A Comprehensive Review on Metallic Trace Elements Toxicity in Fishes and Potential Remedial Measures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
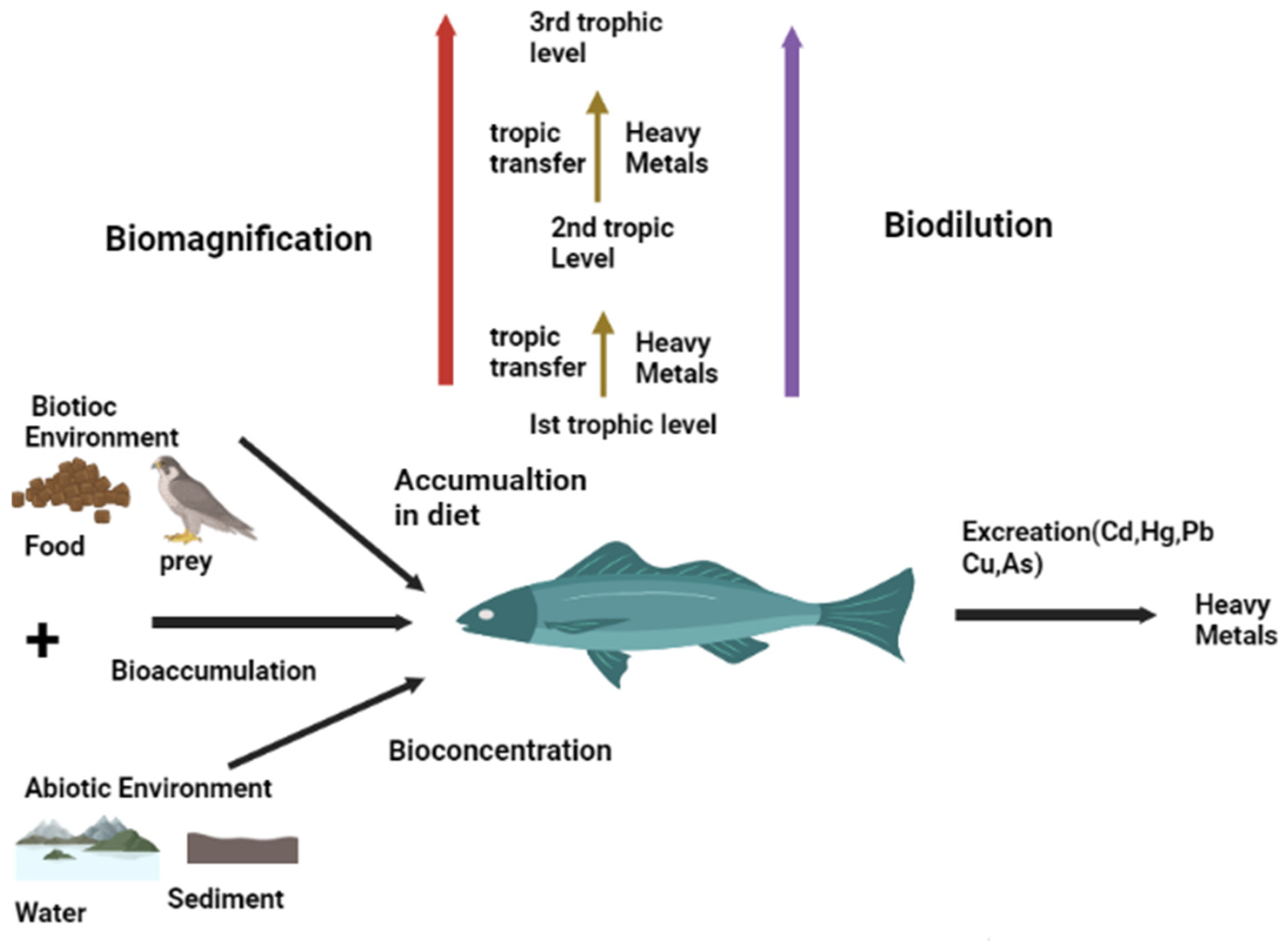
2. Metallic Trace Elements-Induced Toxicity
2.1. Metallic Trace Elements’ Sources in Aquaculture Systems
2.2. Comprehensive Literature Review and Selection Criteria
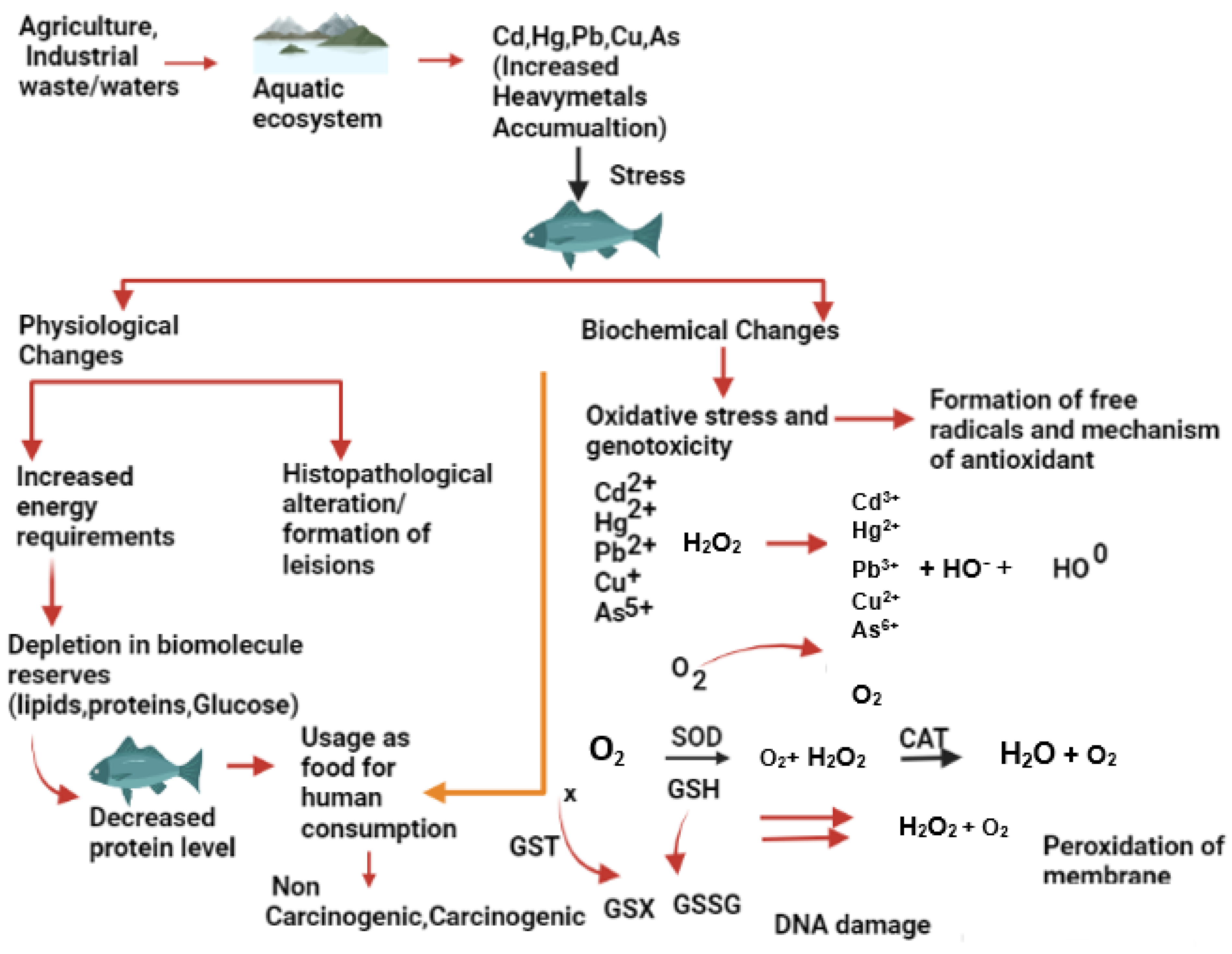
3. Effect of Metallic Trace Elements on Fish Physiology and Biochemistry
3.1. Effect of Metallic Trace Elements on Fish Collected from Contaminated Sites
3.2. Effect on the Nervous System
3.3. Effect on the Reproductive System
3.4. Effect on Embryonic Development
4. Effect of Hazardous Metal Ions
4.1. Effect on Immune System
4.2. Mercury (Hg)
4.3. Lead (Pb)
4.4. Cadmium (Cd)
4.5. Copper (Cu)
4.6. Zinc (Zn)
5. Treatment of Metallic Trace Elements–Contaminated Aquaculture
5.1. Metal Oxides Nanoparticles
5.2. Magnetite Nanoparticles
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, D.H.; Lee, S.-M. Water Pollution and Treatment Technologies. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 2, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; Von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.E.; Costa, P.G.; Lunardelli, B.; De Oliveira, L.F.; Cabrera Lda, C.; Risso, W.E.; Primel, E.G.; Meletti, P.C.; Fillmann, G.; Martinez, C.B. Multiple biomarker responses in Prochilodus lineatus subjected to short-term in situ exposure to streams from agricultural areas in Southern Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, G.; Shoaib, N.; Majid, A. Genotoxic potential of pesticides in the peripheral blood erythrocytes of fish (Oreochromis mossambicus). Pak. J. Zool. 2016, 48, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar]
- Ezemonye, L.I.; Adebayo, P.O.; Enuneku, A.A.; Tongo, I.; Ogbomida, E. Potential health risk consequences of heavy metal concentrations in surface water, shrimp (Macrobrachium macrobrachion) and fish (Brycinus longipinnis) from Benin River, Nigeria. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujari, M.; Kapoor, D. Heavy metals in the ecosystem: Sources and their effects. In Heavy Metals in the Environment; Kumar, V., Sharma, A., Cerdà, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, S.; Zahra, Q.U.A.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Hussain, Z.; Ullah, I.; Li, W.; Kamya, E.; Mehmood, S.; Pei, R.; Wang, J. Heavy Metal Ions Detection Using Nanomaterials-Based Aptasensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Gojenko, B.; Yu, J.; Wei, L.; Luo, D.; Xiao, T. A review of water pollution arising from agriculture and mining activities in Central Asia: Facts, causes and effects. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.; Taher, M.A.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Karimi, F.; Shabani-Nooshabadi, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Al-Othman, A.; Erk, N.; Yegya Raman, P.K.; Karaman, C. Novel enzymatic graphene oxide based biosensor for the detection of glutathione in biological body fluids. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnani, P.; Saucedo, N.M.; Mulchandani, A. Carbon nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for label-free sensing of environmental pollutants. Chemosphere 2016, 143, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Poluri, K.M. Heavy metal detoxification mechanisms by microalgae: Insights from transcriptomics analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, S.; Rezaei Akmal, M.; Salek Maghsoudi, A.; Rahmani, S.; Vakhshiteh, F.; Norouzi, P.; Ganjali, M.R.; Abdollahi, M. High-performance voltammetric aptasensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of bisphenol A as an environmental pollutant. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 574846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Ullah, S.; Yan, J.; Wang, Z.; Ullah, I.; Ahmad, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, L.; Mansoorianfar, M.; et al. Electrospun tannin-rich nanofibrous solid-state membrane for wastewater environmental monitoring and remediation. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehra, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Marrazza, G.; Kaushik, A.; Sonne, C.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, S. Emerging nanobiotechnology in agriculture for the management of pesticide residues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Fu, X.; Sun, D.; Dang, Y.; Holmes, D.E. Development of a whole-cell biosensor based on an ArsR-Pars regulatory circuit from Geobacter sulfurreducens. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2021, 7, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Abdullahi, T.A.; Ogunfowora, L.A.; Emenike, E.C.; Oyekunle, I.P.; Gbadamosi, F.A.; Ighalo, J.O. Mitigation of levofloxacin from aqueous media by adsorption: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, K.; Bao, H.; Zhu, S.; Soleimani-Delfan, A.; He, T.; Mansoorianfar, M.; Wang, R. Bio-control of O157:H7, and colistin-resistant MCR-1-positive Escherichia coli using a new designed broad host range phage cocktail. LWT 2022, 154, 112836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoorianfar, M.; Shahin, K.; Hojjati-Najafabadi, A.; Pei, R. MXene-laden bacteriophage: A new antibacterial candidate to control bacterial contamination in water. Chemosphere 2022, 290, 133383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpor, O.B.; Ohiobor, G.O.; Olaolu, D. Heavy metal pollutants in wastewater effluents: Sources, effects and remediation. Adv. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. Accumulation of heavy metals in fishes: A human health concern. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 2, 659–670. [Google Scholar]
- Naz, S.; Hussain, R.; Ullah, Q.; Chatha, A.M.M.; Shaheen, A.; Khan, R.U. Toxic effect of heavy metals on hematology and histopathology of major carp (Catla catla). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 6533–6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M. Genotoxicity of refinery waste assessed by some DNA damage tests. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabaster, J.S.; Lloyd, R.S. Water Quality Criteria for Freshwater Fish; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Angelo, R.T.; Cringan, M.S.; Chamberlain, D.L.; Stahl, A.J.; Haslouer, S.G.; Goodrich, C.A. Residual effects of lead and zinc mining on freshwater mussels in the Spring River Basin (Kansas, Missouri, and Oklahoma, USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 384, 467–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyna, E.G.; Pacyna, J.M. Global Emission of Mercury from Anthropogenic Sources in 5978, 1995. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 137, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.G.A.; Pitt, R. Stormwater Effects Handbook: A Toolbox for Watershed Managers, Scientists, and Engineers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guibaud, G.; Tixier, N.; Bouju, A.; Baudu, M. Relation between extracellular polymers’ composition and its ability to complex Cd, Cu and Pb. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.; Smith, J.; Smith, L.; Biswas, T.; Correll, R.; Naidu, R. Arsenic in Australian Environment: An Overview. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boularbah, A.; Schwartz, C.; Bitton, G.; Aboudrar, W.; Ouhammou, A.; Morel, J.L. Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: 2. Assessment of metal accumulation and toxicity in plants. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Massaut, L. Risks associated with the use of chemicals in pond aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 1999, 20, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamete, F.; Chacha, M.; Msagati, T.; Raymond, J. Bioaccumulation and distribution pattern of heavy metals in aquaculture systems found in Arusha and Morogoro regions of Tanzania. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 5961–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-W.; Kao, C.-M.; Chen, C.-F.; Dong, C.-D. Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Naz, S.; Ma, Y.; Ullah, Q.; Khan, M.Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, X.; Luosang, D.Z.; Tabassum, S.; Chatha, A.M.M.; et al. An Overview of Comet Assay Application for Detecting DNA Damage in Aquatic Animals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Qu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Xin, W.; Guo, C.; Bowker, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of Aquaculture on Lakes in the Central Yangtze River Basin, China, III: Heavy metals. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2018, 80, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azanu, D.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Darko, G.; Styrishave, B. Simple metal model for predicting uptake and chemical processes in sewage-fed aquaculture ecosystem. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.M.; Rohani, M.F.; Hossain, M.a.R.; Shahjahan, M. Evaluation of heavy metal Contamination in Some Selected Commercial Fish Feeds Used in Bangladesh. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.-R.; El-Houseiny, W.; El-Murr, A.E.; Ebraheim, L.L.M.; Ahmed, A.I.; El-Hakim, Y.M.A. Effect of hexavalent chromium exposure on the liver and kidney tissues related to the expression of CYP450 and GST genes of Oreochromis niloticus fish: Role of curcumin supplemented diet. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, S.; Mansouri, B.; Chatha, A.M.M.; Ullah, Q.; Abadeen, Z.U.; Khan, M.Z.; Khan, A.; Saeed, S.; Bhat, R.A. Water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in surface water at Punjnad Headworks, Punjab, Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 61457–61469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, L.V.; Kutty, R. Sub-lethal effects of potassium dichromate on hematological and histological parameters in climbing perch, Anabas testudineus (Anabantidae). Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2019, 7, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.; Ahmad, M.I.; Usmani, N.; Ahmad, M. Multiple biomarker responses (serum biochemistry, oxidative stress, genotoxicity and histopathology) in Channa punctatus exposed to heavy metal loaded waste water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutukuru, S.S.; Prabhath, N.A.; Raghavender, M.; Yerramilli, A. Effect of Arsenic and Chromium on the Serum Amino-Transferases Activity in Indian Major Carp, Labeo rohita. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2007, 4, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roast, S.D.; Widdows, J.; Jones, M.B. Effects of salinity and chemical speciation on cadmium accumulation and toxicity to two mysid species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, M.; Nayyar, V.; Bansal, R.; Singh, M. Heavy metal pollution in soils and plants through untreated sewage water. In Ground Water Pollution, Proceedings of the International Conference on Water and Environment (WE-2003), Bhopal, India, 15–18 December 2003; Allied Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2003; pp. 487–495. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, G.; Mai, B.; Hu, J.; Li, K.; Wang, Z. Tracing anthropogenic contamination in the Pearl River estuarine and marine environment of South China Sea using sterols and other organic molecular markers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Zouboulis, A.I. Application of biological processes for the removal of arsenic from groundwaters. Water Res. 2004, 38, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, M.; Usmani, N. Histopathology and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Cr, Ni and Pb) in fish (Channa striatus and Heteropneustes fossilis) tissue: A study for toxicity and ecological impacts. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abalaka, S.E.; Enem, S.I.; Idoko, I.S.; Sani, N.A.; Tenuche, O.Z.; Ejeh, S.A.; Sambo, W.K. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and health risks with associated histopathological changes in Clarias gariepinus from the kado fish market, abuja, nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2020, 10, 200602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacik, A.; Tirpak, F.; Tomka, M.; Miskeje, M.; Tvrda, E.; Arvay, J.; Andreji, J.; Slanina, T.; Gabor, M.; Hleba, L.; et al. Trace elements content in semen and their interactions with sperm quality and RedOx status in freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio: A correlation study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Taherianfard, M. The effects of heavy metals exposure on reproductive systems of cyprinid fish from Kor River. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2011, 10, 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sani, A.; Idris, K.M.; Abdullahi, B.A.; Darma, A.I. Bioaccumulation and health risks of heavy metals in Oreochromis niloticus, sediment and water of Challawa river, Kano, Northwestern Nigeria. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAbdel-Kader, H.H.; Mourad, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and physiological/histological changes in gonads of catfish (Clarias gariepinus) inhabiting Lake Maryout, Alexandria, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalaka, S.E. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and histopathological changes in Auchenoglanis occidentalis fish from Tiga dam, Nigeria. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2015, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, M.; Usmani, N.; Firdaus, F.; Zafeer, M.F.; Ahmad, S.; Akhtar, K.; Husain, S.D.; Ahmad, M.H.; Anis, E.; Hossain, M.M. In vivo induction of antioxidant response and oxidative stress associated with genotoxicity and histopathological alteration in two commercial fish species due to heavy metals exposure in northern India (Kali) river. Comp. Biochem. 2015, 176, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.J.; Zhang, S.H. Heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn) concentrations in seven fish species in relation to fish size and location along the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3989–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivakumar, C.; Thippeswamy, B.; Tejaswikumar, M.; Prashanthakumara, S. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and its effect on organs of edible fishes located in Bhadra River, Karnataka. Int. J. Res. Fish. Aquac. 2014, 4, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Módenes, A.N.; Palácio, S.M.; Szymanski, N.; Welter, R.A.; Rizzutto, M.A.; Borba, C.E.; Kroumov, A.D. Evaluation of trace element levels in muscles, liver and gonad of fish species from São Francisco River of the Paraná Brazilian state by using SR-TXRF technique. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2010, 68, 2202–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, P.; Behr, E.R.; Knorr, C.D.L.; Vendruscolo, D.S.; Flores, E.M.; Dressler, V.L.; Baldisserotto, B. Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savassi, L.A.; Paschoalini, A.L.; Arantes, F.P.; Rizzo, E.; Bazzoli, N. Heavy metal contamination in a highly consumed Brazilian fish: Immunohistochemical and histopathological assessments. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arantes, F.P.; Savassi, L.A.; Santos, H.B.; Gomes, M.V.; Bazzoli, N. Bioaccumulation of mercury, cadmium, zinc, chromium, and lead in muscle, liver, and spleen tissues of a large commercially valuable catfish species from Brazil. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2016, 88, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalzochio, T.; Ressel Simões, L.A.; Santos De Souza, M.; Prado Rodrigues, G.Z.; Petry, I.E.; Andriguetti, N.B.; Herbert Silva, G.J.; Gehlen, G.; Basso Da Silva, L. Water quality parameters, biomarkers and metal bioaccumulation in native fish captured in the Ilha River, southern Brazil. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreña-Ramirez, D.A.; Murillo-Perea, E.; Guio-Duque, A.J.; Méndez-Arteaga, J.J. Heavy metals (Cd, Pb and Ni) in fish species commercially important from Magdalena river, Tolima tract, Colombia. Rev. Tumbaga 2012, 2, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Corredor-Santamaría, W.; Serrano Gómez, M.; Velasco-Santamaría, Y.M. Using genotoxic and haematological biomarkers as an evidence of environmental contamination in the Ocoa River native fish, Villavicencio-Meta, Colombia. Springerplus 2016, 5, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatrup, E. Structural and functional effects of Heavy metals on the nervous system, including sense organs, of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1991, 100, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, Y.; Hasan, M. Mercury induced time-dependent alterations in lipid profiles and lipid peroxidation in different body organs of catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 1989, 24, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, V.M.; Dalton, R.A. The acute lethal toxicity to rainbow trout of mixtures of copper, phenol, zinc and nickel. J. Fish Biol. 1970, 2, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.G.; Mackay, W.C. The effects of hardness, alkalinity and pH of test water on the toxicity of copper to rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Water Res. 1980, 14, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Rowse, C.; Hochstein, P. Copper-induced generation of superoxide in human red cell membrane. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1978, 83, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloj Totaro, E.; Pisanti, F.A.; Glees, P.; Continillo, A. The effect of copper pollution on mitochondrial degeneration. Mar. Environ. Res. 1986, 18, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enesco, H.E.; Pisanti, F.A.; Aloj Totaro, E. The effect of copper on the ultrastructure of Torpedo marmorata neurons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1989, 20, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katti, S.R.; Sathyanesan, A.G. Lead nitrate induced changes in the brain constituents of the freshwater fish Clarias batrachus. Neurotoxicology 1986, 7, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.-L.; Yuan, S.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Lv, Z.-M.; Zhu, A.-Y. Circadian time-dependent antioxidant and inflammatory responses to acute cadmium exposure in the brain of zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 182, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.J.; Mattingly, C.J.; Planchart, A. Cadmium Disrupts Vestibular Function by Interfering with Otolith Formation. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, J.; Higgs, D.M. Sublethal effects of cadmium on auditory structure and function in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessnack, M.K.; Matthews, A.L.; Raine, J.C.; Niyogi, S. Interactive effects of chronic waterborne copper and cadmium exposure on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 179, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiter, S.; Sippel, J.; Bouwmeester, M.C.; Lommelaars, T.; Beekhof, P.; Hodemaekers, H.M.; Bakker, F.; Van Den Brandhof, E.-J.; Pennings, J.L.A.; Van Der Ven, L.T.M. Programmed Effects in Neurobehavior and Antioxidative Physiology in Zebrafish Embryonically Exposed to Cadmium: Observations and Hypothesized Adverse Outcome Pathway Framework. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.; Puga, S.; Cardoso, V.; Pinto-Ribeiro, F.; Raimundo, J.; Barata, M.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Pacheco, M.; Almeida, A. Inorganic mercury accumulation in brain following waterborne exposure elicits a deficit on the number of brain cells and impairs swimming behavior in fish (white seabream—Diplodus sargus). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 170, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, K.; Venables, B.; Roberts, A. Effects of dietary methylmercury on th99e dopaminergic system of adult fathead minnows and their offspring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasinger, J.D.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Penglase, S.J.; Ellingsen, S.; Amlund, H. Methylmercury Induced Neurotoxicity and the Influence of Selenium in the Brains of Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, S.; Gonzalez, P.; Mesmer-Dudons, N.; Brethes, D.; Fujimura, M.; Bourdineaud, J.-P. Effects of dietary methylmercury on the zebrafish brain: Histological, mitochondrial, and gene transcription analyses. Biometals 2012, 25, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Bakar, N.; Mohd Sata, N.S.; Ramlan, N.F.; Wan Ibrahim, W.N.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Che Abdullah, C.A.; Ahmad, S.; Amal, M.N. Evaluation of the neurotoxic effects of chronic embryonic exposure with inorganic mercury on motor and anxiety-like responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 59, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Freeman, J.L. Embryonic exposure to 10 μg L−1 lead results in female-specific expression changes in genes associated with nervous system development and function and Alzheimer’s disease in aged adult zebrafish brain. Metallomics 2016, 8, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhou, B. Effect of combined exposure to lead and decabromodiphenyl ether on neurodevelopment of zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bault, Z.A.; Peterson, S.M.; Freeman, J.L. Directional and color preference in adult zebrafish: Implications in behavioral and learning assays in neurotoxicology studies. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Weber, D.; Burge, R.; Vanamberg, K. Neurobehavioral impairments produced by developmental lead exposure persisted for generations in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurotoxicology 2016, 52, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Fan, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zou, F. Effects of cadmium, manganese, and lead on locomotor activity and neurexin 2a expression in zebrafish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Hu, K.; Jiang, J.; Li, S.H.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Copper exposure induces oxidative injury, disturbs the antioxidant system and changes the Nrf2/ARE (CuZnSOD) signaling in the fish brain: Protective effects of myo-inositol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirici, M.; Nedzvetsky, V.S.; Agca, C.A.; Gasso, V.Y. Sublethal doses of copper sulphate initiate deregulation of glial cytoskeleton, NF-kB and PARP expression in Capoeta umbla brain tissue. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2019, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilehvar, A.; Town, R.M.; Blust, R. The effect of copper on behaviour, memory, and associative learning ability of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeonyejiaku, C.D.; Obiakor, M.O.; Ezenwelu, C.O. Toxicity Of Copper Sulphate And Behavioral Locomotor Response Of Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) And Catfish (Clarias gariepinus) Species. Online J. Anim. Feed. Res. 2011, 1, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Baldissarelli, L.A.; Capiotti, K.M.; Bogo, M.R.; Ghisleni, G.; Bonan, C.D. Arsenic alters behavioral parameters and brain ectonucleotidases activities in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 155, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, P.; Shaw, P.; Dey Bhowmik, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sudarshan, M.; Chakraborty, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Combined effect of arsenic and fluoride at environmentally relevant concentrations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain: Alterations in stress marker and apoptotic gene expression. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipp, V.R.; Valles, S.; Ortiz-Kerbertt, H.; Suarez, J.V.; Bardullas, U. Neurobehavioral Alterations in Zebrafish Due to Long-Term Exposure to Low Doses of Inorganic Arsenic. Zebrafish 2018, 15, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, G.; Kumar, V. The Toxic Effect of Fluoride and Arsenic on Behaviour and Morphology of Catfish (Clarias batrachus). Nat. Environ. Pollut. Technol. 2021, 20, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, B.; Capela, R.C.; Sérgio, T.; Caldeira, C.; Gonçalves, F.; Correia, A.T. Effects of chronic exposure to lead, copper, zinc, and cadmium on biomarkers of the European eel, Anguilla anguilla. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 5689–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioda, C.R.; Loro, V.L.; Pretto, A.; Salbego, J.; Dressler, V.; Flores, É.M.M. Sublethal zinc and copper exposure affect acetylcholinesterase activity and accumulation in different tissues of leporinus obtusidens. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2013, 90, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Li, R.; Li, S.; Qiu, D.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Ni, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, H. Oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and intestinal microbial regulation after a chronic zinc exposure: An experimental study on adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Water Reuse 2023, 13, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.T.; Weis, J.S. Effects of methylmercury on sperm and egg viability of two populations of killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1987, 16, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubair, M.; Ahmad, M.; Saleemi, M.K.; Gul, S.T.; Ahmad, M.; Martyniuk, C.J.; Ullah, Q.; Umar, S. Sodium arsenite toxicity on hematology indices and reproductive parameters in Teddy goat bucks and their amelioration with vitamin C. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 15223–15232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomińska, I.; Jezierska, B. The effect of heavy metals on postembryonic development of common carp Cyprinus carpio L. Arch. Ryb. Pol. 2000, 8, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Witeska, M.; Jezierska, B.; Chaber, J. The influence of cadmium on common carp embryos and larvae. Aquaculture 1995, 129, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M.; Sarnowski, P.; Ługowska, K.; Kowal, E. The effects of cadmium and copper on embryonic and larval development of ide Leuciscus idus L. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jezierska, B.; Lugowska, K.; Witeska, M. The effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of fish (a review). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 35, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionkowski, J.; Łuszczek-Trojnar, E.; Popek, W.; Drąg-Kozak, E.; Socha, M. Impact of long-term dietary exposure to lead on some reproductive parameters of a female Common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquac. Res. 2017, 48, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hontela, A.; Daniel, C.; Ricard, A.C. Effects of acute and subacute exposures to cadmium on the interrenal and thyroid function in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat. Toxicol. 1996, 35, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, S.S.; Gupta, P.; Kar, A.; Maiti, P.K. Lead induced thyroid dysfunction and lipid peroxidation in the fish Clarias batrachus with special reference to hepatic type I-5′-monodeiodinase activity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 56, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagdonas, E.; Vosylienė, M. A study of toxicity and genotoxicity of copper, zinc and their mixture to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Biologija 2006, 1, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Cavas, T. In vivo genotoxicity of mercury chloride and lead acetate: Micronucleus test on acridine orange stained fish cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavas, T.; Garanko, N.N.; Arkhipchuk, V.V. Induction of micronuclei and binuclei in blood, gill and liver cells of fishes subchronically exposed to cadmium chloride and copper sulphate. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, G.J.; Chaube, R.J. Differential effects of heavy metals (Cadmium, Cobalt, Lead and Mercury) on oocyte maturation and ovulation of the catfish Heteropneustes fossilis: An In Vitro Study. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2018, 18, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Hamid, N.; Deng, S.; Jia, P.P.; Pei, D.S. Individual and combined toxicogenetic effects of microplastics and heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Zn) perturb gut microbiota homeostasis and gonadal development in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 397, 122795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Marquez, L.; Espinosa-Araujo, J.; Atencio-Garcia, V.; Olivero-Verbel, J. Effects of cadmium exposure on sperm and larvae of the neotropical fish Prochilodus magdalenae. Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Toxicol. Pharmacol. CBP 2019, 225, 108577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, A.; Wulansari, E.; Armando, D.S.; Sofiyanti, A.; Amin, M.H.F.A.; Pramudya, M. Effects of in vitro exposure of mercury on sperm quality and fertility of tropical fish Cyprinus carpio L. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, G.J.; Dietrich, M.; Kowalski, R.; Dobosz, S.; Karol, H.; Demianowicz, W.; Glogowski, J. Exposure of rainbow trout milt to mercury and cadmium alters sperm motility parameters and reproductive success. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 97, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Chen, Q.; Gong, S.; An, J.; Li, Y.; Lian, X.; Liu, Z.; Shen, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Exposure of zebrafish to environmentally relevant concentrations of mercury during early life stages impairs subsequent reproduction in adults but can be recovered in offspring. Aquat. Toxicol. 2020, 229, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Li, Y.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, Q.L. Exposure to mercuric chloride induces developmental damage, oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in zebrafish embryos-larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 181, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.T.A.; Banaee, M.; Sureda, A. Selenium protection against mercury toxicity on the male reproductive system of Clarias gariepinus. Comparative biochemistry and physiology. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 225, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahemal-Balawi, H.F.; Ahmad, Z.; Al-Akel, A.S.; Al-Misned, F.; Suliman, E.-a.M.; Al-Ghanim, K.A. Toxicity bioassay of lead acetate and effects of its sub-lethal exposure on growth, haematological parameters and reproduction in Clarias gariepinus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 11039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Wenjing, G.; Wu, P.; He, X.; Xie, L. Copper caused reproductive endocrine disruption in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 211, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessnack, M.K.; Jamwal, A.; Niyogi, S. Effects of chronic exposure to waterborne copper and nickel in binary mixture on tissue-specific metal accumulation and reproduction in fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Chemosphere 2017, 185, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, N.; Vakurov, A.; Knapen, D.; Blust, R. The chronic toxicity of CuO nanoparticles and copper salt to Daphnia magna. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouhar Vajargah, M.; Mohamadi Yalsuyi, A.; Sattari, M.; Prokic, M.; Faggio, C. Effects of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) on Parturition Time, Survival Rate and Reproductive Success of Guppy Fish, Poecilia reticulata. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, M.J.; Shamushaki, V.-A.J. Effects of different levels of copper sulfate on growth and reproductive performances in guppy (P. reticulate). J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2015, 6, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Wu, C.; Cao, H. Histopathological examination and transcriptome analyses to assess the acute toxic effects of arsenite exposure on rare minnows (Gobiocypris rarus). Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagato, E.G.; D’eon, J.C.; Lankadurai, B.P.; Poirier, D.G.; Reiner, E.J.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J. 1H NMR-based metabolomics investigation of Daphnia magna responses to sub-lethal exposure to arsenic, copper and lithium. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.J.; Kollus, K.M.; Propper, C.R. Environmentally relevant arsenic exposure affects morphological and molecular endpoints associated with reproduction in the Western mosquitofish, Gambusia affinis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gárriz, Á.; Miranda, L.A. Effects of metals on sperm quality, fertilization and hatching rates, and embryo and larval survival of pejerrey fish (Odontesthes bonariensis). Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1072–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouva, E.; Nathanailides, C.; Skoufos, I.; Paschos, I.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Pappas, I.S. Comparative study of the effects of heavy metals on embryonic development of zebrafish. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 3255–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.; Srivastava, P.P.; Kumar, M.; Varghese, T.; Chanu, T.I.; Gupta, S.; Ande, M.P.; Jana, P. The modulation effects of dietary zinc on reproductive performance and gonadotropins’(FSH and LH) expression in threatened Asian catfish, Clarias magur (Hamilton, 1822) broodfish. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 2254–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarek-Gwiazda, E. Heavy metals contents in stone loach Noemacheilus barbatulus (L.) (Cobitidae) living in the river above and below dam reservoir (Dobczyce reservoir, southern Poland). Pol. J. Ecol. 1999, 47, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ellenberger, S.A.; Baumann, P.C.; May, T.W. Evaluation of effects caused by high copper concentrations in Torch Lake, Michigan, on reproduction of yellow perch. J. Great Lakes Res. 1994, 20, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.; Munkittrick, K.; Dixon, D. Relationship between concentrations of copper and zinc in water, sediment, benthic invertebrates, and tissues of white sucker (Catostomus commersoni) at metal-contaminated sites. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammad, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Abbas, Z.; Hu, L.; Ullah, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y. Major Nutritional Metabolic Alterations Influencing the Reproductive System of Postpartum Dairy Cows. Metabolites 2022, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrom, S.; Lamers, L.; Lock, R.; Balm, P.; Bonga, S.W. Interactions between copper and cadmium modify metal organ distribution in mature tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Environ. Pollut. 1995, 90, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P. Accumulation profiles of lead and cadmium in the edible tissues of Oreochromis aureus during acute exposure. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 47, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, D.A.; Holcombe, G. Toxic effects of zinc on fathead minnows Pimephales promelas in soft water. J. Fish Biol. 1978, 13, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, E.W. Acute toxicity, uptake and histopathology of aqueous methyl mercury to fathead minnow embryos. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouthart, A.J.H.X.; Spanings, F.a.T.; Lock, R.a.C.; Bonga, S.E.W. Effects of water pH on chromium toxicity to early life stages of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat. Toxicol. 1995, 32, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stouthart, A.; Spanings, F.; Lock, R.; Bonga, S.W. Effects of low water pH on lead toxicity to early life stages of the common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Aquat. Toxicol. 1994, 30, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, D.A. Toxic effects of hexavalent chromium on brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) and rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Water Res. 1976, 10, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, J.; Pascoe, D. Cadmium uptake by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri eggs and alevins. J. Fish Biol. 1978, 13, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michibata, H. Uptake and distribution of cadmium in the egg of the teleost, Oryzias latipes. J. Fish Biol. 1981, 19, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.; Zubair, M.; Tehseen Gul, S.; Ullah, Q.; Idrees, M. Evaluating the protective effects of vitamin E and selenium on hematology and liver, lung and uterus histopathology of rabbits with cypermethrin toxicity. Toxin Rev. 2020, 39, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, J.C.; Shenker, J. The teratogenic effects of methylmercury on early development of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Aquat. Toxicol. 2000, 48, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Ermak, G.; Mazurkiewicz, J.E.; Baker, J.; Wortsman, J. Characterization of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in human skin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barjhoux, I.; Baudrimont, M.; Morin, B.; Landi, L.; Cachot, J. Effects of copper and cadmium spiked-sediments on embryonic development of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 79, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Greisy, Z.A.; El-Gamal, A.H.A. Experimental studies on the effect of cadmium chloride, zinc acetate, their mixture and the mitigation with vitamin C supplementation on hatchability, size and quality of newly hatched larvae of common carp, Cyprinus carpio. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 41, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnack, L.; Kampe, S.; Muth-Köhne, E.; Erdinger, L.; Henny, N.; Hollert, H.; Schäfers, C.; Fenske, M. Effects of metal exposure on motor neuron development, neuromasts and the escape response of zebrafish embryos. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 50, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaco, A.; Capriello, T.; Grimaldi, M.C.; Schiano, V.; Ferrandino, I. Neurodegeneration in zebrafish embryos and adults after cadmium exposure. Eur. J. Histochem. 2017, 61, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wold, M.; Beckmann, M.; Poitra, S.; Espinoza, A.; Longie, R.; Mersereau, E.; Darland, D.C.; Darland, T. The longitudinal effects of early developmental cadmium exposure on conditioned place preference and cardiovascular physiology in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 191, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ługowska, K.; Kondera, E. Developmental anomalies in ide (Leuciscus idus L.) larvae caused by copper and cadmium. Rocz. Nauk. Pol. Tow. Zootech. 2020, 16, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q. Environmentally relevant concentrations of mercury exposure alter thyroid hormone levels and gene expression in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis of zebrafish larvae. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Viveros, S.; Galar-Martínez, M.; Gasca-Pérez, E.; García-Medina, S.; Ruiz-Lara, K.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Islas-Flores, H. The relationship between embryotoxicity and oxidative stress produced by aluminum, iron, mercury, and their mixture on Cyprinus carpio. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, D.; Zuo, Z. Maternal and embryonic exposure to the water soluble fraction of crude oil or lead induces behavioral abnormalities in zebrafish (Danio rerio), and the mechanisms involved. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, V.; Macirella, R.; Sesti, S.; Ahmed, A.I.M.; Talarico, F.; Tagarelli, A.; Mezzasalma, M.; Brunelli, E. Morphological and Functional Alterations Induced by Two Ecologically Relevant Concentrations of Lead on Danio rerio Gills. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirbisky, S.E.; Weber, G.J.; Lee, J.W.; Cannon, J.R.; Freeman, J.L. Novel dose-dependent alterations in excitatory GABA during embryonic development associated with lead (Pb) neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; He, M.; Yu, L.; Liu, R.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Li, B.; Li, L. Lead Exposure Causes Spinal Curvature during Embryonic Development in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekari, S.; Sadooghi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Effect Of Lead Chloride on Embryonic Stages and Kidney Differentiation in Pterophyllum Scalare. JAPAD 2014, 6, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Lasiene, K.; Straukas, D.; Vitkus, A.; Juodziukyniene, N. The influence of copper sulphate pentahydrate (CuSO4 5H2O) on the embryo development in the guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Fei, W.; Li, L.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Effects of copper exposure on the hatching status and antioxidant defense at different developmental stages of embryos and larvae of goldfish Carassius auratus. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, T.; Anwar, S.; Taslem Mourosi, J.; Hossain, J.; Rabbane, M.G.; Rahman, M.M.; Tahsin, T.; Hasan, M.N.; Shill, M.C.; Hosen, M.J. Arsenic hampered embryonic development: An in vivo study using local Bangladeshi Danio rerio model. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, L.M.; Truong, L.; Barton, C.L.; Chase, T.T.; Gonnerman, G.D.; Wong, C.P.; Tanguay, R.L.; Ho, E. Combinatorial effects of zinc deficiency and arsenic exposure on zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e01838312017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmanan, Y. Developmental Toxicity of Arsenic and its Underlying Mechanisms in the early Embryonic Development. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 9, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, R.; Van Beneden, R.J. Effect of arsenic exposure on early eye development in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Cao, L.; Shan, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Dou, S. Toxic Effects of Zinc on the Development, Growth, and Survival of Red Sea Bream Pagrus major Embryos and Larvae. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.D.; Holdway, D.A. The effects of pulse-exposed cadmium and zinc on embryo hatchability, larval development, and survival of Australian crimson spotted rainbow fish (Melanotaenia fluviatilis). Environ. Toxicol. 2000, 15, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahjahan, M.; Taslima, K.; Rahman, M.S.; Al-Emran, M.; Alam, S.I.; Faggio, C. Effects of heavy metals on fish physiology—A review. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marijić, V.F.; Raspor, B. Metal exposure assessment in native fish, Mullus barbatus L., from the Eastern Adriatic Sea. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saglam, D.; Atli, G.; Dogan, Z.; Baysoy, E.; Gurler, C.; Eroglu, A.; Canli, M. Response of the antioxidant system of freshwater fish (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to metals (Cd, Cu) in differing hardness. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stohs, S.J.; Bagchi, D. Oxidative mechanisms in the toxicity of metal ions. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1995, 18, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Mohanty, B. Histopathological effects of hexavalent chromium in the ovary of a fresh water fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, H.D.; Eller, L.L.; Walsh, D.F. Chronic Effects of Methoxychlor on Bluegills and Aquatic Invertebrates; US Bureau of Sport Fisheries and Wildlife: Falls Church, VA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.; Dutta, A.; Ghosh, R. Impact of carbofuran in the oocyte maturation of catfish, Heteropenustes fossilis (Bloch). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1997, 32, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, M. Malathion induced changes in the ovary of freshwater fish, Glossogobius giuris (Ham). Pollut. Res. 2000, 19, 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, H.; Meijer, H. Sublethal effects of diazinon on the structure of the testis of bluegill, Lepomis macrochirus: A microscopic analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 125, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, S.; Mahanta, R. A study on the effect of organophosphorus pesticide malathion on hepato-renal and reproductive organs of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch). Sci. Probe 2012, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- David, M.; Rao, K. Sodium cyanide induced histopathological changes in kidney of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio under sublethal exposure. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2014, 4, 634–639. [Google Scholar]
- Jayachandran, K.; Pugazhendy, K. Histopathological changes in the gill of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings exposed to atrazine. Am. Eurasian J. Sci. Res. 2009, 4, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, R.; Zuberi, A.; Naeem, M.; Ullah, S. Toxicity to hematology and morphology of liver brain and gills during acute exposure of mahseer (Tor putitora) to cypermethrin. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2015, 17, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, R.F.; Dias, H.M.; Fujimoto, R.Y. Acute toxicity and histopathology in ornamental fish amazon bluespotted corydora (Corydoras melanistius) exposed to formalin. An. Da Acad. Bras. De Ciências 2012, 84, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marutirao, G.R. Histopathological changes in the gills of Puntius ticto (Ham) under Dimethoate toxicity. Bioscan 2012, 7, 423–426. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, J.K.; Ranjana, K.P.; Mishra, A. Histopathological changes in the gills of Channa gachua, an air breathing teleost after short term exposure of hostathion. Bioscan 2014, 9, 925–929. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Sinha, A.; Munshi, J. Malathion induced ultrastructural changes in the gills of Heteropneustes fossilis (Bloch) and their functional significance in oxygen uptake. J. Freshw. Biol. 1998, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Kondera, E.; Witeska, M. Cadmium and copper reduce hematopoietic potential in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) head kidney. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 39, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; Gallagher, E.P. Effects of cadmium on olfactory mediated behaviors and molecular biomarkers in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 140–141, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, D.; Ghosh, D.; Mandal, D.K. Cadmium induced histopathology in the olfactory epithelium of a snakehead fish, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2013, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, J.; Vincent, S.; Nirmala, A. Histopathology changes in freshwater fish Clarias batrachus (Linn.) exposed to mercury and cadmium. Int. J. Life Sci. Pharma Res. 2013, 3, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- García-Medina, S.; Galar-Martínez, M.; Gómez-Oliván, L.M.; Ruiz-Lara, K.; Islas-Flores, H.; Gasca-Pérez, E. Relationship between genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by mercury on common carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 192, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasim, M.A.; Sofian-Azirun, M.; Yusoff, I.; Rahman, M.M. Bioaccumulation and histopathological changes induced by toxicity of mercury (HgCl2) to tilapia fish Oreochromis niloticus. Sains Malays. 2016, 45, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Macirella, R.; Brunelli, E. Morphofunctional Alterations in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Gills after Exposure to Mercury Chloride. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, B.B.; Patnaik, H.; Mathews, T.; Selvanayagam, M. Histopathology of gill, liver, muscle and brain of Cyprinus carpio communis L. exposed to sublethal concentration of lead and cadmium. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 12218–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brraich, O.S.; Manjeet, K. Ultrastructural changes in the gills of a cyprinid fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton, 1822) through scanning electron microscopy after exposure to Lead Nitrate (Teleostei: Cyprinidae). Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2015, 2, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Mandal, A.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Chakraborty, S.; Paul, R.; Kumar Mukhopadhyay, B. Evaluation of water quality and toxicity after exposure of lead nitrate in fresh water fish, major source of water pollution. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalesi, K.; Abedi, Z.; Behrouzi, S.; Eskandari, S.K. Haematological, blood biochemical and histopathological effects of sublethal cadmium and lead concentrations in common carp. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2017, 20, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.M.; Mancera, J.M.; Fontaínhas-Fernandes, A.; Sousa, M. Copper induced alterations of biochemical parameters in the gill and plasma of Oreochromis niloticus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, B.; Maleki, A.; Johari, S.A.; Shahmoradi, B.; Mohammadi, E.; Shahsavari, S.; Davari, B. Copper Bioaccumulation and Depuration in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Following Co-exposure to TiO2 and CuO Nanoparticles. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 71, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bairuty, G.A.; Shaw, B.J.; Handy, R.D.; Henry, T.B. Histopathological effects of waterborne copper nanoparticles and copper sulphate on the organs of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.M.; Bahadur, A. Histopathological Manifestations of Sub Lethal Toxicity of Copper Ions in Catla catla. Am. Eurasian J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M.; Parvin, E.; Akter, M.S.; Khan, M.S. Arsenic induced toxicity and histopathological changes in gill and liver tissue of freshwater fish, tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, S.; Mathivanan, V.; Aravinth, S.; Sangeetha, V. Impact of arsenic metal toxicant on biochemical changes in the grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Int. J. Mod. Res. Rev. 2014, 2, 74–78. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Unni, B.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Wann, S.B.; Rao, P.G. Toxicological effects of arsenic exposure in a freshwater teleost fish, Channa punctatus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 4447–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subashkumar, S.; Selvanayagam, M. First report on: Acute toxicity and gill histopathology of fresh water fish Cyprinus carpio exposed to Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2014, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Warith, A.A.; Younis, E.M.; Al-Asgah, N.A.; Wahbi, O.M. Effect of zinc toxicity on liver histology of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Sci. Res. Essays 2011, 6, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, G.B.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, M.F.; Ullah, Z.; Tabassum, S.; Tedesse, Z. Toxicological impact of zinc nano particles on tilapia fish (Oreochromis mossambicus). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegam, A.; Lopes, M.; Fernandes, T.; Jose, J.; Barreto, A.; Oliveira, M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Trindade, T.; Thomas, S.; Pereira, M.L. Multiorgan histopathological changes in the juvenile seabream Sparus aurata as a biomarker for zinc oxide particles toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30907–30917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankveld, D.P.K.; Van Loveren, H.; Baken, K.A.; Vandebriel, R.J. In vitro testing for direct immunotoxicity: State of the art. Immunotoxicity Test. Methods Protoc. 2010, 598, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitinger, J.M.; Beamer, C.A.; Shepherd, D.M. Environmental immunology: Lessons learned from exposure to a select panel of immunotoxicants. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3217–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehberger, K.; Werner, I.; Hitzfeld, B.; Segner, H.; Baumann, L. 20 Years of fish immunotoxicology—What we know and where we are. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2017, 47, 516–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.C.G.; Reimao, R.V.; Pavesi, T.; Saggioro, E.M.; Moreira, J.C.; Correia, F.V. Lethal and sub-lethal evaluation of Indigo Carmine dye and byproducts after TiO2 photocatalysis in the immune system of Eisenia andrei earthworms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 143, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boverhof, D.R.; Ladics, G.; Luebke, B.; Botham, J.; Corsini, E.; Evans, E.; Germolec, D.; Holsapple, M.; Loveless, S.E.; Lu, H.; et al. Approaches and considerations for the assessment of immunotoxicity for environmental chemicals: A workshop summary. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 68, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, J.; Wang, M.; Guo, R. Fe3O4/PANI/MnO2 core–shell hybrids as advanced adsorbents for heavy metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4058–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Sen, S.S.; Jun, J.W.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Immunotoxicological effects of cadmium on Labeo rohita, with emphasis on the expression of HSP genes. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2016, 54, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.L.; Yuan, S.S.; Wu, C.W.; Lv, Z.M. Acute exposure to waterborne cadmium induced oxidative stress and immunotoxicity in the brain, ovary and liver of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 180, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.T.A.; Banaee, M.; Sureda, A. Genotoxicity, oxidative stress, and biochemical biomarkers of exposure to green synthesized cadmium nanoparticles in Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 242, 108942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huang, W.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Zeng, J.; Cao, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, Y.; Jia, S. Responses of antioxidant defense and immune gene expression in early life stages of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) under methyl mercury exposure. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Espinosa, C.; Romero, D.; Meseguer, J.; Cuesta, A.; Esteban, M.A. Mercury Accumulation, Structural Damages, and Antioxidant and Immune Status Changes in the Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata L.) Exposed to Methylmercury. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, J.C. The immune responses and expression of metallothionein (MT) gene and heat shock protein 70 (HSP 70) in juvenile rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii, exposed to waterborne arsenic (As3+). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 47, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Qian, K.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Q.; Du, Y.; Fu, S. Lead exposure induces structural damage, digestive stress, immune response and microbiota dysbiosis in the intestine of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 262, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Du, X.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Li, Y. Effect of Lead on Antioxidant Ability and Immune Responses of Crucian Carp. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Pu, Y.; Zhong, L.; Wang, K.; Duan, X.; Chen, D. Lead impaired immune function and tissue integrity in yellow catfish (Peltobargus fulvidraco) by mediating oxidative stress, inflammatory response and apoptosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopi, N.; Vijayakumar, S.; Thaya, R.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Al-Anbr, M.N.; Vaseeharan, B. Chronic exposure of Oreochromis niloticus to sub-lethal copper concentrations: Effects on growth, antioxidant, non-enzymatic antioxidant, oxidative stress and non-specific immune responses. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 55, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wen, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Yin, S. Copper nanoparticles induced oxidation stress, cell apoptosis and immune response in the liver of juvenile Takifugu fasciatus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 84, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Kang, J.C. Toxic effects of dietary copper and EGCG on bioaccumulation, antioxidant enzyme and immune response of Korean bullhead, Pseudobagrus fulvidraco. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2021, 111, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Mitra, T.; Purohit, G.K.; Mohanty, S.; Mohanty, B.P. Immunomodulatory effect of arsenic on cytokine and HSP gene expression in Labeo rohita fingerlings. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2015, 44, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola, F.A.; Gónzalez-Párraga, M.P.; Cuesta, A.; Meseguer, J.; Martínez, S.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.J.; Pérez-Sirvent, C.; Esteban, M.A. Immunotoxicological effects of inorganic arsenic on gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 134, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Bhaduri, A.; Srivastava, N.; Mazumder, S. Identification of novel signature genes attesting arsenic-induced immune alterations in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Huo, X.J.; Hou, L.P.; Gong, Z. Immune response induced by major environmental pollutants through altering neutrophils in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 201, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.F.; Wang, C.C.; Guo, S.N.; Zheng, J.L.; Xia, H. The lagged effects of environmentally relevant zinc on non-specific immunity in zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Kim, K.W.; Kang, J.C. Oxidative stress and non-specific immune responses in juvenile black sea bream, Acanthopagrus schlegelii, exposed to waterborne zinc. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, E.Ş.; Kaya, H.; Yilmaz, S.; Akbulut, M.; Tulgar, A. Effects of zinc exposure on the accumulation, haematology and immunology of Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 744–753. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, A.S.; Watzin, M.C.; Brinck-Johnsen, T.; Leiter, J.C. Low levels of dietary methylmercury inhibit growth and gonadal development in juvenile walleye (Stizostedion vitreum). Aquat. Toxicol. 1996, 35, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K. Effects of Hg and Cd upon the eggs and fry of ‘‘goldfish’’ Carassius auratus (Linnaeus). Bull. Fac. Fish Univ. Mie 1979, 6, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- GuéVel, R.L.; Petit, F.; Goff, P.L.; Métivier, R.; Valotaire, Y.; Pakdel, F. Inhibition of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) estrogen receptor activity by cadmium. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 63, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.; Kille, P.; Sweeney, G. Cadmium delays growth hormone expression during rainbow trout development. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezierska, B.; Slominska, I. The effect of copper on common carp [Cyprinus carpio L.] during embryonic and postembryonic development. Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1997, 44, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jezierska, B.; Witeska, M.N. The effect of time and temperature on motility of spermatozoa of common and grass carp. Electron. J. Pol. Agric. Univ. 1999, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Tan, S.X.; Xiao, X.Y.; Qiu, X.S.; Pan, J.Q.; Tang, Z.X. Effects of dietary zinc oxide nanoparticles on growth performance and antioxidative status in broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2014, 160, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomilina, I.I.; Gremyachikh, V.A.; Grebenyuk, L.P.; Klevleeva, T.R. The effect of zinc oxide nano-and microparticles and zinc ions on freshwater organisms of different trophic levels. Inland Water Biol. 2014, 7, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Humánez, M.; Montes-Vides, L.; Almanza-Montero, O. Sol-gel synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticle at three different temperatures and its characterization via XRD, IR and EPR. Dyna 2016, 83, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K. Heavy metals in water, sediments and wetland plants in an aquatic ecosystem of tropical industrial region, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 158, 433–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanhan, P.; Kruatrachue, M.; Pokethitiyook, P.; Chaiyarat, R. Uptake and accumulation of cadmium, lead and zinc by Siam weed [Chromolaena odorata (L.) King & Robinson]. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gautam, N.; Mishra, A.; Gupta, R. Heavy metals and living systems: An overview. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S. Medicinal plants and natural products can play a significant role in mitigation of mercury toxicity. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2018, 11, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Deng, H.; Hwang, H.-M. The current application of nanotechnology in food and agriculture. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudzielwana, R.; Gitari, M.W.; Ndungu, P. Uptake of As (V) from groundwater using Fe-Mn oxides modified kaolin clay: Physicochemical characterization and adsorption data modeling. Water 2019, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.; Trusca, R.; Oprea, O.C.; Surdu, V.A.; Vasile, B.Ș.; Ficai, A.; Ficai, D.; Andronescu, E.; Dițu, L.M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Water Purification. Materials 2021, 14, 4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, M.; Beyki, M.H.; Shemirani, F. One-step and biogenic synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4–Fir sawdust composite: Application for selective preconcentration and determination of gold ions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, J.; Hosseinzadeh Khanmiri, R.; Babazadeh, M.; Ghorbani-Kalhor, E.; Edjlali, L.; Hassanpour, A. Determination of Hg(II) ions in sea food samples after extraction and preconcentration by novel Fe3O4@SiO2@polythiophene magnetic nanocomposite. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Han, N.; Han, J.; Hu, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhou, C.; Guo, R. Mesoporous Hybrid Shells of Carbonized Polyaniline/Mn2O3 as Non-Precious Efficient Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6040–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhao, D.; Chang, Y.; Xing, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y. Synthesis of MnFe2O4@Mn–Co oxide core–shell nanoparticles and their excellent performance for heavy metal removal. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 14261–14267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baby, R.; Hussein, M.Z.; Abdullah, A.H.; Zainal, Z. Nanomaterials for the treatment of heavy metal contaminated water. Polymers 2022, 14, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Xie, J.; Mirshahghassemi, S.; Lead, J. Metal (Cd, Cr, Ni, Pb) removal from environmentally relevant waters using polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated magnetite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3266–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Lai, Q.; Fan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Advances in Portable Heavy Metal Ion Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwesigye, E.; Nnadozie, C.F.; Akamagwuna, F.C.; Noundou, X.S.; Nyakairu, G.W.; Odume, O.N. Microplastics as vectors of chemical contaminants and biological agents in freshwater ecosystems: Current knowledge status and future perspectives. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwetalu, U.J.; Mbajiorgu, C.C.; Ogbuagu, N.J. Remedial ability of maize (Zea-mays) on lead contamination under potted condition and non-potted field soil condition. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greeshma, K.; Kim, H.S.; Ramanan, R. The emerging potential of natural and synthetic algae-based microbiomes for heavy metal removal and recovery from wastewaters. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Fish Specie | Location | Metal Detected | Organ Affected | Effect on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channa striata, Heteropnuestes fossilis | Yamuna Barrage (India) | Cr, Ni, Pb | Kidney, gills, liver, muscle | Ruptured veins, hemorrhages in the liver, necrotic urinary tubules. | [47] |
| Clarias gariepinus | Abuja (Nigeria) | Pb, Cd, Cu, Zn, Cr | Liver, gill, kidney, spleen | Congested central veins in the liver, interstitial hemorrhages in the kidney, congested splenic vein. | [48] |
| Cyprinus carpio | Slovak University of Agriculture in Nitra, University Farm Kolíňany | Cu, As, Pb, Cr, Cd, Hg | Testes | Reduced sperm DNA fragmentation, reduced motility of spermatozoa. | [49] |
| Cyprinus carpio and Capoeta | Kor River (Fars Province) | Hg, Cd, As, Pb | Blood cells, liver, kidney | Hyperemia, cellular degeneration, and vacuolation. | [50] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | Challawa River (Kano, Nigeria) | Zn, Cd, Fe, Pb | Muscles | Higher bioaccumulation in muscles compared to bioaccumulation factor. | [51] |
| Clarias gariepinus | Lake Maryout (Egypt) | Cd, Pb, Hg, As | Gonads | The ovary exhibits lytic characteristics with oocytes at various stages, a decreased quantity of germinal cells, and an augmented interstitial space in the testes. | [52] |
| Auchenoglanis occidentalis | Tiga Dam (Nigeria) | Zn, Cd, Pb, Fe | Gills, liver, kidney | Lesions in the gills, liver, and kidney. | [53] |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, Ctenopharyngodon idellus, Carassius auratus, Cyprinus carpio, Silurus asotus | Yangtze River | Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Pb, Zn | Fish size | Positive and negative relationships were observed between fish size and metal concentration. | [54] |
| Channa striatus, Heteropneustes fossilis | Kali River (India) | Cr, Cd, Pb, Ni | Liver, kidney, gill, muscle, brain | Decreased level of glutathione (GSH), increased oxidative stress. | [55] |
| Etroplus maculates, Cirrhinus reba, and Ompok bimaculatus | Bhadra River (Karnataka) | Cu, Zn, Cd, Ni, Fe, Pb | Liver, kidney, muscle, gills | Degeneration of the hepatocytes in liver, vacuolar degeneration in the tubular epithelium in kidney. | [56] |
| Oreochromis niloticus, Geophagus brasiliensis, Hoplias malabaricus, Astyanax altiparanae, Rhamdia quelen | Sao Francisco do Sul River (Brazil) | Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Se, Pb | Muscle, liver, and gonads | Metals accumulated in the gonads, liver, and muscle, with chromium levels in the muscle reaching fifty times the maximum limit set by Brazilian legislation. | [57] |
| Oligosarcus spp., Chyphocharax voga | Sinos River (Brazil) | Al, As, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Pb | Liver | Detritivores species accumulated more metals than carnivorous species. | [58] |
| Salminus franciscanus | Paraopeba River (Brazil) | Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn, Cr, Hg, Fe | Liver, spleen, and muscle | Hepatocytes exhibited fat accumulation along with pigmented macrophages in the liver. Fibrosis was observed in the spleen, and contaminated fish showed decreased oocyte diameter and increased follicular atresia. | [59] |
| Pseudoplatystoma corruscans | Paraopeba River (Brazil) | Hg, Cd, Zn, Cr, Pb | Liver, muscle, and spleen | The liver and spleen showed higher concentrations of metals compared to the muscle. Additionally, liver fibrosis was observed. | [60] |
| Bryconamericus iheringii | Ilha River (Brazil) | Al, Cd, Mn, Ni, Fe, Pb, Cr, Zn | Blood—micronucleus analysis, gills, and muscle | In rural areas, a higher frequency of micronuclei, nuclear abnormalities, and mucous cells was detected. Conversely, urban areas exhibited a lower condition factor, higher frequencies of lamellar alterations, and higher concentrations of chromium (Cr) and nickel (Ni) in muscle. | [61] |
| Prochilodus magdalenae, Pimelodus blochii | Magdalena River (Colombia) | Cd, Pb, Ni | Gills, liver, and muscle | Pimelodus Blochii showed a higher accumulation of metals, particularly an increased concentration of cadmium (Cd) in the liver. | [62] |
| Aequidens metae, Astyanax bimaculatus | Ocoa River (Colombia) | Hg, Cd | Blood and liver | There was a decrease in the number of erythrocytes, lymphocytes, and neutrophils, as well as a decrease in hemoglobin concentration and hematocrit percentage. | [63] |
| Fish Species | Metal Concentration (mg L−1) | Metal Composition | Stage of Exposure | Exposure Duration | Effect Observed on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Cadmium (Cd) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.970 | Cd † | Juvenile | 12 h | Elevated immunotoxicology. | [72] |
| Danio rerio | 0.040 | CdCl2 | 0–168 hpf | 7 days | Increased rotational movement, Hyperactivity, and decreased size of otolith. | [73] |
| Pimephales promelas | 0.003 | Cd(NO3)2 | Adult | 4 days | Elevated auditory threshold. | [74] |
| Pimephales promelas | 0.060 | CdCl2 | Adult | 21 days | Decreased vitellogenin gene expression and increased estrogen receptor beta. | [75] |
| Danio rerio | 0.112 | CdCl2 | 0–96 hpf | 4 days | Immunotoxicity, behavioural alteration, and oxidative stress. | [76] |
| Effect of Mercury (Hg) | ||||||
| Diplodus sargus | 0.002 | HgCl2 | Juvenile | 7 days | Increased anxiety, decreased number of optic tectum cells, and altered swim behaviour. | [77] |
| Pimephales promelas | 0.720 | MeHg | Adult | 30 days | Decreased levels of dopamine and hyperactivity. | [78] |
| Danio rerio | 10 | MeHg | Adult | 56 days | Mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative phosphorylation. | [79] |
| Danio rerio | 0.720 | MeHg | Adult and embryo | 30 days | Decreased level of dopamine and hyperactivity. | [80] |
| Danio rerio | 0.027 | HgCl2 | 5–72 hpf | ~3 days | Hyperactivity causing mortality. | [81] |
| Effect of Lead (Pb) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.010 | Pb(CH3COO)2 | 0–72 hpf | 3 days | 10 Gene expression changes in 89 genes associated with nervous system development. | [82] |
| Danio rerio | 0.020 | Pb(CH3COO)2 | 0–144 hpf | 6 days | Decreased axon length and decreased locomotion (speed). | [83] |
| Danio rerio | 0.100 | Pb(CH3COO)2 | 2–120 hpf | ~5 days | Altered color preference (adults). | [84] |
| Danio rerio | 0.207 | Pb(CH3COO)2 | 2–24 hpf | ~2 days | Decreased learning (adults). | [85] |
| Danio rerio | 1.730 | Pb(CH3COO)2 | 0–24 hpf | 24 h | Decreased Nrxn2a gene expression. | [86] |
| Effect of Copper (Cu) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.60 | Cu | Juvenile | 96 h | Increases in brain ROS production, lipid peroxidation, and protein oxidation. | [87] |
| Capoeta umbla | 3.0 | CuSO4∙5H2O | 112 ± 5 g | 96 h | Induce astroglial response accompanied by modulations of NF-kB and PARP-1 expression. | [88] |
| Danio rerio | 0.100 | CuSO4∙5H2O | Adult | 10 days | Negatively affect the associative learning capabilities. | [89] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 120 | CuSO4∙5H2O | Adult | 96 h | Loss of balance and exhaustion. | [90] |
| Effect of Arsenic (As) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 15 | Na2HAsO4 | Adult | 96 h | Alteration in behaviour and ectonucleotidase activities. | [91] |
| Danio rerio | 0.050 | As2O3 | Juvenile | 96 h | Antagonistic effects on brain. | [92] |
| Danio rerio | 0.500 | As+ | Larvae, juvenile and adult | 96 h | Alteration in motor function (embryo-adult), effects on associative learning. | [93] |
| Clarias batrachus | 20 | As2O3 | Adult | 96 h | Increased body discoloration, excessive mucous secretion, loosening of the skin, and complete loss of skin (head region and fins). | [94] |
| Effect of Zinc (Zn) | ||||||
| Anguilla anguilla | 0.12 | Zn | Juvenile | 28 days | Cholinergic neurotoxicity did not occurr, only liver GST increased significantly. | [95] |
| Leporinus obtusidens | 4.57 | ZnSO4·5H2O | Adult | 45 days | Significantly increased AChE activity. | [96] |
| Danio rerio | 1750 | ZnCl2 | Adult | 25 days | Significant decrease in acetylcholinesterase activity and abnormal neural signaling. | [97] |
| Fish Species | Metal Concentration (mg L−1) | Metal Composition | Stage of Exposure | Exposure Duration | Effect Observed on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Cadmium (Cd) | ||||||
| Heteropneustes fossilis | 0.050 | CdCl2 | Adult | 24 h | Decreased ovulation. | [110] |
| Pimephales promelas | 0.005 | CdCl2 | 12 months | 21 days | Reduced egg production. | [75] |
| Oryzias melastigma | 0.010 | CdCl2 | 5 months | 30 days | Decreased gonadal development. | [111] |
| Prochilodus magdalenae | 24.90 | CdCl2 | 2 years | 7 days | Reduced fertility rate. | [112] |
| Effect of Mercury (Hg) | ||||||
| Heteropneustes fossilis | 0.050 | HgCl2 | Adult | 24 h | Increased germinal vesicle breakdown. | [110] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 4.990 | HgCl2 | 3 years | 12 h | Decreased motility and fertility of sperms, damaged eggs. | [113] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | 10.00 | HgCl2 | 3 years | 4 h | Reduced motility of sperm. | [114] |
| Danio rerio | 0.015 | HgCl2 | Adult | 5 days | Delayed gonadal development, imbalanced sex hormone. | [115] |
| Danio rerio | 0.030 | HgCl2 | Adult | 30 days | Decreased testosterone level. | [116] |
| Clarias gariepinus | 0.119 | HgCl2 | Adult | 30 days | Disruptive effect on gamete development. | [117] |
| Effect of Lead (Pb) | ||||||
| Heteropneustes fossilis | 0.050 | (Pb(NO3)2 | Adult | 96 h | Increased germinal vesicle breakdown. | [110] |
| Clarias gariepinus | 140.0 | Pb(C2H3O2)2 | Adult | 96 days | Reduced sperm motility. | [118] |
| Oryzias melastigma | 0.050 | PbCl2 | 5 months | 30 days | Decreased gonadal development. | [111] |
| Effect of Copper (Cu) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.040 | CuSO4 | Adult | 30 days | Damaged structure of gonads, altered steroid hormone level. | [119] |
| Pimephales promelas | 0.075 | CuCl2 | 12 months | 21 days | Decreased abundance of post-vitellogenic follicles, increased follicular atresia. | [120] |
| Daphnia magna | 1.041 | CuCl2 | Adult | 21 days | Reduced rate of reproduction. | [121] |
| Poecilia reticulata | 45 | CuO | Adult Larvae | 96 h | Decreased reproduction success. | [122] |
| Poecilia reticulate | 0.026 | CuSO4 5H2O | 2.5–3 months | 56 days | Gonadosomatic index, offspring production decreased. | [123] |
| Effect of Arsenic | ||||||
| Gobiocypris rarus | 40.00 | NaAsO2 | 3 months | 96 days | Accumulation in testis. | [124] |
| Daphnia magna | 0.049 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 48 h | Stable reproduction rate. | [125] |
| Gambusia affinis | 0.075 | NaAsO2 | Juvenile | 30 days | Lower gonadal-somatic indices. | [126] |
| Effect of Zinc (Zn) | ||||||
| Odontesthes bonariensis | 0.021 | ZnSO4 7H2O | Adult | 10 days | Reduced embryo and larval survivability. | [127] |
| Danio rerio | 500 | Zn | Adult | 4 days | Majority of eggs were dead, larger hatching time. | [128] |
| Clarias magur | 300 | Zn(CH3COO)2 | Mature | 60 days | The highest GSI and fecundity. | [129] |
| Oryzias melastigma | 0.010 | ZnSO4·7H2O | Adult | 30 | Irregular oocytes, partly adhesion, empty follicle, and increased follicular atresia, loose follicular lining. | [111] |
| Fish Species | Metal Concentration (mg L−1) | Metal Composition | Stage of Exposure | Exposure Duration | Effect Observed on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Cadmium (Cd) | ||||||
| Leuciscus idus | 0.1000 | CdCl2 | Egg, sperm | 21 dpf | Reduced larval survival, growth, and delayed development. | [102] |
| Oryzias latipes | 0.0019 | CdCl2 2H2O | Embryo, larva | 20 dpf | Morphological abnormalities were observed. | [146] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.06 | CdCl2 | Eggs | 60 dpf | Retardation in the developmental stages of eye pigmentation and spine curvature, lack of tail formation and head. | [147] |
| Danio rerio | 34.8 | CdCl2 | 72 hpf | 72 h | Neuromast damage, coagulated egg, increased mortality rate. | [148] |
| Danio rerio | 0.8018 | CdCl2 | 6 hpf | 24 h | Increased apoptotic event and induced cell death in brain of embryo. | [149] |
| Leuciscus idus | 0.1 | CdCl2 | Embryonic and larval | 21 days | Reduced embryonic survival, increased frequency of malformation, and delayed hatching. | [102] |
| Danio rerio | 0.8909 | CdCl2 | Embryonic and larval | 96 hpf | Increased heartbeat rate of larvae and decreased brain size. | [150] |
| Leuciscus idus L. | 0.1 | CdCl2 | Embryos and newly hatched larvae | 2 h | Reduced egg swelling, slowed the rate of development (especially body movements), and delayed hatching. | [151] |
| Odontesthes bonariensis | 0.00025 | CdCl2 | Advanced-stage embryos and newly hatched larvae | 10 days | Decreased hatching rate and survival of embryo and larvae. | [127] |
| Effect of Mercury (Hg) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.016 | HgCl2 | Adult | 2 hpf | T3 and T4 content in larvae increased. | [152] |
| Danio rerio | 0.016 | HgCl2 | Adult | 168 hpf | Decreased hatching rate, increased mortality, increased malformation rate in larvae. | [116] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.00001 | HgCl2 | Embryo | 96 h | SOD and GPx reduced up to 85%. | [153] |
| Effect of Lead (Pb) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.100 | Pb (C2H3O2)2 | Adult | 30 dpf | Distance moved by juvenile zebra fish decreased, and swimming activity alterations in larvae and juvenile fish. | [154] |
| Danio rerio | 0.005 | Pb (CH3COO)2 | Adult | 144 hpf | Delayed hatching, spinal and tail deformity, pericardial edema, and yolk swelling was observed. | [155] |
| Danio rerio | 99.885 | Pb (C2H3O2)2 | Adult | 72 hpf | Deformed CNS, increased levels of Gamma-aminobutyric acid (primary inhibitory neurotransmitter). | [156] |
| Danio rerio | 1.6 | Pb (NO₃)₂ | Embryo | 120 hpf | Spinal malformation. | [157] |
| Pterophyllum scalar | 20 | PbCl2 | Embryo | 3 days | Tilt, loss of vision or the lack of effect on growth delay. | [158] |
| Effect of Copper (Cu) | ||||||
| Leuciscus idus | 0.100 | CuSO4·5H2O | Egg, sperm | 21 dpf | Reduced larval survival, growth, and delayed development. | [102] |
| Oryzias latipes | 0.0185 | CuCl2 H2O | Embryo, larva | 20 dpf | Percentage of deformed larvae significantly increased. | [146] |
| Poecilia reticulata | 1.50 | CuSO4·5H2O | Embryo | 15 days | Abnormalities in blastodisc to middle-eyed stages of development. | [159] |
| Danio rerio | 0.018 | CuSO4 | 72 hpf | 72 h | Neuromast damage, coagulated egg, increased mortality rate. | [148] |
| Leuciscus idus | 0.10 | CuSO4·5H2O | Embryo and larval | 21 days | Reduced embryonic survival, increased frequency of malformation. | [102] |
| Leuciscus idus L. | 0.10 | CuSO4 | Embryos and newly hatched larvae | 2 h | Reduced egg swelling slowed the rate of development (especially body movements) and delayed hatching. | [151] |
| Odontesthes bonariensis | 0.00025 | CuSO4 | Advanced-stage embryos and newly hatched larvae | 10 days | Decreased hatching rate and survival of embryo and larvae. | [127] |
| Carassius auratus | 1 | Cu2− | Embryo | 24 h post-hatching | Scoliosis and tail curvatures. | [160] |
| Effect of Arsenic (As) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 360.32 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 120 h | Tail bud deformation in embryo. | [161] |
| Danio rerio | 0.5 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 120 hpf | No effect on mortality and developmental deformations. | [162] |
| Labeo rohita | 198.18 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 120 hpf | Reduced survival rate with abnormal development. | [163] |
| Danio rerio | 0.5 | NaAsO2 | Embryo | 14 dpf | Thinning of the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) layer in embryos. | [164] |
| Effect of Zinc (Zn) | ||||||
| Odontesthes bonariensis | 0.021 | ZnSO4 7H2O | Hatchling | 10 days | Cumulative embryo survival was significantly reduced. | [127] |
| Pagrus major | 2.5 | ZnCl2 | 2 years | 10 days | Low hatching rate, high mortality, abnormal pigmentation, hooked tail, spinal deformity, pericardial edema, and visceral hemorrhage. | [165] |
| Melanotaenia fluviatilis | 33.3 | Zn | Embryo | 2 h | Spinal deformities. | [166] |
| Fish Species | Metal Concentration (mg L−1) | Metal Composition | Stage of Exposure | Exposure Duration | Effect Observed on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Cadmium (Cd) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.075 | CdCl2 | 6 months | 4 weeks | Increase in the number of blast cells, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and apoptotic cells of brain. | [184] |
| Oncorhynchus kisutch | 0.347 | Cd | Adult | 48 h | Impaired skin extract avoidance behaviours. | [185] |
| Channa punctatus | 5.00 | CdCl2 | Adult | 45 days | Loss of sensory cells, impaired olfactory functions. | [186] |
| Clarias batrachus | 0.1198 | CdCl2 | Adult | 30 days | Distortion of the gill, liver. | [187] |
| Effect of Mercury (Hg) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.01 | HgCl2 | Adult | 96 h | Oxidative stress and genotoxicity in gills, blood, and liver. | [188] |
| Clarias batrachus | 0.0299 | Hg | Adult | 30 days | Distortion of the gill, liver. | [2] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 0.03 | HgCl2 | Fingerlings | 21 days | Lesions in the epithelial cells, focal proliferation, edema, mucous secretion, vacuolization, or almost empty, congestion, and haemorrhage in gills | [189] |
| Danio rerio | 0.0385 | HgCl2 | Adult | 96 h | Induced severe morphological and ultrastructural changes in the gill apparatus. | [190] |
| Danio rerio | 13.50 | MeHg | Adult | 25 days | Brain mitochondrial impairments. | [80] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 0.3 | HgCl2 | Fingerlings | 96 h | Edema, mucous secretion, vacuolization, lesions in the epithelial cells, focal proliferation, or almost empty, congestion, and haemorrhage. | [189] |
| Effect of Lead (Pb) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 4.295 | Pb(NO3)2 | Fingerling | 28 days | Distortion of the lamella in gills, large polyhedral cells within the network of minute canaliculus in liver. | [191] |
| Labeo rohita | 11.40 | Pb(NO3)2 | Fingerlings | 60 days | Upliftment of gill rakers, hyperplasia. | [192] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 4.50 | Pb(NO3)2 | Adult | 96 h | Loose epithelial lining of cartilaginous core, necrosis, and deformed secondary gill lamellae | [193] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 6.20 | Pb(NO3)2 | Adult | 15 days | Fusion of gill lamellae, vessel dilatation, hyperaemia, and hyperplasia of gill epithelial cells. | [194] |
| Effect of Copper (Cu) | ||||||
| Oreochromis niloticus | 0.40 | Cu2+ | Adult | 21 days | Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase activity in gills. | [195] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 55.00 | CuO NP | Adult | 4 days | The observed effects included curvature, edema, hyperplasia, dilated marginal channel, lamellar fusion, dilated and clubbed tips, epithelium shortening, aneurysm, necrosis, increased mucous secretion, and haemorrhage at the secondary lamellae. | [196] |
| Oncorhynchus mykiss | 0.1.00 | CuSO4 | Juvenile | 10 days | Hyperplasia, aneurysms, and necrosis in secondary lamellae of the gills. | [197] |
| Catla catla | 0.300 | CuSO4 | Fingerling | 3 weeks | Cytolysis, necrosis, pyknosis, and fibrosis in liver. | [198] |
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.075 | CuSO4 | 6 months | 4 weeks | There was an increase in the number of blast cells, proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), and apoptotic cells. | [184] |
| Effect of Arsenic (As) | ||||||
| Oreochromis mossambicus | 49.90 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 192 h | Gills were characterized by epithelial hyperplasia and necrosis, liver tissue showed focal lymphocytic and macrophage infiltration. | [199] |
| Ctenopharyngodon idella | 89.00 | As2O3 | Adult | 28 days | Decrease in glycogen levels in gill, liver, kidney, and brain. | [200] |
| Channa punctatus | 99.80 | NaAsO2 | Adult | 20 h | Fragmentation of liver chromosomal DNA. | [201] |
| Effect of Zinc (Zn) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 16 | ZnO | 120 d | 96 h | Hyperplasia of epithelial cells, lamellar fusion, aneurism, lamellar disorganization and curling in gills. | [202] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 6 | ZnCl2 | Adult | 28 days | Hepatocyte degeneration, nuclear pycnosis, cellular swelling, and congestion of blood vessels. | [203] |
| Oreochromis mossambicus | 0.02 | ZnO NPs, ZnO | Adult | 96 h | lesions in the gills, disorganization of gill lamella, cartilaginous core disruption, lifting of epithelium, loss of secondary gill lamellae, blood congestion, fusion of secondary gills lamellae, shortening of secondary gills lamellae, atrophy, and curling. | [204] |
| Sparus aurata | 1 | ZnO-NPs | Juvenile | 96 h | Hyperplasia of epithelial cells and fusion of secondary lamellae in gills. Lipid vacuolation in various degrees, necrosis of hepatic and pancreatic tissues. Degeneration, atrophy, and necrosis of muscle fibers with edema in muscles. | [205] |
| Fish Species | Metal Concentration (mg L−1) | Metal Composition | Stage of Exposure | Exposure Duration | Effect Observed on Fish | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect of Cadmium (Cd) | ||||||
| Cyprinus carpio | 0.5932 | CdCl2·5H2O | Juvenile | 30 days | Reduced levels of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, GSH-Px). | [211] |
| Labeo rohita | 0.65 | CdCl2 | Mature | 28 dpe | Reduced lysozyme activity, alternative complement pathway activity, phagocytic activity, phagocytic activity. | [212] |
| Danio rerio | 1.000 | Cd | Adult | 96 h | Increase in the protein levels of (TNF-α), increase in the mRNA levels of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and nuclear transcription factor κB (NF-κB), increase in ROS, NO, and MDA. | [213] |
| Oreochromis niloticus | 1.22 | Cd (NO3)2·4H2O | Adult | 96 h | Significant reduction in antioxidant levels, significant decrease in hematological parameters, increase in neutrophils. | [214] |
| Effect of Mercury (Hg) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.016 | HgCl2 | Adult, embryos | 168 hpf | Transcription levels of several representative genes involved in innate immunity were upregulated. | [215] |
| Pylodictis olivaris | 0.010 | HgCl2 | Juvenile | 42 h | mRNA levels of immune-related genes were upregulated. | [152] |
| Pseudosciaena crocea | 0.040 | MeHg | Juvenile | 30 days | Genes related to immunity (TCTP, GST3, Hsp70, Hsp27 mRNA) were all upregulated. | [209] |
| Sparus aurata | 0.010 | CH3HgCl | Mature | 30 days | Leukocyte, peroxidase activities significantly increased. | [216] |
| Effect of Lead (Pb) | ||||||
| Sebastes schlegelii | 240 | Pb (NO3)2 | Juvenile | 28 days | Lysozyme activity significantly increased | [217] |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 0.00384 | Pb (NO3)2 | Adult | 96 h | Immune factors genes were upregulated, increasing the goblet cells’ number, causing the intestinal leukocyte infiltration. | [218] |
| Carassius carassius | 1 | Pb.(CH3COO2) 3H2O | Adult | 60 days | Significant decrease in lysozyme and the content of immunoglobulin M. | [219] |
| Pelteobagrus fulvidraco | 0.050 | Pb.(CH3COO2) 3H2O | Adult | 60 days | Significant decrease inlysozyme (LYZ), complement 3 (C3), and immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels. | [220] |
| Effect of copper (Cu) | ||||||
| Oreochromis niloticus | 0.040 | Cu | Adult | 60 days | Increased levels of lysozymes (LYZ), respiratory burst activity (RBA), and myeloperoxidase (MPO). | [221] |
| Takifugu fasciatus | 0.010 | Cu NPs | Juvenile | 30 days | Physiological indicators of immune response increased. | [222] |
| Pseudobagrus fulvidraco | 0.0011 | CuSO4 | Adult | 42 days | Lysozyme and phagocytosis in the blood were significantly decreased. | [223] |
| Effect of Arsenic (As) | ||||||
| Labeo rohita | 15 | NaAsO2 | Fingerlings | 12 days | Immune-suppressive effect leading to down regulation of both Th1 and Th2 cytokines, regulation of HSP genes. | [224] |
| Sebastes schlegelii | 0.040 | NaAsO2 | Juvenile | 20 days | Increased levels of immunoglobulin M (Ig M) and lysozyme. | [224] |
| Sparus aurata | 0.988 | As2O3 | Adult | 30 days | Leucocyte peroxidase, respiratory burst, and phagocytic activities were significantly increased. | [225] |
| Danio rerio | 0.08 | As2O3 | Adult | 30 days | Hyperactivation of the immune system. | [226] |
| Danio rerio | 0.060 | Na2HAsO4·7H2O | Larvae (7 dpf) | 24 h | Immune suppression due to increased neutrophils, decreased lymphocytes. | [227] |
| Effect of Zinc (Zn) | ||||||
| Danio rerio | 0.060 | ZnSO4 | Larvae (7 dpf) | 24 h | Significant increase in number of neutrophils. | [227] |
| Danio rerio | 0.020 | Zn | 3 months | 42 days | Significant increase in CAT activity, upregulation of stress-related and immune-related genes. | [228] |
| Acanthopagrus schlegeli | 0.040 | ZnO | Adult | 28 days | Increased phagocytosis and lysozyme, increased immune responses. | [229] |
| Oreochromis mossambicus | 5 | ZnSO4·7(H2O)x | Adult | 14 days | Decreased phagocytic activity, increase in lysozyme and myeloperoxidase activities. | [230] |
| Metal Ion | Permissible Limits by WHO (ppm) |
|---|---|
| Hg | 0.001 |
| Cd | 0.005 |
| Cu | 1.5 |
| As | 0.05 |
| Pb | 0.05 |
| Cr | 0.05 |
| Zn | 5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naz, S.; Chatha, A.M.M.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, Q.; Khan, M.Z.; Shah, M.K.; Abbas, G.; Kiran, A.; Mushtaq, R.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Metallic Trace Elements Toxicity in Fishes and Potential Remedial Measures. Water 2023, 15, 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163017
Naz S, Chatha AMM, Téllez-Isaías G, Ullah S, Ullah Q, Khan MZ, Shah MK, Abbas G, Kiran A, Mushtaq R, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Metallic Trace Elements Toxicity in Fishes and Potential Remedial Measures. Water. 2023; 15(16):3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163017
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaz, Saima, Ahmad Manan Mustafa Chatha, Guillermo Téllez-Isaías, Shakeeb Ullah, Qudrat Ullah, Muhammad Zahoor Khan, Muhammad Kamal Shah, Ghulam Abbas, Azka Kiran, Rubina Mushtaq, and et al. 2023. "A Comprehensive Review on Metallic Trace Elements Toxicity in Fishes and Potential Remedial Measures" Water 15, no. 16: 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163017
APA StyleNaz, S., Chatha, A. M. M., Téllez-Isaías, G., Ullah, S., Ullah, Q., Khan, M. Z., Shah, M. K., Abbas, G., Kiran, A., Mushtaq, R., Ahmad, B., & Kari, Z. A. (2023). A Comprehensive Review on Metallic Trace Elements Toxicity in Fishes and Potential Remedial Measures. Water, 15(16), 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163017










