Impact of Hydrodynamic Conditions on the Production and Distribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substance in River Biofilms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biofilm Cultivation
2.2. Biofilm Analysis
2.2.1. Sampling and Preprocessing
2.2.2. Fluorescence Labeling and CLSM Image
2.2.3. Extraction of Extracellular Polymeric Substance
3. Results and Discussion
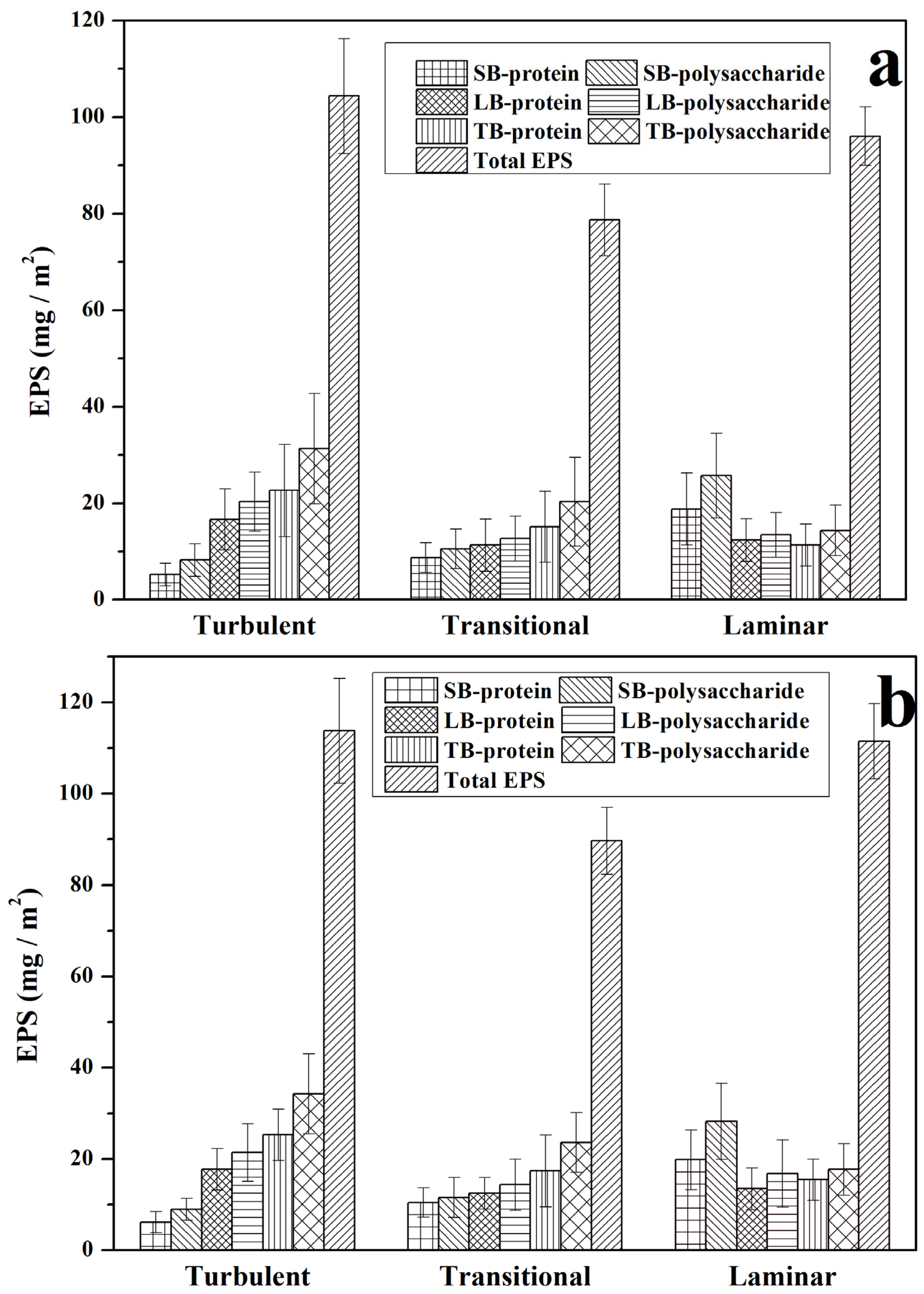
3.1. The Composition and Content of EPS in Biofilms
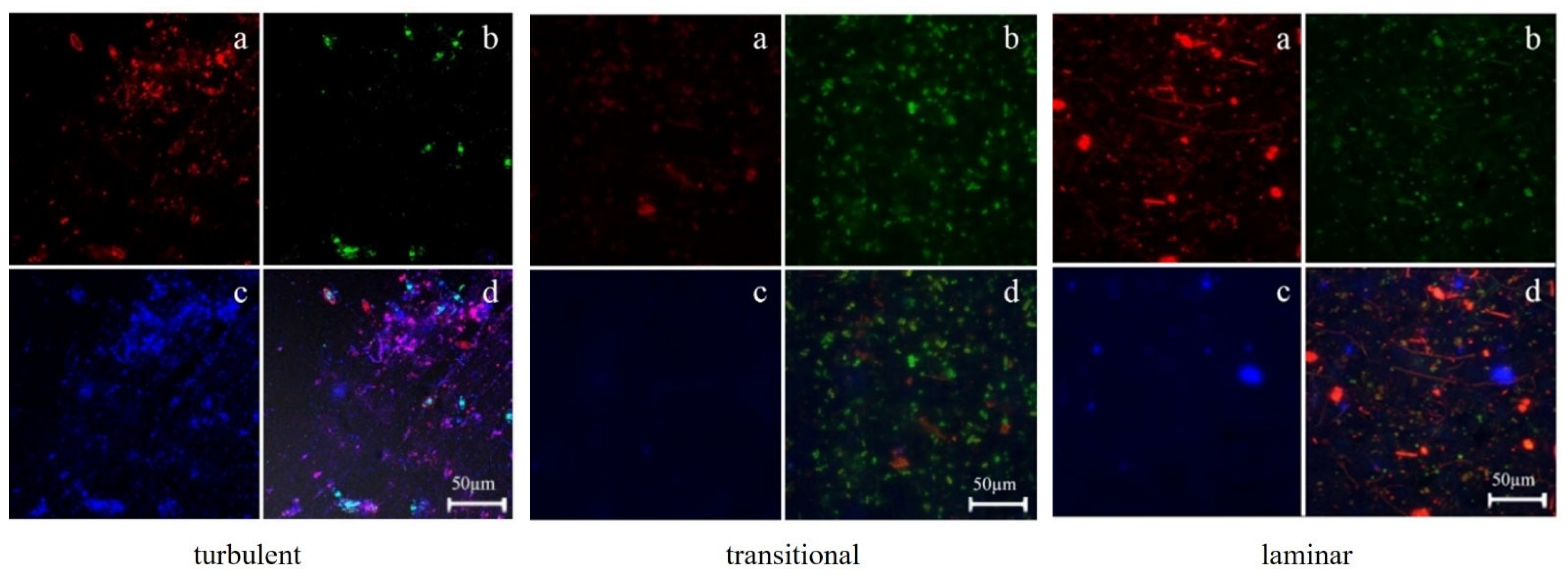
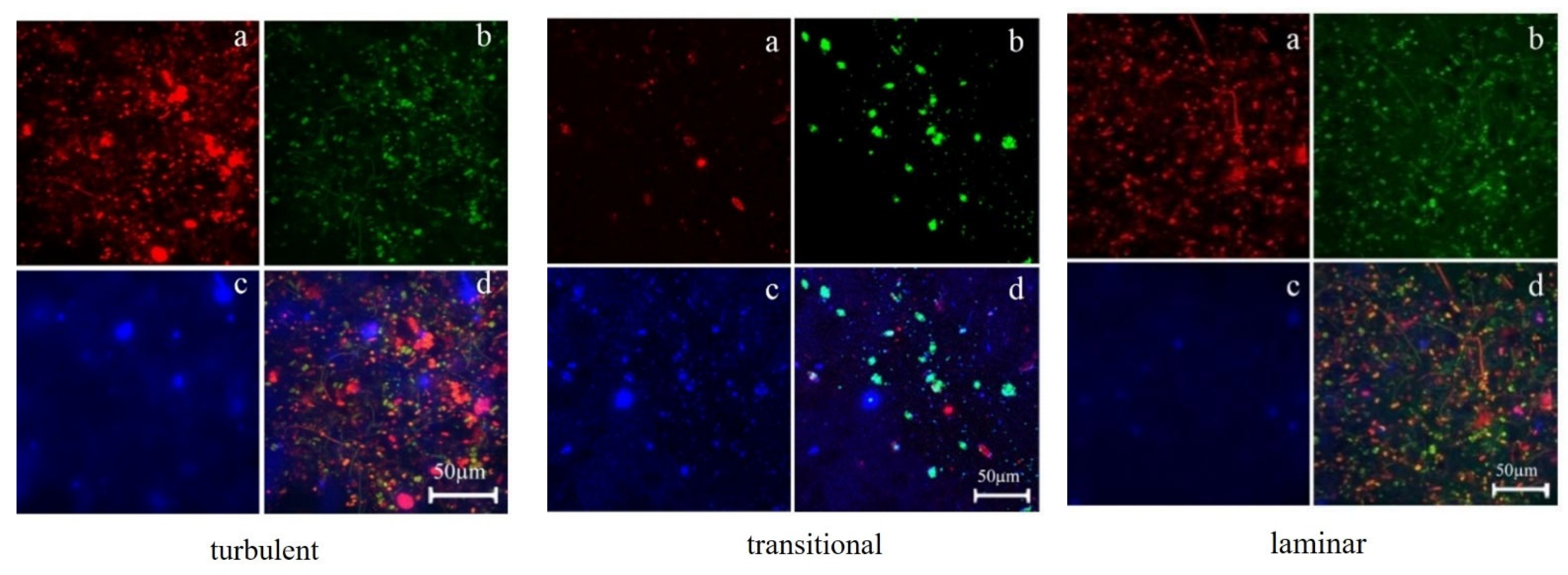
3.2. Distribution of EPS in Biofilms
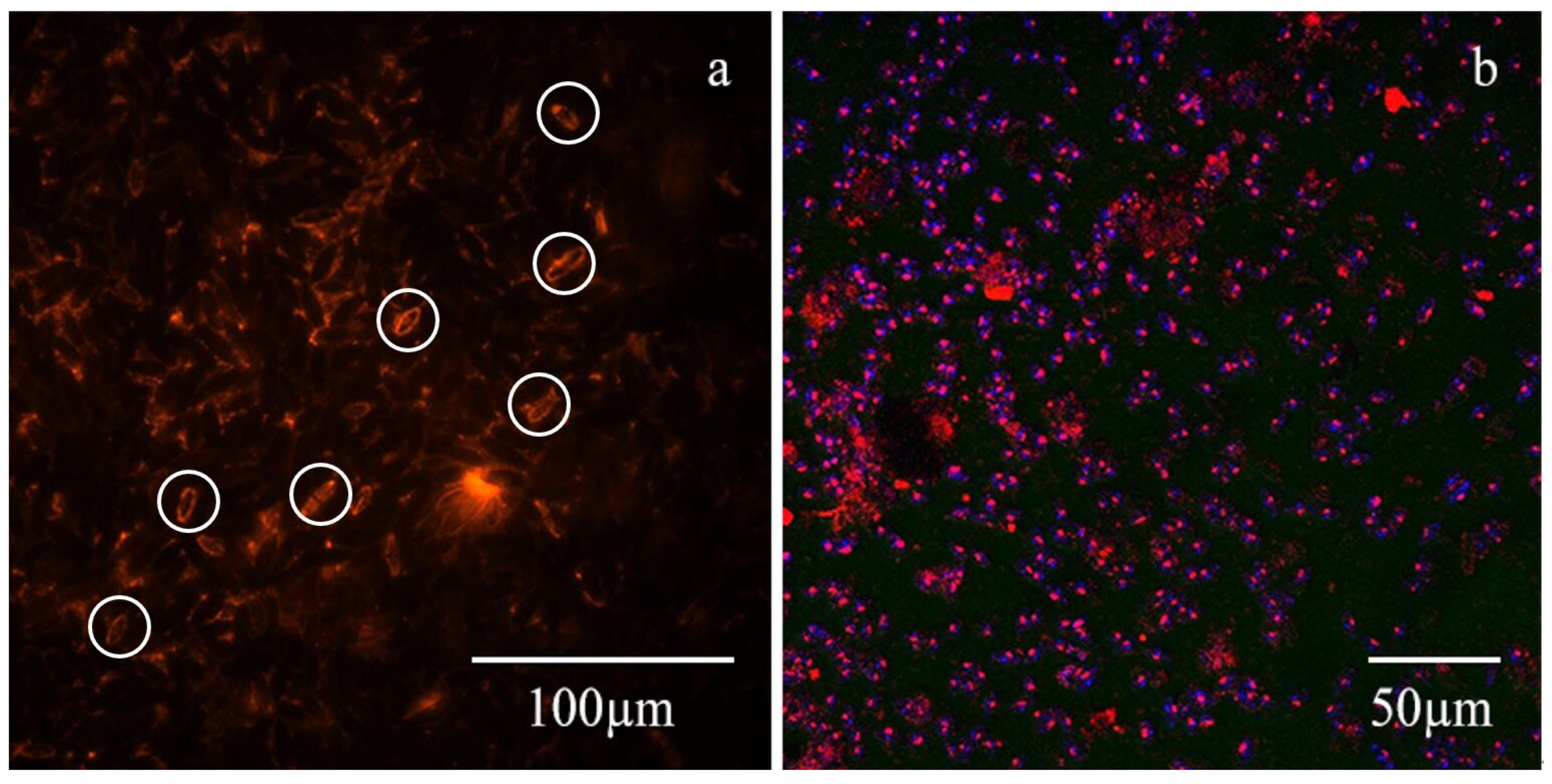
3.2.1. Distribution of TB-EPS and Bacteria around Algae
3.2.2. The Relationship between the Distribution of EPS in Biofilms and Biofilm Formation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| EPS | extracellular polymeric substance |
| SB-EPS | dissolved EPS |
| LB-EPS | loosely bound EPS |
| TB-EPS | tightly bound EPS |
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| CLSM | confocal laser scanning microscope |
| LSM | laser scanning microscope |
| FITC | fluorescein-isothiocyanate concanavalin |
| ConA-TMR | A conjugated with tetramethylrhodamine |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| L | litre |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
References
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risse-Buhl, U.; Anlanger, C.; Kalla, K.; Neu, T.R.; Noss, C.; Lorke, A.; Weitere, M. The role of hydrodynamics in shaping the composition and architecture of epilithic biofilms in fluvial ecosystems. Water Res. 2017, 127, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janissen, R.; Murillo, D.M.; Niza, B.; Sahoo, P.K.; Nobrega, M.M.; Cesar, C.L.; Temperini, M.L.A.; Carvalho, H.F.; de Souza, A.A.; Cotta, M.A. Spatiotemporal distribution of different extracellular polymeric substances and filamentation mediate Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm formation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, M.; Desmond, P.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Derlon, N.; Morgenroth, E.; Picioreanu, C. Effect of biofilm structural deformation on hydraulic resistance during ultrafiltration: A numerical and experimental study. Water Res. 2018, 145, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmond, P.; Best, J.P.; Morgenroth, E.; Derlon, N. Linking composition of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) to the physical structure and hydraulic resistance of membrane biofilms. Water Res. 2018, 132, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osella, M.; Tans, S.J.; Cosentino Lagomarsino, M. The Peculiar Functions of the Bacterial Extracellular Matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Esquivel-Elizondo, S.; Ma, L.; Wu, Y. Uncovering the flocculating potential of extracellular polymeric substances produced by periphytic biofilms. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248 Pt B, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romani, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The ecology and biogeochemistry of stream biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q.; Li, X.Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (eps) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fang, F.; Chen, Y.P.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.X.; Li, C.; Guo, J.S.; Liu, S.Y.; Huang, Y.; et al. Composition of EPS fractions from suspended sludge and biofilm and their roles in microbial cell aggregation. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, X.; Song, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of loosely bound eps release and floc reconstruction on sludge dewaterability. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.P.; Yu, H.Q. Characterization of extracellular polymeric substances of aerobic and anaerobic sludge using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.S.; Fang, F.; Li, C. Functional groups characteristics of eps in biofilm growing on different carriers. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Yang, J.; Ni, B.J.; Yang, C.; Yuan, C.; Li, A. Insight into the generation and consumption mechanism of tightly bound and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances by mathematical modeling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 152359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yang, S.F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; He, P.J.; Shao, L.M. Characteristics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) fractions from excess sludges and their effects on bioflocculability. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3193–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basuvaraj, M.; Fein, J.; Liss, S.N. Protein and polysaccharide content of tightly and loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances and the development of a granular activated sludge floc. Water Res. 2015, 82, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Ding, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R. The effect of hydrodynamics on the succession of autotrophic and heterotrophic organisms of biofilms in river ecosystems. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Li, H.Z.; Han, X.H.; Ma, W.X.; Li, X.; Guo, Q.Y.; Yang, B.R.; Ding, C.; Ma, Y.W. Effects of hydrodynamic conditions on the composition, spatiotemporal distribution of different extracellular polymeric substances and the architecture of biofilms. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romaní, A.M.; Fund, K.; Artigas, J.; Schwartz, T.; Sabater, S.; Obst, U. Relevance of Polymeric Matrix Enzymes During Biofilm Formation. Microb. Ecol. 2008, 56, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proia, L.; Romaní, A.M.; Sabater, S. Nutrients and light effects on stream biofilms: A combined assessment with CLSM, structural and functional parameters. Hydrobiologia 2012, 695, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.A.; Fusaro, R.M. The quantitative enzymic determination of animal liver glycogen. Anal. Biochem. 1966, 15, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterborg, J.H. The Lowry Method for Protein Quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook, 3rd ed.; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ras, M.; Lefebvre, D.; Derlon, N.; Paul, E.; Girbal-Neuhauser, E. Extracellular Polymeric Substances diversity of biofilms grown under contrasted environmental conditions. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Kaplan, L.A.; Newbold, J.D.; Cheng, X.; Hansen, C. Effects of Current Velocity on the Nascent Architecture of Stream Microbial Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5443–5452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgad, O.; Oren, Y.; Walker, S.L.; Herzberg, M. The role of alginate in Pseudomonas aeruginosa EPS adherence, viscoelastic properties and cell attachment. Biofouling 2011, 27, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.C.; Kundukad, B.; Seviour, T.; Van der Maarel, J.R.; Yang, L.; Rice, S.A.; Doyle, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Dynamic remodeling of microbial biofilms by functionally distinct exopolysaccharides. mBio 2014, 5, e01536-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadell, C.D.; Ricaurte, D.; Yan, J.; Drescher, K.; Bassler, B.L. Flow environment and matrix structure interact to determine spatial competition in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Elife 2017, 6, e21855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, S.; Huang, Q.; Peng, C. Bacterial cell surface properties: Role of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (LB-EPS). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besemer, K.; Singer, G.; Limberger, R.; Chlup, A.K.; Hochedlinger, G.; Hodl, I.; Baranyi, C.; Battin, T.J. Biophysical controls on community succession in stream biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4966–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The Crucial Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Biofilms; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2003; pp. 178–210. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, H.C.; Neu, T.R.; Wozniak, D.J. The EPS Matrix: The “House of Biofilm Cells”. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7945–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pippo, F.; Ellwood, N.T.W.; Gismondi, A.; Bruno, L.; Rossi, F.; Magni, P.; De Philippis, R. Characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by seven biofilm-forming cyanobacterial strains for biotechnological applications. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsborough, L.G.; Hickman, M. A comparison of periphytic algal biomass and community structure on Scirpus validus and on a morphologically similar artificial substratum. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halan, B.; Buehler, K.; Schmid, A. Biofilms as living catalysts in continuous chemical syntheses. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Busscher, H.J.; Norde, W.; Sjollema, J. Analysis of the contribution of sedimentation to bacterial mass transport in a parallel plate flow chamber. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, K. The genomics and proteomics of biofilm formation. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniello, V.; Peterson, B.W.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Physico-chemistry from initial bacterial adhesion to surface-programmed biofilm growth. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 261, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; van der Mei, H.C. Microbial adhesion in flow displacement systems. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, M.H.; Idris, A.L.; Fan, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, T. Beyond risk: Bacterial biofilms and their regulating approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, N.G.; Keener, J.P. The role of the biofilm matrix in structural development. Math. Med. Biol. 2004, 21, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranguet, C.; Beusekom, S.A.M.V.; Veuger, B.; Neu, T.R.; Manders, E.M.M.; Sinke, J.J.; Admiraal, W. Studying undisturbed autotrophic biofilms: Still a technical challenge. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Quan, G.; Ma, W.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Ding, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Effect of hydrodynamics on the transformation of nitrogen in river water by regulating the mass transfer performance of dissolved oxygen in biofilm. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 137013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, G.; Besemer, K.; Hödl, I.; Chlup, A.; Hochedlinger, G.; Stadler, P.; Battin, T.J. Microcosm design and evaluation to study stream microbial biofilms. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2006, 4, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lee DJ Tay, J.H. Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic granules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Tay, J.H.; Show, K.Y. Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R. Multiple Fluorescence Labeling and Two Dimensional FTIR–13C NMR Heterospectral Correlation Spectroscopy to Characterize Extracellular Polymeric Substances in Biofilms Produced during Composting. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9224–9231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, M.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, S.; Diao, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Qin, J.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z. Impact of Hydrodynamic Conditions on the Production and Distribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substance in River Biofilms. Water 2023, 15, 3821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213821
Pan M, Li H, Han X, Jiang S, Diao Y, Ma W, Li X, Qin J, Yao J, Wang Z. Impact of Hydrodynamic Conditions on the Production and Distribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substance in River Biofilms. Water. 2023; 15(21):3821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213821
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Mei, Haizong Li, Xiangyun Han, Siyi Jiang, Yusen Diao, Weixing Ma, Xuan Li, Jiaojiao Qin, Jianchun Yao, and Zhitong Wang. 2023. "Impact of Hydrodynamic Conditions on the Production and Distribution of Extracellular Polymeric Substance in River Biofilms" Water 15, no. 21: 3821. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15213821






