Sustainability Perspective of Minjiang Estuary Coastal Fisheries Management—Estimation of Fish Richness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Design and Case Selection
2.2. Survey Site and Sampling Method
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Non-Parametric Estimation of Fish Species Richness
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Fish Species Richness
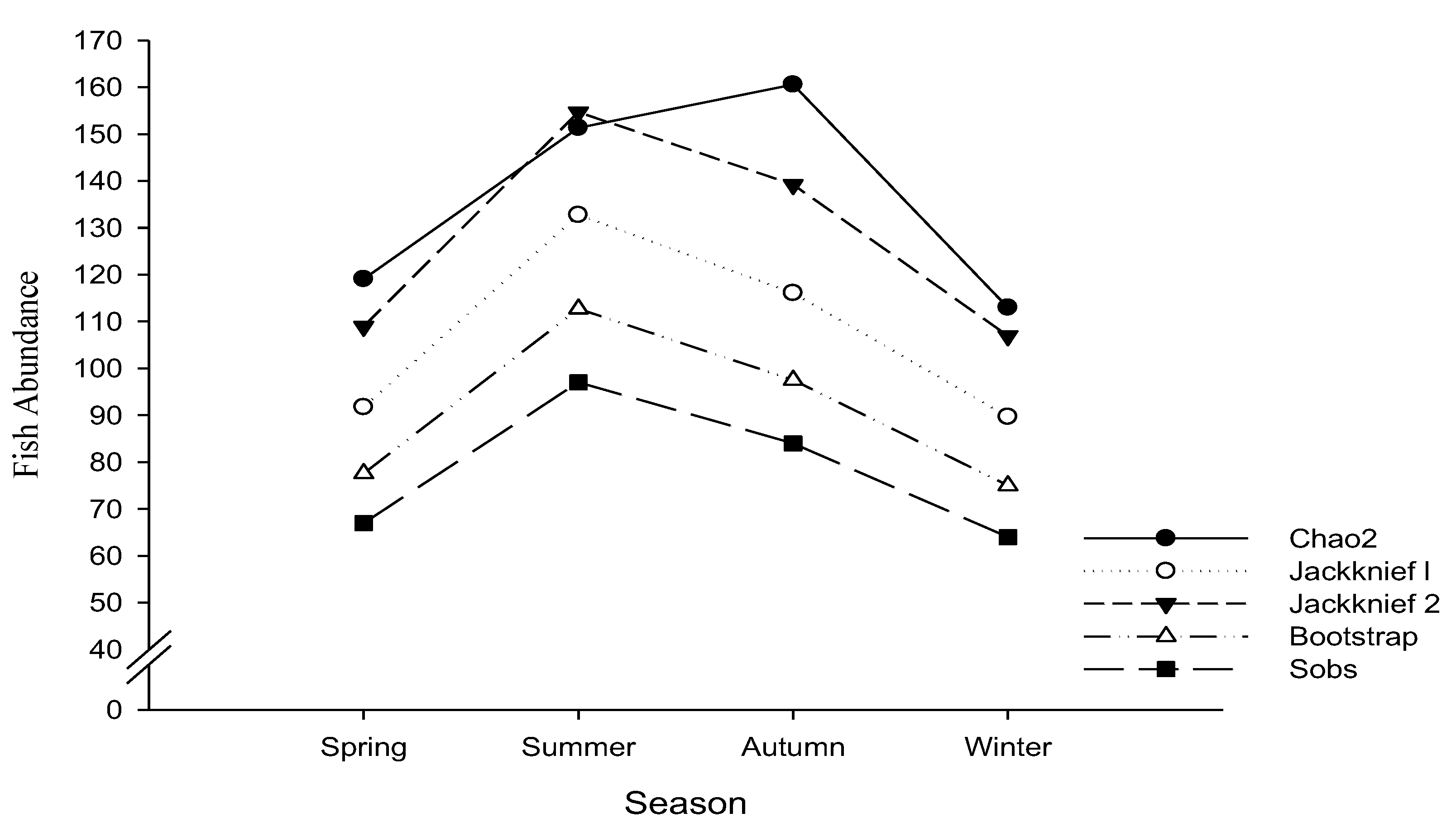
3.2. Changes in Fish Species Richness across Seasons
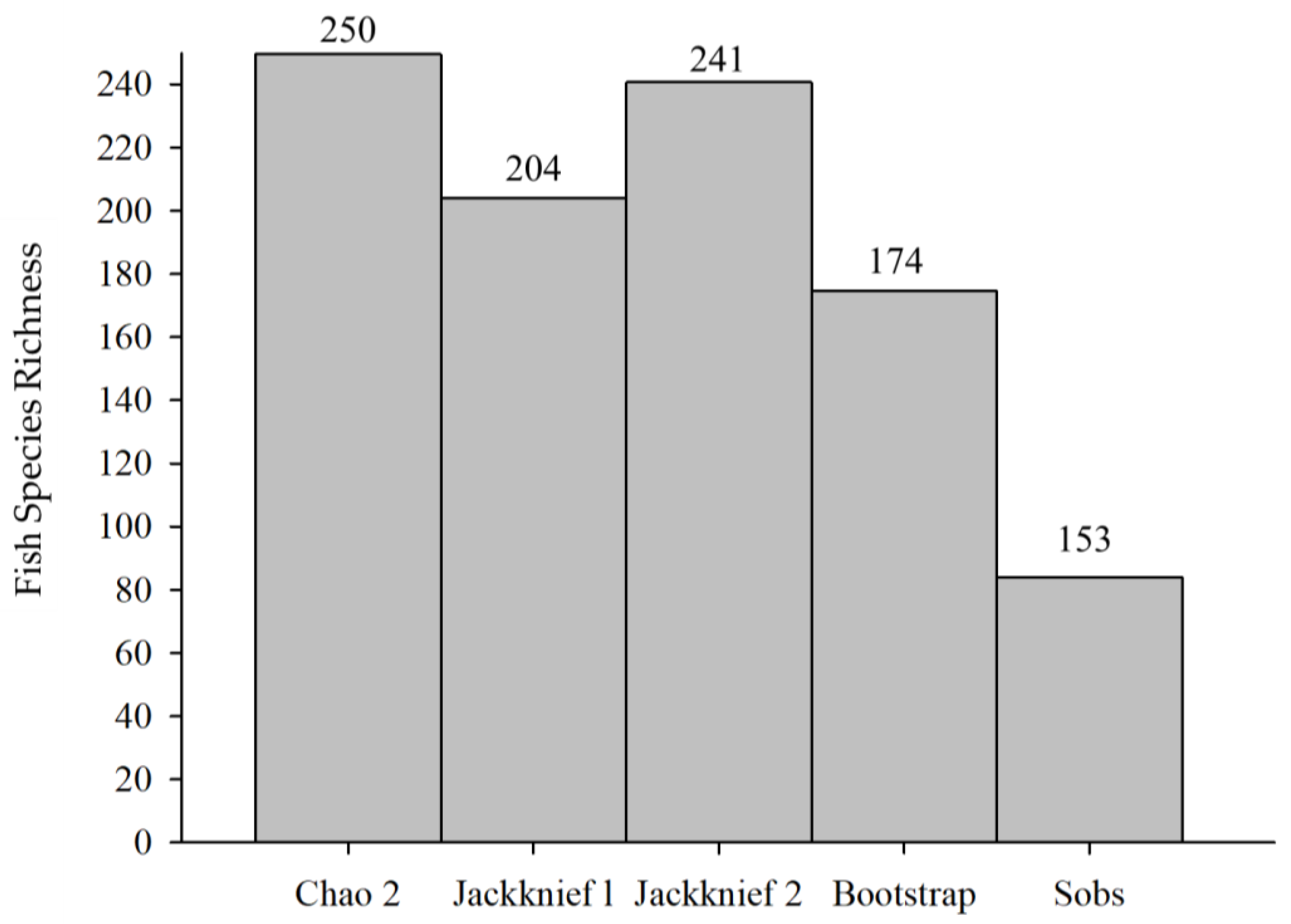
3.3. Non-Parameter Estimation of Fish Species Richness
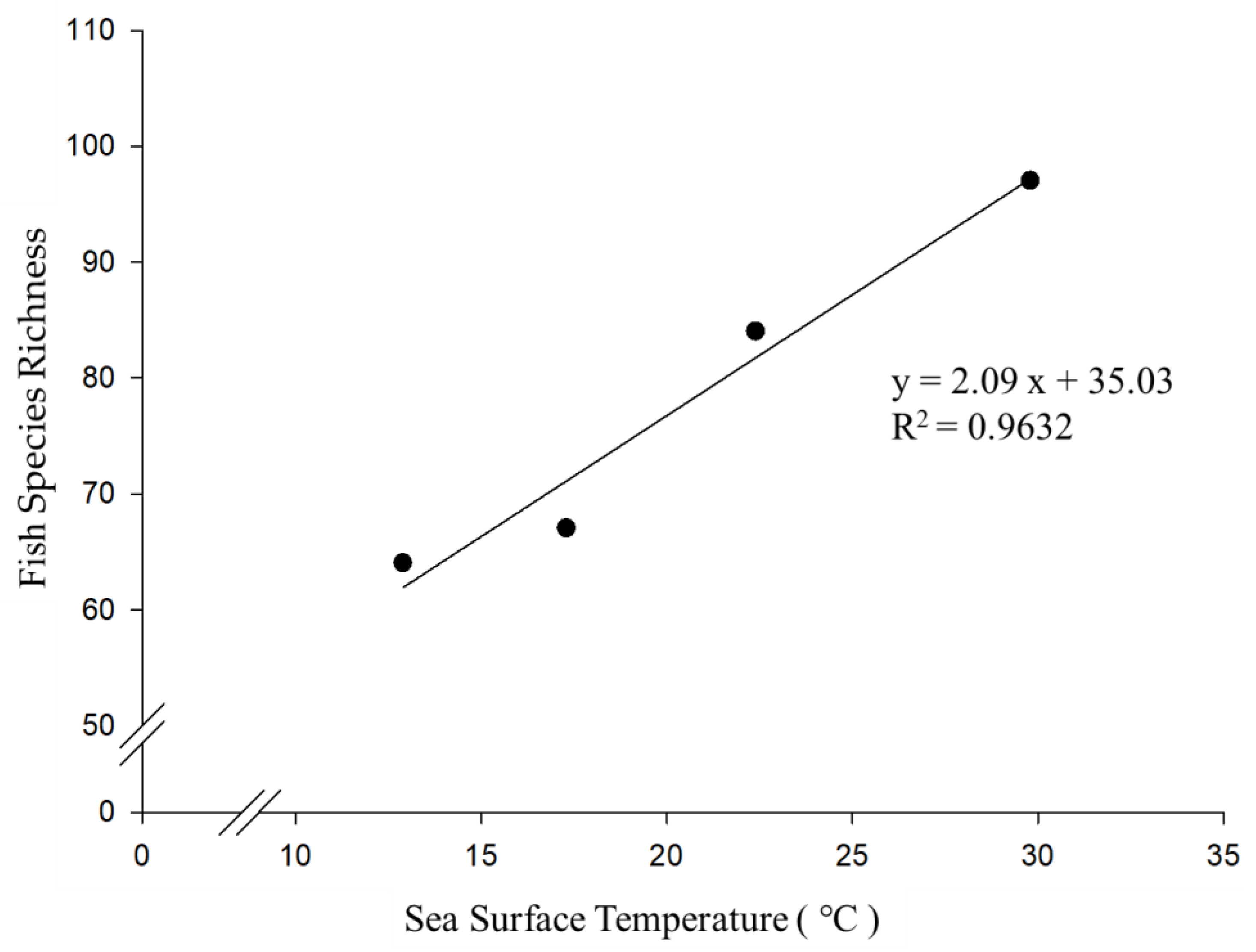
3.4. The Relationship between Fish Richness and Sampling Location
4. Discussion
4.1. The Role of Non-Parametric Estimates of Fish Species Richness
4.2. Data Representativeness and Implications for Fish Species Richness Estimates
4.3. Formulate a Strategy for the Protection of Regional Species
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larsson, T.B.; Angelstam, P.; Balent, G.; Barbati, A.; Bijlsma, R.J.; Boncina, A.; Bradshaw, R.; Bücking, W.; Ciancio, O.; Corona, P.; et al. Biodiversity evaluation tools for European forests. In Biodiversity Evaluation Tools for European Forests; Ecological Bulletins: Oxford, UK, 2001; Volume 50, p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- Sahney, S.; Benton, M.; Ferry, P.A. Links between global taxonomic diversity, ecological diversity and the expansion of vertebrates on land. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.J.; Shih, Y.J.; Shih, C.H.; Wang, J.Q.; Huang, L.M.; Tsai, S.C. Developing a model to select indicator species based on individual species’ contributions to biodiversity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, A.K. Save those molecules! Molecular biodiversity and life. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ren, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y. Sampling intensity influences the estimation of functional diversity indices of fish communities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotov, A.A.; Van Damme, K. Species richness and diversity of aquatic ecosystems: Lessons from a special issue. Water 2022, 14, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Spicer, J.I. Biodiversity: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, A.J. Species diversity or biodiversity? J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 75, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, B.A.; Komarova, A.S.; Rozanova, O.L.; Golubtsov, A.S. Unexpected diversity of feeding modes among chisel-mouthed ethiopian Labeobarbus (Cyprinidae). Water 2021, 13, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.C. Extinction: Are ecologists crying wolf. Science 1991, 253, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberón, J.; Llorente, J. The use of species accumulation functions for the prediction of species richness. Conserv. Biol. 1993, 7, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.C. Strategies for the Assessment of Fish Species Composition in Great Lakes Streams. Master’s Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenegger, J. Species as the basic units in evolution and biodiversity: Recognition of species in the Recent and geological past as exemplified by larger foraminifera. Gondwana Res. 2014, 25, 707–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Z. Species and species diversity. Biodivers. Sci. 2000, 8, 215–226. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gáborčík, N.; Shiyomi, M. A probability distribution model of small-scale species richness in plant communities. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 33, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yamamura, Y.; Hori, Y.; Shiyomi, M.; Yasuda, T.; Zhou, H.K.; Li, Y.N.; Tang, Y.H. Small-scale species richness and its spatial variation in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.P.; Buckley, H.L.; Urlich, S.C.; Stewart, G.H.; Geritzlehner, J. Small-scale species richness in forest canopy gaps: The role of niche limation versus the size of the species pool. J. Veg. Sci. 2008, 9, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Larsen, D.P.; White, D. Estimating regional species richness using a limited number of survey units. Ecoscience 2004, 11, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of world is larger river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, A.E.; Aiello-Lammeens, M.E.; Fisher-Reid, M.C.; Xia, H.; Karanewsky, C.J.; Ryu, H.Y.; Sbeglia, G.C.; Spagnolo, F.; Waldron, J.B.; Warsi, O. How does climate change cause extinction? Proc. R. Soc. B 2013, 280, 20121890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnosky, A.D.; Matzke, N.; Tomiya, S.; Wogan, G.; Swartz, B.; Quenta, T.B.; Marshal, C.; Mcguire, J.L.; Lindsey, E.L.; Maguire, K.C. Has the Earth’s sixth mass extinction already arrived. Nature 2011, 471, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.A.; Hayes, D.B. A comparison of fish community composition of headwater and adventitious streams in a cold water river system. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2006, 21, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, S.Y. A comparison of the macro-invertebrate communities in two Malaysian streams. J. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 20, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falke, J.A.; Gido, K.B. Spatial effects of reservoirs on fish assemblages in Great Plains streams in Kansas, USA. River Res. Appl. 2010, 22, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angermeier, P.L.; Smogor, R.A. Estimating number of species and relative abundances in stream-fish communities: Effects of sampling effort and discontinuous spatial distributions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 52, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackell, N.L.; Frank, K.T. Marine fish diversity on the Scotian Shelf, Canada. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2003, 13, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.D.; Conroy, M.J. Estimation of species richness. In Measuring and Monitoring Biodiversity—Standard Methods for Mammals; Wilson, D.E., Cole, J.D., Rudran, R., Foster, M., Eds.; Smithsonian Institution Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Holtrop, A.M.; Cao, Y.; Dolan, C.R. Estimating sampling effort required for characterizing species richness and site-to-site similarity in fish assemblage surveys of wadeable Illinois streams. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1421–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paller, M.H. Estimating fish species richness across multiple watersheds. Diversity 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillot, D.; Laune, J.; Tomasini, J.A.; Aliaume, C.; Brehmer, P.; Eric Dutrieux, E.; Do Chi, T. Assessment of coastal lagoon quality with taxonomic diversity indices of fish, zoobenthos and macrophyte communities. Hydrobiologia 2005, 550, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. A further biodiversity index applicable to species lists: Variation in taxonomic distinctness. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 216, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Arge, R.D.; Groot, R.D.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Higgins, T.G.; Ferraro, S.P.; Dantin, D.D.; Jordan, S.J.; Chintala, M.M. Habitat scale mapping of fisheries ecosystem service values in estuaries. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee of Comprehensive Survey of Island Resources in Fujian. A Comprehensive Investigation Report on Island Resources in Fujian Province; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P. Ecological Environment and Fishery Resources in Minjiang Estuary; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Q.; Huang, L.M.; Li, J.; Chen, X.J. Evaluation on protection priority of main fish species caught by trawler in the Minjiang River Estuary and adjacent waters. Mar. Fish. 2017, 39, 481–489. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L. Comparison of fish fauna of two different waters (Minjiang estuary and Xingha bay) of the east China sea during spring and summer. Biodivers. Sci. 2011, 19, 79–84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.L. Comparison of fish density between the Minjiang estuary and Xingha bay during spring and summer. J. Fish. China 2010, 34, 1395–1403. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; He, X.B.; Zhao, C.X.; Li, J.; Kang, B. Functional diversity of fishes in the Minjiang Estuary, Southeast China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 3589–3595. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L. Nekton Resources and Community Diversity in the Min River Estuary and Its Adjacent Waters, Fujian Province, China; Xiamen University: Xiamen, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhao, W.W.; Weng, Z.T.; Xu, C.Y.; Zhuang, Z.D.; Cai, J.D.; Xie, S.Q.; Shen, C.C. Research on characteristics of community structure of fish in Minjiang Estuary and adjacent waters in spring and summer. J. Fish. Res. 2022, 44, 467–476. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T. Dynamic monitoring of the water area changes in Minjiang Port using remote sensing technology. Geol. Fujian 2013, 32, 243–248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xie, Y.J.; Liu, Q.D.; Jin, X.S. Current fisheries resources assessment in the Minjiang River Estuary and its neighboring waters. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2010, 29, 142–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Băncilă, R.I.; Cogălniceanu, D.; Plăiasu, R.; Tudor, M.; Cazacu, C.; Hartel, T. Comparative performance of incidence-based estimators of species richness in temperate zone herpetofauna inventories. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Saminathan, R.; Chang, C.W. Uncertainty assessment of non-normal emission estimates using non-parametric bootstrap confidence intervals. J. Environ. Inform. 2017, 28, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.P.; Belle, V.G. Nonparametric estimation of species richness. Biometrics 1984, 40, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, B.A.; Morand, S. Comparative performance of species richness estimation methods. Parasitology 1998, 116, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleece, N.; Gage, J.D.G.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Paterson, G.L.J. BioDiversity Professional Statistics Analysis Software; Scottish Association for Marine Science and the Natural History Museum: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A. Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand. J. Stat. 1984, 11, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.R.; Ma, K.P.; Zhou, W.N.; Zhang, X.S. Measurement Methods of Biodiversity IV, Application of Knife Cutting Method and Self-help Method in Biodiversity Measurement. Biodivers. Sci. 1997, 5, 61–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Colwell, R.K.; Coddington, J.A. Estimating terrestrial biodiversity through extrapolation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1994, 345, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.N.; Chiu, C.H. Nonparametric Estimation and Comparison of Species Richness. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujian Provincial Fisheries Division Office. Fishery Resources in Fujian Province; Fujian Science and Technology Press: Fuzhou, China, 1988; pp. 230–258. [Google Scholar]
- Tittensor, D.P.; Mora, C.; Jetz, W.; Lotze, H.K.; Ricard, D.; Berghe, E.V.; Worm, B. Global patterns and predictors of marine biodiversity across taxa. Nature 2010, 466, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parravicini, V.; Kulbicki, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Friedlander, A.M.; Ari-as-Gonzalez, J.E.; Chabanet, P.; Floeter, S.R.; Myers, R.; Vigliola, L.; D’Agata, S.; et al. Global patterns and predictors of tropical reef fish species richness. Ecography 2013, 36, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisseuil, C.; Cornu, J.F.; Beauchard, O.; Brosse, S.; Darwall, W.; Holland, R. Global diversity patterns and cross-taxa convergence in freshwater systems. J. Anim. Ecol. 2013, 82, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, R.P.; Henriques, S.; Francßa, S.; Pasquaud, S.; Cardoso, I.; La-borde, M.; Cabr, H.N. Global patterns and predictors of fish species richness in estuaries. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.R.; Ma, K.P. Measurement of biotic community diversity V. methods for estimating the number of species in a community. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1997, 06, 601–610. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pasquaud, S.; Vasconcelos, R.P.; Susana, F.; Henriques, S.; Jose, C.M.; Cabral, H. Worldwide patterns of fish biodiversity in estuaries: Effect of global vs. local factors. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 154, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, J.; Rapacciuolo, G.; Costa, G.C.; Graham, C.H.; Brooks, T.M.; Young, B.E.; Radeloff, V.C.; Behm, J.E.; Helmus, M.R.; Hedges, S.B. Evolutionary time drives global tetrapod diversity. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, L.; Mics, F. Introductory Chapter: Factors that affect biodiversity and species richness of ecosystems—A review. In Biodiversity of Ecosystems; Hufnagel, L., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/82587 (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Súarez, Y.R.; Valério, S.B.; Tondado, K.K.; Florentino, A.C.; Felipe, T.R.A.; Ximenes, L.Q.L.; Lourenço, L.S. Fish species diversity in headwaters streams of Paraguay and Paraná Basins. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2007, 50, 1678–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, E.B.; Hacker, S.D.; Kennedy, C.; Koch, E.W.; Stier, A.C.; Silliman, B.B. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services. Ecol. Monogr. 2011, 2, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhuang, P.; Zhan, L.Z.; Hou, J.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, J. Composition and diversity of fish species in the coast of the Yangtze River estuary. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. 2010, 16, 817–821. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lotze, H.K.; Lenihan, H.S.; Bourque, B.J.; Bradbury, R.H.; Cooke, R.G.; Kay, M.C.; Kidwell, S.M.; Kirby, M.X.; Peterson, C.H.; Jackson, J.B.C. Depletion, degradation, and recovery potential of estuaries and coastal seas. Science 2006, 312, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Do Chi, T.; Laugier, T.; Galgani, F.; Laloë, F.; Darnaude, A.M.; Fian-drino, A.; Mouillot, D. Field investigations and multi-indicators for shallow water lagoon management: Perspective for societal benefit. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. 2011, 21, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, P.; Laugier, T.; Kantoussan, J.; Galgani, F.; Mouillot, D. Does coastal lagoon habitat quality affect fish growth rate and their recruitment? Insights from fishing and acoustic surveys. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 126, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Xu, H.G.; Cao, M.C.; Zhang, D.Q.; Wu, W.W. Advances in the study of species richness pattern. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2011, 27, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Brehmer, P.; Do Chi, T.; Mouillot, D. Amphidromous fish school migration revealed by combining fixed sonar monitoring (horizontal beaming) with fishing data. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2006, 334, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzen, K.; Agnalt, A.L.; Blankenship, H.L.; Hines, A.H.; Leber, K.M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Taylor, M.D. Evolving context and maturing science: Aquaculture-based enhancement and restoration enter the marine fisheries management toolbox. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2013, 21, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Shih, Y.J.; Huang, L.M.; Li, J.; Li, W.W.; Shih, C.H.; Chu, T.J. Evaluating the effects related to restocking and stock replenishment of Penaeus penicillatus in the Xiamen Bay, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | No. of Site | Spring (Per Season) | Summer (Per Season) | Autumn (Per Season) | Winter (Per Season) | Total | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990–1991 | / | 18 | 38 | 32 | 30 | 71 | ECCSIR [34] 1 |
| 2006 | 12 | 52 | 79 | 70 | 49 | 129 | Zhuang [35] |
| 2006–2007 | 12 | 67 | 97 | 84 | 64 | 153 | Wang et al. [36] |
| 2008 | 12 | 36 | 57 | / | / | 77 | Xu [37,38] |
| 2015 | 14 | 68 | 79 | 51 | 50 | 136 | Zhuang [35] |
| 2016 | 14 | 51 | 88 | 68 | 44 | 125 | Feng et al. [39] |
| 2017 | 11 | 36 | 51 | 41 | 31 | 111 | Zhang [40] |
| 2018 | 11 | 32 | 49 | 31 | 31 | 113 | Zhang [40] |
| 2021 | 14–16 | 58 | 91 | / | / | 104 | Liu et al. [41] |
| Class | Order | Family | Genus | Species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chondrichthyes | Orectolobiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Rajiformes | 3 | 3 | 4 | |
| Myliobatiformes | 2 | 2 | 6 | |
| Torpediniformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Actinopterygii | Clupeiformes | 2 | 8 | 16 |
| Myctophiformes | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Anguilliformes | 5 | 6 | 6 | |
| Siluriformes | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Gadiformes | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Mugiliformes | 2 | 4 | 7 | |
| Perciformes | 29 | 61 | 81 | |
| Pleuronectiformes | 3 | 4 | 14 | |
| Tetraodontiformes | 2 | 3 | 7 | |
| Lophiiformes | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Total | 57 | 101 | 153 |
| Cruise | Season | Surveyed Period | Site No. | Species No. | Species No. 1 | Species No. 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Summer | 2 September 2006–4 September 2006 | 12 | 97 | 23 | 6 |
| 2 | Winter | 12 January 2007–15 January 2007 | 12 | 64 | 12 | 7 |
| 3 | Spring | 15 April 2007–19 April 2007 | 12 | 67 | 4 | 6 |
| 4 | Autumn | 19 October 2007–24 October 2007 | 12 | 84 | 13 | 5 |
| Total | 48 | 153 | 52 | 14 |
| Site | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MJ1 | 17 | 30 | 21 | 25 | 54 |
| MJ2 | 13 | 32 | 28 | 8 | 49 |
| MJ3 | 17 | 41 | 34 | 23 | 63 |
| MJ4 | 30 | 20 | 25 | 17 | 65 |
| MJ5 | 30 | 20 | 17 | 15 | 51 |
| MJ6 | 20 | 22 | 22 | 24 | 60 |
| MJ7 | 16 | 26 | 28 | 16 | 54 |
| MJ8 | 14 | 27 | 25 | 21 | 54 |
| MJ9 | 18 | 17 | 25 | 29 | 48 |
| MJ10 | 15 | 33 | 32 | 15 | 68 |
| MJ11 | 18 | 22 | 27 | 22 | 54 |
| MJ12 | 16 | 29 | 24 | 25 | 62 |
| Total | 67 | 97 | 84 | 64 | 153 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.-Q.; Li, J.; Shih, Y.-J.; Huang, L.-M.; Wang, X.-R.; Chu, T.-J. Sustainability Perspective of Minjiang Estuary Coastal Fisheries Management—Estimation of Fish Richness. Water 2023, 15, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142648
Wang J-Q, Li J, Shih Y-J, Huang L-M, Wang X-R, Chu T-J. Sustainability Perspective of Minjiang Estuary Coastal Fisheries Management—Estimation of Fish Richness. Water. 2023; 15(14):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142648
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jia-Qiao, Jun Li, Yi-Jia Shih, Liang-Min Huang, Xin-Ruo Wang, and Ta-Jen Chu. 2023. "Sustainability Perspective of Minjiang Estuary Coastal Fisheries Management—Estimation of Fish Richness" Water 15, no. 14: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142648
APA StyleWang, J.-Q., Li, J., Shih, Y.-J., Huang, L.-M., Wang, X.-R., & Chu, T.-J. (2023). Sustainability Perspective of Minjiang Estuary Coastal Fisheries Management—Estimation of Fish Richness. Water, 15(14), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15142648







