Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Irrigation and Drinking Water in Bangong Co Lake Watershed in Northwest Tibetan Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
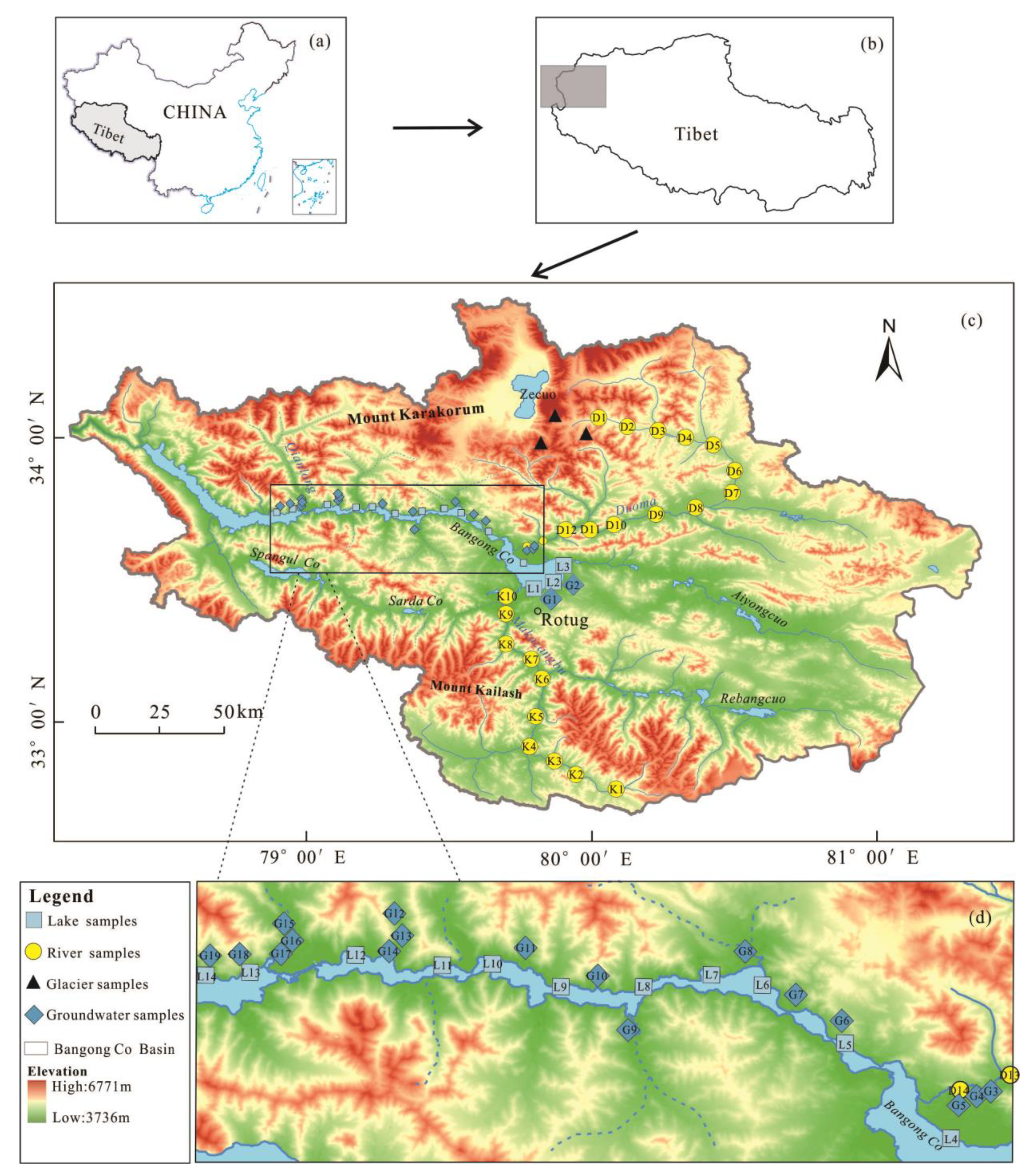
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Different Water Bodies in Bangong Lake Basin
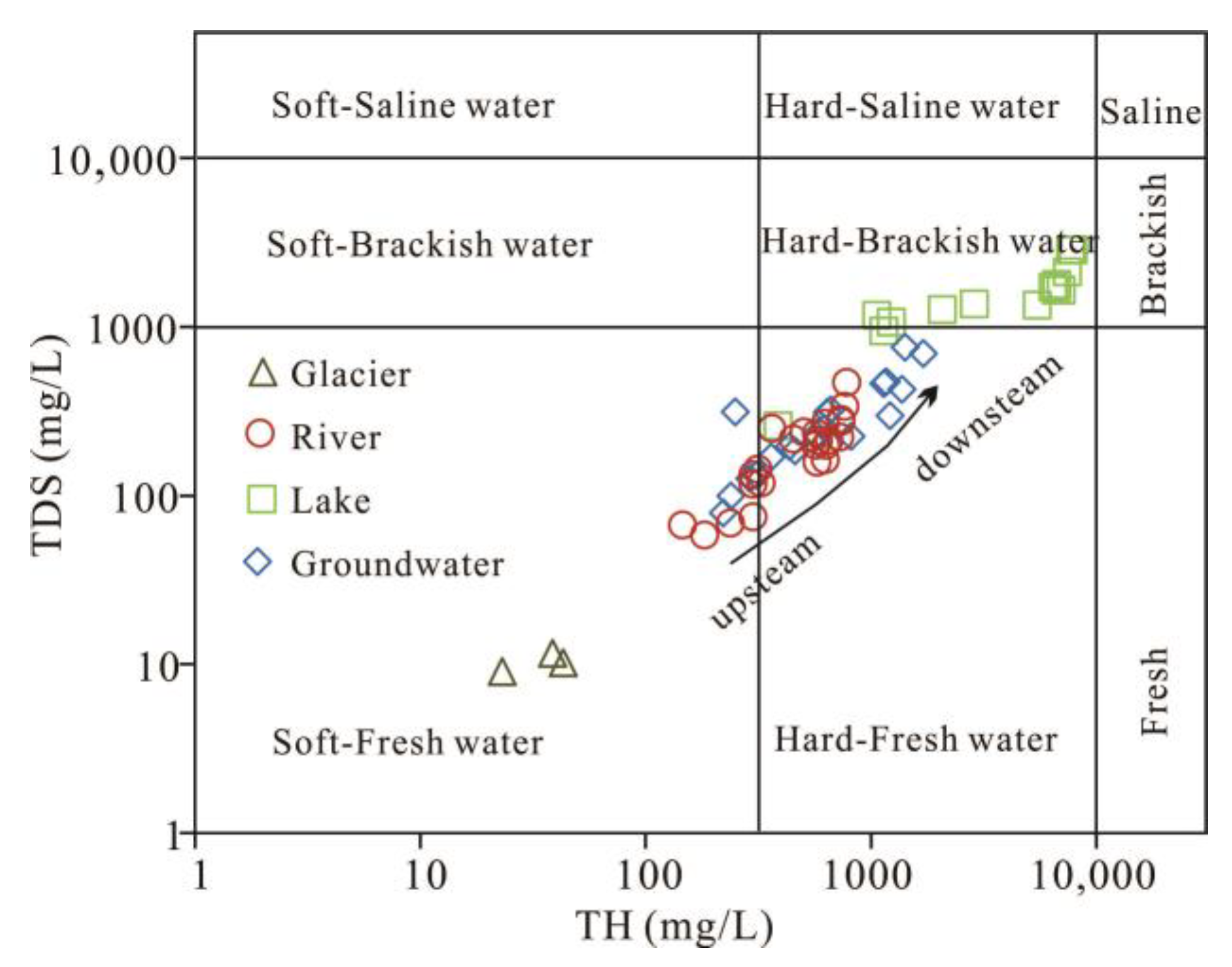
3.1.1. Statistical Characteristics of Parameters
3.1.2. Ion Spatial Distribution
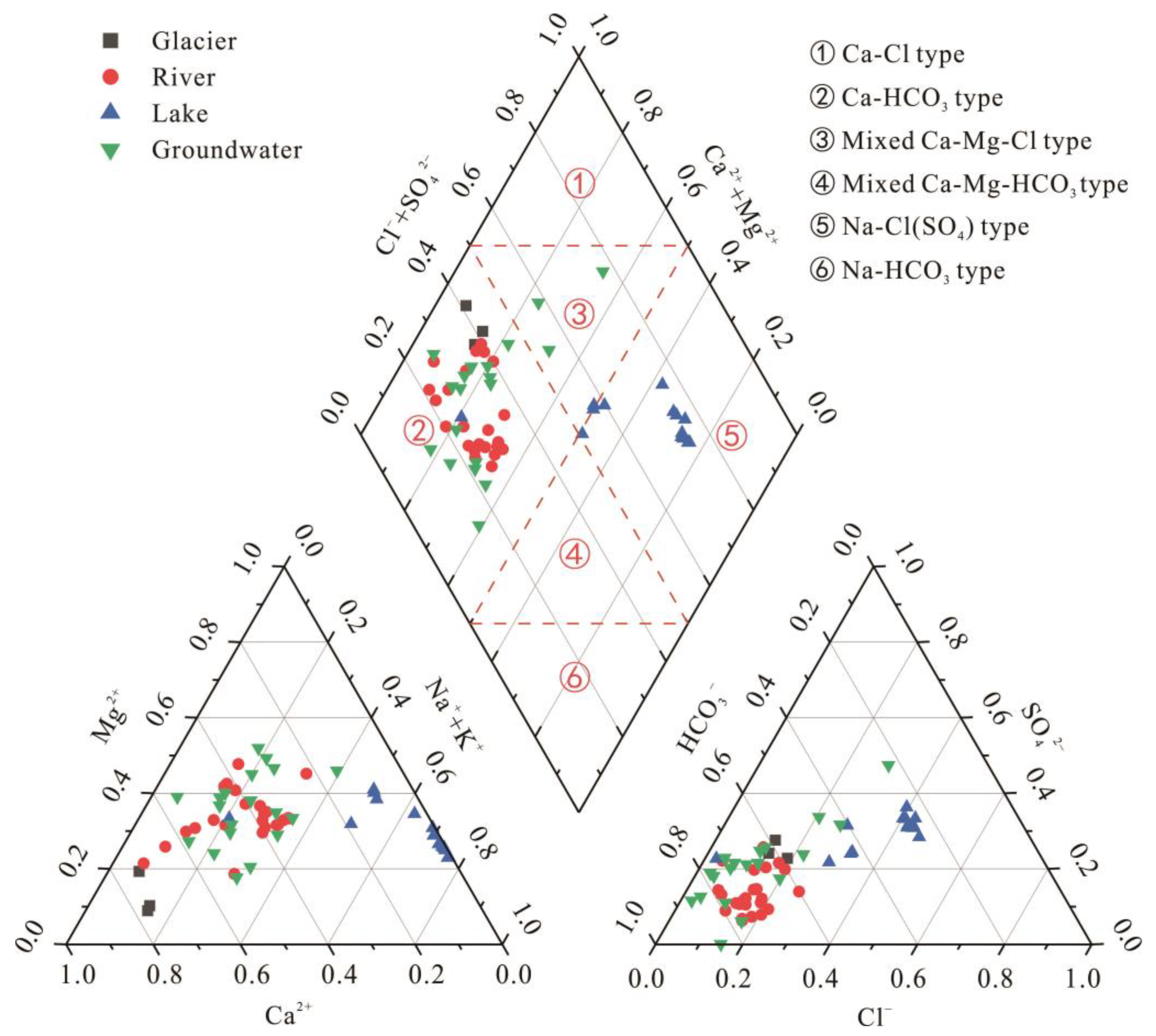
3.1.3. Piper Diagram and Hydrochemical Classification
3.2. Cause Analysis of Hydrochemical Characteristics
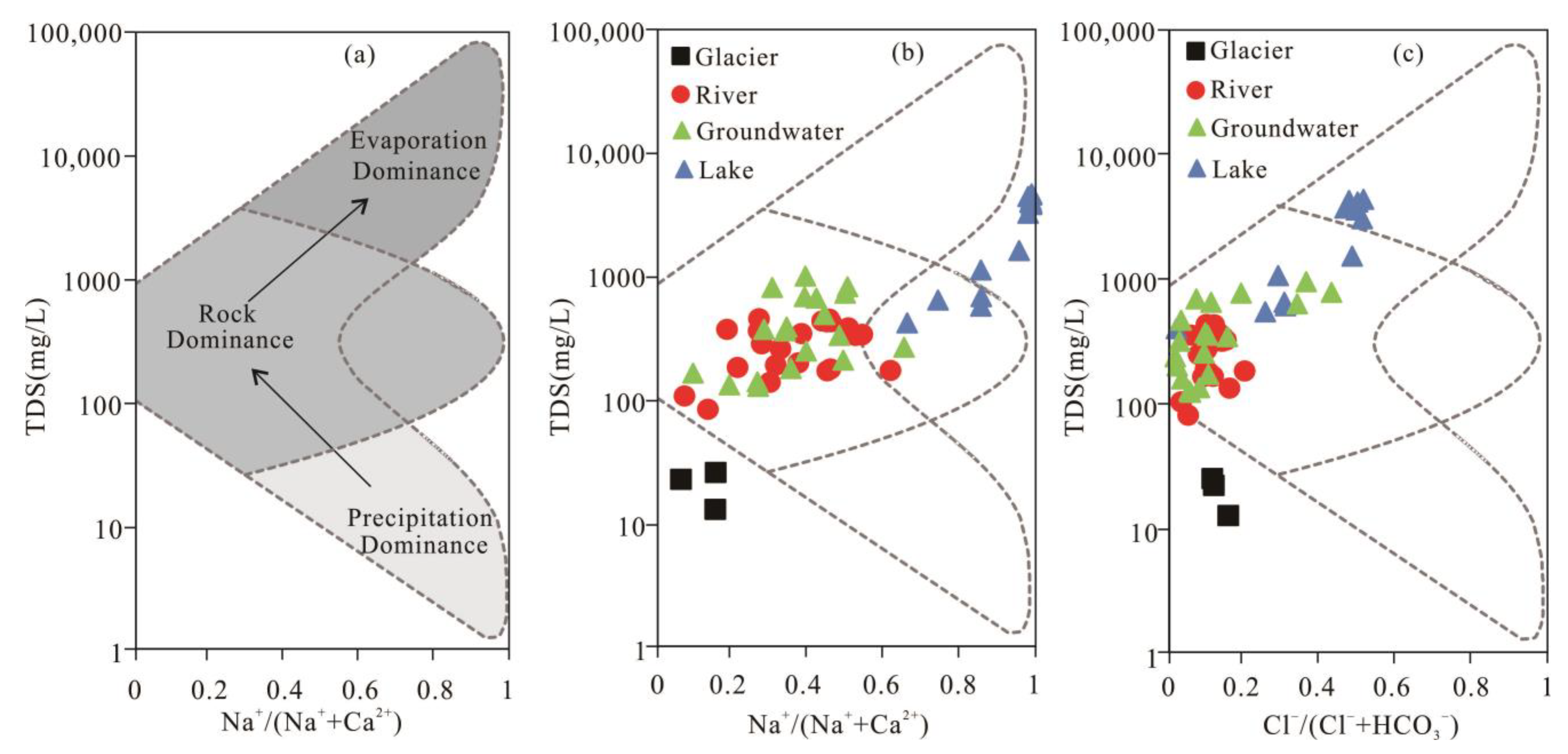
3.2.1. Gibbs Diagrams
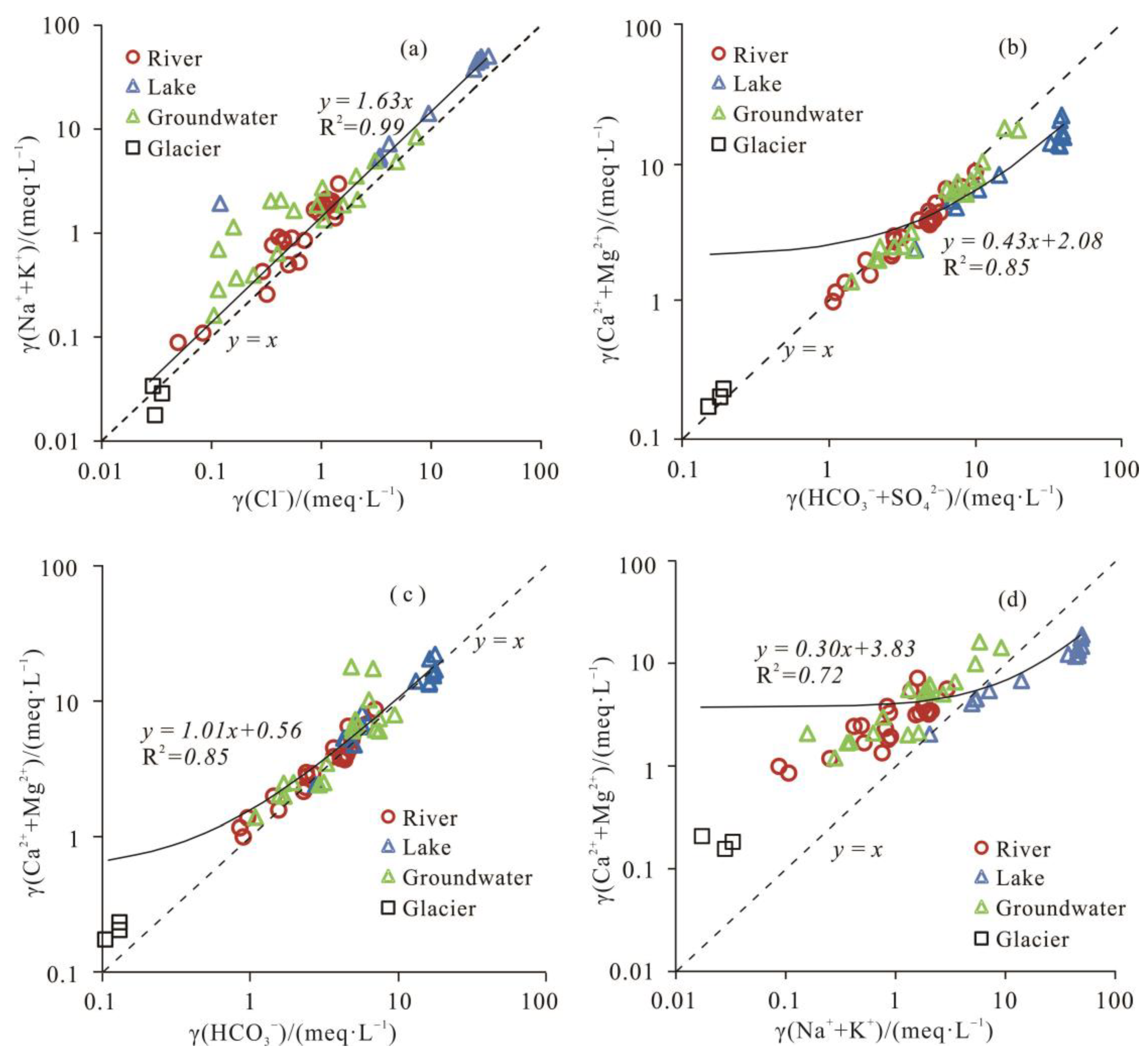
3.2.2. Ion Ratio Analysis
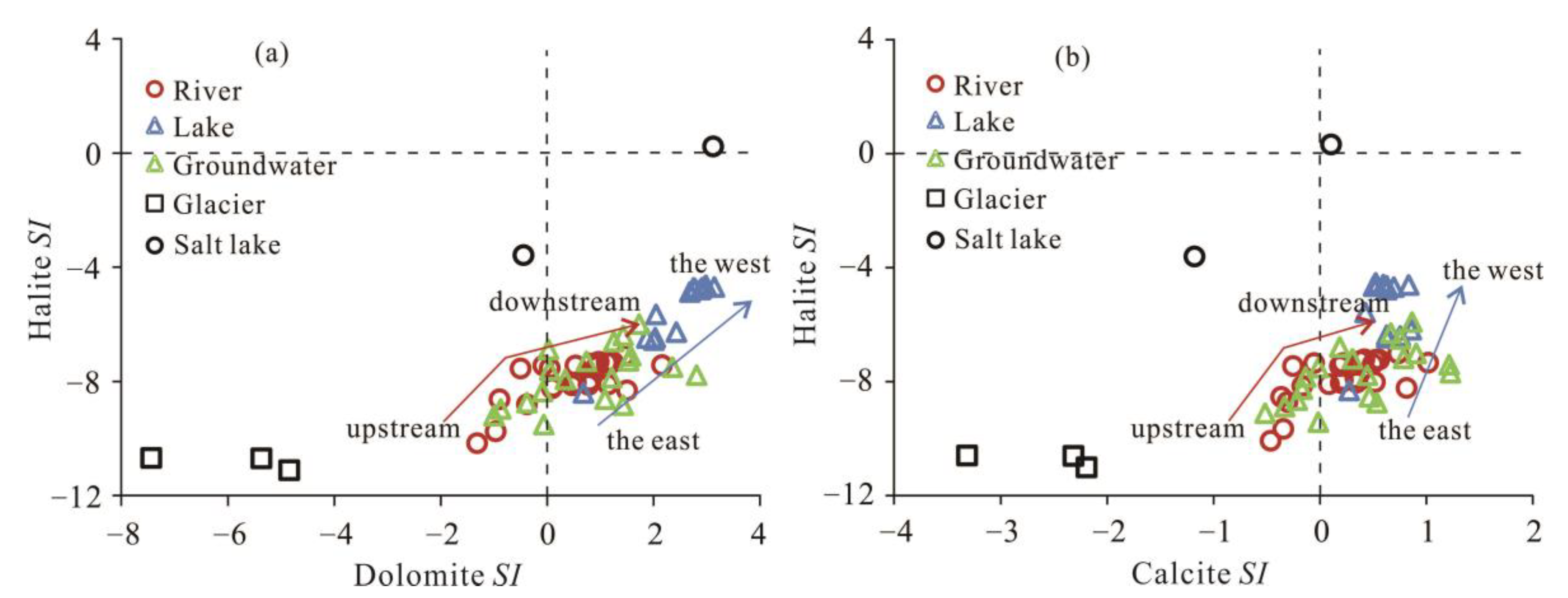
3.2.3. Hydrochemical Modeling of Mineral Saturation Index (SI)
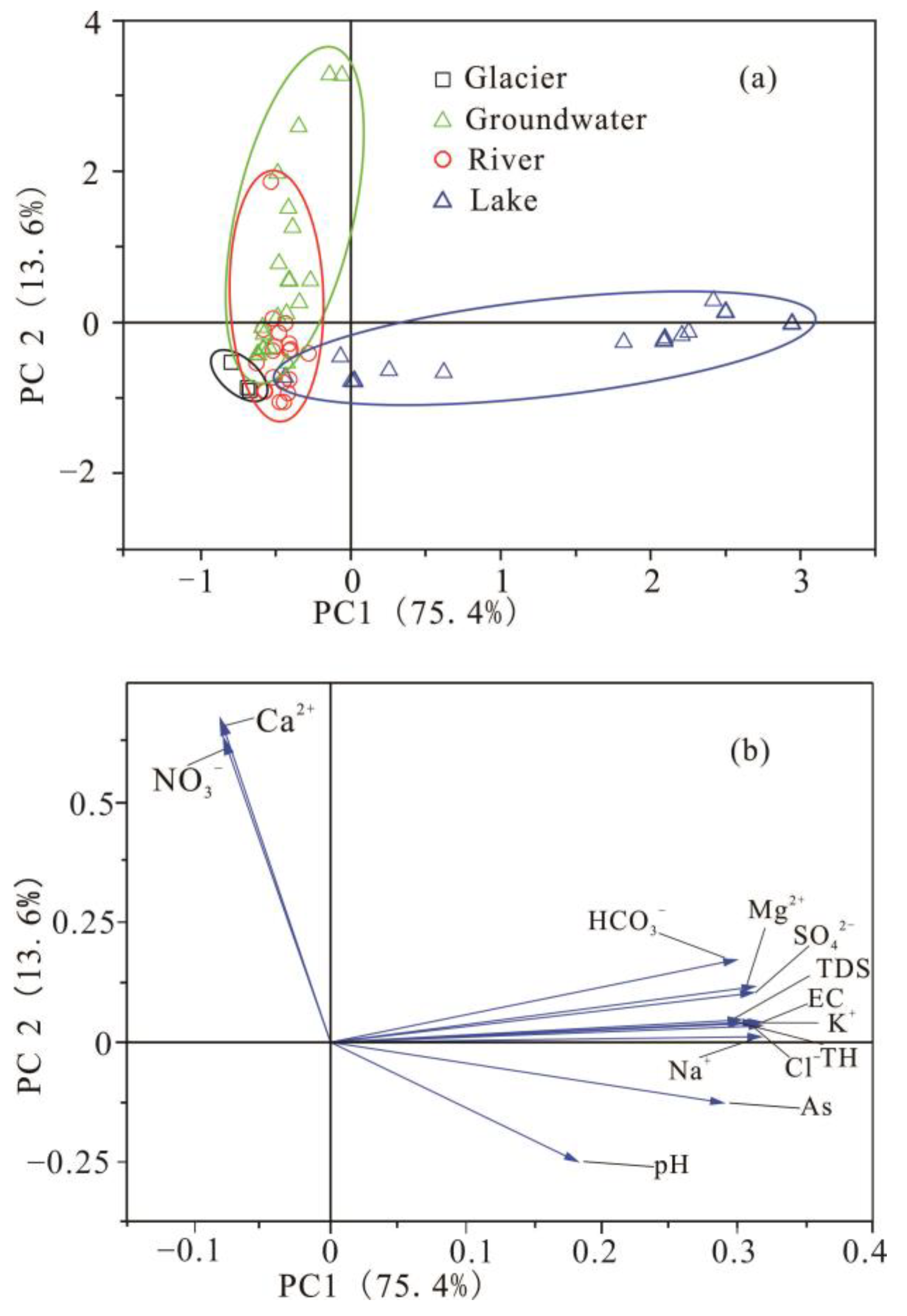
3.2.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.3. Water Quality Evaluation
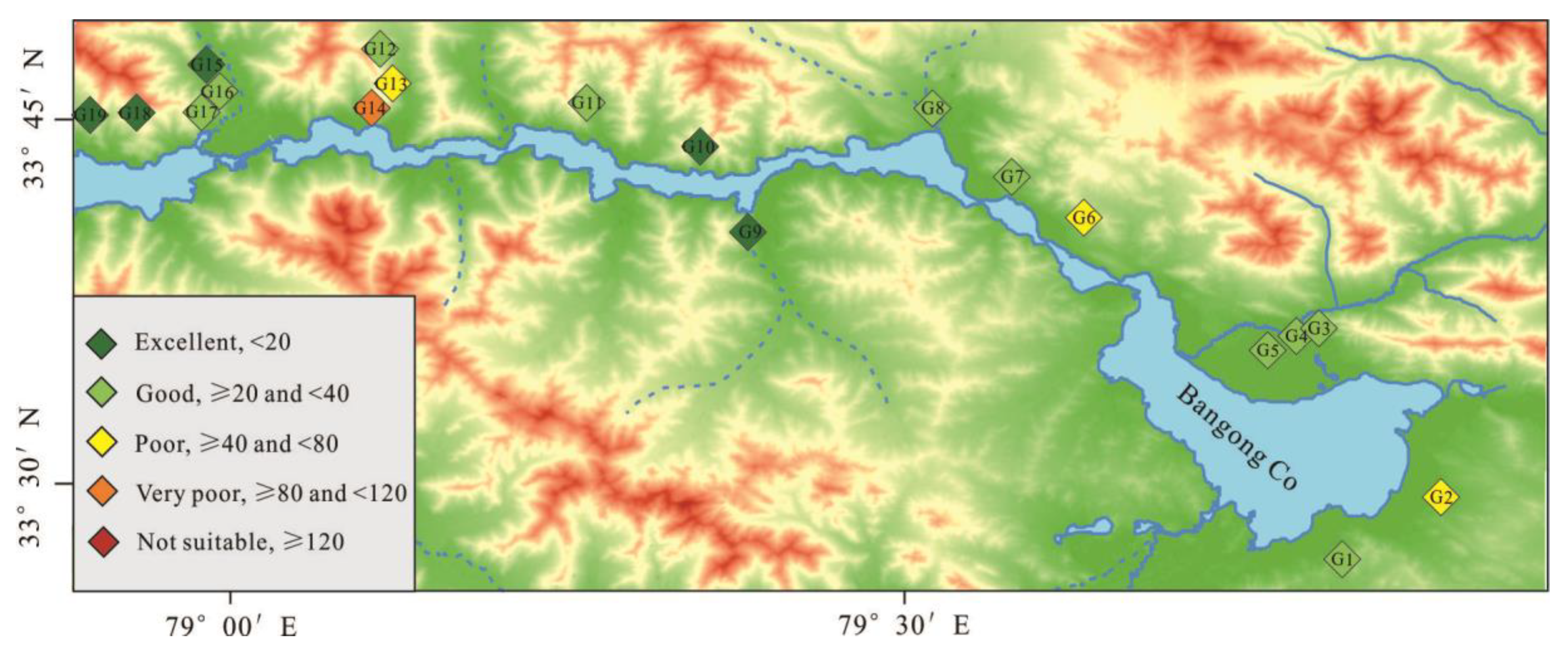
3.3.1. Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Drinking Purposes
3.3.2. Water Evaluation for Irrigation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.P.; Gong, P.; Wang, C.F.; Ren, J.; Yao, T.D. A review of current knowledge and future prospects regarding persistent organic pollutants over the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafeng, S.; Jiawen, R. Glacier recession and lake shrinkage indicating the climatic warming and drying trend in central Asia. Ann. Glaciol. 1990, 14, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, L.J.; Zheng, M.B.; Wei, L.J. Change of the lakes in Tibetan Plateau and its response to climate in the past forty years. Front. Earth Sci. 2016, 23, 310–323. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, L.; Ma, Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Zubaida, M. The consecutive lake group water storage variations and their dynamic response to climate change in the central Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.D.; You, C.F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Hydrological and solute budgets of Lake Qinghai, the largest lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2010, 218, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.P.; Jin, H.A. Hydrochemistry differences and causes of tectonic lakes and glacial lakes in Tibetan Plateau. Water 2020, 12, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Gong, P.; Yao, T. Atmospheric processes of persistent organic pollutants over a remote lake of the central Tibetan Plateau: Implications for regional cycling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 14, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Kuang, X.; Hao, Y.; Shan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Feng, Y.; Zheng, Y. Water quality and health risk assessment of the water bodies in the Yamdrok-tso basin, southern Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, N. Remote sensing estimation of water clarity for various lakes in China. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Niu, Y.Q. Composition characteristics and source analysis of major ions in four small lake-watersheds on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2015, 36, 430–437. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Shang, Y.N.; Shen, L.C. Characteristics and evolution of hydrochemical compositions of freshwater lake in Tibetan plateau. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2013, 34, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunkel, A.; Shadeed, S.; Hartmann, A.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J. Model signatures and aridity indices enhance the accuracy of water balance estimations in a data-scarce Eastern Mediterranean catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medici, G.; Lorenzi, V.; Sbarbati, C.; Manetta, M.; Petitta, M. Structural classification, discharge statistics, and recession analysis from the springs of the Gran Sasso (Italy) carbonate aquifer; comparison with selected analogues worldwide. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.M.; Song, Y.G.; Zhang, C.S.; Zhang, Q.F. Mineral elements exchange patterns in biogeochemical cycle of Jinshuhe River Basin. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2011, 20, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Gao, S.; Li, W.; Qiu, G.; Tian, Z. Temporal and spatial evolution of lakes in the Bashang Plateau for nearly recent 30 years. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2022, 2, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazova, M.; Moiseenko, T. Migration activity of elements in the water of lakes of northwestern Russia. Geochem. Int. 2021, 59, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, D.Y.; Moiseenko, T.I.; Dinu, M.I. Geochemical trends in the formation of atmospheric precipitation in the conditionally background area of the Valdai National Park. Geochem. Int. 2020, 58, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.L.; Liang, X.J.; Wang, B. Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.C.; Lv, Q.Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.C.; Dong, H.L.; Gonsior, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Molecular composition of dissolved organic matter in saline lakes of the Qing-Tibetan Plateau. Org. Geochem. 2022, 167, 104400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hou, Z.; An, Z.; Liu, X.; Dong, J. Major ion chemistry of waters in Lake Qinghai catchments, NE Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Quat. Int. 2010, 212, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Kung, H.-T.; Yushanjiang, A. Hydrogen and oxygen isotope composition and water quality evaluation for different water bodies in the Ebinur Lake Watershed, Northwestern China. Water 2019, 11, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Parvaze, S.; Huda, M.; Allaie, S. The changing water quality of lakes-a case study of Dal Lake, Kashmir Valley. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wu, Y.H. Major ion chemistry of water and its controlling factors in the Yamzhog Yumco Basin, South Tibet. J. Lake Sci. 2012, 24, 600–608. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.M.; Kang, S.C. Temporal and spatial variations of major ions in Nam Co Lake water, Tibetan Plateau. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2012, 33, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontes, J.C.; Gasse, F.; Gibert, E. Holocene environmental changes in Lake Bangong basin (Western Tibet). Part 1: Chronology and stable isotopes of carbonates of a Holocene lacustrine core. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 1996, 120, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xie, S.Y.; Wang, M.D.; He, Y.; Hou, J.Z. Characteristics of water temperature based on fractal and R/S Method in Bangong Co and Dagze Co. Geol. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2015, 34, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Du, P.; Shui, Y.; Cai, A.; Lv, C.; Bao, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, P. Tracing the sources of nitrate in the rivers and lakes of the southern areas of the Tibetan Plateau using dual nitrate isotopes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, G.; He, Z. Biological and ecological features of saline lakes in northern Tibet, China. Hydrobiologia 2006, 541, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Dong, L.; Wang, Z. Hydrochemical composition, distribution, and sources of typical organic pollutants and metals in Lake Bangong Co, Tibet. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9877–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.A.; Li, Z.Q.; Ye, B.S.; Jiao, K.Q. New result of glacier inventory in the drainage basins of the Bangong lake in china. J. Glaciol. 2003, 25, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, G.; Zhi, J.; Ye, B. Regional Geological Survey of 1:250,000 Ritu County, Tibet Autonomous Region (I44C003002); Jiangxi Institute of Geological Survey: Nanchang, China, 2004; pp. 20–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, A.; Harrison, T.M. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 211–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, B.; Shi, R.; Zou, H.; Chen, S.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Yang, J. Intra-continental boninite-series volcanic rocks from the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone, Central Tibet. Lithos 2021, 12, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Gao, C.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Z.M.; Guan, J.L. Age and tectonic significance of Jingzhushan Formation in Bangong Lake Area, Tibet. Geotecton. Et Metallog. 2016, 40, 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Zhou, T. Causes and Tectonic Evolution of Bangong Lake Basin. Earth Sci. J. China Univ. Geosci. 2013, 38, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, M.; Cao, Y. Cashmere Diameter Deviation Of Tibetan Cashmere Goats. Acta Vet. Et Zootech. Sinica 1999, 30, 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Piper, M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R.J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meybeck, M. Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am. J. Sci. 1987, 287, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 308–475. [Google Scholar]
- Adimalla, N.; Li, P.; Venkatayogi, S. Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and integrated interpretation with water quality index studies. Environ. Process. 2018, 5, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Pal, S.C.; Islam, A.R.M.T. Groundwater quality assessment for safe drinking water and irrigation purposes in Malda district, Eastern India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci. 1954, 78, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xue, C.; Tian, R.; Wang, S. Lake water quality assessment: A case study of Shahu Lake in the semiarid loess area of northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, F.; Jin, Z. Spatial characteristics and controlling factors of chemical weathering of loess in the dry season in the middle Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4855–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Mo, H.; Son, J.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, S.E.; Cho, K. Interactive effects of water pH and hardness levels on the growth and reproduction of Heterocypris incongruens (Crustacea: Ostracoda). Hydrobiologia 2015, 753, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, S.; Rifat, M.a.H.; Howlader, S.; Hasan, M.A.; Islam, S.; Alam, M.N.E.; Islam, M.N. Assessment of Bhatiari Lake water quality: Pollution indices, hydrochemical signatures and hydro-statistical analysis. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W. Geological Characteristics and Uplifting Environment Evolution of Salt Lake in the Eastern Section of Pangong Lake in Xizang Province; China University of Geosciences (Wuhan): Wuhan, China, 2014; pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Zheng, M. Distribution and Characteristics of Carbonate and Elementary Geochemistry of Profile TT-1 in Dahyab Tso (Tai Cuo) Tibet and Its Palaeoenvironment Significance. Acta Geol. Sin. 2007, 81, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Y.; Long, A.H.; Deng, M.J.; Xie, L. Water balances of east and west lakes Balkhash and their ptimization management. J. Glaciol. 2011, 33, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Kammoun, A.; Abidi, M.; Zairi, M. Hydrochemical characteristics and groundwater quality assessment for irrigation and drinking purposes: A case of Enfidha aquifer system, Tunisia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadili, A.; Najib, S.; Mehdi, K.; Riss, J.; Makan, A.; Boutayeb, K.; Guessir, H. Hydrochemical features and mineralization processes in coastal groundwater of Oualidia, Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2016, 116, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.F.; Ma, H.Y.; Yang, J.X.; Pan, H.X.; Guo, H.W.; Wan, Q.Z.; Yong, L.L. Effects of Ecological Water Conveyance on the Hydrochemistry of a Terminal Lake in an Inland River: A Case Study of Qingtu Lake in the Shiyang River Basin. Water 2019, 11, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Y.G.; Li, Q.S.; Fang, J.H.; He, B.Y.; Fu, H.B.; Tong, Z.J. Identification of heavy metal sources in the reclaimed farmland soils of the pearl river estuary in China using a multivariate geostatistical approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 105, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Singh, N.; Mazhar, S.N. Hydrochemical characteristics of the groundwater in Trans-Yamuna Alluvial aquifer, Palwal District, Haryana, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şehnaz, Ş.; Şener, E.; Davraz, A.; Varol, S. Hydrogeological and hydrochemical investigation in the Burdur Saline Lake Basin, southwest Turkey. Geochemistry 2019, 80, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Shi, L. Source identification of mine water inrush: A discussion on the application of hydrochemical method. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Z.I.; Gharbi, A.; Zairi, M. Evaluation of groundwater quality in intensive irrigated zone of Northeastern Tunisia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100482. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, M.; Rai, S.C. Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using water quality index in semi arid region of India. J. Geol. Soc. India 2020, 95, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.H. 2022 Government Work Report of Ali Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region; Tibet Daily: Lhasa, China, 2022; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Huntington, E. Pangong: A glacial lake in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geol. 1906, 14, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doneen, L.D. Water Quality for Agriculture, Department of Irrigation; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1964; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of The United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, H. Groundwater hydrology (McGraw-Hill Series in Water Resources and Environmental Engineering Series; McGraw-Hill College: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rajmohan, N.; Masoud, M.H.Z.; Niyazi, B.a.M. Assessment of groundwater quality and associated health risk in the arid environment, Western Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9628–9646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, L. Classification and Use of Irrigation Waters; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1955; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A.; Al-Ruwaih, F.; Shehata, M. Hydrogeochemical processes operating within the main aquifers of Kuwait. J. Arid Environ. 1999, 42, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample Type | pH | TDS | TH | EC | K+ | Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | Cl− | SO42− | HCO3− | NO3− | F− | Fe | Mn | As | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glacier (n = 3) | min | 6.6 | 13 | 9 | 23 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 3.08 | 0.22 | 1.04 | 1.96 | 6.67 | 0.18 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| max | 7.6 | 25 | 12 | 43 | 0.26 | 0.66 | 3.66 | 0.58 | 1.25 | 2.83 | 8.00 | 0.64 | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
| Ave | 7.2 | 20 | 10 | 35 | 0.20 | 0.49 | 3.44 | 0.36 | 1.12 | 2.38 | 7.56 | 0.35 | - | - | - | - | |
| CV | 6 | 27 | 10 | 24 | 24 | 36 | 7 | 43 | 8 | 15 | 8 | 60 | - | - | - | - | |
| River water (n = 24) | min | 7.1 | 81 | 58 | 145 | 0.41 | 1.41 | 10.40 | 3.23 | 1.76 | 7.63 | 52.20 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| max | 8.5 | 438 | 467 | 779 | 6.31 | 65.60 | 88.50 | 52.06 | 50.60 | 132.62 | 427.50 | 63.83 | 0.7 | 0.138 | 0.398 | 0.011 | |
| Ave | 7.8 | 282 | 196 | 498 | 2.28 | 26.98 | 39.93 | 19.89 | 27.65 | 31.89 | 211.56 | 7.68 | 0.2 | 0.044 | 0.115 | 0.005 | |
| CV | 5 | 39 | 47 | 39 | 52 | 61 | 50 | 54 | 54 | 90 | 47 | 213 | 87 | 82 | 143 | 68 | |
| Lake water (n = 14) | min | 8.1 | 406 | 258 | 385 | 1.88 | 46.30 | 6.91 | 14.60 | 3.35 | 38.50 | 168.0 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.002 |
| max | 8.5 | 4491 | 2854 | 7861 | 83.10 | 1089.0 | 39.80 | 266.40 | 1163.60 | 1004.00 | 1092.0 | 1.02 | ND | 0.091 | 0.010 | 0.044 | |
| Ave | 8.4 | 2606 | 1573 | 4546 | 37.85 | 638.31 | 15.84 | 134.06 | 618.50 | 605.25 | 700.64 | 0.10 | - | 0.043 | 0.003 | 0.020 | |
| CV | 1 | 62 | 43 | 61 | 73 | 68 | 56 | 58 | 69 | 65 | 52 | 278 | - | 60 | 76 | 63 | |
| Groundwater (n = 19) | min | 6.8 | 124 | 79 | 220 | 0.94 | 3.10 | 12.33 | 7.43 | 3.40 | 0.33 | 66.50 | 1.09 | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| max | 8.4 | 972 | 754 | 1706 | 23.44 | 184.0 | 180.00 | 93.50 | 256.00 | 528.00 | 581.70 | 68.57 | 1.5 | 0.224 | 0.441 | 0.003 | |
| Ave | 7.7 | 414 | 302 | 729 | 5.79 | 45.75 | 66.79 | 32.98 | 49.52 | 92.43 | 287.19 | 28.83 | 0.5 | 0.060 | 0.127 | 0.002 | |
| CV | 5 | 63 | 61 | 62 | 94 | 96 | 75 | 70 | 132 | 134 | 53 | 68 | 90 | 124 | 117 | 16 | |
| Jieze salt lake [48] | - | - | - | - | 18,149 | 89,232 | 115 | 28,961 | 142,324 | 127,351 | 4054 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Taicuo salt lake [49] | - | - | - | - | 95 ± 37 | 1563 ± 887 | 1.6 ± 1.3 | 133 ± 12 | 1773 ± 653 | 628 ± 227 | 805 ± 413 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| WHO limit [40] | - | 1000 | 500 | - | - | 200 | - | - | 250 | 250 | - | 50 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.01 | |
| Elements | Component | |
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | |
| K+ | 0.305 | 0.041 |
| Na+ | 0.317 | 0.012 |
| Ca2+ | −0.081 | 0.676 |
| Mg2+ | 0.312 | 0.115 |
| Cl− | 0.317 | 0.034 |
| SO42− | 0.311 | 0.102 |
| HCO3− | 0.300 | 0.172 |
| NO3− | −0.079 | 0.636 |
| TDS | 0.317 | 0.041 |
| EC | 0.318 | 0.041 |
| TH | 0.302 | 0.047 |
| pH | 0.182 | −0.248 |
| As | 0.289 | −0.126 |
| Eigenvalue | 9.801 | 1.767 |
| Variance (%) | 75.393 | 13.593 |
| Parameters | Weight | Relative Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 2 | 0.047 |
| Cl− | 4 | 0.093 |
| SO42− | 3 | 0.070 |
| NO3− | 5 | 0.116 |
| TDS | 5 | 0.116 |
| pH | 3 | 0.070 |
| As | 5 | 0.116 |
| TH | 3 | 0.070 |
| Fe | 4 | 0.093 |
| Mn | 4 | 0.093 |
| F− | 5 | 0.116 |
| IWQ Parameters and Equations | Irrigation Problem | Degree of Restriction on Use | Number of Samples (%) | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | Slight to Moderate | Severe | None | Slight to Moderate | Severe | |||
| EC (μS/cm) | Salinty | <700 | 700~3000 | >3000 | 35 (58%) | 17 (28%) | 8 (13%) | [43] |
| SAR = | Permeability | >700 | 700~200 | <200 | 51 (85%) | 1 (2%) | 8 (13%) | [65] [43] |
| PI = | <25 | 25~75 | >75 | 19 (32%) | 41 (68%) | 0 | [63] | |
| MHR = | <50 | >50 | 33 (55%) | - | 27 (45%) | [64] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.; Yan, B.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Feng, G.; Zhang, K.; Gong, K. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Irrigation and Drinking Water in Bangong Co Lake Watershed in Northwest Tibetan Plateau. Water 2023, 15, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142655
Shao Y, Yan B, Liu L, Yu X, Feng G, Zhang K, Gong K. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Irrigation and Drinking Water in Bangong Co Lake Watershed in Northwest Tibetan Plateau. Water. 2023; 15(14):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142655
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Yuxiang, Buqing Yan, Lubaiyang Liu, Xiao Yu, Gang Feng, Kun Zhang, and Kang Gong. 2023. "Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Irrigation and Drinking Water in Bangong Co Lake Watershed in Northwest Tibetan Plateau" Water 15, no. 14: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142655
APA StyleShao, Y., Yan, B., Liu, L., Yu, X., Feng, G., Zhang, K., & Gong, K. (2023). Hydrochemical Characteristics and Quality Evaluation of Irrigation and Drinking Water in Bangong Co Lake Watershed in Northwest Tibetan Plateau. Water, 15(14), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142655








