Refined Calculation of Multi-Objective Ecological Flow in Rivers, North China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
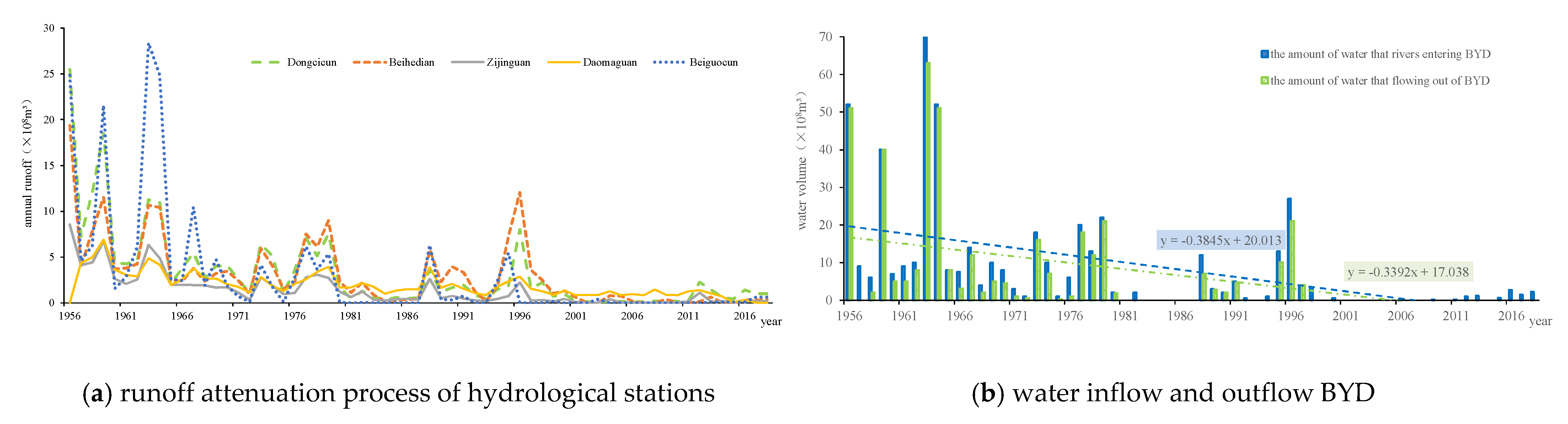
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Data Acquisition
2.2. Methodology
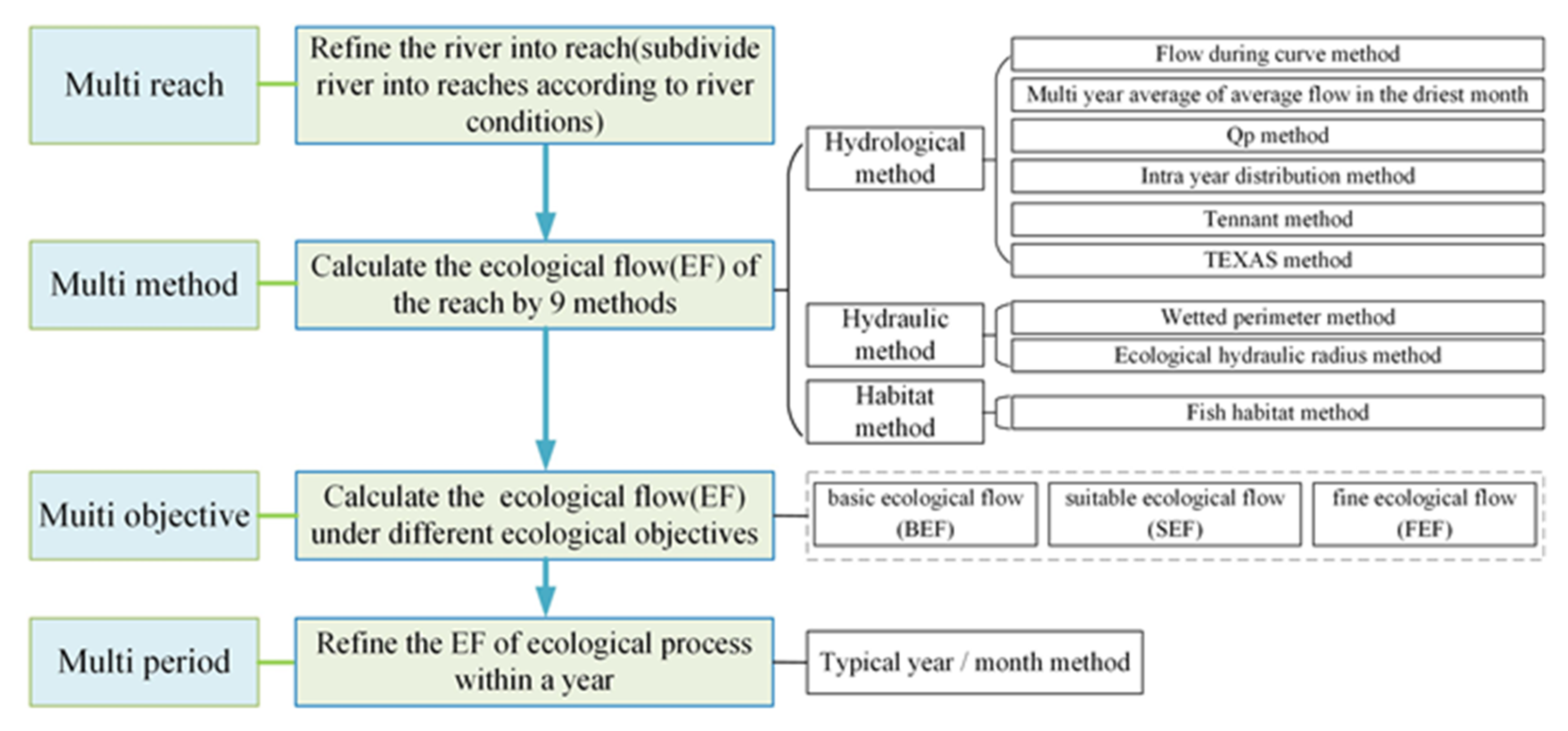
2.2.1. River Refinement
2.2.2. Integration of Multiple Methods
- (1)
- Flow-duration curve method
- (2)
- Intra-year distribution method
- (3)
- Ecological hydraulic radius method
2.2.3. Ecological Flow under Multi-Objective
2.2.4. Process of Ecological Flow under Multi-Period
3. Results
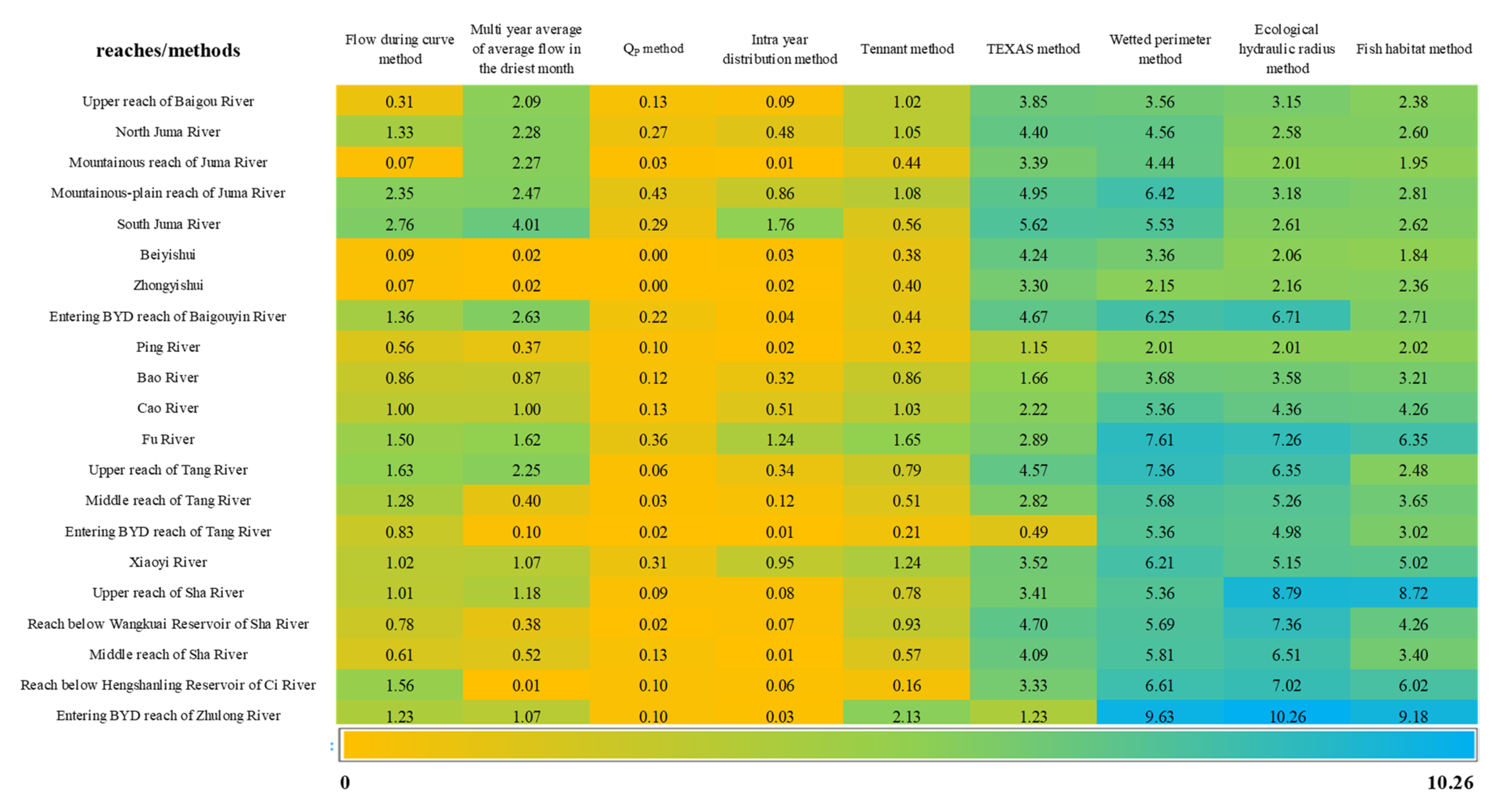
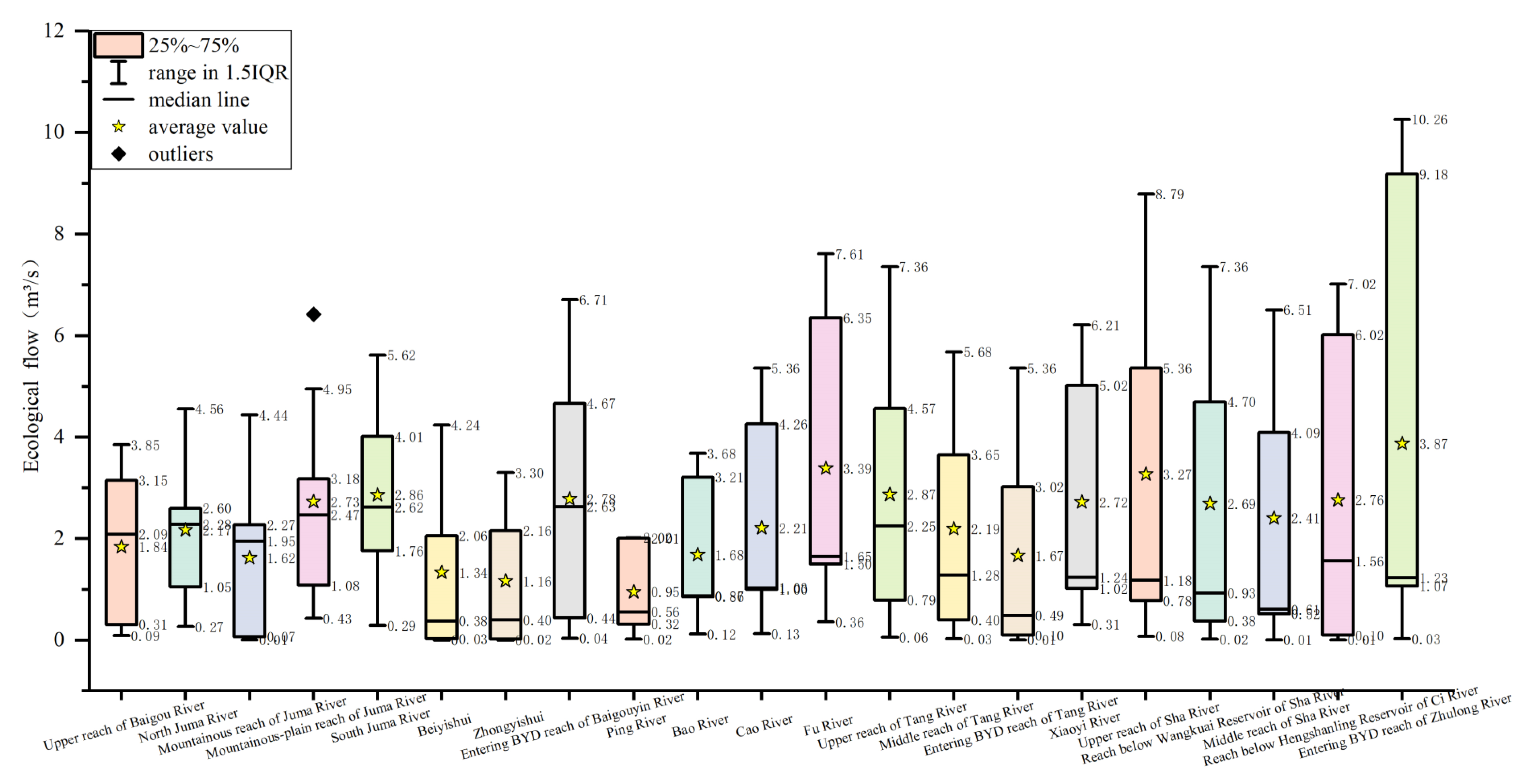
3.1. Basic Ecological Flow
3.2. Ecological Flow under Multi-Objective
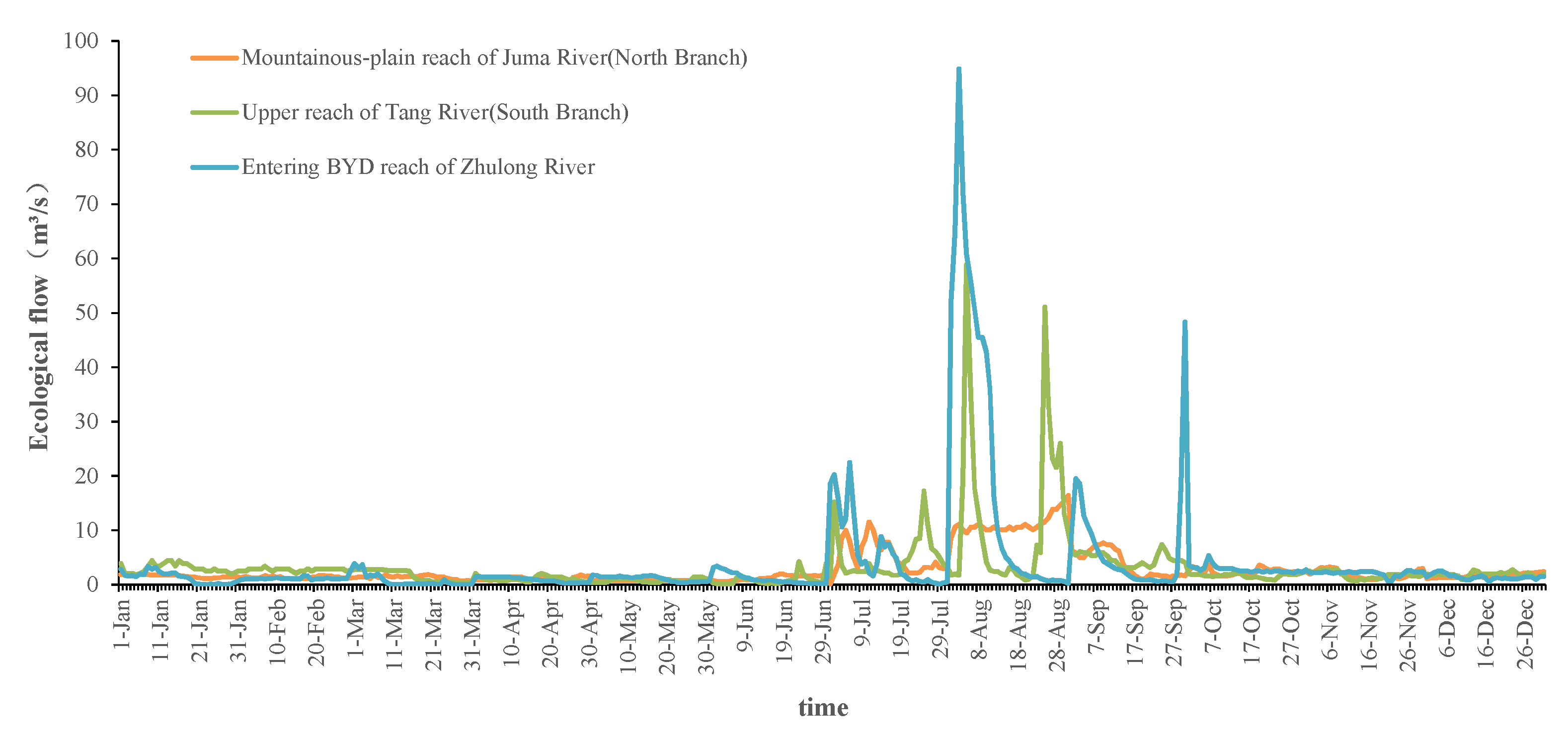
3.3. Annual Water Demand Process
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Feng, H.; Wang, L. The Calculation of River Ecological Flow for the Liao Basin in China. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Yang, Z.F.; Zhao, Y.W.; Chen, B. Effects of Water Recharge on Ecosystem Health in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B.; He, C. Examination of wetlands system using ecological network analysis: A case study of Baiyangdian Basin, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y. Investigation of water pollution in Baiyangdian Lake, China. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2010, 2, 737–748. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Yang, Z.F.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.W. Ecosystem Health Assessment of Baiyangdian Lake Based on Thermodynamic Indicators. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 2402–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.; Feng, Q.; Yu, T.; Zhao, C. Inland river terminal lake preservation: Determining basin scale and the ecological water requirement. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Peng, W.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y. A new method for calculating the downstream ecological flow of diversion-type small hydropower stations. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covich, A.P. Water and ecosystems. In Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World’s Fresh Water Resources; Gleick, P.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Gleick, P.H. Water in crisis: Paths to sustainable water use. Ecol. Appl. 1998, 8, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, G.L.; Mader, T.L.; Eigenberg, R.A. A global perspective on environmental flow assessment: Emerging trends in the development and application of environmental flow methodologies for rivers. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 397–441. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, W.C.; Chuang, M. Habitat evaluation using suitability index and habitat type diversity: A case study involving a shallow forest stream in central Taiwan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 172, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Ma, H.; Wei, M. Calculation of the minimum ecological water requirement of an urban river system and its deployment: A case study in Beijing central region. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 3271–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, L.H. Study on integrated calculation of ecological water demand for basin system. Sci. China (Technol. Sci.) 2011, 54, 2638–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xia, Z.; Yu, L.; Guo, L. Calculation and analysis of the instream ecological flow for the Irtysh River. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S. A general multi-objective minimum ecological flow water bodies programming model for or water level of inland. J. Arid Land 2015, 7, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Yi, R.; Chang, J.; Shu, C.; Yin, Z.; Han, S.; Feng, Z.; Lyu, Y. A new method for calculating ecological flow: Distribution flow method. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 045118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Gao, C.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Lei, K.; Long, R.; Zhang, L. Cascade hydropower plants operation considering comprehensive ecological water demands. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 180, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wan, Z.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y. Calculation of ecological water requirements of urban rivers using a hydrological model: A case study of Beiyun River. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, J. Incorporating fish habitat requirements of the complete life cycle into ecological flow regime estimation of rivers. Ecohydrology 2020, 13, e2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Leng, J.; Zhao, J.; Na, Y.; Wu, W. Quantitative Calculation and Optimized Applications of Ecological Flow based on Nature-based Solutions. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Wang, F.; Song, L. Calculation and configuration of ecological water requirements for Yongding river Guanting Gorge. Beijing Water 2017, 2, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, P.E.; Gómez Ma, A.; Saldaña, P. Requirements to Implement Environmental Flow in Mexico; Editorial IMTA-Alianza: Morelos, Mexico, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sedighkia, M.; Abdoli, A.; Datta, B. Optimizing monthly ecological flow regime by a coupled fuzzy physical habitat simulation–genetic algorithm method. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2021, 41, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.; Sarma, A.K. Ecological flow assessment using hydrological and hydrodynamic routing model in Bhogdoi river, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Target EF | Ecological Connotations | Explanations |
|---|---|---|
| BEF | basic ecological function | water condition when a river is at the edge of a critical state |
| SEF | integrity of species | the minimum flow to maintain the basic integrity of aquatic species |
| FEF | maintain the stability of ecosystems | with the natural ecological service function, diversifying the ecological landscape, and having a certain amount of water resources for use |
| Serial Numbers | Rivers | Reaches | Hydrological Methods | Hydraulic Methods | Habitat Methods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flow-Duration Curve Methods | Multi-Year Average of Average Flow in the Driest Month | Qp Method | Intra-Year Distribution Method | Tennant Method | TEXAS Method | Wetted Perimeter Method | Ecological Hydraulic Radius Method | Fish Habitat Method | |||
| 1 | Baigou River | Upper reach of Baigou River | 0.31 | 2.09 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 1.02 | 3.85 | 3.56 | 3.15 | 2.38 |
| 2 | North Juma River | 1.33 | 2.28 | 0.27 | 0.48 | 1.05 | 4.40 | 4.56 | 2.58 | 2.60 | |
| 3 | Mountainous reach of Juma River | 0.07 | 2.27 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.44 | 3.39 | 4.44 | 2.01 | 1.95 | |
| 4 | Mountainous-plain reach of Juma River | 2.35 | 2.47 | 0.43 | 0.86 | 1.08 | 4.95 | 6.42 | 3.18 | 2.81 | |
| 5 | South Juma River | 2.76 | 4.01 | 0.29 | 1.76 | 0.56 | 5.62 | 5.53 | 2.61 | 2.62 | |
| 6 | Beiyishui | 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.38 | 4.24 | 3.36 | 2.06 | 1.84 | |
| 7 | Zhongyishui | 0.07 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.40 | 3.30 | 2.15 | 2.16 | 2.36 | |
| 8 | Entering BYD reach of Baigouyin River | 1.36 | 2.63 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 4.67 | 6.25 | 6.71 | 2.71 | |
| 9 | Ping River | Ping River | 0.56 | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.32 | 1.15 | 2.01 | 2.01 | 2.02 |
| 10 | Bao River | Bao River | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 0.86 | 1.66 | 3.68 | 3.58 | 3.21 |
| 11 | Cao River | Cao River | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 1.03 | 2.22 | 5.36 | 4.36 | 4.26 |
| 12 | Fu River | Fu River | 1.50 | 1.62 | 0.36 | 1.24 | 1.65 | 2.89 | 7.61 | 7.26 | 6.35 |
| 13 | Tang River | Upper reach of Tang River | 1.63 | 2.25 | 0.06 | 0.34 | 0.79 | 4.57 | 7.36 | 6.35 | 2.48 |
| 14 | Middle reach of Tang River (Xidayang reservoir-Beixindian) | 1.28 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.51 | 2.82 | 5.68 | 5.26 | 3.65 | |
| 15 | Entering BYD reach of Tang River (Beixindian-BYD) | 0.83 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.21 | 0.49 | 5.36 | 4.98 | 3.02 | |
| 16 | Xiaoyi River | Xiaoyi River | 1.02 | 1.07 | 0.31 | 0.95 | 1.24 | 3.52 | 6.21 | 5.15 | 5.02 |
| 17 | Zhulong River | Upper reach of Sha River | 1.01 | 1.18 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.78 | 3.41 | 5.36 | 8.79 | 8.72 |
| 18 | Reach below Wangkuai Reservoir of Sha River | 0.78 | 0.38 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.93 | 4.70 | 5.69 | 7.36 | 4.26 | |
| 19 | Middle reach of Sha River | 0.61 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.57 | 4.09 | 5.81 | 6.51 | 3.40 | |
| 20 | Reach below Hengshanling Reservoir of Ci River | 1.56 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 3.33 | 6.61 | 7.02 | 6.02 | |
| 21 | Entering BYD reach of Zhulong River (Beiguocun-BYD) | 1.23 | 1.07 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 2.13 | 1.23 | 9.63 | 10.26 | 9.18 | |
| Serial Numbers | Rivers | Reaches | BEF | SEF | FEF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baigou River | Upper reach of Baigou River | 0.31 | 0.51 | 0.71 |
| 2 | North Juma River | 2.28 | 6.28 | 11.54 | |
| 3 | Mountainous reach of Juma River | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.12 | |
| 4 | Mountainous-plain reach of Juma River | 2.35 | 6.48 | 11.93 | |
| 5 | South Juma River | 2.86 | 7.91 | 14.73 | |
| 6 | Beiyishui | 1.34 | 3.65 | 6.37 | |
| 7 | Zhongyishui | 1.16 | 3.15 | 5.38 | |
| 8 | Entering BYD reach of Baigouyin River | 2.78 | 7.68 | 14.29 | |
| 9 | Ping River | Ping River | 0.95 | 2.56 | 4.23 |
| 10 | Bao River | Bao River | 1.68 | 4.60 | 8.24 |
| 11 | Cao River | Cao River | 2.21 | 6.09 | 11.16 |
| 12 | Fu River | Fu River | 3.39 | 9.39 | 17.65 |
| 13 | Tang River | Upper reach of Tang River | 1.63 | 4.46 | 7.97 |
| 14 | Middle reach of Tang River (Xidayang reservoir-Beixindian) | 2.19 | 6.03 | 11.05 | |
| 15 | Entering BYD reach of Tang River (Beixindian-BYD) | 1.67 | 4.58 | 8.19 | |
| 16 | Xiaoyi River | Xiaoyi River | 2.72 | 7.52 | 13.96 |
| 17 | Zhulong River | Upper reach of Sha River | 1.01 | 2.73 | 4.56 |
| 18 | Reach below Wangkuai Reservoir of Sha River | 2.69 | 7.43 | 13.80 | |
| 19 | Middle reach of Sha River | 2.41 | 6.65 | 12.26 | |
| 20 | Reach below Hengshanling Reservoir of Ci River | 2.76 | 7.63 | 14.18 | |
| 21 | Entering BYD reach of Zhulong River (Beiguocun-BYD) | 3.87 | 10.74 | 20.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Cui, Y. Refined Calculation of Multi-Objective Ecological Flow in Rivers, North China. Water 2023, 15, 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15051003
Jiao Y, Liu J, Li C, Xu Z, Cui Y. Refined Calculation of Multi-Objective Ecological Flow in Rivers, North China. Water. 2023; 15(5):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15051003
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Yufei, Jia Liu, Chuanzhe Li, Zhenghe Xu, and Yingjie Cui. 2023. "Refined Calculation of Multi-Objective Ecological Flow in Rivers, North China" Water 15, no. 5: 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15051003
APA StyleJiao, Y., Liu, J., Li, C., Xu, Z., & Cui, Y. (2023). Refined Calculation of Multi-Objective Ecological Flow in Rivers, North China. Water, 15(5), 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15051003








