Assessing Water Quality Dynamics in Tidally Influenced Blackwater Rivers along a Rural–Urban Gradient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
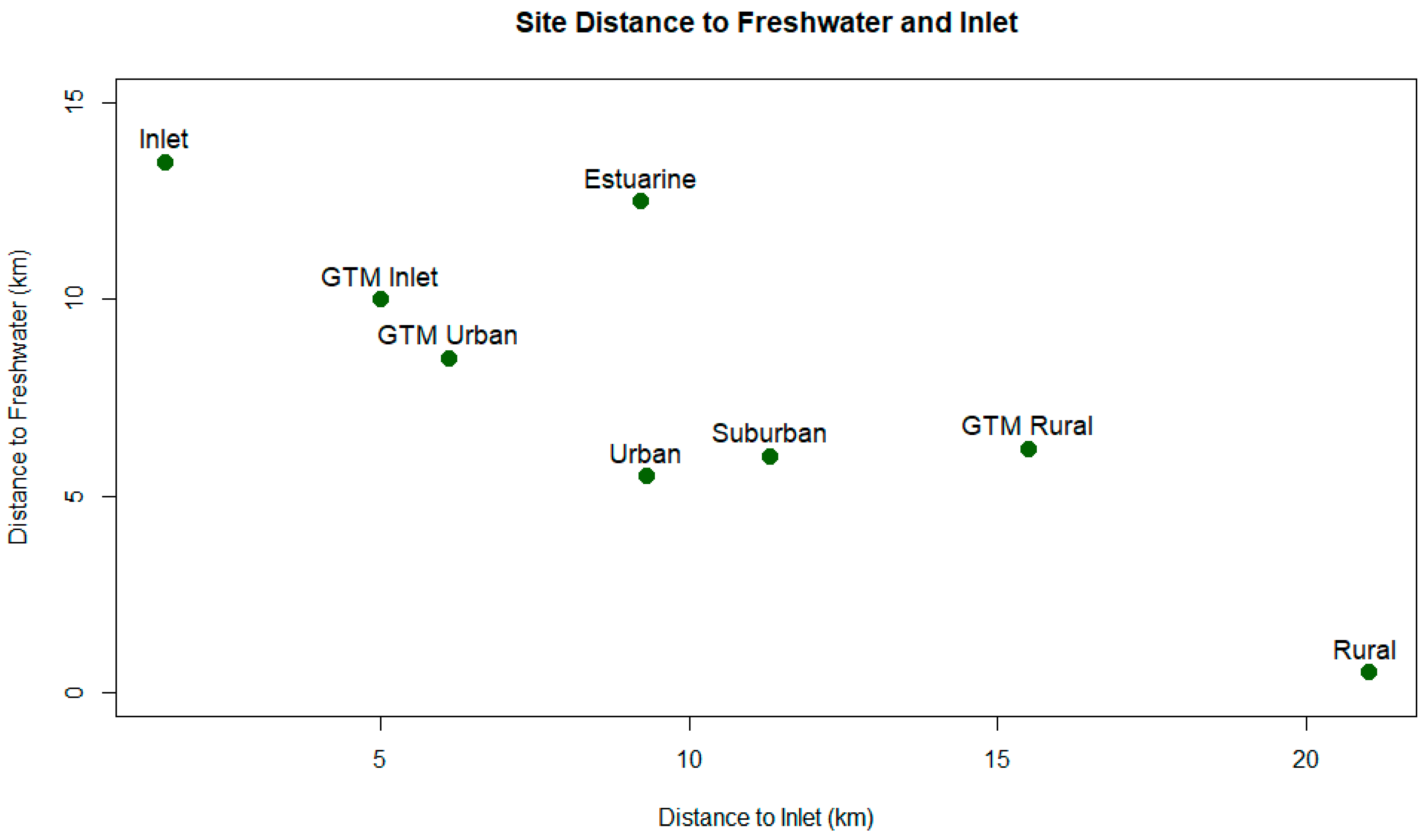
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Parameter Response
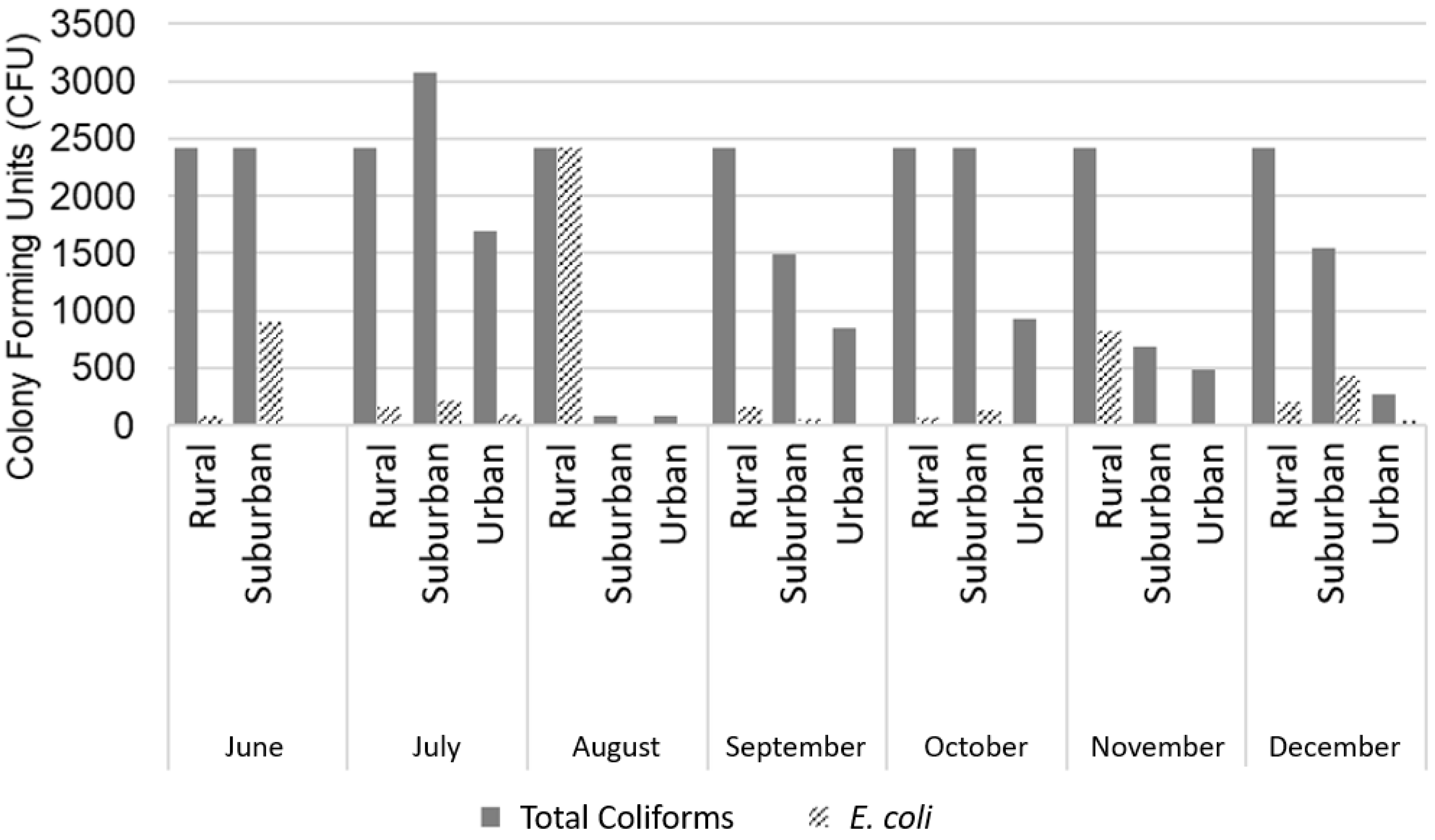
3.2. Nutrient Response
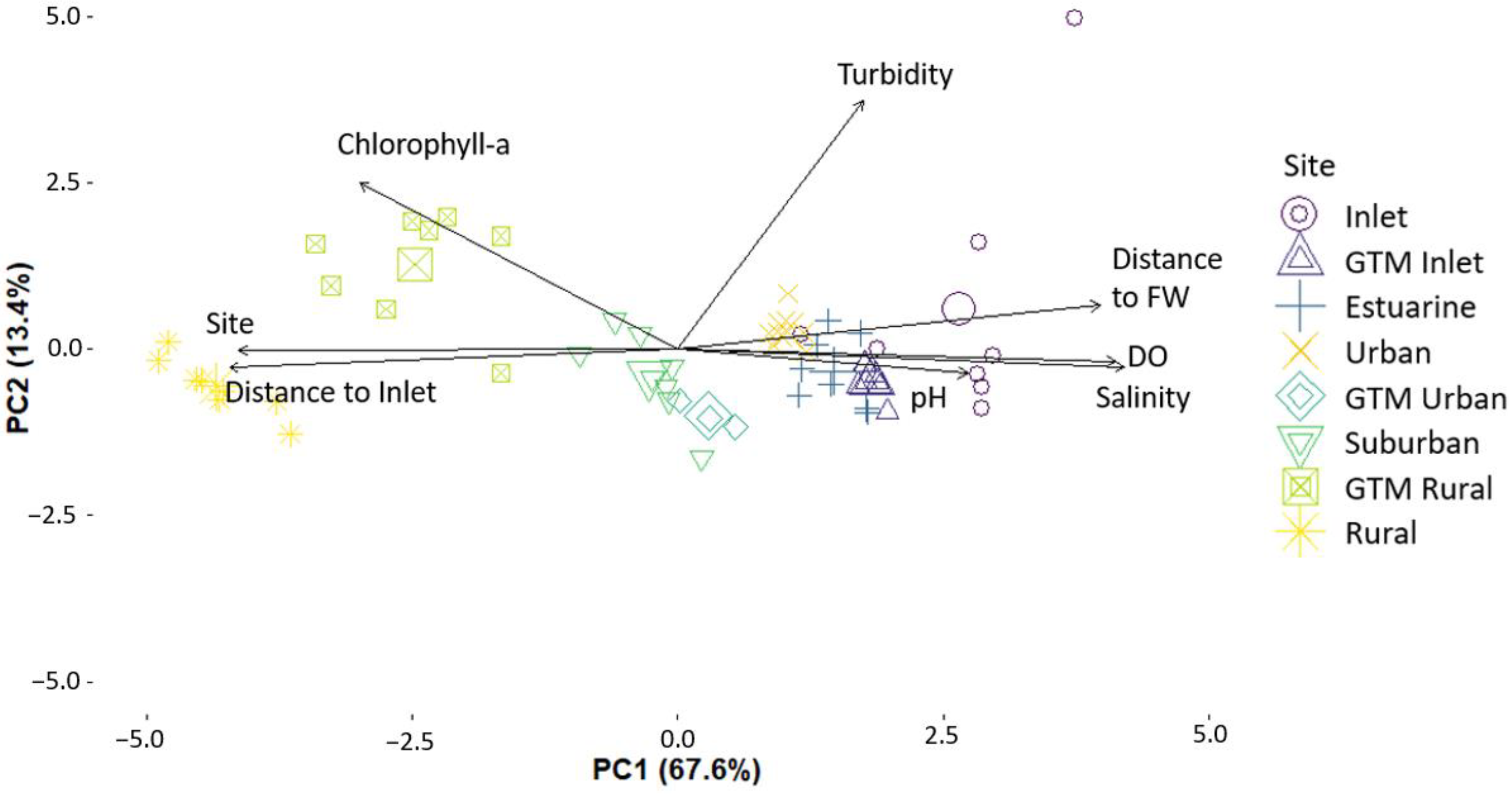
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutrients
4.2. Tidal Flushing
4.3. Storm Events
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Office of Economic & Demographic Research. Demographic Estimating Conference Executive Summary. 2022. Available online: http://edr.state.fl.us/content/conferences/population/archives/220718demographic.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Terando, A.J.; Costanza, J.; Belyea, C.; Dunn, R.R.; McKerrow, A.; Collazo, J.A. The Southern Megalopolis: Using the Past to Predict the Future of Urban Sprawl in the Southeast U.S. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A. Land Use and Water Quality. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.J.; Pickett, S.T.A. Ecosystem Structure and Function along Urban-Rural Gradients: An Unexploited Opportunity for Ecology. Ecology 1990, 71, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.R.; Cuffney, T.F.; Coles, J.F.; Fitzpatrick, F.; McMahon, G.; Steuer, J.; Bell, A.H.; May, J.T. Urban Streams across the USA: Lessons Learned from Studies in 9 Metropolitan Areas. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2009, 28, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Nkedi-Kizza, P.; Wu, Q.T.; Shinde, D.; Huang, C.H. Assessment of Seasonal Variations in Surface Water Quality. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3800–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toor, G.S.; Occhipinti, M.L.; Yang, Y.Y.; Majcherek, T.; Haver, D.; Oki, L. Managing Urban Runoff in Residential Neighborhoods: Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Lawn Irrigation Driven Runoff. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusk, M.G.; Toor, G.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Mechtensimer, S.; De, M.; Obreza, T.A. A Review of the Fate and Transport of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Pathogens, and Trace Organic Chemicals in Septic Systems. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 455–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufford, D.L.; Samarghitan, C.L.; McKellar, H.N.; Porter, D.E.; Hussey, J.R. Impacts of Urbanization on Nutrient Concentrations in Small Southeastern Coastal Streams. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mei, K.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Wang, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, M. Impacts of Land Use and Population Density on Seasonal Surface Water Quality Using a Modified Geographically Weighted Regression. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smucker, N.J.; Kuhn, A.; Charpentier, M.A.; Cruz-Quinones, C.J.; Elonen, C.M.; Whorley, S.B.; Jicha, T.M.; Serbst, J.R.; Hill, B.H.; Wehr, J.D. Quantifying Urban Watershed Stressor Gradients and Evaluating How Different Land Cover Datasets Affect Stream Management. Environ. Manag. 2015, 57, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Lusk, M.G. Nutrients in Urban Stormwater Runoff: Current State of the Science and Potential Mitigation Options. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2018, 4, 112–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Toor, G.S. Stormwater Runoff Driven Phosphorus Transport in an Urban Residential Catchment: Implications for Protecting Water Quality in Urban Watersheds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.J.; Roy, A.H.; Feminella, J.W.; Cottingham, P.D.; Groffman, P.M.; Morgan, R.P. The Urban Stream Syndrome: Current Knowledge and the Search for a Cure. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2005, 24, 706–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.B.; Gao, P.; Xu, M.; Guan, D.; Tang, X.; Ma, L.Q. Background Concentrations of Trace Metals As, Ba, Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Pb, Se, and Zn in 214 Florida Urban Soils: Different Cities and Land Uses. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- House, M.A.; Ellis, J.B.; Herricks, E.E.; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T.; Seager, J.; Lijklema, L.; Aalderink, H.; Clifforde, I.T. Urban Drainage Impacts on Receiving Waters. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 117–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.E.; Brown, M.T.; Sansalone, J.J. Characterization of Storm Water–Suspended Sediments and Phosphorus in an Urban Catchment in Florida. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 139, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, G. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Associating with Different Size Suspended Solids in Roof and Road Runoff in Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 15788–15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Österlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The Pollution Conveyed by Urban Runoff: A Review of Sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Liao, Q.; Titi, H.H.; Li, J. Turbidity of Stormwater Runoff from Highway Construction Sites. J. Environ. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, M.T.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Mueller, S.E.; Hartley, D.M.; Frodge, J.D.; Funke, D.E. Non-Point-Source Impacts on Stream Nutrient Concentrations along a Forest to Urban Gradient. Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenmueller, E.A.; Criss, R.E.; Winston, W.E.; Shaughnessy, A.R. Stream Hydrology and Geochemistry along a Rural to Urban Land Use Gradient. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, S.J.; Brush, M.J. Contribution of Nutrient and Organic Matter Sources to the Development of Periodic Hypoxia in a Tributary Estuary. Estuar. Coasts 2015, 38, 2149–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.S. The Role and Distribution of Total Suspended Solids in the Macrotidal Coastal Waters of Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 135, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, Â.; Biguino, B.; Borges, C.; Cereja, R.; Cruz, J.P.C.; Sousa, F.; Dias, J.; Brotas, V.; Palma, C.; Brito, A.C. Tidal Variability of Water Quality Parameters in a Mesotidal Estuary (Sado Estuary, Portugal). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketchum, B.H.; Rawn, A.M. The Flushing of Tidal Estuaries. Sew. Ind. Waste 1951, 23, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phlips, E.J.; Love, N.; Badylak, S.; Hansen, P.; Lockwood, J.; John, C.V.; Gleeson, R. A Comparison of Water Quality and Hydrodynamic Characteristics of the Guana Tolomato Matanzas National Estuarine Research Reserve and the Indian River Lagoon of Florida. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 20, 93–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, R.D.; Purdie, D.A.; Haigh, I.D. Modelling the Influence of Riverine Inputs on the Circulation and Flushing Times of Small Shallow Estuaries. Estuar. Coasts 2021, 44, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uncles, R.J.; Stephens, J.A.; Smith, R.E. The Dependence of Estuarine Turbidity on Tidal Intrusion Length, Tidal Range and Residence Time. Cont. Shelf Res. 2002, 22, 1835–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, D.W. Dispersion and Flushing of Pollutants in Estuaries. J. Hydraul. Div. 1969, 95, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario-Llantín, J.-A.; Zarillo, G.A. Flushing Rates and Hydrodynamical Characteristics of Mosquito Lagoon (Florida, USA). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30019–30034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianesella, S.M.F.; Saldanha-Correa, F.M.P.; Teixeira, C. Tidal Effects on Nutrients and Phytoplankton Distribution in Bertioga Channel, Sao Paula, Brazil. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association. NOAA Tide Predictions. Available online: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/noaatidepredictions.html?id=8720686 (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Dix, N.; Noel, A.; Brockmeyer, R.; Hyun Jung, C.; Shauna Ray, A.; Radabaugh, K. Coastal Habitat Integrated Mapping and Monitoring Program Report for the State of Florida. Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Fish and Wildlife Research Institute Technical Report No. 21; Chapter 13 Northeast Florida. 2017, pp. 144–154. Available online: https://myfwc.com/research/habitat/coastal-wetlands/chimmp/ (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Schafer, T.; Ward, N.; Julian, P.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Impacts of Hurricane Disturbance on Water Quality across the Aquatic Continuum of a Blackwater River to Estuary Complex. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzar, T. Land Use and Water Quality Data within the GTM NERR. Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/apps/webappviewer/index.html?id=13873bbef4ab43cea2382cf1558a8502 (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- YSI Inc. YSI EXO Manual. Available online: https://www.ysi.com/File%20Library/Documents/Manuals/EXO-User-Manual-Web.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Kennish, M.J. NERRS Research and Monitoring Initiatives. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 45, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, N.G.; Phlips, E.J.; Gleeson, R.A. Water Quality Changes in the Guana Tolomato Matanzas National Estuarine Research Reserve, Florida, Associated with Four Tropical Storms. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 10055, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NERR National Estuarine Research Reserve System-Centralized Data Management Office. Available online: https://cdmo.baruch.sc.edu (accessed on 30 April 2020).
- Caccia, V.G.; Boyer, J.N. Spatial Patterning of Water Quality in Biscayne Bay, Florida as a Function of Land Use and Water Management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Gołaś, I.; Koc, J.; Gotkowska-Płachta, A.; Harnisz, M.; Rochwerger, A. The Impact of Urban Areas on the Water Quality Gradient along a Lowland River. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, A.; Abdu, A. Application of Principal Component Analysis in Surface Water Quality Monitoring. Princ. Compon. Anal.-Eng. Appl. 2012, 2, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, T.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Achari, G. Clusterization of Surface Water Quality and Its Relation to Climate and Land Use/Cover. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 04, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridger, K. FINAL TMDL Report Fecal Coliform TMDL for the Pellicer Creek (WBID 2580B). 2012. Available online: https://floridadep.gov/sites/default/files/pellicer-creek-coliform-tmdl.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2020).
- Frenzel, S.A.; Couvillion, C.S. Fecal-Indicator Bacteria in Streams Alonga Gradient of Residential Development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2002, 38, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumo, D.; Arnone, E.; Francipane, A.; Caracciolo, D.; Noto, L.V. Potential Implications of Climate Change and Urbanization on Watershed Hydrology. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliosa, P.; Fonseca, A.; Barbosa, F.; Braga, E. Urbanization Impact on Subtropical Estuaries: A Comparative Study of Water Properties in Urban Areas and in Protected Areas. J. Coast. Res. 2006, II, 731–735. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.B.; Grimm, N.B. Hierarchical Regulation of Nitrogen Export from Urban Catchments: Interactions of Storms and Landscapes. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 2347–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panton, A.; Couceiro, F.; Fones, G.R.; Purdie, D.A. The Impact of Rainfall Events, Catchment Characteristics and Estuarine Processes on the Export of Dissolved Organic Matter from Two Lowland Rivers and Their Shared Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, E.W.; Arrington, D.A. Nutrient Inputs from an Urbanized Landscape May Drive Water Quality Degradation. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9–10, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, P.; Lucas, S. Contamination of Estuaries from Failing Septic Tank Systems: Difficulties in Scaling up from Monitored Individual Systems to Cumulative Impact. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 2132–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincaid, D.W.; Seybold, E.C.; Adair, E.C.; Bowden, W.B.; Perdrial, J.N.; Vaughan, M.C.H.; Schroth, A.W. Land Use and Season Influence Event-Scale Nitrate and Soluble Reactive Phosphorus Exports and Export Stoichiometry from Headwater Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, e2020WR027361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Krom, M.D.; Wang, F.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Q.; Chen, N. Simultaneous Observations Revealed the Non-Steady State Effects of a Tropical Storm on the Export of Particles and Inorganic Nitrogen through a River-Estuary Continuum. J. Hydrol. 2022, 606, 127438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Krom, M.D.; Lin, J.; Cheng, P.; Chen, N. Effects of a Storm on the Transformation and Export of Phosphorus Through a Subtropical River-Turbid Estuary Continuum Revealed by Continuous Observation. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2022JG006786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, D. Understanding How the Release of E. coli and Nutrients from Septic Tanks into the Guana- Tolomato-Matanzas Estuary and the Adjacent Ocean Affect Human, Plant and Animal Health; One Health Final Report; University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lapointe, B.E.; Herren, L.W.; Paule, A.L. Septic Systems Contribute to Nutrient Pollution and Harmful Algal Blooms in the St. Lucie Estuary, Southeast Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 2017, 70, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.W.; Spoelstra, J.; Robertson, W.D.; Klemt, W.; Schiff, S.L. Contribution of Phosphorus to Georgian Bay from Groundwater of a Coastal Beach Town with Decommissioned Septic Systems. J. Great. Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 1016–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, R.A. Characterization of Surface Water Quality Along a Watershed Disturbance Gradient. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1994, 30, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, K.M.; Smith, E.M.; Lang, S.Q.; Osburn, C.L.; Benitez-Nelson, C.R. Particulate and Dissolved Organic Matter in Stormwater Runoff Influences Oxygen Demand in Urbanized Headwater Catchments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 952–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, B.; Raymond, P.A. Dissolved Organic Matter Export from a Forested Watershed during Hurricane Irene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, A.C.; Thompson, S.P.; Magel, C.L.; Piehler, M.F. Urbanization Alters Coastal Plain Stream Carbon Export and Dissolved Oxygen Dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, T.J.; Osburn, C.L. Changes in CDOM Fluorescence from Allochthonous and Autochthonous Sources during Tidal Mixing and Bacterial Degradation in Two Coastal Estuaries. Mar. Chem. 2004, 89, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Zhang, Y.; Podgorski, D.C.; Chen, C.; Ding, Y.; et al. Response of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter Dynamics to Tidal Oscillations and Anthropogenic Disturbances in a Large Subtropical Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosskey, M.G.; Bertsch, P.M. Forest Sources and Pathways of Organic Matter Transport to a Blackwater Stream: A Hydrologic Approach. Biogeochemistry 1994, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Dash, P.; Silwal, S.; Feng, G.; Adeli, A.; Moorhead, R.J. Influence of Land Use and Land Cover on the Spatial Variability of Dissolved Organic Matter in Multiple Aquatic Environments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14124–14141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.P.; Tutak, B.; Davis, J.R.; Paramygin, V. Circulation and Flushing in the Lagoonal System of the Guana Tolomato Matanzas National Estuarine Research Reserve (GTMNERR), Florida. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 10055, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Anderson, K.W.; Chapman, A. The Impact of Tides on Microbial Water Quality at an Inland River Beach. J. Environ. Qual. 2018, 47, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsooli, R.; Orton, P.M.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Smith, H. Residence Time of a Highly Urbanized Estuary: Jamaica Bay, New York. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiLorenzo, J.L.; Filadelfo, R.J.; Surak, C.R.; Litwack, H.S.; Gunawardana, V.K.; Najarian, T.O. Tidal Variability in the Water Quality of an Urbanized Estuary. Estuaries 2004, 27, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubeny, J.B.; Kenney, M.; Warren, B.; Louisos, J. Multi-Faceted Monitoring of Estuarine Turbidity and Particulate Matter Provenance: Case Study from Salem Harbor, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.B.; Lawler, D.M.; West, J.R.; Couperthwaite, J.S. Use of Continuous Turbidity Sensor in the Prediction of Fine Sediment Transport in the Turbidity Maximum of the Trent Estuary, UK. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 58, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Thomas, S.; Mitsch, W.J. Design of Real-Time and Long-Term Hydrologic and Water Quality Wetland Monitoring Stations in South Florida, USA. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 108, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, K.; Feng, P.; Dong, L. The Effects of Surface Pollution on Urban River Water Quality under Rainfall Events in Wuqing District, Tianjin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.A.; Erler, D.V.; Ferguson, A.; Maher, D.T. The Tidal Freshwater River Zone: Physical Properties and Biogeochemical Contribution to Estuarine Hypoxia and Acidification—The “Hydrologic Switch”. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 268, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan Tanim, A.; Goharian, E. Developing a Hybrid Modeling and Multivariate Analysis Framework for Storm Surge and Runoff Interactions in Urban Coastal Flooding. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, Z.; Su, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Hydrodynamic Interactions between Tide and Runoff in the Luanhe Estuary in Bohai Sea, China: From Aquaculture Reclamation to Restoration. Ocean Coast Manag. 2023, 239, 106586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemond, B.; de Swart, H.E.; Dijkstra, H.A.; Díez-Minguito, M. Estuarine Salinity Response to Freshwater Pulses. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2022, 127, e2022JC018669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Site | Residential | Commercial | Industrial | Agriculture | Parks | Other | % Urban |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 38.9 | 15.4 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 43.7 | 56.2 |
| Suburban | 34.2 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 29.5 | 5.9 | 23.1 | 41.6 |
| Rural | 4.3 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 4.9 | 22.8 | 67.5 | 4.8 |
| Site | Salinity | pH | DO | Turbidity | Chl-a | Temp. | FDOM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 29.7 | 7.9 | 89.2 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 19.2 | 55.2 |
| (1.6) | (0.1) | (7.3) | (2.7) | (1.7) | (4.1) | (6.5) | |
| GTM Urban | 32.7 | 7.9 | 86.0 | 11.0 | 9.5 | 26.1 | |
| (2.2) | (0.2) | (11.9) | (48.2) | (3.8) | (4.5) | ||
| Suburban | 27.5 | 7.6 | 73.2 | 10.1 | 6.3 | 27.0 | 71.5 |
| (7.2) | (0.2) | (14.1) | (17.2) | (3.9) | (4.7) | (50.1) | |
| Inlet | 34.2 | 8.0 | 91.6 | 10.7 | 7.5 | 27.3 | 16.4 |
| (1.9) | (1.1) | (9.4) | (16.0) | (10.70) | (2.8) | (16.3) | |
| GTM Inlet | 33.1 | 7.9 | 89.4 | 7.5 | 6.7 | 26.1 | |
| (2.0) | (0.1) | (10.0) | (39.2) | (3.4) | (4.4) | ||
| Estuarine | 29.9 | 7.9 | 86.4 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 26.3 | 56.4 |
| (4.4) | (0.2) | (11.3) | (9.2) | (8.2) | (4.5) | (40.3) | |
| GTM Rural | 8.9 | 7.0 | 63.2 | 10.7 | 16.1 | 26.0 | |
| (7.0) | (0.4) | (14.3) | (7.0) | (4.2) | (5.4) | ||
| Rural | 0.2 | 6.6 | 47.6 | 2.2 | 11.7 | 23.8 | 171.2 |
| (0.3) | (0.3) | (11.8) | (10.8) | (5.2) | (4.7) | (26.6) |
| Salinity | pH | DO | Turb. | Chl-a | Temp | FDOM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | 1 | ||||||
| pH | 0.93 | 1 | |||||
| % DO | 0.82 | 0.82 | 1 | ||||
| Turbidity | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 1 | |||
| Chl-a | −0.34 | −0.34 | −0.23 | 0.07 | 1 | ||
| Temp | 0.28 | 0.18 | −0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 1 | |
| FDOM | −0.93 | −0.81 | −0.77 | −0.19 | 0.29 | −0.34 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaya, T.M.; Schafer, T.B.; Osborne, T.Z. Assessing Water Quality Dynamics in Tidally Influenced Blackwater Rivers along a Rural–Urban Gradient. Water 2023, 15, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234154
Chaya TM, Schafer TB, Osborne TZ. Assessing Water Quality Dynamics in Tidally Influenced Blackwater Rivers along a Rural–Urban Gradient. Water. 2023; 15(23):4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234154
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaya, Taryn M., Tracey B. Schafer, and Todd Z. Osborne. 2023. "Assessing Water Quality Dynamics in Tidally Influenced Blackwater Rivers along a Rural–Urban Gradient" Water 15, no. 23: 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234154
APA StyleChaya, T. M., Schafer, T. B., & Osborne, T. Z. (2023). Assessing Water Quality Dynamics in Tidally Influenced Blackwater Rivers along a Rural–Urban Gradient. Water, 15(23), 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15234154





