The Role of Ferrate (VI) in the Pretreatment of Algal Cells and Algal Organic Matters: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
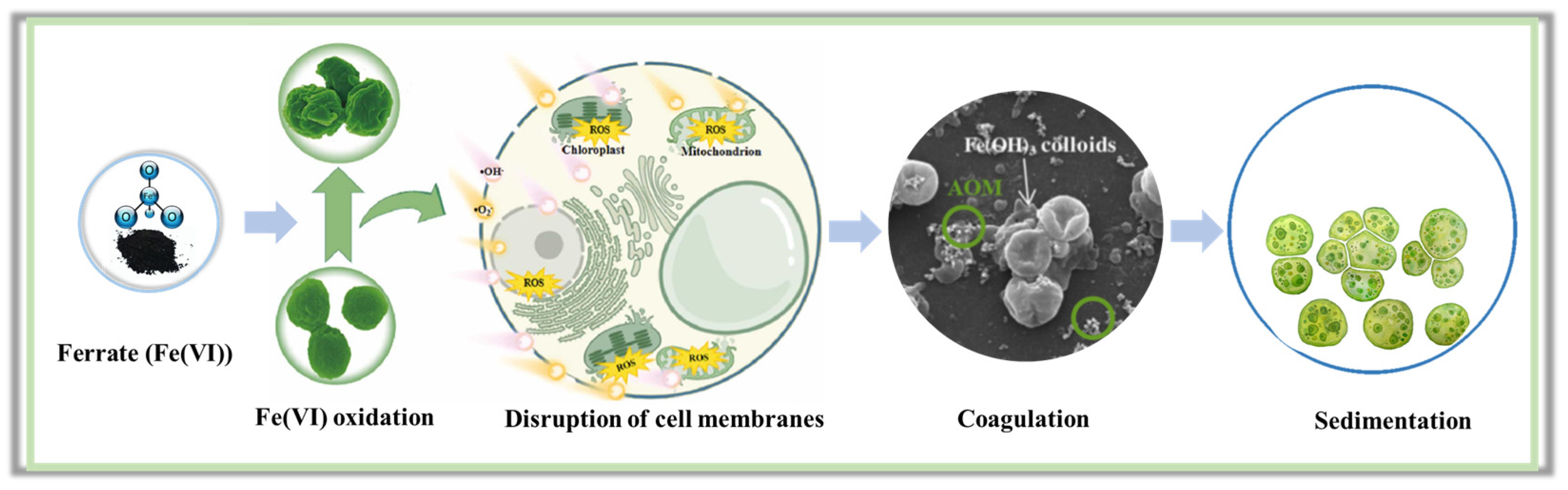
2. Damage of Algal Cells by Fe(VI)
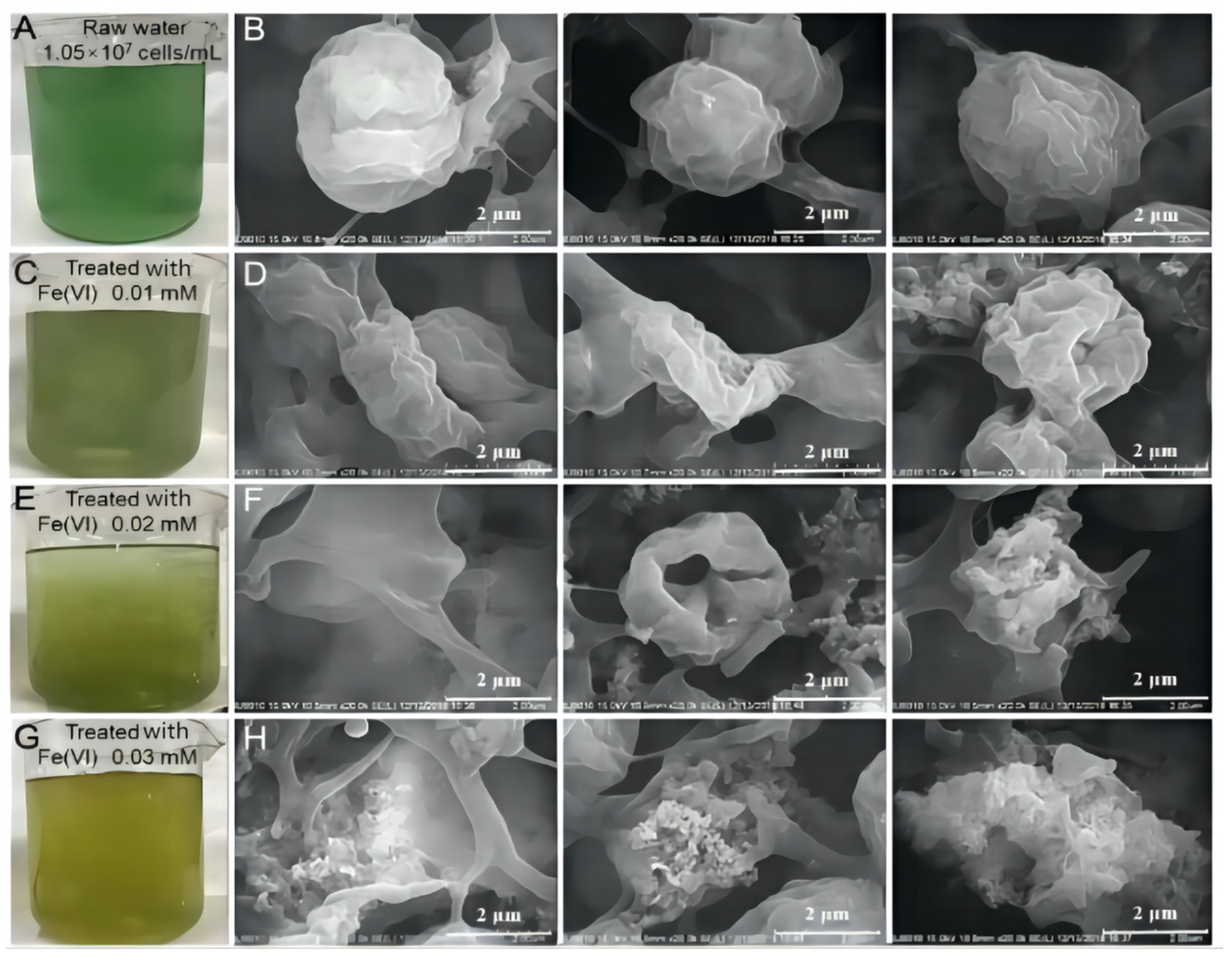
2.1. The Destruction of Different Algae
2.2. Factors Affecting Fe(VI) Removal Efficiency
| Species of Algae | Parameters | Removal Efficiency | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| C. aegagropila | Fe(VI) concentration = 3.57 mM, pH 9.0, application time 120 min | 98% | Ref. [24] |
| M. aeruginosa | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.27 mM, pH 7.2, application time 16 d | 64% | Ref. [7] |
| M. aeruginosa | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.54 mM, pH 7.2, application time 16 d | 70% | Ref. [7] |
| M. aeruginosa | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.13 mM, pH 5.5, application time 90 min | 95.3% | Ref. [6] |
| M. aeruginosa | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.02 mM, pH 7.5, application time 90 min | 40.4% | Ref. [6] |
| Chlorella sp. | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.29 mM, pH 7.0, application time 30 min | 46.2% | Ref. [35] |
| P. limnetica | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.29 mM, pH 7.0, application time 30 min | 58.1% | Ref. [35] |
| Chaetoceros affinis | Fe(VI) concentration = 0.05 mM, pH 9.0 application time 80 min | 94–100% | Ref. [29] |
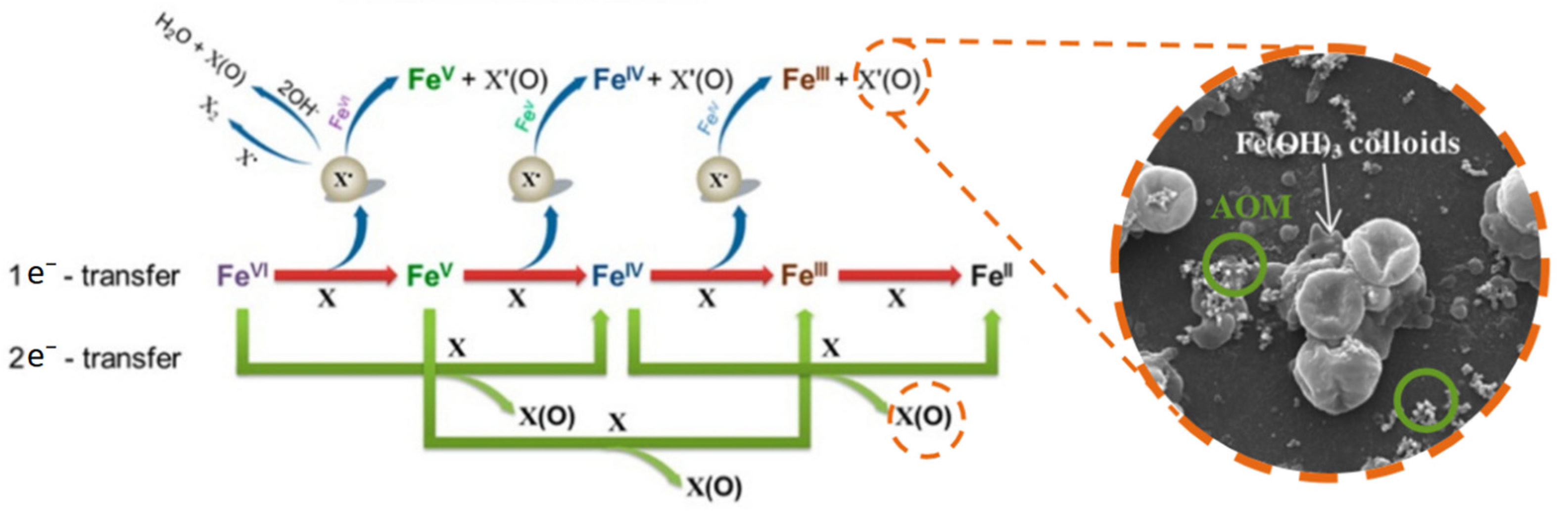
2.3. Mechanism of Algal Damage
3. Degradation of Algae-Derived Organic Matters by Fe(VI)
3.1. Degradation of AOM by Fe(VI)
3.2. Degradation of Algal Toxins by Fe(VI)
4. Fe(VI) Combined with Aluminum Sulfate for Algal Removal
5. Fe(VI) Combined with Fe(II) for Algal Removal
6. Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, G.Q. Enhanced algae removal by Ti-based coagulant: Comparison with conventional Al- and Fe-based coagulants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 13147–13158. [Google Scholar]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Dodds, W.K. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wires Water 2019, 6, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, W. Effectiveness and mechanism of potassium ferrate(VI) preoxidation for algae removal by coagulation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Sundaram, S.; Sinha, S.; Rahman, M.A.; Kapur, S. Recent advances in CO2 uptake and fixation mechanism of cyanobacteria and microalgae. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 1297–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Fu, C.; Feng, M.; Wang, D.; Song, S.; Li, C.; Sharma, V.K. Simultaneous generation of free radicals, Fe (IV) and Fe (V) by ferrate activation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Acosta, Y.; Hsu, T.T.D. Addressing harmful algal blooms (HABs) impacts with ferrate(VI): Simultaneous removal of algal cells and toxins for drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, W.L.; David, B.E.; Wu, M.; Ma, F. Impacts of potassium ferrate(VI) on the growth and organic matter accumulation, production, and structural changes in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11299–11308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieterse, A.; Cloot, A. Algal cells and coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation processes. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Zboril, R.; Varma, R.S. Ferrates: Greener Oxidants with Multimodal Action in Water Treatment Technologies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, H.; Ondruschka, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Bremner, D.H. Removal of blue-green algae using the hybrid method of hydrodynamic cavitation and ozonation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, J.; Lin, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Song, S. Oxidation of chloroquine drug by ferrate: Kinetics, reaction mechanism and antibacterial activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J. Studies on the degradation of trace phenol and indole odorants by chlorine and permanganate in drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2021, 286, 131551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellman, C.; Goodwill, J.E.; Addison, E.L. Physicochemical implications of cyanobacteria oxidation with Fe(VI). Chemosphere 2020, 266, 128956. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, W.; Xiao, P. Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa and control of algal organic matters by potassium ferrate(VI) pre-oxidation enhanced Fe(II) coagulation. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Fu, C.; Meng, Z.; Lin, Q.; Li, J.; Zeng, T.; Song, S. A two-stage Fe (VI) oxidation process enhances the removal of bisphenol A for potential application. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, Z.; Pi, K.; Deng, Y. One-step ferrate(VI) treatment as a core process for alternative drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2019, 242, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, R.K.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. The impact of differing cell and algogenic organic matter (AOM) characteristics on the coagulation and flotation of algae. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Lin, Q.; Li, C.; He, G.; Deng, Y. Impacts of pre-oxidation on the formation of disinfection byproducts from algal organic matter in subsequent chlor (am) ination: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y. Simultaneous removal of algae, microcystins and disinfection byproduct precursors by peroxymonosulfate(PMS)-enhanced Fe(III) coagulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 445, 136689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, C.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S.; Pang, W. A Review of Research Progress in the Preparation and Application of Ferrate (VI). Water 2023, 15, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Y.; Qiu, W.; Liu, Y.L. Effect of ferrate pre-oxidation on algae-laden water ultrafiltration: Attenuating membrane fouling and decreasing formation potential of disinfection byproducts. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Chen, Y.M.; Chou, H.N. First report of microcystins in Taiwan. Toxicon 1998, 36, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.J.; Lu, Y.M.; Yu, W.L. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of monomethylmercury in freshwater cyanobacteria: Oscillatoria tenuisa and Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ. Forensics 2012, 13, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubinakova, M. Effect of ferrate on green algae removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21894–21901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Jiang, J.Q. Comparative removal of imidacloprid, bisphenol-S, and azithromycin with ferrate and FeCl3 and assessment of the resulting toxicity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareema, B.Y.; Tameemi, H.M.A. The effectiveness and kinetics of petrolim refinery wastewater treatment using potassim ferrate as an oxidant and coagulant. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 1, 2450. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kissner, R.; Von Gunten, U. Reaction of Ferrate(VI) with ABTS and Self-Decay of Ferrate(VI): Kinetics and Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5154–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Deng, Y. Coagulation of colloidal particles with ferrate (VI). Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahri, A.H.; Fortunato, L.; Zaouri, N.; Ghaffour, N.; Leiknes, T.O. Role of dissolved air flotation (DAF) and liquid ferrate on mitigation of algal organic matter (AOM) during algal bloom events in RO desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 256, 117795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrawski, K.L.; Cataldo, M.; Dubrawski, Z.; Mazumder, A.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Mohseni, M. In-situ electrochemical Fe(VI) for removal of microcystin-LR from drinking water: Comparing dosing of the ferrate ion by electrochemical and chemical means. J. Water Health 2018, 16, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasarukkai, Y.S.; Gagnon, G.A. Influence of the Mixing Energy Consumption Affecting Coagulation and Floc Aggregation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3480–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, M.; Garrido, J.G.; Galluzzo, M. Optimization of the Coagulation–Flocculation Treatment: Influence of Rapid Mix Parameters. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K. Coagulant mixing revisited: Theory and practice. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2013, 62, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lou, Y.; Li, A.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y. Effects of pre-oxidation by ozone, permanganate and ferrate on generation and toxicities of disinfection byproducts. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 16, 5969–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, K.; Sharma, V.K. Ferrate (VI) pre-treatment and subsequent chlorination of blue-green algae: Quantification of disinfection byproducts. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Enhanced algae removal by drinking water treatment of chlorination coupled with coagulation. Desalination 2011, 271, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-D.; Xu, X.-J.; Liang, J.-L.; Wang, Q.; Dong, Q.; Liang, W.-L. Enhanced coagulation for treating slightly polluted algae-containing surface water combining polyaluminum chloride (PAC) with diatomite. Desalination 2011, 279, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, J.D.; Zhao, Z.; Bielski, B.H. Reaction of ferrate (VI)/ferrate (V) with hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion—A stopped-flow and premix pulse radiolysis study. Free Radic. Res. 1996, 24, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Song, L. Physiological responses to ferrate (VI) stress in Microcystis aeruginosa. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and Transportation Engineering, Nanjing, China, 24–26 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 5153–5156. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S. Impacts of Potassium Ferrate (VI) on the Growth, Protein, and Enzyme of the Microcystis aeruginosa. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2019, 230, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.-Y.; Lu, X.-S.; Feng, M.-B.; Wang, W.-L.; Du, Y.; Yang, L.-L.; Hu, H.-Y. Reduction of cytotoxicity and DNA double-strand break effects of wastewater by ferrate (VI): Roles of oxidation and coagulation. Water Res. 2021, 205, 117667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Parsons, S.A.; Jefferson, B. Characterisation of algogenic organic matter extracted from cyanobacteria, green algae and diatoms. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clasen, J.; Mischke, U.; Drikas, M. An improved method for detecting electrophoretic mobility of algae during the destabilisation process of flocculation: Flocculant demand of different species and the impact of DOC. J. Water Supply 2000, 49, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, X.; Luo, X.; Xu, J.; Tan, F.; Wu, D.; Liang, H. Mutual activation between ferrate and calcium sulfite for surface water pre-treatment and ultrafiltration membrane fouling control. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, Q.-S.; Hu, S.-F.; Wang, H.-Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.-M. Simultaneous removal of algae and its odor metabolites in raw water by potassium ferrate. Desalin Water Treat. 2014, 52, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivokonsky, M.; Kloucek, O.; Pivokonska, L. Evaluation of the production, composition and aluminum and iron complexation of algogenic organic matter. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3045–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Dong, B.; Liu, Z.; Chu, W. Characteristic of algogenic organic matter and its effect on UF membrane fouling. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Villacorte, L.O.; Ekowati, Y.; Neu, T.R.; Kleijn, J.M.; Winters, H.; Amy, G.; Schippers, J.C.; Kennedy, M.D. Characterisation of algal organic matter produced by bloom-forming marine and freshwater algae. Water Res. 2015, 73, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Mi, J.; Du, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, D.; Song, W.; Shao, M.; Jia, R. UV/H2O2/O3 removal efficiency and characterization of algae-derived organic matter and odorous substances. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, K. Characterization of intracellular & extracellular algae organic matters (AOM) of Microcystic aeruginosa and formation of AOM-associated disinfection byproducts and odor & taste compounds. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahri, A.H.; Fortunato, L.; Ghaffour, N.E.; Leiknes, T.O. Advanced coagulation using in-situ generated liquid ferrate, Fe (VI), for enhanced pretreatment in seawater RO desalination during algal blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Quan, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Song, L.; Gan, N. Fast removal of cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR by a low-cytotoxic microgel-Fe(III) complex. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1482–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Al-Osman, M.; Kamegni, R.B.; Zeng, W.M. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon Int. J. Devoted Exch. Knowl. Poisons Deriv. Anim. Plants Microorg. 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, M.G.; Boraei, I.; Solakidou, M.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Abhishek, M.; Lawton, L.A.; Edwards, C. Enhancing photocatalytic degradation of the cyanotoxin microcystin-LR with the addition of sulfate-radical generating oxidants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, J.; Giani, A. Microcystin production and regulation under nutrient stress conditions in toxic microcystis strains. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, Y.L.; Conklin, A.; Westrick, J.; Weavers, L.K.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Lenhart, J.J.; Mouser, P.J.; Szlag, D.; Walker, H.W. Toxic cyanobacteria and drinking water: Impacts, detection, and treatment. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, C.; Santiago-Vázquez, L.; Paul, V. Toxin release in response to oxidative stress and programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Kiliç, G.; Costa, C.; Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Pásaro, E.; Teixeira, J.P.; Laffon, B. Effects of iron oxide nanoparticles: Cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, developmental toxicity, and neurotoxicity. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Chen, L.; Batchu, S.R.; Gardinali, P.R.; Jasa, L.; Marsalek, B.; Zboril, R.; Dionysiou, D.D.; O’Shea, K.E.; Sharma, V.K. Oxidation of Microcystin-LR by Ferrate(VI): Kinetics, Degradation Pathways, and Toxicity Assessments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12164–12172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Jeon, D.; Ra, J.; Shin, J.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, Y. Transformation of microcystin-LR and olefinic compounds by ferrate(VI): Oxidative cleavage of olefinic double bonds as the primary reaction pathway. Water Res. 2018, 141, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botté, A.; Zaidi, M.; Guery, J.; Fichet, D.; Leignel, V. Aluminium in aquatic environments: Abundance and ecotoxicological impacts. Aquat. Ecol. 2022, 56, 751–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.A.; Gad Mohamed, A.M.; Farrag, A.E.H.A.; Aboeldahb, S.A. Evaluation of the most promising techniques overcoming the algal problems takes place during the purification of drinking water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44239–44248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Jun, M.; Liu, W. Enhanced removal of lead (II) and cadmium (II) from water in alum coagulation by ferrate (VI) pretreatment. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 2420–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, K.T.; Graham, N.; Jiang, J.-Q. Evaluating the coagulation performance of ferrate: A preliminary study. In Proceedings of the ACS Symposium Series, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alshahri, A.H.; Giagnorio, M.; Dehwah, A.H.; Obaid, M.; Missimer, T.M.; Leiknes, T.; Ghaffour, N.; Fortunato, L. Advanced coagulation with liquid ferrate as SWRO desalination pretreatment during severe algal bloom. Process performance, environmental impact, and cost analysis. Desalination 2022, 537, 115864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.-L.; Qu, J.-H.; Fu, M.-L. Removal of cyanobacterial microcystin-LR by ferrate oxidation–coagulation. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, F.; Xu, B.; Ma, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, R.; Sun, C.; Cheng, X.; Guo, N. Iron-based technology coupling moderate preoxidation with hybrid coagulation for highly effective removal and moderate growth inhibition of Oscillatoria in drinking water treatment plants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, B.; Jiang, J.-Q.; Kim, H.; Machala, L.; Zboril, R.; Sharma, V.K. Advances made in understanding the interaction of ferrate (VI) with natural organic matter in water. In Water Reclamation and Sustainability; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 183–197. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Chen, H.; Lin, Q. The Role of Ferrate (VI) in the Pretreatment of Algal Cells and Algal Organic Matters: A Review. Water 2024, 16, 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101361
Wang S, Yang S, Chen H, Lin Q. The Role of Ferrate (VI) in the Pretreatment of Algal Cells and Algal Organic Matters: A Review. Water. 2024; 16(10):1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101361
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Saige, Shuyi Yang, Huan Chen, and Qiufeng Lin. 2024. "The Role of Ferrate (VI) in the Pretreatment of Algal Cells and Algal Organic Matters: A Review" Water 16, no. 10: 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101361
APA StyleWang, S., Yang, S., Chen, H., & Lin, Q. (2024). The Role of Ferrate (VI) in the Pretreatment of Algal Cells and Algal Organic Matters: A Review. Water, 16(10), 1361. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101361





