An Efficient Water Quality Prediction and Assessment Method Based on the Improved Deep Belief Network—Long Short-Term Memory Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Water quality prediction methods based on mechanism models
- (2)
- Water quality prediction methods based on data-driven models
2. LSTM and DBN Networks
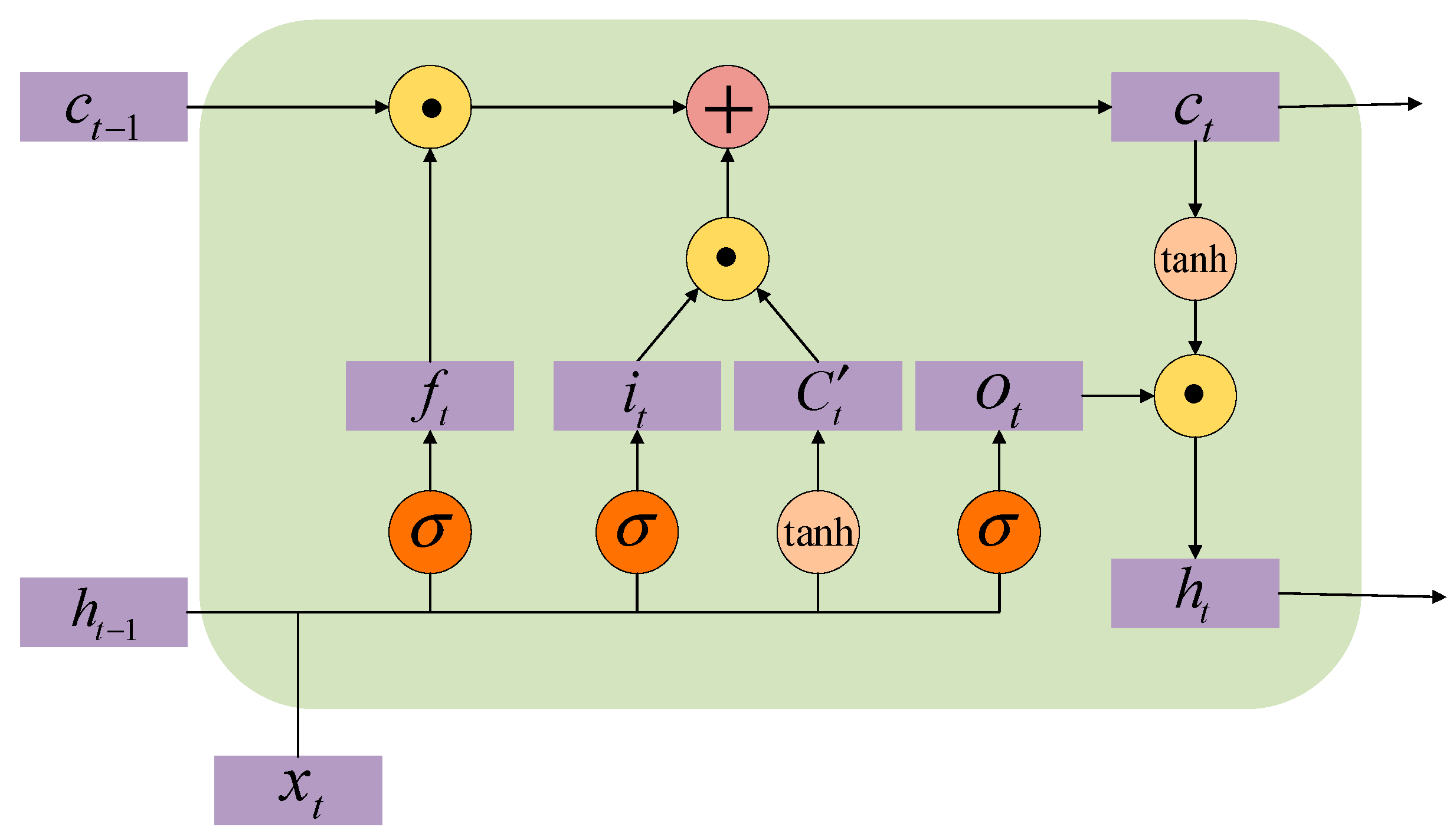
2.1. LSTM Network
- (1)
- Forget gate: In this gate, it is decided with a certain probability whether to forget the previous layer of the hidden neuron cell state or not, and the corresponding mathematical expression is given by
- (2)
- Input gate: This gate handles the input for the current sequence position, and it is defined as follows:
- (3)
- Output gate: The output at moment depends on the implicit state and the current input , which can be expressed as follows:
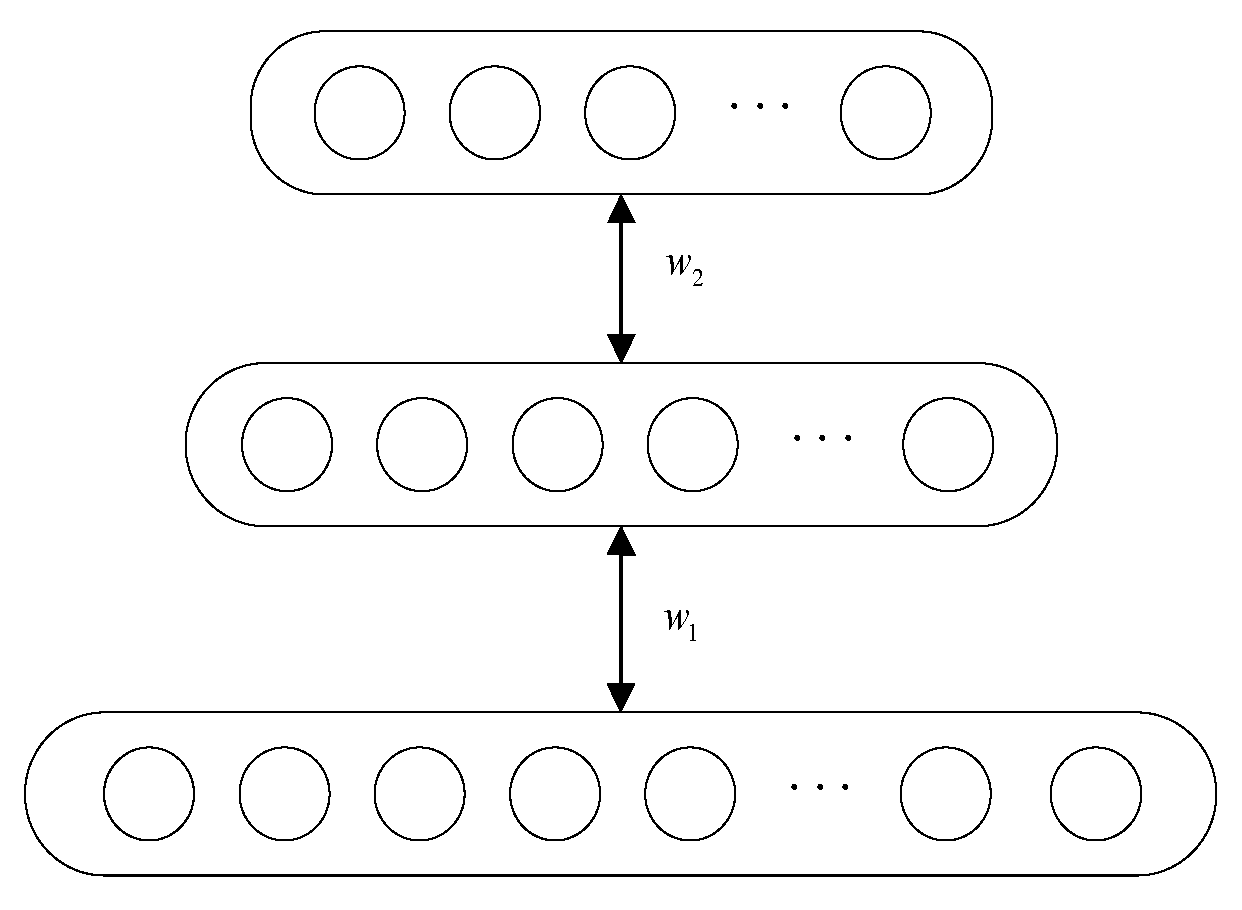
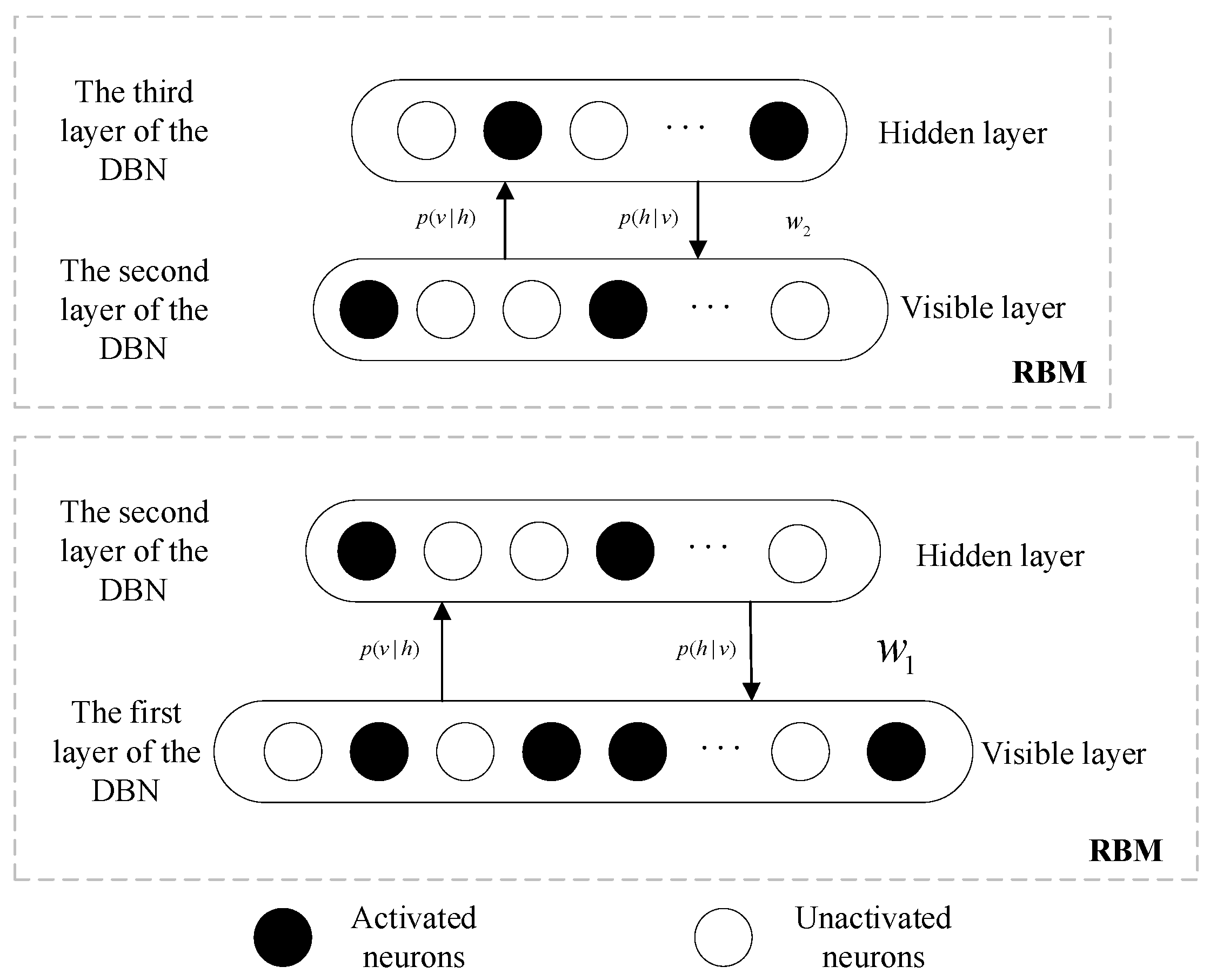
2.2. DBN Network
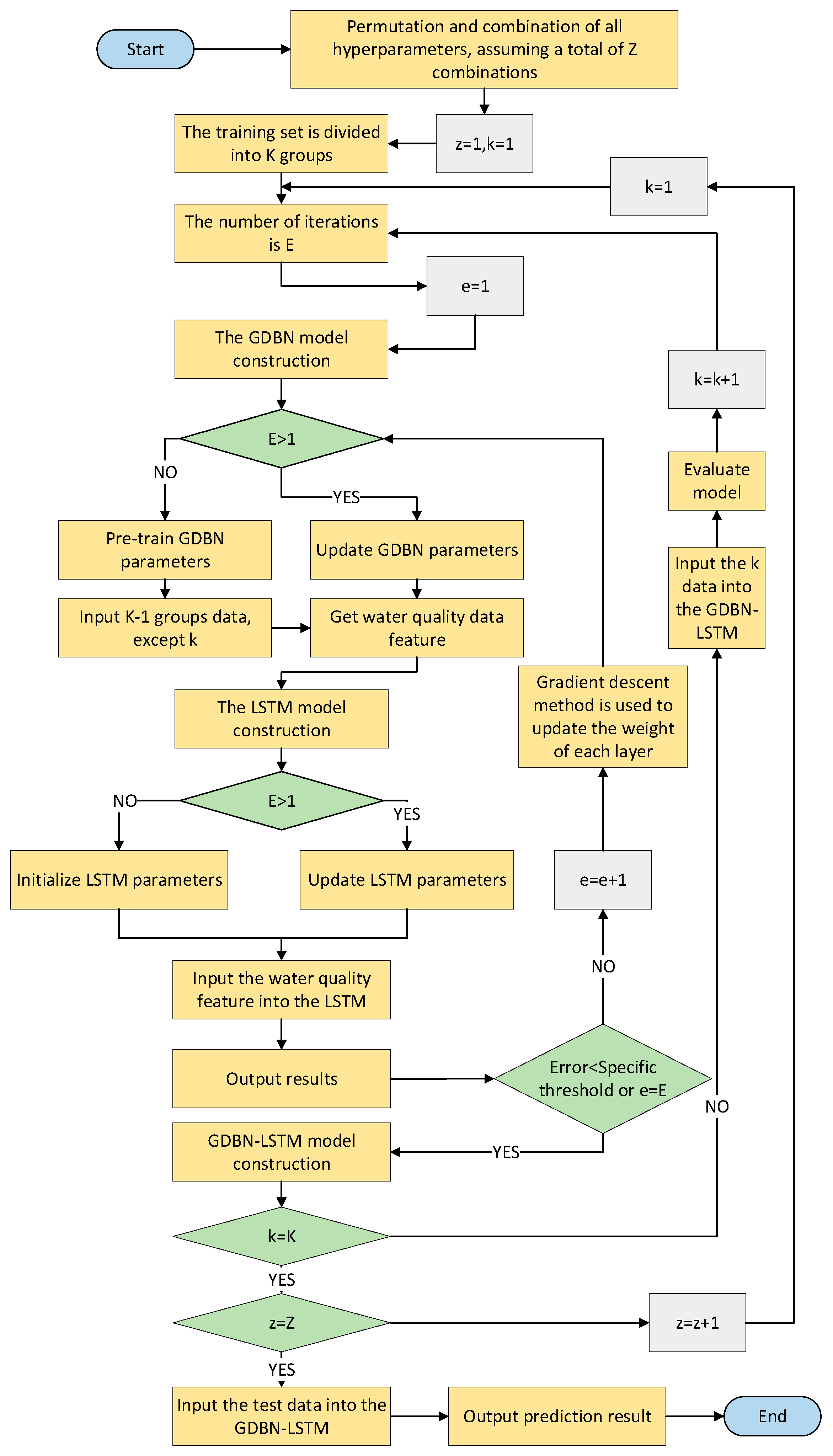
3. Proposed GDBN-LSTM Model
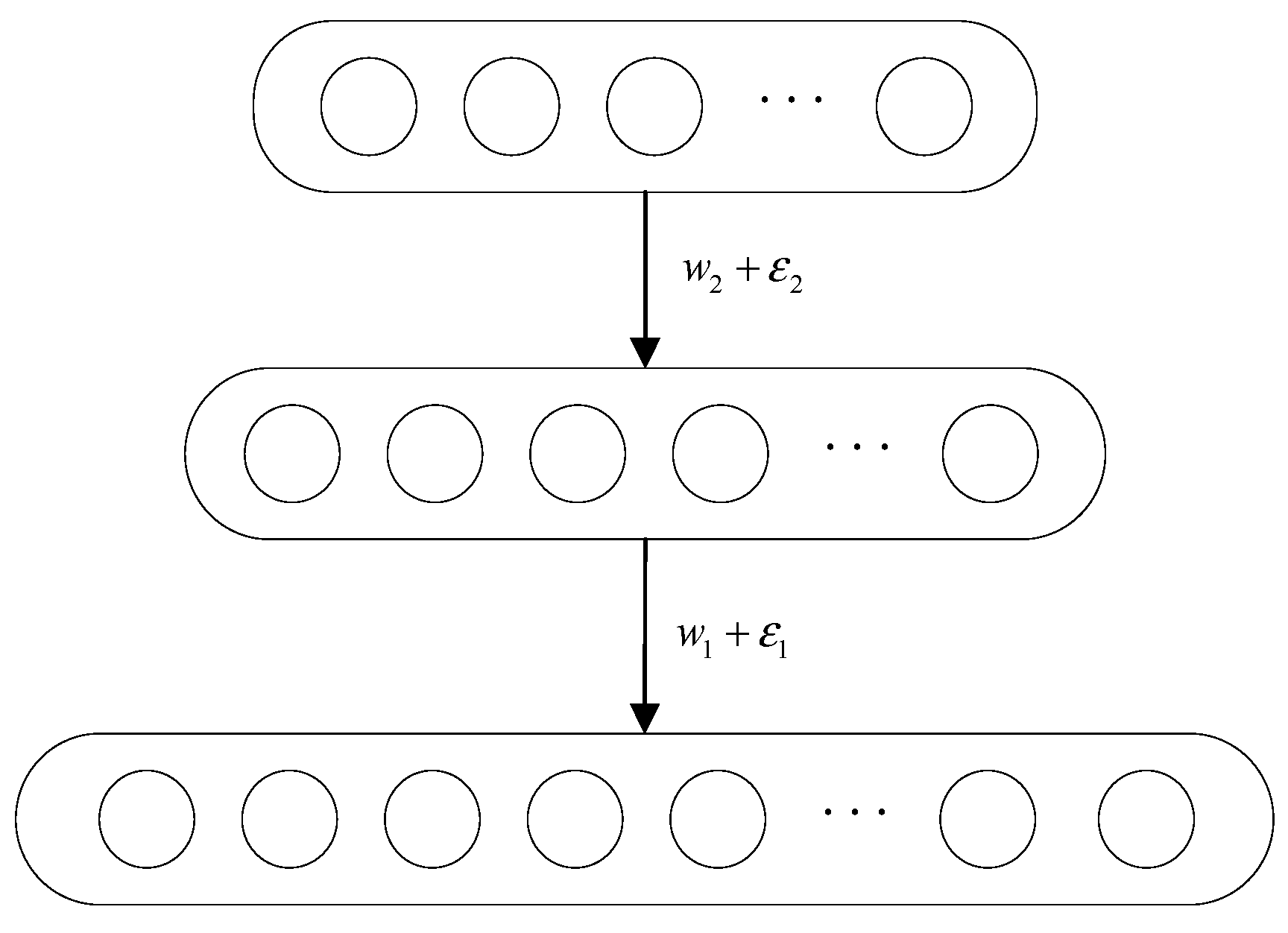
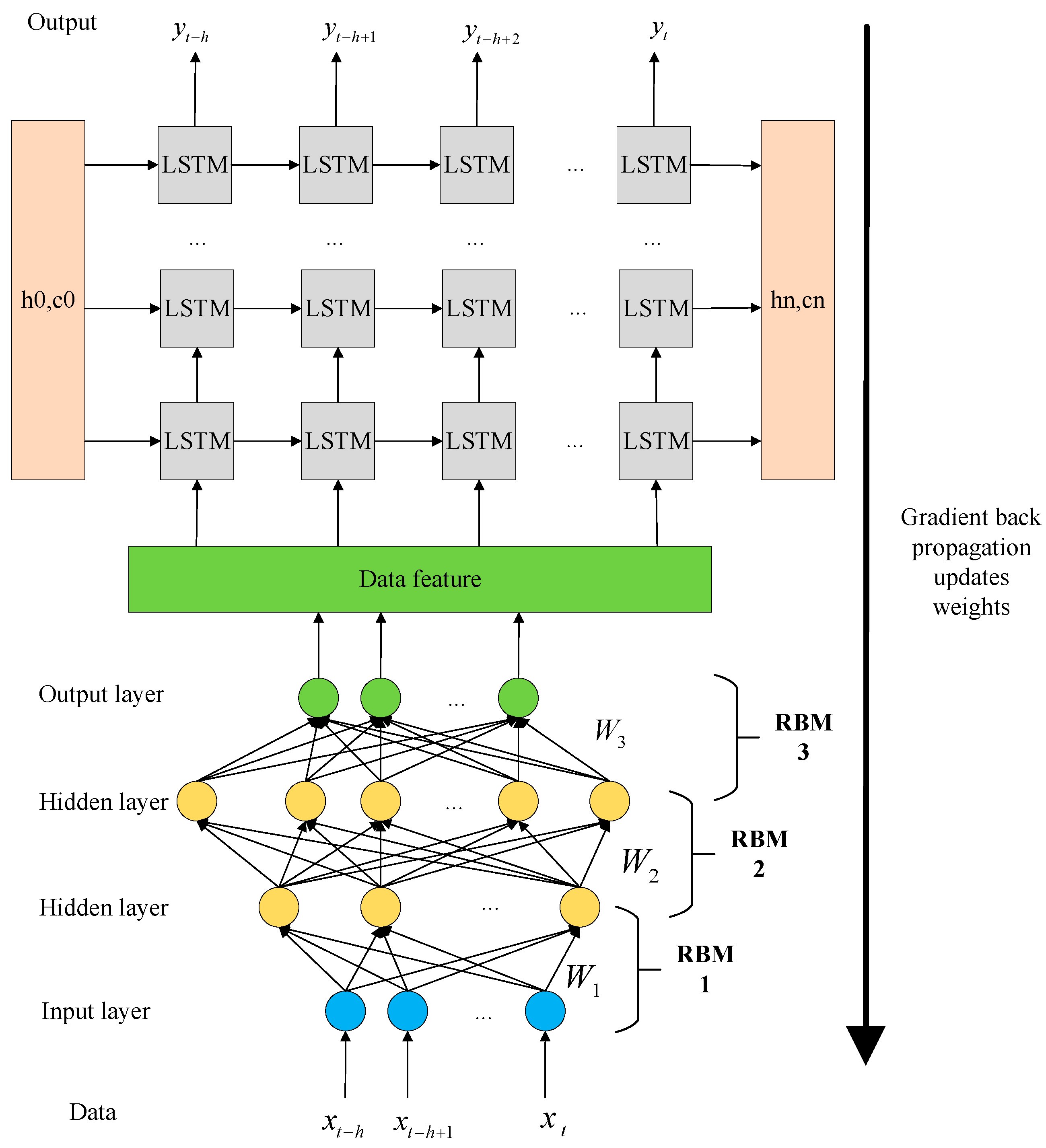
3.1. GDBN Model
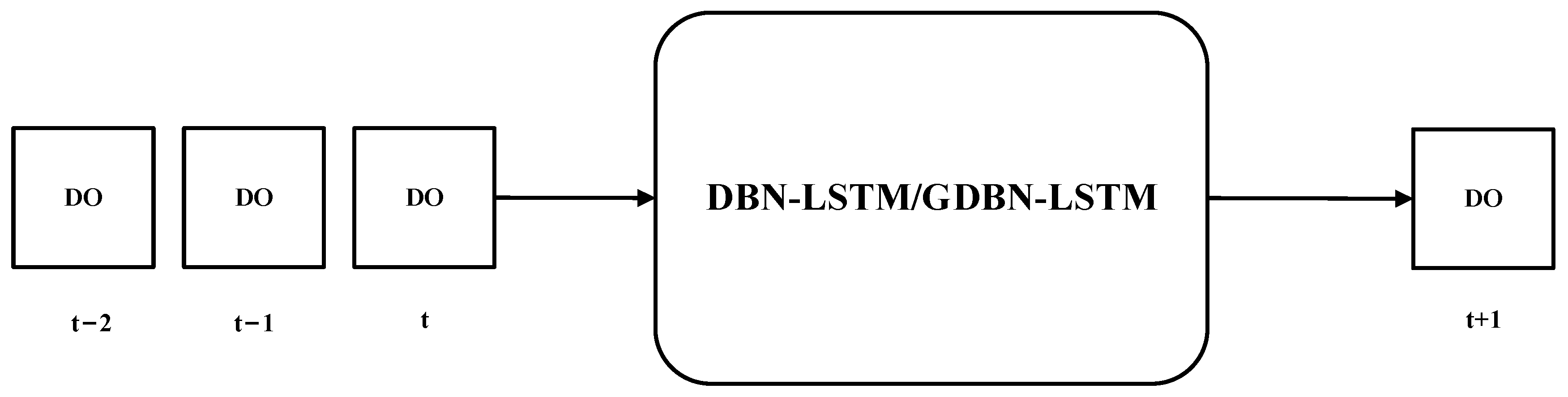
3.2. GDBN-LSTM Design
3.3. Water Quality Assessment Method
3.3.1. Single-Factor Index Evaluation Method
3.3.2. Trophic Status Index
3.4. Performance Evaluation
4. Experimental Verification
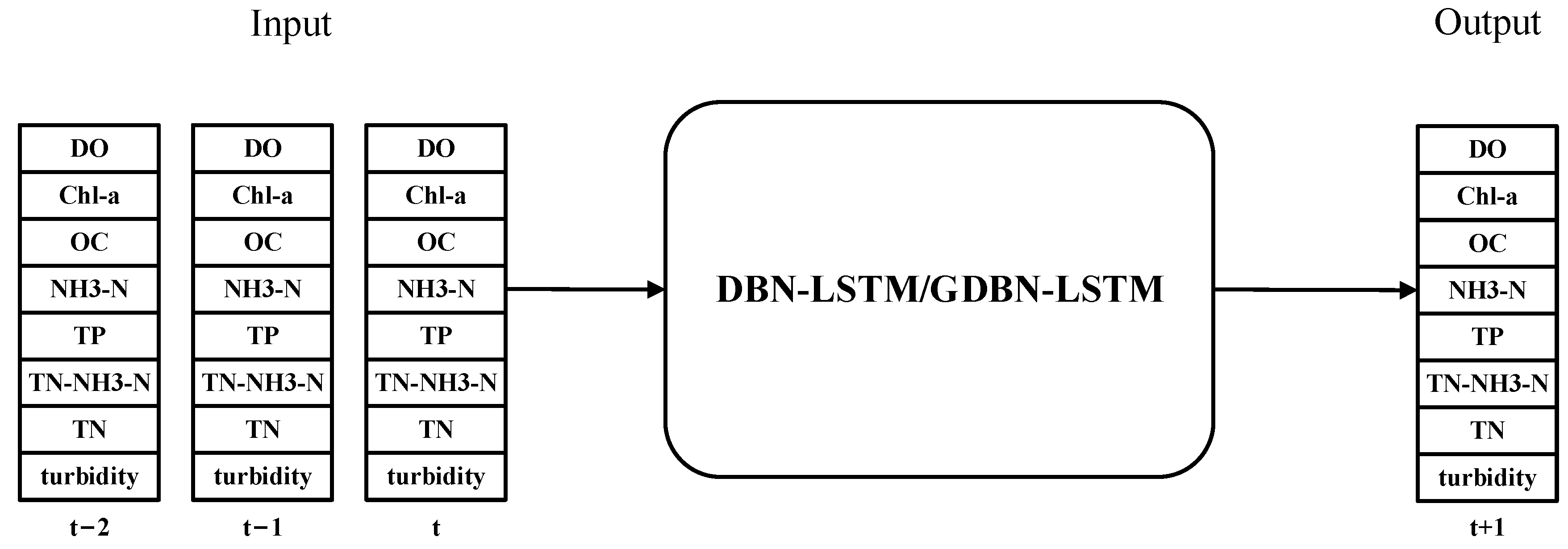
4.1. Multivariable Timing Prediction and Evaluation
4.1.1. Data Selection and Preprocessing
4.1.2. Experimental Parameter Settings
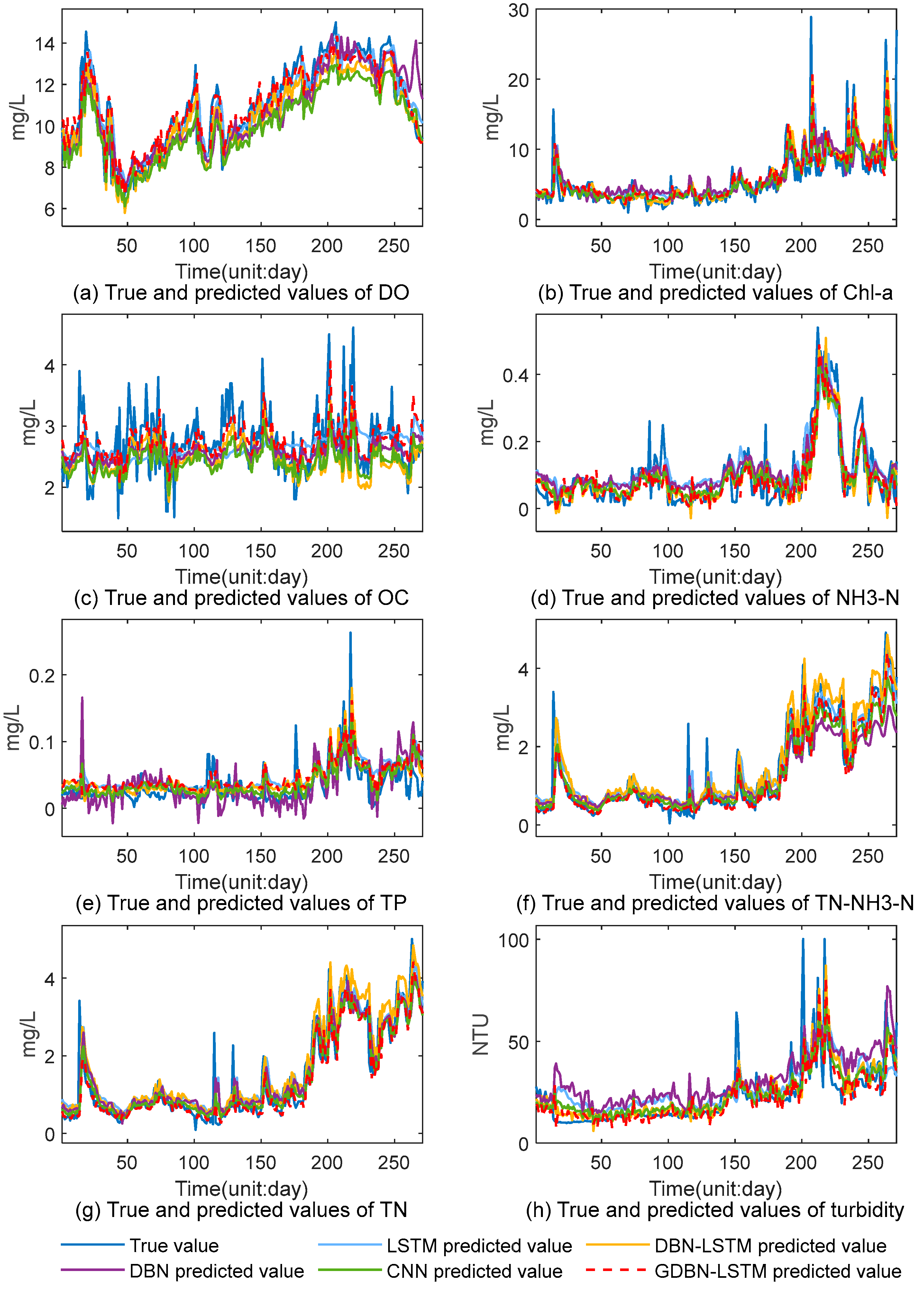
4.1.3. Experimental Results Analysis
4.1.4. Water Quality Evaluation Experiment
4.2. Univariable Timing Prediction and Evaluation
4.2.1. Data Selection and Preprocessing
4.2.2. Experimental Parameter Settings
4.2.3. Experimental Results Analysis
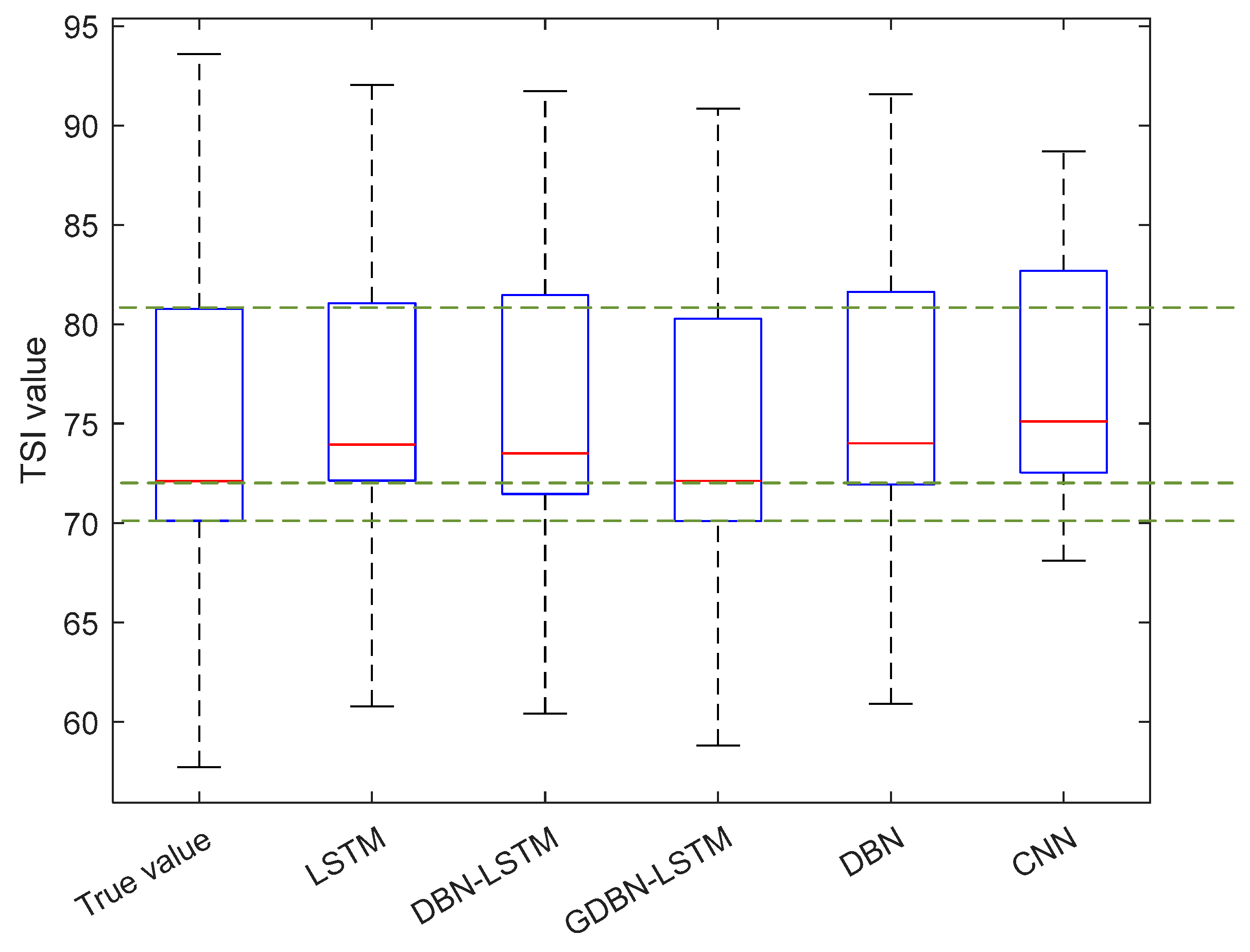
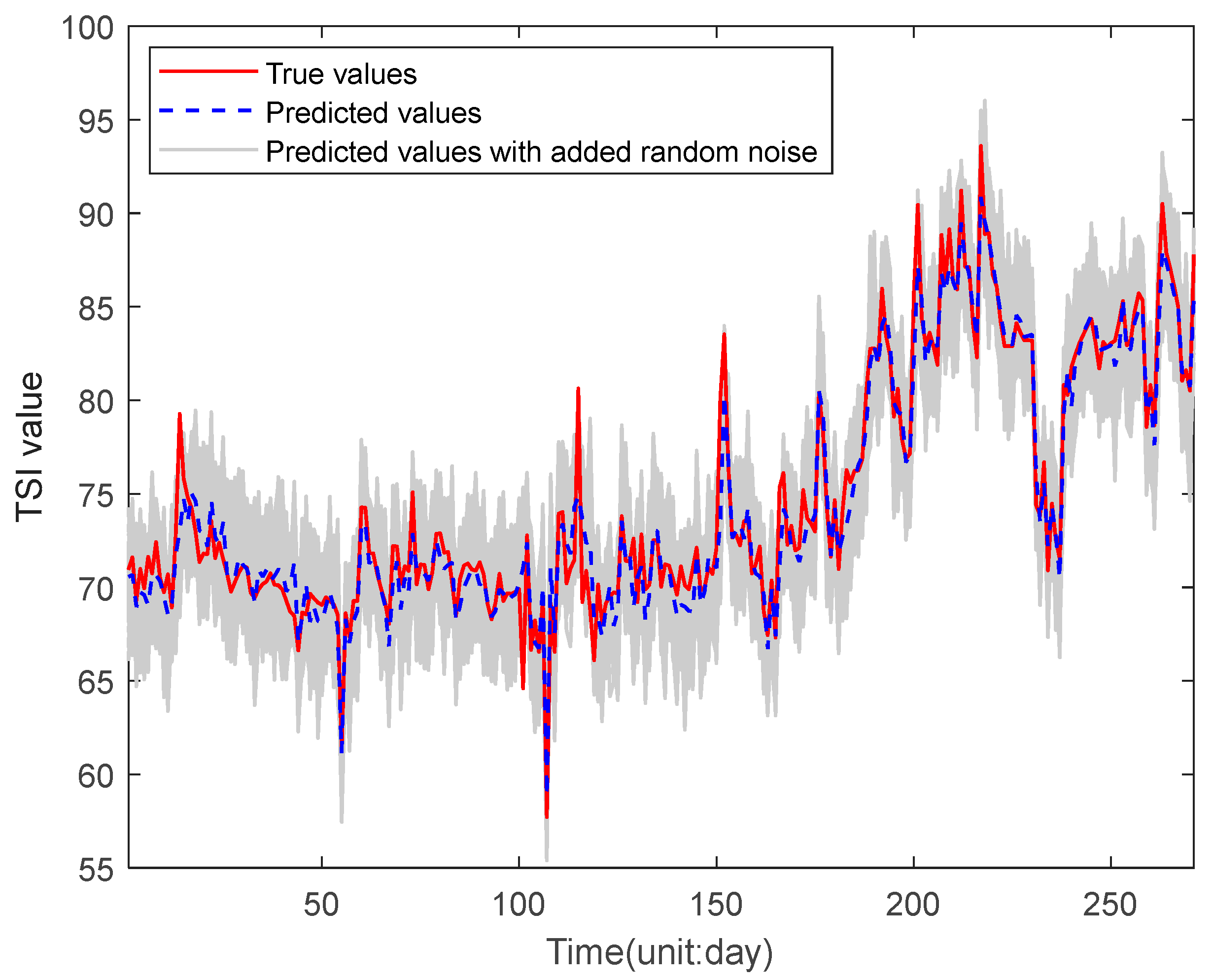
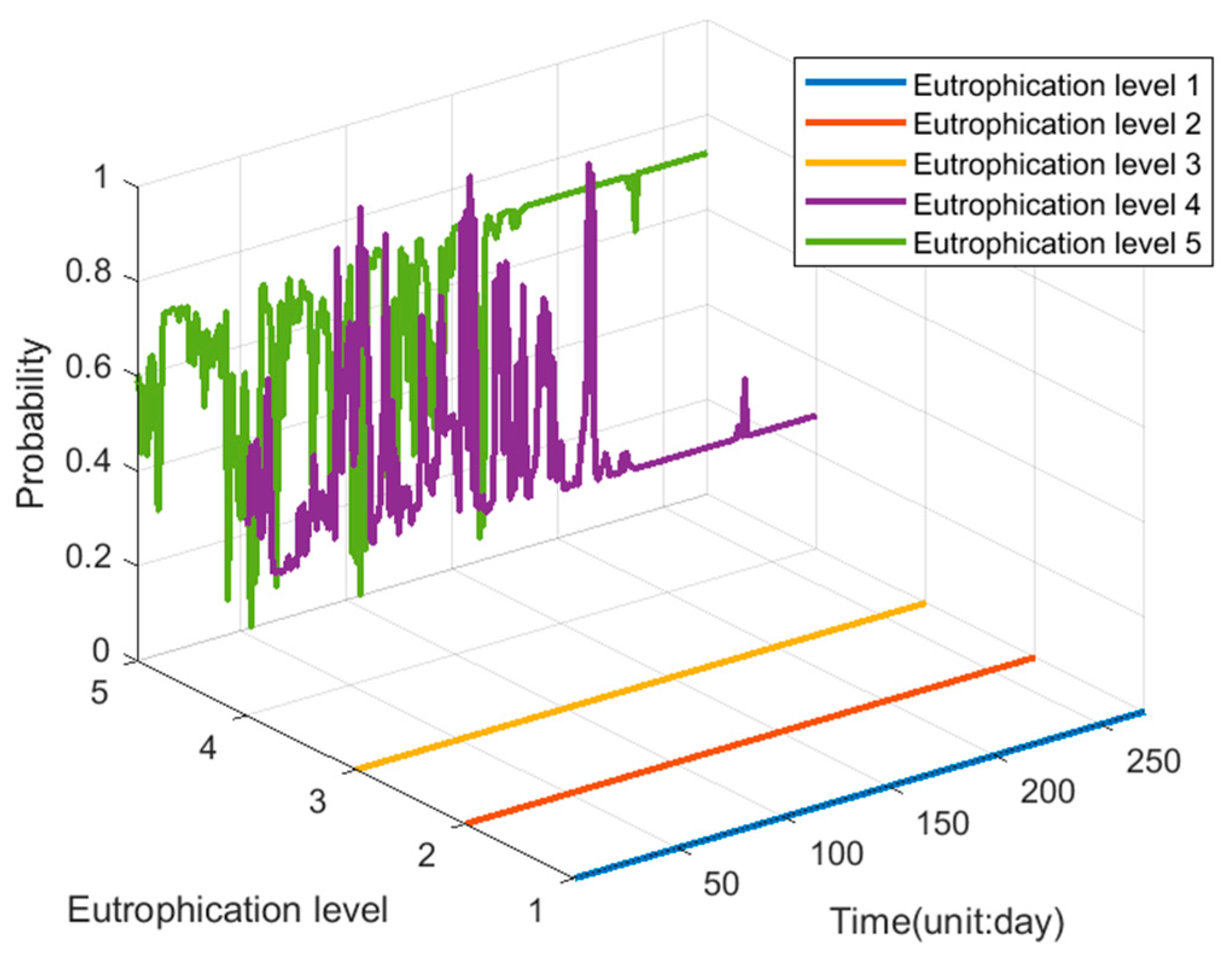
4.2.4. Water Quality Evaluation Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.J.; Chen, C.; Lin, P.F.; Hou, A.X.; Niu, Z.B.; Wang, J. Emergency drinking water treatment during source water pollution accidents in China: Origin analysis, framework and technologies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loi, J.X.; Chua, A.S.; Rabuni, M.F.; Tan, C.K.; Lai, S.H.; Takemura, Y.; Syutsubo, K. Water quality assessment and pollution threat to safe water supply for three river basins in Malaysia. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Hao, L.; Liu, N. Climate Variability Masked Greening Effects on Water Yield in the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2018. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedri, Z.; Corkery, A.; O’Sullivan, J.J.; Deering, L.A.; Demeter, K.; Meijer, W.G.; O’Hare, G.; Masterson, B. Evaluating a microbial water quality prediction model for beach management under the revised EU Bathing Water Directive. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.S.; Shen, S.L.; Zhou, A.; Lyu, H.M. Assessment and management of lake eutrophication: A case study in Lake Erhai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 751, 141618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, J. A novel water quality mechanism modeling and eutrophication risk assessment method of lakes and reservoirs. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 96, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L. Prediction momel of ecological environmental water demand based on big data analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, Z. Assessment and a review of research on surface water quality modeling. Ecol. Model. 2022, 466, 109888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Feng, C. Simulation of the improving effect of graphene visible-light photocatalysis using the MIKE11 model of an urban landscape river in the Chaohu Lake Basin, China. Nat. Resour. Model. 2022, 35, e12344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Chong, K.Y.; Lin, J.Y. A combined catchment-reservoir water quality model to guide catchment management for reservoir water quality control. Water. Environ. J. 2021, 35, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valikhan Anaraki, M.; Mahmoudian, F.; Nabizadeh Chianeh, F.; Farzin, S. Dye Pollutant Removal from Synthetic Wastewater: A New Modeling and Predicting Approach Based on Experimental Data Analysis, Kriging Interpolation Method, and Computational Intelligence Techniques. J. Environ. Inform. 2022, 40, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Zhang, X.; Chu, X.; Zheng, H. Automatic Calibration for CE-QUAL-W2 Model Using Improved Global-Best Harmony Search Algorithm. Water 2021, 13, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Cai, S.; Jiang, D.; Liu, J. A data-driven model for real-time water quality prediction and early warning by an integration method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 30374–30385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, J. An adaptive task-oriented RBF network for key water quality parameters prediction in wastewater treatment process. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 11401–11414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Bai, Y. Water quality evolution mechanism modeling and health risk assessment based on stochastic hybrid dynamic systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 193, 116404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in Lake Poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Sharma, R.C. Assessment of water quality index and multivariate analysis of high altitude sacred Lake Prashar, Himachal Pradesh, India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 16, 6125–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Xing, X. A dynamic water quality index model based on functional data analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 32, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, W.A.; Ahmad, H.R.; Farooqi, Z.U.; Sabir, M.; Ayub, M.A.; Rizwan, M.; Ilic, P. Surface water quality assessment of Skardu springs using Water Quality Index. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 20537–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotova, G.; Varbanov, M.; Tcherkezova, E.; Tsakovski, S. Water quality assessment of a river catchment by the composite water quality index and self-organizing maps. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 57, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, R.E., Jr.; Yasarer, L.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Locke, M.A.; Knight, S.S. Long-Term Oxbow Lake Trophic State under Agricultural Best Management Practices. Water 2021, 13, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomfim, E.D.; Kraus, C.N.; Lobo, M.T.; Nogueira, I.D.; Peres, L.G.; Boaventura, G.R.; Laques, A.E.; Garnier, J.; Seyler, P.; Marques, D.M.; et al. Trophic state index validation based on the phytoplankton functional group approach in Amazon floodplain lakes. Inland Waters 2019, 9, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markad, A.T.; Landge, A.T.; Nayak, B.B.; Inamdar, A.B.; Mishra, A.K. Trophic state modeling for shallow freshwater reservoir: A new approach. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-K.; Peng, S.; Zhao, X.-H.; Li, X. Development of a two-dimensional eutrophication model in an urban lake (China) and the application of uncertainty analysis. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Khozani, Z.S.; Banadkooki, F.B.; Ehteram, M.; Ahmed, A.N.; El-Shafie, A. Combining autoregressive integrated moving average with Long Short-Term Memory neural network and optimisation algorithms for predicting ground water level. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, J.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Xie, Y.; Yin, X. Analysis and Prediction of Water Quality Using LSTM Deep Neural Networks in IoT Environment. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Conzen, S.D. A new dynamic Bayesian network (DBN) approach for identifying gene regulatory networks from time course microarray data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Gao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, H.; Xu, Z. A Prediction Model Based on Deep Belief Network and Least Squares SVR Applied to Cross-Section Water Quality. Water 2020, 12, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.S.; Jin, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zang, S.F.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Pu, J. From Class-Specific to Class-Mixture: Cascaded Feature Representations via Restricted Boltzmann Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 69393–69406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Salakhutdinov, R.R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science 2006, 313, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imneisi, I.; Aydin, M. Water quality assessment for Elmali stream and Karaomak stream using the comprehensive pollution index (CPI) in Karaomak watershed, Kastamonu, Turkey. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 7031–7038. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R. A Trophic State Index for Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, A. Trophic state and limiting nutrient evaluations using trophic state/level index methods: A case study of Borka Dam Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z. A Hybrid Model for Water Quality Prediction Based on an Artificial Neural Network, Wavelet Transform, and Long Short-Term Memory. Water 2022, 14, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

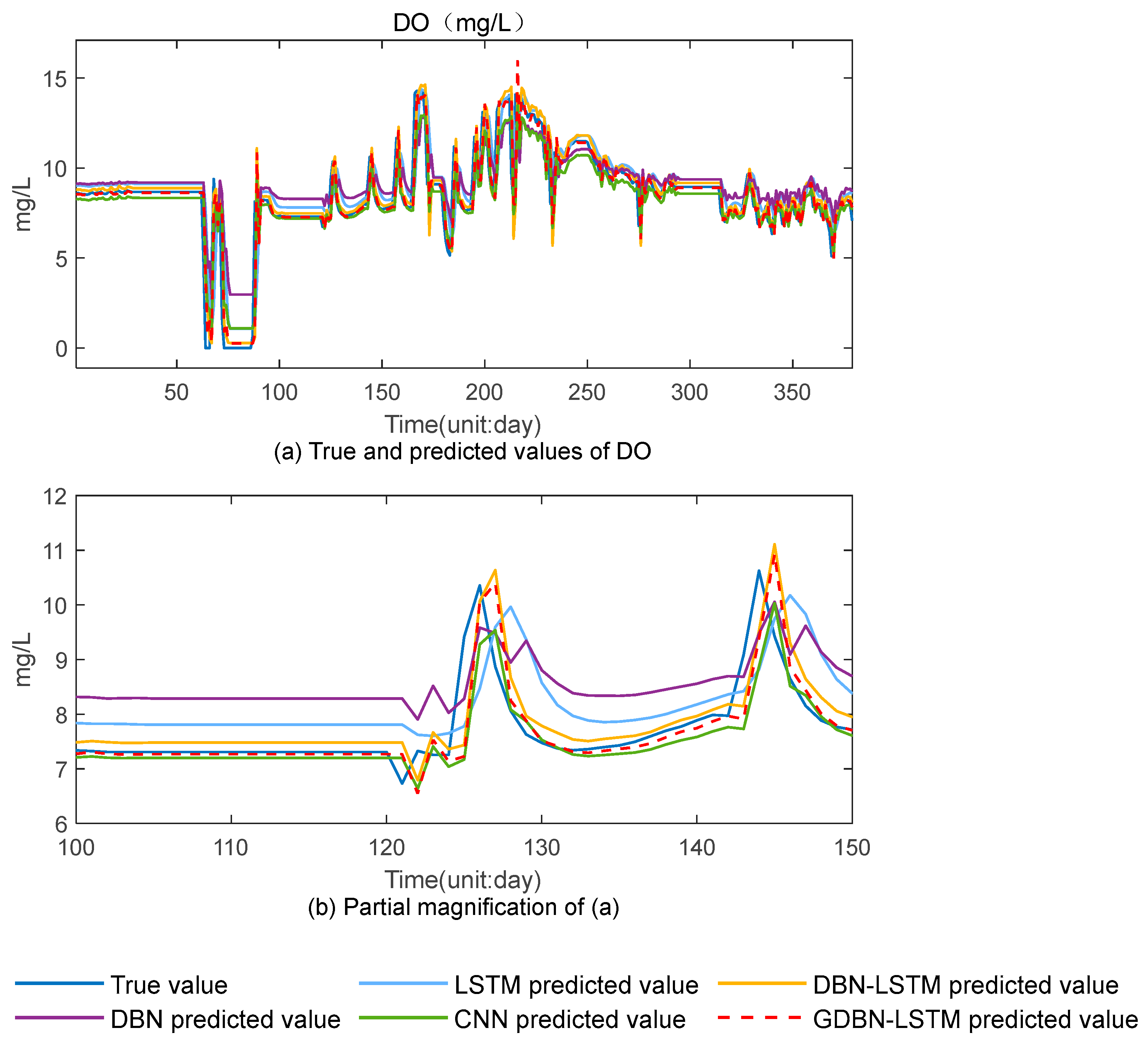
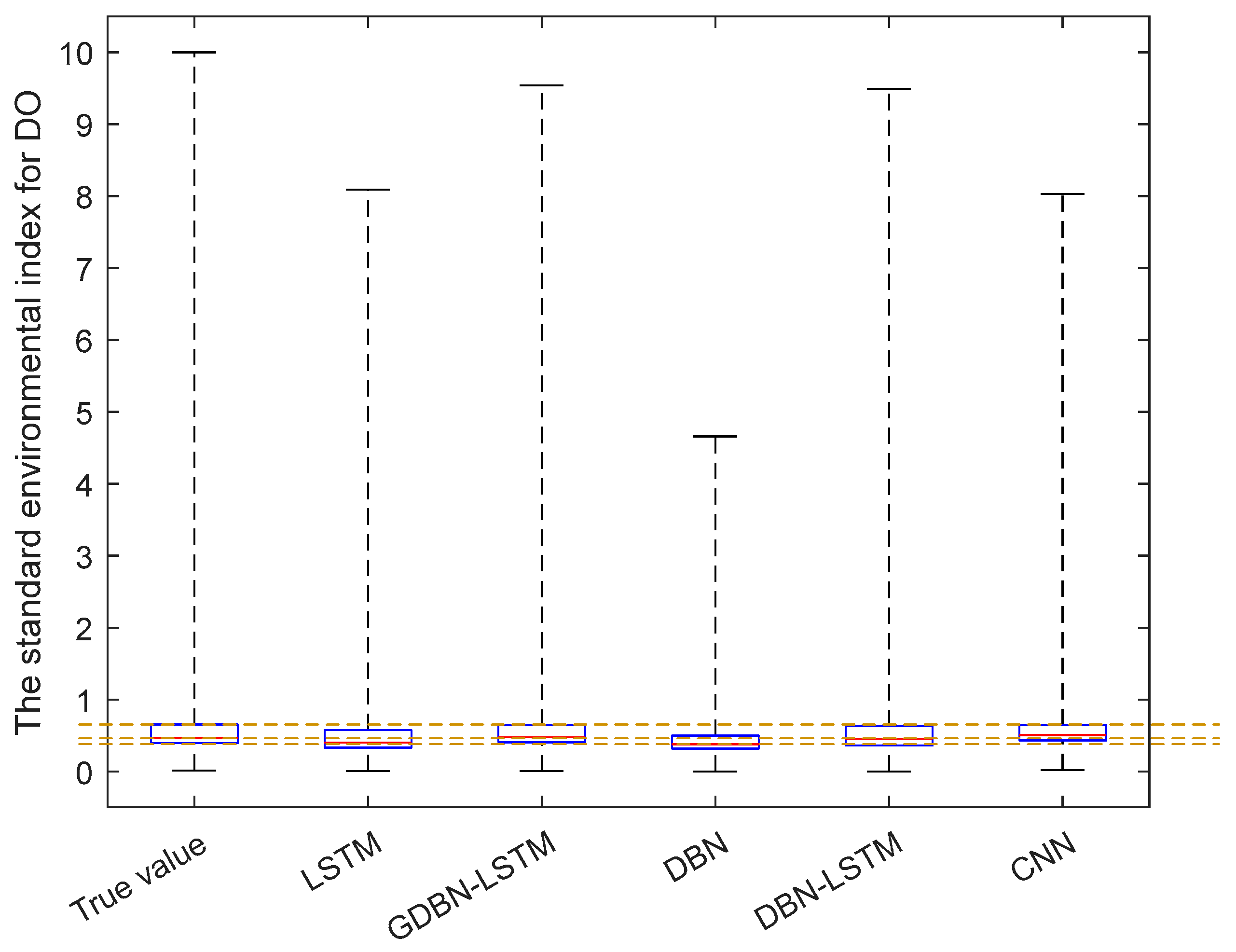
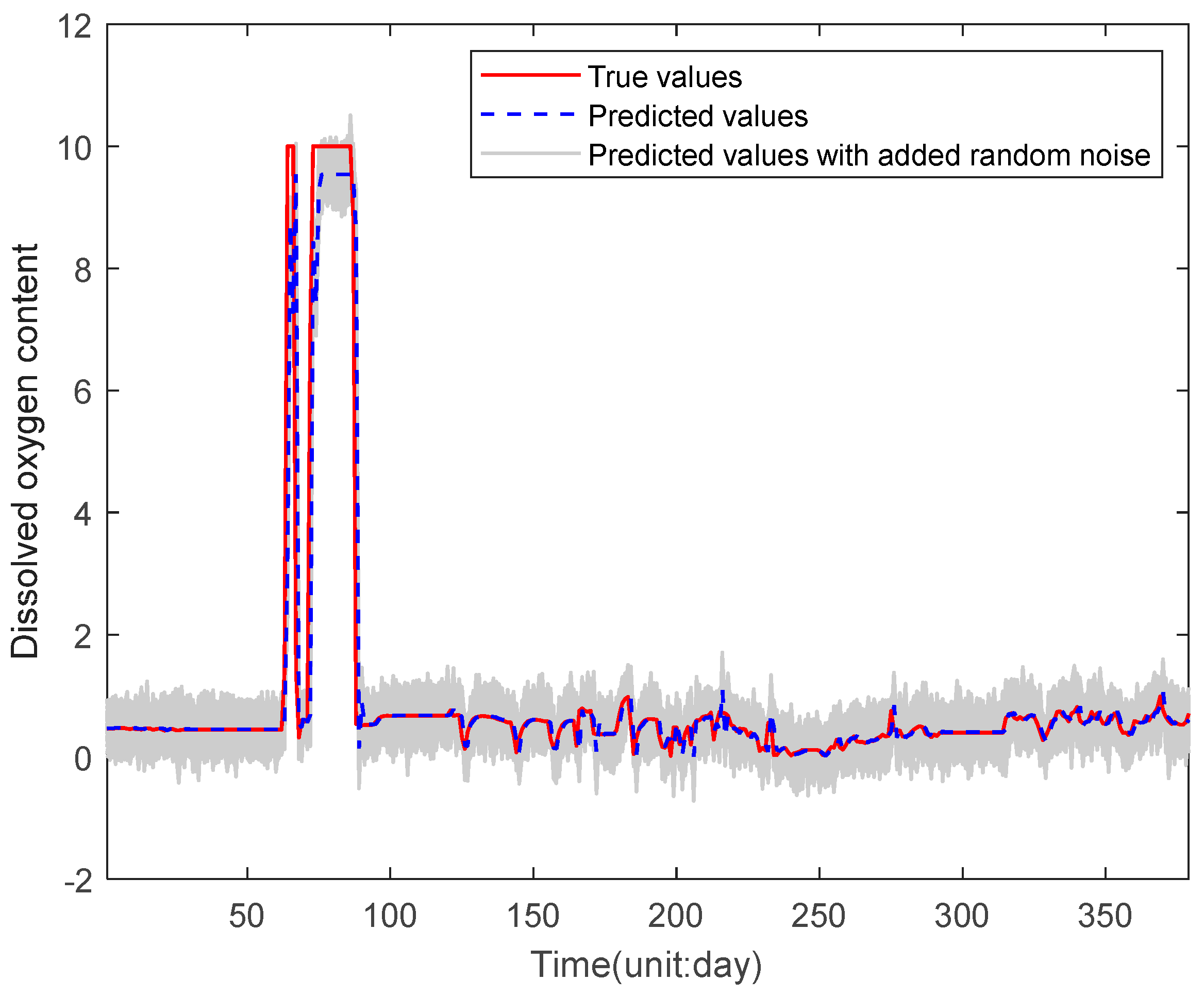
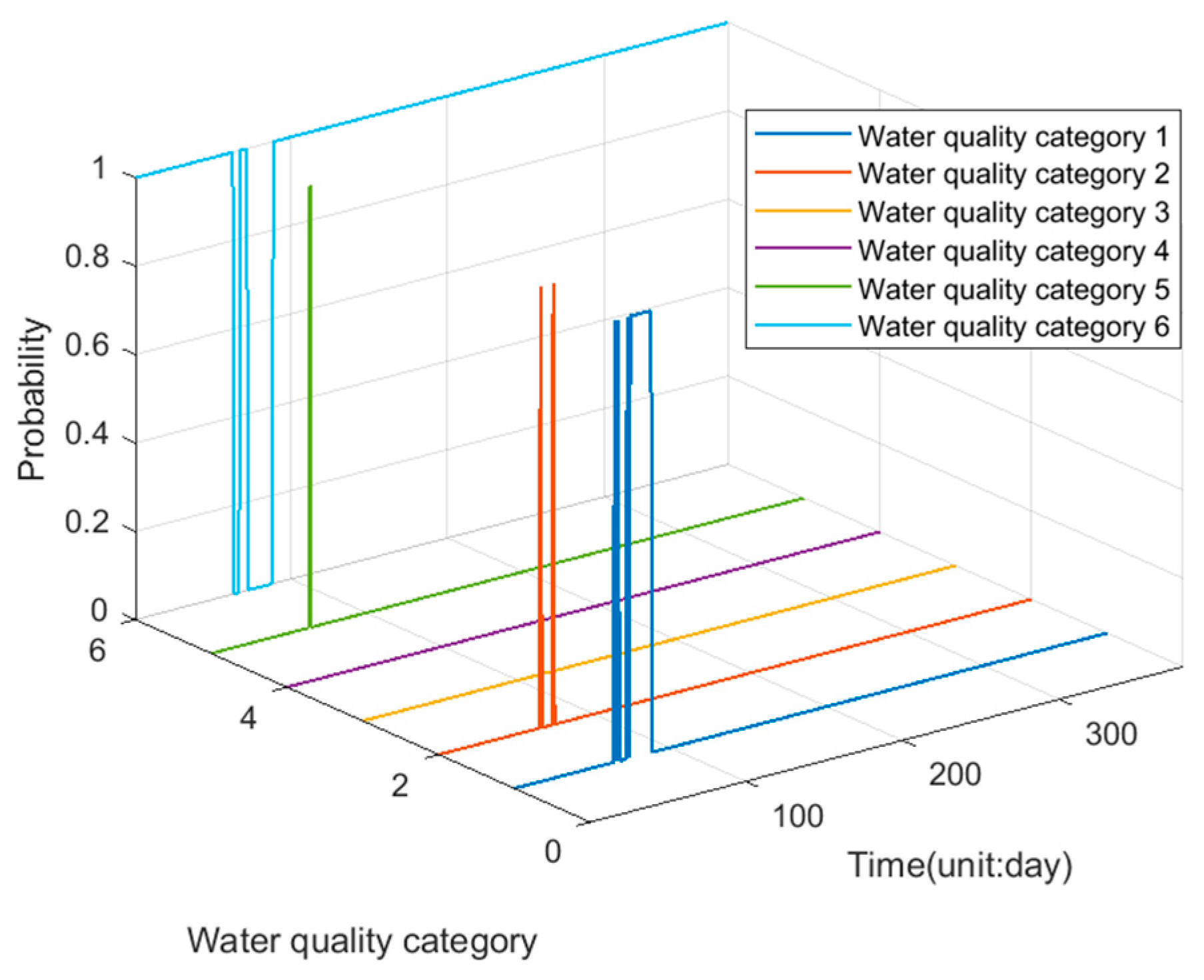
| Water Quality Category | DO Content (mg/L) |
|---|---|
| I | 7.5 |
| II | 6 |
| III | 5 |
| IV | 3 |
| V | 2 |
|
TSI |
SD (m) |
TP (μg P/L) |
Chl-a (μg/L) |
TN (mg N/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultraoligotrophic | 0 | 64 | 0.75 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Ultraoligotrophic | 10 | 32 | 1.5 | 0.12 | 0.05 |
| Ultraoligotrophic | 20 | 16 | 3 | 0.34 | 0.09 |
| Oligotrophic | 30 | 8 | 6 | 0.94 | 0.18 |
| Oligotrophic | 40 | 4 | 12 | 2.6 | 0.37 |
| Mesotrophic | 45 | 2.8 | 17 | 5 | 0.52 |
| Mesotrophic | 50 | 2 | 24 | 6.4 | 0.74 |
| Eutrophic | 53 | 1.6 | 30 | 10 | 0.92 |
| Eutrophic | 60 | 1 | 48 | 20 | 1.47 |
| Hypereutrophic | 70 | 0.5 | 96 | 56 | 2.94 |
| Hypereutrophic | 80 | 0.25 | 192 | 154 | 5.89 |
| Hypereutrophic | 90 | 0.12 | 384 | 427 | 11.7 |
| Hypereutrophic | 100 | 0.062 | 768 | 1183 | 23.6 |
| SMAPE | RMSE | MAE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.0429 | 0.9105 | 0.6716 | 0.8102 |
| DBN | 0.0550 | 1.1395 | 0.8816 | 0.7028 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.0415 | 0.8523 | 0.6720 | 0.8337 | |
| CNN | 0.0605 | 1.1687 | 0.9943 | 0.6874 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.0329 | 0.7196 | 0.5105 | 0.8815 | |
| Chl-a (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.1826 | 2.9331 | 1.6166 | 0.4254 |
| DBN | 0.1939 | 2.9282 | 1.6808 | 0.4273 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.1570 | 2.8669 | 1.5746 | 0.4511 | |
| CNN | 0.1451 | 2.8392 | 1.4729 | 0.4589 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.1319 | 2.7544 | 1.3509 | 0.4958 | |
| OC (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.0932 | 0.5020 | 0.3810 | 0.1979 |
| DBN | 0.0839 | 0.4632 | 0.3455 | 0.1652 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.0931 | 0.5006 | 0.3792 | 0.1919 | |
| CNN | 0.0972 | 0.5204 | 0.3996 | 0.1599 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.0791 | 0.4403 | 0.3212 | 0.3554 | |
| NH3-N (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.4857 | 0.0641 | 0.0517 | 0.6455 |
| DBN | 0.4516 | 0.0571 | 0.0455 | 0.7191 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.3828 | 0.0546 | 0.0389 | 0.7429 | |
| CNN | 0.3694 | 0.0543 | 0.0390 | 0.7454 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.3578 | 0.0539 | 0.0381 | 0.7491 | |
| TP (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.4077 | 0.0263 | 0.0198 | 0.2924 |
| DBN | 0.4480 | 0.0303 | 0.0205 | 0.2078 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.3389 | 0.0240 | 0.0163 | 0.2475 | |
| CNN | 0.3013 | 0.0230 | 0.0185 | 0.3073 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.2886 | 0.0202 | 0.0145 | 0.4702 | |
| TN-NH3-N (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.2250 | 0.4793 | 0.3358 | 0.8228 |
| DBN | 0.1976 | 0.5598 | 0.3610 | 0.7581 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.2200 | 0.4796 | 0.3578 | 0.8225 | |
| CNN | 0.1471 | 0.4378 | 0.2610 | 0.8521 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.1297 | 0.4164 | 0.2278 | 0.8662 | |
| TN (mg/L) | LSTM | 0.2243 | 0.4949 | 0.3581 | 0.8283 |
| DBN | 0.1869 | 0.4560 | 0.3087 | 0.8542 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.2094 | 0.4808 | 0.3634 | 0.8379 | |
| CNN | 0.1389 | 0.4266 | 0.2508 | 0.8783 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.1218 | 0.4127 | 0.2328 | 0.8747 | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | LSTM | 0.2178 | 11.0218 | 7.7475 | 0.4289 |
| DBN | 0.2894 | 12.5788 | 10.1933 | 0.2561 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.1375 | 9.2058 | 5.3354 | 0.6016 | |
| CNN | 0.1465 | 9.9364 | 5.3282 | 0.6245 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.1391 | 9.2617 | 5.2647 | 0.6967 |
| SMAPE | MAE | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSI value | LSTM | 2.3279 | 1.7207 | 0.8950 | 2.1064 |
| DBN | 2.3012 | 1.6994 | 0.8935 | 2.1211 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 1.4260 | 1.0678 | 0.9490 | 1.4685 | |
| CNN | 3.3654 | 1.9339 | 0.7764 | 3.4011 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 1.3391 | 1.0012 | 0.9543 | 1.3902 |
| SMAPE | RMSE | MAE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DO | LSTM | 0.1613 | 1.4565 | 0.9234 | 0.6839 |
| DBN | 0.5514 | 1.4094 | 1.0103 | 0.7040 | |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.1563 | 1.2508 | 0.9520 | 0.7669 | |
| CNN | 0.1001 | 1.1228 | 0.7415 | 0.8016 | |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.0949 | 1.1204 | 0.6962 | 0.8130 |
| SMAPE | RMSE | MAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.2418 | 1.1983 | 0.3470 | 0.6592 |
| DBN | 0.2832 | 1.4825 | 0.4528 | 0.4932 |
| DBN-LSTM | 0.2771 | 0.8018 | 0.2527 | 0.8467 |
| CNN | 0.1902 | 0.9251 | 0.2273 | 0.7936 |
| GDBN-LSTM | 0.1821 | 0.7929 | 0.1963 | 0.8496 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Fan, B.; Zhou, Y. An Efficient Water Quality Prediction and Assessment Method Based on the Improved Deep Belief Network—Long Short-Term Memory Model. Water 2024, 16, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101362
Zhao Z, Fan B, Zhou Y. An Efficient Water Quality Prediction and Assessment Method Based on the Improved Deep Belief Network—Long Short-Term Memory Model. Water. 2024; 16(10):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101362
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhiyao, Bing Fan, and Yuqin Zhou. 2024. "An Efficient Water Quality Prediction and Assessment Method Based on the Improved Deep Belief Network—Long Short-Term Memory Model" Water 16, no. 10: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101362
APA StyleZhao, Z., Fan, B., & Zhou, Y. (2024). An Efficient Water Quality Prediction and Assessment Method Based on the Improved Deep Belief Network—Long Short-Term Memory Model. Water, 16(10), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101362






