Suspended Sediment Transport in Mediterranean Streams: Monitoring and Load Estimation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
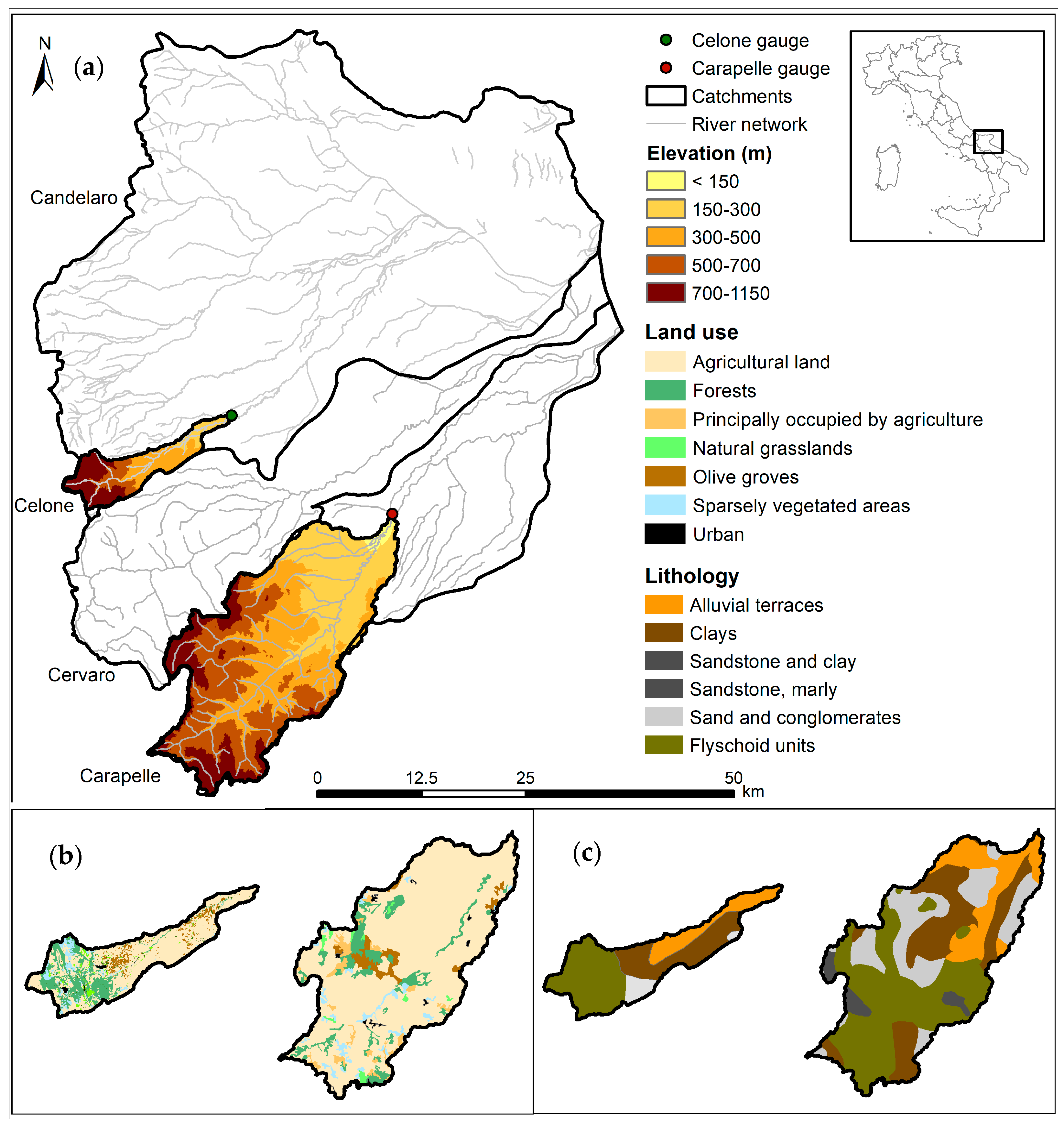
2. Study Area: The Carapelle and the Celone River Basins
3. Materials and Methods
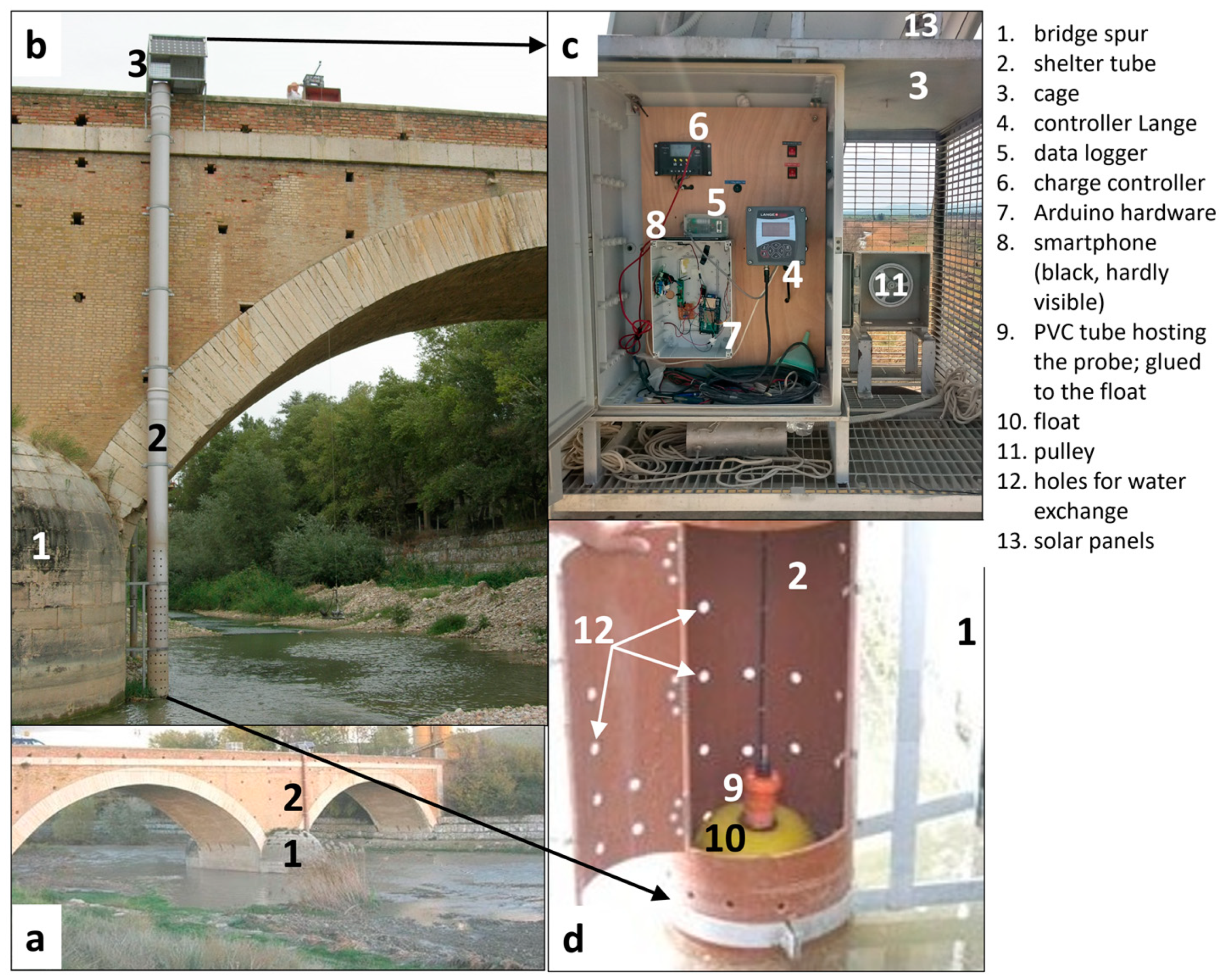
3.1. Monitoring SSC and Q
3.2. Developing Sediment Rating Curves
4. Results
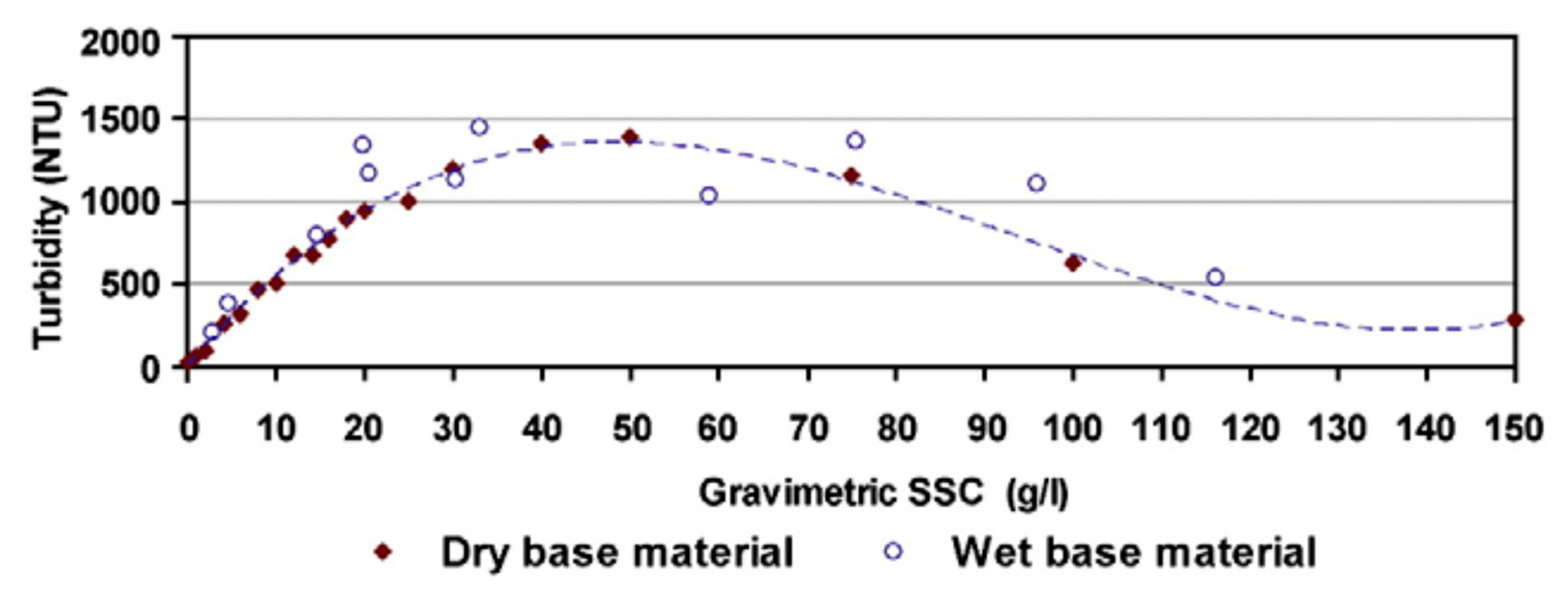
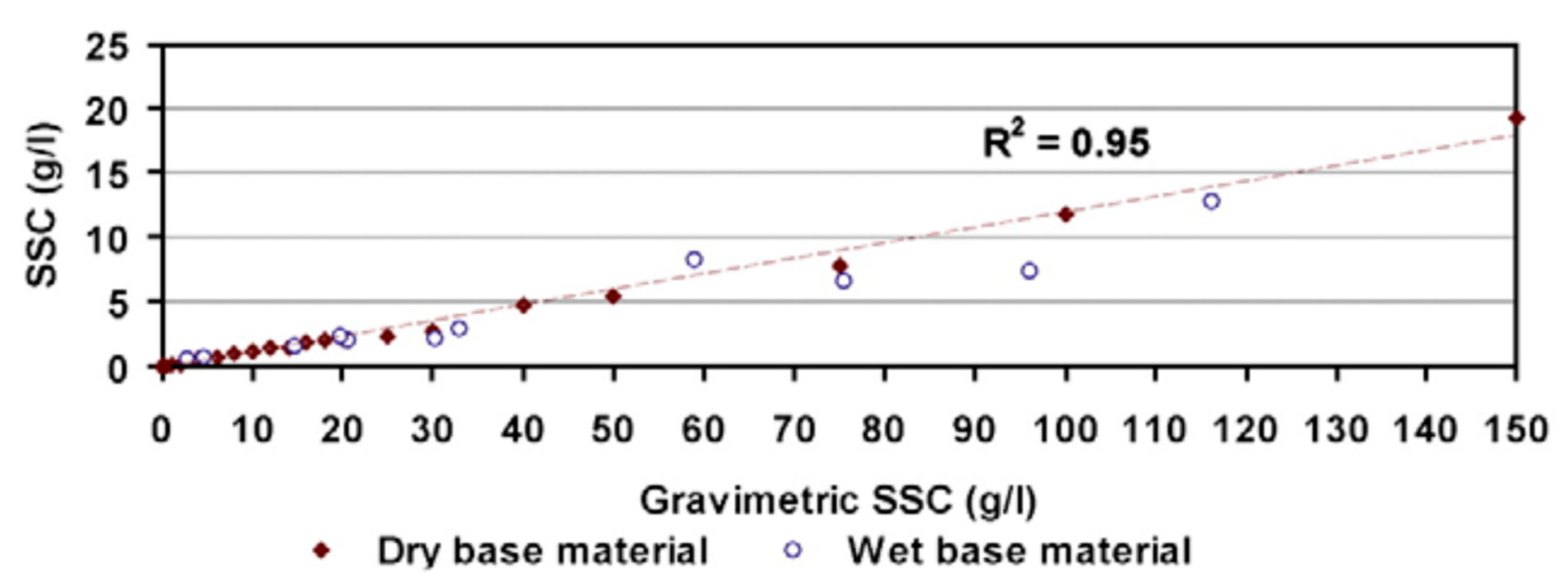
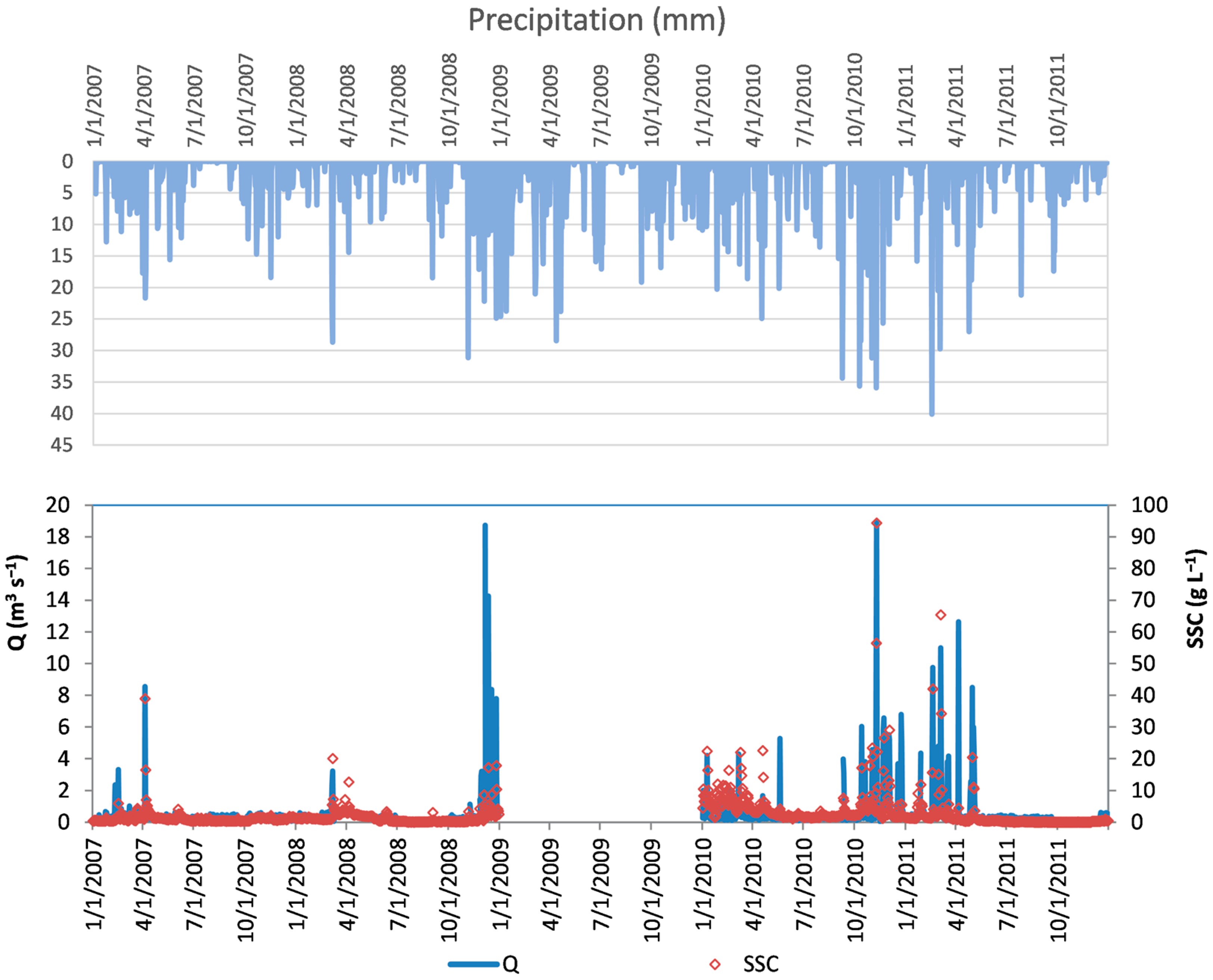
4.1. Monitoring Streamflow and SSC
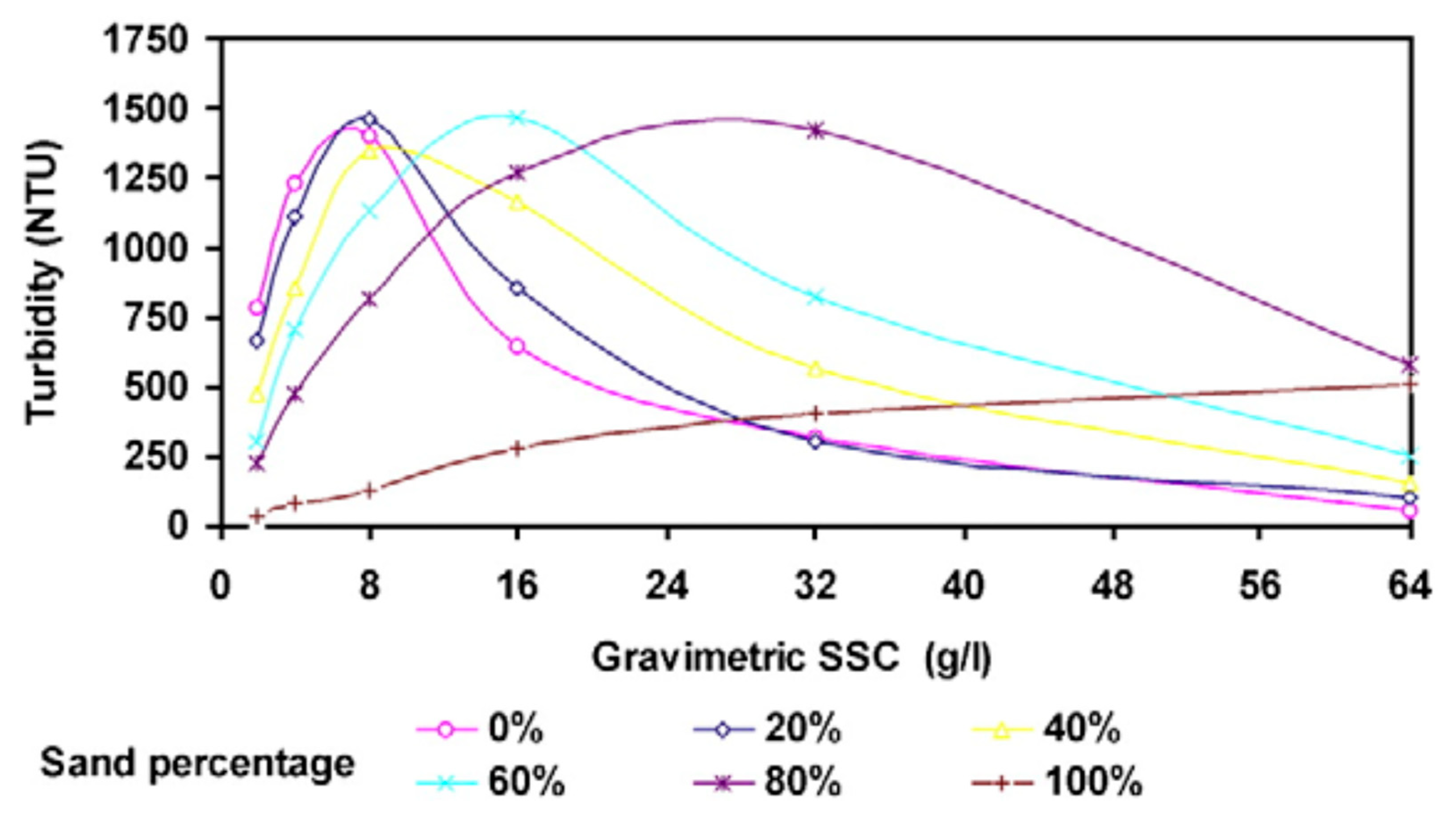
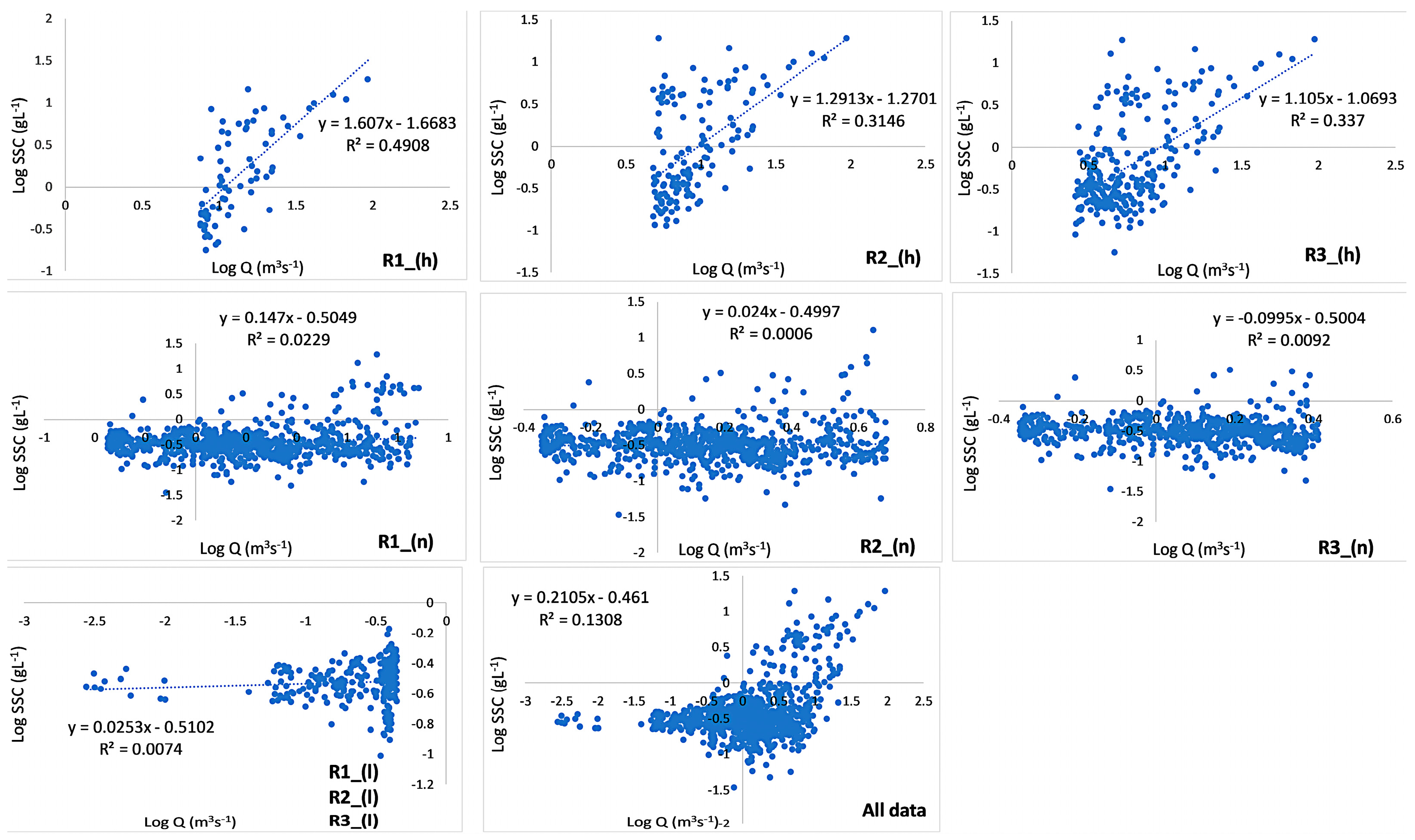
4.2. Developing Sediment Rating Curves
4.3. Sediment Loads
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jones, A.; Panagos, P.; Barcelo, S.; Bouraoui, F.; Bosco, C.; Dewitte, O.; Gardi, C.; Erhard, M.; Hervás, J.; Hiederer, R.; et al. State of Soil in Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.F.; D’Ambrosio, E.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Gentile, F. Efficiency and Feasibility of Best Management Practices to Reduce Nutrient Loads in an Agricultural River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pillo, R.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Lo Porto, A.; Todisco, M.T. Detecting the Drivers of Suspended Sediment Transport in an Intermittent River: An Event-Based Analysis. CATENA 2023, 222, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Tarazón, J.A.; Estrany, J. Exploring Suspended Sediment Delivery Dynamics of Two Mediterranean Nested Catchments. Hydrol. Process 2017, 31, 698–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, S.G.; Rainato, R.; García-Rama, A.; Gentile, F.; Lenzi, M.A. Analysis of Suspended Sediment Dynamics at Event Scale: Comparison between a Mediterranean and an Alpine Basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Spanò, M.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Ricci, G.F.; Gentile, F. Developing a Nitrogen Load Apportionment Tool: Theory and Application. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 226, 105806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzoffi, P.; Abbatista, F.; Vanino, S.; Napoli, R.; Fais, A.; Nino, P. Loss of Water Storage Capacity of Reservoirs in Southern Italy: Economic Implicances of Sedimentation. In Proceedings of the OECD Workshop on Agriculture and Water: Sustainability, Markets and Policies, Adelaide, Australia, 14–18 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Fortesa, J.; Ricci, G.F.; García-Comendador, J.; Gentile, F.; Estrany, J.; Sauquet, E.; Datry, T.; De Girolamo, A.M. Analysing Hydrological and Sediment Transport Regime in Two Mediterranean Intermittent Rivers. CATENA 2021, 196, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.F.; De Girolamo, A.M.; Gentile, F. Monitoring Suspended Sediment Transport in Two Moutainous River Basins: The Carapelle and the Celone (Apulia, Italy). In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Workshop on Metrology for Agriculture and Forestry (MetroAgriFor), Perugia, Italy, 3–5 November 2022; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, G.F.; Romano, G.; Leronni, V.; Gentile, F. Effect of Check Dams on Riparian Vegetation Cover: A Multiscale Approach Based on Field Measurements and Satellite Images for Leaf Area Index Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Pappagallo, G.; Lo Porto, A. Temporal Variability of Suspended Sediment Transport and Rating Curves in a Mediterranean River Basin: The Celone (SE Italy). CATENA 2015, 128, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Di Pillo, R.; Lo Porto, A.; Todisco, M.T.; Barca, E. Identifying a Reliable Method for Estimating Suspended Sediment Load in a Temporary River System. CATENA 2018, 165, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moatar, F.; Meybeck, M. Compared Performances of Different Algorithms for Estimating Annual Nutrient Loads Discharged by the Eutrophic River Loire. Hydrol. Process 2005, 19, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, R.A.; Jakeman, A.J.; Merritt, W.S.; McKee, L.J.; Eyre, B.D.; Baginska, B. Review of Techniques to Estimate Catchment Exports. Environ. Prot. Auth. 1999. Available online: https://s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/ap-st01.ext.exlibrisgroup.com/61SCU_INST/storage/alma/46/23/CF/BC/A4/41/B1/C4/37/90/C5/4E/CF/06/BC/40/fulltext.pdf?response-content-type=application%2Fpdf&X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Date=20230726T153307Z&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&X-Amz-Expires=119&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAJN6NPMNGJALPPWAQ%2F20230726%2Fap-southeast-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Signature=52411230030f2f472e4d1b11f6bc67fb3eea1e357b9987fae64ac71ae0212b15 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C.; Alvarez, P.; Anache, J.A.A.; Baartman, J.; Ballabio, C.; Bezak, N.; Biddoccu, M.; Cerdà, A.; Chalise, D.; et al. Soil Erosion Modelling: A Global Review and Statistical Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Bingner, R.L.; Milillo, F.; Gentile, F. Evaluation of Alternative Management Practices with the AnnAGNPS Model in the Carapelle Watershed. Soil Sci. 2016, 181, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, V.; Porto, P. Sediment Delivery Distributed (SEDD) Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2000, 5, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagarello, V.; Ferro, V.; Pampalone, V.; Porto, P.; Todisco, F.; Vergni, L. Predicting Soil Loss in Central and South Italy with a Single USLE-MM Model. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 3365–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Cerdan, O.; Grangeon, T.; Ricci, G.F.; Vandromme, R.; Lo Porto, A. Modelling Effects of Forest Fire and Post-Fire Management in a Catchment Prone to Erosion: Impacts on Sediment Yield. CATENA 2022, 212, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J. Turbidity-Controlled Suspended Sediment Sampling for Runoff-Event Load Estimation. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.J. An Evaluation of Sediment Rating Curves for Estimating Suspended Sediment Concentrations for Subsequent Flux Calculations. Hydrol. Process 2003, 17, 3387–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.B. Estimating a Sediment Rating Curve of the Reventazón River at Palomo Using Logged Mean Loads within Discharge Classes. J. Hydrol. 1996, 183, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, N.E.M. Fitting and Interpretation of Sediment Rating Curves. J. Hydrol. 2000, 234, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilino, M.; Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Iacobellis, V.; Gentile, F. Evaluating the Potential of GeoEye Data in Retrieving LAI at Watershed Scale. Remote Sens. Agric. Ecosyst. Hydrol. XVI 2014, 9239, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.; Tarantino, E.; Fratino, U.; Iacobellis, V.; Romano, G.; Gentile, F. A Data Fusion Algorithm Based on the Kalman Filter to Estimate Leaf Area Index Evolution in Durum Wheat by Using Field Measurements and MODIS Surface Reflectance Data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 7, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisantino, T.; Gentile, F.; Milella, P.; Liuzzi, G.T. Effect of Time Scale on the Performance of Different Sediment Transport Formulas in a Semiarid Region. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadar, M.J.; Hach, C.C. Turbidity Science: Technical Information Series; Hach Company: Loveland, CO, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, F.; Bisantino, T.; Corbino, R.; Milillo, F.; Romano, G.; Liuzzi, G.T. Monitoring and Analysis of Suspended Sediment Transport Dynamics in the Carapelle Torrent (Southern Italy). CATENA 2010, 80, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Girolamo, A.M.; Balestrini, R.; D’Ambrosio, E.; Pappagallo, G.; Soana, E.; Lo Porto, A. Antropogenic Input of Nitrogen and Riverine Export from a Mediterranean Catchment. The Celone, a Temporary River Case Study. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 187, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, R.W.; Smillie, G.M. Bias in Hydrologic Prediction Using Log-Transformed Regression Models. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1986, 22, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.I. River Loads Underestimated by Rating Curves. Water Resour. Res. 1986, 22, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradu, D.; Mundlak, Y. Estimation in Lognormal Linear Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1970, 65, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N. Smearing Estimate: A Nonparametric Retransformation Method. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1983, 78, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, E.J.; Hirsch, R.M.; Cohn, T.A. Mean Square Error of Regression-Based Constituent Transport Estimates. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Webb, B.W. Erosion and Sediment Yield: Global and Regional Perspectives. In Proceedings of the International Symposium, Exeter, UK, 15–19 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, N.; Anandhi, A.; Jeong, J. Estimation of Stream Health Using Flow-Based Indices. Hydrology 2018, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, R.M.; Fennessey, N.M. Flow Duration Curves Ll: A Review of Applications in Water Resources Planning. Water Resour. Bull. 1995, 31, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganora, D.; Claps, P.; Laio, F.; Viglione, A. An Approach to Estimate Nonparametric Flow Duration Curves in Ungauged Basins. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smakhtin, V.U. Low Flow Hydrology: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2001, 240, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmel, R.D.; Cooper, R.J.; Slade, R.M.; Haney, R.L.; Arnold, J.G. Cumulative Uncertainty in Measured Streamflow and Water Quality Data for Small Watersheds. Trans. ASABE 2006, 49, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V.; Mirabile, S. Comparison between Grain-Size Analyses Using Laser Diffraction and Sedimentation Methods. Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 106, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, N.J.; Richards, K.S.; Brown, R.A.; Lane, S.N. Laboratory and Field Assessment of an Infrared Turbidity Probe and Its Response to Particle Size and Variation in Suspended Sediment Concentration. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1995, 40, 771–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estrany, J.; Garcia, C.; Batalla, R.J. Suspended Sediment Transport in a Small Mediterranean Agricultural Catchment. Earth Surf. Process Landf. 2009, 34, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulot, F.; Dewals, B.J.; Erpicum, S.; Archambeau, P.; Pirotton, M. 6.13—Long-Term Sediment Management for Sustainable Hydropower. In Comprehensive Renewable Energy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 355–376. ISBN 9780080878737. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, S.A.; Topping, D.J.; Rubin, D.M.; Melis, T.S. An Approach for Modeling Sediment Budgets in Supply-Limited Rivers. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, S.T.; Harrington, J.R. An Assessment of the Suspended Sediment Rating Curve Approach for Load Estimation on the Rivers Bandon and Owenabue, Ireland. Geomorphology 2013, 185, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Webb, B.W. The Reliability of Rating Curve Estimates of Suspended Sediment Yield: Some Further Comments. In Proceedings of the Porto Alegre Meeting, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 14–21 December 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Xu, L.; Su, L.; Deng, Y.; Yang, C. Comparing Flow Duration Curves and Discharge Hydrographs to Assess Eco-Flows. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4681–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E. Limitations of the Rating Curve Technique for Estimating Suspended Sediment Loads, With Particular Reference to The Use of Cs-137 and Pb-210 Measurements for the Assessment of Soil Erosion and Sedimentation in the Riva Basin (Istanbul, NW Turkey) View Project. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Des-Walling/publication/253921527_Limitations_of_the_Rating_Curve_Technique_for_Estimating_Suspended_Sediment_Loads_With_Particular_Reference_to_British_Rivers/links/53edb5bb0cf23733e80ad89d/Limitations-of-the-Rating-Curve-Technique-for-Estimating-Suspended-Sediment-Loads-With-Particular-Reference-to-British-Rivers.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Chen, L.; Schumer, R.; Knust, A.; Forsee, W. Impact of Temporal Resolution of Flow-Duration Curve on Sediment Load Estimation. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benselama, O.; Mazour, M.; Hasbaia, M.; Djoukbala, O.; Mokhtari, S. Analysis of the Suspended Sediment Yield at Different Time Scales in Mediterranean Watershed, Case of Wadi El Maleh (North-West of Algeria). J. Mediterr. Earth Sci. 2019, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liquete, C.; Canals, M.; Ludwig, W.; Arnau, P. Sediment Discharge of the Rivers of Catalonia, NE Spain, and the Influence of Human Impacts. J. Hydrol. 2009, 366, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rompaey, A.; Bazzoffi, P.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Modeling Sediment Yields in Italian Catchments. Geomorphology 2005, 65, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borrelli, P.; Märker, M.; Panagos, P.; Schütt, B. Modeling Soil Erosion and River Sediment Yield for an Intermountain Drainage Basin of the Central Apennines, Italy. CATENA 2014, 114, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Verstraeten, G.; de Vente, J.; Ocakoglu, F. Sediment Yield in Europe: Spatial Patterns and Scale Dependency. Geomorphology 2011, 130, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, E.B. Rates of Soil Formation: Implications for Soil-Loss Tolerance. Soil Sci. 1988, 145, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, F.G.A.; Jones, R.J.A.; Rickson, R.J.; Smith, C.J. Tolerable versus Actual Soil Erosion Rates in Europe. Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 94, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alewell, C.; Egli, M.; Meusburger, K. An Attempt to Estimate Tolerable Soil Erosion Rates by Matching Soil Formation with Denudation in Alpine Grasslands. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bazzoffi, P. Soil Erosion Tolerance and Water Runoff Control: Minimum Environmental Standards. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2009, 9, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, C.; Ferro, V. Establishing Soil Loss Tolerance: An Overview. J. Agric. Eng. 2016, 47, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Europe’s Environment: The Second Assessment—European Environment Agency. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/92-828-3351-8 (accessed on 31 May 2023).
- Di Stefano, C.; Nicosia, A.; Pampalone, V.; Ferro, V. Soil Loss Tolerance in the Context of the European Green Deal. Heliyon 2023, 9, e12869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soil and Land. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/soil-and-land_en (accessed on 31 May 2023).





| Celone River | Carapelle River | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R1 | R2 | R3 | |
| High flow | 2.04 | 2.12 | 2.20 | 1.64 | 2.06 | 1.87 |
| Normal flow | 4.69 | 3.62 | 3.13 | 1.41 | 1.25 | 1.16 |
| Low flow | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.24 | 1.04 | 1.04 | 1.04 |
| Celone River | Carapelle River | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R1 | R2 | R3 | |
| High flow | 19.10 | 29.61 | 35.52 | 36.64 | 59.98 | 40.08 |
| Normal flow | 98.94 | 191.49 | 126.39 | 19.98 | 15.53 | 13.15 |
| Low flow | 99.97 | 99.97 | 99.97 | 4.67 | 4.67 | 4.67 |
| R1 | R1_CF | R2 | R2_CF | R3 | R3_CF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carapelle | ||||||
| 2007 | 0.878 | 0.881 | 0.878 | 0.880 | 0.878 | 0.879 |
| 2008 | 1.479 | 1.542 | 1.475 | 1.543 | 1.474 | 1.565 |
| 2010 | 7.426 | 7.437 | 7.430 | 7.452 | 7.431 | 7.449 |
| 2011 | 3.420 | 3.439 | 3.424 | 3.459 | 3.429 | 3.465 |
| Celone | ||||||
| 2010–2011 | 2.610 | 6.060 | 2.550 | 5.780 | 2.400 | 5.200 |
| R1 (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | R1_CF (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | R2 (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | R2_CF (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | R3 (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | R3_CF (t ha−1 yr−1) | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carapelle | ||||||||||||
| High Flow | 2.74 | 83.2 | 2.75 | 82.8 | 3.00 | 91.0 | 3.02 | 90.8 | 3.14 | 95.2 | 3.17 | 95.0 |
| Normal Flow | 0.54 | 16.5 | 0.56 | 16.9 | 0.29 | 8.7 | 0.30 | 8.9 | 0.15 | 4.5 | 0.15 | 4.6 |
| Low Flow | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.4 |
| Celone | ||||||||||||
| High Flow | 2.23 | 85.6 | 4.91 | 81.1 | 2.27 | 89.2 | 4.83 | 83.5 | 2.27 | 94.3 | 4.62 | 88.8 |
| Normal Flow | 0.36 | 13.7 | 1.12 | 18.5 | 0.26 | 10.1 | 0.93 | 16.1 | 0.26 | 4.9 | 0.56 | 10.7 |
| Low Flow | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.02 | 0.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Girolamo, A.M.; Ricci, G.F.; Abdelwahab, O.M.M.; Lo Porto, A.; Milillo, F.; Netti, A.M.; Gentile, F. Suspended Sediment Transport in Mediterranean Streams: Monitoring and Load Estimation. Water 2023, 15, 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152715
De Girolamo AM, Ricci GF, Abdelwahab OMM, Lo Porto A, Milillo F, Netti AM, Gentile F. Suspended Sediment Transport in Mediterranean Streams: Monitoring and Load Estimation. Water. 2023; 15(15):2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152715
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Girolamo, Anna Maria, Giovanni Francesco Ricci, Ossama M. M. Abdelwahab, Antonio Lo Porto, Fabio Milillo, Addolorata Maria Netti, and Francesco Gentile. 2023. "Suspended Sediment Transport in Mediterranean Streams: Monitoring and Load Estimation" Water 15, no. 15: 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152715
APA StyleDe Girolamo, A. M., Ricci, G. F., Abdelwahab, O. M. M., Lo Porto, A., Milillo, F., Netti, A. M., & Gentile, F. (2023). Suspended Sediment Transport in Mediterranean Streams: Monitoring and Load Estimation. Water, 15(15), 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15152715









