Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Infiltration under Ponded Conditions
3.2. Pressure Head–Soil Moisture Research
3.2.1. First Drainage
3.2.2. Second Imbibition
3.2.3. Characteristic Curves of the Two Layers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| a | Hydraulic parameter in Van Genuchten’s model |
| θ | soil moisture |
| θi | initial water content |
| θs | soil moisture at saturation |
| C | Specific water capacity |
| CC | Ceramic capsule(s) |
| D | Diffusivity |
| h | Suction |
| Hf | Suction at the wet front |
| H0 | Pressure head at the soil surface |
| I | Cumulative infiltration |
| GA | Green and Ampt |
| Ki | Hydraulic conductivity |
| Ks | Hydraulic conductivity at saturation |
| LS-layer | Loamy sand layer |
| m | Hydraulic parameter in Van Genuchten’s model |
| n | Hydraulic parameter in Van Genuchten’s model |
| P | Parlange |
| PT | Pressure transducer(s) |
| S | Sorptivity |
| S-layer | Sand layer |
| Sm | A series of coefficients in Philip’s Equation |
| SWCC | Soil water characteristic curve(s) |
| t | time |
| TDR | Time domain reflectometry |
References
- Sallwey, J.; Jurado, A.; Barquero, F.; Fahl, J. Enhanced Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern through Hydraulic Adjustments in Soil Aquifer Treatment. Water 2020, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, B.; Dyck, M.; Parkin, G. Flow and Transport in Layered Soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Wenke, W.; Ming, Z.; Zhitong, M.; Chuan, L.; Ying, L. Interaction between Surface Water and Groundwater in Yinchuan Plain. Water 2020, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Otman, M.; Anouar, C.; Charif, A. Response of Clementine Mandarin to Water-Saving Strategies under Water Scarcity Conditions. Water 2000, 12, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Chao, C. An Investigation of the Frequency and Duration of a Drive Spoon–Dispersed Water Jet and Its Influence on the Hydraulic Performance of a Large-Volume Irrigation Sprinkler. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Textural Layering on Water Regimes in Sandy Soils in a Desert-Oasis Ecotone, Northwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 627500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Shao, M.-A.; Melegy, A.A. Soil Water Distribution and Movement in Layered Soils of a Dam Farmland. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, Z.; Cheraghi, A.; Willardson, L. Water movement in horizontally layered soils. J. Irrig. Drain Div. ASCE 1989, 115, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Mao, X.; Shukla, M.K. Evaluating the effects of layered soils on water flow, solute transport, and crop growth with a coupled agro-eco-hydrological model. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3442–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettl, J.; Lee Barbour, S.; Huang, M.; Si, B.; Leskiw, L.A. Influence of textural layering on field capacity of coarse soils. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, M.; Si, B.C.; Yu, M.; Shao, M. The differences of water balance components of Caragana korshinkii grown in homogeneous and layered soils in the desert–Loess Plateau transition zone. J. Arid. Environ. 2013, 98, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Hongjian, L.; Jiwen, Z. Infiltration Law of Water in Undisturbed Loess and Backfill. Water 2020, 12, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, C.; Goffeau, A.; Heibloem, M. Chapter 2. Soil and Water. In FAO-Irrigation Water Management; Land and Water Development Division FAO Via delle Terme di Caracalla 00100; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1985; pp. 2.1–2.3. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, M.; Lauenroth, W.K. The influence of soil texture on the soil water dynamics and vegetation structure of a shortgrass steppe ecosystem. Plant Ecol. 1997, 133, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Elshorbagy, A.; Barbour, S.L.; Zettl, J.; Si, B.C. System dynamics modeling of infiltration and drainage in layered coarse soil. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 91, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, D.J.; Brown, K.W.; Thomas, J.C. The Effectiveness of Capillary Barriers to Hydraulically Isolate Salt Contaminated Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1998, 104, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Huang, M. Fine root distributions and water consumption of alfalfa grown in layered soils with different layer thicknesses. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.; Alani, E.; Abid, M. Modeling Infiltration and Water Distribution Process of Layered Soils Using HYDRUS-1D. Indian J. Ecol. 2021, 48, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Gao, Y. Numerically Simulated Water Movement in Reclaimed Multi-Layered Soil Backfilled with Yellow River Sediments. 2021; preprint available at Research Square. [Google Scholar]
- Angelaki, A.; Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M.; Tzimopoulos, C. Laboratory experiments and estimation of cumulative infiltration and sorptivity. Water Air Soil Pollut. Focus 2004, 4, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, A.; Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M.; Tzimopoulos, C. Theoretical and Experimental Research of Cumulative Infiltration. Transp. Porous Media 2013, 100, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, A.; Sihag, P.; Makrantonaki, M.S.; Tzimopoulos, C. The effect of sorptivity on cumulative infiltration. Water Supply 2020, 21, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaki, A.; Dionysidis, A.; Sihag, P.; Golia, E.E. Assessment of Contamination Management Caused by Copper and Zinc Cations Leaching and Their Impact on the Hydraulic Properties of a Sandy and a Loamy Clay Soil. Land 2022, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Cook, F. Sorptivity of Soils. In Encyclopedia of Agrophysics; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, D.; Parlange, J.-Y. Wetting Front Instability in Layered Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1972, 36, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J. Theory of infiltration: 1. The infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J. Theory of infiltration: 4. Sorptivity and algebraic infiltration equations. Soil Sci. 1957, 84, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J. Numerical solution of equations of the diffusion type with diffusivity concentration—Dependent. II. Austr. J. Phys. 1957, 10, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J. Theory of infiltration: 6. Effect of water depth over soil. Soil Sci. 1958, 85, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J. Theory of infiltration. Adv. Hydrosci. 1969, 5, 215–296. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, J. On solving the unsaturated flow equation: 1. The flux—concentration relation. Soil Sci. 1973, 116, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabovský, A.; Pavel, D.; Artemi, C.; Jozef, K. The Impacts of Vineyard Afforestation on Soil Properties, Water Repellency and Near-Saturated Infiltration in the Little Carpathians Mountains. Water 2020, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauclin, M.; Haverkamp, R. Solutions quasi analytiques de l’ equation d’ absorption de l’ eau par les sols non saturs. I. Analyse critique. Agronomie 1985, 5, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.H.; Ampt, A. Studies on soil physics: The flow of air and water through soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Palrlange, J. Theory of water movement in soils: 1. One—Dimensional absorption. Soil Sci. 1971, 111, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palrlange, J. Theory of water movement in soils: 2. One—Dimensional infiltration. Soil Sci. 1971, 111, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palrlange, J. Theory of water movement in soils. 6. Effect of water depth over soil. Soil Sci. 1972, 133, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palrlange, J. Theory of water movement in soils. 8. One—Dimensional infiltration with constant flux at the surface. Soil Sci. 1972, 114, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlange, J.-Y. A Note on The Green and Ampt Equation. Soil Sci. 1975, 119, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous medium. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mualem, Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Genuchten, R. Calculating the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity with a new closed form analytical model. Water Res. Prog. Res. Rep. 1978, 78, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Page, A. Methods of Soil Analysis-Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties, 2nd ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 421–422. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, A.T.; Corey, A.T. Hydraulic Properties of Porous Media; Hydrology Papers Colorado State University: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 1964; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Wenbin, Y.; Hongbin, Z.; Qunou, J.; Mingchangi, S.; Yunqi, W. On the Origin of Deep Soil Water Infiltration in the Arid Sandy Region of China. Water 2020, 12, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.-C. Behavior of Unsaturated Layered Soil Columns during Infiltration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2006, 11, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, T.; Liqiao, L.; Gen, L. The Influence of Horizontal Variability of Hydraulic Conductivity on Slope Stability under Heavy Rainfall. Water 2020, 12, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihag, P.; Angelaki, A.; Jain, B.C. Estimation of the recharging rate of ground water using Random Forest Technique. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyo, E.; Ng’ambi, S.; Abbey, S.J. An overview of soil–water characteristic curves of stabilised soils and their influential factors. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2022, 34, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Rahardjo, H.; Satyanaga, A.; Dai, G.; Zhuang, Y. Framework to estimate the soil-water characteristic curve for soils with different void ratios. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2020, 79, 4399–4409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.M.; Rekapalli, M. Identifying the dominant mode of moisture transport during drying of unsaturated soils. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topp, G.C. Soil-Water Hysteresis Measured in a Sandy Loam and Compared with the Hysteretic Domain Model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1969, 33, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Khorshidi, M. Mechanisms for Soil-Water Retention and Hysteresis at High Suction Range. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2015, 141, 04015032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulovassilis, A. Hysteresis of pore water, an application of the concept of independent domains. Soil Sci. 1962, 93, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Hoff, W. Water Transport in Brick, Stone and Concrete, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.J.; Bakera, A.T.; Alexander, M.G. A critical review of the Water Sorptivity Index (WSI) parameter for potential durability assessment: Can WSI be considered in isolation of porosity? J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2021, 63, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, R.; Lozano, L.A.; Melani, E.M.; Salazar, M.P.; Otero, M.F.; Soracco, C.G. Diffusivity and sorptivity determination at different soil water contents from horizontal infiltration. Geoderma 2019, 338, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou-Makrantonaki, M.; Angelaki, A.; Evangelides, C.; Bota, V.; Tsianou, E.; Floros, N. Experimental Determination of Hydraulic Conductivity at Unsaturated Soil Column. Procedia Eng. 2016, 162, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amanabadi, S.; Vazirinia, M.; Vereecken, H.; Vakilian, K.A.; Mohammadi, M.H. Comparative Study of Statistical, Numerical and Machine Learning-based Pedotransfer Functions of Water Retention Curve with Particle Size Distribution Data. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 1555–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

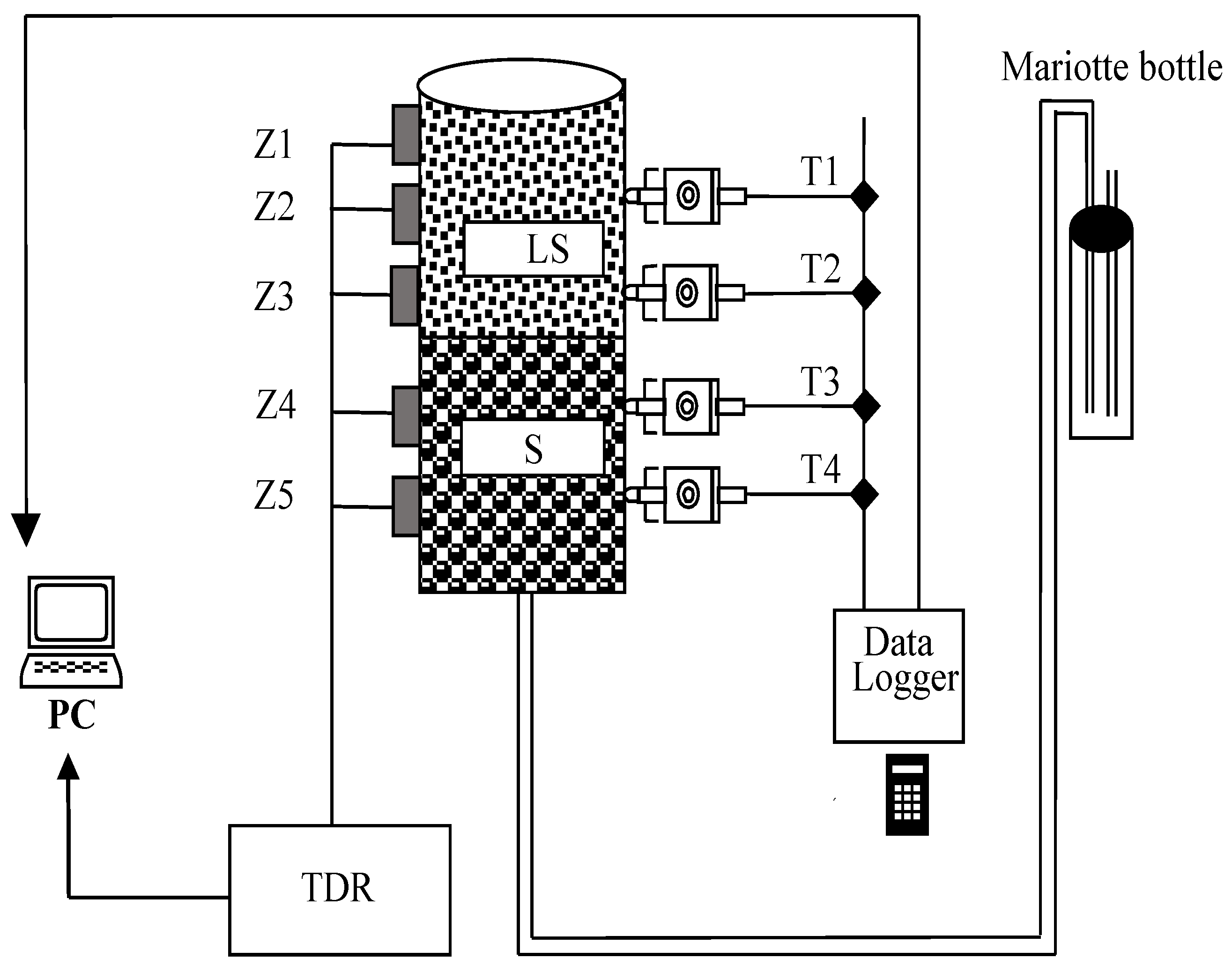
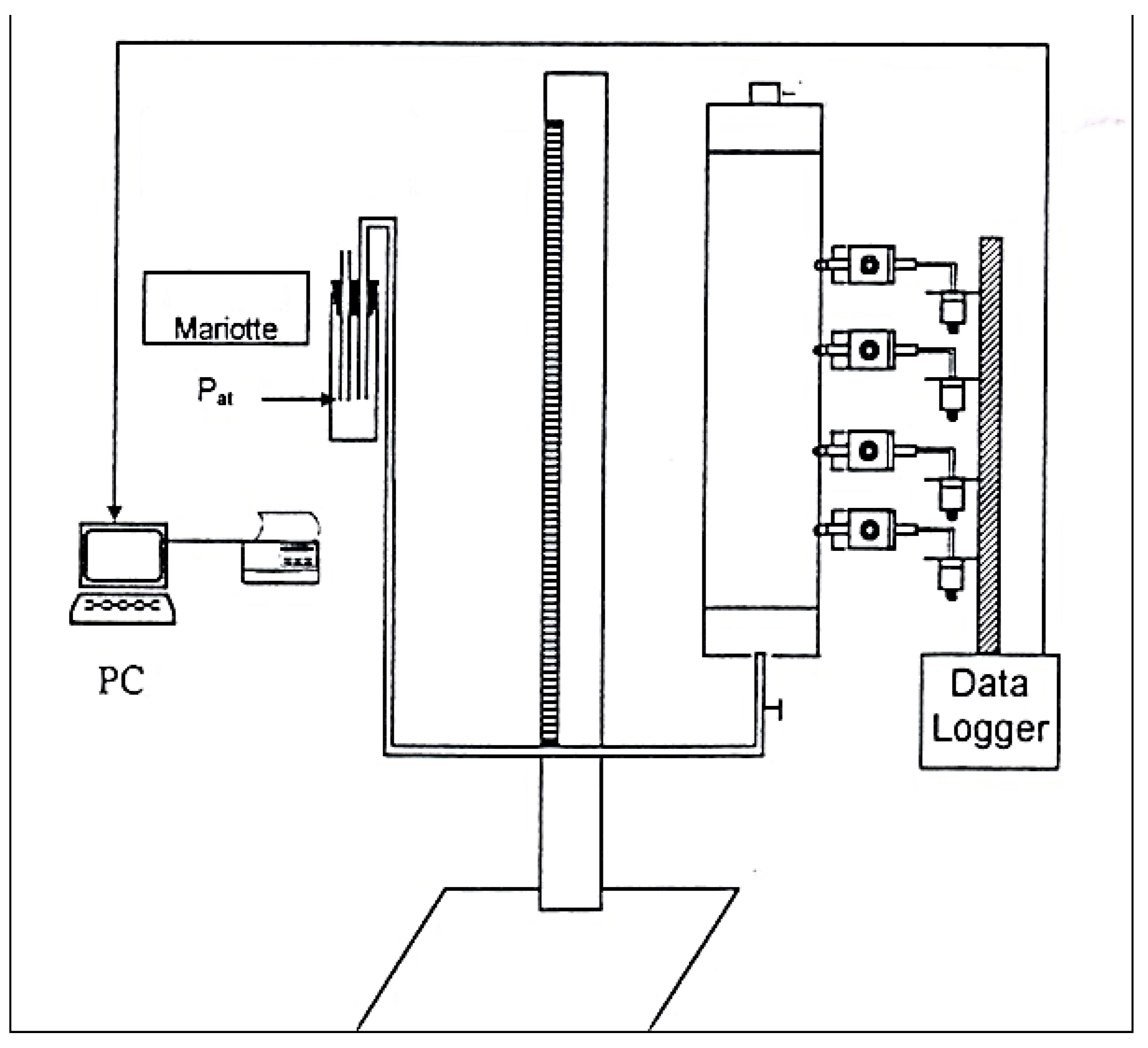
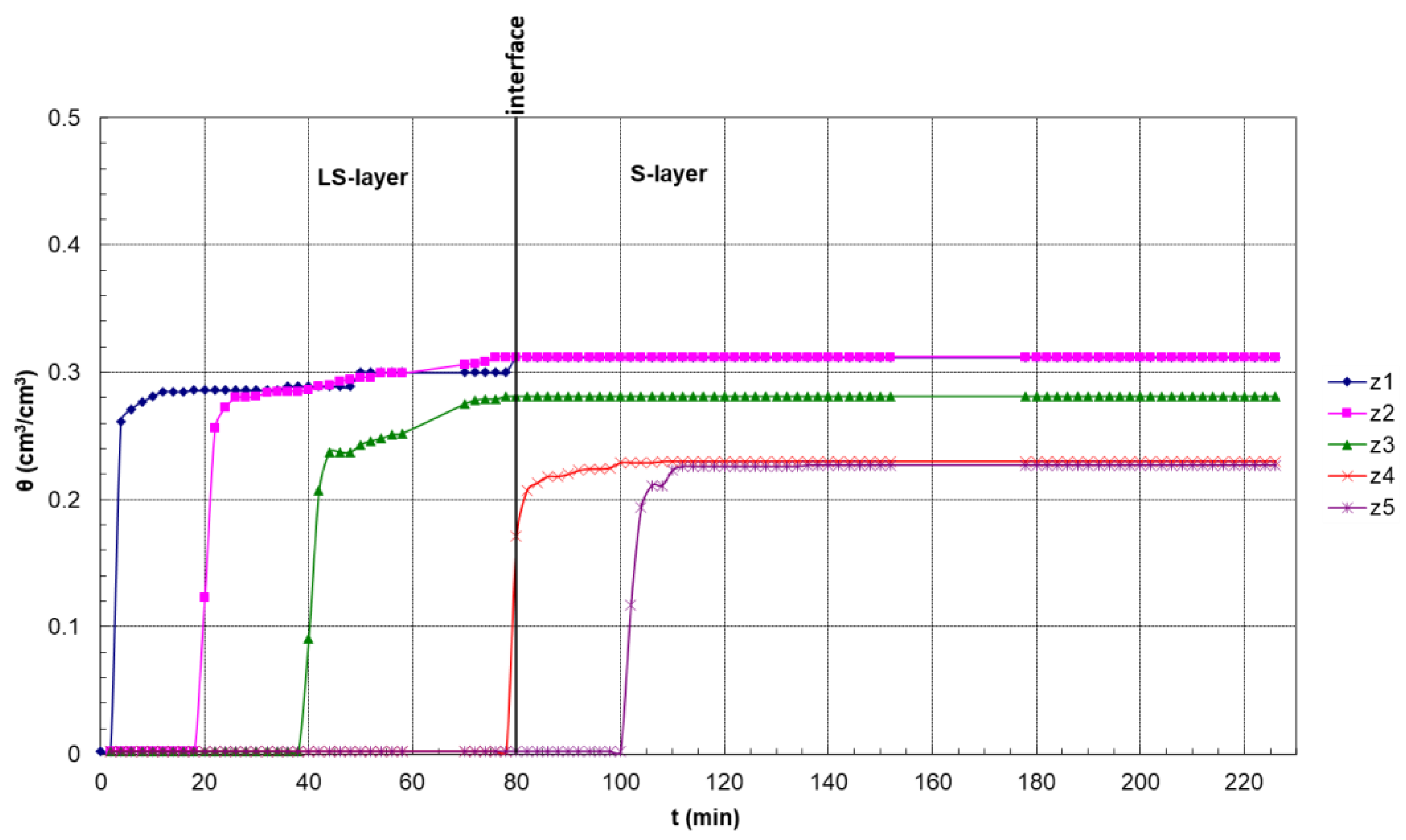
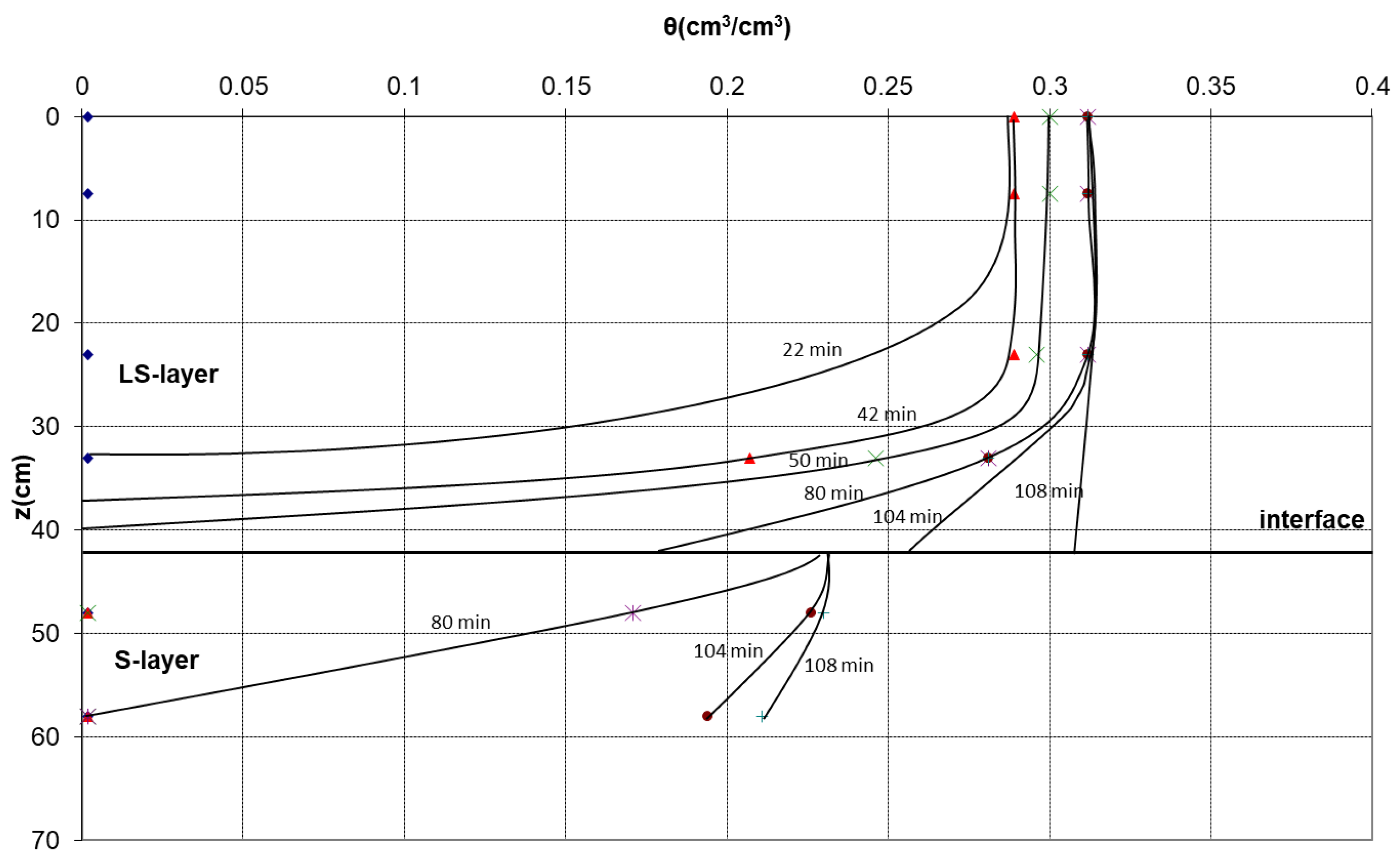

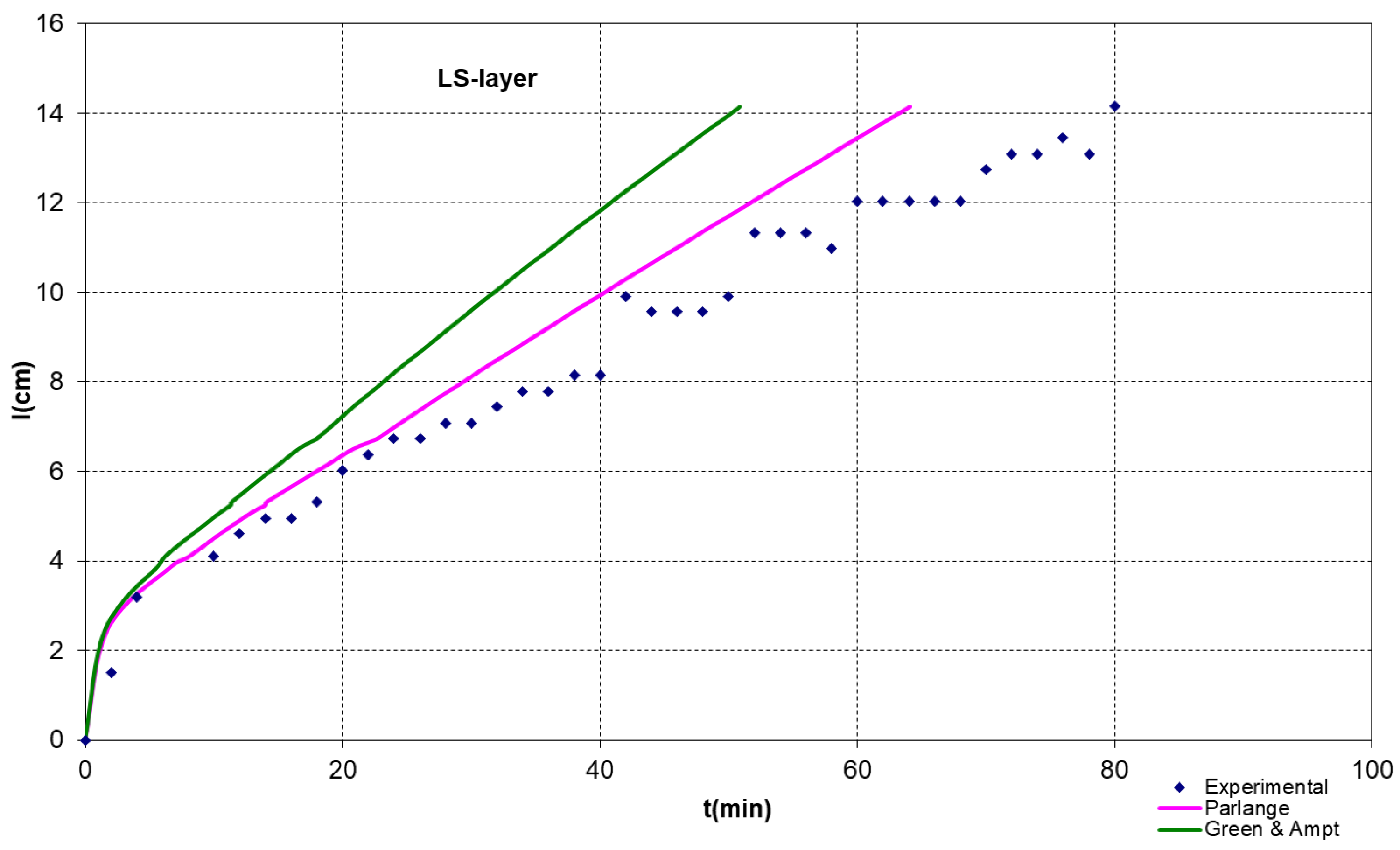
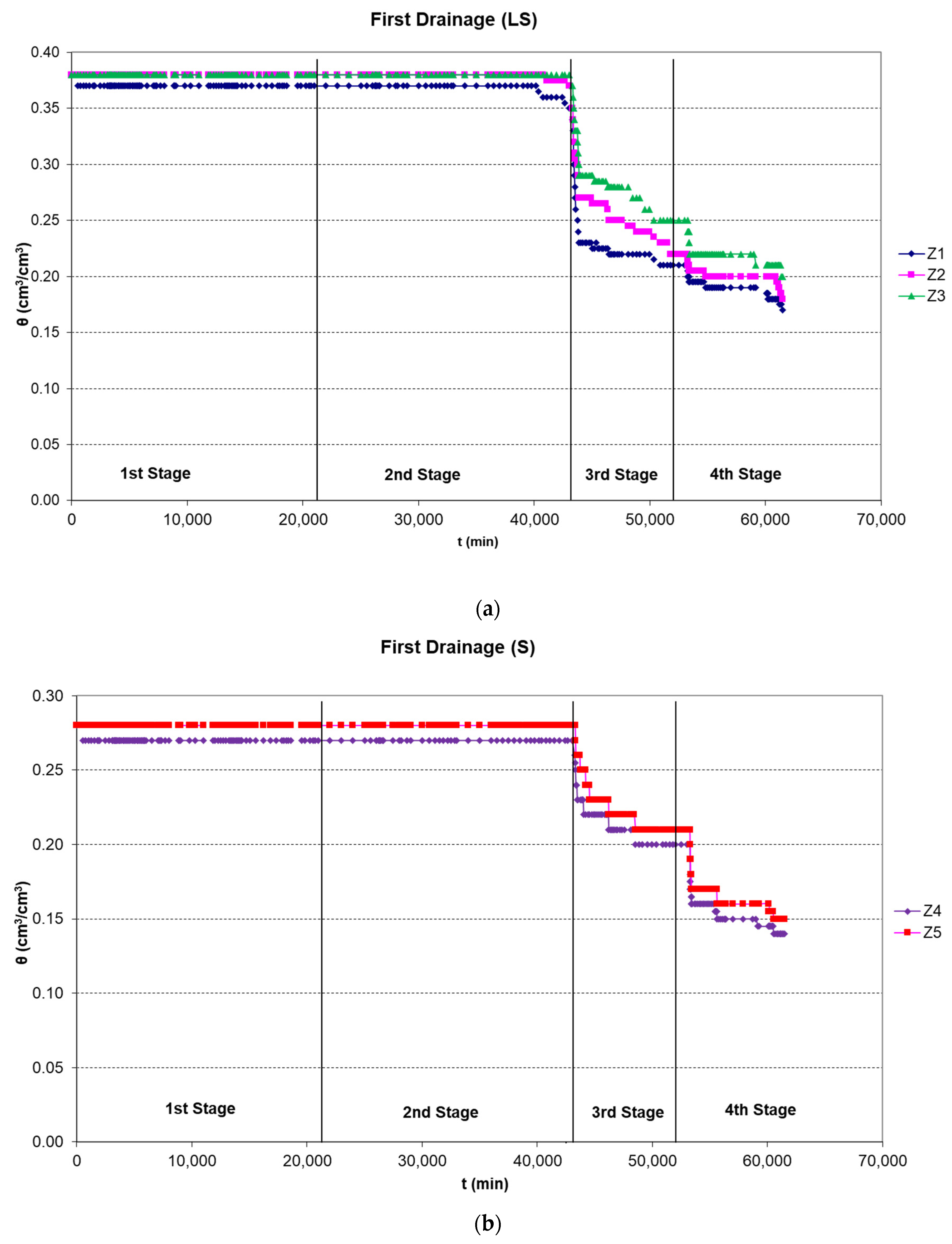
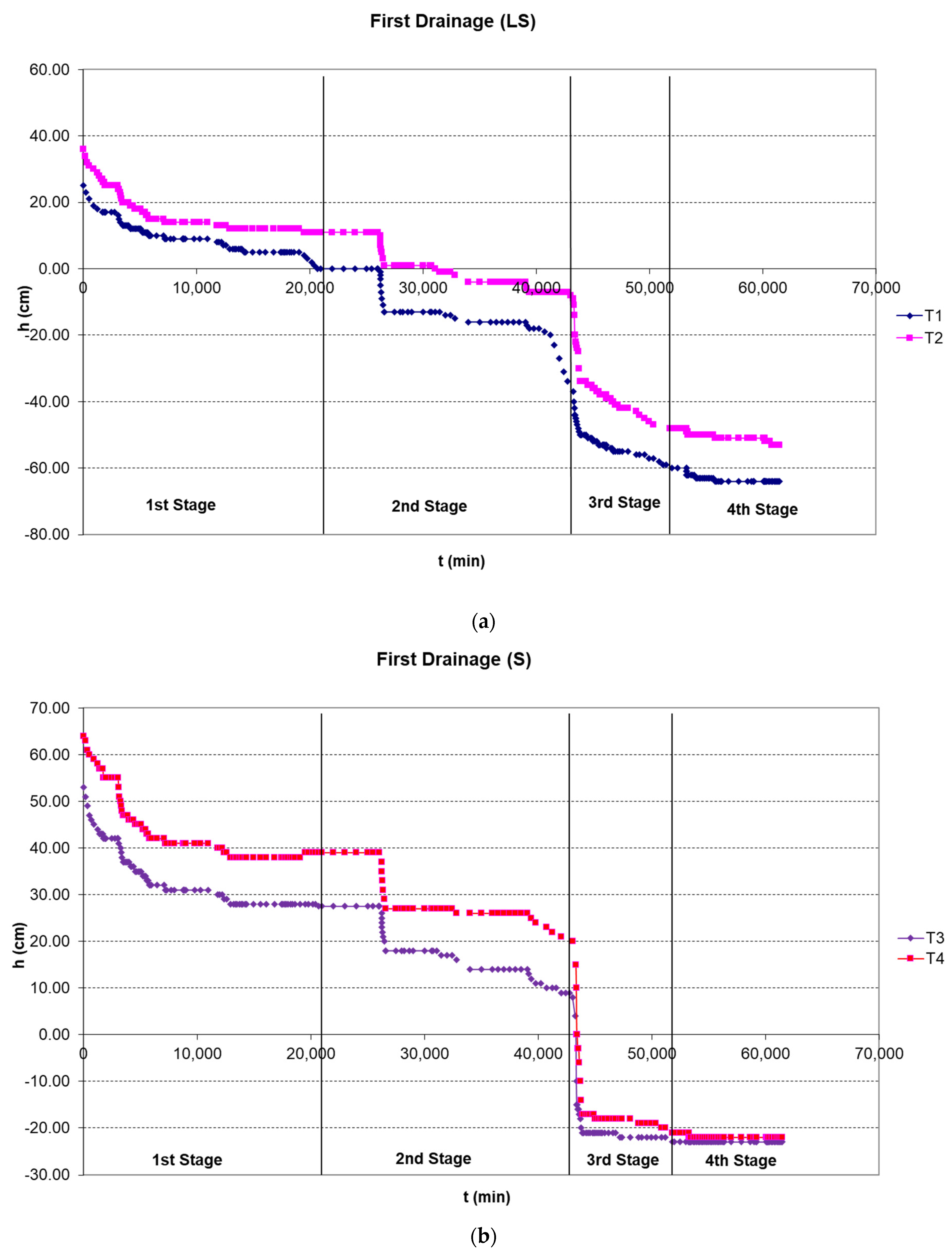



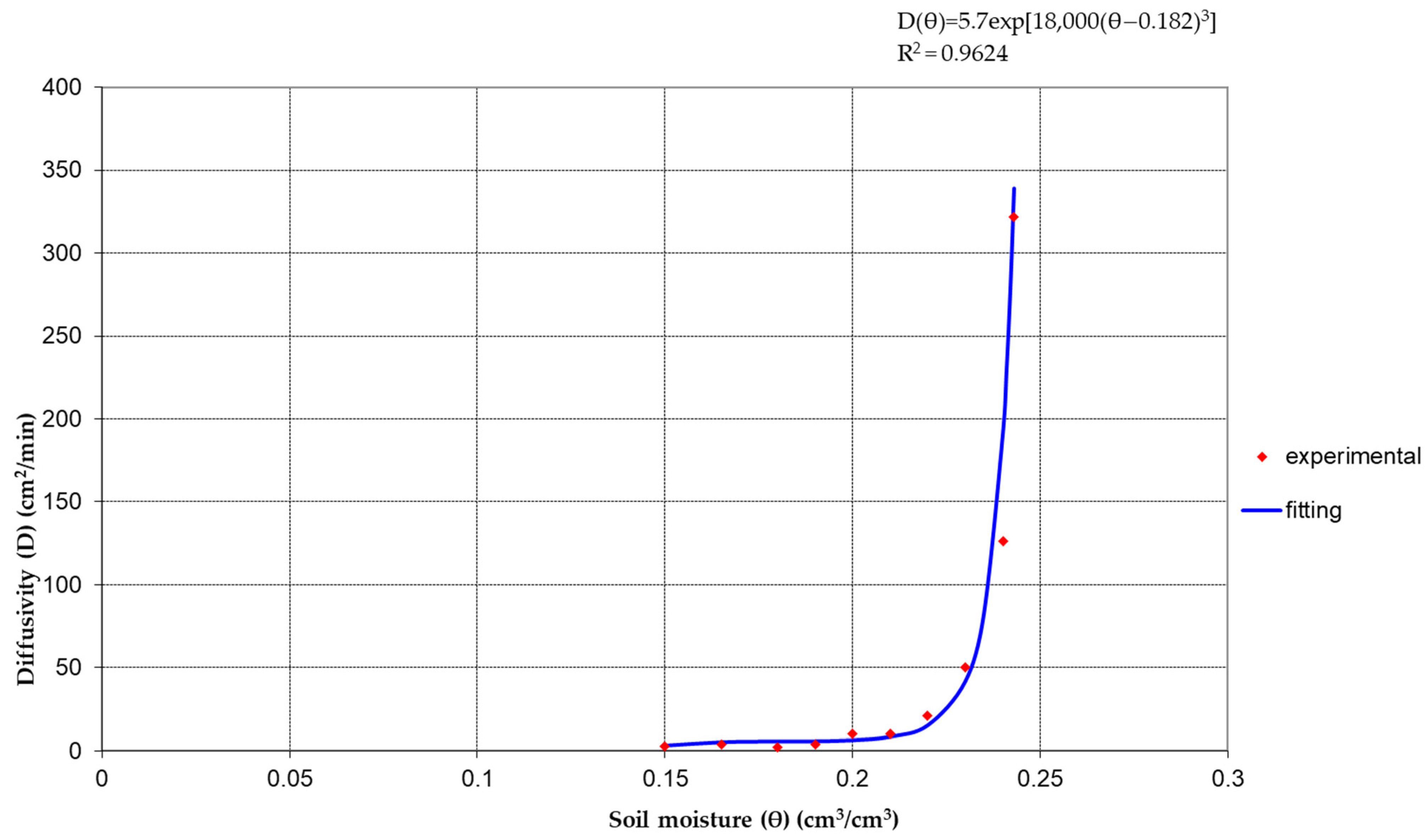
| Hydraulic Parameter | θs | θr | α | n | m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RETC value | 0.24937 | 0.16 | 0.0797 | 6.47629 | 0.845591 |
| 1st part: (θ: 0.15–0.18) | D1 = 84.632θ − 9.5346 (R2 = 1) | |
| 2nd part: (θ: 0.18–0.21) | D2 = 92.099θ − 10.879 (R2 = 1) | |
| 3rd part: (θ: 0.21–0.24) | D3 = 6085.9θ − 1269.6 (R2 = 1) | |
| S2 = 1.5012 cm·min−0.5 | ||
| S= 1.2252 cm min−0.5 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Batsilas, I.; Angelaki, A.; Chalkidis, I. Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column. Water 2023, 15, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020221
Batsilas I, Angelaki A, Chalkidis I. Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column. Water. 2023; 15(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleBatsilas, Ioannis, Anastasia Angelaki, and Iraklis Chalkidis. 2023. "Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column" Water 15, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020221
APA StyleBatsilas, I., Angelaki, A., & Chalkidis, I. (2023). Hydrodynamics of the Vadose Zone of a Layered Soil Column. Water, 15(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15020221






