Monitoring of Contamination of the Warta River in Poznan by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. SPE Procedure
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szymonik, A.; Lach, J. Obecność Farmaceutyków w Wodach Powierzchniowych i Przeznaczonych Do Spożycia. In Proceedings of the ECOpole’13 Conference, Jarnołtówek, Poland, 23–26 October 2013; pp. 735–743. [Google Scholar]
- Nannou, C.I.; Kosma, C.I.; Albanis, T.A. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in Surface Waters: Analytical Method Development and Environmental Risk Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2015, 95, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makała, A.; Dymaczewski, Z.; Jeż-Walkowiak, J.; Strykowska, A.; Zembrzuska, J. Impact of Artificial Infiltration on the Removal of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs during Treatment of Surface Water. Energies 2021, 14, 8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljanić, D.; de Gennaro, B.; Daković, A.; Galzerano, B.; Germinario, C.; Izzo, F.; Rottinghaus, G.E.; Langella, A. Removal of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs from Water by Zeolite-Rich Composites: The Interference of Inorganic Anions on the Ibuprofen and Naproxen Adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, G.-G.; Zhao, J.-L.; Zhou, L.-J.; Liu, S. Fate and Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment (Surface Water and Sediment). In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 453–557. [Google Scholar]
- Płuciennik-Koropczuk, E. Non-Steroid Anti-Infflamatory Drugs in Municipal Wastewater and Surface Waters/Niesteroidowe Leki Przeciwzaplane W Ściekach Mieskich I Wodach Powierzchniowych. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2014, 14, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashton, D.; Hilton, M.; Thomas, K.V. Investigating the Environmental Transport of Human Pharmaceuticals to Streams in the United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 333, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Farré, M.; Pérez, S.; Kantiani, L.; Barceló, D. Fate and Toxicity of Emerging Pollutants, Their Metabolites and Transformation Products in the Aquatic Environment. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öllers, S.; Singer, H.P.; Fässler, P.; Müller, S.R. Simultaneous Quantification of Neutral and Acidic Pharmaceuticals and Pesticides at the Low-Ng/l Level in Surface and Waste Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 911, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togola, A.; Budzinski, H. Multi-Residue Analysis of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Aqueous Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1177, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, S.; Berger, U.; Jensen, E.; Kallenborn, R.; Thoresen, H.; Hühnerfuss, H. Determination of Selected Pharmaceuticals and Caffeine in Sewage and Seawater from Tromsø/Norway with Emphasis on Ibuprofen and Its Metabolites. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiffre, A.; Degiorgi, F.; Buleté, A.; Spinner, L.; Badot, P.-M. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals in WWTP Effluents and Their Impact in a Karstic Rural Catchment of Eastern France. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 25427–25441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, V.F.; Duarte, I.A.; Duarte, B.; Freitas, A.; Pouca, A.S.V.; Barbosa, J.; Gillanders, B.M.; Reis-Santos, P. Environmental Risk Assessment and Bioaccumulation of Pharmaceuticals in a Large Urbanized Estuary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zając, A. Skuteczność Usuwania Wybranych Niesteroidowych Leków Przeciwzapalnych Ze Ścieków Metodą Osadu Czynnego; Poznan University of Technology: Poznań, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Guzik, U.; Hupert-Kocurek, K.; Mazur, A.; Wojcieszyńska, D. Biotransformacja wybranych niesteroidowych leków przeciwzapalnych w środowisku. In Bromatologia i Chemia Toksykologiczna; Polskie Towarzystwo Farmaceutyczne: Warszawa, Poland, 2013; p. 105. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical Pollution of the World’s Rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, L.; Petitjean, Q.; Côte, J.; Laffaille, P.; Jean, S. Effects of Pollution on Fish Behavior, Personality, and Cognition: Some Research Perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, S.; Cardoso, V.V.; Duarte, L.; Carneiro, R.N.; Almeida, C.M.M. Characterization of Five Portuguese Wastewater Treatment Plants: Removal Efficiency of Pharmaceutical Active Compounds through Conventional Treatment Processes and Environmental Risk. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debska, J.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Namiesnik, J. Determination of Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs in Water Samples Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode-Array Detector and Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2005, 28, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M. Selective Degradation of Ibuprofen and Clofibric Acid in Two Model River Biofilm Systems. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alygizakis, N.A.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Borova, V.L.; Pavlidou, A.; Hatzianestis, I.; Thomaidis, N.S. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of 158 Pharmaceuticals, Drugs of Abuse and Related Metabolites in Offshore Seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ek Henning, H.; Putna Nimane, I.; Kalinowski, R.; Perkola, N.; Bogusz, A.; Kublina, A.; Haiba, E.; Barda, I.; Karkovska, I.; Schütz, J.; et al. Pharmaceuticals in the Baltic Sea Region—Emissions, Consumption and Environmental Risks; Report No. 2020:28; Länsstyrelsen Östergötland: Linköping, Sweden, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ternes, T.A. Occurrence of Drugs in German Sewage Treatment Plants and Rivers. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3245–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsik, P.; Rezek, J.; Židková, M.; Kramulová, B.; Tauchen, J.; Vaněk, T. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in the Watercourses of Elbe Basin in Czech Republic. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D. Wastewater Treatment Plants as a Pathway for Aquatic Contamination by Pharmaceuticals in the Ebro River Basin (Northeast Spain). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, I.; Kowalski, B. A Rapid UHPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Drugs from Different Therapeutic Groups in Surface Water and Wastewater. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 89, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helenkár, A.; Sebők, Á.; Záray, G.; Molnár-Perl, I.; Vasanits-Zsigrai, A. The Role of the Acquisition Methods in the Analysis of the Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in Danube River by Gas Chromatography—Mass Spectrometry. Talanta 2010, 82, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosjek, T.; Heath, E.; Krbavčič, A. Determination of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug (NSAIDs) Residues in Water Samples. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alygizakis, N.; Galani, A.; Rousis, N.I.; Aalizadeh, R.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Thomaidis, N.S. Change in the Chemical Content of Untreated Wastewater of Athens, Greece under COVID-19 Pandemic. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegel, S.; Aulinger, A.; Brockmeyer, R.; Harms, H.; Löffler, J.; Reincke, H.; Schmidt, R.; Stachel, B.; von Tümpling, W.; Wanke, A. Pharmaceuticals in the River Elbe and Its Tributaries. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcárcel, Y.; Alonso, S.G.; Rodríguez-Gil, J.L.; Maroto, R.R.; Gil, A.; Catalá, M. Analysis of the Presence of Cardiovascular and Analgesic/Anti-Inflammatory/Antipyretic Pharmaceuticals in River- and Drinking-Water of the Madrid Region in Spain. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamtam, F.; Mercier, F.; Le Bot, B.; Eurin, J.; Tuc Dinh, Q.; Clément, M.; Chevreuil, M. Occurrence and Fate of Antibiotics in the Seine River in Various Hydrological Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 393, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, T.V.; Barreiro, J.C.; Rocha, M.J.; Rocha, E.; Cass, Q.B.; Tiritan, M.E. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Pharmaceuticals in the Douro River Estuary (Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5513–5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokoszka, K.; Wilk, J.; Felis, E.; Bajkacz, S. Application of UHPLC-MS/MS Method to Study Occurrence and Fate of Sulfonamide Antibiotics and Their Transformation Products in Surface Water in Highly Urbanized Areas. Chemosphere 2021, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciślak, M.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Zembrzuska, J.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D. Estrogen Pollution of the European Aquatic Environment: A Critical Review. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Fiorentino, A.; Grassi, M.; Attanasio, D.; Guida, M. Advanced Treatment of Urban Wastewater by Sand Filtration and Graphene Adsorption for Wastewater Reuse: Effect on a Mixture of Pharmaceuticals and Toxicity. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.A.; Klaper, R.D. Psychoactive Pharmaceuticals Induce Fish Gene Expression Profiles Associated with Human Idiopathic Autism. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Tiwari, M.K.; Ghangrekar, M.M. A Review on Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity and Microbial Degradation of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IQVIA. The Global Use of Medicines 2023: Outlook to 2027. Available online: https://www.iqvia.com/insights/the-iqvia-institute/reports/the-global-use-of-medicines-2022 (accessed on 28 May 2023).
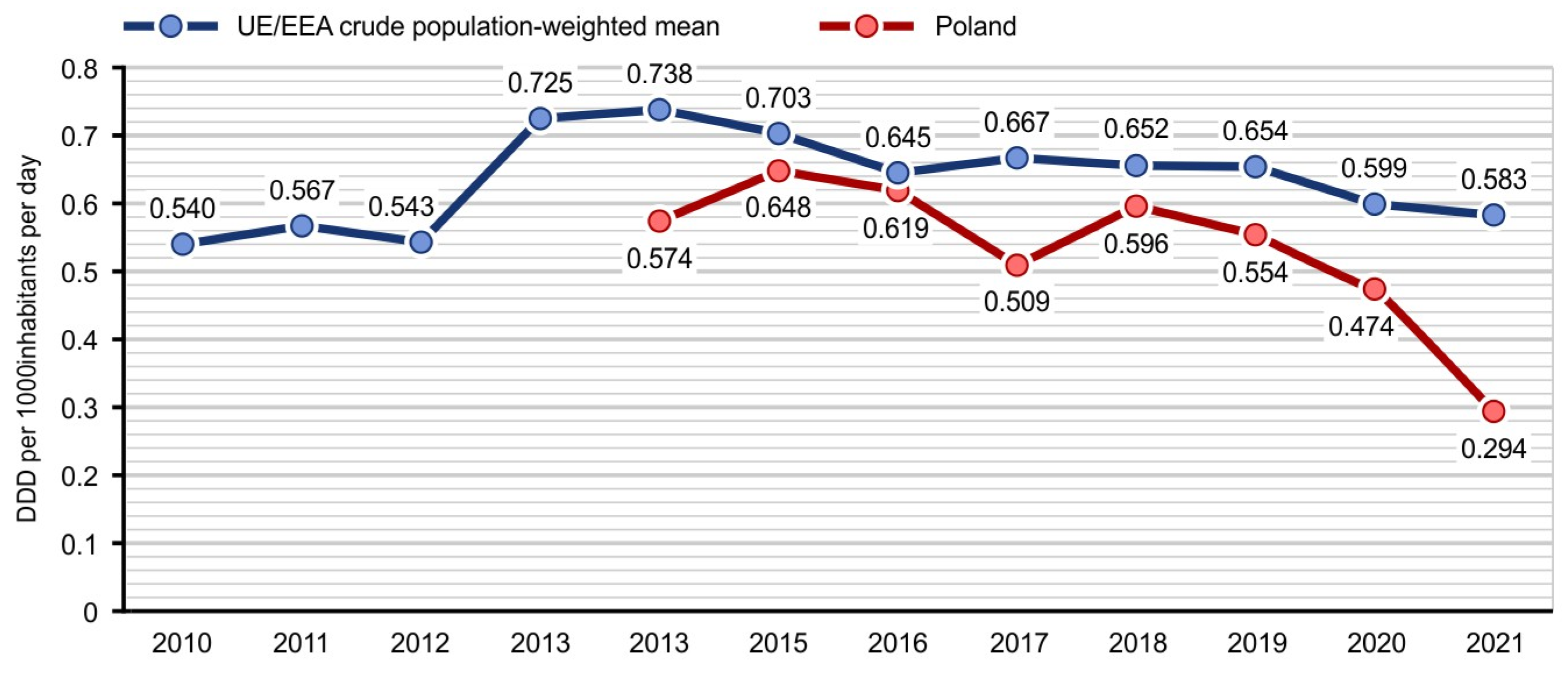
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA (ESAC-Net)- Annual Epidemiological Report 2021; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022.
- PN-EN ISO 5667-6:2016-12; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 6: Guidelines for Sampling Rivers and Streams. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2016.
- Oliveira, C.; Lima, D.L.D.; Silva, C.P.; Calisto, V.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Photodegradation of Sulfamethoxazole in Environmental Samples: The Role of PH, Organic Matter and Salinity. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhlmann, N.; Olsson, O.; Kümmerer, K. Transformation Products of Sulfonamides in Aquatic Systems: Lessons Learned from Available Environmental Fate and Behaviour Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-García, E.; Mastroianni, N.; Ponsà-Borau, N.; Barceló, D.; Postigo, C.; López de Alda, M. Drugs of Abuse and Their Metabolites in River Sediments: Analysis, Occurrence in Four Spanish River Basins and Environmental Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dong, D.; Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z. Distribution and Photodegradation of Typical Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in an Ice-Water System: Simulation of Surface Waters with an Ice Cover. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Luo, R.; Shang, J.-G.; Liao, Q.-J.-H. Migration of Two Antibiotics during Resuspension under Simulated Wind–Wave Disturbances in a Water–Sediment System. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

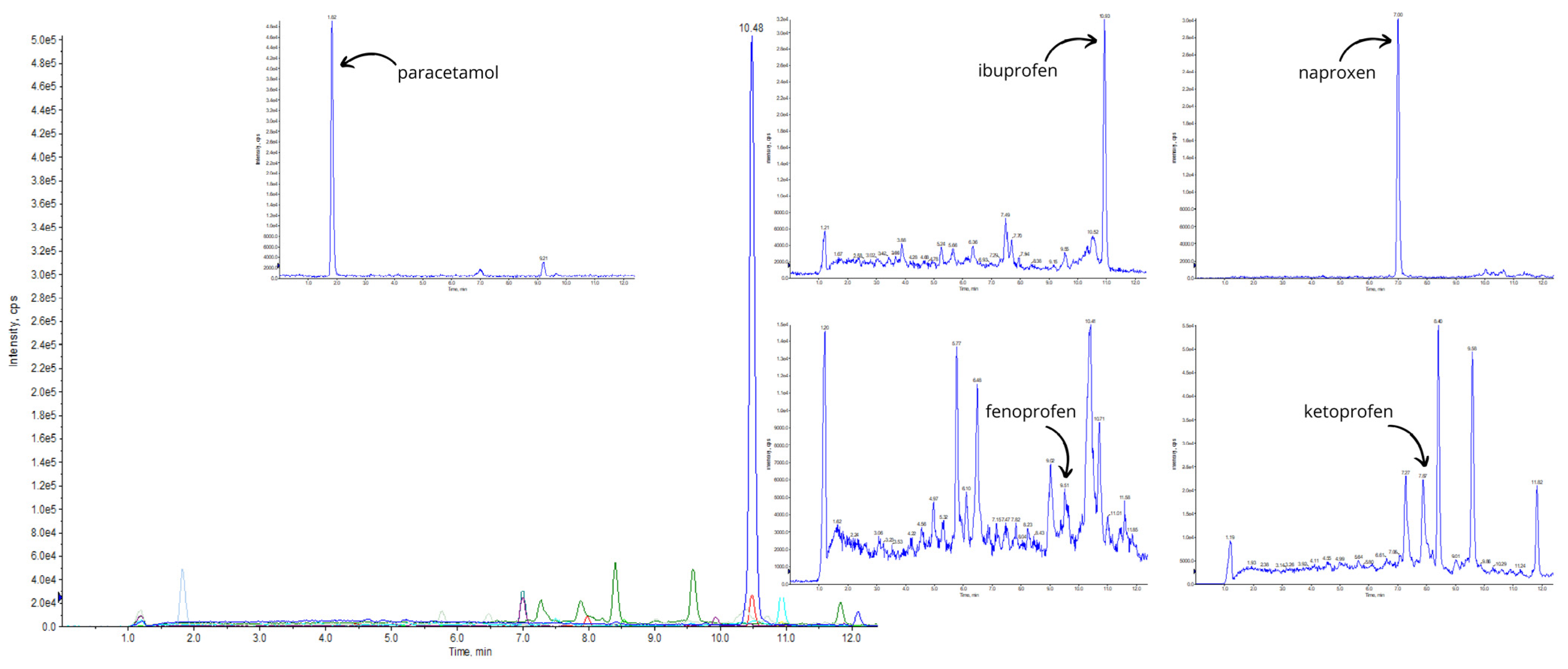
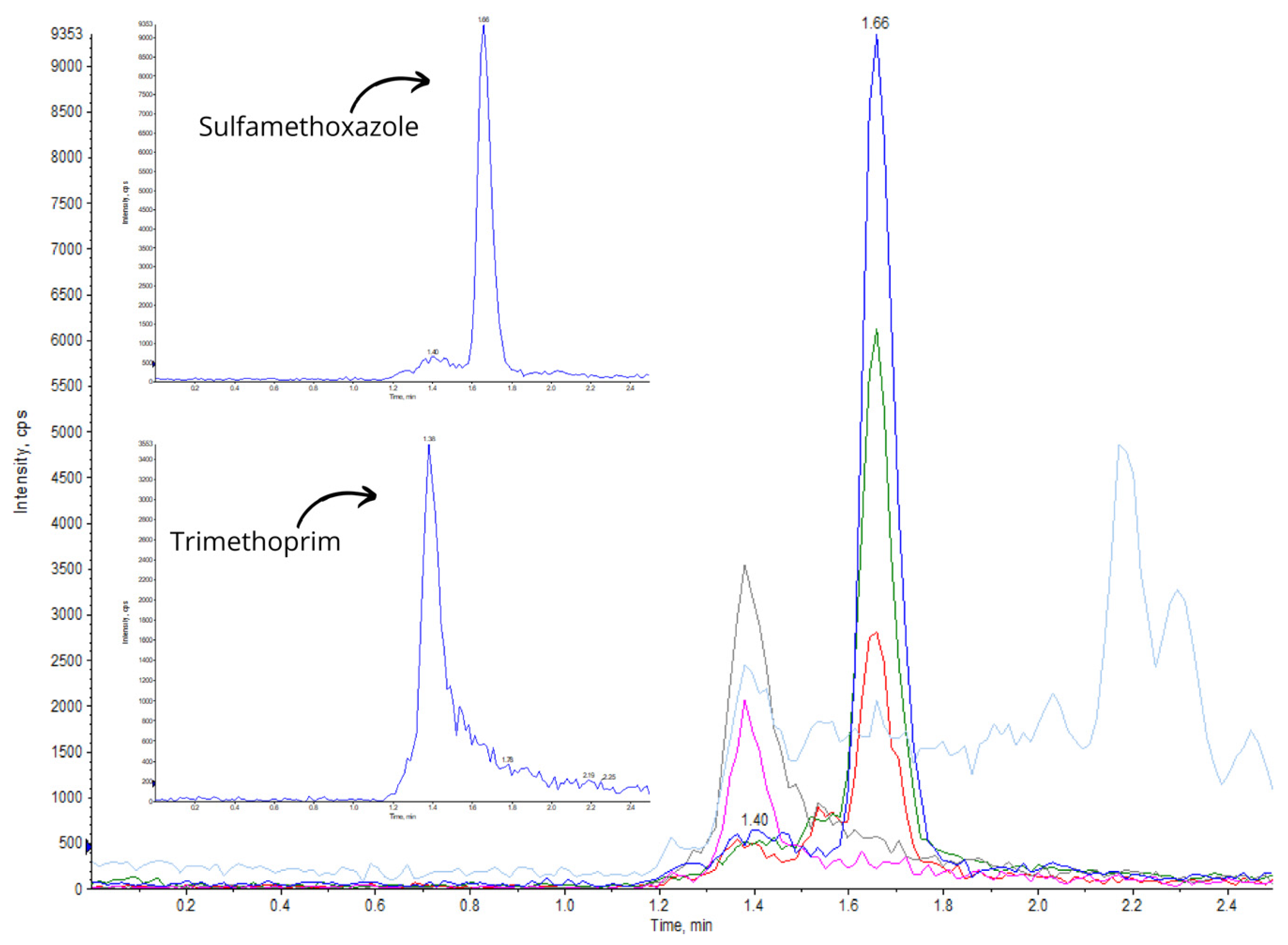



| Type | Name | Location | Concentration [ng/L] | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Ibuprofen | Poland (surface waters) | 50–100 | [15] |
| Poland (Gdańsk-sea water) | 170 | [19] | ||
| Poland (lake in Somonino) | 55 | [19] | ||
| Poland (lake in Gdańsk) | 104 | [19] | ||
| France (surface waters) | <4.5 | [15] | ||
| Italy (Po River) | 17.4 | |||
| Germany (Elbe River) | 70–87 | [20] | ||
| Diclofenac | Greece (Saronikos Gulf and the Elefsis Bay) | >1.4–16.3 | [21] | |
| Estonia (river Pärnu) | 11–53 | [22] | ||
| Poland (river Rokitnica) | 12–2200 | [22] | ||
| Germany (Tollense river) | 0–350 | [22] | ||
| Ketoprofen | Germany (surface waters) | 120 | [23] | |
| Czech Republic (Leba River) | 929.8 | [24] | ||
| Spain (Ebro River) | 70 | [25] | ||
| Poland (river Rokitnica) | 2.4–280 | [22] | ||
| Estonia (river Pärnu) | >2.1 | [22] | ||
| Germany (Tollenseriv-er) | 0–2.13 | [22] | ||
| Naproxen | Poland (Warta River) | 100 | [26] | |
| Poland (river Rokitnica) | 5.7–56 | [22] | ||
| Hungary (Danube River) | 5.7–62 | [27] | ||
| Slovenia (surface waters) | 17–80 | [28] | ||
| Greece (Aisonas River) | 72 | [29] | ||
| Greece (Saronikos Gulf and the Elefsis Bay) | >0.01–0.8 | [21] | ||
| Germany (Tollense river) | 0–35 | [22] | ||
| Estonia (river Pärnu) | 1.0–12 | [22] | ||
| Fenoprofen | Germany (Leba River) | 2–54 | [30] | |
| Poland (river in Straszyn) | 84 | [19] | ||
| Poland (river in Somonino) | 55 | [19] | ||
| Poland (lake in Somonino) | 20 | [19] | ||
| Poland (lake in Gdańsk) | 24 | [19] | ||
| Analgesic and antipyretic | Paracetamol | Spain (Madrid’s surface waters) | 188–2813 | [31] |
| Greece (Saronikos Gulf and the Elefsis Bay) | >40.5 | [21] | ||
| Antibiotics | Sulfamethoxazole | France (Seine River) | 75 | [32] |
| Portugal (Douro River) | 53.3 | [33] | ||
| Portugal (The Tejo estuary) | 1.11–2.01 | [13] | ||
| Poland (Paprocany resort, the Gostynia Stream) | 75.88 | [34] | ||
| Poland (Mikołów-rural location) | 34.18 | [34] | ||
| Greece (Saronikos Gulf and the Elefsis Bay) | >0.1–6.3 | [21] | ||
| Trimethoprim | France (Seine River) | 20 | [32] | |
| Portugal (Douro River) | 15.7 | [33] | ||
| Portugal (The Tejo estuary) | 4.57–5.18 | [13] | ||
| Estonia (river Pärnu) | <1.2 | [22] | ||
| Poland (river Rokitnica) | 0–54 | [22] | ||
| Germany (Tollense river) | 0–5.7 | [22] |
| Name | Operating Parameters for NSAIDs | Operating Parameters for Antibiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Mode of ionization | ESI | ESI |
| Mode of operation | Negative | Positive |
| Temperature [°C] | 400 | 600 |
| Curtain gas [psi] | 20 | 20 |
| Nebulizer [psi] | 50 | 40 |
| Auxiliary gas [psi] | 50 | 45 |
| Ion spray voltage [V] | −4500 | 5500 |
| Compound | Precursor Ion [M−H]− m/z [M+H]+ * | Declustering Potential (V) | MRM 1 Transition-Quantitation Ion (Precursor Ion m/z → Product Ion m/z) | Collision Energy (V) | MRM 2 Transitions-Confirmation Ion (Precursor Ion m/z → Product Ion m/z) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naproxen | 229 | −45 | 229 → 161 | −12 | 205 → 159 | −8 |
| Ketoprofen | 253 | −50 | 253 → 209 | −12 | 253 → 197 | −10 |
| Ibuprofen | 205 | −50 | 205 → 161 | −12 | 205 → 159 | −8 |
| Paracetamol | 150 | −20 | 150 → 107 | −24 | 150 → 60 | −14 |
| Fenoprofen | 241 | −40 | 241 → 197 | −12 | 241 → 93 | −52 |
| Trimethoprim * | 291 | 11 | 291 → 230 | 33 | 291 → 123 | 35 |
| Sulfamethoxazole * | 254 | 76 | 254 → 156 | 21 | 254 → 108 | 31 |
| Compound | Linearity [ng/L] | Correlation Coefficient | LOD [ng/L] | LOQ [ng/L] | Recovery [% ± RSD] | Concentration Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naproxen | 6.0–750 | 0.9994 | 1.96 | 5.88 | 100.5 ± 6.97 | 2000 |
| Ketoprofen | 2.5–750 | 0.9999 | 0.67 | 2.02 | 100.0 ± 5.00 | 2000 |
| Ibuprofen | 9.5–750 | 0.9996 | 3.02 | 9.04 | 100.3 ± 5.98 | 2000 |
| Paracetamol | 0.21–750 | 0.9996 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 81.2 ± 3.69 | 2000 |
| Fenoprofen | 6.5–750 | 0.9999 | 2.14 | 6.41 | 100.5 ± 7.96 | 2000 |
| Trimethoprim | 100–1.0 × 105 | 0.9994 | 5 | 100 | 82.4 ± 4.85 | 100 |
| Sulfamethoxazole | 250–1.0 × 106 | 0.9942 | 20 | 250 | 71.0 ± 4.93 | 100 |
| Date | Water Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|
| 2012 March | |
| 2012 April | |
| 2012 May | |
| 2012 June | |
| 2012 July | |
| 2012 August | - |
| 2012 September | |
| 2012 October | |
| 2012 November | |
| 2012 December | |
| 2013 November | 8.9 |
| 2013 December | 4.9 |
| 2014 January | 4.8 |
| 2014 February | 4.8 |
| 2014 March | 14.6 |
| 2014 April | 16.0 |
| 2019 May | 13.1 |
| 2019 June | 25.9 |
| 2019 August | 24.4 |
| 2019 September | 14.6 |
| 2019 October | 10.9 |
| 2019 November | 5.3 |
| 2020 January | 2.1 |
| 2020 March | 5.1 |
| 2020 July | 21.5 |
| 2020 August | 20.2 |
| 2020 October | 11.8 |
| 2021 January | - |
| 2021 May | 15.5 |
| 2021 June | 26.1 |
| Drug | Ketoprofen | Paracetamol | Naproxen | Ibuprofen | Fenoprofen | Sulfamethoxazole | Trimethoprim | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | [ng/L] | |||||||
| 2012 March | 2.00 | 4.60 | 12.10 | 23.20 | 7.10 | - | - | |
| 2012 April | 1.80 | 13.50 | 65.00 | 28.50 | 6.10 | - | - | |
| 2012 May | 12.30 | 67.60 | 8.20 | 25.00 | 5.30 | - | - | |
| 2012 June | 41.40 | 51.60 | 12.60 | 99.30 | 19.10 | - | - | |
| 2012 July | 12.30 | 2.90 | 14.70 | 16.80 | 18.10 | - | - | |
| 2012 August | 0.40 | 18.60 | 9.60 | 13.10 | 9.00 | - | - | |
| 2012 September | 5.20 | 9.50 | 54.70 | 20.20 | 3.40 | - | - | |
| 2012 October | 2.50 | 3.30 | 11.10 | 22.10 | 1.10 | - | - | |
| 2012 November | 2.90 | 3.90 | 13.00 | 25.90 | 1.30 | - | - | |
| 2012 December | 20.70 | 107.20 | 13.70 | 34.40 | 9.10 | - | - | |
| Median 2012 | 4.05 | 11.50 | 12.80 | 24.10 | 6.60 | - | - | |
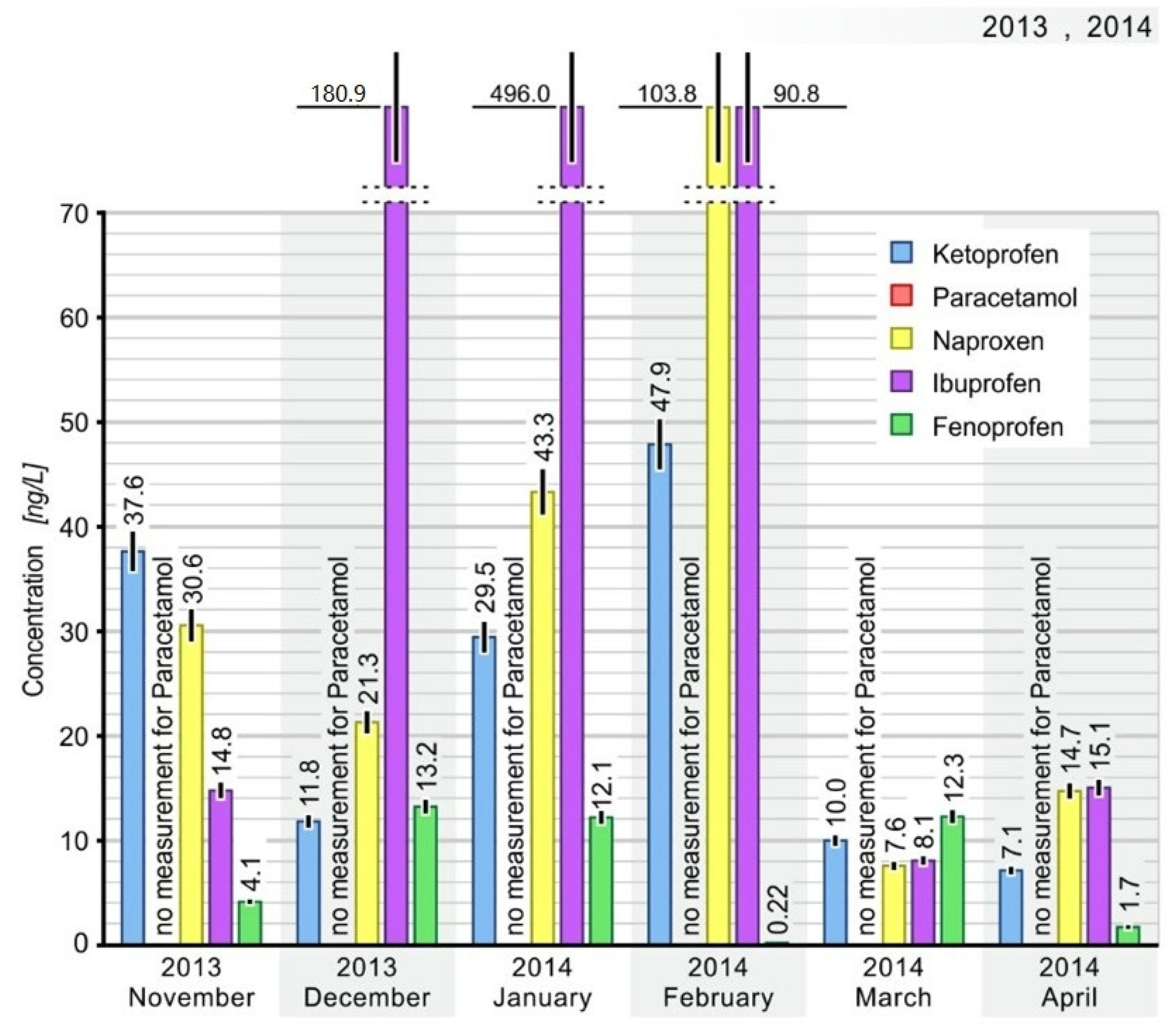
| 2013 November | 37.64 | - | 30.57 | 14.79 | 4.15 | - | - | |
| 2013 December | 11.83 | - | 21.30 | 180.92 | 13.24 | - | - | |
| 2014 January | 29.45 | - | 43.32 | 495.95 | 12.06 | - | - | |
| 2014 February | 47.86 | - | 103.78 | 90.79 | 0.22 | - | - | |
| 2014 March | 10.00 | - | 7.58 | 8.08 | 12.29 | - | - | |
| 2014 April | 7.14 | - | 14.73 | 15.05 | 1.73 | - | - | |
| Median 2013–2014 | 20.64 | - | 25.94 | 52.92 | 8.11 | - | - | |
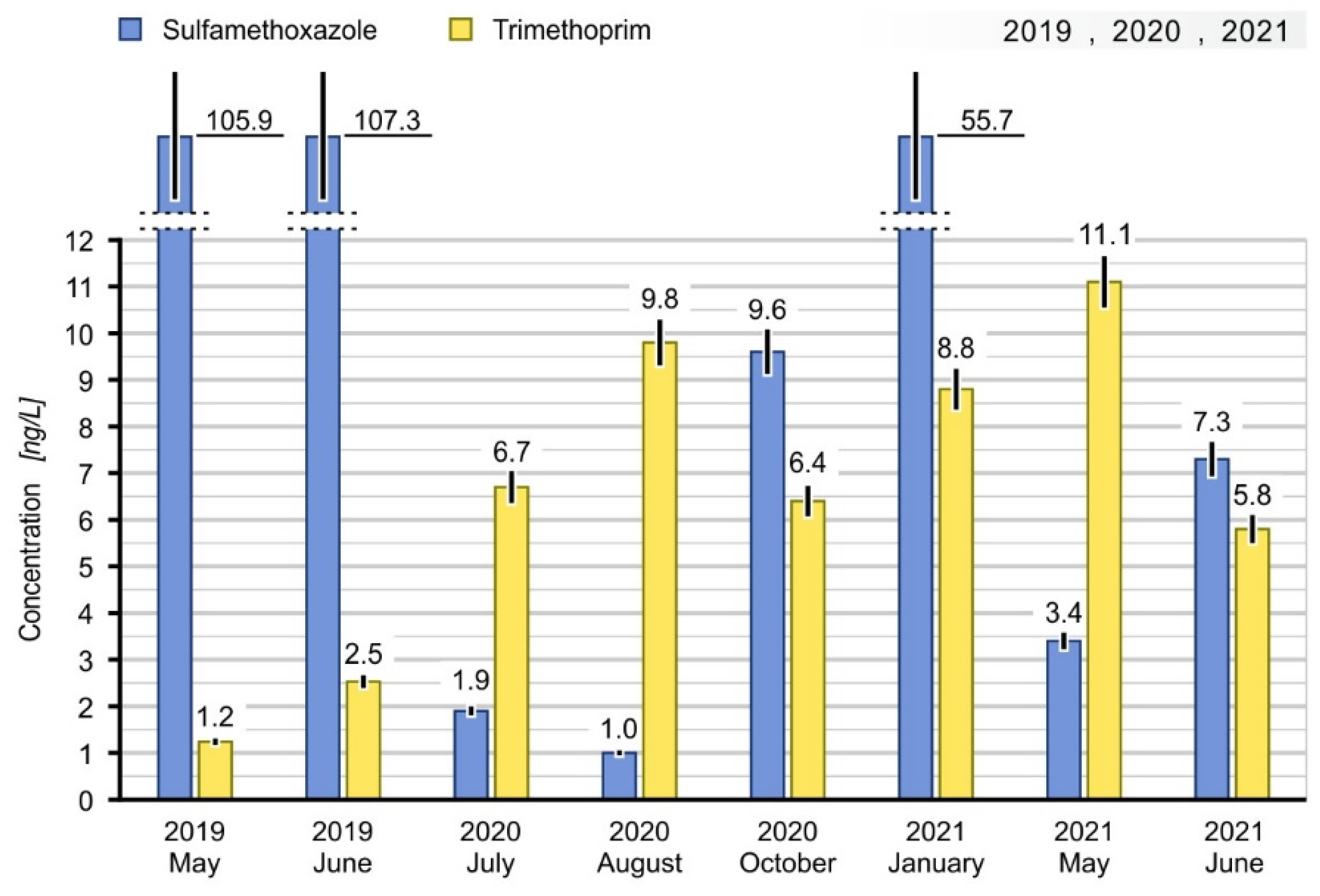
| 2019 May | - | - | - | - | - | 105.90 | 1.24 | |
| 2019 June | - | - | - | - | - | 107.31 | 2.53 | |
| 2019 August | 16.46 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 3.51 | - | - | - | |
| 2019 September | 5.91 | 1.46 | 1.46 | 12.28 | - | - | - | |
| 2019 October | 7.09 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.60 | - | - | - | |
| 2019 November | 4.04 | 9.39 | 9.39 | 7.33 | - | - | - | |
| 2020 January | 4.35 | 0.37 | 10.83 | 9.48 | - | - | - | |
| 2020 March | 5.39 | 0.52 | 11.08 | 32.33 | - | - | - | |
| 2020 July | 19.66 | 3.91 | 9.03 | 251.17 | 3.17 | 1.90 | 670 | |
| 2020 August | 5.46 | 4.33 | 11.96 | 59.17 | 3.27 | 1.00 | 9.80 | |
| 2020 October | 8.33 | 3.66 | 10.42 | 13.62 | 3.26 | 9.60 | 6.40 | |
| 2021 January | 8.51 | 3.97 | 17.27 | 15.92 | 3.31 | 55.70 | 8.80 | |
| 2021 May | 19.51 | 3.68 | 13.90 | 5.33 | 3.06 | 3.40 | 11.10 | |
| 2021 June | 9.36 | 3.54 | 8.88 | 23.22 | 3.35 | 7.30 | 5.80 | |
| Median 2019–2021 | 7.71 | 3.67 | 9.91 | 12.95 | 3.27 | 8.45 | 6.55 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antos, J.; Zembrzuska, J.; Jeż-Walkowiak, J.; Makała, A.; Ginter-Kramarczyk, D.; Kruszelnicka, I.; Uwimpaye, F. Monitoring of Contamination of the Warta River in Poznan by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics. Water 2023, 15, 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152716
Antos J, Zembrzuska J, Jeż-Walkowiak J, Makała A, Ginter-Kramarczyk D, Kruszelnicka I, Uwimpaye F. Monitoring of Contamination of the Warta River in Poznan by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics. Water. 2023; 15(15):2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152716
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntos, Joanna, Joanna Zembrzuska, Joanna Jeż-Walkowiak, Aleksandra Makała, Dobrochna Ginter-Kramarczyk, Izabela Kruszelnicka, and Fasilate Uwimpaye. 2023. "Monitoring of Contamination of the Warta River in Poznan by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics" Water 15, no. 15: 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152716
APA StyleAntos, J., Zembrzuska, J., Jeż-Walkowiak, J., Makała, A., Ginter-Kramarczyk, D., Kruszelnicka, I., & Uwimpaye, F. (2023). Monitoring of Contamination of the Warta River in Poznan by Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Antibiotics. Water, 15(15), 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152716








