Synthesis of Sulfur-Doped Magnetic Iron Oxides for Efficient Removal of Lead from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Sx–Fe3O4
2.3. Characteristics of S–Fe3O4
2.4. Adsorption of Lead from Water
3. Results and Discussion
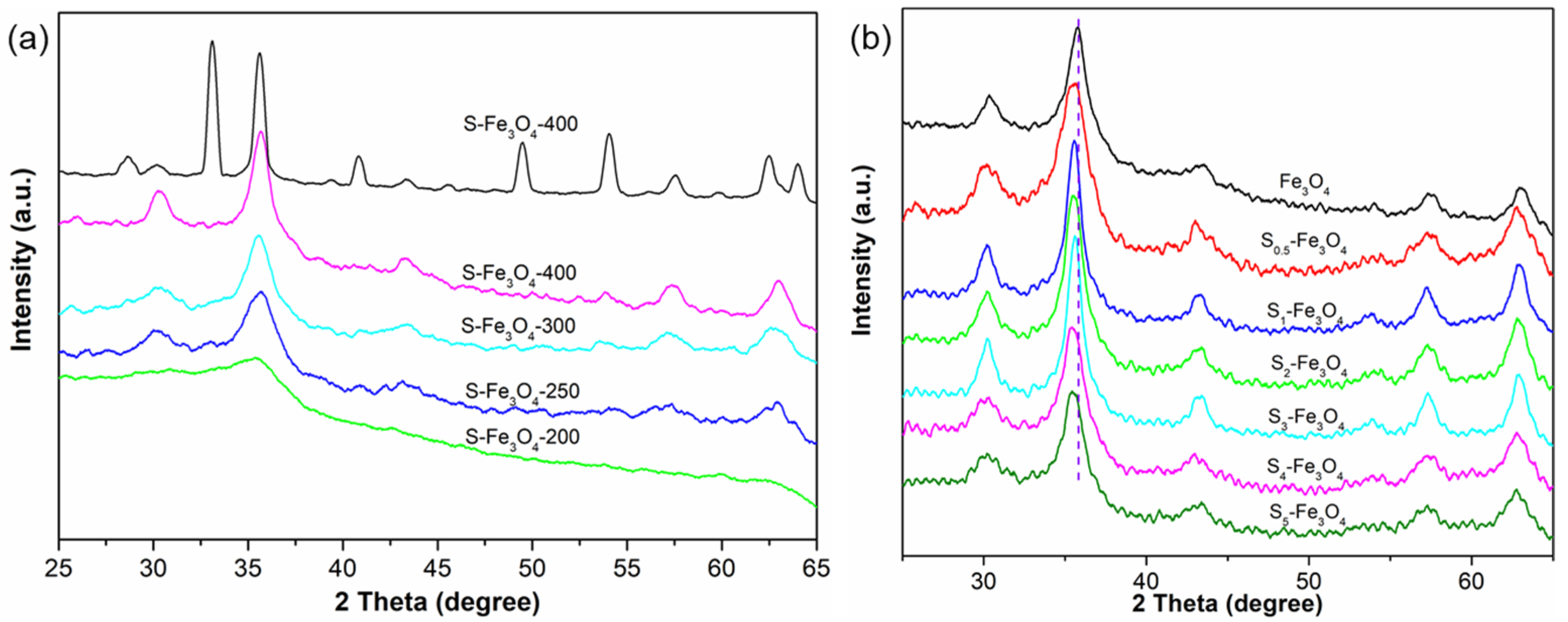
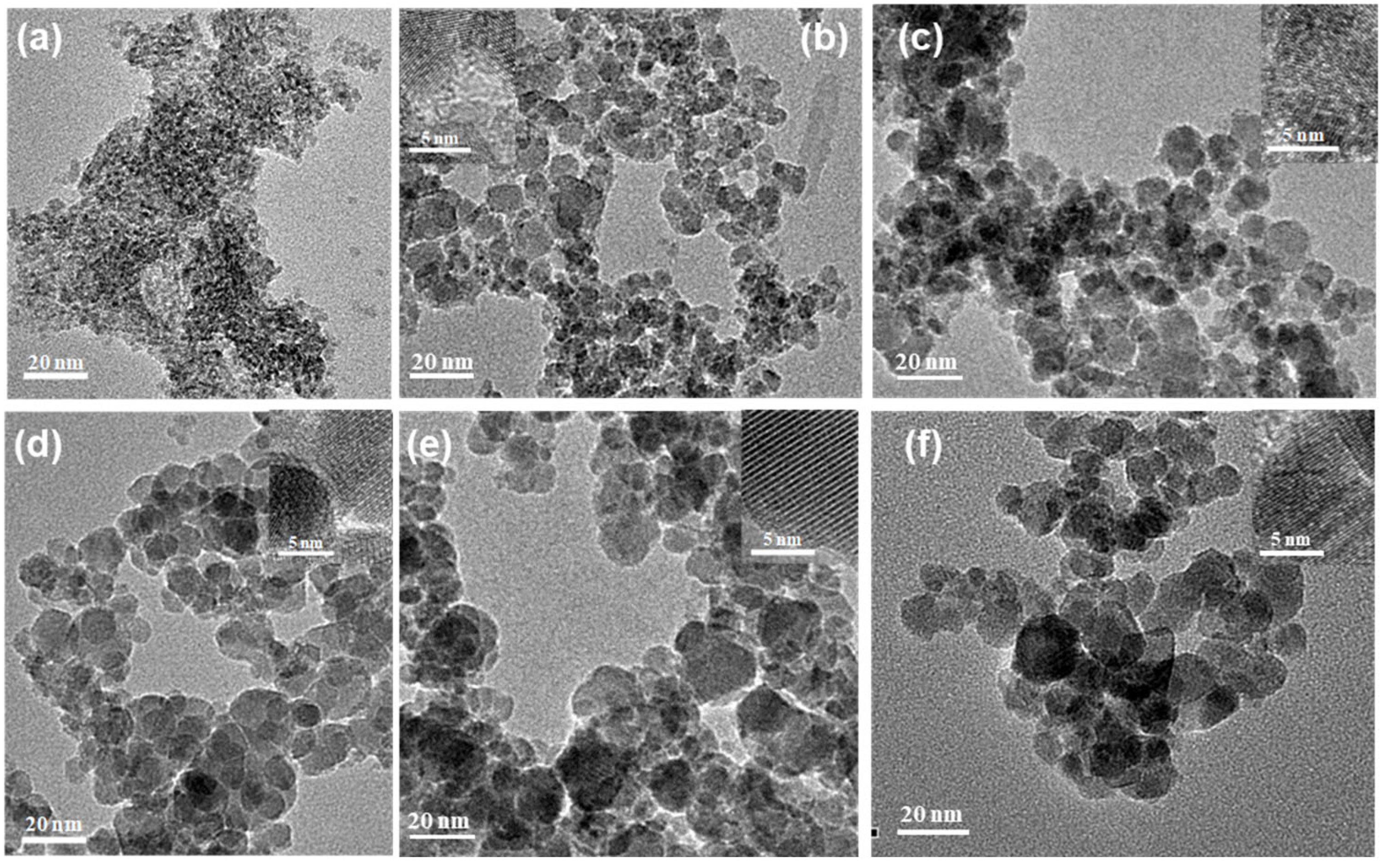
3.1. The Morphology and Structure of S–Fe3O4
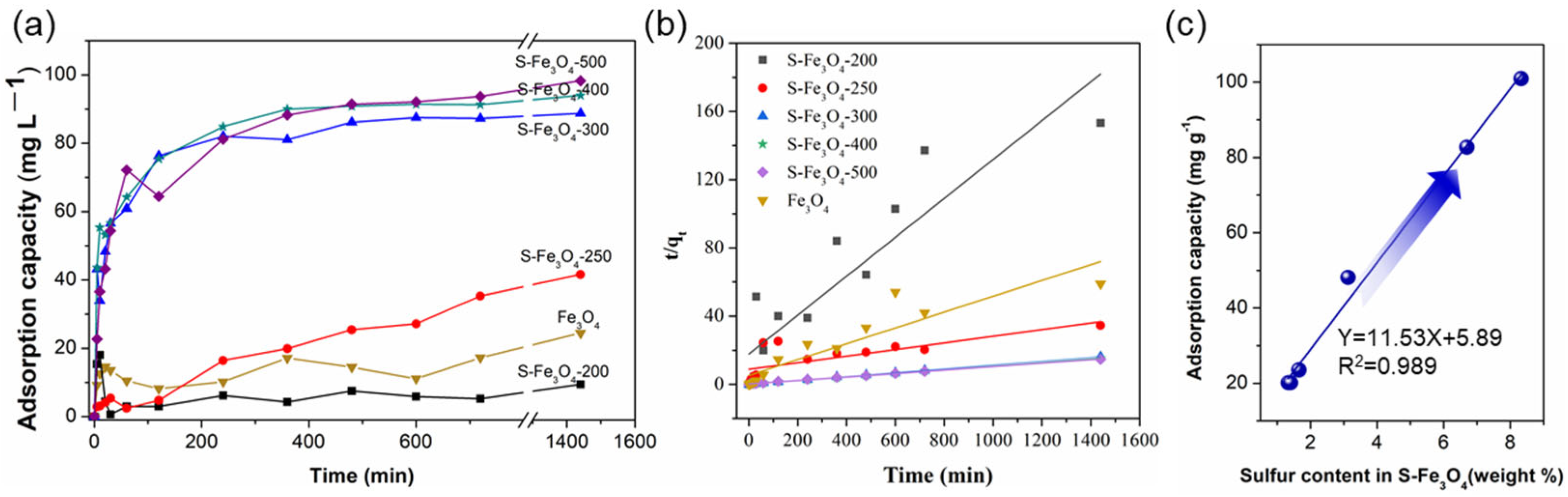
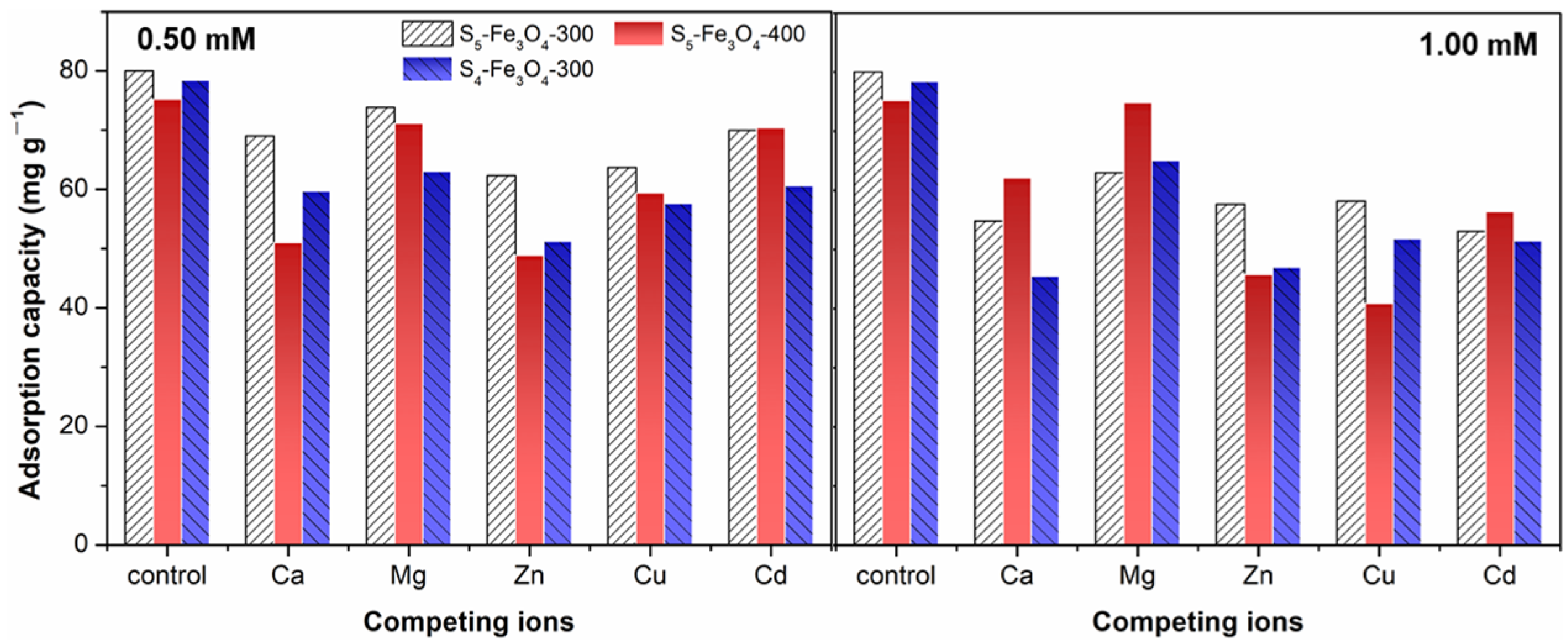
3.2. Adsorption Performance of Sx–Fe3O4
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, A.; Liu, R.; Tian, Y. Unique Lead Adsorption Behavior of Activated Hydroxyl Group in Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4113–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, Q.; Hua, M.; Jiao, T.; Gao, F.; Pan, B. Sorption Enhancement of Lead Ions from Water by Surface Charged Polystyrene-Supported Nano-Zirconium Oxide Composites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6536–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhao, B.; Lyu, H.; Li, D. Development of a novel pyrite/biochar composite (BM-FeS2@BC) by ball milling for aqueous Cr(VI) removal and its mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Yang, N.; Li, Y.; Ren, B.; Ding, X.; Bian, H.; Yao, X. Total concentrations and sources of heavy metal pollution in global river and lake water bodies from 1972 to 2017. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Pu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, A.; Zhang, X.; Pan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Adsorption and Reduction of Cr(VI) Together with Cr(III) Sequestration by Polyaniline Confined in Pores of Polystyrene Beads. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12602–12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Islam, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Kanatzidis, M.G. Highly Selective and Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals by Layered Double Hydroxide Intercalated with the MoS42- Ion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2858–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, Z.; Mackey, H.R.; Mahmoud, K.A. A critical overview of MXenes adsorption behavior toward heavy metals. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ke, Y.; Shang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liao, G. Fabrication of multifunctional biomass-based aerogel with 3D hierarchical porous structure from waste reed for the synergetic adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Xu, M.; Yu, H.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W. Mechanistic insight into selective adsorption and easy regeneration of carboxyl-functionalized MOFs towards heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Liu, X.; Yu, D.; Luo, J.; Wang, Z.; Crittenden, J.C. Highly Efficient and Selective Hg(II) Removal from Water Using Multilayered Ti(3)C(2)O(x) MXene via Adsorption Coupled with Catalytic Reduction Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 16212–16220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haounati, R.; Ighnih, H.; Ouachtak, H.; Malekshah, R.E.; Hafid, N.; Jada, A.; Addi, A.A. Z-Scheme g-C3N4/Fe3O4/Ag3PO4@ Sep magnetic nanocomposites as heterojunction photocatalysts for green malachite degradation and dynamic molecular studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 671, 131509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighnih, H.; Haounati, R.; Ouachtak, H.; Regti, A.; El Ibrahimi, B.; Hafid, N.; Jada, A.; Taha, M.L.; Addi, A.A. Efficient removal of hazardous dye from aqueous solutions using magnetic kaolinite nanocomposite: Experimental and Monte Carlo simulation studies. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonel, A.G.; Mansur, A.A.; Mansur, H.S. Advanced Functional Nanostructures based on Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanomaterials for Water Remediation: A Review. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yantasee, W.; Warner, C.L.; Sangvanich, T.; Addleman, R.S.; Carter, T.G.; Wiacek, R.J.; Fryxell, G.E.; Timchalk, C.; Warner, M.G. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Systems with Thiol Functionalized Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5114–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, J. Thiol modified Fe3O4@SiO2 as a robust, high effective, and recycling magnetic sorbent for mercury removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, J.; Pan, B. Fabrication of Novel Magnetic Nanoparticles of Multifunctionality for Water Decontamination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Zhu, D.; He, P.; Han, P.; Wei, G. Self-assembled peptide nanosheets functionalized with Fe3O4 nanoparticles with enhanced nanozymatic activity for sensitive colorimetric detection and selective adsorption of Hg2+. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Song, T.; Tang, C.; Meng, Y.; Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Chai, L.; et al. Synthesis of Core-Shell Magnetic Fe3O4@poly(m-Phenylenediamine) Particles for Chromium Reduction and Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5654–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Niu, C.-G.; Li, X.-T.; Liang, C.; Guo, H.; Lin, L.-S.; Zheng, C.-W.; Zeng, G.-M. Efficient removal of Cd2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solution with amino- and thiol-functionalized activated carbon: Isotherm and kinetics modeling. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 635, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromah, V.; Zhang, G. Aqueous Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Metal Sulfide Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Application. Water 2021, 13, 1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Modification, application and reaction mechanisms of nano-sized iron sulfide particles for pollutant removal from soil and water: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, D. Immobilization of Mercury by Carboxymethyl Cellulose Stabilized Iron Sulfide Nanoparticles: Reaction Mechanisms and Effects of Stabilizer and Water Chemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Hanpei, Y.; Lina, W.; Siqi, C.; Ruichen, Z.; Junming, W.; Xiaona, L. Facile integration of FeS and titanate nanotubes for efficient removal of total Cr from aqueous solution: Synergy in simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and adsorption of Cr(III). J. Hazard Mater. 2020, 398, 122834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, X.-B.; Zeng, R.J. Reactivity enhancement of iron sulfide nanoparticles stabilized by sodium alginate: Taking Cr (VI) removal as an example. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 333, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.-J.; Shi, J.-W.; Yuan, B.; Fu, M.-L. Synthesis of porous magnetic ferrite nanowires containing Mn and their application in water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5902–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Fan, J.; Wan, K.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Bo, W.; Gao, M.; Miao, Z. Calcium-Modified Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Encapsulated in Humic Acid for the Efficient Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Langmuir 2021, 37, 10994–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Joshi, T.P.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. Synthesis of Ce(III)-doped Fe3O4 magnetic particles for efficient removal of antimony from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 329, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.B.; Patil, K.R.; Pardeshi, S.K. Ecofriendly synthesis and solar photocatalytic activity of S-doped ZnO. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, N. Re-examination of characteristic FTIR spectrum of secondary layer in bilayer oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huberty, J.; Madix, R. An FTIR study of the bonding of methoxy on Ni(100): Effects of coadsorbed sulfur, carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Surf. Sci. 1996, 360, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Rad, A.T.; Zheng, W.; Nieh, M.P.; Cornelius, C.J. Hybrid organic-inorganic 6FDA-6pFDA and multi-block 6FDA-DABA polyimide SiO2-TiO2 nanocomposites: Synthesis, FFV, FTIR, swelling, stability, and X-ray scattering. Polymer 2017, 108, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and Their Magnetic Properties. In Proceedings of the 2011 Chinese Materials Conference, Beijing, China, 18–23 August 2011; Volume 27, pp. 632–637. [Google Scholar]
- Jegadeesan, G.; Al-Abed, S.R.; Sundaram, V.; Choi, H.; Scheckel, K.G.; Dionysiou, D.D. Arsenic sorption on TiO2 nanoparticles: Size and crystallinity effects. Water Res. 2010, 44, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of Arsenic(V) and Arsenic(III) Sorption onto Iron Oxide Minerals: Implications for Arsenic Mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Yang, L.; Shao, P.; Shi, H.; Chang, Z.; Fang, D.; Wei, Y.; Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, K.; et al. Proton Self-Enhanced Hy-droxyl-Enriched Cerium Oxide for Effective Arsenic Extraction from Strongly Acidic Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10412–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, R.-L.; Wu, F.-C. Inferring the favorable adsorption level and the concurrent multi-stage process with the Freundlich constant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

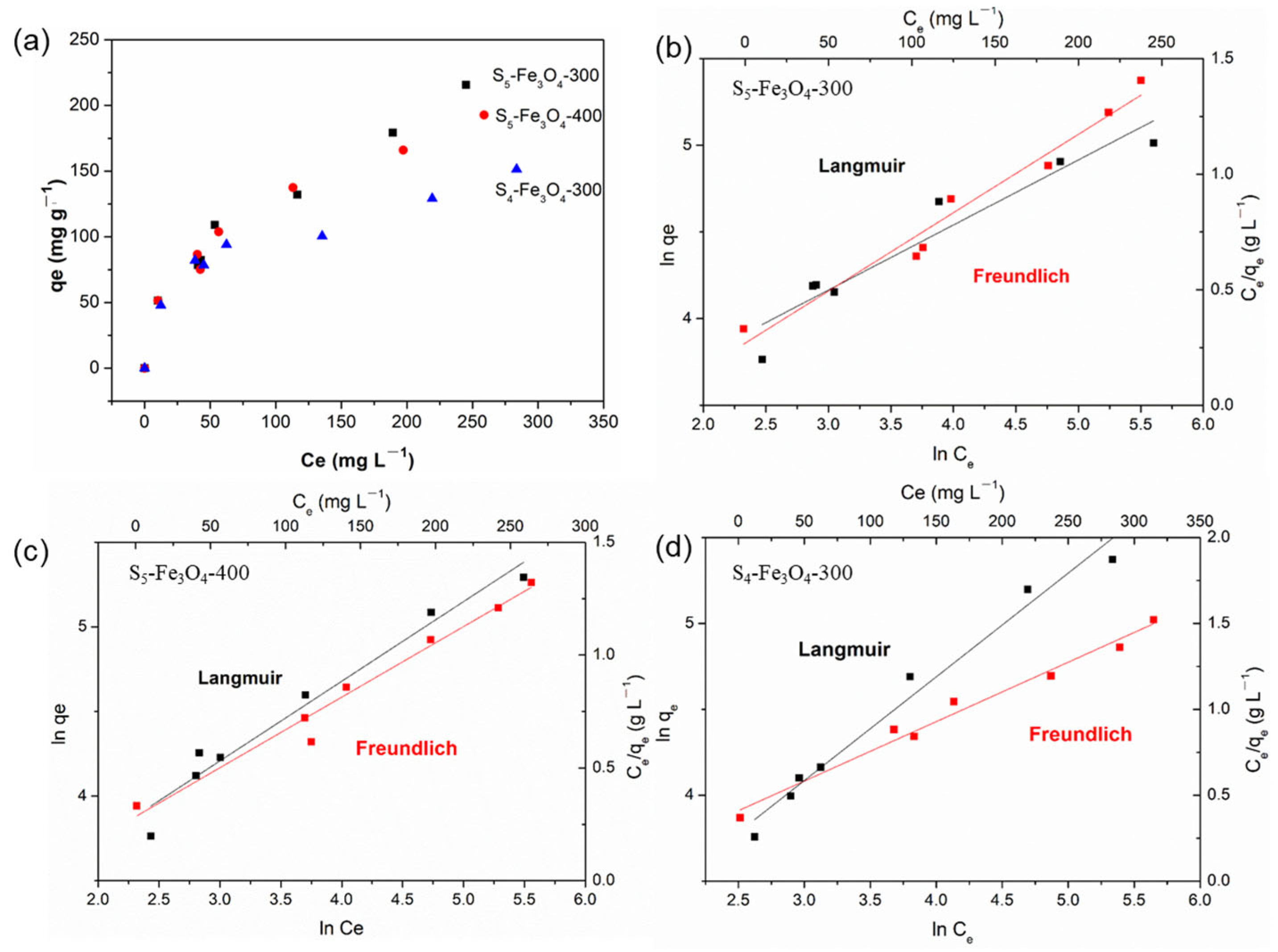
| Adsorbents | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | KL | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| S5–Fe3O4-300 | 333.33 | 0.0096 | 0.920 | 16.49 | 0.451 | 0.967 |
| S5–Fe3O4-400 | 250.00 | 0.0140 | 0.964 | 18.47 | 0.416 | 0.974 |
| S4–Fe3O4-300 | 166.67 | 0.0212 | 0.978 | 21.01 | 0.345 | 0.981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Pan, M.; Zou, C.; Huang, X.; Hagio, T.; Ichino, R.; Kong, L.; Li, L. Synthesis of Sulfur-Doped Magnetic Iron Oxides for Efficient Removal of Lead from Aqueous Solutions. Water 2023, 15, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203667
Xu J, Pan M, Zou C, Huang X, Hagio T, Ichino R, Kong L, Li L. Synthesis of Sulfur-Doped Magnetic Iron Oxides for Efficient Removal of Lead from Aqueous Solutions. Water. 2023; 15(20):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203667
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Junqing, Meitian Pan, Cong Zou, Xueqiong Huang, Takeshi Hagio, Ryoichi Ichino, Long Kong, and Liang Li. 2023. "Synthesis of Sulfur-Doped Magnetic Iron Oxides for Efficient Removal of Lead from Aqueous Solutions" Water 15, no. 20: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15203667






