Water Masses of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea: An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
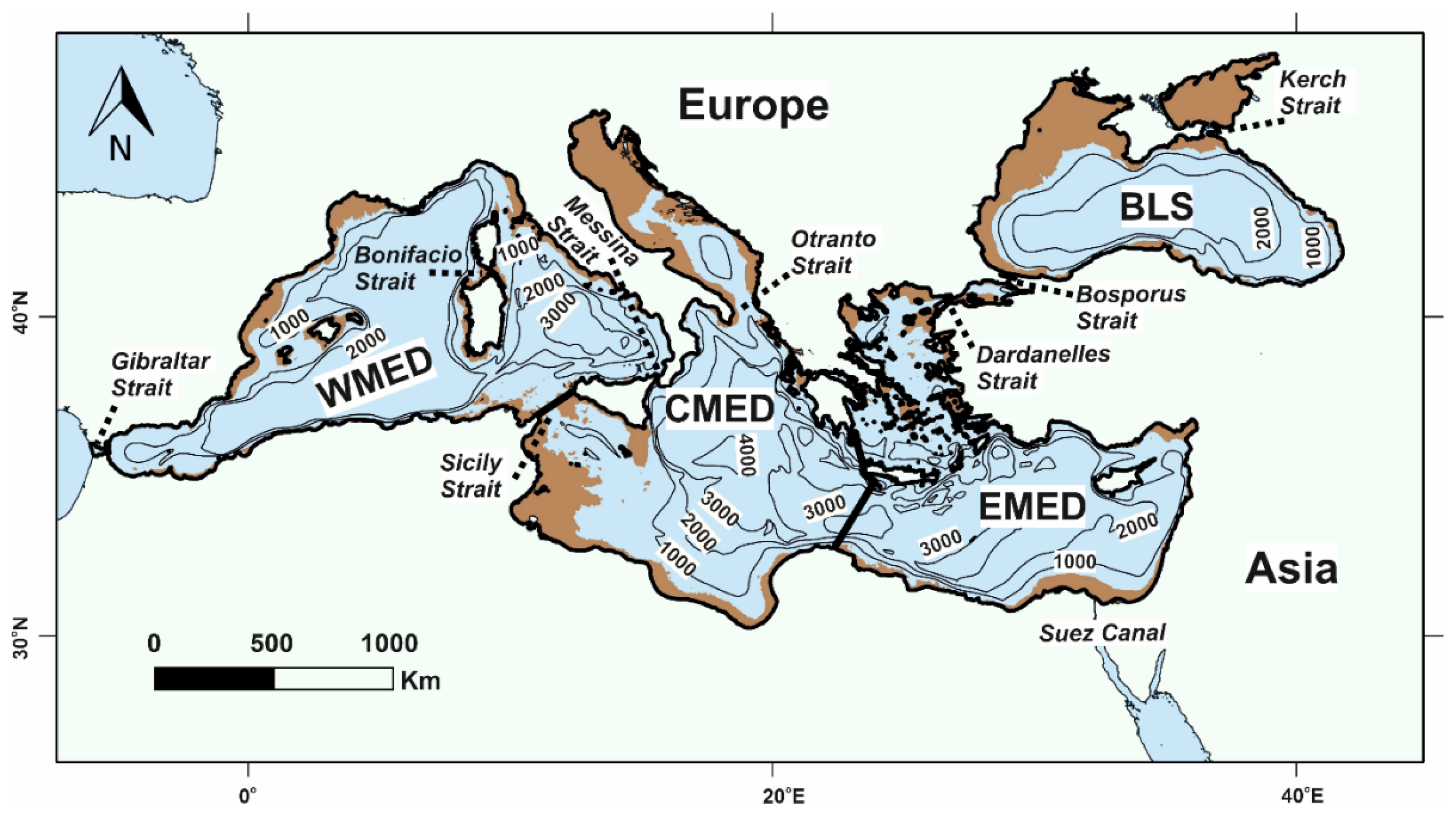
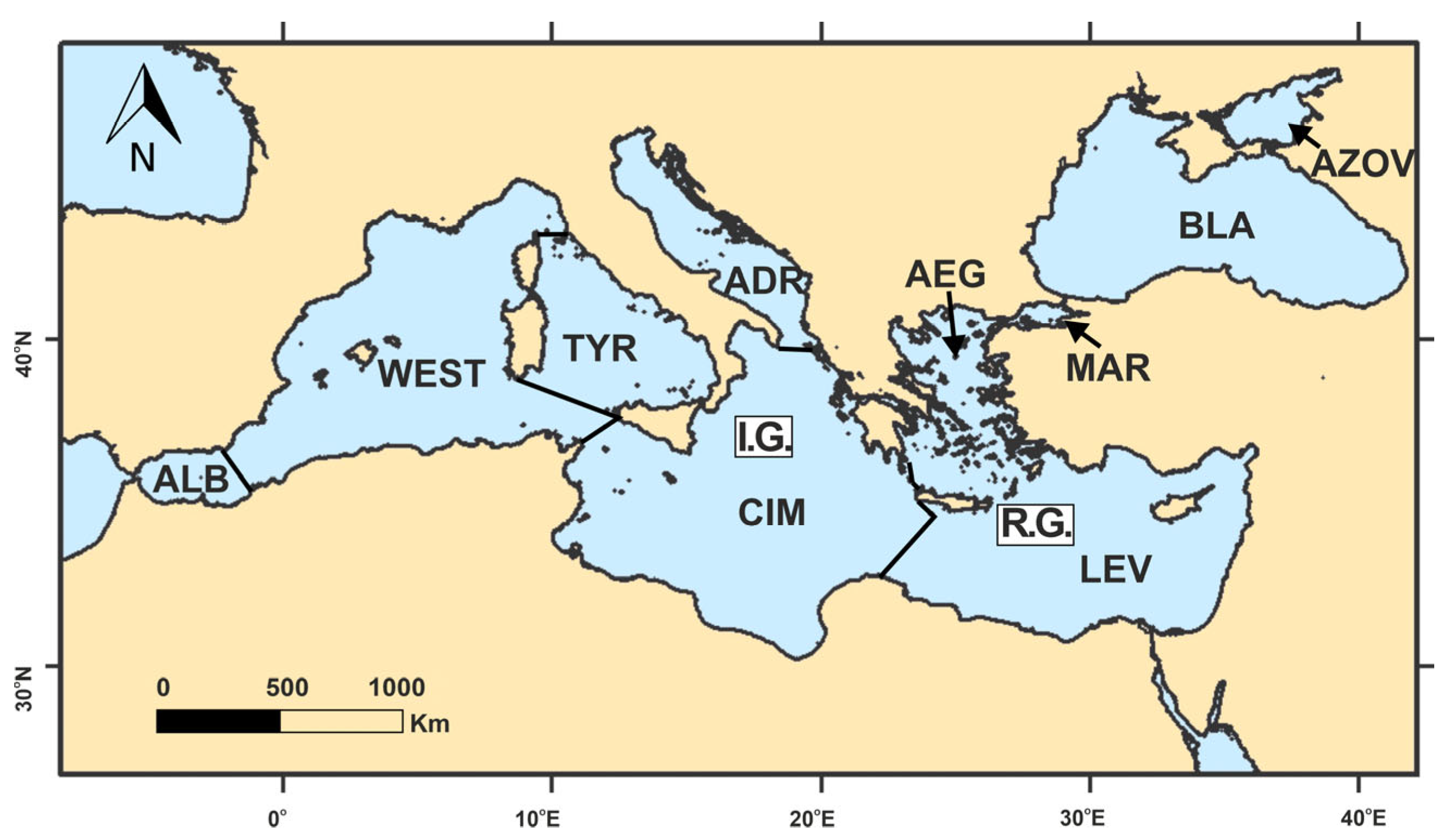
2. Physico-Geographical Setting
| GIBR. ST. | MED | MED (excl. MAR) | BLS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea surface area (SS in km2) | 1630 | 2,530,148 | 2,518,261 | 463,509 |
| Depth mean/maximum (m) | 365/900 | 1544/5267 | 1539/5267 | 1195/2590 |
| Volume (V in 106 km3) | 0.0006 | 3.88 | 3.87 | 0.55 |
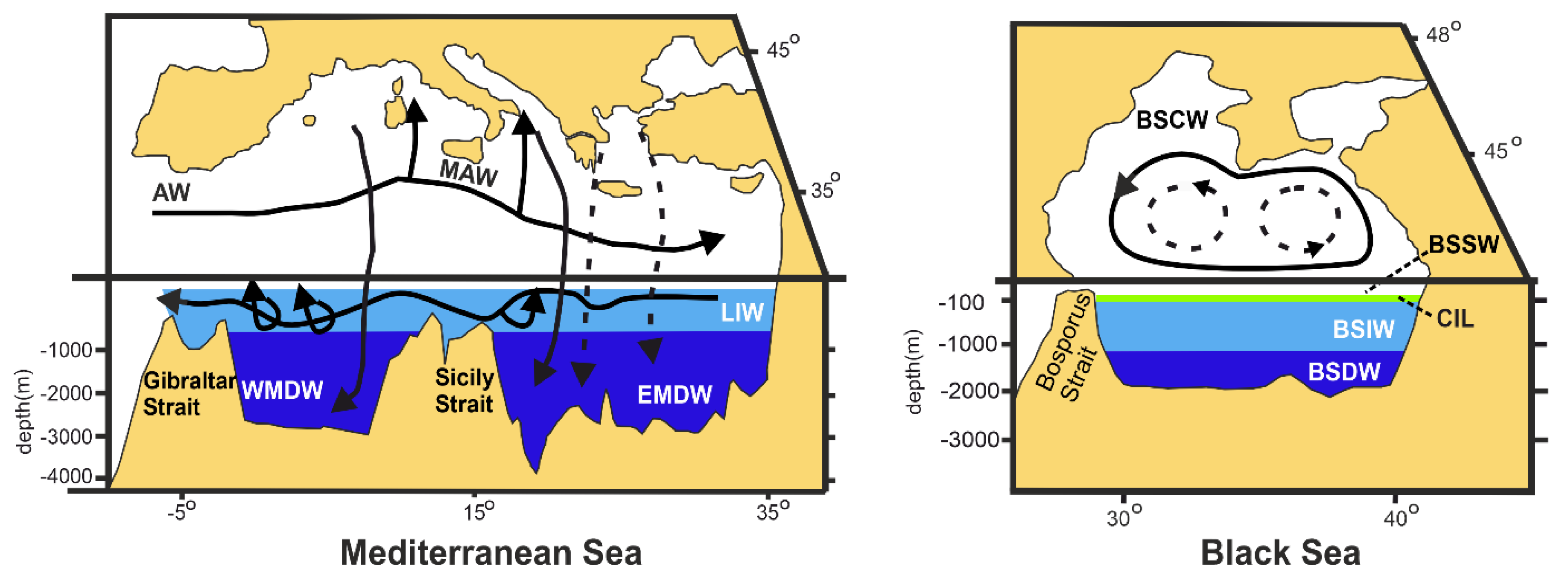
3. Water Masses
3.1. Strait of Gibraltar
3.2. Western Mediterranean (WMED)
3.2.1. Surface Waters
3.2.2. Intermediate Water Masses
3.2.3. Deep Waters
| W.M. | θ (°C) | S | σθ (kg/m3) | Depth (m) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alboran M.R. | |||||
| MAW | >15.0 14.01 ± 0.33–15.08 ± 0.47 | 36.60 37.26 ± 0.24–37.79 ± 0.22 | <27.425 | 0–150/200 | [47] [70] |
| WIW | 13.30 ± 0.12 | 38.23 ± 0.10 | [70] | ||
| LIW | 13.23 13.13 ± 0.02 | 38.50 38.49 ± 0.01 | 29.06 | 200–600 | [47] [70] |
| WMDW | 12.90 12.97± 0.01 | 38.48 38.48 ± 0.04 | 28.74 | >600 | [47] [70] |
| West M.R. | |||||
| MAW | 16.16 | 36.61 | 26.95 | 0–50 | [46] |
| WIW | 11.5–13.0 | 37.7–38.3 | 28.78–28.72 | 100–300 | [70] |
| LIW | 14.07 | 38.85 | ≈29.15 | 300–600 | [46] |
| WMDW | 12.5–14.5 | 37.8–38.6 | >1000 1480 | [59] [46] [68] | |
| 12.86 | 38.46 | ||||
| 12.70–12.75 | 38.40–38.44 | 20.09–29.11 | |||
| Tyrrhenian M.R. | |||||
| MAW | 15.0–18.0 | 36.2–38.2 | 26.74–27.72 | 0–150 | [48] |
| TIW | 13.9–14.4 | 38.1–38.20 | 100/150–200/300 | [48] | |
| LIW | 14.1–14.7 | 38.4–38.8 | 28.82–28.97 | 200–700 | [48] |
| TDW | 12.75–12.85 13.3–13.8 | 38.42–38.46 38.45–38.8 | 700–1500 | [67] [48] | |
3.3. Central Mediterranean (CMED)
3.3.1. Surface Waters
3.3.2. Intermediate Waters
3.3.3. Deep Waters
3.4. Eastern Mediterranean (EMED)
3.4.1. Levantine M.R.
3.4.1.1. Surface Waters
3.4.1.2. Intermediate Waters
3.4.1.3. Deep Waters
3.4.2. Aegean M.R.
3.4.2.1. Surface Waters
3.4.2.2. Intermediate Waters
3.4.2.3. Deep Water Masses
3.4.3. Marmara Sea
3.5. Black Sea
3.5.1. Black Sea Secondary M.R. (BLA)
3.5.1.1. Surface Water Masses
3.5.1.2. Intermediate Waters
3.5.1.3. Deep Waters
3.5.2. Azov M.R.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Marine regions | |
| MED | Mediterranean Sea |
| WMED | Western Mediterranean Sea |
| CMED | Central Mediterranean Sea |
| EMED | Eastern Mediterranean Sea |
| MAR | Marmara Sea (Propontis) |
| BLS | Black Sea (or Pontus Euxinus) (including Azov Sea) |
| BLA | Black Sea (excluding AZOV) |
| AZOV | Azov Sea |
| ALB | Alboran Sea |
| WEST | West Mediterranean |
| TYR | Tyrrhenian Sea |
| ICM | Ionian Sea and Central Mediterranean Sea |
| ADR | Adriatic Sea |
| LEV | Levantine Sea |
| AEG | Aegean Sea |
| Water Masses | |
| ADW * | Adriatic Deep Water |
| AgIW (or MLIW): | Aegean Intermediate Water (or Modified Levantine Intermediate Water) |
| ASW * | Adriatic Surface Water |
| AW * | Atlantic Water |
| AZW | Azov Water |
| BSCW | Black Sea Coastal Water |
| BSDW | Black Sea Deep Water |
| BSIW | Black Sea Intermediate Water |
| BSSW | Black Sea Surface Water |
| BSW * | Black Sea Water |
| CAgDW | Central Aegean Deep Water |
| CDW * | Cretan Deep Water |
| CIL | Cold Intermediate Layer (Black Sea) |
| CIW * | Cretan Intermediate Water |
| CSW | Cretan Surface Water |
| EMDW * | Eastern Mediterranean Deep Water |
| ISW | Ionian Surface Water |
| LDW * | Levantine Deep Water |
| LIW * | Levantine Intermediate Water |
| LSW * | Levantine Surface Water |
| MaBSW | Marmara Black Sea Water |
| MAdSW | Middle Adriatic Surface Waters |
| MaMSW | Marmara Mediterranean Sea water |
| MAW | Modified Atlantic Water |
| MOW * | Mediterranean Outflow Water |
| NAdDW * | North Adriatic Deep Water (formerly NADW) |
| NAdSW | North Adriatic Surface Water |
| SAdSW | South Adriatic Surface Water |
| TDW * | Tyrrhenian Deep Water |
| TIW | Transitional Mediterranean Water |
| WIW * | Western Intermediate Water (formerly Winter Intermediate Water) |
| WMDW * | Western Mediterranean Deep Water |
| (*): agreed acronyms for major Mediterranean water masses in 36th CIESM Congress, Monte Carlo, 26 September 2001). | |
Appendix A
| ALB | WEST | TYR | WMED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Surface area (SS) (km2) | 54,173 | 573,340 | 217,497 | 845,010 |
| SS/SSMED (%) | 2.14 | 22.66 | 8.60 | 33.40 |
| Depth mean/maximum (m) | 753/2342 | 1798/3225 | 1640/3648 | 1691/3648 |
| Volume (V) (106 km3) | 0.041 | 1.026 | 0.358 | 1.424 |
| V/VMED (%) | 1.053 | 26.48 | 9.20 | 36.73 |
| ADR | ICM | CMED | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Surface area (SS) (km2) | 140,320 | 789,414 | 929,734 |
| SS/SSMED | 5.55 | 84.9 | 36.75 |
| Depth mean/maximum (m) | 258/1264 | 26.4 | 1465/5267 |
| Volume (V) (106 km3) | 0.036 | 3.8% | 1.360 |
| V/VMED (%) | 0.935 | 1.32 | 35.07 |
| LEV | AEG | ΜAR | EMED | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Surface (SS) (km2) | 551,609 | 191,908 | 11,887 | 755,404 |
| SS/SSMED | 21.80 | 7.58 | 0.47 | 29.86 |
| Depth mean /max (m) | 1816/4538 | 457/2842 | 311/1288 | 1462/4538 |
| Volume (V) (103 km3) | 1.9 | 876 | 3.7 | 1131 |
| V/VMED (%) | 25.84 | 2.26 | 0.10 | 28.20 |
| BLA | AZOV | BLS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sea Surface area (SS) (km2) | 422,235 | 41,274 | 463,509 |
| SS/BLS (%) | 91.1 | 8.9 | |
| Depth mean/ maximum (m) | 1302/2590 | 8.6/15 | 1195/2590 |
| Slope mean (%) | 2.2 | 0.04 | 2.0 |
| Volume (V) (106 km3) | 0.5497 | 0.00035 | 0.5499 |
References
- Poulos, S.E. The Mediterranean and Black Sea Marine System: An overview of its physico-geographic and oceanographic characteristics. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 200, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.R.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Hecht, A.; Michelato, A.; Roether, W.; Theocharis, A.; Ünlüata, Ü.; Pinardi, N.; Artegiani, A.; Bergamasco, A.; et al. General circulation of the Eastern Mediterranean. Earth Sci. Rev. 1992, 32, 285–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C. Circulation in the western Mediterranean Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 423–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopoulos, P.G.; Lascaratos, A. Modelling the Mediterranean Sea, Seasonal Forcing. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C.; Taupier-Letage, I. Circulation in the Mediterranean Sea. In Modelling the Pelagic Ecosystem Dynamics: The NW Mediterranean, The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Cruzado, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, K.; Ribotti, A.; Borghini, M.; Sorgente, R.; Perilli, A.; Gasparini, G.P. An extensive western Mediterranean deep-water renewal between 2004 and 2006. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L18605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Arneri, E.; Crise, A.; Ravaioli, M.; Zavatarelli, M. The physical, sedimentary and ecological structure and variability of shelf areas in the Mediterranean Sea (27). Sea 2006, 14, 1243–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Theocharis, A. Variability of the thermohaline properties in the Eastern Mediterranean during the post-EMT period (1995–2008) and SST changes in the Aegean (1985–2008). In Dynamics of Mediterranean Deep Waters. N° 38 in CIESM Workshop Monographs; CIESM: Monaco City, Monaco, 2009; pp. 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pinardi, N.; Zavatarelli, M.; Adani, M.; Coppini, G.; Fratianni, C.; Oddo, P.; Simoncelli, S.; Tonani, M.; Lyubartsev, V.; Dobricic, S.; et al. Mediterranean Sea large-scale low-frequency ocean variability and water mass formation rates from 1987 to 2007: A retrospective analysis. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 132, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T.; Latun, V.S.; Latif, M.A.; Vladimirov, V.V.; Sur, H.I.; Markov, A.A.; Özsoy, E.; Eremeev, V.V.; Ünlüata, Ü. Circulation in the surface and intermediate layers of the Black Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1993, 40, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, E.V.; Staneva, J.V. The impact of the baroclinic eddies and basin oscillations on the transitions between different quasi-stable states of the Black Sea circulation. J. Mar. Syst. 2000, 24, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotaev, G.K.; Saenko, O.A.; Koblinsky, C.J. Satellite altimetry observations of the Black Sea level. J. Geophys. Res. C Oceans 2001, 106, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaş, G.; James, A.; Al-Barakati, A. Modelling subsurface dynamics in the Black Sea. Oceanol. Acta 2002, 25, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguz, T. General oceanographic properties: Physico-chemical and climatic features. In State of the Environment of the Black Sea (2001–2006/7); Oguz, T., Ed.; Publications of the Commission on the Protection of the Black Sea Against Pollution (BSC): Istanbul, Turkey, 2008; Chapter 1A; pp. 39–60. [Google Scholar]
- Toderascu, R.; Rusu, E. Evaluation of the circulation patterns in the Black Sea using remotely sensed and in situ measurements. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, N.V. On the Black Sea deepwater circulation features derived from numerical modeling and measurement data. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 899, 052011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordone, A.; Pennecchi, F.; Raiteri, G.; Reseghetti, F. ARGO floats vs. Ship-based CTDs: An overall metrological comparison in the whole Mediterranean Sea. In Proceedings of the IMEKO TC-19 International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Genoa, Italy, 3–5 October 2019; pp. 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Román, A.; Ruiz, S.; Pascual, A.; Mourre, B.; Guinehut, S. On the mesoscale monitoring capability of Argo floats in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. 2017, 13, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.T.; Flanagan, J.P.; Jones, C.R.; Marchant, F.L.; Murhinson, R.R.; Rebman, J.H.; Sylvester, J.C.; Whitney, J.C. A new bathymetric chart and physiography of the Mediterranean Sea. In The Mediterranean Sea: A Natural Sedimentation Laboratory; Stanley, D.J., Ed.; Dowden, Hutchinson and Ross Pennsylvania: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 1972; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.M.; Panagiotidis, P.; Reker, J. Delineation of the MSFD Article 4 Marine Regions and Subregions; Technical Document (Version 1.0); European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; 21p, Available online: https://data.europa.eu/euodp/data/dataset/data_msfd-regions-and-subregions (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- IHO (International Hydrographic Organisation). Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd ed.; IHO: Monaco City, Monaco, 1953; 17p. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP/MAP/MED POL. Transboundary Diagnostic Analysis (TDA) for the Mediterranean Sea; UNEP/MAP: Athens, Greece, 2005; 228p. [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig, W.; Dumont, E.; Meybeck, M.; Heussner, S. River discharges of water and nutrients to the Mediterranean and Black Sea: Major drivers for ecosystem changes during past and future decades? Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 80, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, W.; Bouwman, A.F.; Dumont, E.; Lespinas, F. Water and nutrient fluxes from major Mediterranean and Black Sea rivers: Past and future trends and their implications for the basin-scale budgets. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, GB0A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/MAP. State of the Mediterranean Marine and Coastal Environment; UNEP/MAP-Barcelona Convention: Athens, Greece, 2012; 92p. [Google Scholar]
- EMODnet Digital Bathymetry (DTM 2018). EMODnet Bathymetry Consortium. 2018. Available online: https://sextant.ifremer.fr/record/18ff0d48-b203-4a65-94a9-5fd8b0ec35f6/ (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Poulos, S.; Kotinas, V. Physio-geographical characteristics of the marine regions and their catchment areas of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea marine system. Phys. Geogr. 2021, 42, 297–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A. Chemistry of Mediterranean waters. In Western Mediterranean; Margalef, R., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1985; pp. 126–147. [Google Scholar]
- Woodward, J. (Ed.) The Physical Geography of the Mediterranean; OUP Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns and threats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argo: Argo Float Data and Metadata from Global Data Assembly Centre (Argo GDAC), SEANOE [Data Set]. 2020. Available online: https://www.seanoe.org/data/00311/42182/ (accessed on 4 February 2022).
- Bergamasco, A.; Malanotte-Rizzoli, P. The circulation of the Mediterranean Sea: A historical review of experimental investigations. Adv. Oceanogr. Limnol. 2010, 1, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryden, H.L.; Kinder, T.H. Steady two-layer exchange through the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1991, 38, S445–S463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, J. Mediterranean water and global circulation. In International Geophysics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 77, pp. 419–448. [Google Scholar]
- Tanhua, T.; Hainbucher, D.; Schroeder, K.; Cardin, V.; Álvarez, M.; Civitarese, G. The Mediterranean Sea system: A review and an introduction to the special issue. Ocean Sci. 2013, 9, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, S.; Lafuente, J.G.; Garrido, J.S.; De los Santos, F.J.; Fanjul, E.Á.; Naranjo, C.; Bruno, M.; Calero, C. A numerical model analysis of the tidal flows in the Bay of Algeciras, Strait of Gibraltar. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 72, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, G.; Mauri, E.; Notarstefano, G.; Poulain, P.M. Characterization of the Atlantic Water and Levantine Intermediate Water in the Mediterranean Sea using 20 years of Argo data. Ocean Sci. 2022, 18, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lafuente, J.; Sammartino, S.; Huertas, I.E.; Flecha, S.; Sánchez-Leal, R.F.; Naranjo, C.; Nadal, I.; Bellanco, M.J. Hotter and weaker mediterranean outflow as a response to basin-wide alterations. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 613444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.; Sammartino, S.; García-Lafuente, J.; Bellanco, M.J.; Taupier-Letage, I. Mediterranean waters along and across the Strait of Gibraltar, characterization and zonal modification. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2015, 105, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Bryden, H.L. Estimation of the transports through the Strait of Gibraltar. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2000, 47, 2219–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Yáñez, M.; Plaza, F.; Garcıa-Lafuente, J.; Sarhan, T.; Vargas, J.M.; Vélez-Belchi, P. About the seasonal variability of the Alboran Sea circulation. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 35, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.B.; Schroeder, K.; Sammari, C.; Gasparini, G.P.; Borghini, M.; Aleya, L. Interannual variability of water mass properties in the Tunisia-Sicily Channel. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 135, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C. Levantine Intermediate Water characteristics: An astounding general misunderstanding! Sci. Mar. 2013, 77, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D.; Poulain, P.-M.; Testor, P.; Mortier, L.; Bosse, A.; Du Madron, X. Review of the circulation and characteristics of intermediate water masses of the Mediterranean-implications for cold-water coral habitats. Coral Reefs Mediterr. 2019, 9, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas-Yáñez, M.; Juza, M.; Balbín, R.; Velez-Belchí, P.; García-Martínez, M.C.; Moya, F.; Hernández-Guerra, A. Climatological hydrographic properties and water mass transports in the Balearic Channels from repeated observations over 1996–2019. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 568602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.E.R.; Guglielmi, V.; Gemayel, E.; Goyet, C.; Abboud-Abi Saab, M.; Giani, M.; Ziveri, P.; Ingrosso, G.; Touratier, F. Is the Mediterranean Sea circulation in a steady state. J. Water Resour. Ocean. Sci. 2015, 4, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.; García-Lafuente, J.; Sammartino, S.; Sánchez-Garrido, J.C.; Sánchez-Leal, R.; Jesús Bellanco, M. Recent changes (2004–2016) of temperature and salinity in the Mediterranean outflow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5665–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, R.; Napolitano, E.; Palma, M.; Sannino, G. The Tyrrhenian Sea circulation: A review of recent work. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinot, J.M.; Ganachaud, A. The role of winter intermediate waters in the spring-summer circulation of the Balearic Sea: 1. Hydrography and inverse box modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 29843–29864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, J.; Font, J. Water mass structure near and offshore the Catalan coast during the winters of 1982 and 1983. Ann. Geophys. B 1987, 5, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini, G.P.; Zodiatis, G.; Astraldi, M.; Galli, C.; Sparnocchia, S. Winter intermediate water lenses in the Ligurian Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 20, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juza, M.; Renault, L.; Ruiz, S.; Tintoré, J. Origin and pathways of Winter Intermediate Water in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea using observations and numerical simulation. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6621–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, C. Another description of the Mediterranean Sea outflow. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 82, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Gasparini, G.P.; Tangherlini, M.; Astraldi, M. Deep and intermediate water in the western Mediterranean under the influence of the Eastern Mediterranean Transient. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L21607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astraldi, M.; Balopoulos, S.; Candela, J.; Font, J.; Gacic, M.; Gasparini, G.P.; Manca, B.; Theocharis, A.; Tintoré, J. The role of straits and channels in understanding the characteristics of Mediterranean circulation. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 65–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Send, U.; Font, J.; Krahmann, G.; Millot, C.; Rhein, M.; Tintoré, J. Recent advances in observing the physical oceanography of the western Mediterranean Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 37–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, F.; Cancet, M.; Estournel, C. Aspects of the Seasonal Variability of the Northern Current (NW Mediterranean Sea) Observed by Altimetry. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 81, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, E.; Iacono, R.; Ciuffardi, T.; Reseghetti, F.; Poulain, P.M.; Notarstefano, G. The Tyrrhenian Intermediate Water (TIW): Characterization and formation mechanisms. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 170, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruzado, A.; Bernardello, R.; Ahumada-Sempoal, M.A.; Bahamon, N. Modelling the Pelagic Ecosystem Dynamics: The NW Mediterranean. In Marine Ecosystems; Cruzado, A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 38–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lascaratos, A. Estimation of deep and intermediate water mass formation rates in the Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1993, 40, 1327–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roether, W.; Manca, B.B.; Klein, B.; Bregant, D.; Georgopoulos, D.; Beitzel, V.; Kovačević, V.; Luchetta, A. Recent changes in eastern Mediterranean deep waters. Science 1996, 271, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Chiggiato, J.; Bryden, H.L.; Borghini, M.; Ben Ismail, S. Abrupt climate shift in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houpert, L.; Durrieu de Madron, X.; Testor, P.; Bosse, A.; d’Ortenzio, F.; Bouin, M.N.; Dausse, D.; Le Goff, H.; Kunesch, S.; Labaste, M.; et al. Observations of open-ocean deep convection in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea: Seasonal and interannual variability of mixing and deep water masses for the 2007–2013 Period. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 8139–8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incarbona, A.; Martrat, B.; Mortyn, P.G.; Sprovieri, M.; Ziveri, P.; Gogou, A.; Jordà, G.; Xoplaki, E.; Luterbacher, J.; Langone, L.; et al. Mediterranean circulation perturbations over the last five centuries: Relevance to past Eastern Mediterranean Transient-type events. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, G.P.; Ortona, A.; Budillon, G.; Astraldi, M.; Sansone, E. The effect of the Eastern Mediterranean Transient on the hydrographic characteristics in the Strait of Sicily and in the Tyrrhenian Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2005, 52, 915–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, M.; Send, U.; Klein, B.; Krahmann, G. Interbasin deep water exchange in the western Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1999, 104, 23495–23508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammari, C.; Millot, C.; Taupier-Letage, I.; Stefani, A.; Brahim, M. Hydrological characteristics in the Tunisia-Sardinia-Sicily area during spring 1995. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1999, 46, 1671–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuda, J.L.; Etiope, G.; Millot, C.; Favali, P.; Calcara, M.; Smriglio, G.; Boschi, E. Warming, salting and origin of the Tyrrhenian Deep Water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, P.; Trani, M.; Zambianchi, E. Water mass structure and deep mixing processes in the Tyrrhenian Sea: Results from the VECTOR project. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 113, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Yáñez, M.; Zunino, P.; Schroeder, K.; López-Jurado, J.L.; Plaza, F.; Serra, M.; Castro, C.; García-Martínez, M.D.C.; Moya, F.; Salat, J. Extreme western intermediate water formation in winter 2010. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 105, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanotte-Rizzoli, P.; Manca, B.B.; d’Alcalà, M.R.; Theocharis, A.; Bergamasco, A.; Bregant, D.; Budillon, G.; Civitarese, G.; Georgopoulos, D.; Michelato, A.; et al. A synthesis of the Ionian Sea hydrography, circulation and water mass pathways during POEM-Phase I. Prog. Oceanogr. 1997, 39, 153–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimeris, A.; Kassis, D. Sea surface circulation variability in the Ionian-Adriatic Seas. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 189, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Mikolajewicz, U.; Six, K.D. Drivers of the decadal variability of the North Ionian Gyre upper layer circulation during 1910–2010: A regional modelling study. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 58, 2065–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gačić, M.; Civitarese, G.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L.; Kovačević, V.; Poulain, P.M.; Theocharis, A.; Menna, M.; Catucci, A.; Zarokanellos, N. On the relationship between the decadal oscillations of the northern Ionian Sea and the salinity distributions in the eastern Mediterranean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, C12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civitarese, G.; Gačić, M.; Lipizer, M.; Eusebi Borzelli, G.L. On the impact of the Bimodal Oscillating System (BiOS) on the biogeochemistry and biology of the Adriatic and Ionian Seas (Eastern Mediterranean). Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 3987–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, B.B.; Kovaĉević, V.; Gaĉić, M.; Viezzoli, D. Dense water formation in the Southern Adriatic Sea and spreading into the Ionian Sea in the period 1997–1999. J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 33, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzelli, G.L.E.; Gačić, M.; Cardin, V.; Civitarese, G. Eastern Mediterranean Transient and reversal of the Ionian Sea circulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L15108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gačić, M.; Borzelli, G.E.; Civitarese, G.; Cardin, V.; Yari, S. Can internal processes sustain reversals of the ocean upper circulation? The Ionian Sea example. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budillon, G.; Bue, N.L.; Siena, G.; Spezie, G. Hydrographic characteristics of water masses and circulation in the Northern Ionian Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulos, S.E. River systems and their water and sediment fluxes towards the marine regions of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea earth system. An overview. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, M.; Burnett, W.C.; Cable, J.E.; Turner, J.V. Investigation of submarine groundwater discharge. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 2115–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artegianni, A. The Adriatic sea hydrography, the European anchovy and its environment (Palomera, I. and Rubies P. eds.). Sci. Mar. 1996, 60 (Suppl. S2), 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, A.; Artegiani, A. Adriatic Sea hydrography. Sci. Mar. 1996, 60 (Suppl. S2), 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Orlic, M.; Gacic, M.; Laviolette, P.E. The currents and circulation of the Adriatic Sea. Oceanol. Acta 1992, 15, 109–124. [Google Scholar]
- Artegiani, A.; Bregant, D.; Paschini, E.; Pinardi, N.; Raicich, F.; Russo, A. The Adriatic Sea general circulation. Part I: Air-sea interactions and water mass structure. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1997, 27, 1492–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Krokos, G.; Nittis, K.; Theocharis, A. Dense intermediate water outflow from the Cretan Sea: A salinity driven, recurrent phenomenon, connected to thermohaline circulation changes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 4797–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibić, I.; Orlić, M. Adriatic water masses, their rates of formation and transport through the Otranto Strait. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2002, 49, 1321–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skliris, N. Past, present and future patterns of the Thermohaline Circulation and characteristic water masses of the Mediterranean Sea. In The Mediterranean Sea: Its History and Present Challenges; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 29–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov, I.M.; Zats, V.I.; Krivosheya, V.G.; Udodov, A.I. Formation of the deep Eastern Mediterranean waters in the Adriatic Sea. Oceanology 1985, 25, 911–917. [Google Scholar]
- Roether, W.; Schlitzer, R. Eastern Mediterranean deep water renewal on the basis of chlorofluoromethane and tritium data. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 1991, 15, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lionello, P.; Zampato, L.; Malguzzi, P.; Tomasin, A.; Bergamasco, A. On the correct surface stress for the prediction of the wind wave field and the storm surge in the northern Adriatic Sea. Nuovo C 1998, 21, 515–532. [Google Scholar]
- Vilibić, I. An analysis of dense water production on the North Adriatic shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 56, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supić, N.; Vilibić, I. Dense water characteristics in the northern Adriatic in the 1967–2000 interval with respect to surface fluxes and Po river discharge rates. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supić, N.; Kraus, R.; Kuzmić, M.; Paschini, E.; Precali, R.; Russo, A.; Vilibić, I. Predictability of northern Adriatic winter conditions. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 90, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeković, I.; Mihanović, H.; Vilibić, I.; Tudor, M. Extreme cooling and dense water formation estimates in open and coastal regions of the Adriatic Sea during the winter of 2012. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 3200–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilibić, I.; Mihanović, H.; Janeković, I.; Denamiel, C.; Poulain, P.M.; Orlić, M.; Dunić, N.; Dadić, V.; Pasarić, M.; Muslim, S.; et al. Dense water formation in the coastal northeastern Adriatic Sea: The NAdEx 2015 experiment. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, S. Estimation of the Adriatic Sea General Circulation Using Data Assimilation Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Oceanografia e Dinamica della Zona Costiera, Facolt‘A di Scienze Matematiche, Fisiche e Naturali, Universita di Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2012; 170p. (In English). [Google Scholar]
- Mantziafou, A.; Lascaratos, A. An eddy resolving numerical study of the general circulation and deep-water formation in the Adriatic Sea. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 921–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruggiero, P.; Zanchettin, D.; Bensi, M.; Hainbucher, D.; Stenni, B.; Pierini, S.; Rubino, A. Water masses in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea: An analysis of measured isotopic oxygen. In Meteorology and Climatology of the Mediterranean and Black Seas; Birkhäuser: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 327–344. [Google Scholar]
- Artegiani, A.; Gacic, M.; Michelato, A.; Kovacevic, V.; Russo, A.; Paschini, E.; Scarazzato, P.; Smircic, A. The Adriatic Sea hydrography and circulation in spring and autumn (1985–1987). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1993, 40, 1143–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Papadopoulos, V.P.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Cardin, V.; Civitarese, G. Water masses and hydrography during April and June 2016 in the Cretan sea and Cretan passage (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2019, 164, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, T.; Gertman, I.; Kress, N.; Silverman, J.; Herut, B. Interannual thermohaline (1979–2014) and nutrient (2002–2014) dynamics in the Levantine surface and intermediate water masses; SE Mediterranean Sea. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 151, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, A.; Pinardi, N.; Robinson, A.R. Currents; water masses, eddies and jets in the Mediterranean Levantine Basin. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1320–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Georgopoulos, D.; Lascaratos, A.; Nittis, K. Water masses and circulation in the central region of the Eastern Mediterranean: Eastern Ionian, South Aegean and Northwest Levantine, 1986–1987. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 1993, 40, 1121–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Hecht, A.; Ünlüata, Ü. Circulation and hydrography of the Levantine Basin. Results of POEM coordinated experiments 1985–1986. Prog. Oceanogr. 1989, 22, 125–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascaratos, A.; Roether, W.; Nittis, K.; Klein, B. Recent changes in deep water formation and spreading in the eastern Mediterranean Sea: A review. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 5–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervatis, V.D.; Sofianos, S.S.; Theocharis, A. Distribution of the thermohaline characteristics in the Aegean Sea related to water mass formation processes (2005–2006 winter surveys). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116, C09034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.; Roether, W.; Manca, B.B.; Bregant, D.; Beitzel, V.; Kovacevic, V.; Luchetta, A. The large deep water transient in the Eastern Mediterranean. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1999, 46, 371–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Chiggiato, J.; Josey, S.A.; Borghini, M.; Aracri, S.; Sparnocchia, S. Rapid response to climate change in a marginal sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theocharis, A.; Klein, B.; Nittis, K.; Roether, W. Evolution and status of the Eastern Mediterranean Transient (1997–1999). J. Mar. Syst. 2002, 33, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Balopoulos, E.; Kioroglou, S.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Iona, A. A synthesis of the circulation and hydrography of the South Aegean Sea and the Straits of the Cretan Arc (March 1994–January 1995). Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 469–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zervakis, V.; Georgopoulos, D.; Drakopoulos, P.G. The role of the North Aegean in triggering the recent Eastern Mediterranean climatic changes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 105, 26103–26116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Civitarese, G.; Giani, M.; Gogou, A.; Rahav, E.; Zervoudaki, S. Revisiting the Eastern Mediterranean: Recent knowledge on the physical, biogeochemical and ecosystemic states and trends (Volume II). Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2020, 171, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roether, W.; Klein, B.; Manca, B.B.; Theocharis, A.; Kioroglou, S. Transient Eastern Mediterranean deep waters in response to the massive dense-water output of the Aegean Sea in the 1990s. Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 74, 540–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis, M.N.; Velegrakis, D.; Drakopoulos, P.G.; Theocharis, A.; Collins, M.B. Cretan DeepWater Outflow into the Eastern Mediterranean. Prog. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovačević, V.; Manca, B.B.; Ursella, L.; Schroeder, K.; Cozzi, S.; Burca, M.; Mauri, E.; Gerin, R.; Notarstefano, G.; Deponte, D. Water mass properties and dynamic conditions of the Eastern Mediterranean in June 2007. Prog. Oceanogr. 2012, 104, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainbucher, D.; Rubino, A.; Cardin, V.; Tanhua, T.; Schroeder, K.; Bensi, M. Hydrographic situation during cruise M84/3 and P414 (spring 2011) in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. 2014, 10, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayın, E.; Beşiktepe, Ş.T. Temporal evolution of the water mass properties during the Eastern Mediterranean Transient (EMT) in the Aegean Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C10025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydoğdu, A.; Pinardi, N.; Özsoy, E.; Danabasoglu, G.; Gürses, Ö.; Karspeck, A. Circulation of the Turkish Straits System under interannual atmospheric forcing. Ocean Sci. 2018, 14, 999–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugrul, S.; Besiktepe, T.; Salihoglu, I. Nutrient exchange fluxes between the Aegean and Black Seas through the Marmara Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2002, 3, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertman, I.; Pinardi, N.; Popov, Y.; Hecht, A. Aegean Sea water masses during the early stages of the Eastern Mediterranean climatic transient (1988–1990). J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 1841–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Zervakis, V.; Theocharis, A. The physical characteristics and dynamics of the Aegean water masses. In The Aegean Sea Environment: The Natural System, The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Anagnostou, C., Kostianoy, A., Mariolakos, I., Panayotidis, P., Soilemezidou, M., Tsaltas, G., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cardin, V.; Gačić, M.; Nittis, K.; Kovačević, V.; Perini, L. Sub-inertial variability in the Cretan Sea from the M3A buoy. In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2003; Volume 21, pp. 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Velaoras, D.; Krokos, G.; Theocharis, A. Recurrent intrusions of transitional waters of Eastern Mediterranean origin in the Cretan Sea as a tracer of Aegean Sea dense water formation events. Prog. Oceanogr. 2015, 135, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, R.; Roether, W.; Oster, H.; Junghans, H.G.; Hausmann, M.; Johannsen, H.; Michelato, A. Chlorofluoromethane and oxygen in the Eastern Mediterranean. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1991, 38, 1531–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaoras, D.; Lascaratos, A. North-Central Aegean Sea surface and intermediate water masses and their role in triggering the Eastern Mediterranean Transient. J. Mar. Syst. 2010, 83, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Nittis, K.; Kontoyiannis, H.; Papageorgiou, E.; Balopoulos, E. Climatic changes in the Aegean Sea influence the Eastern Mediterranean thermohaline circulation (1986–1997). Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, A.; Georgopoulos, D. Dense water formation over the Samothraki and Limnos Plateaux in the north Aegean Sea (eastern Mediterranean Sea). Cont. Shelf Res. 1993, 13, 919–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassis, D.; Korres, G. Recent hydrological status of the Aegean Sea derived from free drifting profilers. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlülata, Ü.; Oğuz, T.; Latif, M.A.; Özsoy, E. On the physical oceanography of the Turkish Straits. In The Physical Oceanography of Sea Straits; Pratt, L.J., Ed.; NATO-ASI Series; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 5–60. [Google Scholar]
- Beşiktepe, Ş.T.; Sur, H.I.; Özsoy, E.; Latif, M.A.; Oǧuz, T.; Ünlüata, Ü. The circulation and hydrography of the Marmara Sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 1994, 34, 285–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Altıok, H. A Review of Hydrography of the Turkish Straits System. In The Sea of Marmara-Marine Biodiversity, Fisheries, Conservation and Governance, Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TÜDAV) Publication No. 42; Özsoy, E., Çağatay, M.N., Balkıs, N., Balkıs, N., Öztürk, B., Eds.; Turkish Marine Research Foundation (Tudav): İstanbul, Turkey, 2016; pp. 13–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.A.; Belokopytov, V.N. Oceanography of the Black Sea. In National Academy of Science of Ukraine; Ivanov, V.A., Belokopytov, V.N., Eds.; Marine Hydrophysical Institute: Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2013; 210p. [Google Scholar]
- Mamayev, O.I.; Arkhipkin, V.S.; Tuzhilkin, V.S. TS-analysis of the Black Sea waters. Oceanol. Russ. Acad. Sci. 1994, 34, 154–168. [Google Scholar]
- Belokopytov, V.N. Thermohaline and Hydroacoustic Structure of the Black Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Marine Hydrophysical Institute, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 2004. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Miladinova, S.; Stips, A.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Moy, D.M. Formation and changes of the Black Sea cold intermediate layer. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 167, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolsky, A.D.; Zalogin, B.S. Seas of the USSR; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 1982; 192p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kosarev, A.N.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Shiganova, T.A. The Sea of Azov; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
| W.M.s | θ (°C) | S | σθ (kg/m3) | Depth (m) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AW | 14–16 10–16 | 36.0–36.5 34.9–36.0 | 26.5–27.0 | <100 | [32] [31] |
| MOW | 12.95–13.15 11–12 | 38.48–38.50 ca. 36.0 | ca. 28.999 | >700 | [38] [31] |
| W.M. | θ (°C) | S | σθ (kg/m3) | Depth (m) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central-Ionian Mediterranean M.R. | |||||
| ISW | 18.0–23.0 | 38.77 (w)-38.93 (s) | 27.94–26.92 | 0–50 (?) | [79] |
| MAW | 15.0–20.0 | 38.4–38.73 | 28.60–27.61 | 30–100 | [79] |
| CIW | 14.8–15.3 | 38.77–38.93 | 27.56–28.94 | 100–200 | [79] |
| LIW | 14.0–15.0 14.5 | 38.9–39.0 38.75–38.89 | 29.0–29.1 28.98–29.09 | 200–600 | [88] [79] |
| TMW | 13.75 13.5–13.6 | 38.75 38.66–38.76 | 29.14 29.13–29.18 | 400–600/800 | [88] [79] |
| CDW | 13.2–13.6 | 38.70–38.77 | 29.22–29.19 | ca. 700–900 | [79] |
| EMDW | 13.60 13.04 | 38.70 38.70 | 29.14 29.25 | >1000 | [76] [88] |
| Adriatic M.R. | |||||
| NAdSW MAdSW SAdSW | <11.5 11.5–13.5 >13.5 | <38.0 38.0–38.5 38.3–38.6 | <29.02–>29.08 | 0–ca. 50 | [83] |
| LIW | 13.5 | 38.5–38.6 | ≈29.04 | [83] | |
| ADW | 11.35–13.16 | 38.3–38.6 | 29.28–29.15 | [83] | |
| W.M. | θ (°C) | S | σθ (kg/m3) | Depth (m) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levantine M.R. | |||||
| LSW LSW (Main basin) LSW (South Cretan Passage) | >17.0 22.0–29.0 >18.0 | ≥39.0 39.0–39.7 39.1–39.3 | 0–>50 0–100 | [104] [102] [101] | |
| MAW (Main basin) MAW (South Cretan Passage) | 17.0–23.5 17.0–23.0 | 36.6–39.1 ≤38.9 | 28.51–26.90 | 0–50 | [102] [101] |
| LIW LΙW (Main basin) LΙW (South Cretan Passage) | 16.20 ± 0.6 15.2–17.3 15.6–16.8 | 39.09 ± 0.05 38.94–39.33 39.04–39.14 | 28.85 ± 0.1 28.75–28.95 | 130–350 85–170 | [104] [102] [101] |
| TMW (South Cretan Passage) | 13.5–13.6 | 38.74–38.76 | 29.17–29.19 | 600–1200 | [101] |
| CDW | 13.56–13.60 | 38.75–38.78 | 29.18–29.19 | 1400–2550 | [101] |
| EMDW | 13.44–13.51 13.6–13.7 | 38.73–38.75 38.6–38.7 | 29.194 ± 0.002 | >3000 1000–2000 | [101] [104] |
| Aegean M.R. | |||||
| BSW (N. Aegean) BSW (Cretan Sea) | >14.0 15.9–17.0 | 30.0–36.0 38.87–39.01 | 22.7–26.5 26.3–26.81 | <40/50 45–60 | [119] [101] |
| MAW (Cretan Sea) | 12.99–25.44 | 37.17–39.69 | 28.75–28.60 | 50–150 | [101] |
| LSW (Cretan Sea, summer) | >18.0 (sum.) | 39.1–39.3 | <28.49 | [101] | |
| CSW | >18.0 | 39.0–39.1 | <40 | [101] | |
| AgIW (MLIW) | 13.9–14.4 14.39–14.43 | 38.70–39.00 38.93–38.95 | 29.10–29.18 | 100–350 140–430 | [107] [121] |
| LIW LIW | 14.3–16.0 16.2–16.7 | 38.89–39.11 39.11–39.14 | 28.8–28.9 | <700–1000 120–300 | [104] [101] |
| CIW | 15.5–15.7 | 39.05–39.07 | 28.90–29.01 | 200–400 | [101] |
| TMW (summer) | 13.90–14.15 | 38.85–38.94 | 29.17–29.18 | 600–800 | [101] |
| NAgDW | 13.2–13.3 12.72–12.78 | 38.80–38.85 38.76–38.82 | 29.27–9.32 | ≈740 | [128] [121] |
| CAgDW | 13.2–13.9 13.38–13.44 14.20 | ≥38.7 38.82–39.06 39.00 | 29.22 | ≈740 | [121] [112] [127] |
| CDW (EMT 1992–1995) | 14.0–14.02 | ≤39.05 39.08 | >29.31 29.40 | >2000 >1500 | [101] [86] |
| Marmara M.R. | |||||
| MaBSW (Mar./1990) MaBSW (Aug./1987) | 10.0–12.0 20.0–27.0 | 22.0–25.0 20.0–25.0 | 15.74–16.14 | 0–25 | [132] |
| MaMSW (Mar./1990) MaMSW (Aug./1987) | 14.0–16.0 10.0–15.0 | 35.0–39.0 35.0–39.0 | 28.51–28.90 | >25 | [132] |
| W.M. | θ (°C) | S | σθ (kg/m3) | Depth (m) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black Sea M.R. | |||||
| BSCW | >3.0 | <15.0 (or <17.8) | 14.18–13.99 | 0–30/60 | [133,134] |
| BSSW | 6.9–23.8 | 17.4–18.6 | 12.42–11.33 | 0–50/60 | [135] |
| CIL | 6.0–7.75 5.0–6.3 | 18.0–19.0 18.6–20.0 | 14.0–14.8 - | 50–70 | [135] [134] |
| BSIW | 7.75–8.82 7.40–8.98 | 19.0–22.30 18.9–22.30 | 14.77–17.19 - | 90/100–1100/1200 | [134] [133] |
| BSDW | 8.98–9.11 | 22.30–22.35 | >1100/1200 | [133] | |
| Azov M.R. | |||||
| AZW | 0–30 | 12.0–15.0 | - | - | [137] |
| Mediterranean Sea (Excluding Marmara) | Black Sea (Excluding Azov) | |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | 3.88 | 0.55 |
| Sea surface/drainage basin | 0.54 | 0.23 |
| Riverine influx | 576 | 418 |
| Heat budget | −(4–11) W/m2 | −(5–7) W/m2 |
| Water budget | −457.4 mm | + 497 ± 108 |
| No. of main marine regions | 3 | 1 |
| No. of secondary marine regions | 7 | 1 |
| No. of water masses | 21 | 5 |
| No. of surface water masses | 7 | 2 |
| No. of intermediate water masses | 6 | 2 |
| No. of deep water masses | 5 | 1 |
| Range of surface water mass properties (θ, in °C and salinity) | θ = 14–29 S = 36.6–39.7 | θ = 3–24 S = 12–18.6 |
| Range of intermediate water mass properties (θ, in °C and salinity) | θ = 13.2–16.7 S = 38.5–39.1 | θ = 5–9 S = 18–22.3 |
| Range of deep water mass properties (θ, in °C and salinity) | θ = 13–13.8 S = 38.4–38.8 | θ = 9.0 S = 22.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulos, S.E. Water Masses of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea: An Overview. Water 2023, 15, 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183194
Poulos SE. Water Masses of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea: An Overview. Water. 2023; 15(18):3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183194
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulos, Serafeim E. 2023. "Water Masses of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea: An Overview" Water 15, no. 18: 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183194
APA StylePoulos, S. E. (2023). Water Masses of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea: An Overview. Water, 15(18), 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15183194











