Performance of Sand and Mixed Sand–Biochar Filters for Treatment of Road Runoff Quantity and Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
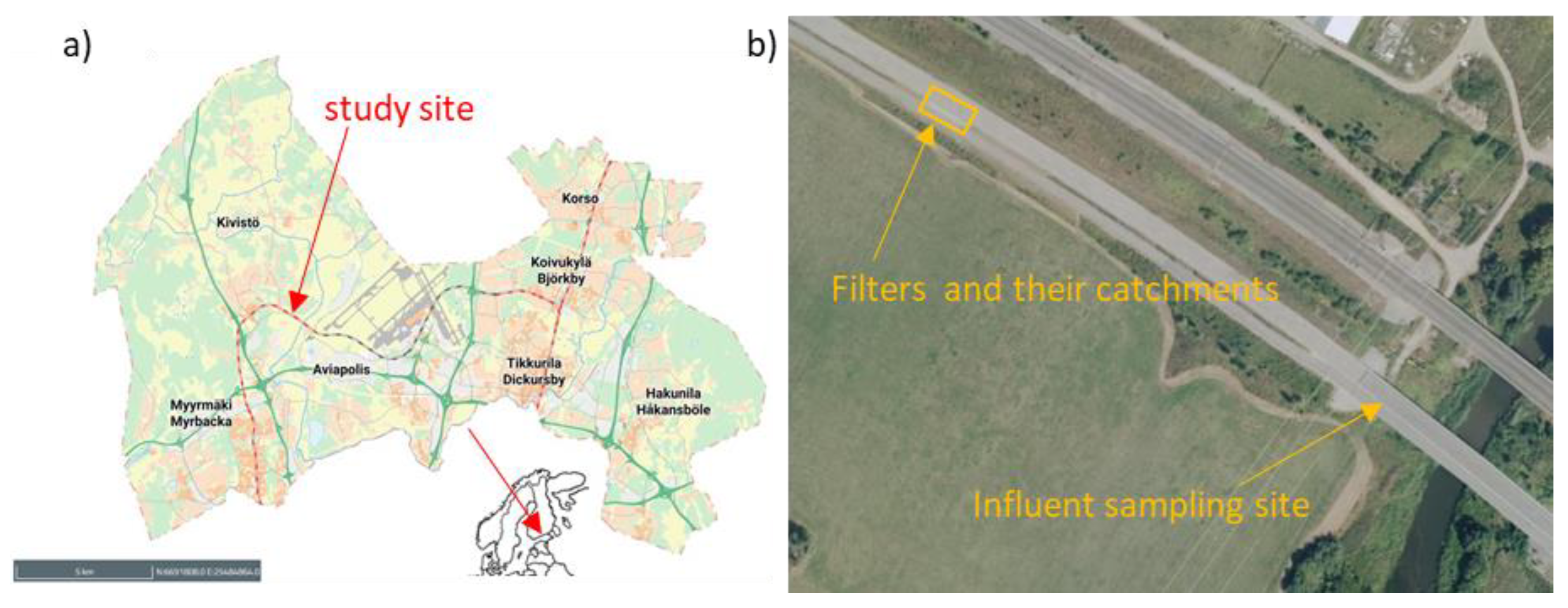
2.1. Site Description and Data
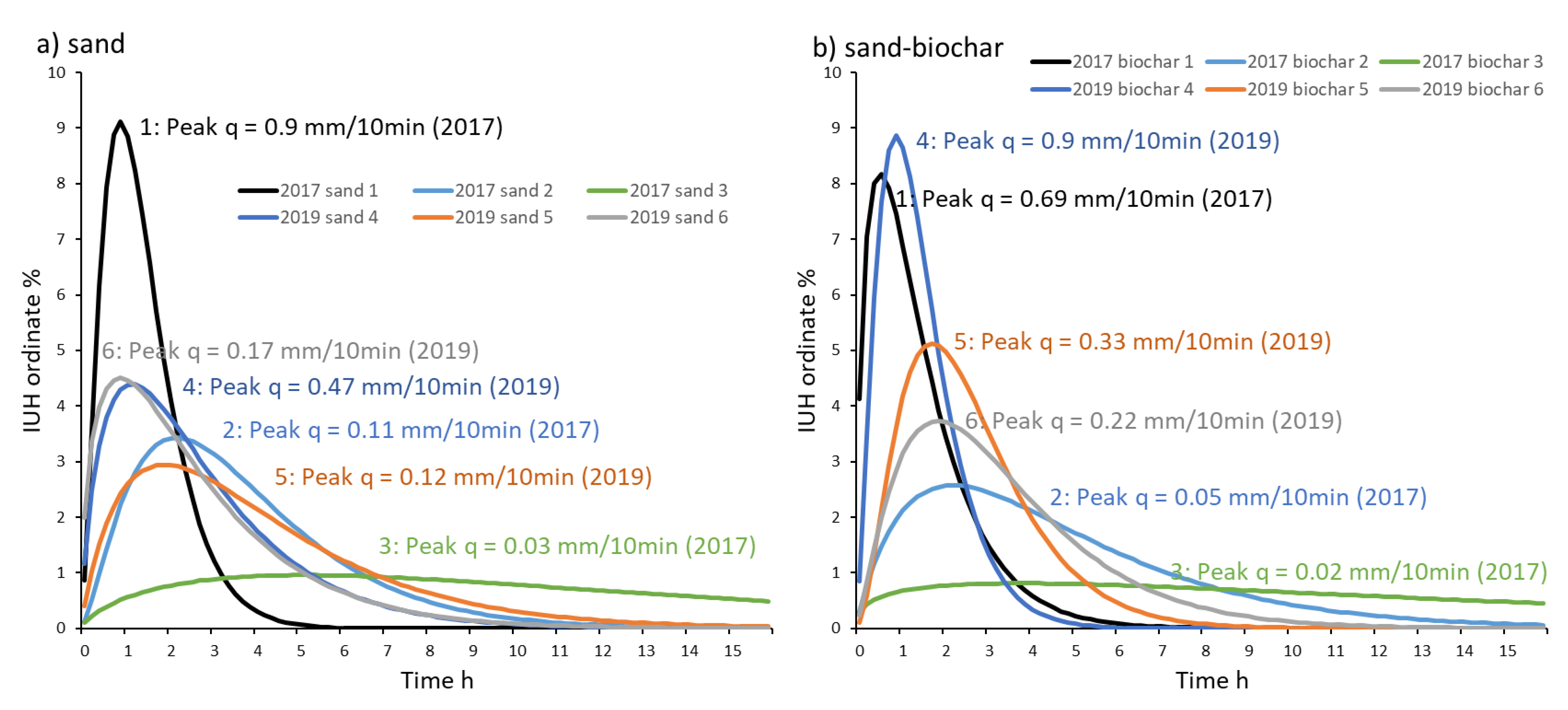
2.2. Hydrological Analyses
2.3. Analysis of Water Quality Data
3. Results
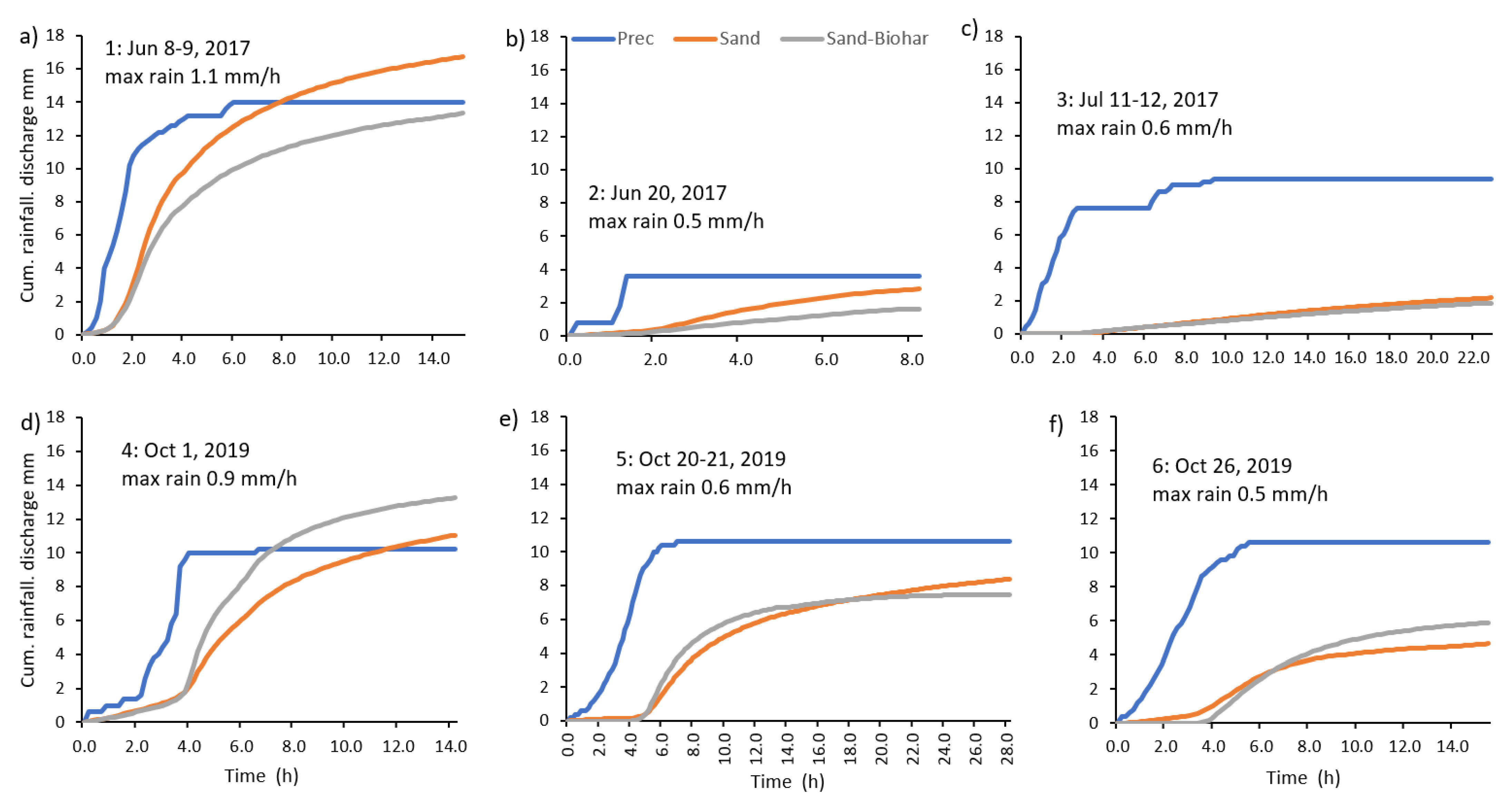
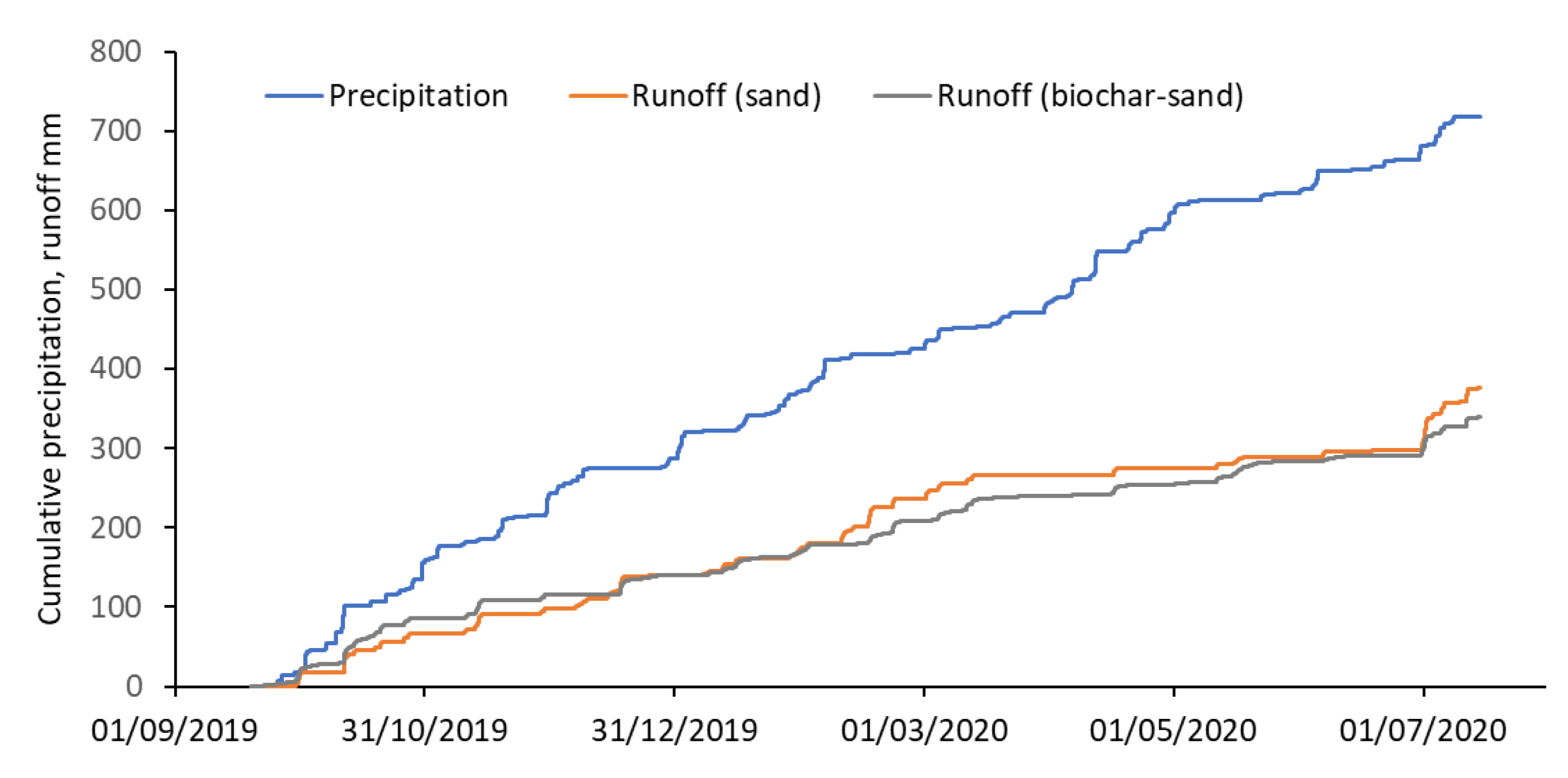
3.1. Discharge Response to Rainfalls
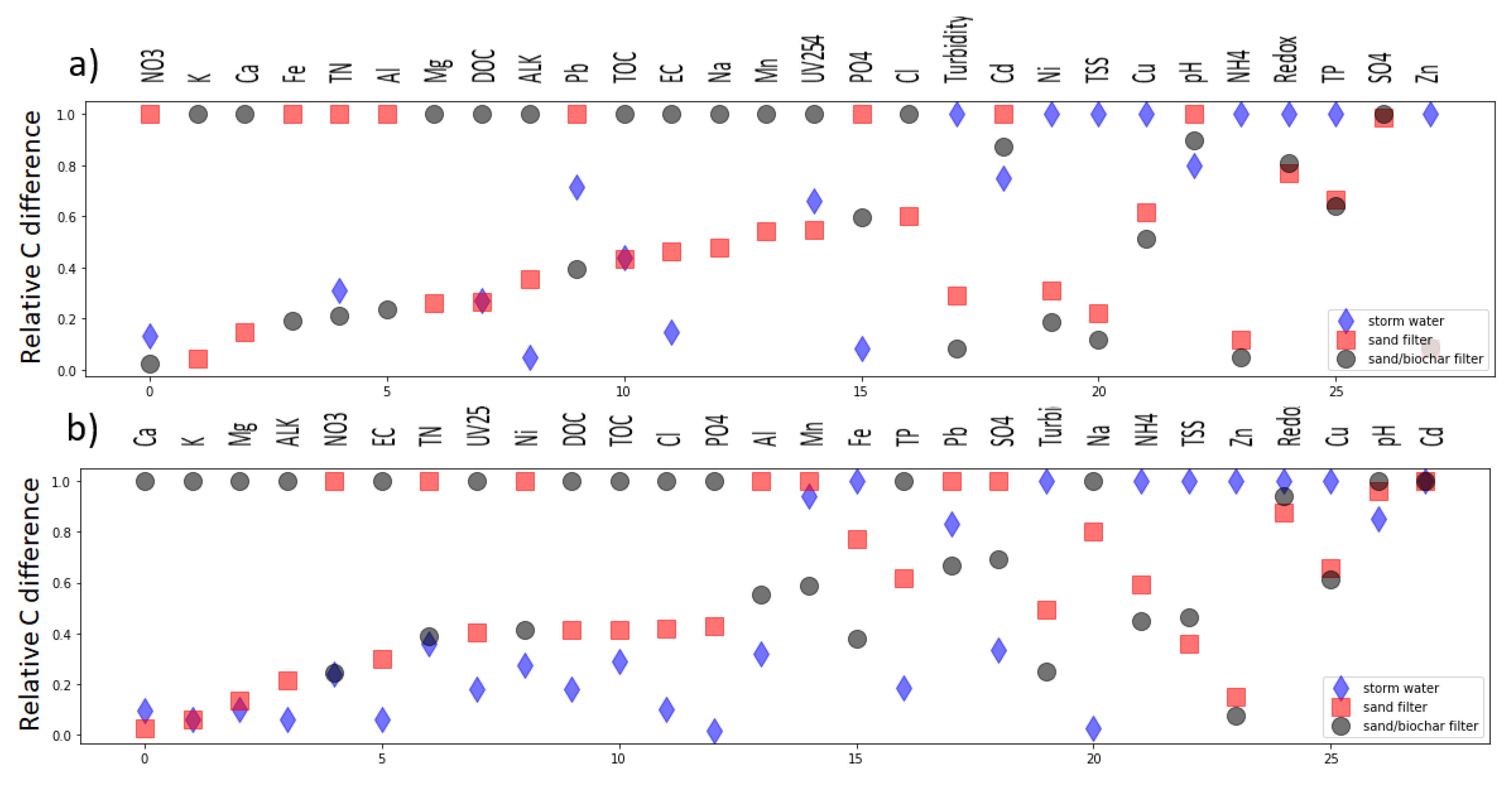
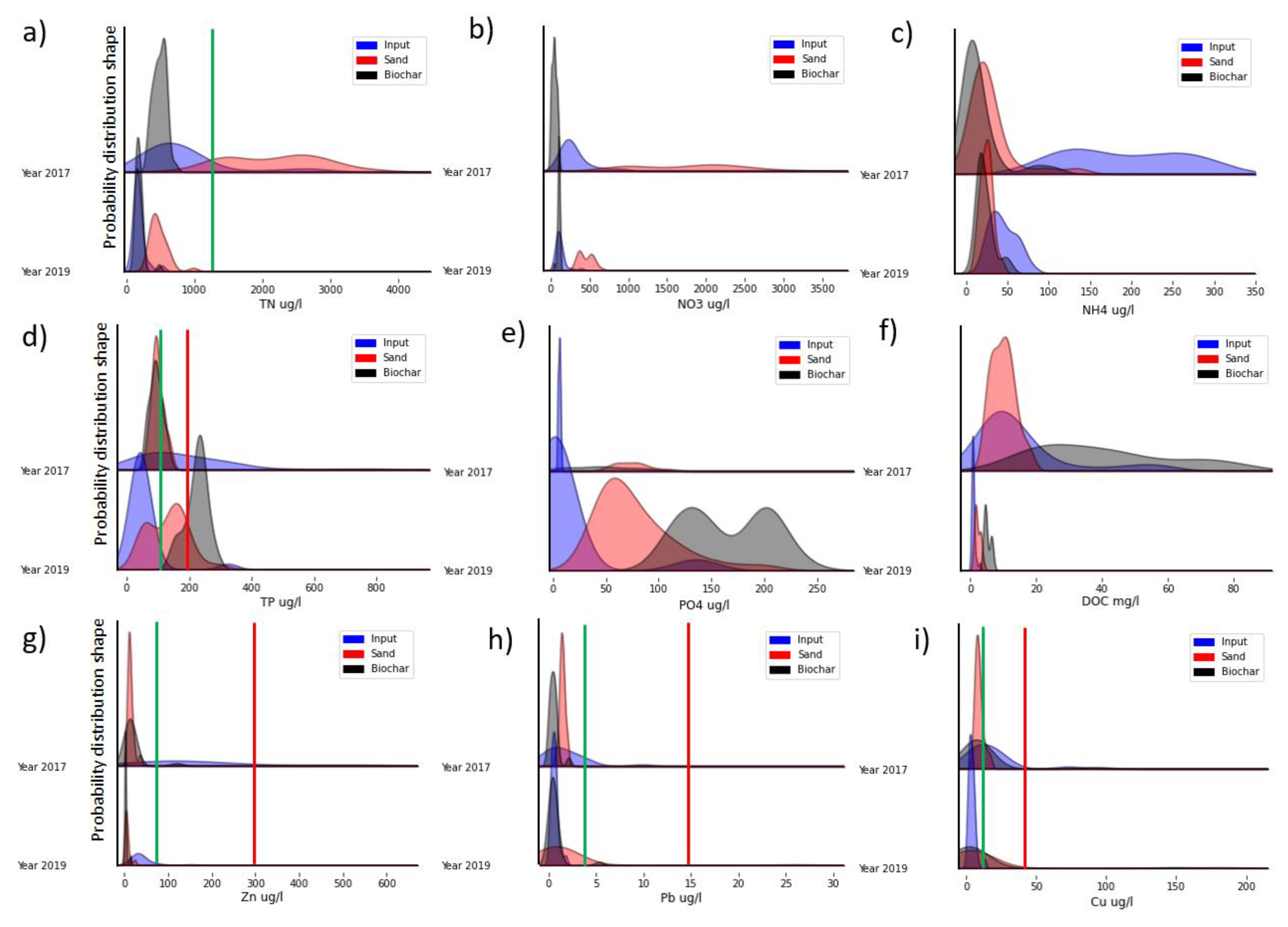
3.2. Discharge Water Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kõiv-Vainik, M.; Kill, K.; Espenberg, M.; Uuemaa, E.; Teemusk, A.; Maddison, M.; Palta, M.M.; Török, L.; Mander, Ü.; Scholz, M.; et al. Urban stormwater retention capacity of nature-based solutions at different climatic conditions. Nat.-Based Solut. 2022, 2, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, T.D.; Shuster, W.; Hunt, W.F.; Ashley, R.; Butler, D.; Arthur, S.; Trowsdale, S.; Barraud, S.; Semadeni-Davies, A.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; et al. SUDS, LID, BMPs, WSUD and more—The evolution and application of terminology surrounding urban drainage. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Sillanpää, N.; Koivusalo, H. Modeling and assessment of hydrological changes in a developing urban catchment. Hydrol. Proc. 2015, 29, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsalek, J.; Rochfort, Q.; Brownlee, B.; Mayer, T.; Servos, M. An exploratory study of urban runoff toxicity. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennino, M.J.; McDonald, R.I.; Jaffe, P.R. Watershed-scale impacts of stormwater green infrastructure on hydrology, nutrient fluxes, and combined sewer overflows in the mid-Atlantic region. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedan, E.S.; Clausen, J.C. Stormwater runoff quality and quantity from traditional and low impact development watersheds. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, K.G.; Loperfido, J.V.; Craig, L.S.; Noe, G.B.; Hogan, D.M. Comparison of sediment and nutrient export and runoff characteristics from watersheds with centralized versus distributed stormwater management. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Winston, R.J.; Wituszynski, D.M.; Tirpak, R.A.; Boening-Ulman, K.M.; Martin, J.F. Effects of watershed-scale green infrastructure retrofits on urban stormwater quality: A paired watershed study to quantify nutrient and sediment removal. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 186, 106835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagge, J.H.; Davis, A.P.; Jamil, E.; Kim, H. Performance of grass swales for improving water quality from highway runoff. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6731–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lähde, E.; Khadka, A.; Tahvonen, O.; Kokkonen, T. Can We Really Have It All?—Designing Multifunctionality with Sustainable Urban Drainage System Elements. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, H.; Myers, B.; Boland, J.; Hewa, G.; Johnson, T. Stormwater runoff reduction benefits of distributed curbside infiltration devices in an urban catchment. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Guntu, R.K.; Agarwal, A.; Villuri, V.G.K.; Pasupuleti, S.; Kaushal, D.R.; Gosian, A.K.; Bronstert, A. Multi-objective optimization for stormwater management by green-roofs and infiltration trenches to reduce urban flooding in central Delhi. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendling, L.; Loimula, K.; Korkealaakso, J.; Kuosa, H.; Iitti, H.; Holt, E. StormFilter Material Testing Summary Report—Performance of Stormwater Filtration Systems. Research Report VTT-R-05980-17. 2017. Available online: https://cris.vtt.fi/ws/files/20239863/VTT_R_05980_17.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Li, C.; Widlak, R.; Zalewski, M. Stormwater Gravel-Peat Infiltration Filter—An Ecohydrological Technology with Good Urban Design. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, A.S.; Fu, G.Y.; Yunus, A.I. Treatment of highway stormwater runoff using sustainable biochar: A review. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 149, 03122005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Tsen-Tieng, D.L.; Balasubramanian, R. Biochar-based bioretention systems for removal of chemical and microbial pollutants from stormwater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Farooq, M.; Nawaz, A.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Solaiman, Z.M.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Ammara, U.; Ok, Y.S.; Siddique, K.H.M. Biochar for crop production: Potential benefits and risks. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 685–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Y.; Huang, G. Hydrology and rainfall runoff pollutant removal performance of biochar-amended bioretention facilities based on field-scale experiments in lateritic red soil regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 143252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Boguta, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: Pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blecken, G.-T.; Zinger, Y.; Deletić, A.; Fletcher, T.D.; Viklander, M. Influence of intermittent wetting and drying conditions on heavy metal removal by stormwater biofilters. Water Res. 2009, 43, 4590–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D. Water Quality Improvement through Bioretention: Lead, Copper, and Zinc Removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Treatment Performance of Gravel Filter Media: Implications for Design and Application of Stormwater Infiltration Systems. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Hydraulic and pollutant removal performance of fine media stormwater filtration systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ameri, M.; Hatt, B.; Le Coustumer, S.; Fletcher, T.; Payne, E.; Deletic, A. Accumulation of heavy metals in stormwater bioretention media: A field study of temporal and spatial variation. J. Hydrol. 2018, 567, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A. Hydrologic and pollutant removal performance of stormwater biofiltration systems at the field scale. J. Hydrol. 2009, 365, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Deletic, A.; McCarthy, D.T.; Hatt, B.E.; Payne, E.G.I.; Chandrasena, G.; Li, Y.; Pham, T.; Jamali, B.; et al. The impact of stormwater biofilter design and operational variables on nutrient removal-a statistical modelling approach. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrooz, A.N.; Boehm, A.B. Effects of submerged zone, media aging, and antecedent dry period on the performance of biochar-amended biofilters in removing fecal indicators and nutrients from natural stormwater. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 102, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Deletic, A.; McCarthy, D.T. Copper-zeolite integrated stormwater biofilter for nutrient removal–the impact of intermittent wetting and drying conditions. Blue-Green Syst. 2020, 2, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, G.; Gelardi, D.L.; Huang, L.; Khan, E.; Mašek, O.; Parikh, S.J.; Ok, Y.S. Evaluating biochar and its modifications for the removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate in water. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segismundo, E.Q.; Kim, L.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, B.S. A laboratory study on the filtration and clogging of the sand-bottom ash mixture for stormwater infiltration filter media. Water 2017, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, E.G.; Pham, T.; Cook, P.L.; Fletcher, T.D.; Hatt, B.E.; Deletic, A. Biofilter design for effective nitrogen removal from stormwater–influence of plant species, inflow hydrology and use of a saturated zone. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Zimmerman, A.R. Organic carbon and nutrient release from a range of laboratory-produced biochars and biochar–soil mixtures. Geoderma. 2013, 193, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Drake, J.; Thomas, S.C. Biochar granulation, particle size, and vegetation effects on leachate water quality from a green roof substrate. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 318, 115506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuoppamäki, K.; Lehvävirta, S. Mitigating nutrient leaching from green roofs with biochar. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 152, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, S.H.; Stinshoff, P.; Helmreich, B. Sequential extraction of heavy metals from sorptive filter media and sediments trapped in stormwater quality improvement devices for road runoff. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuoppamäki, K.; Hagner, M.; Valtanen, M.; Setälä, H. Using biochar to purify runoff in road verges of urbanised watersheds: A large-scale field lysimeter study. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2019, 1, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.S.; Davis, A.P. Spatial accumulation and strength of affiliation of heavy metals in bioretention media. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmuth, E.; Sillanpää, N.; Wendling, L.; Koivusalo, H. Impact of Biochar on Treatment Performance of Roadside Sand Filters—Field Monitoring and Geochemical Modelling. In Proceedings of the New Trends in Urban Drainage Modelling, the 11th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling, UDM 2018, Palermo, Italy, 23–26 September 2018; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Assmuth, E. Performance of Roadside Filtration Systems in the Treatment of Stormwater. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University School of Engineering, Espoo, Finland, 5 February 2018. Available online: https://aaltodoc.aalto.fi/handle/123456789/30076 (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Kokkonen, T.; Koivusalo, H.; Karvonen, T.; Croke, B.; Jakeman, A. Exploring streamflow response to effective rainfall across event magnitude, temporal and spatial scales. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1467–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, N.; Koivusalo, H. Urban development impacts on runoff event characteristics and unit hydrographs across warm and cold seasons in high latitudes. J. Hydrol. 2015, 521, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, V. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall–runoff models. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1015–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, C.; Viklander, M.; Bäckström, M. Seasonal variations in road runoff quality in Luleå, Sweden. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockholm Vatten, A.B. Klassificering Av Dagvatten Och Recipienter Samt Riktlinjer För reningskrav- del 2, Dagvattenklassificering. 2001. Available online: https://www.stockholmvattenochavfall.se/globalassets/pdfer/rapporter/dagvatten/dagvattenklassificeringdel2.pdf (accessed on 11 January 2023). (In Swedish).
- Jeon, M.; Guerra, H.B.; Choi, H.; Kim, L.-H. Long-Term Monitoring of an Urban Stormwater Infiltration Trench in South Korea with Assessment Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Water 2022, 14, 3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, D.; Croft, K.; Pamuru, S.T.; Yuan, C.; Davis, A.P.; Kjellerup, B.V. Considerations for evaluating innovative stormwater treatment media for removal of dissolved contaminants of concern with focus on biochar. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtanen, M.; Sillanpää, N.; Setälä, H. The effects of urbanization on runoff pollutant concentrations, loadings and their seasonal patterns under cold climate. Wat. Air Soil Poll. 2014, 225, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, N. Effects of Suburban Development on Runoff Generation and Water Quality. Doctoral Dissertation, Aalto University Publication Series, Espoo, Finland, 2013; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Taka, M.; Sillanpää, N.; Niemi, T.; Warsta, L.; Kokkonen, T.; Setälä, H. Heavy metals from heavy land use? Spatio-temporal patterns of urban runoff metal loads. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.B.; Revitt, D.M.; Llewellyn, N. Transport and the environment: Effects of organic pollutants on water quality. Water Environ. J. 1997, 11, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
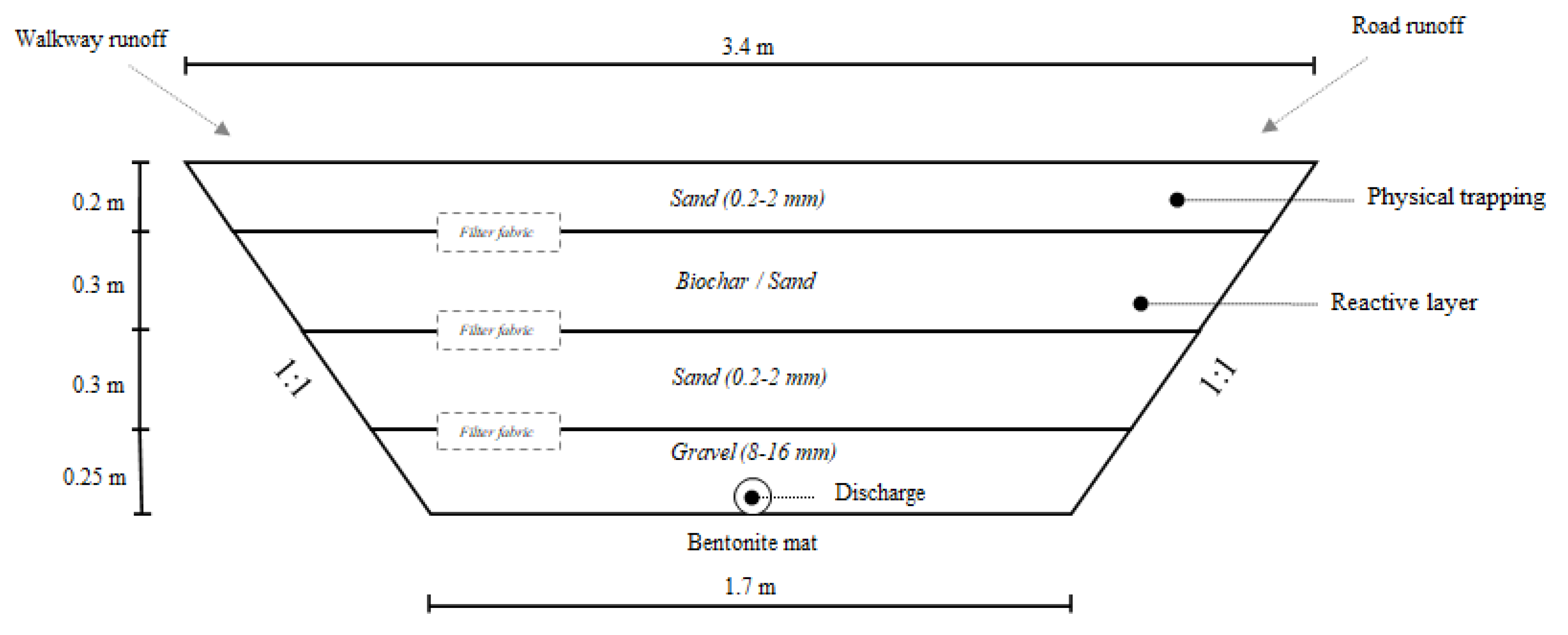

| Depth from Surface [m] | Sand Filter | Sand–Biochar Filter |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0.2 | Sand 0.2–2 mm | Sand 0.2–2 mm |
| 0.2 | Filter fabric | |
| 0.2–0.5 | Sand 0.2–2 mm | Birch biochar |
| 0.5 | Filter fabric | |
| 0.5–0.8 | Sand 0.2–2 mm | Sand 0.2–2 mm |
| 0.8 | Filter fabric | Filter fabric |
| 0.8–1.25 | Gravel 8–16 mm | Gravel 8–16 mm |
| 1.25 | Bentonite mat | Bentonite mat |
| 1.25–1.4 | Sub-Base KaM 0–32 mm | Sub-Base KaM 0–32 mm |
| Variable (xa-ya-za, xb-yb-zb) | Variable (xa-ya-za, xb-yb-zb) |
|---|---|
| Total N (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Cd (17-18-16, 30-30-25) |
| NH4 (26-36-16, 30-30-25) | Cu (17-18-16, 30-30-25) |
| NO3 (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Pb (17-18-16, 30-30-25) |
| TP (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Ni (17-18-16, 30-30-25) |
| PO4 (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Zn (17-18-16, 30-30-25) |
| TOC (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Mn (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| DOC (26-26-44, 30-30-25) | Si (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| Alkalinity (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Fe (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| Electrical cond. (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Ca (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| Turbidity (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Mg (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| TSS (38-40-44, 20-20-20) | K (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| UV absorbance (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Al (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| Redox pot. (38-40-44, 30-30-25) | Cl (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| SO4 (4-4-0, 30-30-25) | Na (4-4-0, 30-30-25) |
| Sand | Biochar | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event | α | β | tm (h) | Event | α | β | tm (h) |
| 1 | 2.68 | 0.53 | 1.43 | 4 | 2.65 | 0.55 | 1.47 |
| 6 | 1.51 | 1.78 | 2.68 | 1 | 1.59 | 0.92 | 1.47 |
| 4 | 1.74 | 1.58 | 2.75 | 5 | 3.00 | 0.88 | 2.64 |
| 2 | 2.46 | 1.52 | 3.73 | 6 | 2.29 | 1.47 | 3.37 |
| 5 | 1.88 | 2.19 | 4.13 | 2 | 1.90 | 2.49 | 4.73 |
| 3 | 1.69 | 7.42 | 12.56 | 3 | 1.33 | 11.39 | 15.21 |
| Sand Filter | Biochar Filter | Influent | High Density | Low Density | Developing Area | |
| TP 2017 | 44 | 38 | 126 | 36–108 | 7–40 | 50–115 |
| TP 2019 | 66 | 96 | 38 | |||
| TN 2017 | 1046 | 200 | 620 | 230–1300 | 180–800 | 1400–6000 |
| TN 2019 | 205 | 71 | 140 | |||
| TSS 2017 | 13 | 6 | 113 | 22–58 | 2–17 | 41–72 |
| TSS 2019 | 4 | 5 | 24 | |||
| Cu 2017 | 4.1 | 3.1 | 12.7 | 2.8–14.5 | 0.9–2.7 | |
| Cu 2019 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 3.1 | |||
| Zn 2017 | 6 | 5 | 127 | 12–60 | 2–14 | |
| Zn 2019 | 2 | 1 | 30 | |||
| Pb 2017 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.4–2.4 | 0.1–0.5 | |
| Pb 2019 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koivusalo, H.; Dubovik, M.; Wendling, L.; Assmuth, E.; Sillanpää, N.; Kokkonen, T. Performance of Sand and Mixed Sand–Biochar Filters for Treatment of Road Runoff Quantity and Quality. Water 2023, 15, 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081631
Koivusalo H, Dubovik M, Wendling L, Assmuth E, Sillanpää N, Kokkonen T. Performance of Sand and Mixed Sand–Biochar Filters for Treatment of Road Runoff Quantity and Quality. Water. 2023; 15(8):1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081631
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoivusalo, Harri, Maria Dubovik, Laura Wendling, Eero Assmuth, Nora Sillanpää, and Teemu Kokkonen. 2023. "Performance of Sand and Mixed Sand–Biochar Filters for Treatment of Road Runoff Quantity and Quality" Water 15, no. 8: 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081631
APA StyleKoivusalo, H., Dubovik, M., Wendling, L., Assmuth, E., Sillanpää, N., & Kokkonen, T. (2023). Performance of Sand and Mixed Sand–Biochar Filters for Treatment of Road Runoff Quantity and Quality. Water, 15(8), 1631. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081631









