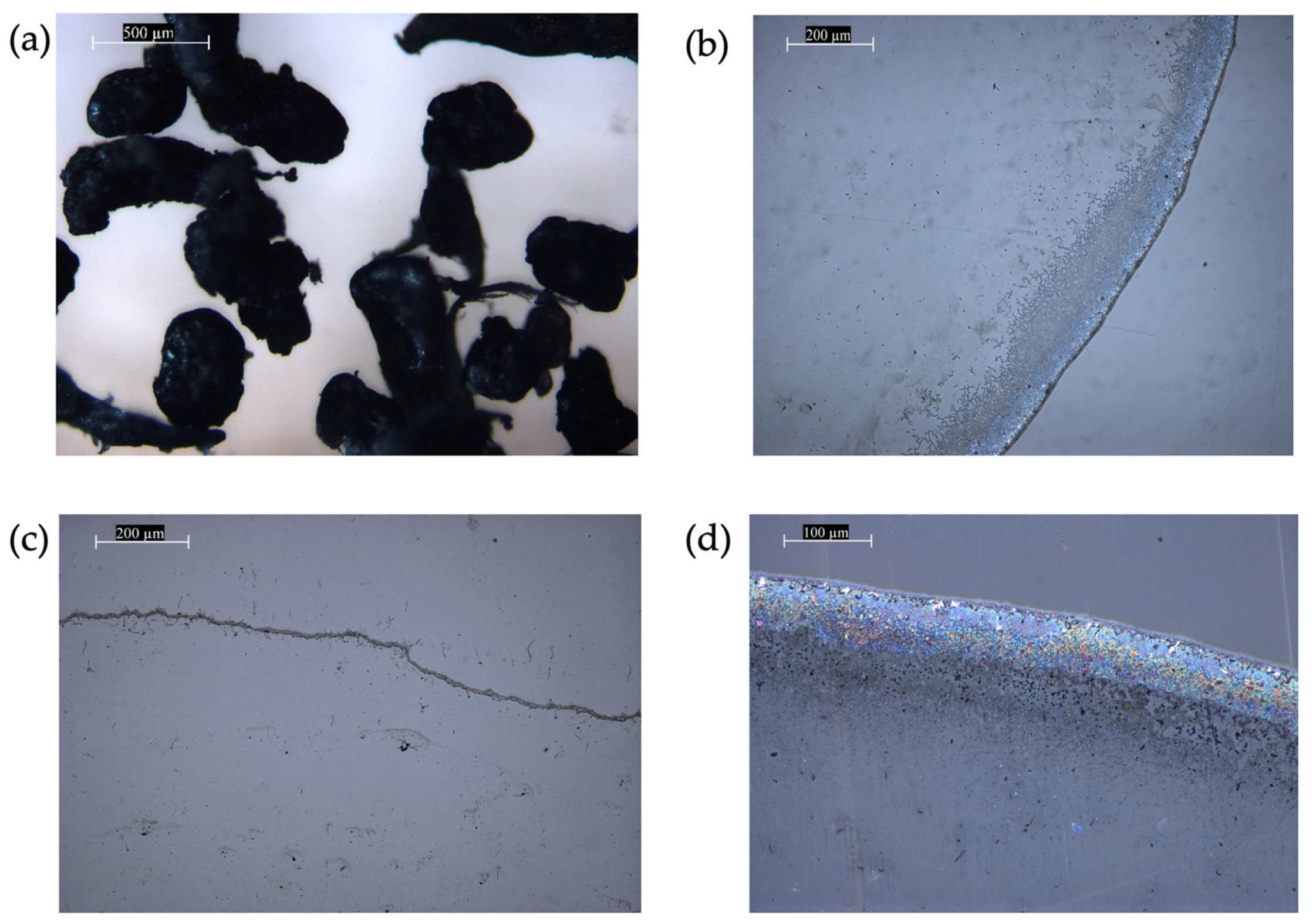
3.3. Treatment of Water from Microplastics by Sorption Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, H.; Chao, L.; Wan, H.; Zhu, Q. Microplastic Pollution in Water Systems: Characteristics and Control Methods. Diversity 2024, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’avignon, G.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Ricciardi, A. Microplastics in lakes and rivers: An issue of emerging significance to limnology. Environ. Rev. 2022, 30, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Luo, Y.; Lu, S.; Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Lei, L. Microplastics in soils: Analytical methods, pollution characteristics and ecological risks. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 109, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Zhou, Q. Microplastic Pollution in the Soil Environment: Characteristics, Influencing Factors, and Risks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. Microplastics in the atmosphere: A review. J. Environ. Exp. Asses. 2022, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad López, A.P.; Trilleras, J.; Arana, V.A.; García-Alzate, L.S.; Grande-Tovar, C.D. Atmospheric microplastics: Exposure, toxicity, and detrimental health effects. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 7468–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Dai, X.; Wang, Q.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Ni, B.J. Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Detection, occurrence and removal. Water Res. 2019, 152, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, M.; Martín-Lara, M.A.; Godoy, V.; Quesada, L.; Martínez, D.; Peula, F.; Soto, J.M. Characterization of plastic materials present in municipal solid waste: Preliminary study for their mechanical recycling. Detritus 2018, 4, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Int-Veen, I.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Identification of microplastic in effluents of waste water treatment plants using focal plane array-based micro-Fourier-transform infrared imaging. Water Res. 2017, 108, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Cermakova, L.; Novotna, K.; Peer, P.; Cajthaml, T.; Janda, V. Occurrence of microplastics in raw and treated drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintenig, S.M.; Löder, M.G.J.; Primpke, S.; Gerdts, G. Low numbers of microplastics detected in drinking water from ground water sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, W.; Eftekhardadkhah, M.; Svendsen, C. Mapping Microplastic in Norwegian Drinking Water. Available online: www.norskvann.no (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Zuccarello, P.; Ferrante, M.; Cristaldi, A.; Copat, C.; Grasso, A.; Sangregorio, D.; Fiore, M.; Oliveri Conti, G. Exposure to microplastics (<10 μm) associated to plastic bottles mineral water consumption: The first quantitative study. Water Res. 2019, 157, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Herrera, A.; Llorca, M.; Borrel-Diaz, X.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Abad, E.; Villanueva, C.M.; Farré, M. Polymers of micro(nano) plastic in household tap water of the Barcelona Metropolitan Area. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oßmann, B.E.; Sarau, G.; Holtmannspötter, H.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Christiansen, S.H.; Dicke, W. Small-sized microplastics and pigmented particles in bottled mineral water. Water Res. 2018, 141, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrete Velasco, A.; Ramseier Gentile, S.; Zimmermann, S.; Le Coustumer, P.; Stoll, S. Contamination and removal efficiency of microplastics and synthetic fibres in a conventional drinking water treatment plant in Geneva, Switzerland. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Dobaradaran, S.; Schmidt, T.C.; Malakootian, M.; Spitz, J. Emerging contaminants migration from pipes used in drinking water distribution systems: A review of the scientific literature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75134–75160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.W.L.; Ho, H.T.; Ma, A.T.H.; Fok, L. Microplastic Contamination of Surface Water-Sourced Tap Water in Hong Kong—A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambino, I.; Bagordo, F.; Grassi, T.; Panico, A.; De Donno, A. Occurrence of Microplastics in Tap and Bottled Water: Current Knowledge. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Kerpen, J.; Wolff, S.; Langer, R.; Eschweiler, V. Investigation of microplastics contamination in drinking water of a German city. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.D.; Weinstein, J.E. Size- and shape-dependent effects of microplastic particles on adult daggerblade grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Green, C.; Reynolds, A.; Shi, H.; Rotchell, J.M. Microplastics in mussels sampled from coastal waters and supermarkets in the United Kingdom. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaiman, L.; Aljomah, A.; Bineid, M.; Aljeldh, F.M.; Aldawsari, F.; Liebmann, B.; Lomako, I.; Sexlinger, K.; Alarfaj, R. The occurrence and dietary intake related to the presence of microplastics in drinking water in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rangioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato-Lourenço, L.F.; Carvalho-Oliveira, R.; Júnior, G.R.; dos Santos Galvão, L.; Ando, R.A.; Mauad, T. Presence of airborne microplastics in human lung tissue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.; Nelson, K. Trophic level transfer of microplastic: Mytilus edulis (L.) to Carcinus maenas (L.). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; Depledge, M.H. Where is the evidence that human exposure to microplastics is safe? Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Cho, J.; Sohn, J.; Kim, C. Health Effects of Microplastic Exposures: Current Issues and Perspectives in South Korea. Yonsei Med. J. 2023, 64, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, E.B.; Sankhla, M.S.; Bhat, R.A.; Bhagat, D.S. Microplastics from food packaging: An overview of human consumption, health threats, and alternative solutions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Boz, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, H.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacaratte, F.; Cuevas, P.; Becerra-Herrera, M.; Manzano, C.A. Early screening of suspected microplastics in bottled water in the Santiago Metropolitan Region of Chile. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Almuhtaram, H.; McKie, M.J.; Andrews, R.C. Assessment of microplastic sampling and extraction methods for drinking waters. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Williams, R.J.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Lahive, E. Large microplastic particles in sediments of tributaries of the River Thames, UK—Abundance, sources and methods for effective quantification. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 114, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Performance Index. Available online: https://epi.yale.edu/epi-results/2022/component/epi (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Most Sustainable Countries—U.S. News. Available online: https://www.usnews.com/news/best-countries/most-sustainable-countries (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Nurtazin, S.; Pueppke, S.; Ospan, T.; Mukhitdinov, A.; Elebessov, T. Quality of Drinking Water in the Balkhash District of Kazakhstan’s Almaty Region. Water 2020, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikova, N.S.; Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Alimova, K.K.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.E. Analysis of the Water Quality of the Ishim River within the Akmola Region (Kazakhstan) Using Hydrochemical Indicators. Water 2021, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikova, N.S.; Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.E.; Urazbayeva, S.E.; Askarova, A.Z.; Magzhanov, K.M. Environmental Assessment of Microplastic Pollution Induced by Solid Waste Landfills in the Akmola Region (North Kazakhstan). Water 2023, 15, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikova, N.S.; Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Makeyeva, L.A.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.E.; Tleuova, Z.O.; Makhmutova, A.D. Monitoring of Microplastics in Water and Sediment Samples of Lakes and Rivers of the Akmola Region (Kazakhstan). Water 2024, 16, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zheng, B.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, P.; Tian, Y. Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in water supply systems: In water and pipe scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, T.; Chen, W. Occurrence and removal of microplastics in an advanced drinking water treatment plant (ADWTP). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acarer, S. Abundance and characteristics of microplastics in drinking water treatment plants, distribution systems, water from refill kiosks, tap waters and bottled waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuldeyev, E.I.; Orynbekov, Y.S.; Mansurov, Z.A.; Nurlybayev, R.E.; Zhumadilova, Z.O.; Murzagulova, A.A. Applicability of Zeolite from the Daubabinsk and Chankanai Deposits as a Sorbent for Natural Waters. Water 2023, 15, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, M.; Nguyen Dihn, C.; Marzec, M.; Bazarkina, E.; Kvashnina, K.O.; Cwanek, A.; Lokas, E.; Bajda, E. Insights into uranium sequestration by coal fly-ash-derived zeolites: Understanding via wet chemistry, and advanced spectroscopies. J. Clean Prod. 2024, 449, 141206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilina, A.S.; Bakhtin, V.D.; Burukhin, S.B.; Askhadullin, S.R. Sorption of cations of heavy metals and radionuclides from the aqueous media by new synthetic zeolite-like sorbent. Nucl. Energy Technol. 2017, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marisela, A.; Franco, M.; Rojas García, E.; Medina, R.L.; Arturo, A.; Ramírez, C. Properties and applications of natural zeolites. Braz. J. Develop. 2024, 10, 1713–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Hu, T.; Huang, W.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. Removal of microplastics from wastewater with aluminosilicate filter media and their surfactant-modified products: Performance, mechanism and utilization. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 421, 129918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spacilova, M.; Dytrych, P.; Lexa, M.; Wimmerova, L.; Masin, P.; Kvacek, R.; Solcova, O. An Innovative Sorption Technology for Removing Microplastics from Wastewater. Water 2023, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, A.G.; Liu, Z.; McKie, M.J.; Almuhtaram, H.; Andrews, R.C. Microplastic Removal from Drinking Water Using Point-of-Use Devices. Polymers 2023, 15, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ST RK GOST R 51593-2003; Drinking Water. Sampling. State Standard of the Republic of Kazakhstan: Republic of Kazakhstan. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=30015917 (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Kondratyeva, E.M. Monitoring of surface waters of the southern Baikal in conditions of increasing anthropogenic load. Innov. Sci. Educ. 2021, 35, 60–64. Available online: https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=46324676 (accessed on 11 April 2024). (In Russian).
- Oni, B.A.; Sanni, S.E. Occurrence of Microplastics in Borehole Drinking Water and Sediments in Lagos, Nigeria. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson, K.; da Silva, V.H.; Deonarine, A.; Louie, S.M.; Gondikas, A. Monitoring anthropogenic particles in the environment: Recent developments and remaining challenges at the forefront of analytical methods. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, D. Comprehensive Comparison of Various Microplastic Sampling Methods in Sea Water: Implications for Data Compilation. Water 2023, 15, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.S.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Prata, J.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Girao, A.V.; Lopes, P.; Cristovao, T.; da Costa, J.P. A straightforward method for microplastic extraction from organic-rich freshwater samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munno, K.; Helm, P.A.; Jackson, D.A.; Rochman, C.; Sims, A. Impacts of temperature and selected chemical digestion methods on microplastic particles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirkey, A.; Upadhyay, L.S.B. Microplastics: An overview on separation, identification and characterization of microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faure, F.; Demars, C.; Wieser, O.; Kunz, M.; De Alencastro, L.F. Plastic pollution in Swiss surface waters: Nature and concentrations, interaction with pollutants. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Webb, H.; Lindeque, P.K.; Fileman, E.S.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Isolation of microplastics in biota-rich seawater samples and marine organisms. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, L.M.R.; Balcer, M. Microplastics in freshwater environments: A review of quantification assessment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminah, I.S.; Ikejima, K. Potential sources of microplastic contamination in laboratory analysis and a protocol for minimising contamination. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesch, C.; Elert, A.M.; Wörner, M.; Braun, U.; Klein, R.; Paulus, M. Assuring quality in microplastic monitoring: About the value of clean-air devices as essentials for verified data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermsen, E.; Pompe, R.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A. Detection of low numbers of microplastics in North Sea fish using strict quality assurance criteria. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 122, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interstate Standard 31868-2012; Water. Interstate Standard 31868-2012; Water. Methods for Determining Color. Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification: Moscow, Russia, 2019; p. 12. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200097407 (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Interstate Standard 3351-74; Drinking Water. Method for Determination of Odour, Taste, Color and Turbidity. Publishing House of Standards: Moscow, Russia, 2003; p. 8. Available online: https://meganorm.ru/Index2/1/4294850/4294850608.htm (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- State Mandatory Standard 26449.1-85; Stationary Distillation and Desalination Plants. Methods for Chemical Analysis of Salt Waters. USSR State Committee on Standards: Moscow, Russia, 1985; p. 101. Available online: https://files.stroyinf.ru/Index2/1/4294850/4294850335.htm (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- ISO Standard 4316-2019; Surfactants. Determination of pH of Aqueous Solutions. Potentiometric Method. Technical Committee ISO/TC91. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1977. Available online: https://online.zakon.kz/Document/?doc_id=33823182&pos=30;-10#pos=30;-10 (accessed on 31 March 2024).
- Kuldeyev, E.; Seitzhanova, M.; Tanirbergenova, S.; Tazhu, K.; Doszhanov, E.; Mansurov, Z.; Azat, S.; Nurlybaev, R.; Berndtsson, R. Modifying Natural Zeolites to Improve Heavy Metal Adsorption. Water 2023, 15, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauanov, Z.; Azat, S.; Baibatyrova, A. A mini-review on coal fly ash properties, utilization and synthesis of zeolites. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2022, 42, 1968–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstić, V. Role of zeolite adsorbent in water treatment. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Wastewater Treatment: Fundamentals and Scale up Issues; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 417–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmon, C. Recent developments in water treatment by ion exchange. React. Polym. Ion Exch. Sorbents 1986, 4, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Datar, A.; Jeong, C.; Deng, X.; Chung, Y.G.; Lin, L.-C. Surface Area Determination of Porous Materials Using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Method: Limitations and Improvements. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 20195–20209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bureau of National Statistics of the Agency for Strategic Planning and Reforms of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Available online: https://old.stat.gov.kz/for_users/ecologic_indicators/ecologic_indicator/water_consumption (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Salikova, N.S.; Alimova, K.K. Communal, Domestic and Industrial Water Supply in Kazakhstan: Interim Report on the Project IRN AP14869081 “Modelling of Health Risks Based on Identification of Microplastics in Water Systems and Justification of Actions to Manage the Quality of Water Resources”; Abay Myrzakhmetov Kokshetau University: Kokshetau, Kazakhstan, 2022; 57p, Available online: https://kuam.edu.kz/sites/default/files/2022/salikova_n.s._alimova_k.k._communal_domestic_and_industrial_water_supply_in_kazakhstan._interim_report_on_the_project_irn_ap14869081.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Order of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Kazakhstan from 20 February 2023 №26 ‘Sanitary and Epidemiological Requirements for Water Sources, Places of Water Intake for Household and Drinking Purposes, Household and Drinking Water Supply and Places of Cultural and Domestic Water Use and Safety of Water Bodies’. 2023. Available online: https://adilet.zan.kz/rus/docs/V2300031934 (accessed on 11 April 2024).
- Miao, M.; Liu, J.; Dou, Y.; Hao, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Effects of microplastics on DBPs formation under the chlorination of natural organic matters. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Yu, B.; Cheng, X.; Hao, T.; Dou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y. Effects of chlorination on microplastics pollution: Physicochemical transformation and chromium adsorption. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rullander, G.; Lorenz, C.; Herbert, R.B.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Vollertsen, J.; Dalahmeh, S.S. How effective is the retention of microplastics in horizontal flow sand filters treating stormwater? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, N.; Pirsaheb, M.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Nodehi, R.N. Microplastics removal from aquatic environment by coagulation: Selecting the best coagulant based on variables determined from a systematic review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, K.; Magnusson, K.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G.-T. Removal of rubber, bitumen and other microplastic particles from stormwater by a gross pollutant trap—bioretention treatment train. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.Y. Sedimentation in Water and Used Water Purification. In Handbook of Water and Used Water Purification; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziembowicz, S.; Kida, M.; Koszelnik, P. Efficient removal of polyethylene and polyvinyl chloride microplastics from water using a modified coagulation process supported by the addition of a surfactant. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 288, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Diehl, A.; Lewandowski, A.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Baker, T. Removal efficiency of micro- and nanoplastics (180 nm–125 μm) during drinking water treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, S.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, J.-T.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Chung, J.; Kim, E.-J. Microplastic removal in conventional drinking water treatment processes: Performance, mechanism, and potential risk. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.B.; Yu, J.; Banik, P.; Noman, A.; Nur, A.-A.U.; Haque, R.; Rahman, M.; Albeshr, M.F.; Arai, T. First evidence of microplastics and their characterization in bottled drinking water from a developing country. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1232931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Quinlivan, P.A.; Knappe, D.R. Effects of activated carbon surface chemistry and pore structure on the adsorption of organic contaminants from aqueous solution. Carbon 2002, 40, 2085–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Cho, H.H.; Poster, D.L.; Ball, W.P. Evidence for a pore-filling mechanism in the adsorption of aromatic hydrocarbons to a natural wood char. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, C.; Li, F.; Chen, L. Fatigue resistance, re-usable and biodegradable sponge materials from plant protein with rapid water adsorption capacity for microplastics removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 129006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, Q.-X.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.-H. Adsorption and thermal degradation of microplastics from aqueous solutions by Mg/Zn modified magnetic biochars. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, E.; Singh, N.; Khandelwal, N.; Monikh, F.A.; Darbha, G.K. Application of Zn/Al layered double hydroxides for the removal of nano-scale plastic debris from aqueous systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmau-Soler, J.; Ballesteros-Cano, R.; Ferrer, N.; Boleda, M.R.; Lacorte, S. Microplastics throughout a tap water supply network. Water Environ. J. 2022, 36, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, H.; Ghayebzadeh, M.; Ganji, F.; Mousavi, S.; Azizi, N. Tracking microplastics contamination in drinking water in Zahedan, Iran: From source to consumption taps. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. Metro station free drinking water fountain- A potential “microplastics hotspot” for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.; Ball, H.; Cross, R.; Horton, A.A.; Jürgens, M.D.; Read, D.S.; Vollertsen, J.; Svendsen, C. Identification and Quantification of Microplastics in Potable Water and Their Sources within Water Treatment Works in England and Wales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12326–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuptsov, A.; Zhizhin, G. Fourier-Raman and Fourier-IR Spectra of Polymers; Fizmatlit: Moscow, Russia, 2001; 657p, Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262416516_Kupcov_AH_Zizin_GN_Fure-KR_i_Fure-IK_spektry_polimerov_m_Fizmatlit_2001_657_s/references (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Pittroff, M.; Mueller, Y.K.; Witzig, C.S.; Scheurer, M.; Storck, F.R.; Zumbuelte, N. Microplastic analysis in drinking water based on fractionated filtration sampling and Raman microspectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59439–59451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, Q.; Wei, X.-F.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Crittenden, J.C.; Liu, B. Tracing microplastics in rural drinking water in Chongqing, China: Their presence and pathways from source to tap. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaremisa, G.; Tutu, H.; Saad, D. Detection and characterisation of microplastics in tap water from Gauteng, South Africa. Chemosphere 2024, 141903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, J.; Feld, L.; Murphy, F.; Mackevica, A.; Hartmann, N.B. Analysis of Microplastic Particles in Danish Drinking Water; APA: Aarhus, Denmark, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mukotaka, A.; Kataoka, T.; Nihei, Y. Rapid analytical method for characterization and quantification of microplastics in tap water using a Fourier-transform infrared microscope. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
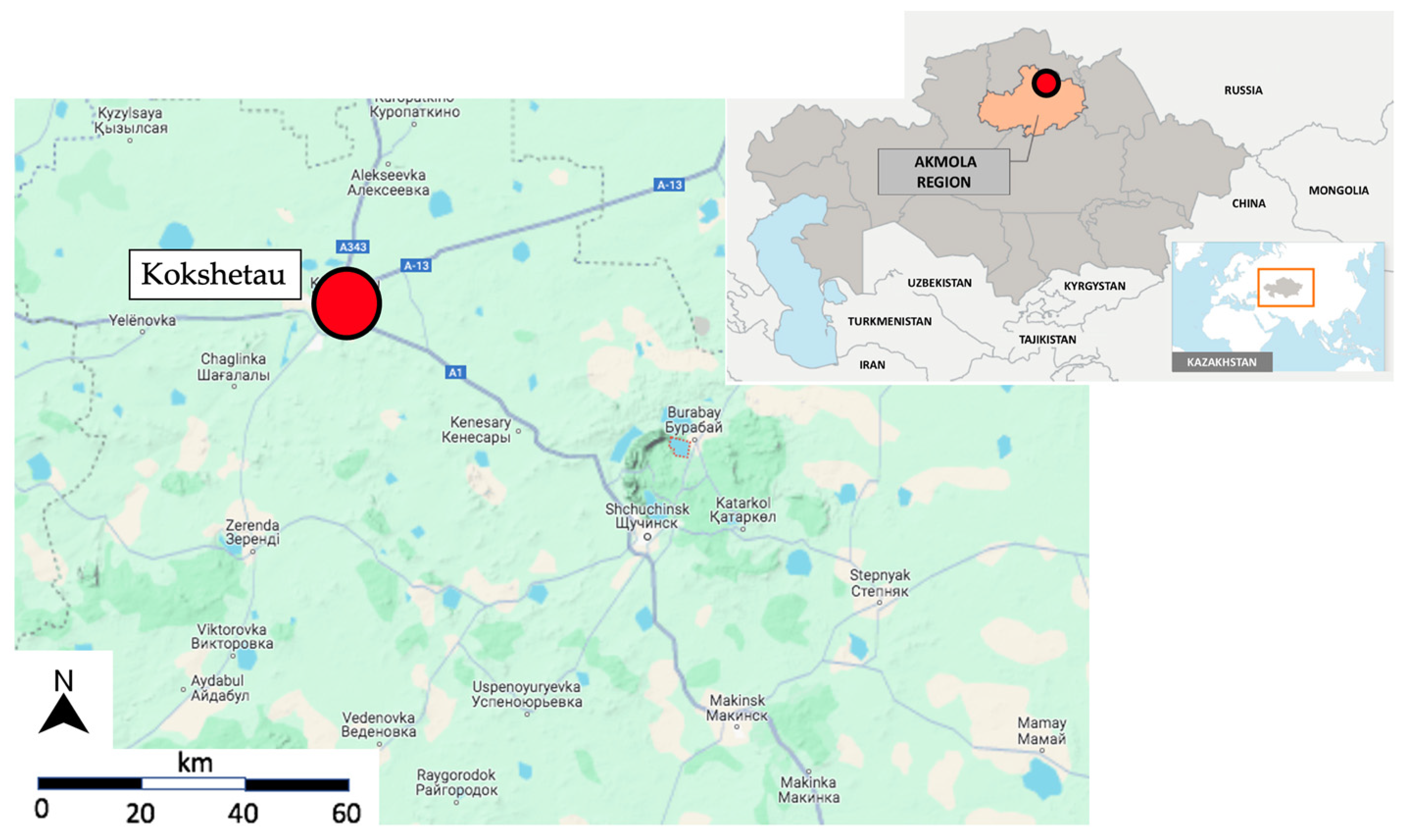
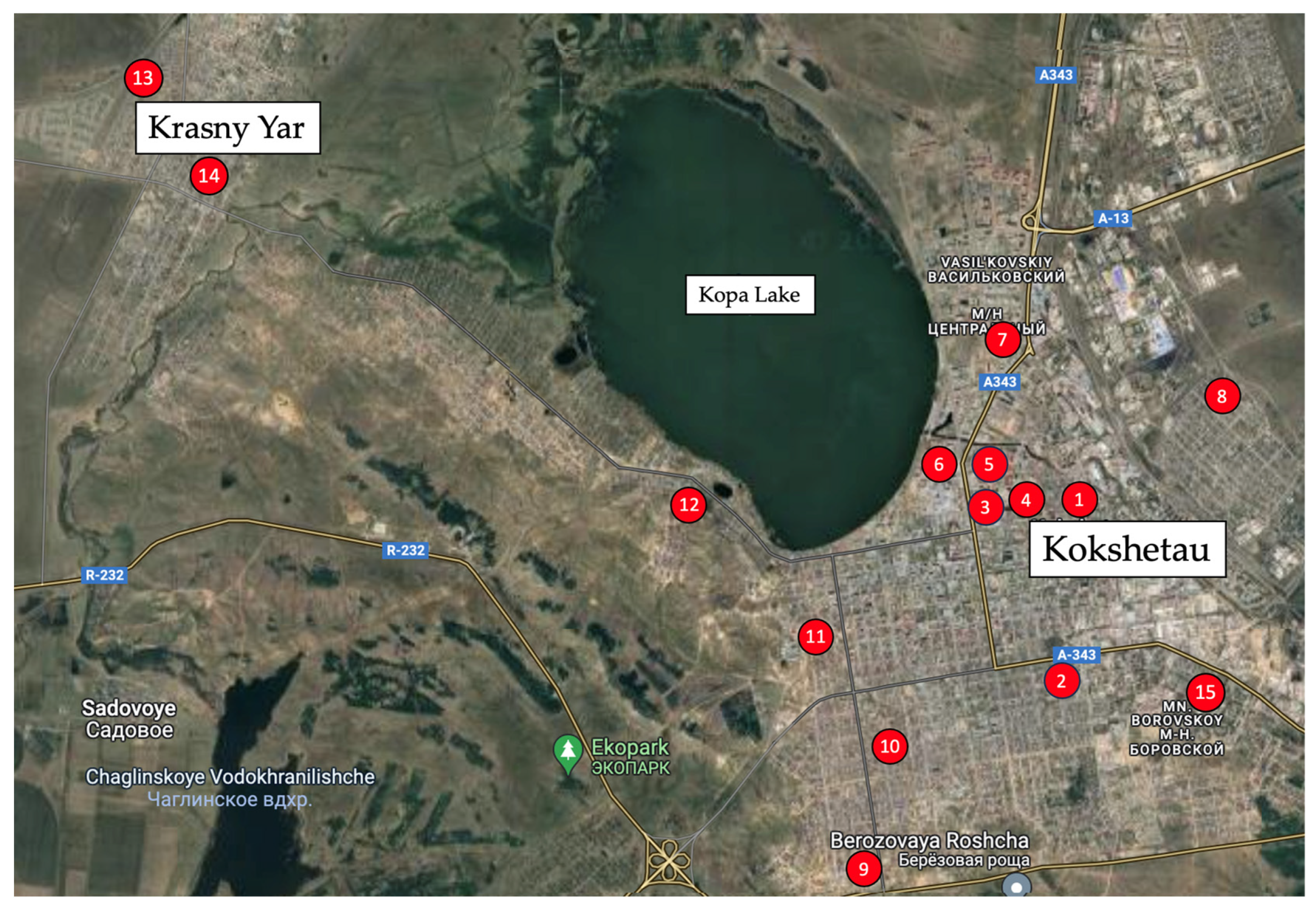





| Sample No. | UTM X | UTM Y | Sample No. | UTM X | UTM Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 53.289008 | 69.404590 | 9 | 53.252827 | 69.359687 |
| 2 | 53.274207 | 69.405828 | 10 | 53.264980 | 69.371940 |
| 3 | 53.289204 | 69.391170 | 11 | 53.277500 | 69.361754 |
| 4 | 53.289488 | 69.392308 | 12 | 53.292318 | 69.336518 |
| 5 | 53.293338 | 69.386138 | 13 | 53.329990 | 69.253996 |
| 6 | 53.292478 | 69.386359 | 14 | 53.322229 | 69.264094 |
| 7 | 53.306466 | 69.389917 | 15 | 53.271033 | 69.428809 |
| 8 | 53.302045 | 69.427693 |
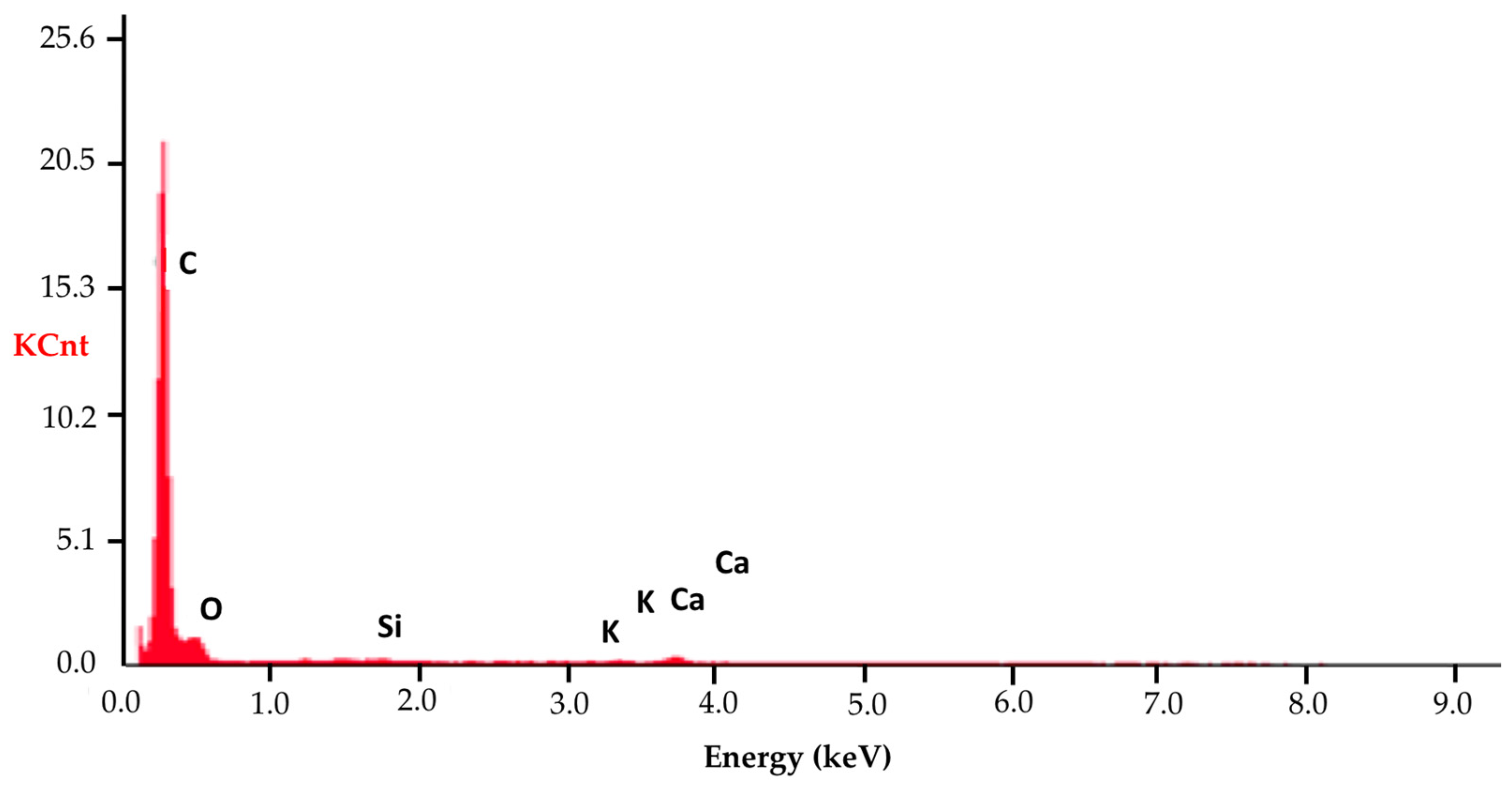
| Chemical Element | C | O | Si | K | Ca |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Share (%) | 92.45 | 6.87 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.44 |
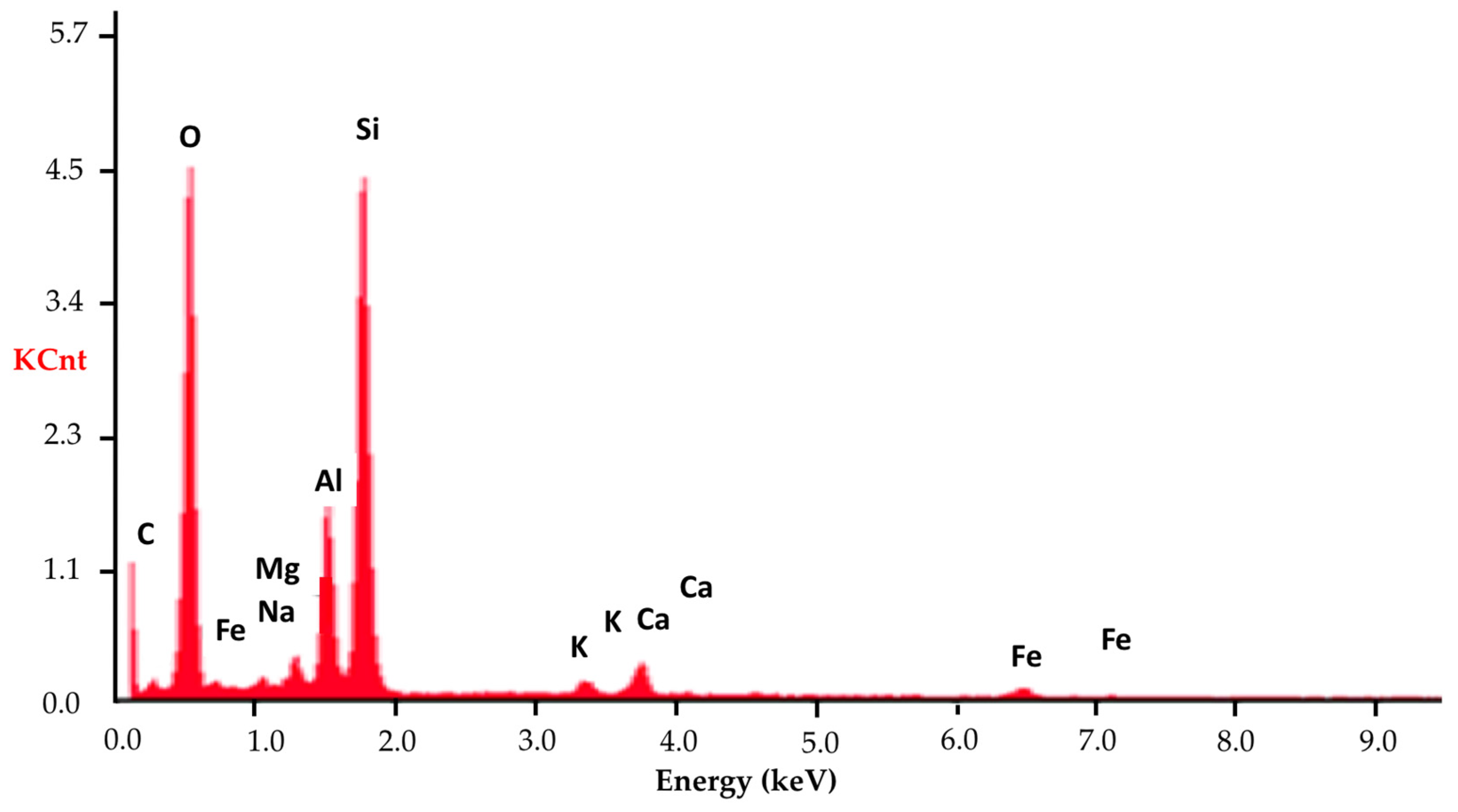
| Chemical Element | C | O | Na | Mg | Al | Si | K | Ca | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Share (%) | 8.52 | 60.09 | 0.52 | 1.15 | 6.91 | 19.29 | 0.68 | 1.62 | 1.22 |
| Chemical Element | C | O | Al | Si | Ca | In |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Share (%) | 84.06 | 14.03 | 0.75 | 0.61 | 0.35 | 0.20 |
| Sample No. | Color (Degrees) | Turbidity (mg/dm3) | pH | Oxidization (mg/dm3) | Microplastic Concentration (Particles/dm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPC | ≤20 | ≤1.5 | 6–9 | ≤5 | - |
| 1 | 18 | 9.51 | 6.82 | 6.8 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| 2 | 11 | 4.52 | 6.81 | 5.4 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| 3 | 15 | 3.42 | 6.80 | 5.8 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| 4 | 14 | 4.13 | 6.83 | 4.7 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 5 | 37 | 5.22 | 6.82 | 3.3 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 6 | 23 | 2.64 | 7.01 | 3.3 | 6.0 × 10−2 |
| 7 | 22 | 3.10 | 7.10 | 3.2 | 6.0 × 10−2 |
| 8 | 32 | 3.13 | 7.12 | 3.2 | 6.0 × 10−2 |
| 9 | 18 | 3.82 | 7.13 | 2.4 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 10 | 35 | 2.91 | 7.04 | 2.9 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| 11 | 29 | 3.50 | 7.10 | 3.2 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 12 | 16 | 1.90 | 7.03 | 2.8 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 13 | 6 | 0.34 | 7.12 | 0.7 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 14 | 7 | 0.46 | 7.10 | 0.8 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| 15 | 26 | 4.93 | 7.02 | 2.9 | 4.0 × 10−2 |
| Reference | Location | Number of Samples | Microplastic Concentration (Particles/dm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| This study | Kokshetau and Krasny Yar (Kazakhstan) | 15 | 4.0 × 10−2–6.0 × 10−2 |
| [23] | Central region (Saudi Arabia) | 2 | 1.8 |
| [86] | Barcelona city (Spain) | 21 | 0–5.0 × 10−2 |
| [40] | Tianjin (China) | 1 | 13.23 |
| [87] | Zahedan (Iran) | 10 | 7.5 × 10−2–40.0 × 10−2 |
| [88] | Mexico City (Mexico) | 42 | 5.0–91.0 |
| [11] | North-western region (Germany) | 24 | 1 × 10−4–100 |
| [89] | England and Wales (UK) | 39 | 0–2.4 × 10−2 |
| [90] | Baden-Wurttemberg (Germany) | 2 | 0.6 × 10−2–7.4 × 10−2 |
| [91] | Chongqing (Southwest China) | 1 | 1.4 |
| [92] | Gauteng (South Africa) | 30 | 4.7–31 |
| [93] | Denmark | 17 | 8.0 × 10−2–60.0 × 10−2 |
| [94] | Japan | 28 | 29–45 |
| Polymer | Fractional Size of Microplastic (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.105 | 0.2 | 0.45 | |
| Complex (CSM + ion exchange resins) | |||
| PET | 82.7 | 85.2 | 86.0 |
| PE | 91.7 | 92.1 | 93.6 |
| PP | 85.8 | 85.7 | 89.9 |
| Average efficiency by sorbent | 86.7 | 87.7 | 89.8 |
| Zeolite | |||
| PET | 91.0 | 91.3 | 91.2 |
| PE | 90.2 | 90.8 | 94.3 |
| PP | 89.9 | 90.0 | 92.8 |
| Average efficiency by sorbent | 90.4 | 90.7 | 92.8 |
| Carbon sorption material (CSM) | |||
| PET | 92.7 | 92.6 | 93.3 |
| PE | 95.3 | 97.2 | 97.8 |
| PP | 95.0 | 94.9 | 96.8 |
| Average efficiency by sorbent | 94.3 | 94.9 | 96.0 |
| Sample No. | Color (Degrees) | Turbidity (mg/dm3) | pH | Oxidization (mg/dm3) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | EFFICIENCY (%) | Initial | Final | Efficiency (%) | Initial | Final | Efficiency (%) | Initial | Final | Efficiency (%) | |
| Sorbent 1—Zeolite | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 1 | 90.0 | 1.87 | 1.41 | 24.6 | 8.05 | 7.52 | 6.5 | 132.0 | 0.67 | 99.5 |
| 2 | 9 | 0 | 90.0 | 1.87 | 1.43 | 23.5 | 7.96 | 7.53 | 5.4 | 132.8 | 0.70 | 99.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 1 | 90.0 | 1.90 | 1.51 | 20.5 | 8.00 | 7.53 | 5.8 | 132.7 | 0.60 | 99.5 |
| Sorbent 2—CSM | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 0 | 100.0 | 1.87 | 0.50 | 73.3 | 8.05 | 7.38 | 8.3 | 132.0 | 0.32 | 99.8 |
| 2 | 9.0 | 0.0 | 100.0 | 1.87 | 0.46 | 75.4 | 7.96 | 7.38 | 7.2 | 132.8 | 0.25 | 99.8 |
| 3 | 10 | 0 | 100.0 | 1.90 | 0.48 | 74.7 | 8.00 | 7.39 | 7.6 | 132.7 | 0.30 | 99.8 |
| Sorbent 3—(CSM + ion exchange resins) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 10 | 2 | 80.0 | 1.87 | 0.77 | 58.8 | 8.05 | 7.63 | 5.2 | 132.0 | 4.32 | 96.7 |
| 2 | 9 | 2 | 77.7 | 1.87 | 0.73 | 61.0 | 7.96 | 7.62 | 4.2 | 132.8 | 4.40 | 96.7 |
| 3 | 10 | 2 | 80.0 | 1.90 | 0.72 | 62.1 | 8.00 | 7.60 | 5.0 | 132.7 | 4.25 | 96.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salikova, N.S.; Kerimkulova, A.R.; Rodrigo-Ilarri, J.; Alimova, K.K.; Rodrigo-Clavero, M.-E.; Kapbassova, G.A. Sorption-Based Removal Techniques for Microplastic Contamination of Tap Water. Water 2024, 16, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101363
Salikova NS, Kerimkulova AR, Rodrigo-Ilarri J, Alimova KK, Rodrigo-Clavero M-E, Kapbassova GA. Sorption-Based Removal Techniques for Microplastic Contamination of Tap Water. Water. 2024; 16(10):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101363
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalikova, Natalya S., Almagul R. Kerimkulova, Javier Rodrigo-Ilarri, Kulyash K. Alimova, María-Elena Rodrigo-Clavero, and Gulzhanat A. Kapbassova. 2024. "Sorption-Based Removal Techniques for Microplastic Contamination of Tap Water" Water 16, no. 10: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101363
APA StyleSalikova, N. S., Kerimkulova, A. R., Rodrigo-Ilarri, J., Alimova, K. K., Rodrigo-Clavero, M.-E., & Kapbassova, G. A. (2024). Sorption-Based Removal Techniques for Microplastic Contamination of Tap Water. Water, 16(10), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101363












