Water Environmental Functional Zoning at County Level and Environmental Contamination Carrying Capacity Accounting in the Mainstream of Xiaofu River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
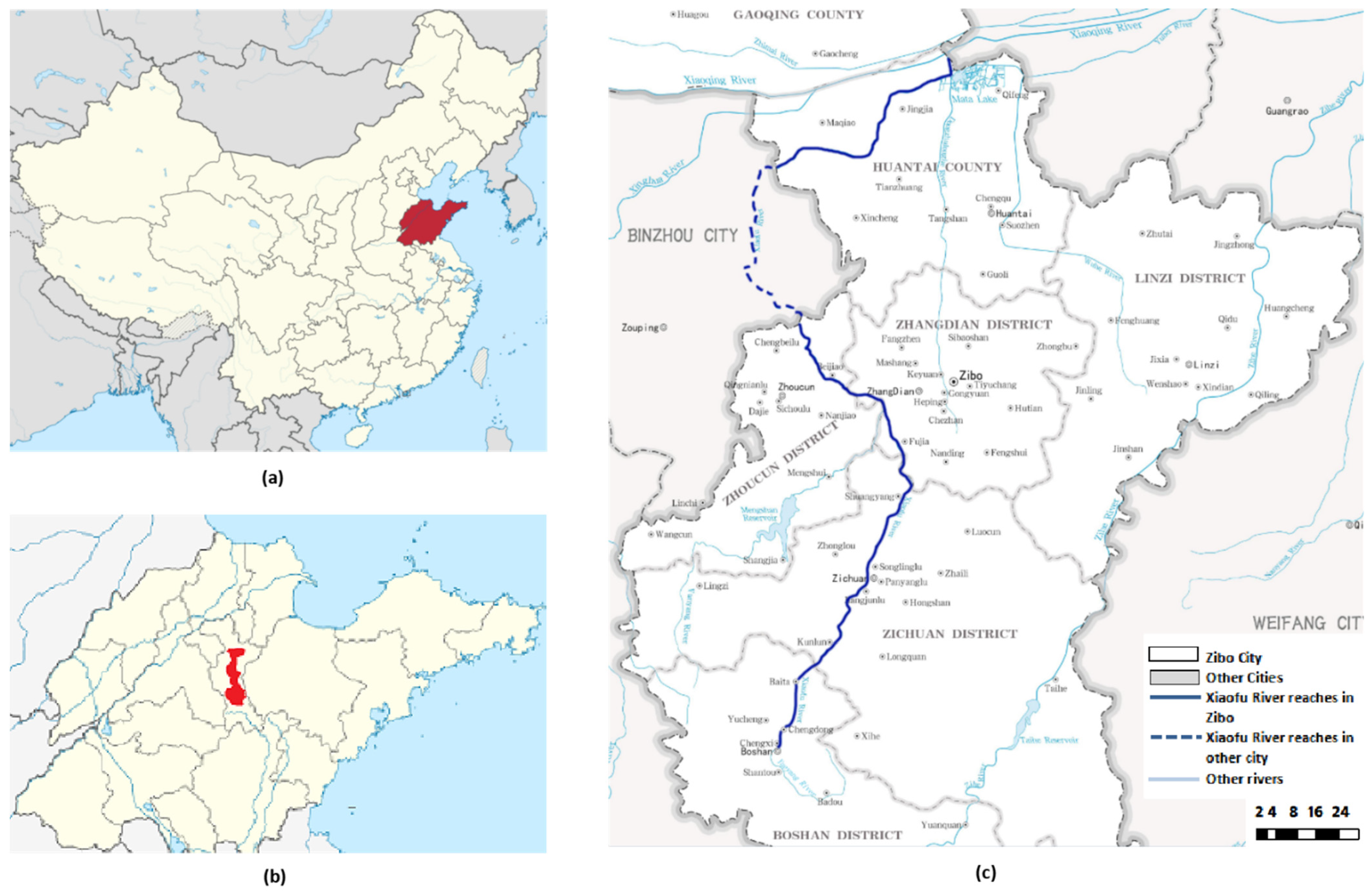
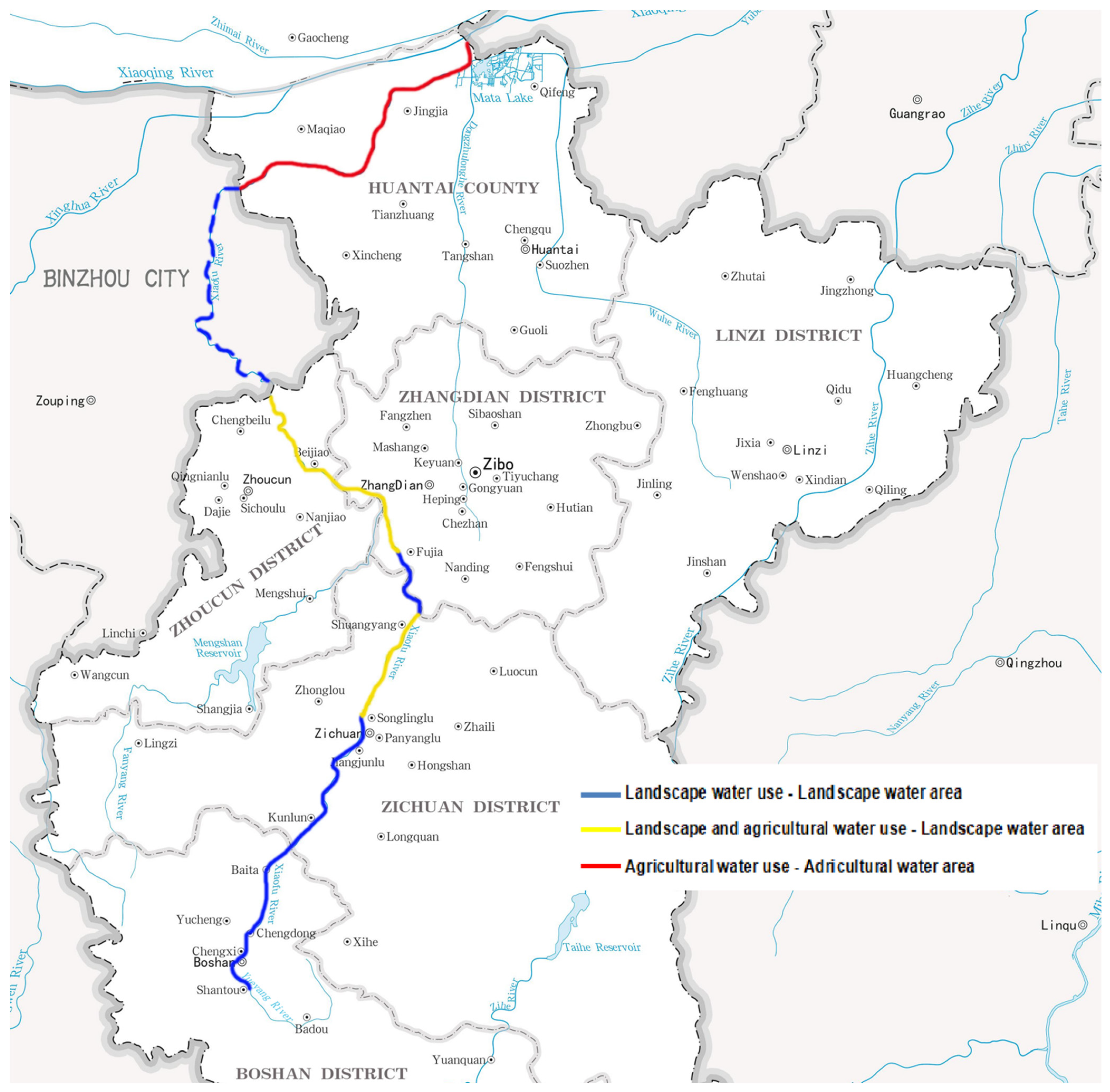
2.1. Study Area: Xiaofu River System Profile
2.2. Water Quality Data and Evaluation
2.2.1. Water Sampling and Analysis
2.2.2. Evaluation Criterion
2.2.3. Evaluation Methodology
2.3. Procedures and Methods of Regionalization
2.3.1. General Thought on Regionalization
2.3.2. Determination of Dominant Functions
2.3.3. Setting of Control Section
2.3.4. Naming of Water Functional Zoning
2.3.5. Procedures and Methods of Regionalization
2.3.6. Setting of the Water Quality Objectives
2.4. Contamination Capacity Accounting Method
2.4.1. Hydrological Parameters and Statistics
2.4.2. Water Quality Model
2.4.3. Water Quality Target Values and Pollution Factors
2.4.4. Designed Flow and Velocity of the Functional Zoning
2.4.5. Comprehensive Degradation Coefficient of Pollutants
2.4.6. Water Quality Model and Parameters
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Xiaofu River Municipal Functional Zoning Situation
3.2. Water Quality Current Situation of Xiaofu River Truck Stream
3.3. Zoning Scheme
3.3.1. First-Level Water Functional Zoning Scheme
3.3.2. Second-Level Water Functional Zoning Scheme
3.4. Contamination Capacity Accounting Results
3.5. Current Pollutant Discharge and Reduction Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Xie, G.; Cao, S.; Leng, Y.; Yu, X. The Distribution Patterns of China’s County Ecological Function. Resour. Sci. 2012, 34, 1636–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, X. Environmental function zoning for spatially differentiated environmental policies in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 255, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Thatje, S. Temperature effects on life-history traits cause challenges to the management of brachyuran crab fisheries in the Humboldt Current: A review. Fish. Res. 2018, 183, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Fu, B. Landscape functional zoning at a county level based on ecosystem services bundle: Methods comparison and management indication. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barral, M.P.; Oscar, M.N. Land-use planning based on ecosystem service assessment: A case study in the Southeast Pampas of Argentina. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 154, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.Q.; Liu, N.L.; Hu, X. Progress in research and practice of the ecological environmental space control system in China. Environ. Prot. 2019, 47, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Q.; Rozelle, S. Water governance and water use efficiency: The five principles of WUA management and performance in China. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 665–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Can Environmental Protection in Ecological Functional Zones Break Free from the Constraints of Focusing Just on Economic Benefits?—A Case Study of the Plateau Ecological Zone’s Tiamitcheen. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2018, 6, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.Z.; Mou, Y.M.; Yu, H.Y.; Hang, D.W.; Shen, H.; Huang, Y.L. Environmental function zoning at regional scale: A case study in Pinghu, China. Fourth Int. Conf. Agro-Geoinform. 2015, 7248086, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Song, Y.S.; Yang, C. Water function zoning and water environment capacity analysis on surface water in jiamusi urban area. Procedia Eng. 2012, 28, 458–463. [Google Scholar]
- Bychkov, I.V.; Gagarinova, O.V.; Orlova, I.I.; Bogdanov, V.N. Water protection zoning as an instrument of preservation for Lake Baikal. Water 2018, 10, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jafar, N.; Ahmad, N.; Ehsan, N.; Morteza, A. GIS-based agro-ecological zoning for crop suitability using fuzzy inference system in semi-arid regions. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.R. Water Function Area System in China and its Corresponding Classification. China Water Resour. 2001, 12, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Stanislav, V.; Dubrova, I.; Podlipskiy, I.; Vitaliy, V.; Kurilenko, W.S. Functional city zoning. Environmental assessment of eco-geological substance migration flows. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, X.H.; Zhang, J.Y. Thoughts on top-level design of water resources protection in China. China Water Resour. 2017, 19, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.D.; Mu, J.B. Study on Water Environmental Capacity of Rivers in Shandong Province, 1st ed.; Shandong University Publisher: Jinan, China, 2007; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, A. Spatial Variation and Contamination Assessment of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Xiaofu River. Health Environ. Res. 2013, 6, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.G.; Sun, Z.L.; Zhang, Z. Characters and Formation Reasons of Sulfate Contamination in Pore Water of Xiao Fu River Basin in Zibo City. Environ. Pollut. Control 2000, 22, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Wang, H.; Pan, J.; Li, M. Relationship between heavy metals speciation and microbial community structure in surface sediments of Xiaofu River. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.R.; Zhu, G.R.; Wang, X.Q. Study Oil Exploitation of Groundwater at Headstream Area of Xiaofu River. Geol. J. China Univ. 2001, 7, 237. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.P.; Chi, Y.Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.N. Study on the Progress and Outlook of Environmental Function Zoning. Environ. Prot. 2017, 45, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, R.K.; Gupta, V.K. A pollution attenuation coefficient concept for optimization of green belt. Atmos. Environ. 1984, 18, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J.; Shen, W.B.; Gao, K.; Liu, J.S. Study on the integrated attenuation coefficient of NH3-N in the sectors of main stream of Songhua River in Jilin Province. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2013, 13, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Water Resources. Supplementary Technical Rules for the Protection of Surface Water Resources in the Comprehensive National Water Resources Plan, 1st ed.; Ministry of Water Resources: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 30–34.
- Uluatam, S.S. Calibration of modqual for karasu river. Water Res. 1993, 27, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Water Quality Parameters | Class I | Class II | Class III | Class IV | Class V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic parameters | pH (dimensionless) | 6–9 | ||||
| Dissolved oxygen (DO)≥ | Saturation rate 90% (or 7.5) | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Permanganate index≤ | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 15 | |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD)≤ | 15 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 | |
| Five-day biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)≤ | 3 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | |
| NH3-N≤ | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | |
| Total phosphorus (TP) | 0.02 (lake/reservoir 0.01) | 0.1 (lake/reservoir 0.025) | 0.2 (lake/reservoir 0.05) | 0.3 (lake/reservoir 0.1) | 0.4 (lake/reservoir 0.4) | |
| Cu≤ | 0.01 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| Zn≤ | 0.05 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| Fluoride≤ | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Se≤ | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| As≤ | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Hg≤ | 0.00005 | 0.00005 | 0.0001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | |
| Cd≤ | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.01 | |
| Cr (hexavalent)≤ | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | |
| Pb≤ | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | |
| Cyanide≤ | 0.005 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |
| Volatile phenol≤ | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.01 | 0.1 | |
| Anionic surface activity | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |
| Sulfide≤ | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| Supplement parameters by water source area | Sulfate≤ | 250 | ||||
| Chloride≤ | 250 | |||||
| Nitrate nitrogen≤ | 10 | |||||
| Fe≤ | 0.3 | |||||
| Mn≤ | 0.1 | |||||
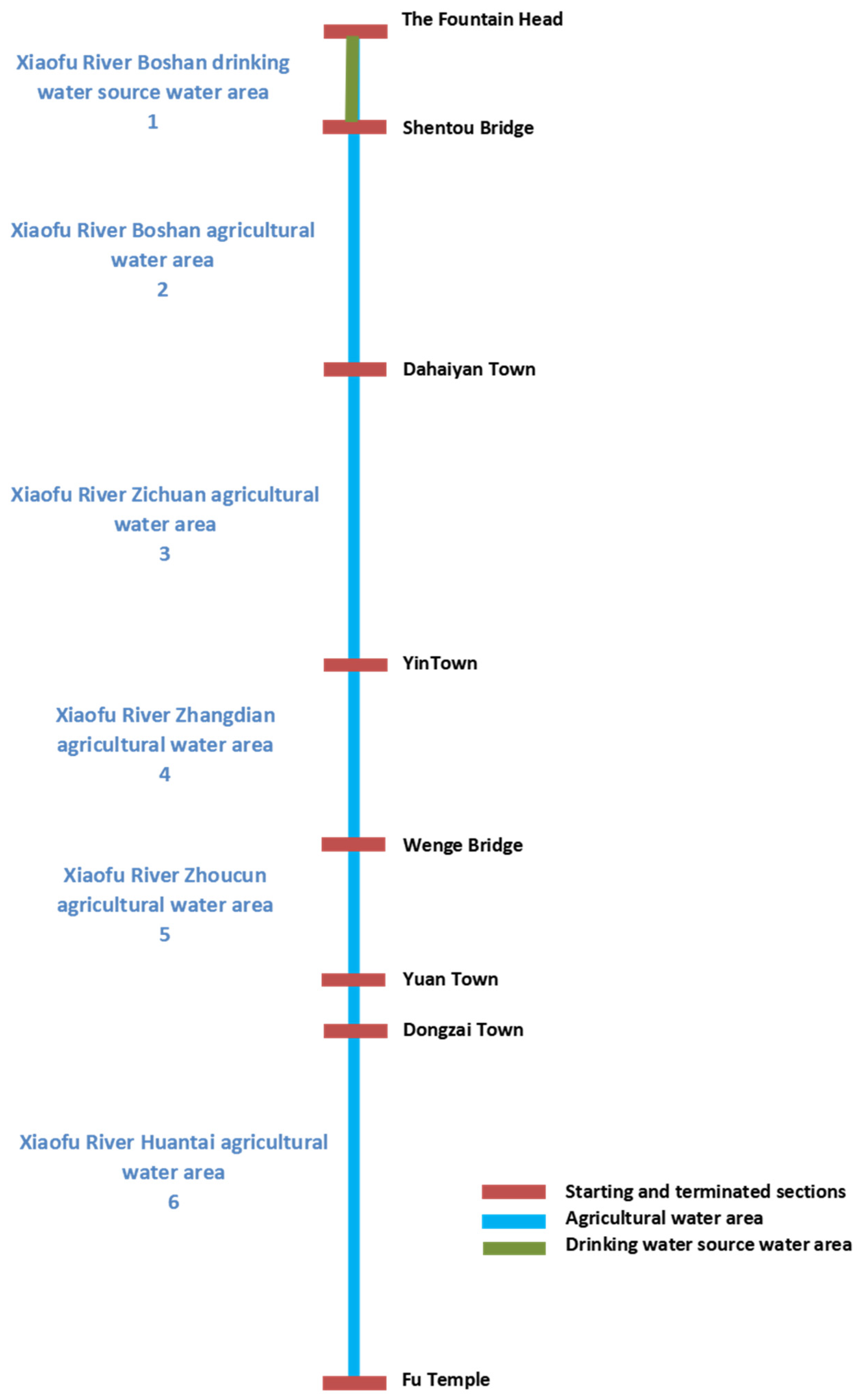
| No. | Monitoring Section | Length (km) | COD (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | Double Indexes Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linli Lake | 8 | 6.0 | 0.26 | Class III |
| 2 | Dahaiyan Town | 19 | 22.6 | 3.60 | Class V |
| 3 | Yin Town | 24 | 28.0 | 3.72 | Class IV |
| 4 | Yiji Town | 16 | 28.3 | 3.22 | Class IV |
| 5 | Yuan Town | 13 | 31.2 | 2.70 | Class V |
| 6 | Fu Temple | 29 | 37.6 | 1.38 | Class V |
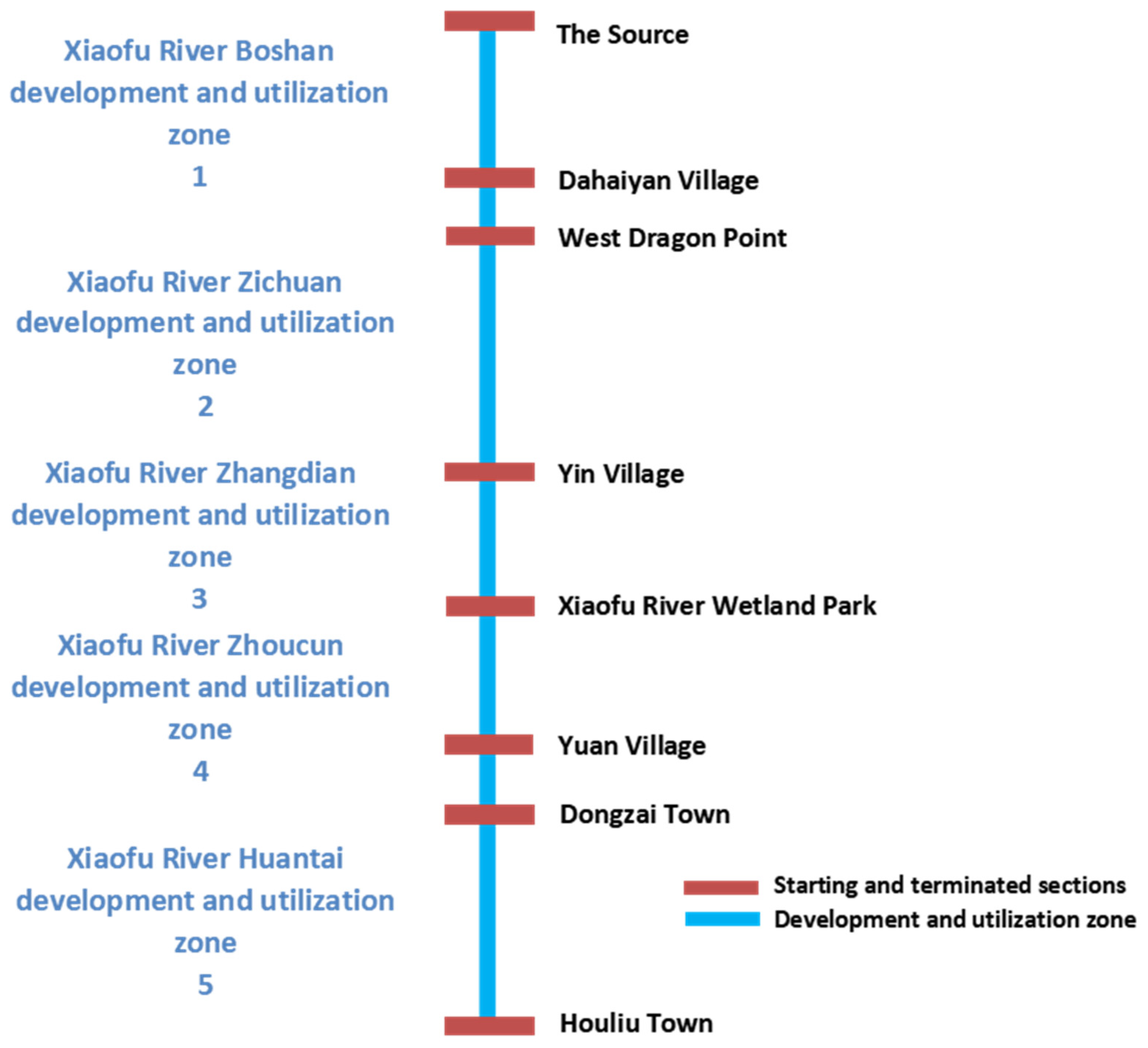
| No. | Catchment | Basin | River | Length (km) | Current Water Quality | Targeted Water Quality | Zoning Basis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Huai River | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 11.7 | IV | III–V | City-level zoning |
| 2 | Huai River | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 26.3 | V | V | City-level zoning |
| 3 | Huai River | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | Left bank: 2.6 Right bank: 8.7 | V | V | City-level zoning |
| 4 | Huai River | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 11.6 | V | V | City-level zoning |
| 5 | Huai River | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 24.8 | V | V | City-level zoning |
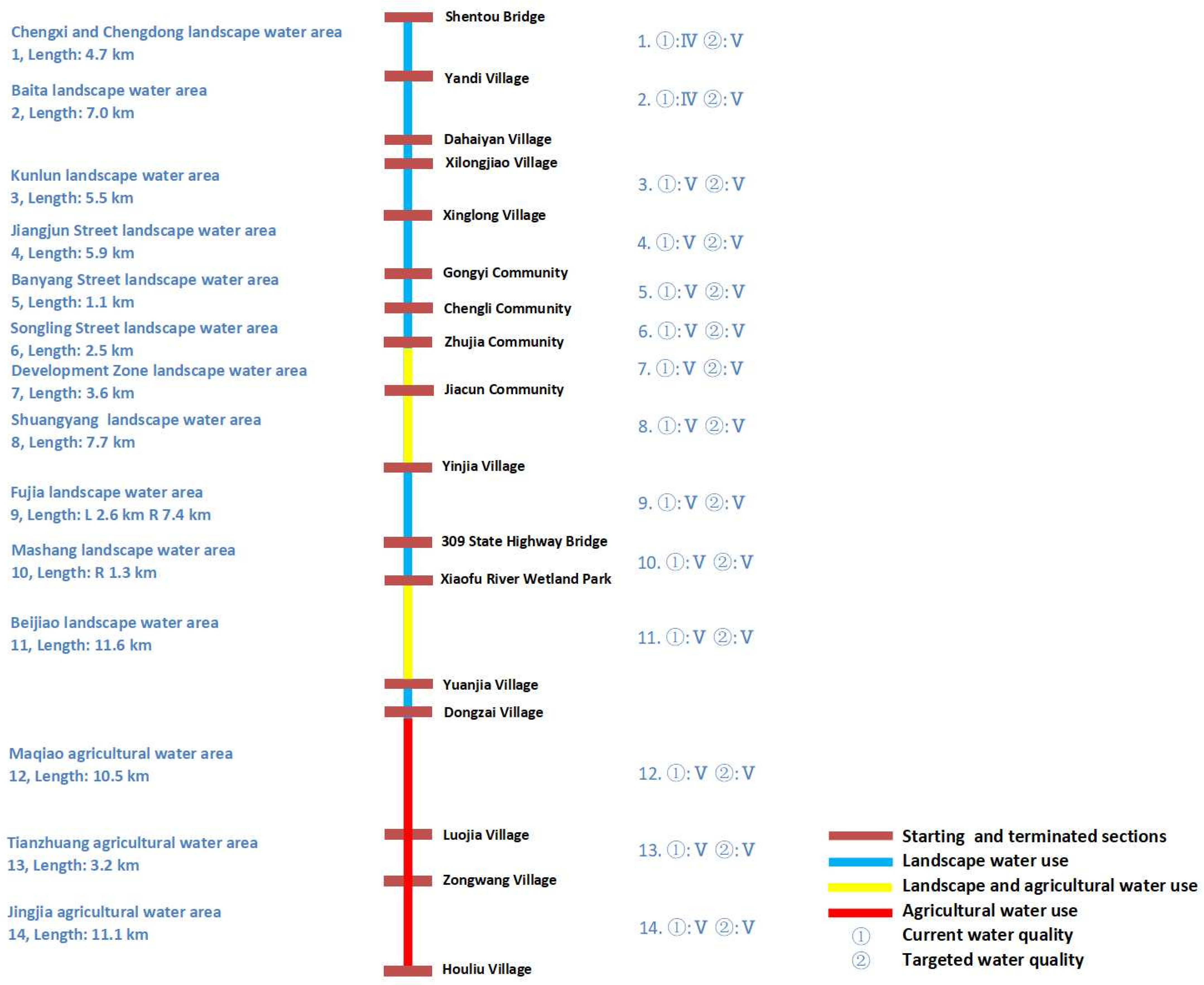
| No. | Second-Level Water Functional Zones’ Name | Basin | River | Length (km) | Targeted Water Quality | Annual Contamination Capacity (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH3-N | ||||||
| 1 | Chengxi and Chengdong landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 4.7 | V | 9.28 × 105 | 4.69 × 104 |
| 2 | Baita landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 7.0 | V | 1.94 × 105 | 9.04 × 103 |
| 3 | Kunlun landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 5.5 | V | 1.52 × 105 | 7.09 × 103 |
| 4 | Jiangjun Street landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 5.9 | V | 1.63 × 105 | 7.62 × 103 |
| 5 | Banyang Street landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 1.1 | V | 3.04 × 104 | 1.42 × 103 |
| 6 | Songling Street landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 2.5 | V | 6.91 × 104 | 3.23 × 103 |
| 7 | Development Zone landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 3.6 | V | 9.96 × 104 | 4.65 × 103 |
| 8 | Shuangyang landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 7.7 | V | 2.13 × 105 | 9.94 × 103 |
| 9 | Fujia landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | Left bank: 2.6 Right bank: 7.4 | V | 7.19 × 104 | 3.36 × 103 |
| 1.02 × 105 | 9.55 × 103 | ||||||
| 10 | Mashang landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | Right bank: 1.3 | V | 3.59 × 104 | 1.68 × 103 |
| 11 | Beijiao landscape water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 11.6 | V | 3.21 × 105 | 1.49 × 104 |
| 12 | Maqiao agricultural water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 10.5 | V | 2.91 × 105 | 1.36 × 104 |
| 13 | Tianzhuang agricultural water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 3.2 | V | 8.85 × 104 | 4.13 × 103 |
| 14 | Jingjia agricultural water area | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 11.1 | V | 3.07 × 105 | 1.43 × 104 |
| 15 | Total | Xiaoqing River | Xiaofu River | 85.7 | V | 3.07 × 106 | 1.51 × 105 |
| No. | Name of Sewage Plant | Effluent (104 m3/d) | Concentration of Emission (mg/L) | Current Pollutant Annual Discharge (kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | NH3-N | COD | NH3-N | |||
| 1 | Huanke Sewage Treatment Plant | 7.5 | 30.0 | 1.5 | 8.21 × 105 | 4.11 × 104 |
| 2 | Baita Sewage Treatment Plant | 1.5 | 30.0 | 1.5 | 1.64 × 105 | 8.21 × 103 |
| 3 | Yueyang Sewage Treatment Plant | 0.3 | 30.0 | 1.5 | 3.29 × 104 | 1.64 × 103 |
| 4 | Bashan Sewage Treatment Plant | 1.0 | 30.0 | 1.5 | 1.10 × 105 | 5.47 × 103 |
| 5 | Gezhouba Group Water Zichuan Water Plant | 3.0 | 30.0 | 1.5 | 3.29 × 105 | 1.64 × 104 |
| 6 | Limin sewage purification plant | 6.0 | 40.0 | 2.0 | 8.76 × 105 | 4.38 × 104 |
| 7 | Watt Sewage Treatment Plant | 3.0 | 40.0 | 2.0 | 4.38 × 105 | 2.19 × 104 |
| 8 | Total | 22.3 | 30.0–40.0 | 1.5–2.0 | 2.77 × 106 | 1.39 × 105 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Ding, J.; Lu, J. Water Environmental Functional Zoning at County Level and Environmental Contamination Carrying Capacity Accounting in the Mainstream of Xiaofu River. Water 2022, 14, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040615
Ding S, Wang F, Sun X, Ding J, Lu J. Water Environmental Functional Zoning at County Level and Environmental Contamination Carrying Capacity Accounting in the Mainstream of Xiaofu River. Water. 2022; 14(4):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040615
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Shaoxuan, Fangshun Wang, Xining Sun, Jincheng Ding, and Jie Lu. 2022. "Water Environmental Functional Zoning at County Level and Environmental Contamination Carrying Capacity Accounting in the Mainstream of Xiaofu River" Water 14, no. 4: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040615
APA StyleDing, S., Wang, F., Sun, X., Ding, J., & Lu, J. (2022). Water Environmental Functional Zoning at County Level and Environmental Contamination Carrying Capacity Accounting in the Mainstream of Xiaofu River. Water, 14(4), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040615





