Tuning the Optical Properties of ZnO by Co and Gd Doping for Water Pollutant Elimination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
3.3. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer
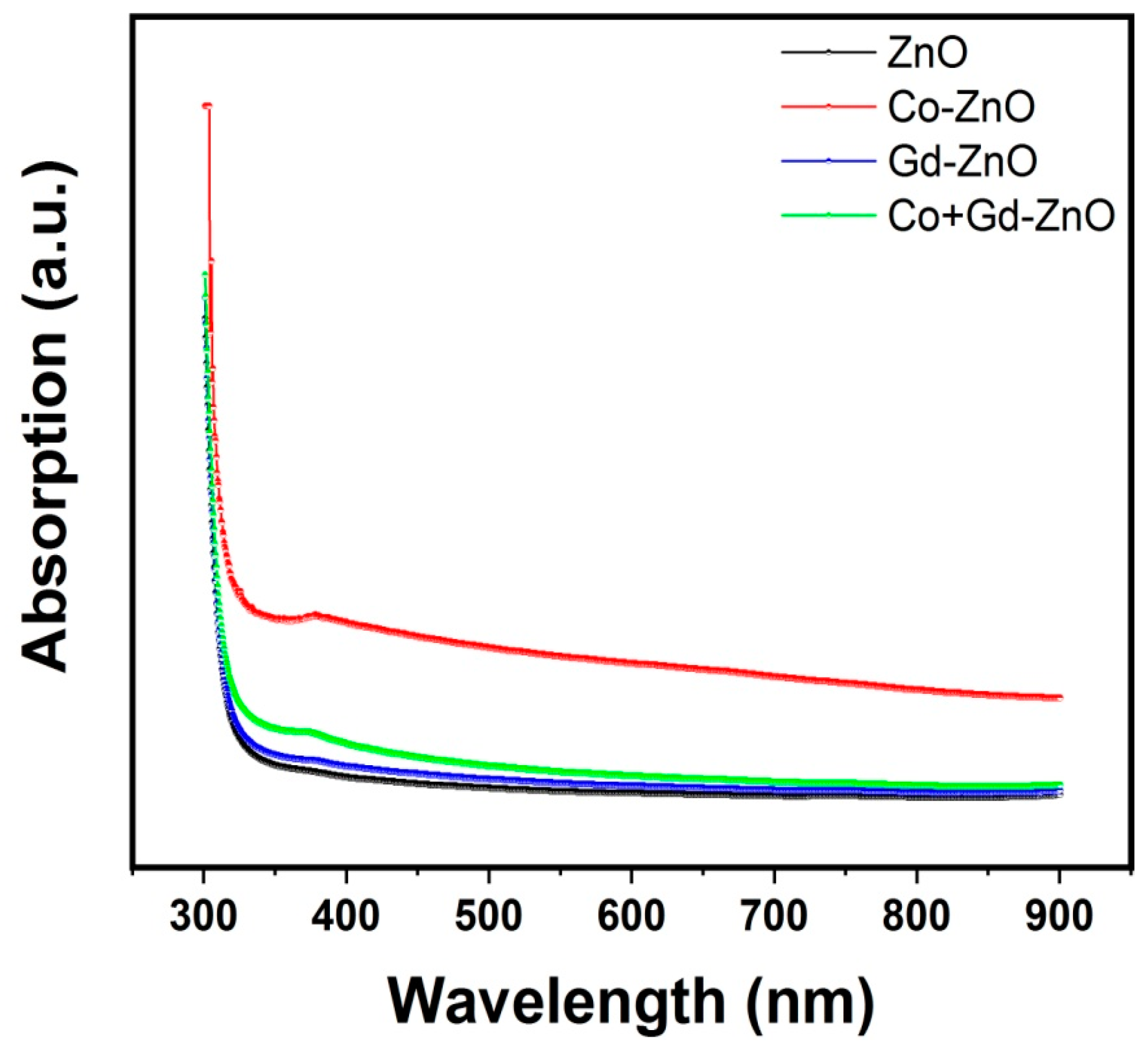
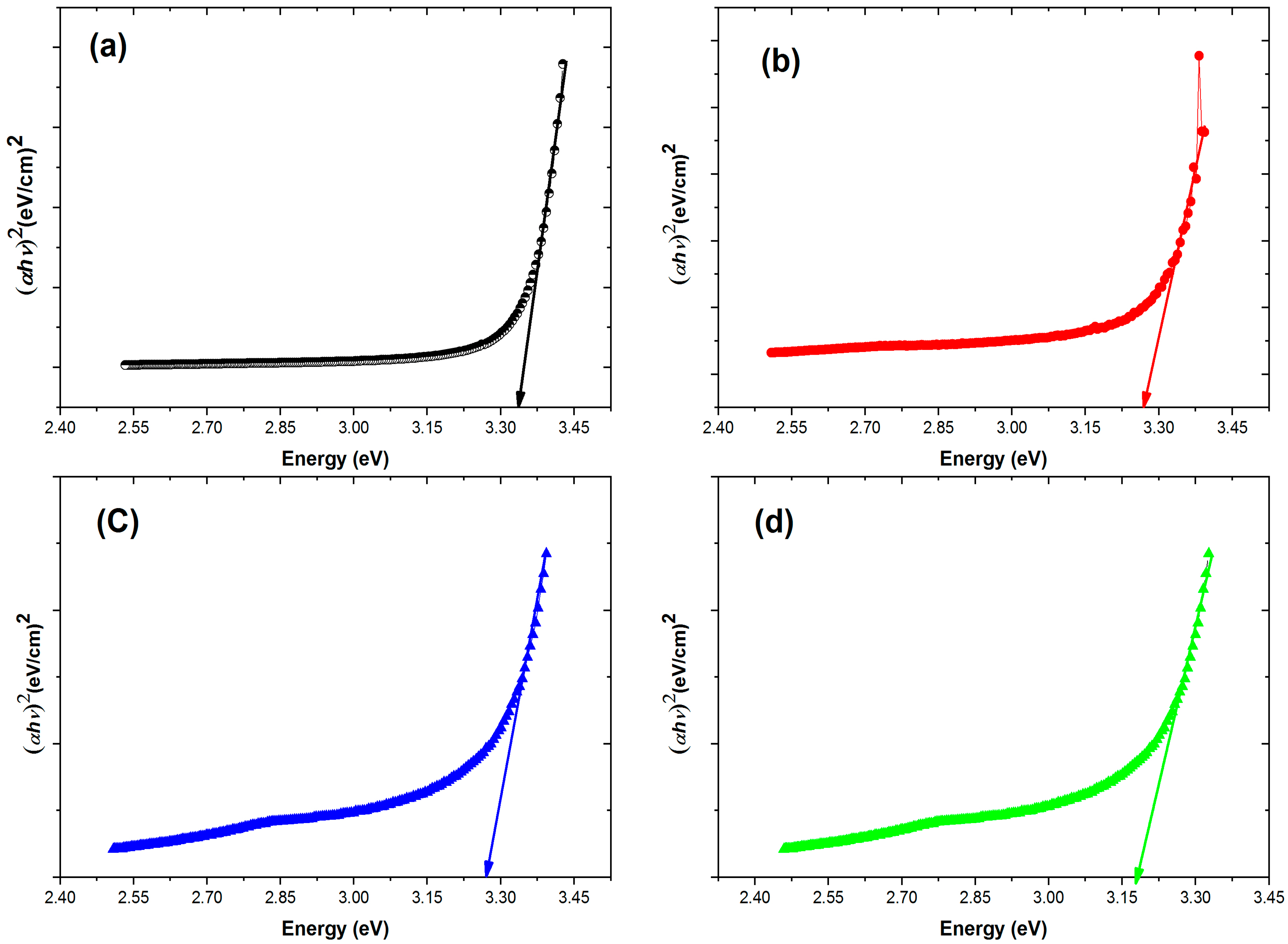
3.4. Optical Properties
3.5. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy
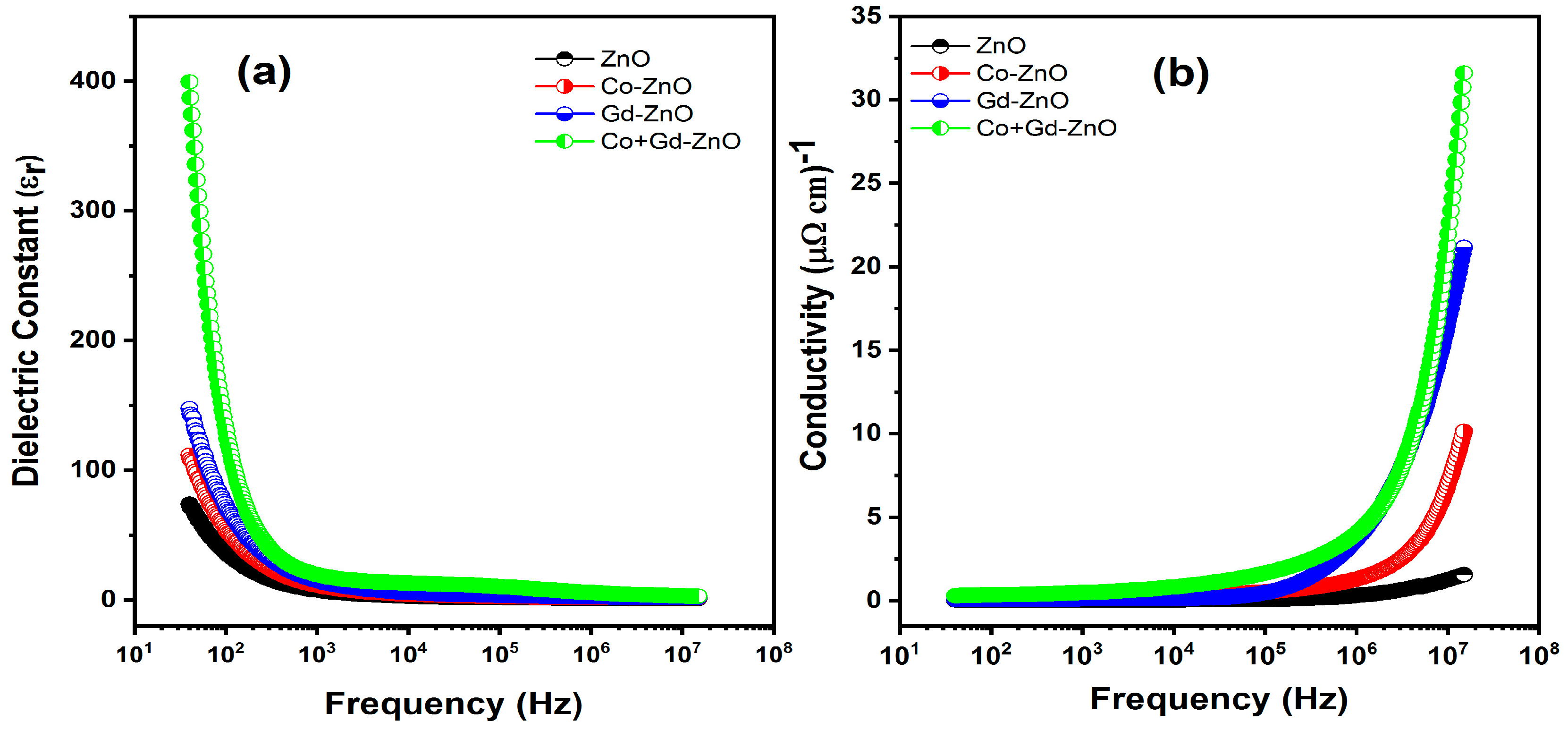
3.6. Electrical Properties
3.6.1. Dielectric Properties
3.6.2. Electrical Conductivity
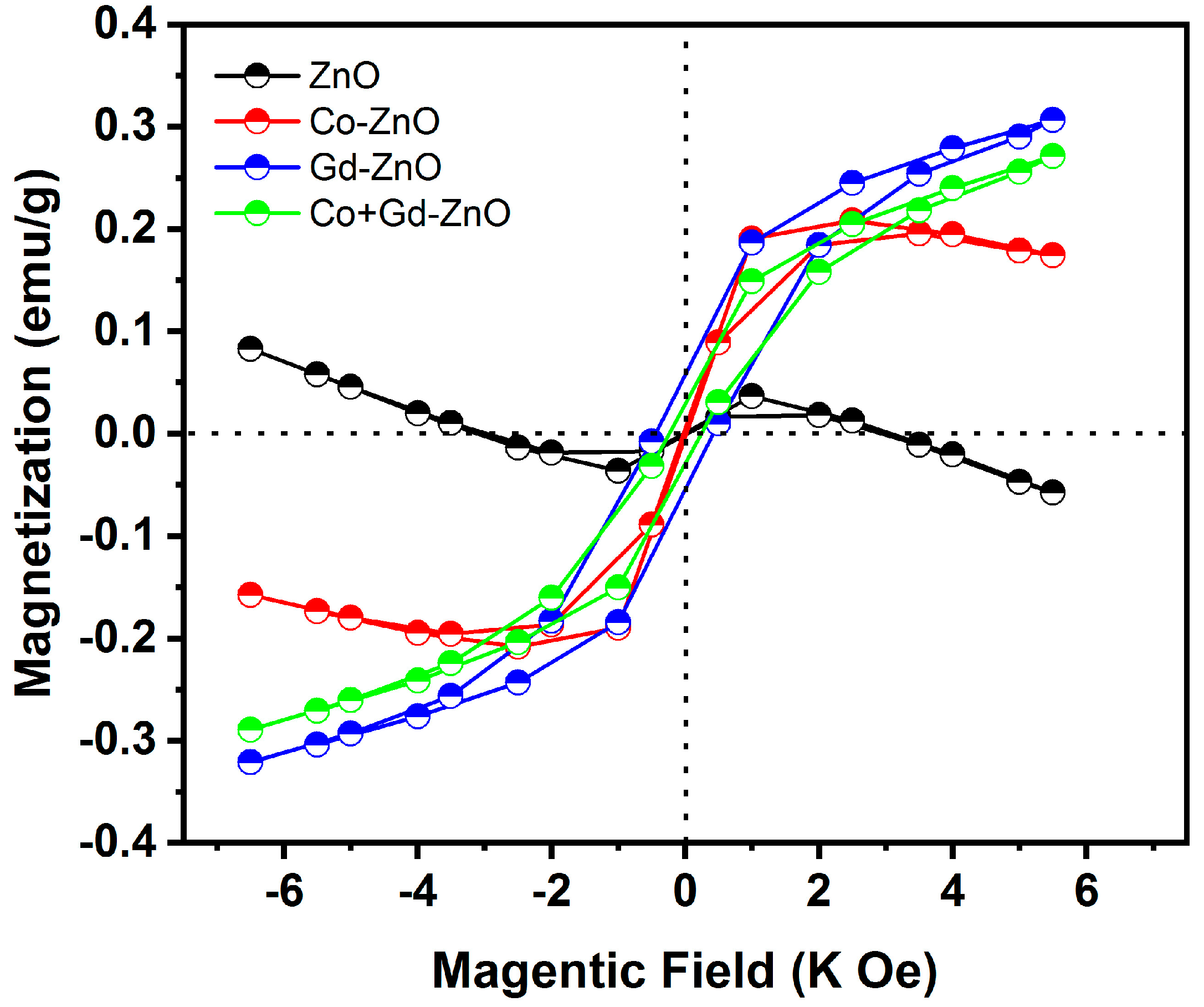
3.7. Magnetic Properties
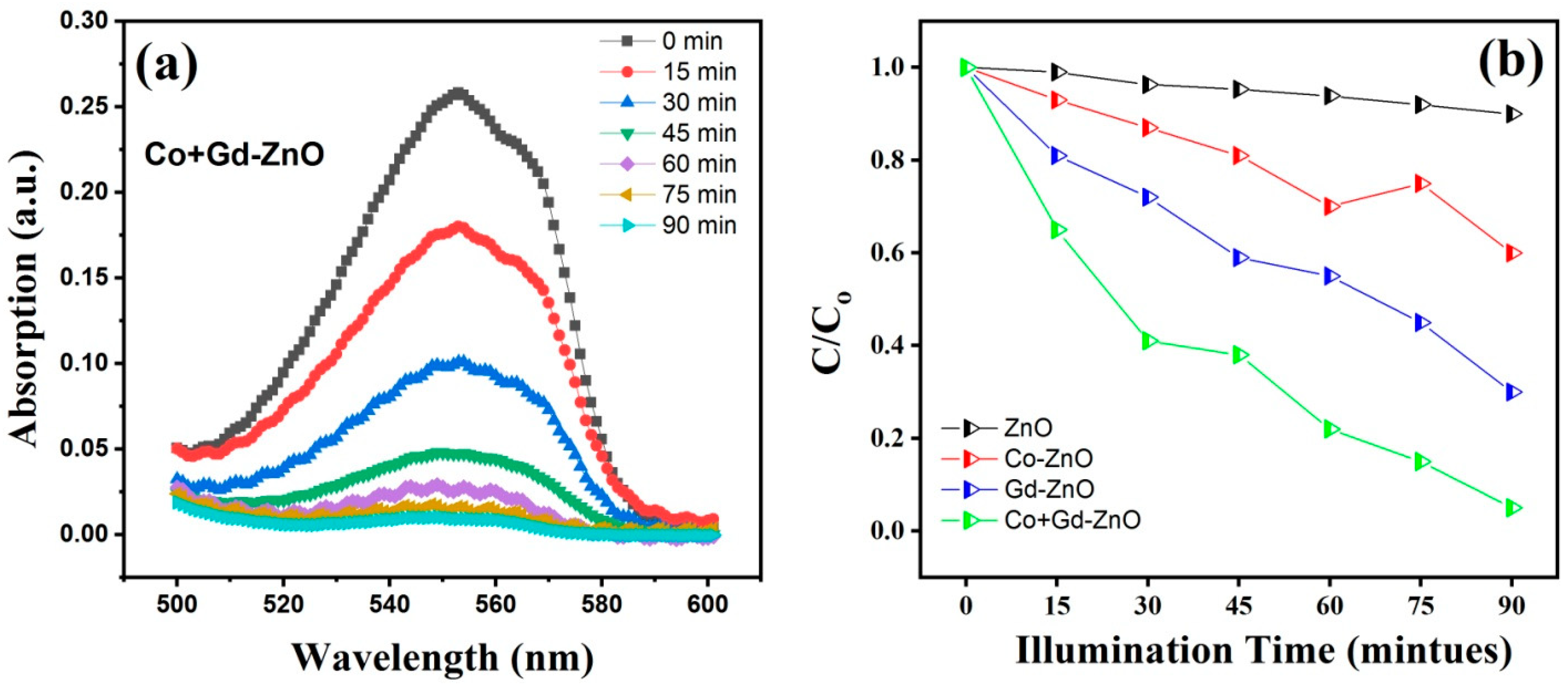
3.8. Photocatalytic Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tao, X.; Liu, D.; Cong, W.; Huang, L. Controllable synthesis of starch-modified ZnMgAl-LDHs for adsorption property improvement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, M.; Afyaz, S.; Khalid, A.; Ahmad, P.; Khandaker, M.U.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, J.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Emran, T.B. Synthesis of cobalt and sulphur doped titanium dioxide photocatalysts for environmental applications. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annu, A.A.; Ahmed, S. Green synthesis of metal, metal oxide nanoparticles, and their various applications. Handb. Ecomater. 2018, 2018, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Almoussawi, M.; Abdallah, A.; Habanjar, K.; Awad, R. Effect of (Sm, Co) co-doping on the structure and electrical conductivity of ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 105011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherbi, B.; Laouini, S.E.; Meneceur, S.; Bouafia, A.; Hemmami, H.; Tedjani, M.L.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Barhoum, A.; Menaa, F. Effect of pH value on the bandgap energy and particles size for biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Efficiency for photocatalytic adsorption of methyl orange. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hezam, A.; Drmosh, Q.; Ponnamma, D.; Bajiri, M.A.; Qamar, M.; Namratha, K.; Zare, M.; Nayan, M.; Onaizi, S.A.; Byrappa, K. Strategies to enhance ZnO photocatalyst’s performance for water treatment: A comprehensive review. Chem. Rec. 2022, 22, e202100299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadi, M.; Zirak, M.; Naseri, A.; Khorashadizade, E.; Moshfegh, A.Z. Recent progress on doped ZnO nanostructures for visible-light photocatalysis. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 605, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daksh, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. Rare earth-doped zinc oxide nanostructures: A review. Rev. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Lai, C.W.; Ngai, K.S.; Juan, J.C. Recent developments of zinc oxide based photocatalyst in water treatment technology: A review. Water Res. 2016, 88, 428–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Sun, Q.; Zuo, C.; Pei, Y.; Yang, S.; Zheng, H.; Liu, F. A highly efficient porous rod-like Ce-doped ZnO photocatalyst for the degradation of dye contaminants in water. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Mohan, M.K.; Navaneethan, M.; Ponnusamy, S.; Muthamizhchelvan, C. Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of Gd doped ZnO nanoparticles for enhanced degradation of methylene blue under visible light. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 103, 104622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P. Visible-light driven photocatalytic performance of eco-friendly cobalt-doped ZnO nanoarrays: Influence of morphology, cobalt doping, and photocatalytic efficiency. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 274, 121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharat, T.; Mondal, S.; Gupta, H.; Singh, P.; Das, A. Synthesis of doped zinc oxide nanoparticles: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 11, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayapao, O.; Thongtem, T.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, S. Synthesis and characterization of highly efficient Gd doped ZnO photocatalyst irradiated with ultraviolet and visible radiations. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 39, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Zekker, I.; Zhang, B.; Hendi, A.H.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, S.; Zada, N.; Ahmad, H.; Shah, L.A. Review on methylene blue: Its properties, uses, toxicity and photodegradation. Water 2022, 14, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaprasath, G.; Murugan, R.; Hayakawa, Y.; Ravi, G. Optical and magnetic studies on Gd doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Lumin. 2016, 178, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeen, A.; Safeen, K.; Shafique, M.; Iqbal, Y.; Ahmed, N.; Rauf Khan, M.A.; Asghar, G.; Althubeiti, K.; Al Otaibi, S.; Ali, G.; et al. The effect of Mn and Co dual-doping on the structural, optical, dielectric and magnetic properties of ZnO nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 11923–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, G.; Asri, S.; Khusro, S.N.; Tariq, G.H.; Awan, M.; Irshad, M.; Safeen, A.; Iqbal, Y.; Shah, W.H.; Anis-ur-Rehman, M. Enhanced magnetic properties of barium hexaferrite. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 4318–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphle, A.; Borunda, M.F.; Hari, P. Influence of cobalt doping on residual stress in ZnO nanorods. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 84, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, J.Z.; de Paula, L.F.; Longo, E.; Patrocinio, A.O.; Lima, R.C. Effect of Gd 3+ doping on structural and photocatalytic properties of ZnO obtained by facile microwave-hydrothermal method. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Das, S.; Das, D.; Sutradhar, S. Tailoring of room temperature ferromagnetism and electrical properties in ZnO by Co (3d) and Gd (4f) element co-doping. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 691, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Shah, W.H.; Safeen, A.; Ali, L.; Tufail, M.; Ullah, Z.; Safeen, K.; Eldin, S.M.; R Ali, M.; Sohail, M. Effect of Ca doping on the arbitrary canting of magnetic exchange interactions in La1-xCaxMnO3 nanoparticles. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1117793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Althubeiti, K.; Algethami, M.; Rahman, N.; Sohail, M.; Mao, Q.; Zaman, Q.; Ullah, A.; Ilyas, N.; Afzal, A.M. Observation of quantum criticality in antiferromagnetic based (Ce1− xYx) 2Ir3Ge5 Kondo-Lattice system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 556, 169361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdi, S.; Smaoui, H.; Guermazi, S.; Leroy, G.; Duponchel, B. Enhancing the structural, optical and electrical conductivity properties of ZnO nanopowders through Dy doping. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 109819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed, N.; Hassan, M.S.; Hassan, M. Effects of aluminum (Al) incorporation on structural, optical and thermal properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. -Pol. 2018, 36, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesaros, A.; Ghitulica, C.D.; Popa, M.; Mereu, R.; Popa, A.; Petrisor Jr, T.; Gabor, M.; Cadis, A.I.; Vasile, B.S. Synthesis, structural and morphological characteristics, magnetic and optical properties of Co doped ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 2835–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Rasid, N.F.; Tawil, S.N.M.; Norhidayah, C.A.; Sahdan, M.Z. Influence of Gd doping on the structural and optical properties of ZnO. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2015, 773, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muktaridha, O.; Adlim, M.; Suhendrayatna, S.; Ismail, I. Progress of 3d metal-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles and the photocatalytic properties. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahy, B.; Aslam, M.; Bahadur, D. Aqueous synthesis of Mn-and Co-doped ZnO nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 11758–11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghafar, H.H.; Radwan, E.K.; El-Wakeel, S.T. Removal of hazardous contaminants from water by natural and zwitterionic surfactant-modified clay. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 6834–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safeen, A.; Safeen, K.; Ullah, R.; Zulfqar; Shah, W.H.; Zaman, Q.; Althubeiti, K.; Al Otaibi, S.; Rahman, N.; Iqbal, S.; et al. Enhancing the physical properties and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles via cobalt doping. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 15767–15774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.-L.; Yu, S. Optical and Magnetic Properties of Zn1–x Mn x O Nanorods Grown by Chemical Vapor Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 6443–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeen, K.; Micheli, V.; Bartali, R.; Gottardi, G.; Safeen, A.; Ullah, H.; Laidani, N. Synthesis of conductive and transparent Nb-doped TiO2 films: Role of the target material and sputtering gas composition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 66, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwali, K.; Ming-Hu, F. Dielectric and magnetic properties of (Zn, Co) co-doped SnO2 nanoparticles. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 127803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safeen, K.; Micheli, V.; Bartali, R.; Gottardi, G.; Safeen, A.; Ullah, H.; Laidani, N. Influence of intrinsic defects on the electrical and optical properties of TiO2: Nb films sputtered at room temperature. Thin Solid Film. 2018, 645, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, H.; Rhouma, F.; Benzarti, Z.; Bougrioua, Z.; Guermazi, S.; Khirouni, K. Electrical conductivity improvement of Fe doped ZnO nanopowders. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 129, 110884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Arshi, N.; Anwar, M.; Danish, R.; Koo, B.H. Morphological evolution of ZnO nanostructures and their aspect ratio-induced enhancement in photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 29249–29263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, A.; Manikandan, E.; Meenatchi, B.; Vadivel, S.; Jaganathan, S.; Ladchumananandasivam, R.; Henini, M.; Maaza, M.; Aanand, J.S. Rare earth element (REE) lanthanum doped zinc oxide (La: ZnO) nanomaterials: Synthesis structural optical and antibacterial studies. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 723, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galdámez-Martinez, A.; Santana, G.; Güell, F.; Martínez-Alanis, P.R.; Dutt, A. Photoluminescence of ZnO nanowires: A review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Cai, C.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W. Structure, photoluminescence, and magnetic properties of Co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 12917–12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakar, C.; Muthukumaran, S.; Raja, V. Influence of defects on the structural, optical, photoluminescence and magnetic properties of Cr/Mn dual doped ZnO nanostructures. Chem. Phys. Impact 2021, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; de Araujo, C.I.L.; Khan, T.; Khattak, S.A.; Ahmed, E.; Khan, A.; Ullah, B.; Khan, G.; Safeen, K.; Safeen, A. Effect of thermal calcination on the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of (ZnO–Ni) semiconductor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 3396–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Khan, A.; Hua, T.; Ilyas, N.; Fashu, S.; Afzal, A.M.; Safeen, M.A.; Khan, R. Oxygen vacancies induced room temperature ferromagnetism and enhanced dielectric properties in Co and Mn co-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 9463–9474. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.; Fashu, S. Effect of annealing on Ni-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the co-precipitation method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 10122–10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Xiang, L.; Komarneni, S. Synthesis, properties and applications of ZnO nanomaterials with oxygen vacancies: A review. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7357–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapilashrami, M.; Xu, J.; Ström, V.; Rao, K.V.; Belova, L. Transition from ferromagnetism to diamagnetism in undoped ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 033104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, M.M.; Jappor, H.R.; Al-Marzoki, K.; Al-Hydary, I.A.; Edrees, S.J.; Shukur, M.M. Unraveling the effect of Gd doping on the structural, optical, and magnetic properties of ZnO based diluted magnetic semiconductor nanorods. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33207–33221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sahare, P. Gd3+ incorporated ZnO nanoparticles: A versatile material. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 51, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birajdar, S.D.; Khirade, P.P.; Humbe, A.V.; Jadhav, K. Presence of intrinsic defects and transition from diamagnetic to ferromagnetic state in Co2+ ions doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 5575–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithira, P.; John, T.T. Correlation among oxygen vacancy and doping concentration in controlling the properties of cobalt doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 496, 165928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Heterojunction photocatalysts. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1601694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubeen, K.; Irshad, A.; Safeen, A.; Aziz, U.; Safeen, K.; Ghani, T.; Khan, K.; Ali, Z.; ul Haq, I.; Shah, A. Band Structure Tuning of ZnO/CuO Composites for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2023, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Patra, M.; Bhagavathiachari, M.; Nair, R.G. Defect-induced visible-light-driven photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical performance of ZnO–CeO2 nanoheterojunctions. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 858, 157730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Li, J. S-scheme heterojunction ZnO/g-C3N4 shielding polyester fiber composites for the degradation of MB. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2021, 36, 045025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, D.; Geng, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Hydrothermal synthesis of hexagonal CuSe nanoflakes with excellent sunlight-driven photocatalytic activity. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 9185–9190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Han, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, P. Preparation of ZnO/Bi2WO6 heterostructures with improved photocatalytic performance. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 106, 104761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakib, A.A.M.; Masum, S.M.; Hoinkis, J.; Islam, R.; Molla, M.A.I. Synthesis of CuO/ZnO nanocomposites and their application in photodegradation of toxic textile dye. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Samples | 2θ (Degree) | FWHM (β) (rad) | D (nm), by Scherrer Equation | D (nm), by W-H Method | Microstrain× 10−3 (Error × 10−5) | Lattice Parameters | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b (Å) | c (Å) | |||||||
| ZnO | 36.58° | 0.3710 | 23.57 ± 0.7 | 35.8 ± 0.8 | 5.94 ± 6.4 | 3.2427 | 5.1948 | 47.30 |
| Co-ZnO | 36.25° | 0.4371 | 19.98 ± 0.8 | 31.2 ± 0.9 | 6.02 ± 4.2 | 3.2530 | 5.2130 | 47.77 |
| Gd-ZnO | 36.31° | 0.5121 | 17.06 ± 0.5 | 28.5 ± 1.1 | 6.21 ± 1.8 | 3.2541 | 5.2150 | 47.82 |
| Co + Gd-ZnO | 36.28° | 0.6021 | 14.51 ± 0.9 | 25.2 ± 0.5 | 6.35 ± 1.2 | 3.2710 | 5.230 | 48.45 |
| Sample | Atomic Percentage (%) | Weight Percentage (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | O | Co | Gd | Total | Zn | O | Co | Gd | Total | |
| ZnO | 42.63 | 57.37 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 75.22 | 24.78 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Co-ZnO | 47.97 | 51.90 | 0.13 | 0 | 100 | 78.91 | 20.90 | 0.19 | 0 | 100 |
| Gd-ZnO | 47.5 | 52.18 | 0 | 0.32 | 100 | 77.81 | 21.83 | 0 | 0.36 | 100 |
| Co + Gd-ZnO | 59.64 | 39.46 | 0.39 | 0.50 | 100 | 85.10 | 13.78 | 0.47 | 0.65 | 100 |
| S. No. | Sample | Bandgap (eV) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pure ZnO | 3.34 |
| 2 | Co-doped ZnO | 3.28 |
| 3 | Gd-doped ZnO | 3.27 |
| 4 | Co/Gd-doped ZnO | 3.18 |
| Sample | Coercive Field (Oe) | Remanent Magnetization (emu/g) | Saturation Magnetization (emu/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO | 0.503 | 0.001 | 0.038 |
| Co-ZnO | 0.970 | 0.007 | 0.211 |
| Gd-ZnO | 1.002 | 0.029 | 0.273 |
| Co + Gd-ZnO | 1.010 | 0.058 | 0.307 |
| Catalyst | Model Dye Pollutant | Degradation Time | Degradation Rate | Source of Light | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO-g-C3N4@PET | MB | 120 min | 92% | Visible light irradiation | [54] |
| CuSe nanoflakes | MB | 90 min | 76% | Sunlight | [55] |
| ZnO/Bi2WO6 | MB | 120 min | 90% | 250 W Hg lamp | [56] |
| ZnO/CuO | MB | 120 min | 91% | Sunlight | [57] |
| Co-Gd-ZnO | MB | 90 min | 93.1% | Xe lamp | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safeen, K.; Safeen, A.; Arif, D.; Shah, W.H.; Ali, A.; Ali, G.; Hussain, F.; Imran, N.; Ullah Shah, A.; Alataway, A.; et al. Tuning the Optical Properties of ZnO by Co and Gd Doping for Water Pollutant Elimination. Water 2023, 15, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081470
Safeen K, Safeen A, Arif D, Shah WH, Ali A, Ali G, Hussain F, Imran N, Ullah Shah A, Alataway A, et al. Tuning the Optical Properties of ZnO by Co and Gd Doping for Water Pollutant Elimination. Water. 2023; 15(8):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081470
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafeen, Kashif, Akif Safeen, Danish Arif, Wiqar H. Shah, Akhtar Ali, Ghafar Ali, Fayaz Hussain, Naveed Imran, Atta Ullah Shah, Abed Alataway, and et al. 2023. "Tuning the Optical Properties of ZnO by Co and Gd Doping for Water Pollutant Elimination" Water 15, no. 8: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15081470






