A Computational Tool to Track Sewage Flow Discharge into Rivers Based on Coupled HEC-RAS and DREAM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
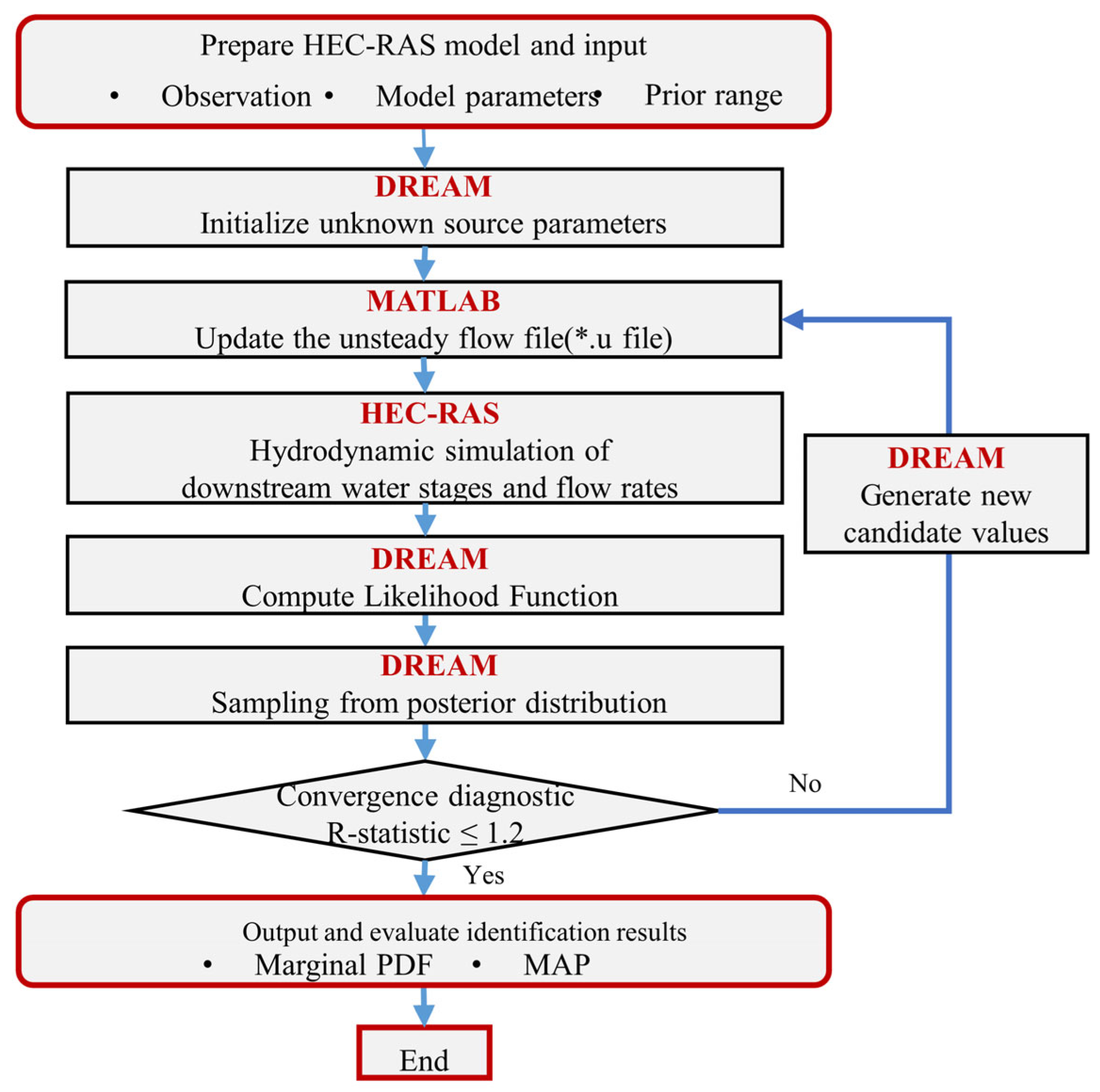
2. Framework Design
2.1. HEC-RAS Modeling
Governing Equations
2.2. DREAM Algorithm
2.2.1. Bayesian Theorem
2.2.2. Differential-Evolution and Metropolis Estimator
2.2.3. DREAM Algorithm
2.3. Coupling HEC-RAS with DREAM in MATLAB
2.4. Modeling Performance Metrics
3. Modeling Tool Demonstration
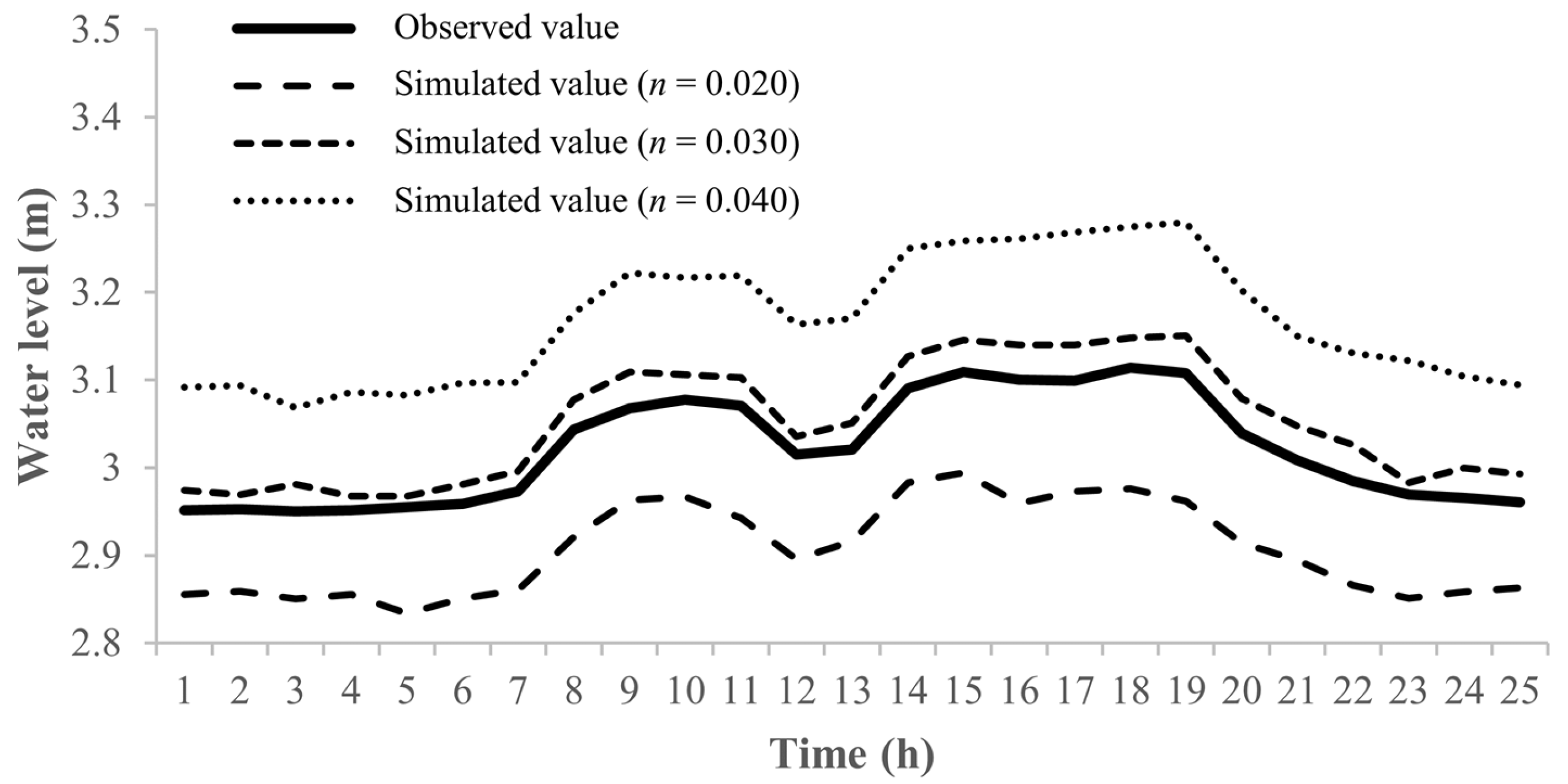
3.1. Hypothetical Case
3.2. Real Case
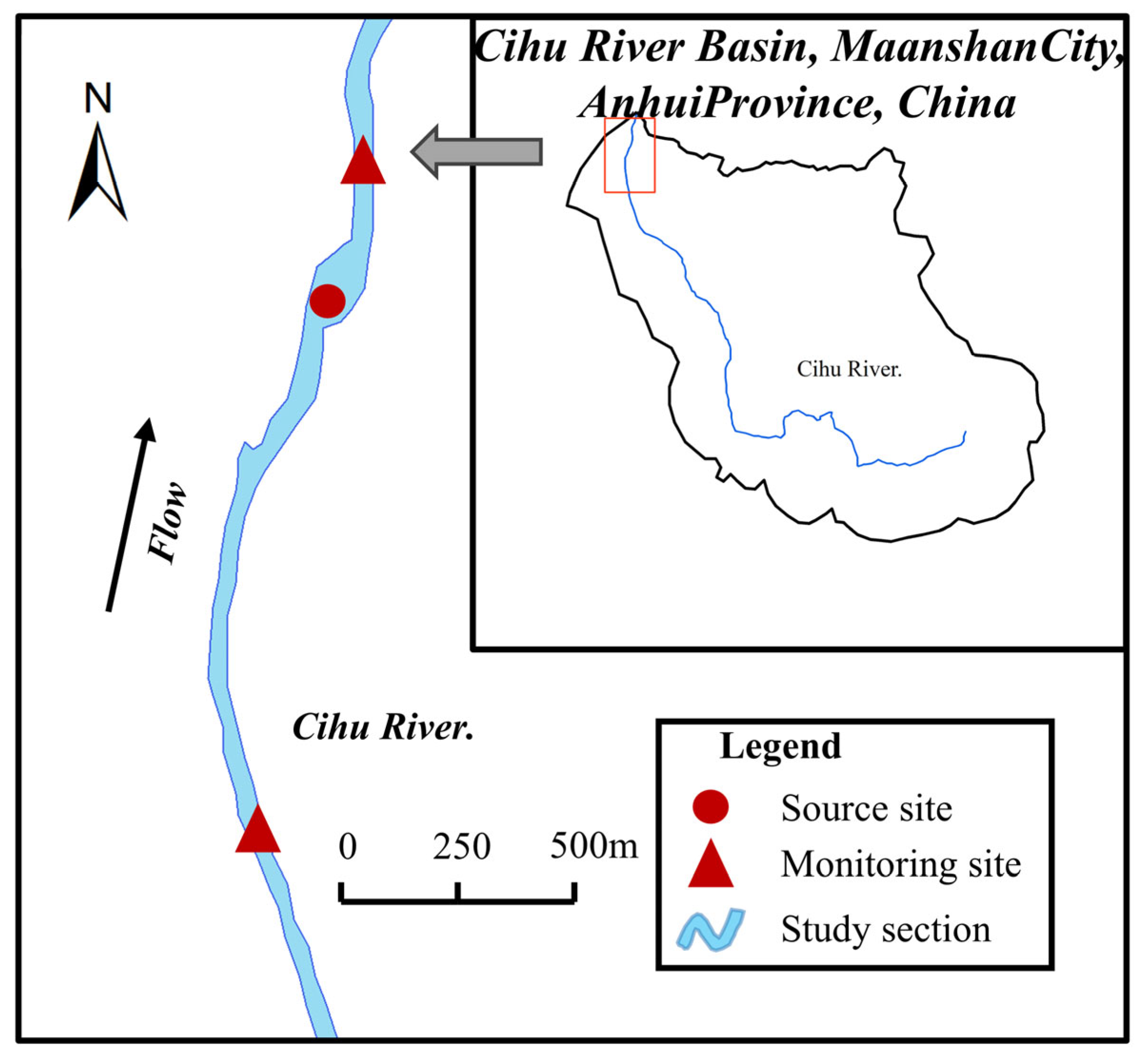
3.2.1. Real Case 1: Source Tracking of a Time-Variable Industrial Discharge into the River
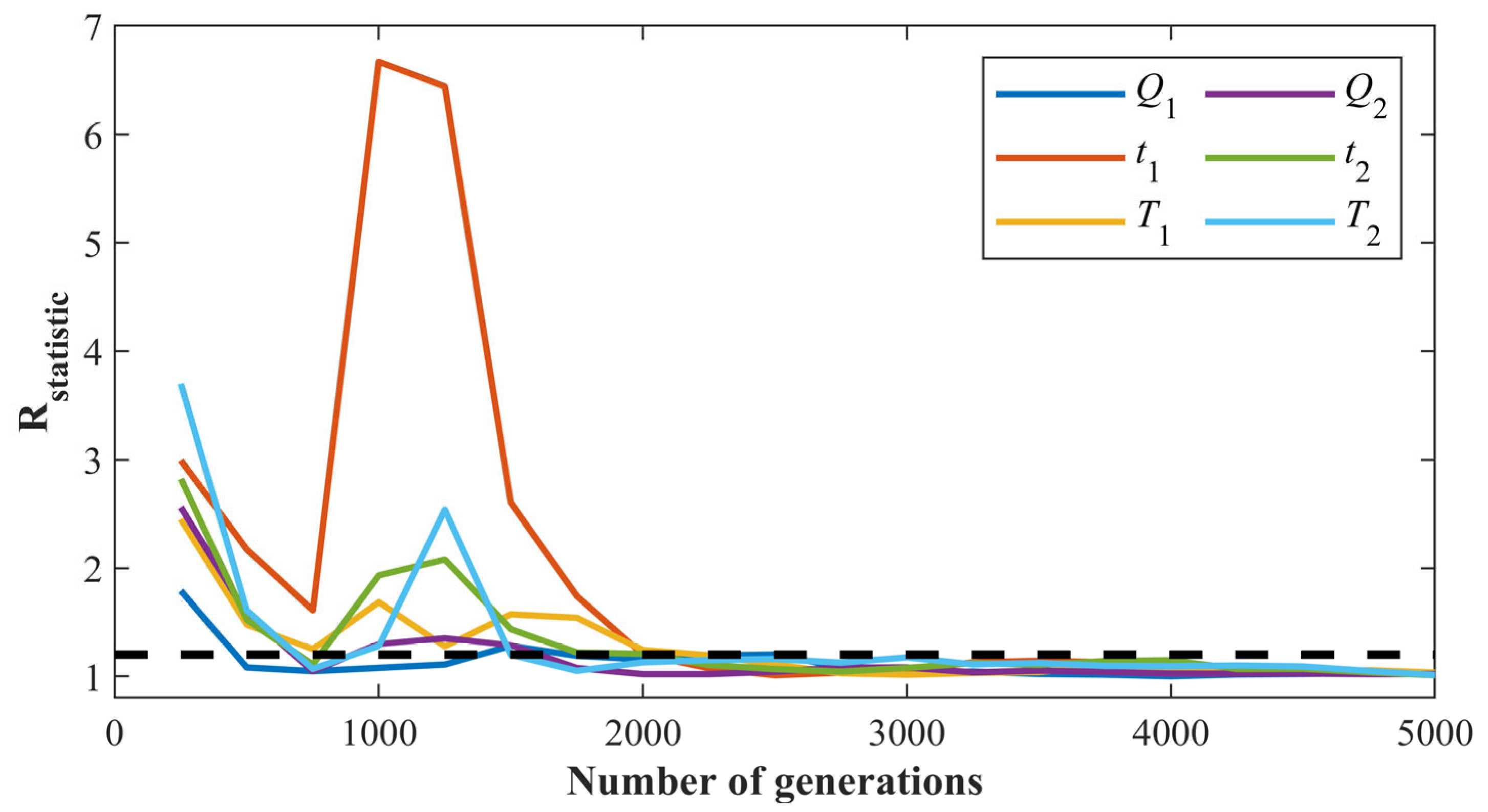
3.2.2. Real Case 2: Source Tracking of Multiple Sewage Discharges into the River
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez, S.; Lopez-Roldan, R.; Cortina, J.L. Presence and biological effects of emerging contaminants in Llobregat River basin: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Jiang, D.; Nan, J.; Zhu, W. An integrated data-driven framework for surface water quality anomaly detection and early warning. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmadja, J.; Bagtzoglou, A.C. State of the Art Report on Mathematical Methods for Groundwater Pollution Source Identification. Environ. Forensics 2001, 2, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghani, B.Y.; Mahinthakumar, K.G.; Tryby, M.E.; Ranjithan, R.S.; Zechman, E.M. A parallel evolutionary strategy based simulation–optimization approach for solving groundwater source identification problems. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Rani, R. A least-squares inversion technique for identification of a point release: Application to Fusion Field Trials 2007. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, M.T. A hybrid simulation–optimization approach for solving the areal groundwater pollution source identification problems. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, M.; Datta, B. Three-Dimensional Groundwater Contamination Source Identification Using Adaptive Simulated Annealing. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.P.; Jia, Y. Identification of contaminant point source in surface waters based on backward location probability density function method. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Huai, W.; Lu, X. Inversion of multiple parameters for river pollution accidents using emergency monitoring data. Water Env. Res. 2019, 91, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghane, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Mohammad Vali Samani, J. Location and release time identification of pollution point source in river networks based on the Backward Probability Method. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 180, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z. Development of a DREAM-based inverse model for multi-point source identification in river pollution incidents: Model testing and uncertainty analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Shao, D.; Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Ye, X. Multi-point source identification of sudden water pollution accidents in surface waters based on differential evolution and Metropolis–Hastings–Markov Chain Monte Carlo. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Noh, H.; Seo, I.; Jung, S.H.; Baek, D. Identification Framework of Contaminant Spill in Rivers Using Machine Learning with Breakthrough Curve Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-p.; Xin, X.-k. Pollutant source identification model for water pollution incidents in small straight rivers based on genetic algorithm. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1955–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Y. Inverse identification of pollution source release information for surface river chemical spills using a hybrid optimization model. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 113022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, S.; Mazaheri, M.; Samani, J.M.V. Introducing a general framework for pollution source identification in surface water resources (theory and application). J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 248, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.; Asif, Z. Identification of point source emission in river pollution incidents based on Bayesian inference and genetic algorithm: Inverse modeling, sensitivity, and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.P.; Chen, Y.S.; Wang, B.Y. Pollution Source Identification for River Chemical Spills by Modular-Bayesian Approach: A Retrospective Study on the ‘Landmark’ Spill Incident in China. Hydrology 2019, 6, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Diks, C.G.H.; Robinson, B.A.; Hyman, J.M.; Higdon, D. Accelerating Markov Chain Monte Carlo Simulation by Differential Evolution with Self-Adaptive Randomized Subspace Sampling. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2009, 10, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A. Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation using the DREAM software package: Theory, concepts, and MATLAB implementation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 273–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.L.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Wu, R.B.; Xu, Z.X. Identification of pollution sources in rivers using a hydrodynamic diffusion wave model and improved Bayesian-Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamiru, H.; Wagari, M. Machine-learning and HEC-RAS integrated models for flood inundation mapping in Baro River Basin, Ethiopia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 8, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshays, R.; Segovia, P.; Duviella, E. Design of a MATLAB HEC-RAS Interface to Test Advanced Control Strategies on Water Systems. Water 2021, 13, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.S.; Tang, Y.; Qin, L.; Chen, D. A MATLAB framework for forecasting optimal flow releases in a multi-storage system for flood control. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 125, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, A.S.; Goodell, C. Controlling HEC-RAS using MATLAB. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 84, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB; Version 9.5.0.944444 (R2018b); The Mathworks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018.
- HEC-RAS. Version 5.0, Hydrologic Engineering Center, US Army Corps of Engineers. Available online: https://www.hec.usace.army.mil/software/hec-ras/ (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- Lamichhane, N.; Sharma, S. Development of Flood Warning System and Flood Inundation Mapping Using Field Survey and LiDAR Data for the Grand River near the City of Painesville, Ohio. Hydrology 2017, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, N.; Sharma, S. Effect of input data in hydraulic modeling for flood warning systems. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 938–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Gupta, H.V.; Robinson, B.A. Equifinality of formal (DREAM) and informal (GLUE) Bayesian approaches in hydrologic modeling? Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2008, 23, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laloy, E.; Vrugt, J.A. High-dimensional posterior exploration of hydrologic models using multiple-try DREAM(ZS) and high-performance computing. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W01526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Ren, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, M. Identification of source information for sudden water pollution incidents in rivers and lakes based on variable-fidelity surrogate-DREAM optimization. Environ. Model. Softw. 2020, 133, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, J. Bayesian Methods: A Social and Behavioral Sciences Approach, 3rd ed.; Chapman Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, Y. Combined Bayesian statistics and load duration curve method for bacteria nonpoint source loading estimation. Water Res. 2010, 44, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braak, C.J.F.T. A Markov Chain Monte Carlo version of the genetic algorithm Differential Evolution: Easy Bayesian computing for real parameter spaces. Stat. Comput. 2006, 16, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from Iterative Simulation Using Multiple Sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.P.; Gelman, A. General methods for monitoring convergence of iterative simulations. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1998, 7, 434–455. [Google Scholar]

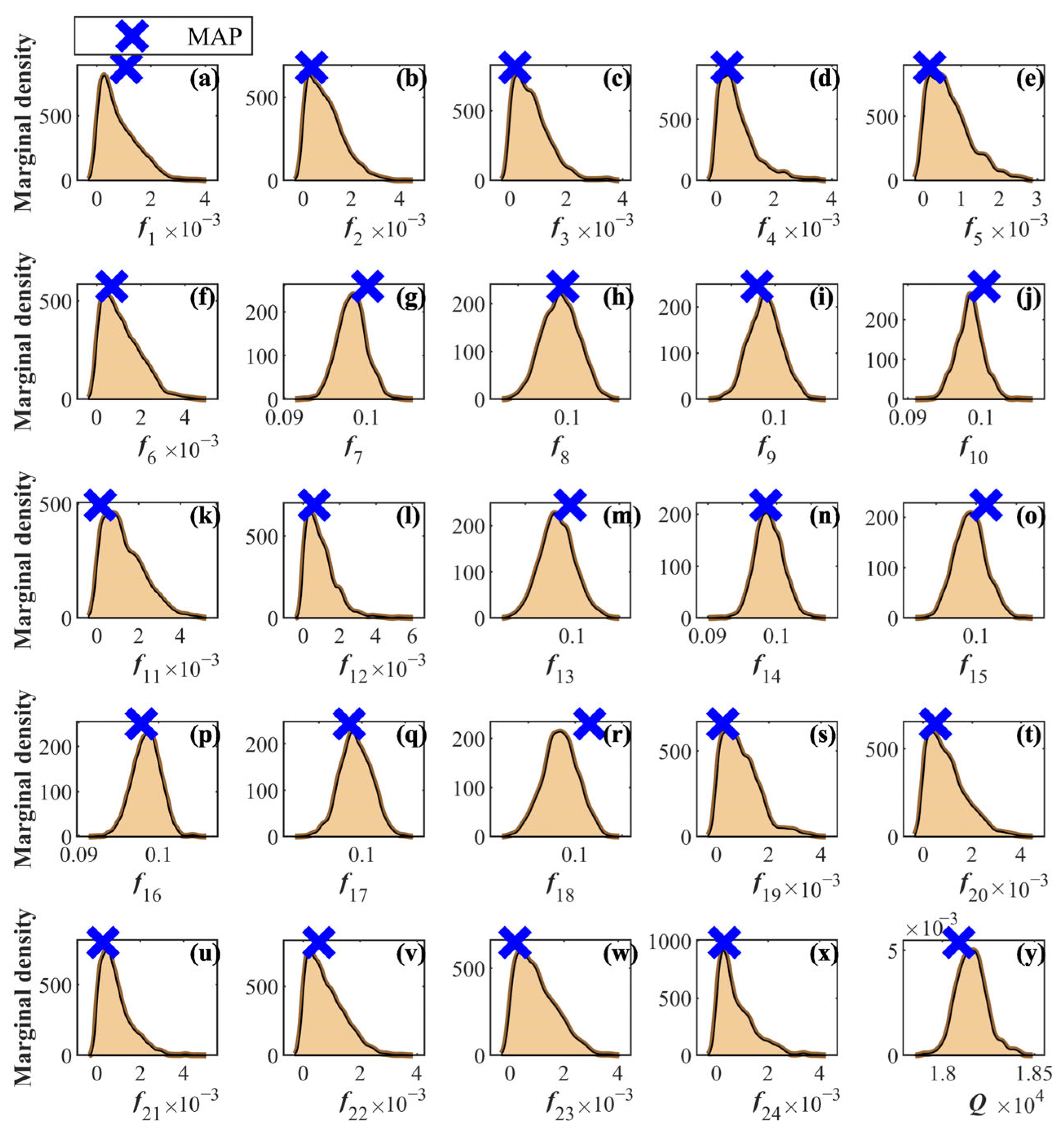

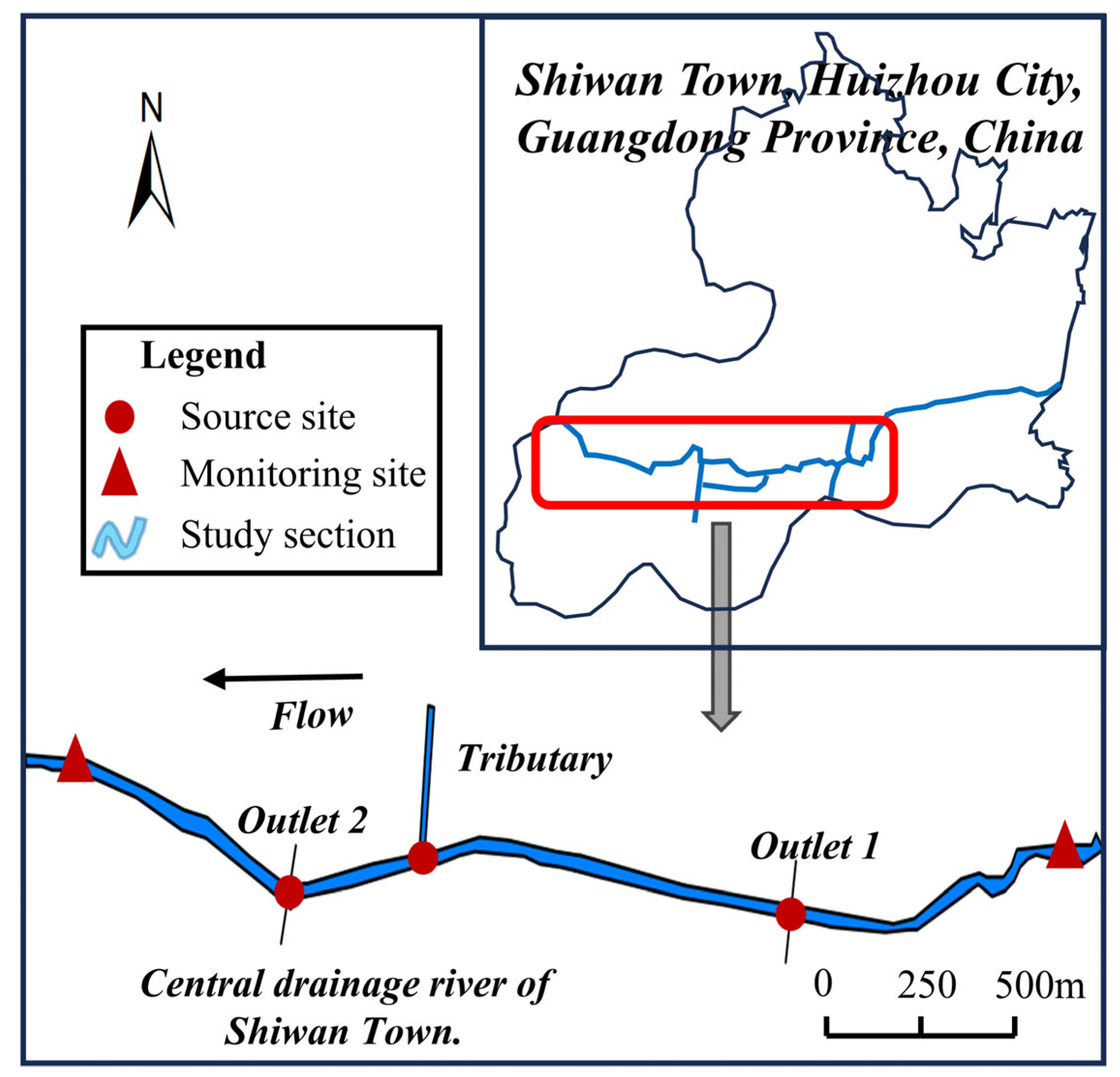
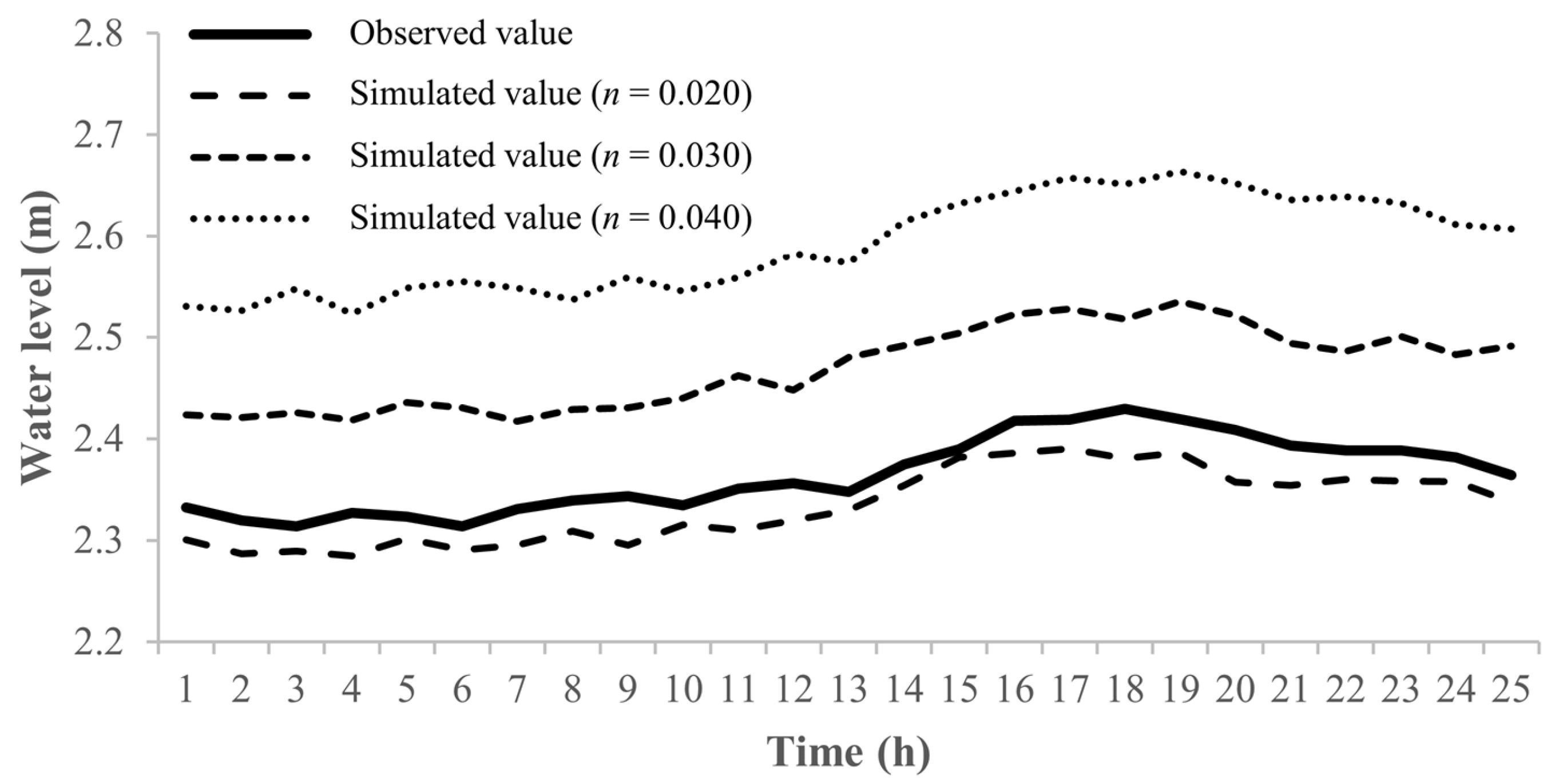

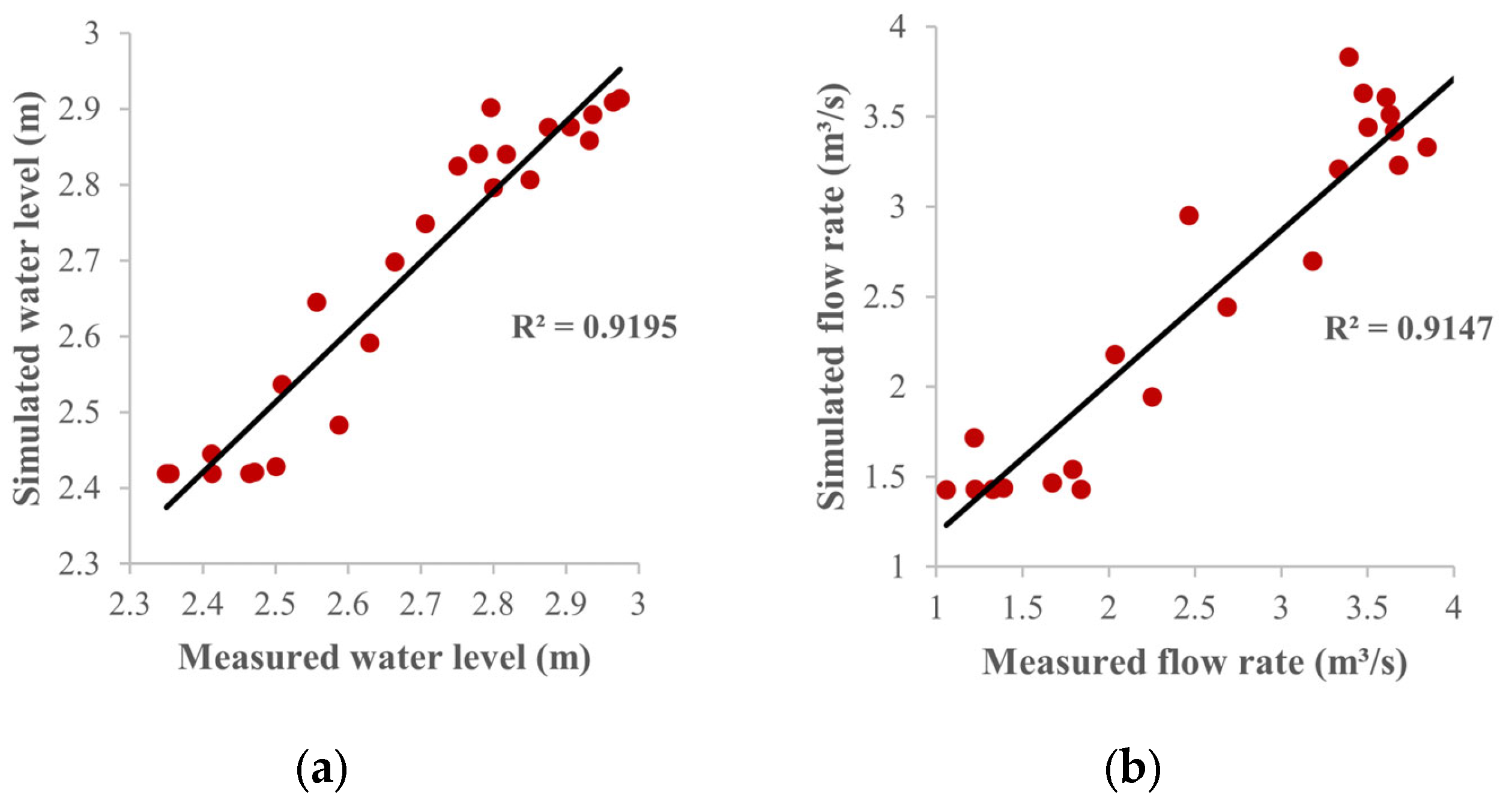
| Grid Size (m) | Computation Time (s) | R2 | RMSE | NSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 m | 18,020 | 0.986 | 0.001 | 0.985 |
| 200 m | 15,350 | 0.985 | 0.001 | 0.985 |
| R2 | RMSE | NSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water level | 0.960 | 0.012 | 0.959 |
| Flow Rate | 0.950 | 0.072 | 0.949 |
| (a) Dry weather | |||
| Dry weather | (m3/s) | (h) | (h) |
| Outlet 1 | 0.123 | 7 | 11 |
| Outlet 2 | 0.219 | 12 | 4 |
| Tributary | 0.292 | 0 | 24 |
| (b) Wet weather | |||
| Wet weather | (m3/s) | (h) | (h) |
| Outlet 1 | 0.254 | 6 | 12 |
| Outlet 2 | 0.330 | 7 | 10 |
| Tributary | 0.426 | 0 | 24 |
| (a) Dry weather | |||
| Dry weather | R2 | RMSE | NSE |
| Water level | 0.935 | 0.010 | 0.933 |
| Flow Rate | 0.930 | 0.043 | 0.924 |
| (b) Wet weather | |||
| Wet weather | R2 | RMSE | NSE |
| Water level | 0.920 | 0.057 | 0.919 |
| Flow Rate | 0.915 | 0.333 | 0.901 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, J.; Ju, M.; Jia, Z.; Su, L.; Wu, S.; Su, Y.; Liufu, W.; Yin, H. A Computational Tool to Track Sewage Flow Discharge into Rivers Based on Coupled HEC-RAS and DREAM. Water 2024, 16, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010051
Wen J, Ju M, Jia Z, Su L, Wu S, Su Y, Liufu W, Yin H. A Computational Tool to Track Sewage Flow Discharge into Rivers Based on Coupled HEC-RAS and DREAM. Water. 2024; 16(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Junbo, Mengdie Ju, Zichen Jia, Lei Su, Shanshan Wu, Yuting Su, Wenxiao Liufu, and Hailong Yin. 2024. "A Computational Tool to Track Sewage Flow Discharge into Rivers Based on Coupled HEC-RAS and DREAM" Water 16, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010051
APA StyleWen, J., Ju, M., Jia, Z., Su, L., Wu, S., Su, Y., Liufu, W., & Yin, H. (2024). A Computational Tool to Track Sewage Flow Discharge into Rivers Based on Coupled HEC-RAS and DREAM. Water, 16(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16010051





