Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
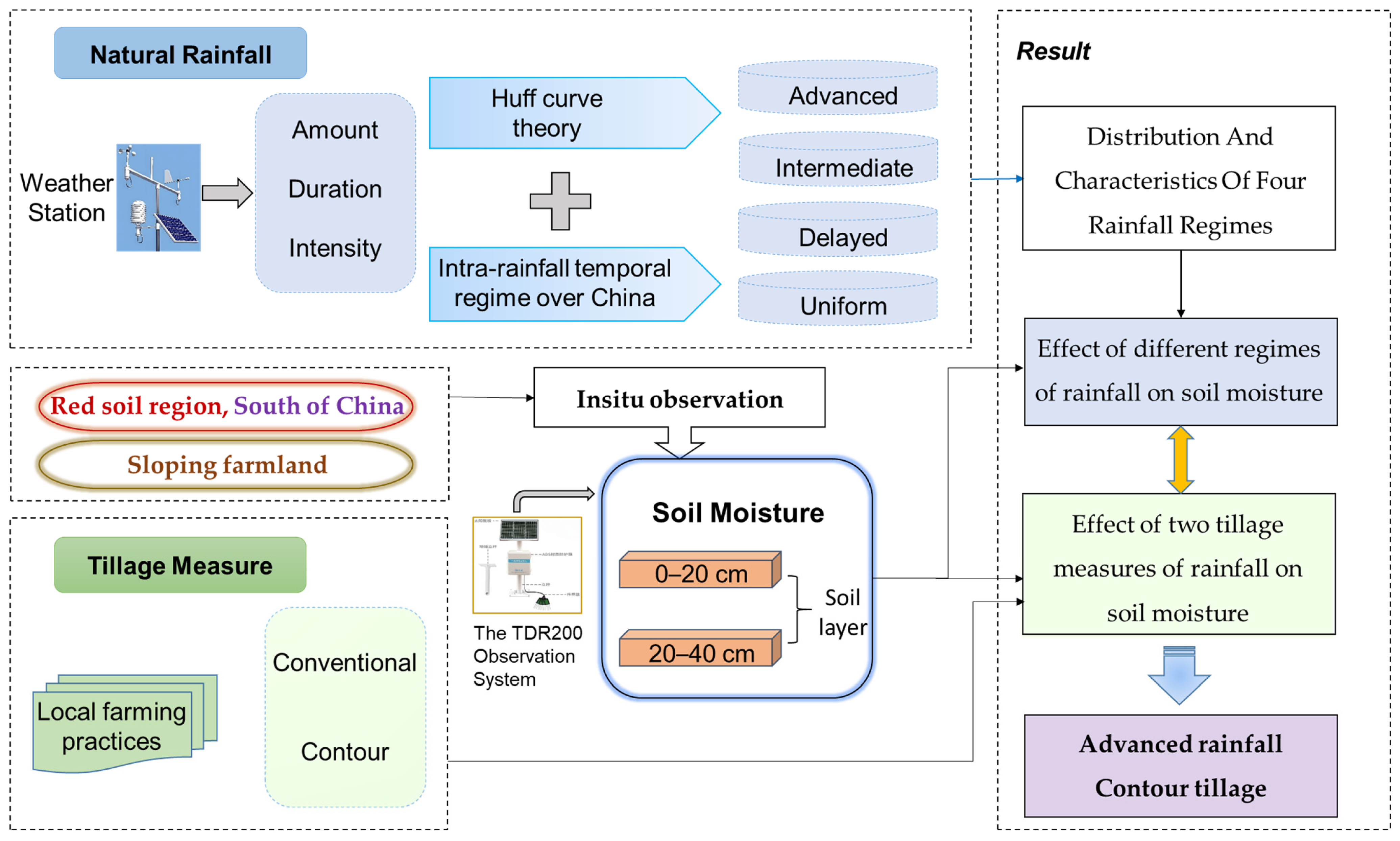
2. Materials and Methods
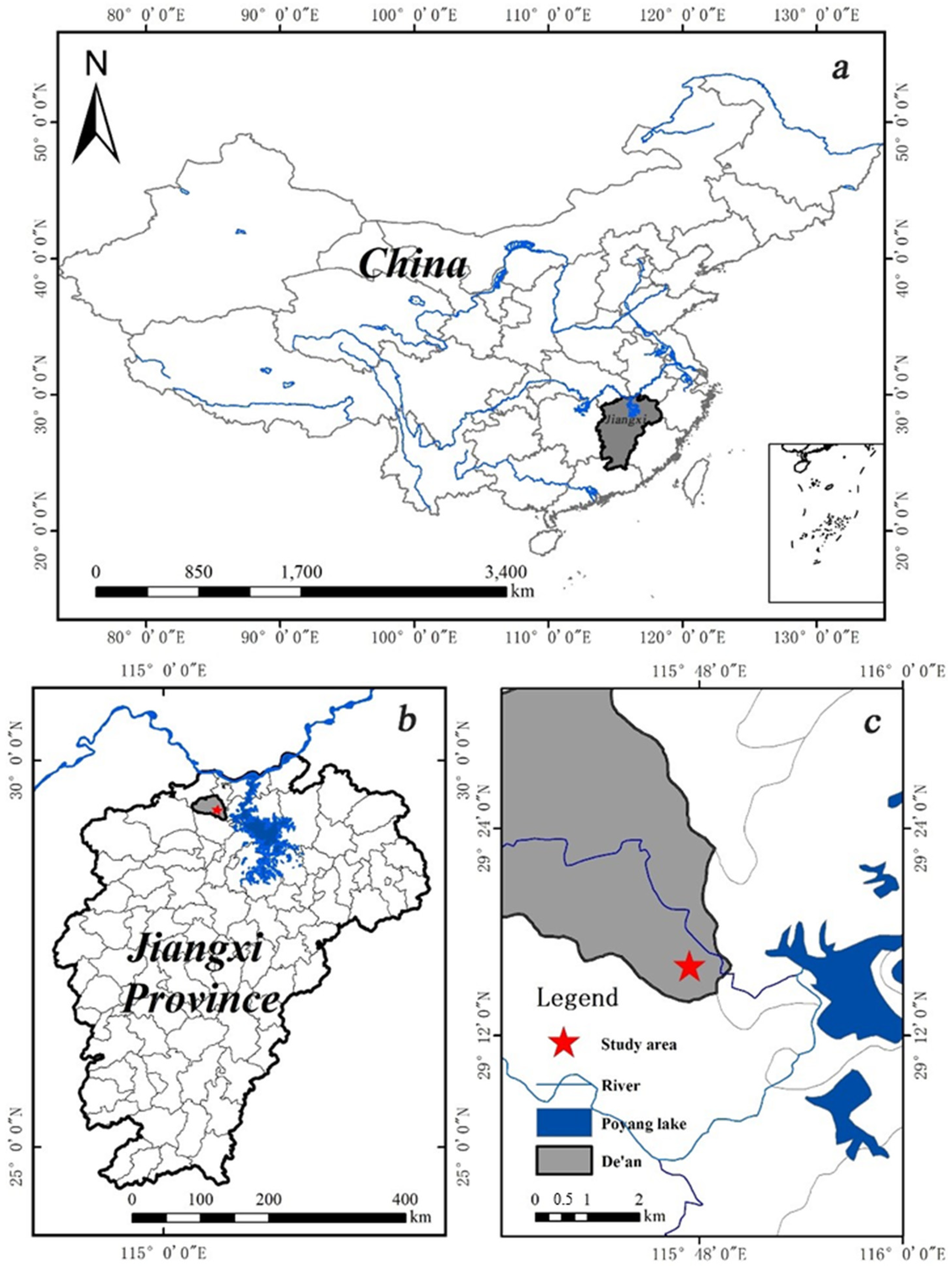
2.1. Study Site
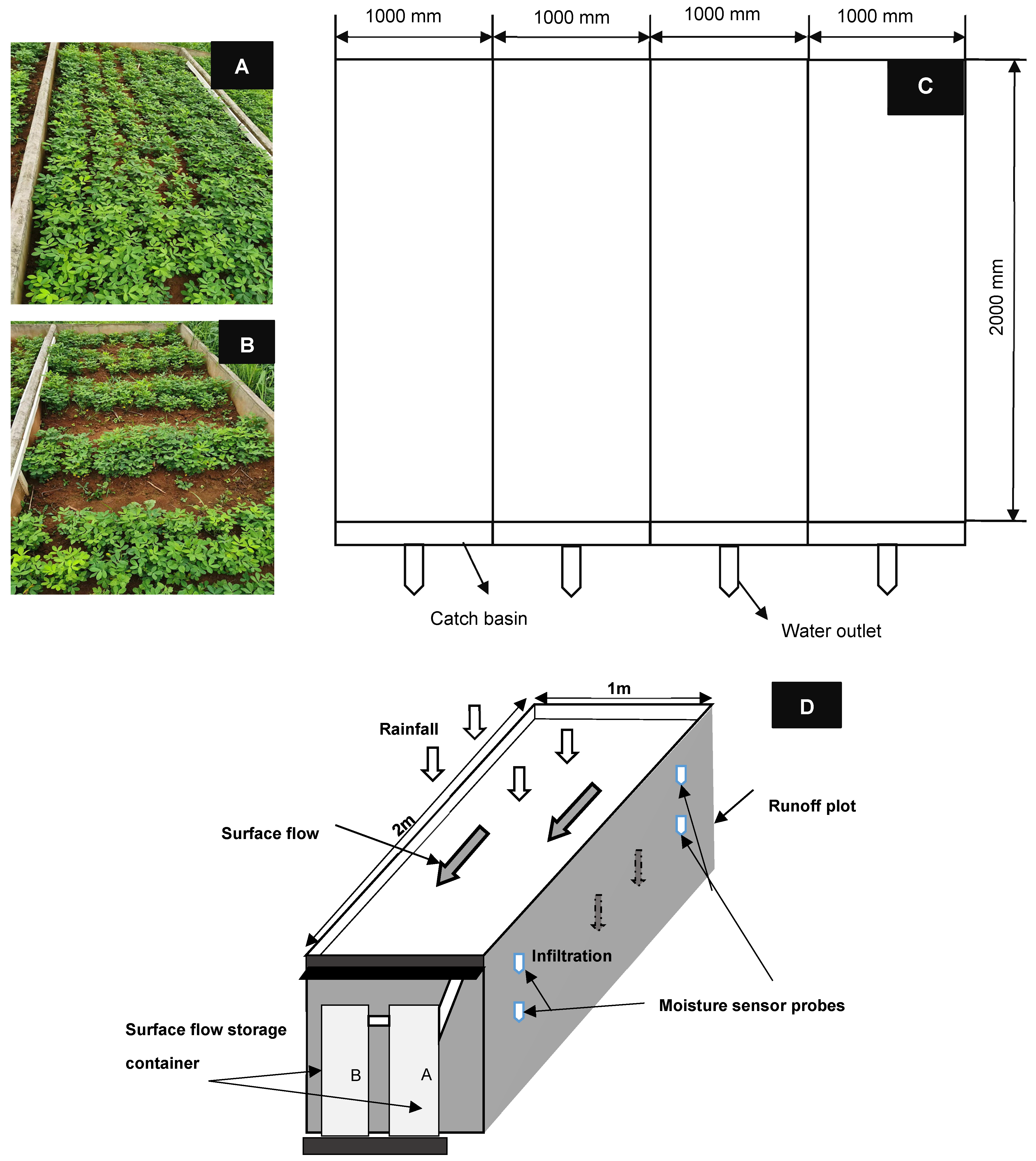
2.2. Plot and Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement of Soil Moisture
2.4. In Situ Observation
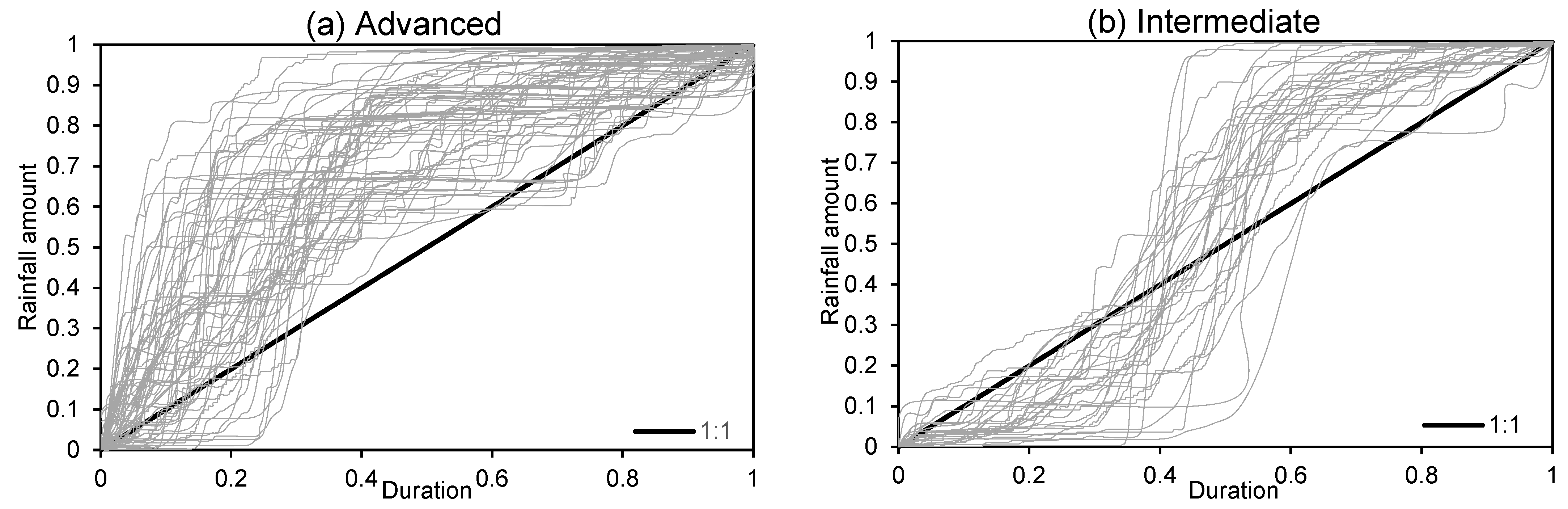
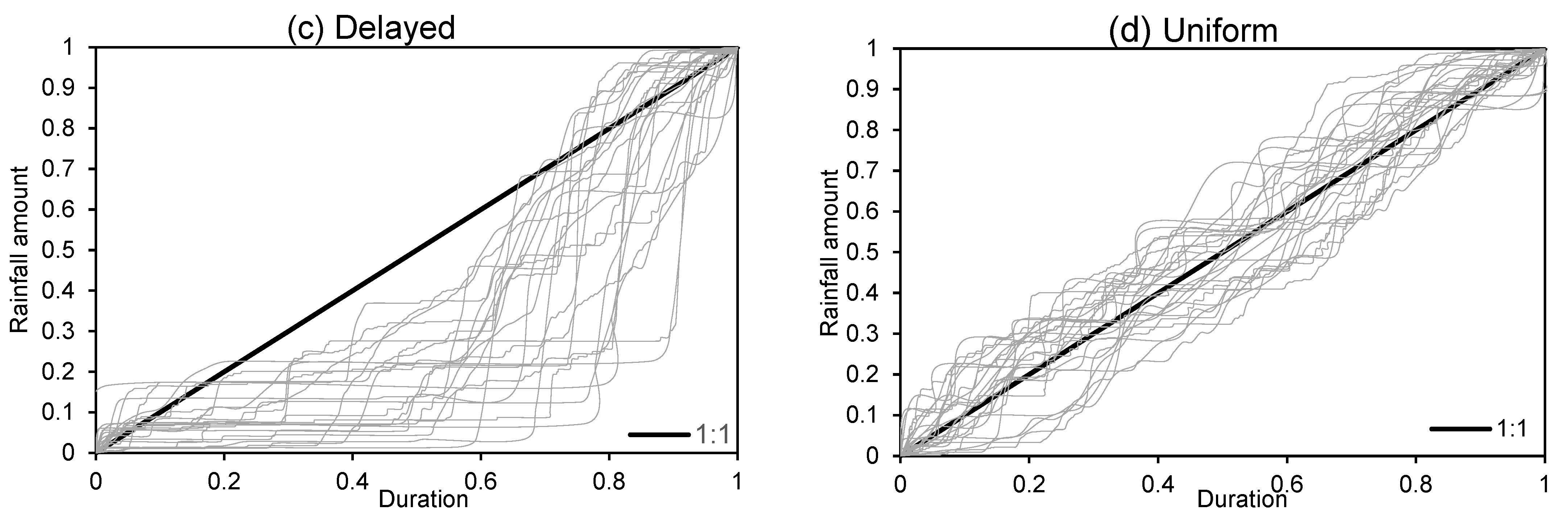
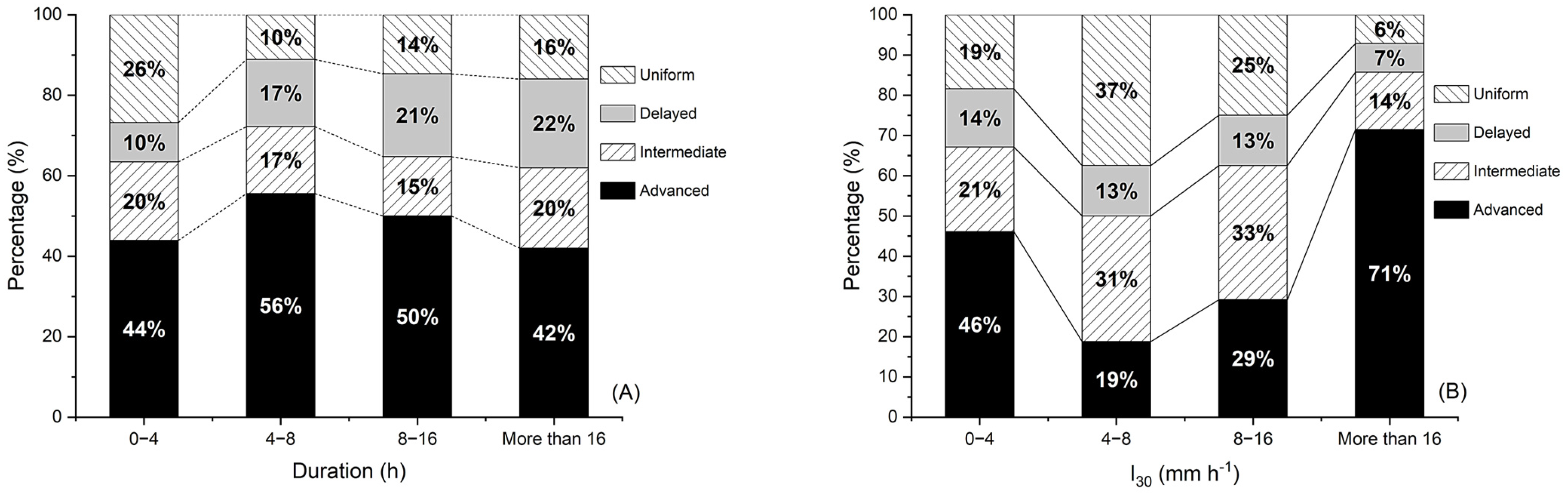
2.5. Determination of Rainfall Regimes and Rainfall Duration Curves
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
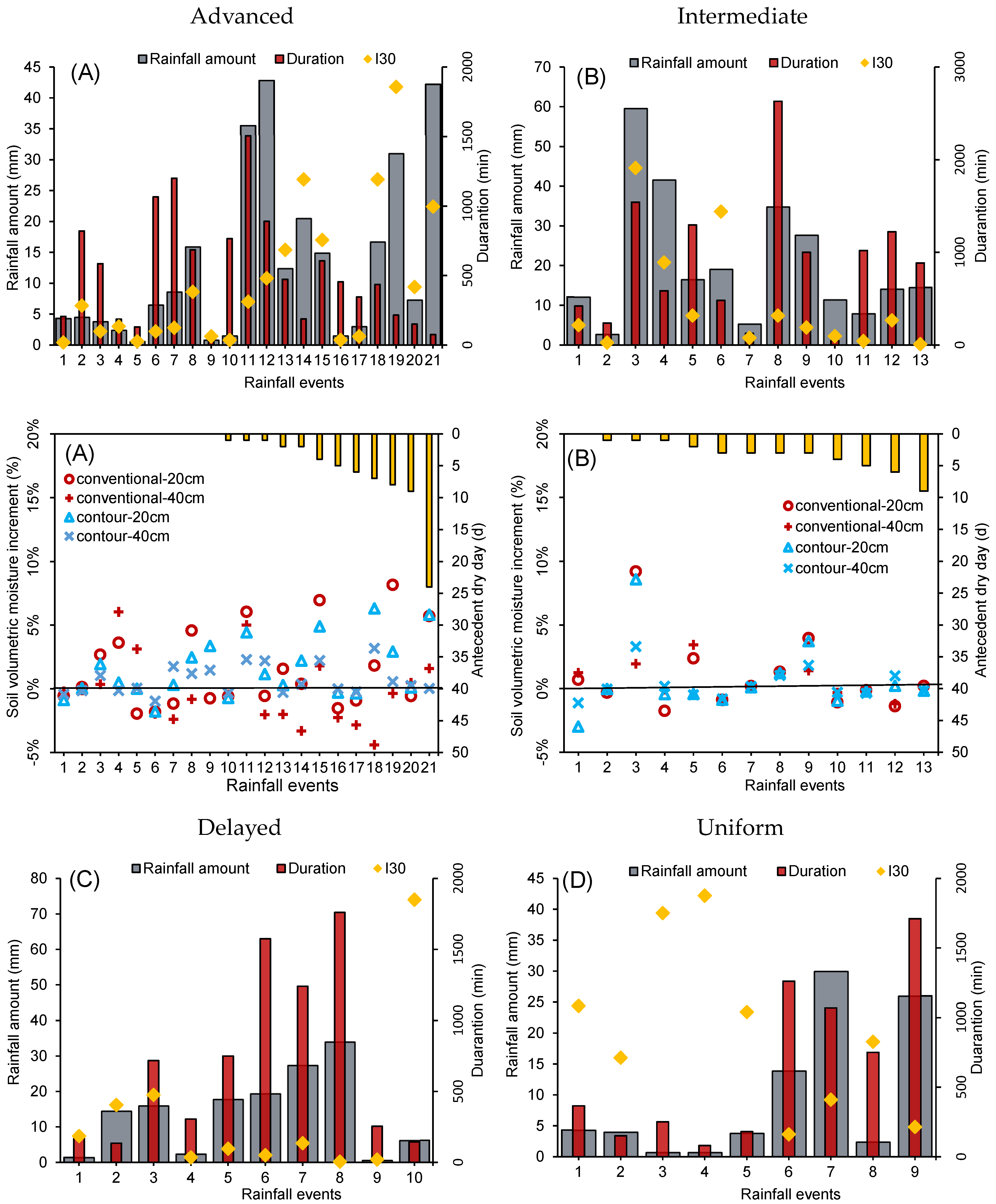
3.1. Rainfall Regimes
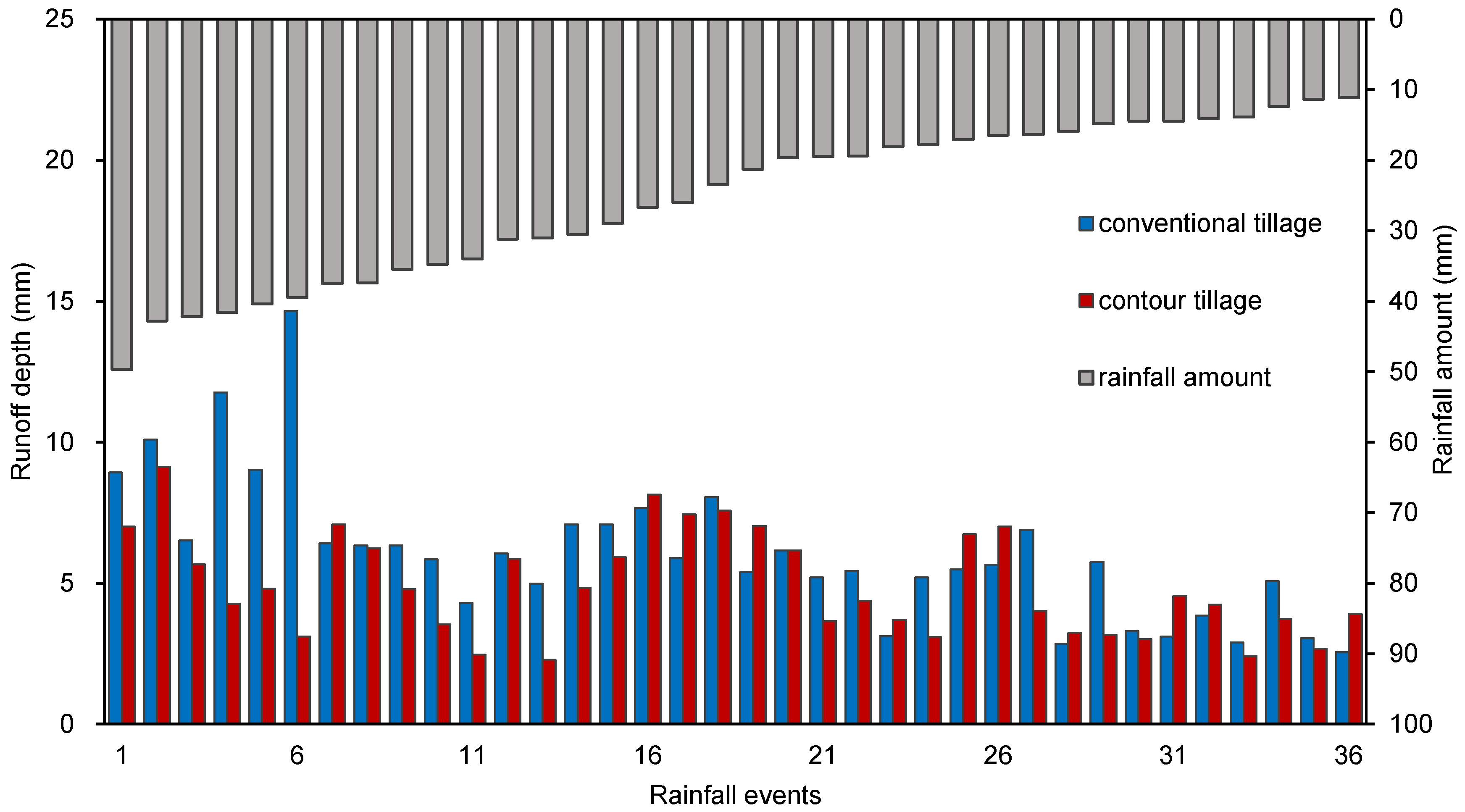
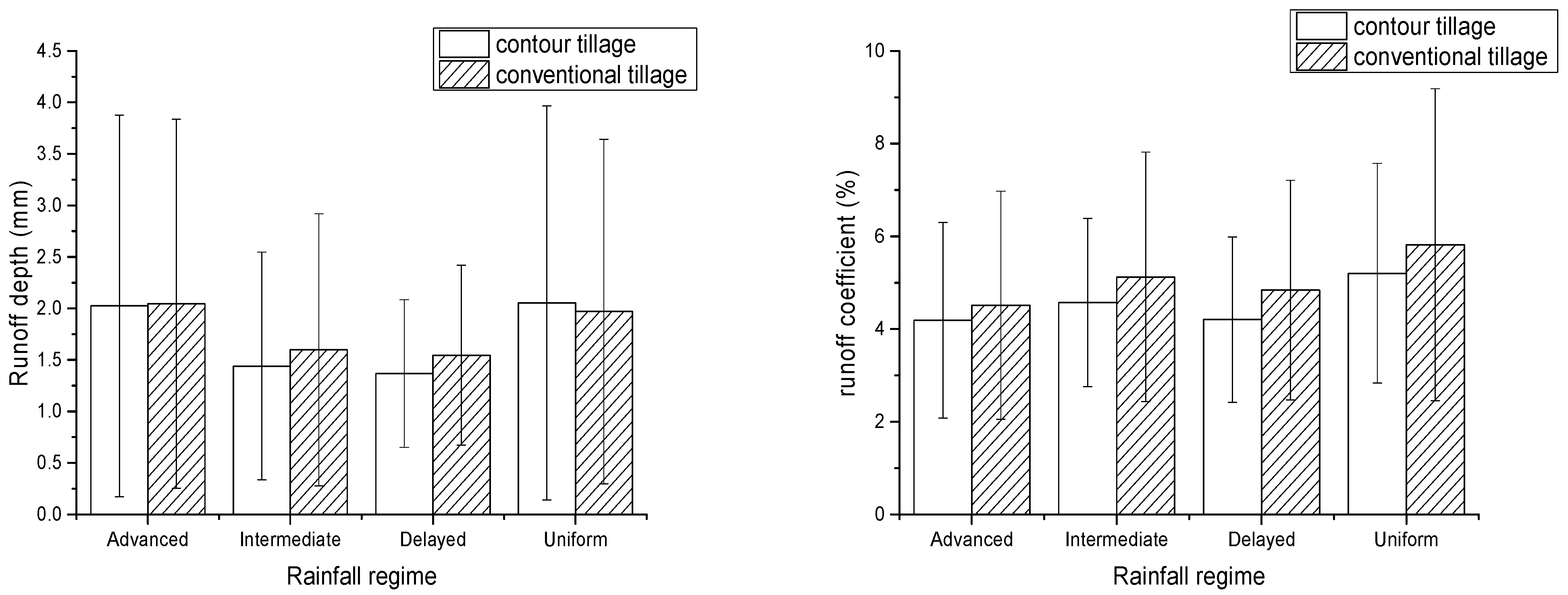
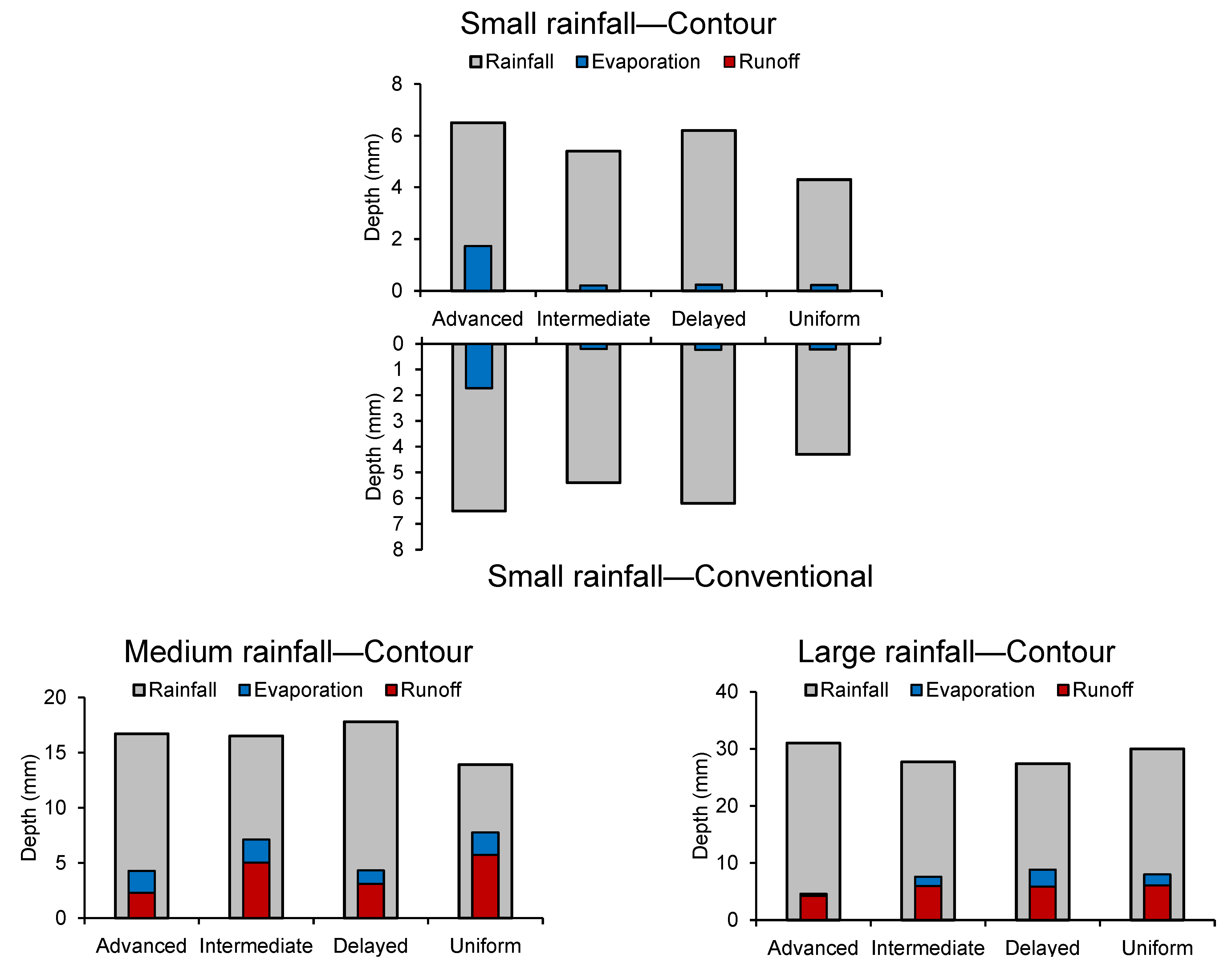
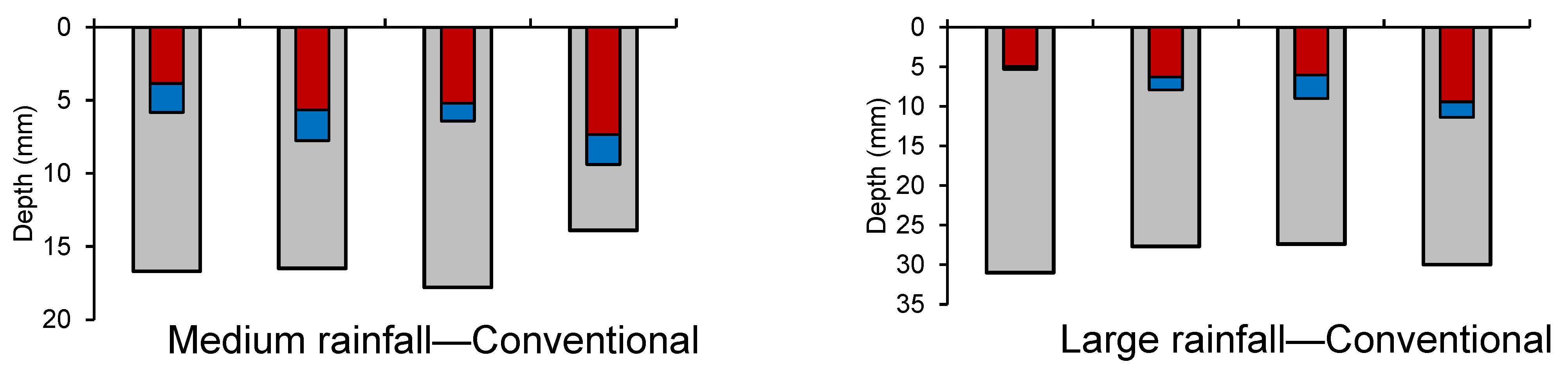
3.2. Runoff Depth and Coefficient with Different Tillage Measures and Four Rainfall Regimes
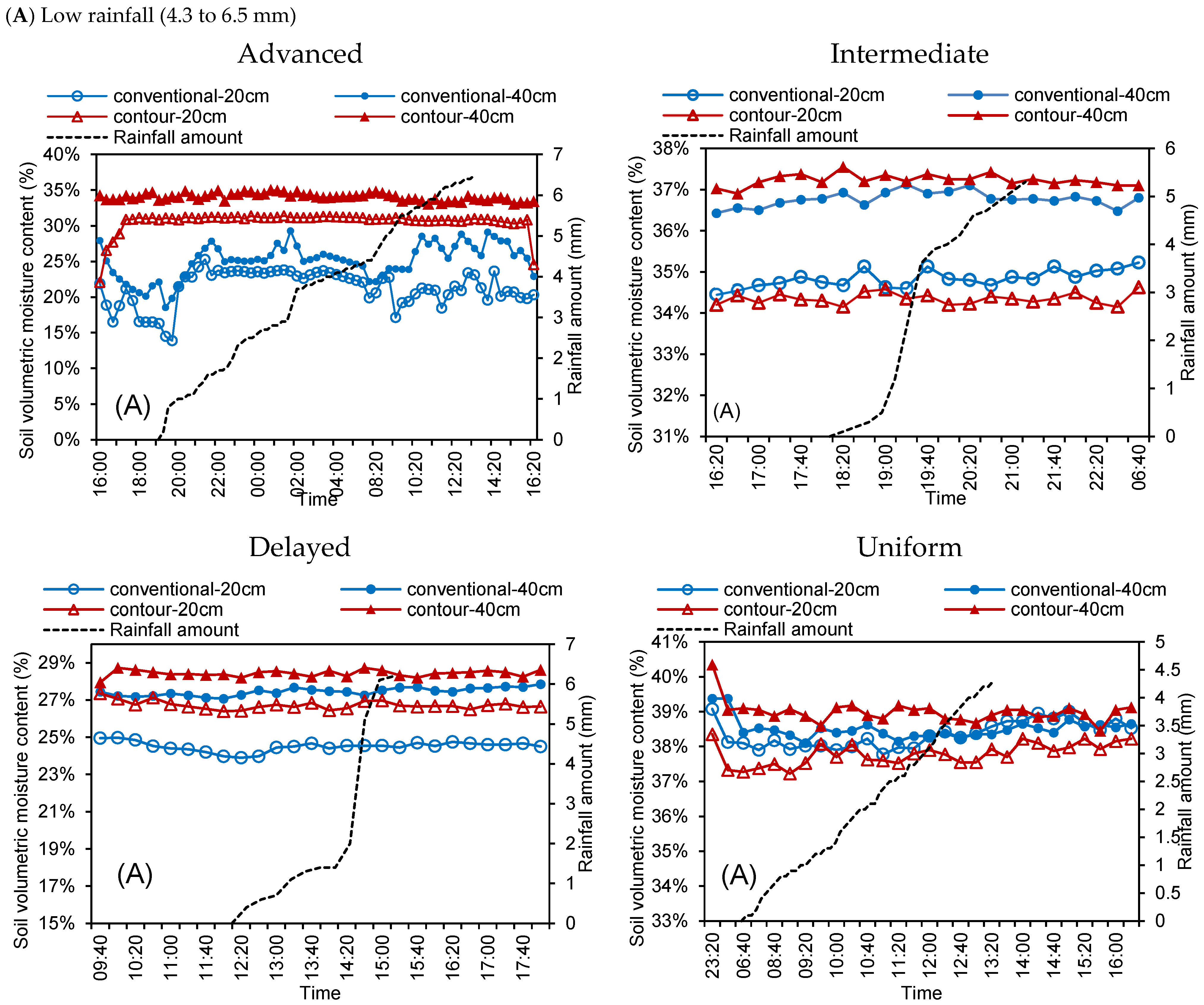
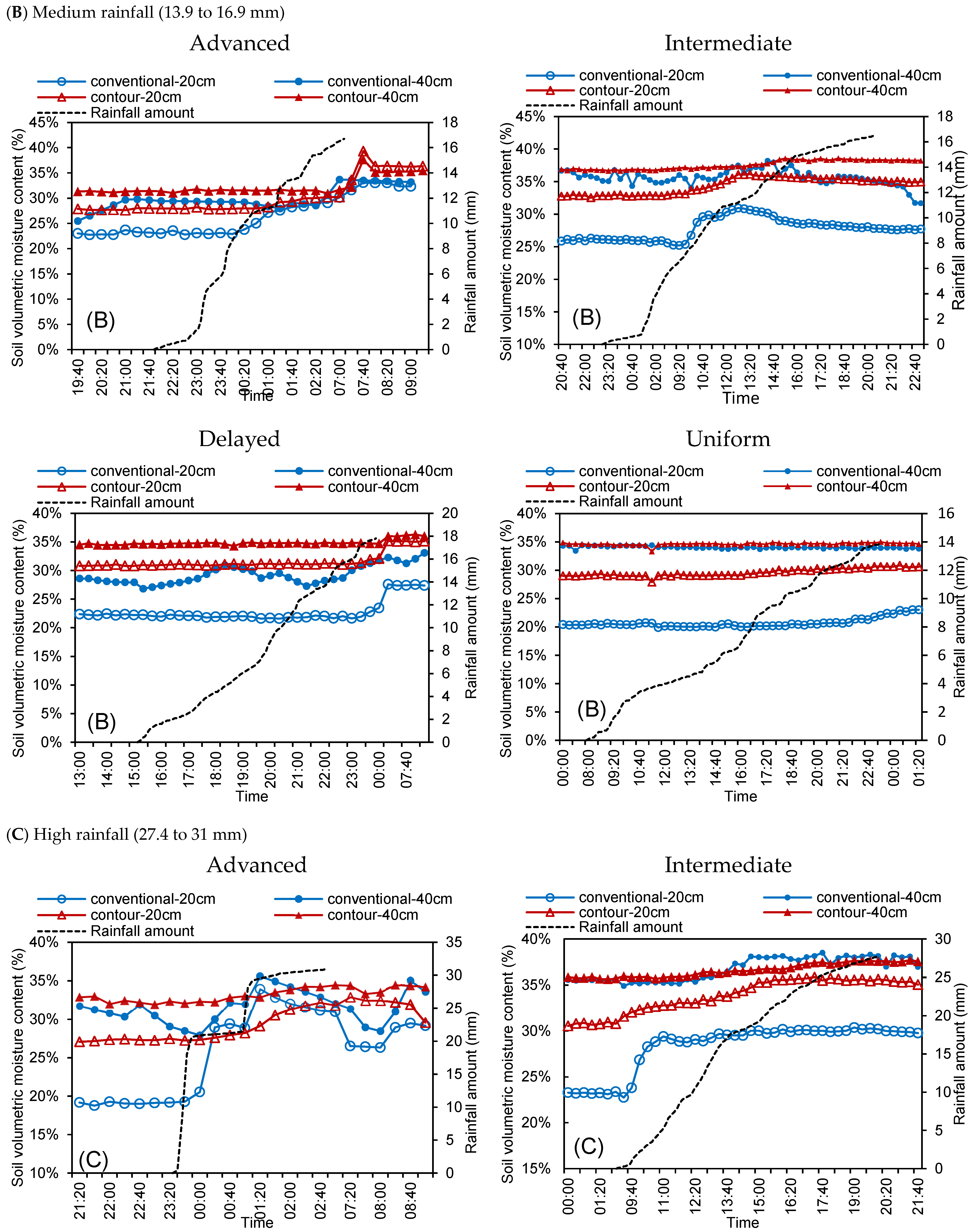
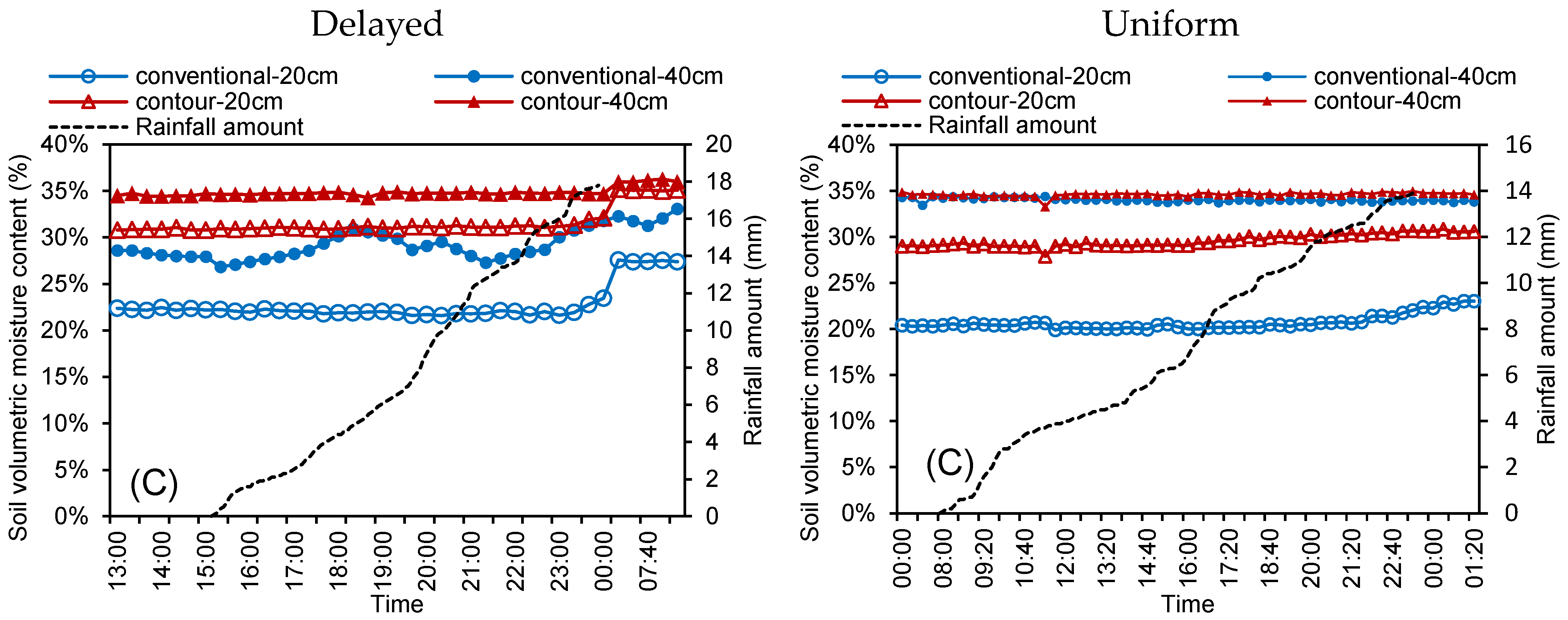
3.3. Processes of the Soil Moisture Varied for Four Rainfall Regimes
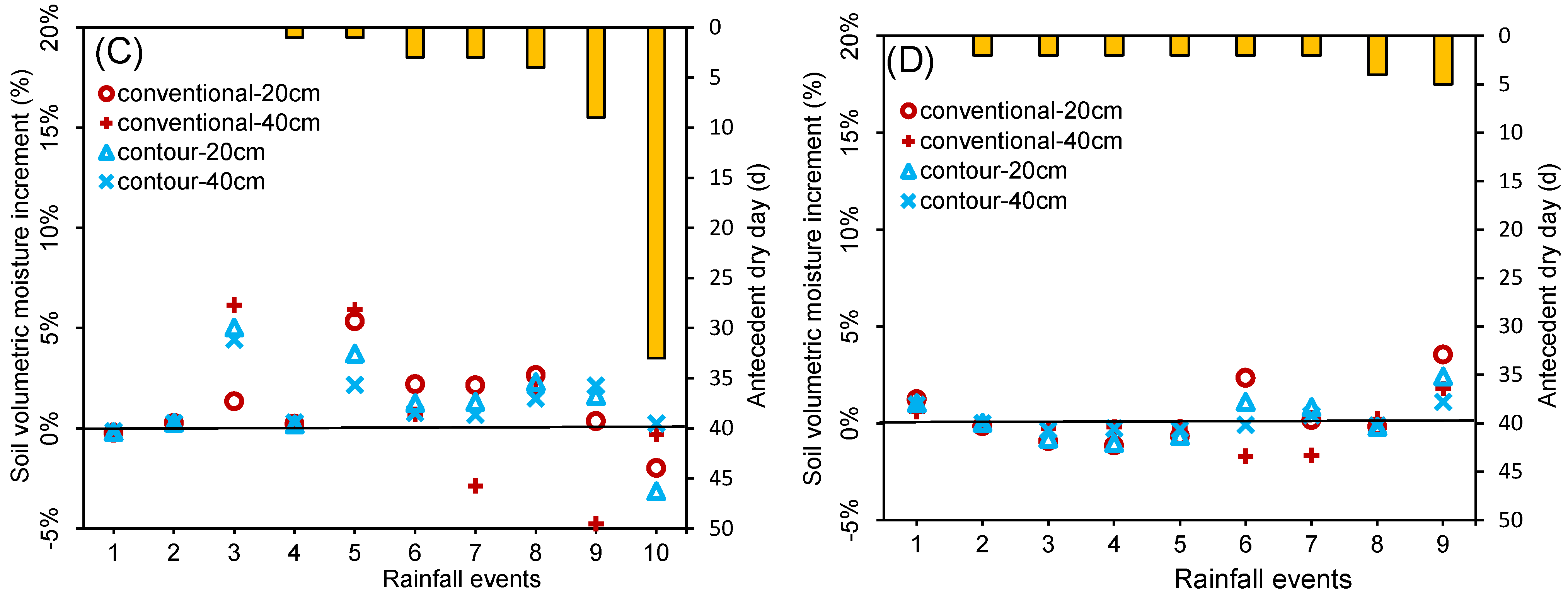
3.4. Response of the Increment in Soil Moisture for Different Rainfall Regimes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hillel, D. Environmental Soil Physics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Rolston, D.E. Introduction to Environmental Soil Physics. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 170, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Chaney, N.W.; Roundy, J.K.; Herrera-Estrada, J.E.; Wood, E.F. High-resolution modeling of the spatial heterogeneity of soil moisture: Applications in network design. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 619–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Chang, X. The response of soil moisture to rainfall event size in subalpine grassland and meadows in a semi-arid mountain range: A case study in northwestern China’s Qilian Mountains. J. Hydrol. 2012, 420–421, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heathman, G.C.; Larose, M.; Cosh, M.H.; Bindlish, R. Surface and profile soil moisture spatio-temporal analysis during an excessive rainfall period in the Southern Great Plains, USA. CATENA 2009, 78, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, E.; Porporato, A. A review of soil moisture dynamics: From rainfall infiltration to ecosystem response. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2005, 22, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, M.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Effects of land use on spatial and temporal distribution of soil moisture within profiles. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S.; Musiake, K. Global Hydrological Cycle and World Water Resources. J. Membr. Musiake 2003, 28, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. J. Earth Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, R.B.; Western, A.W. Towards areal estimation of soil water content from point measurements: Time and space stability of mean response. J. Hydrol. 1998, 207, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.P.; Li, Z.B.; Liu, X.L.; Li, P.; Cheng, S.D.; Xu, G.C. Comparing watershed afforestation and natural revegetation impacts on soil moisture in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucco, G.; Brocca, L.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Influence of land use on soil moisture spatial-temporal variability and monitoring. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Kamai, T.; Harter, T.; Kasteel, R.; Hopmans, J.; Vanderborght, J. Explaining soil moisture variability as a function of mean soil moisture: A stochastic unsaturated flow perspective. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, G. The Preliminarily Study on the Ecological Environment Effects of Land-use Change in Red Earth Hilly Area in Southeast China. J. Prog. Geogr. 2010, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L. Effects of Soil and Water Conservation Measures on Runoff and Sediment Yield in Red Soil Slope Farmland under Natural Rainfall. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Niu, Z.; Wang, C.; Xie, S.; Li, S. Spatial-temporal Characteristics of Soil Moisture on Small Red Soil Slope. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 35, 28–34+39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, N.R. Estimating growing-season root zone soil moisture from vegetation index-based evapotranspiration fraction and soil properties in the Northwest Mountain region, USA. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Tang, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y. Soil Moisture Distribution and Time Stability of Aerially Sown Shrubland in the Northeastern Margin of Tengger Desert (China). Water 2023, 15, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, G.C.; Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic determination of soil water content: Measurements in coaxial transmission lines. J. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltineanu, I.C.; Starr, J.L. Real-time soil water dynamics using multisensor capacitance probes: Laboratory calibration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1997, 61, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmugge, T.J.; Jackson, T.J.; Mckim, H.L. Survey of Methods for Soil Moisture Determination. J. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanzy, A.; Tarussov, A.; Judge, A.; Bonn, F. Soil water content determination using a digital ground-penetrating radar. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allred, B.; Freeland, R.; Grote, K.; McCoy, E.; Martinez, L.; Gamble, D. Ground-Penetrating Radar Water Content Mapping of Golf Course Green Sand Layers. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2016, 21, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet-Martí, A.; Morales-Santos, A.; Nolz, R.; Langergraber, G.; Stumpp, C. Quantification of water fluxes and soil water balance in agricultural fields under different tillage and irrigation systems using water stable isotopes. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 231, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X. Linking soil thickness and plot-scale hydrological processes on the sloping lands in the Three Gorges Area of China: A hydropedological approach. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 2248–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Ni, J.Y.; Du, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhou, Y.Q. Soil water content estimation using ground penetrating radar data via group intelligence optimization algorithms: An application in the Northern Shaanxi Coal Mining Area. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2021, 39, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zhang, P.; Yang, X.; Zhen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Aitkenhead, M. Comparison of the accuracy of two soil moisture sensors and calibration models for different soil types on the loess plateau. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 37, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Tao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Tian, Z.; Lin, L.; He, Y.; Chen, J.J.G. Soil moisture dynamics near a gully head in relation to the trigger of collapse in granite red soil slope in southern China. Geomorphology 2023, 420, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.-M.; Tang, C.-J.; Zheng, H.-J. Characteristics of the surface–subsurface flow generation and sediment yield to the rainfall regime and land-cover by long-term in-situ observation in the red soil region, Southern China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Lin, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, X.; Tu, X.; Bai, C. Spatial interpolation of red bed soil moisture in Nanxiong basin, South China. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 242, 103860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Salam, M.; Miao, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Y. Potential disintegration and transport of biochar in the soil-water environment: A case study towards purple soil. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Huang, C. Soil moisture variations at different topographic domains and land use types in the semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2018, 165, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Fan, J.; Luo, Z. Response of soil moisture and vegetation growth to precipitation under different land uses in the Northern Loess Plateau, China. CATENA 2024, 236, 107728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhou, Q.; Cai, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Regional Soil Moisture Content in the Humid Karst Areas—A Case Study of Southwest China. Water 2021, 13, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.A.; Sperl, C.; Bouten, W.; Verstraten, J.M. Soil water content measurements at different scales: Accuracy of time domain reflectometry and ground-penetrating radar. J. Hydrol. 2001, 245, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindroth, A.; Grelle, A.; Moren, A.S. Long-term measurements of boreal forest carbon balance reveal large temperature sensitivity. Glob. Chang. Biol. 1998, 4, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler-White, J.L.; Knapp, A.K.; Kelly, E.F. Increasing precipitation event size increases aboveground net primary productivity in a semi-arid grassland. Oecologia 2008, 158, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.P.; Cui, Y.; Pan, Y.X.; Li, X.R.; Yu, Z.; Young, M.H. Effects of rainfall characteristics on infiltration and redistribution patterns in revegetation-stabilized desert ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2008, 358, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.N.; Huang, Y.M.; Li, E.G.; Li, X.Y.; Guo, W.H. Effects of rainfall and vegetation to soil water input and output processes in the Mu Us Sandy Land, northwest China. CATENA 2018, 161, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Kemp, P.R.; Ogle, K.; Fernández, R.J. Modifying the ‘pulse-reserve’ paradigm for deserts of North America: Precipitation pulses, soil water, and plant responses. Oecologia 2004, 141, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; He, C.; Han, Z.; Bogena, H.R.; Huisman, J.A. Dynamic response patterns of profile soil moisture wetting events under different land covers in the Mountainous area of the Heihe River Watershed, Northwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 271, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Emanuel, R.E.; McGlynn, B.L.; Miniat, C.F. Soil Moisture Responses to Rainfall: Implications for Runoff Generation. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseef, N.R.; Yakir, D.; Rotenberg, E.; Schiller, G.; Cohen, S. Ecohydrology of a semi-arid forest: Partitioning among water balance components and its implications for predicted precipitation changes. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aixia, R.; Zhao, W.; Anwar, S.; Lin, W.; Ding, P.; Hao, R.; Wang, P.; Zhong, R.; Tong, J.; Gao, Z.; et al. Effects of tillage and seasonal variation of rainfall on soil water content and root growth distribution of winter wheat under rainfed conditions of the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 268, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Ma, L. Effect of afforestation on soil water dynamics and water uptake under different rainfall types on the Loess hillslope. CATENA 2022, 213, 106216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y. Response of forestland soil water content to heavy rainfall on Beijing Mountain, northern China. J. For. Res. 2016, 3, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.J. A spatial-temporal model of storm rainfall. J. Hydrol. 1983, 62, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.A.; Kavian, A. Effects of rainfall patterns on runoff and soil erosion in field plots. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2015, 3, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.; Fu, B.; Huang, Z.; Wu, D.; Gui, L. The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Nie, X.; Zhou, X.; Liao, K.; Li, H. Soil moisture response to rainfall at different topographic positions along a mixed land-use hillslope. CATENA 2014, 119, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Effects of rainfall intensity fluctuations on infiltration and runoff: Rainfall simulation on dryland soils, Fowlers Gap, Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 26, 2211–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, F.A. Time Distribution Rainall in Heavy Storm. Water Resour. Res. 1967, 3, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azli, M.; Rao, A.R. Development of Huff curves for Peninsular Malaysia. J. Hydrol. 2010, 388, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, R.F.; Silva, M.L.N.; de Freitas, D.A.F.; Curi, N.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil Losses from Typic Cambisols and Red Latosol as Related To Three Erosive Rainfall Patterns. Rev. Bras. Ciência Solo 2013, 37, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, W. Intra-Storm Attributes of Extreme Storm Events in the Drakensberg, South Africa. Phys. Geogr. 2007, 28, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Effects of four storm patterns on soil loss from five soils under natural rainfall. CATENA 2016, 141, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Tullo, T.; Melone, F.; Moramarco, T.; Morbidelli, R. Catchment scale soil moisture spatial–temporal variability. J. Hydrol. 2012, 422–423, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, H.H.; Mata, M.G.; Guerra, J.G.; Carvalho, D.F.; Wendroth, O.O.; Ceddia, M.B. Spatial and temporal patterns of soil water content in an agroecological production system. Sci. Agric. 2017, 74, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, M.G.; da Silva, T.G.; Zolnier, S.; Jardim, A.M.; de Souza, C.A.; Júnior, G.D.; de Morais, J.E.; de Souza, L.S. Spatial and temporal dynamics of soil moisture for surfaces with a change in land use in the semi-arid region of Brazil. CATENA 2020, 188, 104457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, J.; Tang, C.-J.; Shi, Z.-H. Role of groundcover management in controlling soil erosion under extreme rainfall in citrus orchards of southern China. J. Hydrol. 2020, 582, 124290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rötzer, K.; Montzka, C.; Vereecken, H. Spatio-temporal variability of global soil moisture products. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparison of deep soil moisture in two re-vegetation watersheds in semi-arid regions. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Jia, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Xiao, P. Field studies on the influence of rainfall intensity, vegetation cover and slope length on soil moisture infiltration on typical watersheds of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 4904–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.R.; Chen, Q.W.; Zhang, J.G.; Shi, W.Y.; Li, G.; Du, S. Soil moisture variations in response to precipitation in different vegetation types: A multi-year study in the loess hilly region in China. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.W.; Blair, J.M.; Fay, P.A.; Knapp, A.K.; Carlisle, J.D. Increased rainfall variability and reduced rainfall amount decreases soil CO2flux in a grassland ecosystem. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerley, D. Identifying individual rain events from pluviograph records: A review with analysis of data from an Australian dryland site. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 5024–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Nearing, M.A. Minimum Inter-Event Times for Rainfall in the Eastern Monsoon Region of China. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, A.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xie, S. Effect of minimum inter-event time for rainfall event separation on rainfall properties and rainfall erosivity in a humid area of southern China. Geoderma 2023, 431, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. A Rainfall Erosion Index for a Universal Soil-Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, R.; Sun, W. Duration and seasonality of hourly extreme rainfall in the central eastern China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 27, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Xie, Y.; Liu, B.; Nearing, M.A. Rainfall erosivity estimation based on rainfall data collected over a range of temporal resolutions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4113–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torell, L.A.; McDaniel, K.C.; Koren, V. Estimating Grass Yield on Blue Grama Range From Seasonal Rainfall and Soil Moisture Measurements. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 64, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Shi, Z.H.; Zhu, H.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ai, L.; Yin, W. Soil moisture dynamics within soil profiles and associated environmental controls. CATENA 2016, 136, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devita, P.; Dipaolo, E.; Fecondo, G.; Difonzo, N.; Pisante, M. No-tillage and conventional tillage effects on durum wheat yield, grain quality and soil moisture content in southern Italy. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembele, C.O.; Traore, K.; Karembe, M.; Zemadim, B.; Cisse, F.; Samake, O. Contour Ridge Tillage for Improved Crops and Fodder Trees Production in the Villages of Kani and Noumpinesso, Southern- Mali. J. Agric. Stud. 2022, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y. Characterizing spatial-temporal patterns and abrupt changes in deep soil moisture across an intensively managed watershed. Geoderma 2019, 341, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, F.; Sun, S. Tracing the soil water response to autumn rainfall in different land uses at multi-day timescale in a subtropical zone. CATENA 2019, 180, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, R.; Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Govindaraju, R.S. Scaling of surface soil moisture over heterogeneous fields subjected to a single rainfall event. J. Hydrol. 2014, 516, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiekenkamp, I.; Huisman, J.A.; Bogena, H.R.; Lin, H.S.; Vereecken, H. Spatial and temporal occurrence of preferential flow in a forested headwater catchment. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Duan, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y. Experimental analysis of soil moisture response to rainfall in a typical grassland hillslope under different vegetation treatments. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Fu, R.; Guo, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, F.; Cao, G. Soil Moisture Variations in Response to Precipitation Across Different Vegetation Types on the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 854152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, P.; Man, X.; Duan, L.; Cai, T. Responsive characteristics of soil water regimes to rainfall events in a boreal larch forest in China: Dynamic processes and decoupling effects. Geoderma 2024, 441, 116741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Shao, J.; Li, L.; Chen, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, R. Experimental Investigation of Relationship between Infiltration Rate and Soil Moisture under Rainfall Conditions. Water 2022, 14, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.; Jackson, C.R.; Parker, A.J. Variation of surficial soil hydraulic properties across land uses in the southern Blue Ridge Mountains, North Carolina, USA. J. Hydrol. 2010, 383, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tillage Measures | Soil Bulk Density | Total Porosity | Capillary Porosity | Non-Capillary Porosity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | 0–20 cm | 50.80 ± 3.45 | 1.28 ± 0.07 | 37.97 ± 1.86 | 12.83 ± 1.96 |
| 20–40 cm | 45.08 ± 3.43 | 1.44 ± 0.07 | 35.83 ± 2.21 | 9.25 ± 1.23 | |
| Contour | 0–20 cm | 52.81 ± 4.70 | 1.22 ± 0.10 | 38.11 ± 1.58 | 14.70 ± 2.30 |
| 20–40 cm | 44.61 ± 3.12 | 1.44 ± 0.06 | 36.38 ± 1.99 | 8.22 ± 2.47 | |
| Rainfall Regimes | Parameter | Frequency | Mean | Std. Dev | Median | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced | Rainfall amount (mm) | 68 | 16.82 | 23.27 | 7.95 | 0.60 | 109.10 |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 784.72 | 957.09 | 482.00 | 30.00 | 7065.00 | ||
| I30 (mm h−1) | 9.72 | 14.05 | 4.10 | 0.60 | 74.00 | ||
| Intermediate | Rainfall amount (mm) | 32 | 22.19 | 17.89 | 16.45 | 0.90 | 70.30 |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 900.00 | 720.58 | 750.00 | 45.00 | 2630.00 | ||
| I30 (mm h−1) | 13.00 | 11.49 | 7.80 | 1.20 | 44.60 | ||
| Delayed | Rainfall amount (mm) | 24 | 15.17 | 17.18 | 12.80 | 0.60 | 84.50 |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 740.00 | 574.08 | 680.00 | 110.00 | 2235.00 | ||
| I30 (mm h−1) | 9.88 | 9.59 | 7.10 | 0.80 | 38.60 | ||
| Uniform | Rainfall amount (mm) | 24 | 13.33 | 28.10 | 3.70 | 0.30 | 117.10 |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 874.24 | 1435.81 | 350.00 | 30.00 | 6310.00 | ||
| I30 (mm h−1) | 3.54 | 5.34 | 1.40 | 0.20 | 21.20 |
| Month/ Year | Rainfall (mm) | Total Duration (min) | I30 (mm h−1) | Conventional Tillage | Contour Tillage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | ||||
| 05/2019 | 90.40 | 6255.00 | 7.72 | 35.94 ± 0.95 a | 37.19 ± 0.79 a | 35.45 ± 0.97 a | 37.70 ± 0.66 a |
| 06/2019 | 151.10 | 7480.00 | 7.34 | 35.67 ± 1.54 a | 37.33 ± 0.78 a | 35.39 ± 1.36 a | 37.79 ± 0.83 a |
| 07/2019 | 278.10 | 4455.00 | 16.83 | 30.74 ± 4.54 b | 36.12 ± 2.55 b | 32.79 ± 3.25 b | 36.98 ± 1.95 b |
| 08/2019 | 48.90 | 240.00 | 28.20 | 20.56 ± 2.27 i | 25.76 ± 1.69 i | 23.93 ± 1.90 i | 28.16 ± 1.46 g |
| 09/2019 | 7.90 | 1020.00 | 4.00 | 16.92 ± 0.48 j | 22.08 ± 0.34 j | 20.26 ± 0.60 k | 25.09 ± 0.38 j |
| 10/2019 | 11.60 | 1910.00 | 1.80 | 16.09 ± 0.44 l | 21.71 ± 0.40 k | 19.13 ± 0.60 l | 24.31 ± 0.49 j |
| 11/2019 | 27.20 | 3190.00 | 1.30 | 17.65 ± 1.66 l | 22.46 ± 0.84 k | 19.57 ± 0.79 l | 24.70 ± 0.66 j |
| 12/2019 | 30.60 | 4875.00 | 1.87 | 19.31 ± 0.93 j | 23.56 ± 1.23 j | 21.69 ± 1.52 j | 25.51 ± 0.29 i |
| 01/2020 | 198.30 | 12,205.00 | 4.63 | 24.57 ± 4.16 d | 32.41 ± 5.84 f | 30.85 ± 4.48 d | 33.27 ± 4.95 d |
| 02/2020 | 101.70 | 6320.00 | 2.20 | 24.56 ± 2.82 c | 33.39 ± 4.23 c | 32.14 ± 1.94 c | 36.39 ± 1.23 c |
| 03/2020 | 182.90 | 7180.00 | 6.11 | 23.84 ± 3.31 c | 29.04 ± 4.91 d | 31.84 ± 2.79 c | 35.72 ± 2.02 e |
| 04/2020 | 89.30 | 3605.00 | 8.83 | 21.98 ± 3.20 e | 28.55 ± 4.65 e | 29.42 ± 3.98 e | 33.76 ± 2.53 ef |
| 05/2020 | 180.00 | 5160.00 | 9.29 | 18.72 ± 2.52 g | 28.19 ± 1.83 g | 27.31 ± 1.03 g | 32.56 ± 0.56 f |
| 06/2020 | 238.40 | 7630.00 | 8.70 | 18.82 ± 2.13 f | 22.12 ± 5.54 d | 28.33 ± 2.66 f | 35.64 ± 1.58 j |
| 07/2020 | 393.40 | 9144.00 | 18.91 | 21.37 ± 3.18 e | 24.63 ± 5.36 d | 28.96 ± 3.73 e | 35.60 ± 2.11 h |
| 08/2020 | 149.60 | 3282.00 | 22.07 | 17.00 ± 4.86 h | 25.68 ± 4.09 h | 24.49 ± 3.90 h | 31.88 ± 2.66 g |
| Mean (%) | 22.73 ± 6.13 | 28.14 ± 5.41 | 27.59 ± 5.32 | 32.19 ± 4.82 | |||
| CV (%) | 26.957 | 19.226 | 19.905 | 15.460 | |||
| Rainfall Amount (mm) | Rainfall Regime | Before the Rain 1 | In the Rain 1 | After the Rain 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | ||
| 6.5 | Advanced | 21.86 ± 2.98 | 25.49 ± 5.48 | 21.90 ± 2.44 | 23.33 ± 4.70 | 22.68 ± 1.83 | 26.64 ± 4.31 |
| 5.4 | Intermediate | 34.68 ± 0.24 | 36.66 ± 0.26 | 34.84 ± 0.18 | 36.85 ± 0.14 | 34.87 ± 0.19 | 36.87 ± 0.18 |
| 6.2 | Delayed | 25.09 ± 0.39 | 27.43 ± 0.26 | 24.46 ± 0.20 | 27.48 ± 0.12 | 24.36 ± 0.54 | 27.38 ± 0.32 |
| 4.3 | Uniform | 37.82 ± 0.78 | 38.42 ± 0.56 | 38.11 ± 0.22 | 38.37 ± 0.13 | 38.55 ± 0.28 | 38.62 ± 0.17 |
| 16.7 | Advanced | 20.59 ± 3.40 | 25.18 ± 3.01 | 25.49 ± 2.68 | 25.52 ± 3.82 | 22.32 ± 7.58 | 19.66 ± 8.39 |
| 16.5 | Intermediate | 25.13 ± 1.21 | 31.17 ± 4.18 | 28.03 ± 1.75 | 32.64 ± 4.14 | 26.71 ± 1.06 | 28.34 ± 5.27 |
| 17.8 | Delayed | 22.78 ± 1.72 | 26.23 ± 4.39 | 22.00 ± 0.38 | 26.80 ± 2.62 | 27.36 ± 1.49 | 31.79 ± 3.82 |
| 13.9 | Uniform | 20.24 ± 1.15 | 30.72 ± 5.00 | 20.47 ± 0.46 | 34.02 ± 0.17 | 22.58 ± 1.06 | 29.04 ± 4.79 |
| 31.0 | Advanced | 18.46 ± 1.41 | 28.25 ± 3.09 | 29.06 ± 4.57 | 28.20 ± 4.22 | 27.62 ± 1.68 | 30.85 ± 4.47 |
| 27.7 | Intermediate | 23.44 ± 0.64 | 34.42 ± 2.91 | 29.06 ± 1.7 | 36.7 ± 1.68 | 27.96 ± 1.33 | 36.02 ± 2.41 |
| 27.4 | Delayed | 25.18 ± 1.12 | 33.40 ± 3.29 | 25.78 ± 1.90 | 33.15 ± 2.63 | 27.78 ± 0.80 | 31.26 ± 4.40 |
| 30.0 | Uniform | 25.88 ± 1.14 | 27.20 ± 4.38 | 27.56 ± 2.37 | 24.95 ± 4.63 | 26.13 ± 0.43 | 26.16 ± 4.09 |
| Rainfall Amount (mm) | Rainfall Regime | Before the Rain 1 | In the Rain 1 | After the Rain 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | 20 cm (%) | 40 cm (%) | ||
| 6.5 | Advanced | 30.36 ± 2.44 | 33.99 ± 1.87 | 30.06 ± 2.47 | 33.95 ± 1.42 | 30.24 ± 2.44 | 33.73 ± 3.09 |
| 5.4 | Intermediate | 34.29 ± 0.24 | 37.13 ± 0.22 | 34.32 ± 0.08 | 37.26 ± 0.10 | 34.41 ± 0.16 | 37.22 ± 0.13 |
| 6.2 | Delayed | 27.43 ± 0.38 | 28.36 ± 0.20 | 26.72 ± 0.18 | 28.49 ± 0.15 | 26.40 ± 0.41 | 28.35 ± 0.26 |
| 4.3 | Uniform | 37.41 ± 0.57 | 38.87 ± 0.58 | 37.67 ± 0.22 | 38.94 ± 0.17 | 38.01 ± 0.23 | 39.19 ± 0.25 |
| 16.7 | Advanced | 27.13 ± 0.79 | 30.99 ± 0.34 | 28.96 ± 1.48 | 31.51 ± 0.27 | 35.72 ± 0.91 | 35.95 ± 0.85 |
| 16.5 | Intermediate | 33.08 ± 0.45 | 36.92 ± 0.39 | 34.55 ± 1.23 | 37.60 ± 0.68 | 34.32 ± 0.41 | 37.87 ± 0.25 |
| 17.8 | Delayed | 30.68 ± 0.82 | 33.79 ± 1.89 | 31.15 ± 0.27 | 34.73 ± 0.12 | 34.19 ± 0.38 | 36.11 ± 0.21 |
| 13.9 | Uniform | 29.01 ± 0.19 | 34.46 ± 0.25 | 29.51 ± 0.59 | 34.61 ± 0.24 | 30.33 ± 0.21 | 34.49 ± 0.19 |
| 31.0 | Advanced | 27.11 ± 2.10 | 32.51 ± 1.30 | 29.55 ± 1.90 | 33.25 ± 0.83 | 32.04 ± 1.48 | 34.13 ± 0.56 |
| 27.7 | Intermediate | 30.81 ± 0.27 | 35.68 ± 0.26 | 34.28 ± 1.35 | 36.62 ± 0.63 | 34.41 ± 0.56 | 37.56 ± 0.19 |
| 27.4 | Delayed | 32.68 ± 0.23 | 36.79 ± 0.25 | 33.02 ± 0.98 | 36.74 ± 0.14 | 35.05 ± 0.28 | 38.28 ± 0.28 |
| 30.0 | Uniform | 33.99 ± 0.17 | 37.67 ± 0.11 | 35.16 ± 0.99 | 38.02 ± 0.56 | 34.90 ± 0.25 | 38.29 ± 0.20 |
| Rainfall Regime | Parameter | Conventional Tillage | Contour Tillage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 cm | 40 cm | 20 cm | 40 cm | ||
| Advanced | ADD (days) | 0.367 | 0.039 | 0.482 * | −0.043 |
| I30 (mm h−1) | 0.581 * | 0.101 | 0.536 * | −0.036 | |
| Rainfall amount (mm) | 0.568 ** | 0.121 | 0.590 ** | 0.420 * | |
| Rainfall duration (min) | −0.050 | 0.043 | −0.111 | 0.292 | |
| Intermediate | ADD (days) | −0.288 | −0.424 | −0.118 | −0.079 |
| I30 (mm h−1) | 0.435 | 0.022 | 0.525 | 0.419 | |
| Rainfall amount (mm) | 0.657 * | 0.352 | 0.741 ** | 0.736 ** | |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 0.436 | 0.401 | 0.448 | 0.511 | |
| Delayed | ADD (days) | −0.551 | −0.217 | −0.666 * | −0.213 |
| I30 (mm h−1) | −0.020 | 0.375 | 0.190 | 0.250 | |
| Rainfall amount (mm) | 0.628 | 0.300 | 0.430 | 0.202 | |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 0.625 | 0.194 | 0.430 | 0.192 | |
| Uniform | ADD (days) | 0.355 | 0.418 | 0.307 | 0.110 |
| I30 (mm h−1) | 0.367 | −0.351 | 0.558 | 0.419 | |
| Rainfall amount (mm) | 0.628 | −0.119 | 0.765 * | 0.597 | |
| Rainfall duration (min) | 0.850 ** | 0.063 | 0.854 ** | 0.567 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z. Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China. Water 2024, 16, 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101331
Liang Z, Chen X, Wang C, Zhang Z. Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China. Water. 2024; 16(10):1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101331
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Ziwei, Xiaoan Chen, Ce Wang, and Zhanyu Zhang. 2024. "Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China" Water 16, no. 10: 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101331
APA StyleLiang, Z., Chen, X., Wang, C., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Response of Soil Moisture to Four Rainfall Regimes and Tillage Measures under Natural Rainfall in Red Soil Region, Southern China. Water, 16(10), 1331. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16101331





